Experimental Study of Particle Transport and Deposition Distribution over Complex Terrains Based on Spherical Alumina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
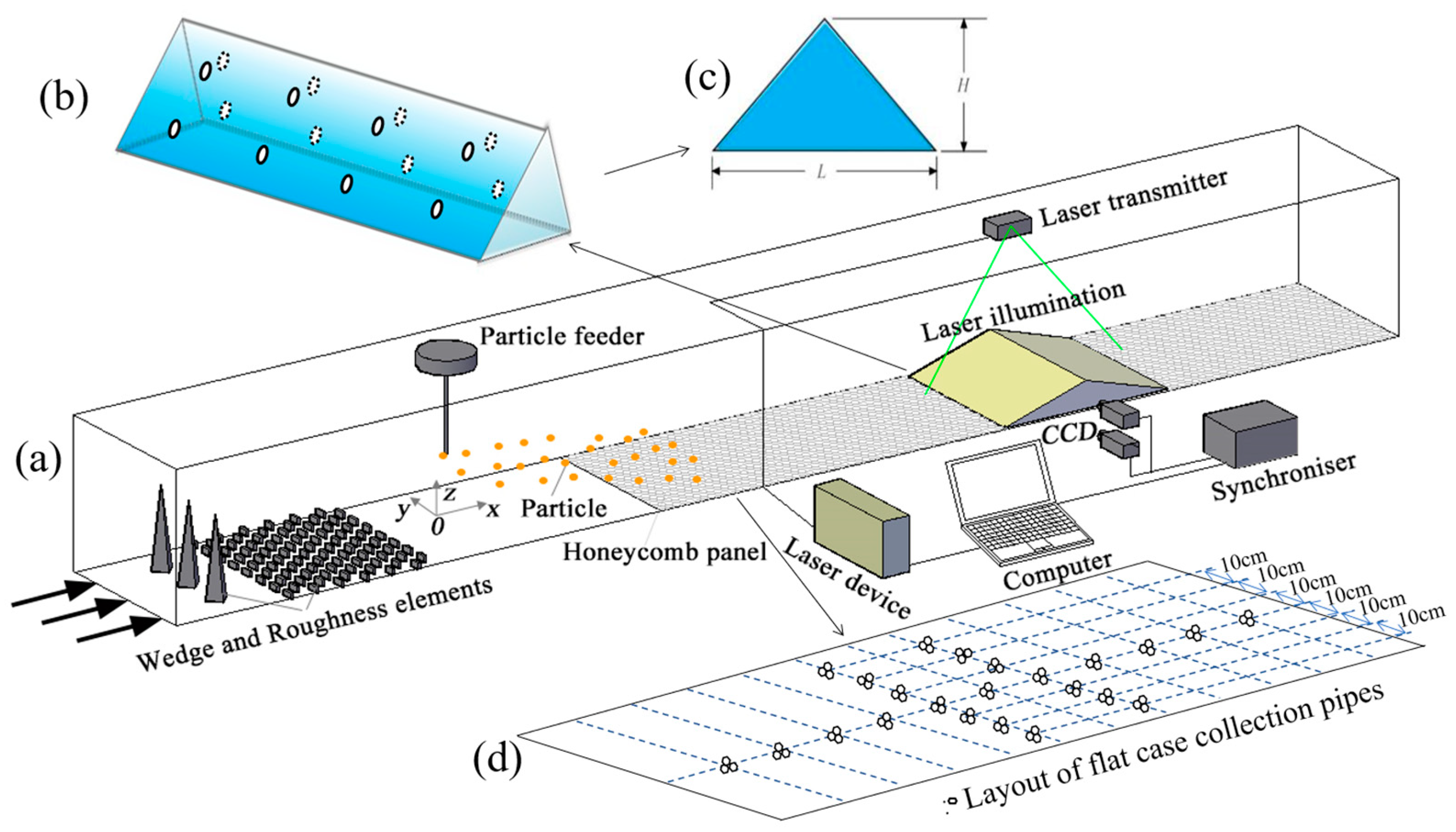
2.1. Wind Tunnel Experimental Environment Settings
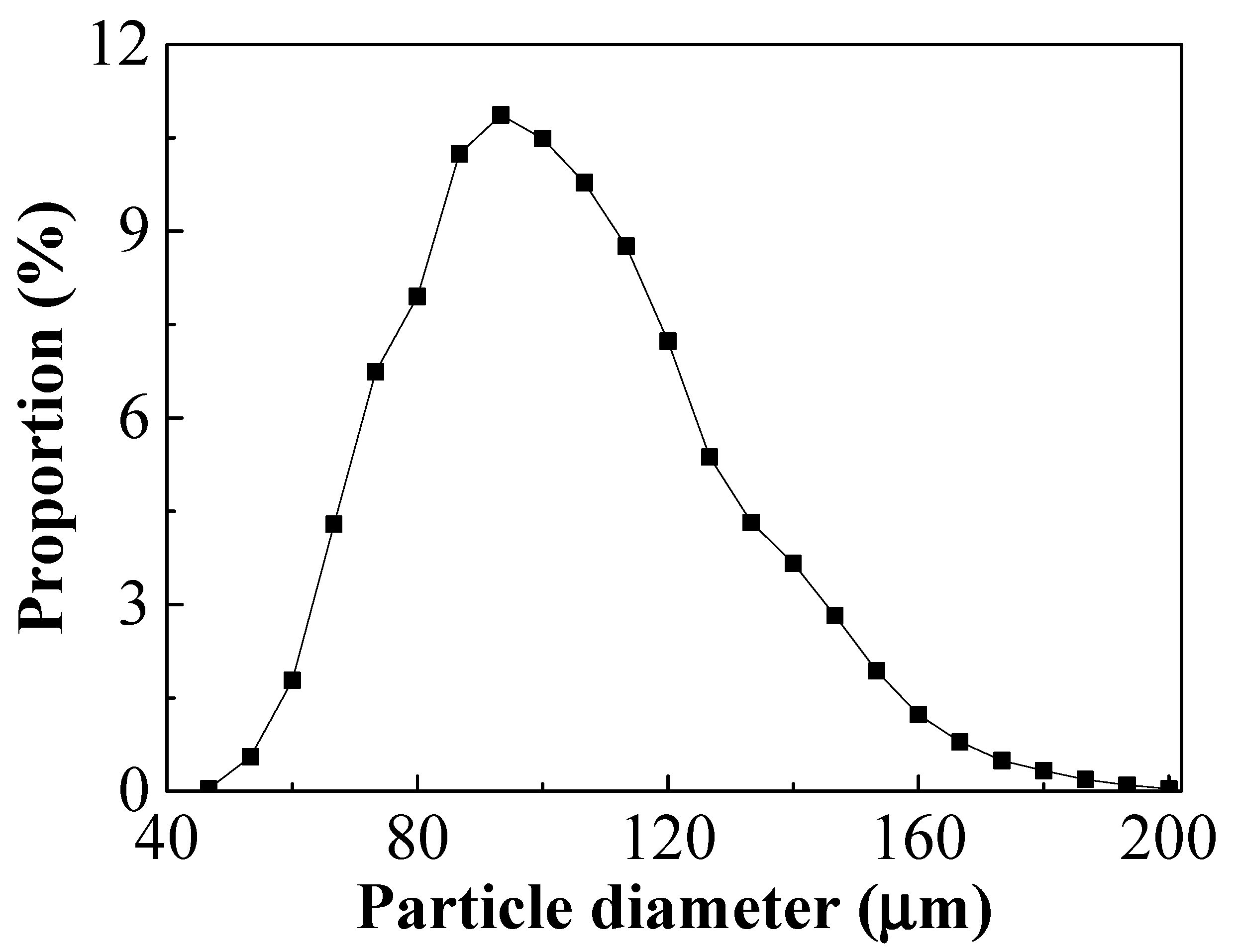
2.2. Observation Equipment and Particle Samples
2.3. Experimental Cases and Procedures
- Measurement of wind speed profile, from the position of the feeding point to the back end of the measurement area, measurement of wind speed profile at positions 1–7 (measurement at 9 heights, under 2 wind conditions, for 3 min per point).
- PIV measurement, taking PIV images of the observation area (20 min for each group, divided into 10 shots).
- Measurement of surface deposition, feeding a fixed amount of material within 20 min. The quantity of feed can be divided according to the sampling quantity. The collected deposit was carefully weighed, and we recorded the information on the position of the collection tube and the initial/final weight. After each group of experiments, the collection pipe, honeycomb plate, and surface were carefully cleaned, and the feeding speed was checked to determine the feeding amount.
3. Results
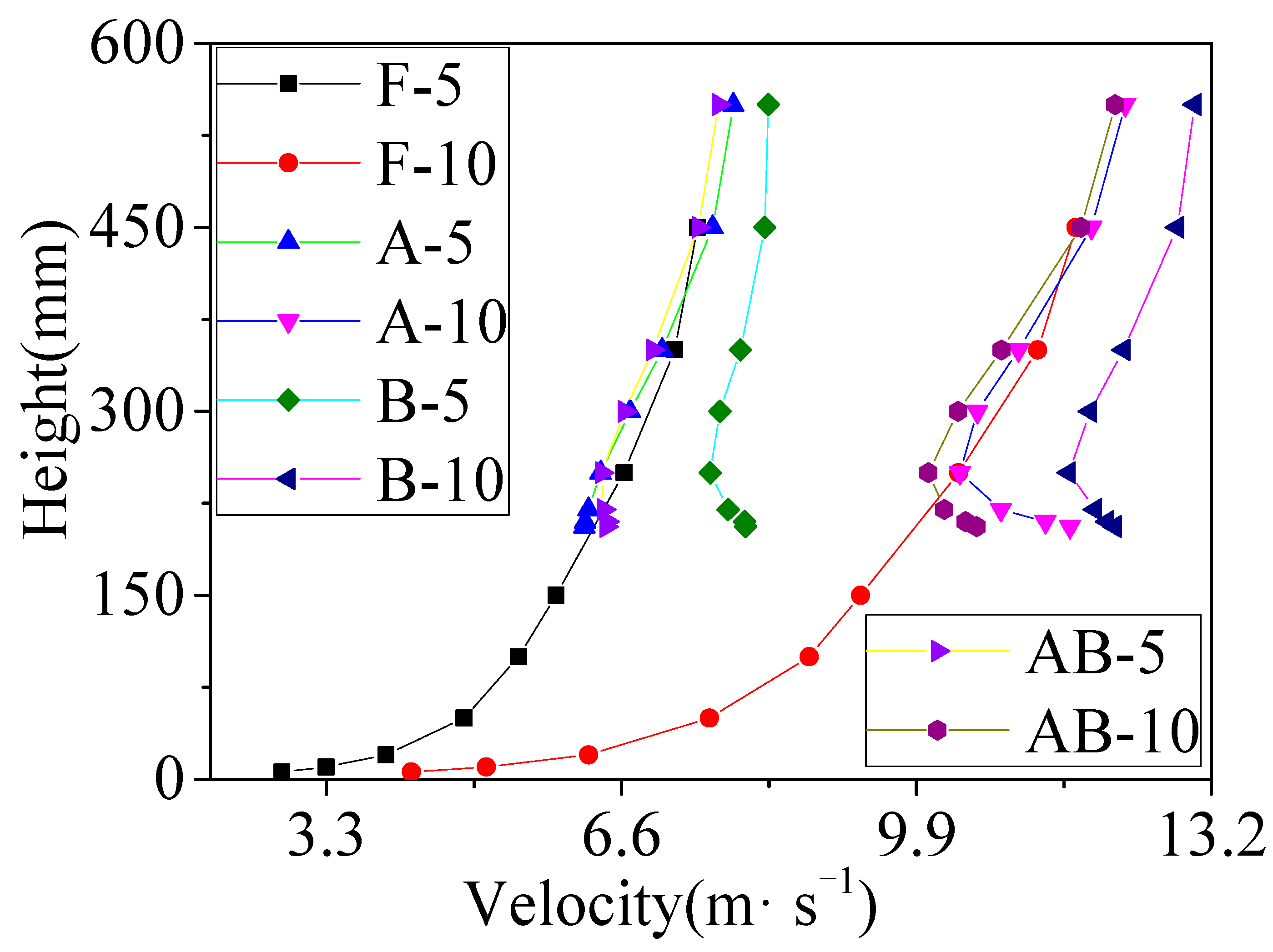
3.1. Wind Field Variation Characteristics along the Flow Direction
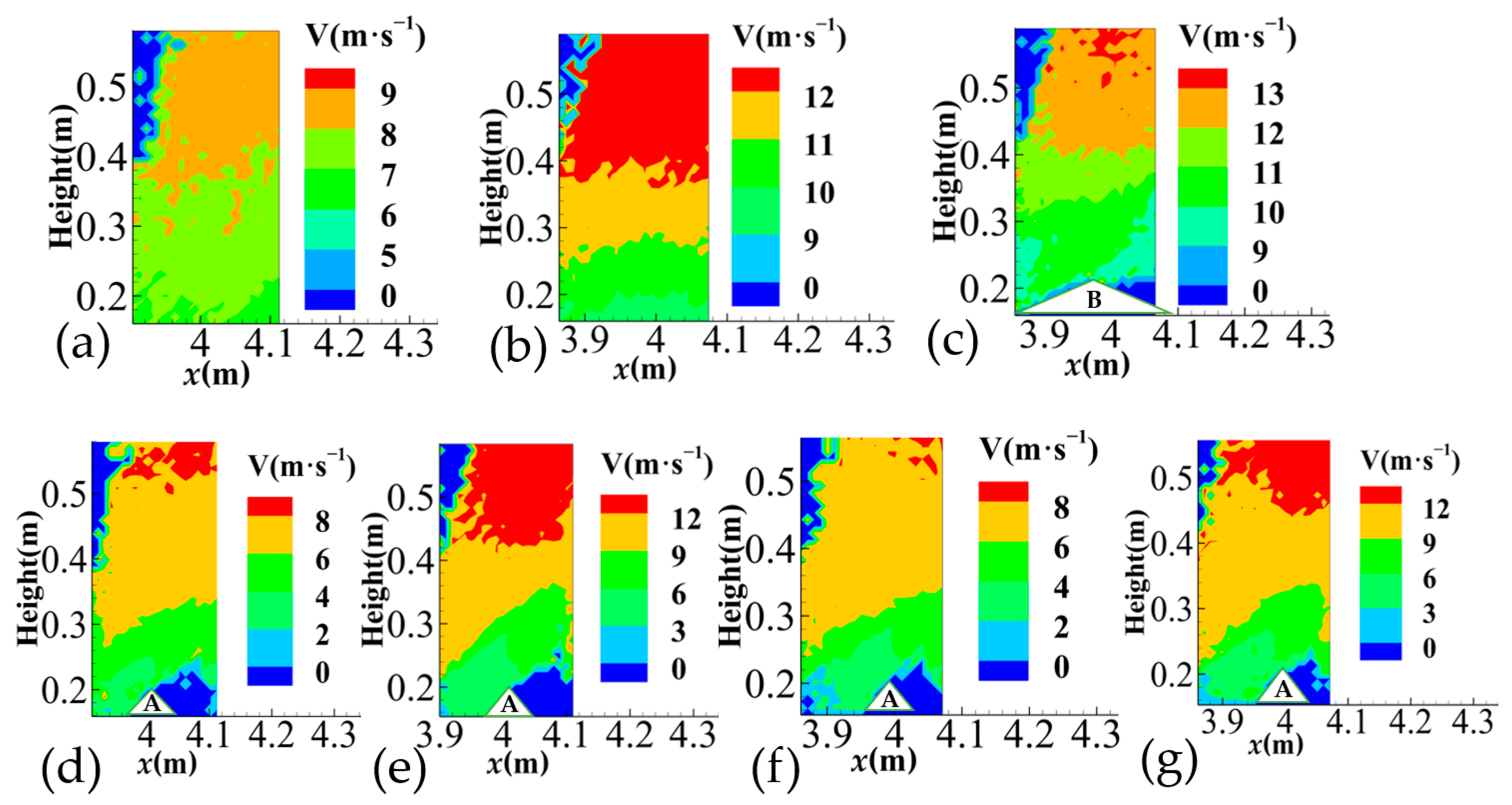
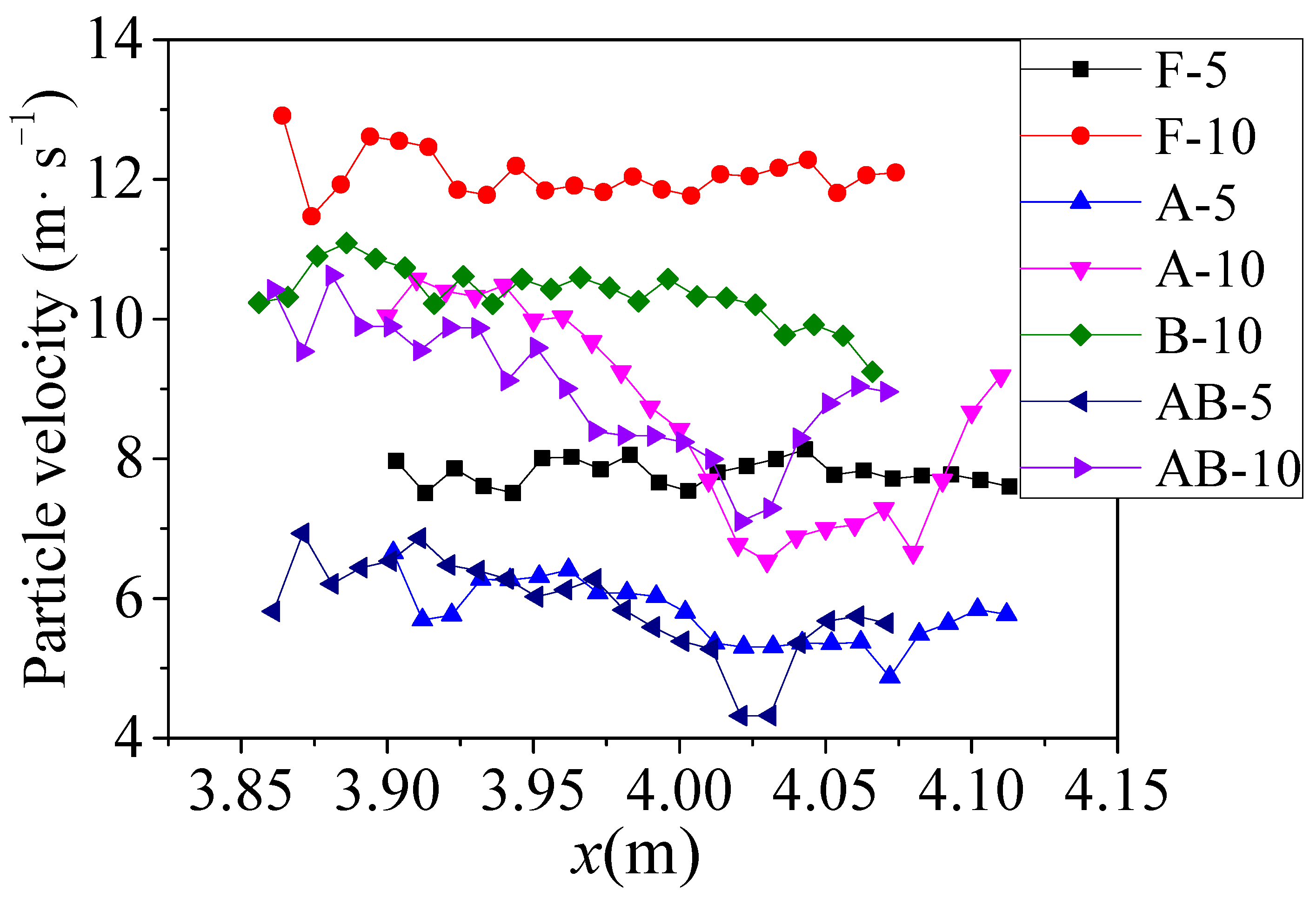
3.2. Distribution of Particle Velocity around Mountain Model
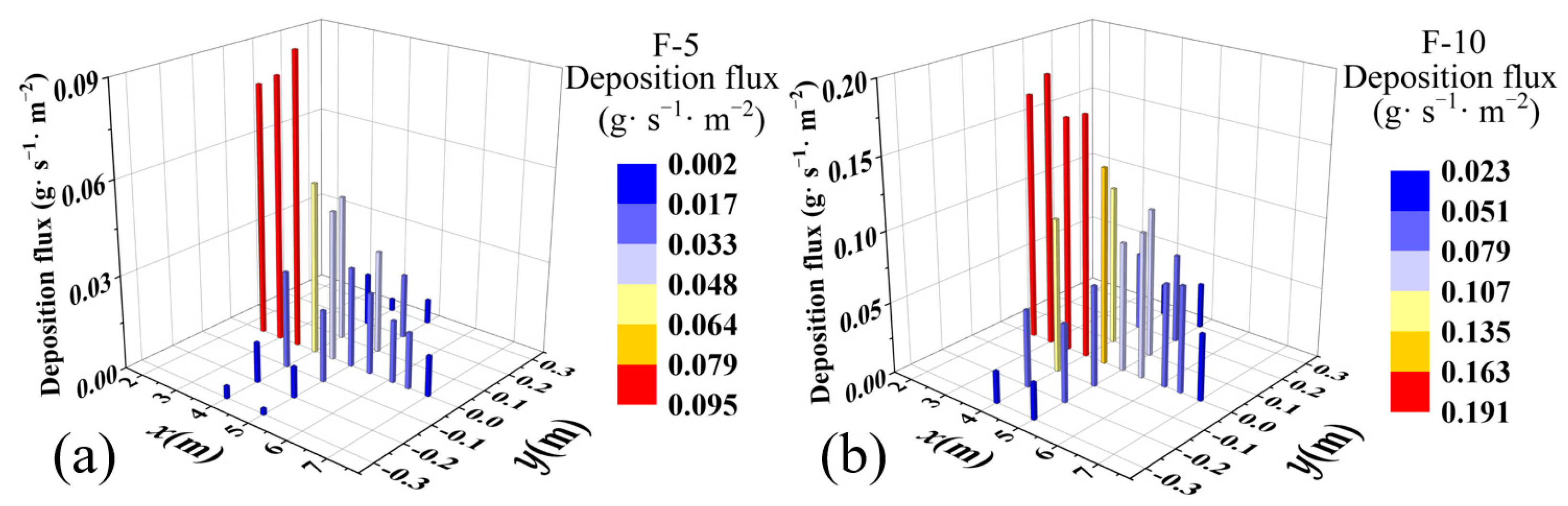
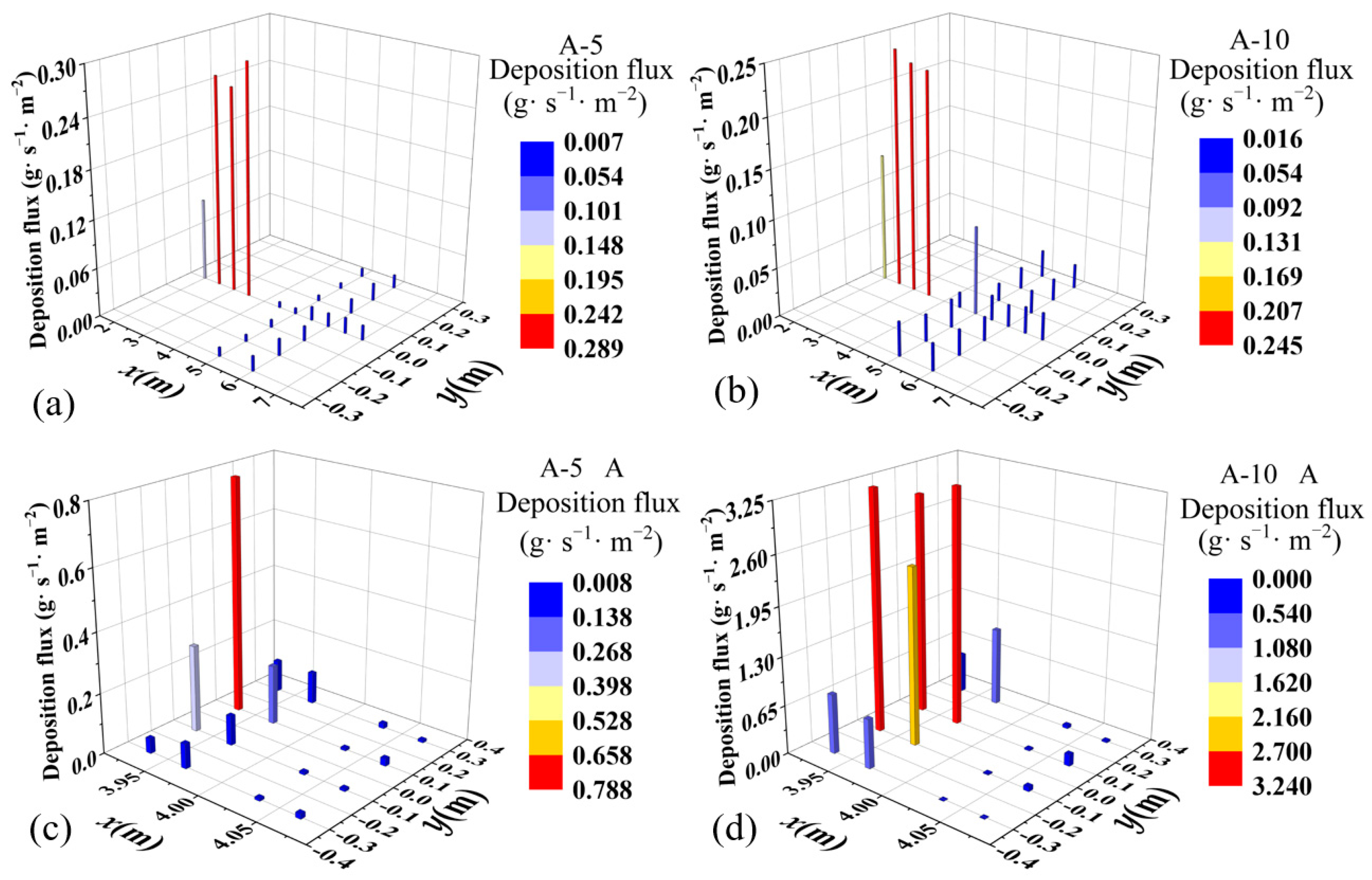
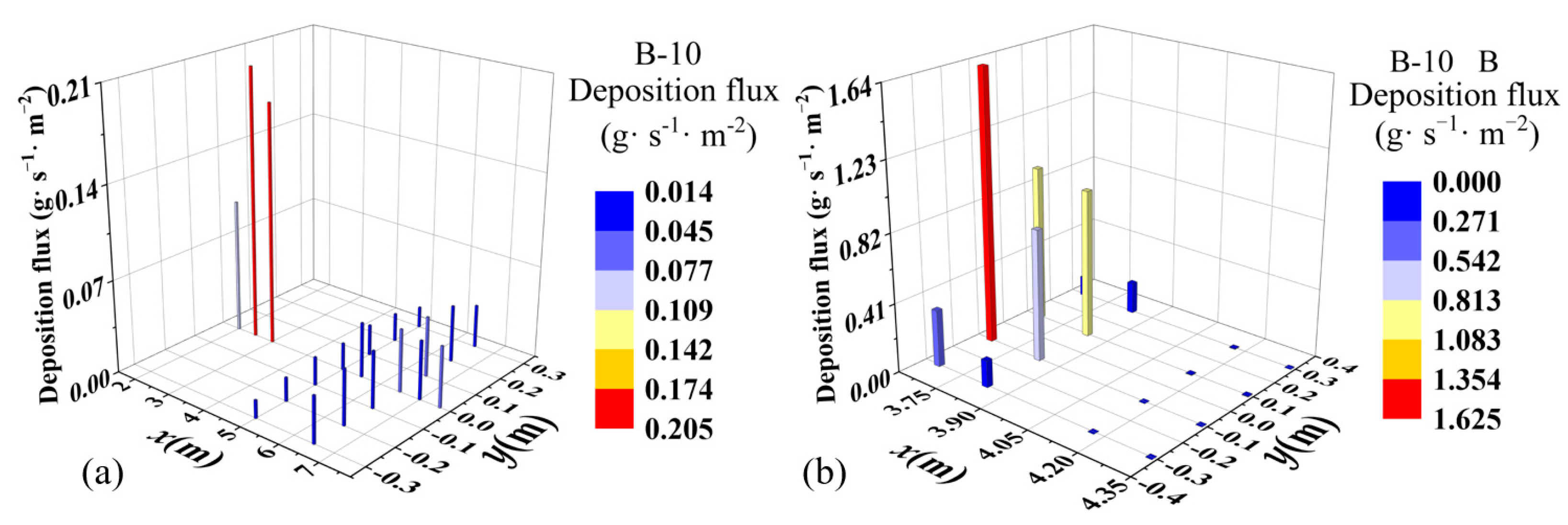
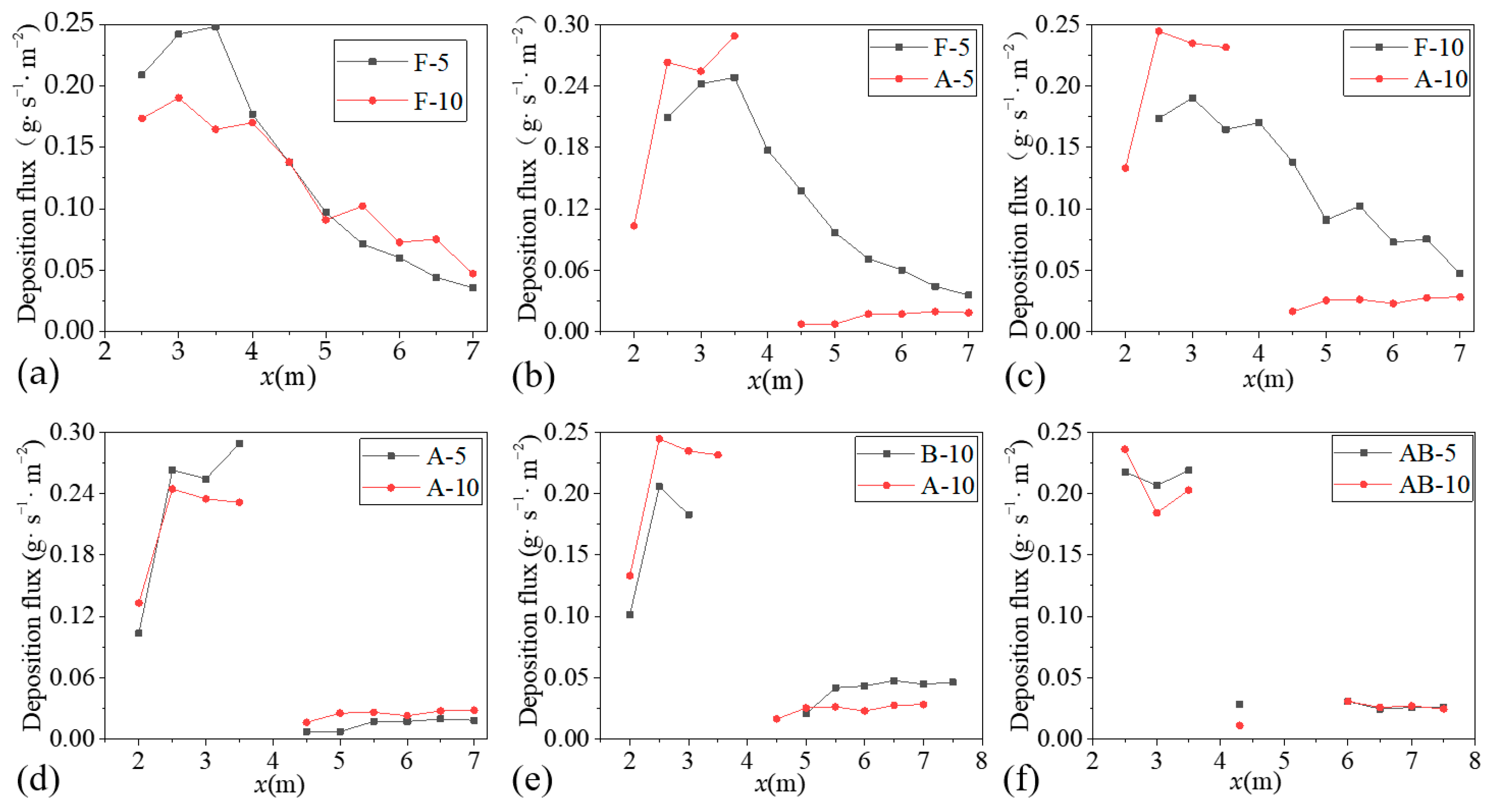
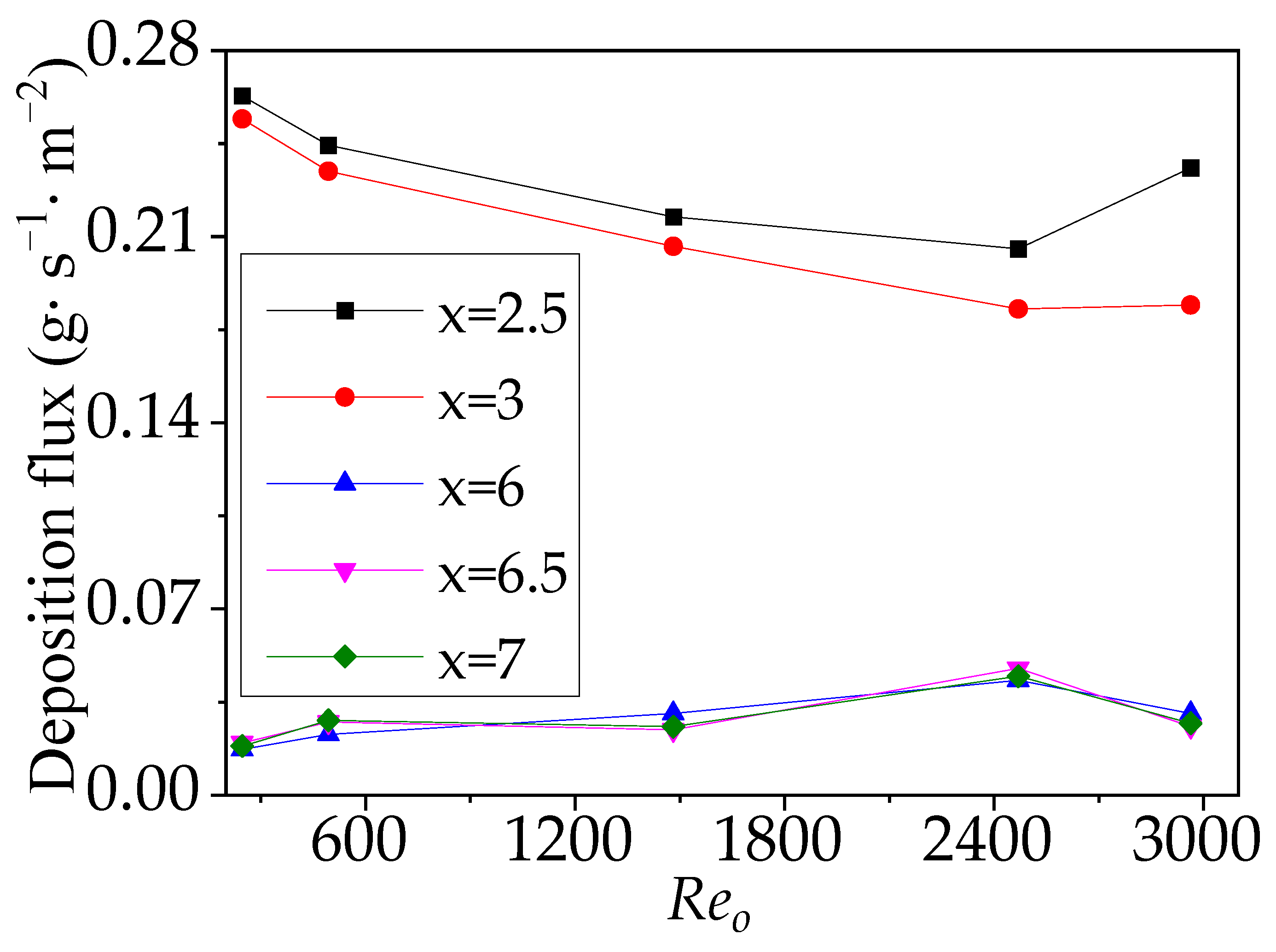
3.3. Particle Surface Deposition Flux
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of Wind Field Measurement Results
4.2. Discussion of Deposition Flux Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, A.; Kok, J.F.; Murray, B.J.; Ryder, C.L.; Stuut, J.B.W.; Kahn, R.A.; Knippertz, P.; Formenti, P.; Mahowald, N.M.; Garcia-Pando, C.P.; et al. A review of coarse mineral dust in the Earth system. Aeolian Res. 2023, 60, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutnik, V.S.; Leonard, J.; Alkidim, S.; DePrima, F.J.; Ravi, S.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Mohanty, S.K. Distribution of microplastics in soil and freshwater environments: Global analysis and framework for transport modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.H. Reconstructing the electrical structure of dust storms from locally observed electric field data. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pähtz, T.; Clark, A.H.; Valyrakis, M.; Durán, O. The Physics of Sediment Transport Initiation, Cessation, and Entrainment Across Aeolian and Fluvial Environments. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Albani, S.; Kok, J.F.; Engelstaeder, S.; Scanza, R.; Ward, D.S.; Flanner, M.G. The size distribution of desert dust aerosols and its impact on the Earth system. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witze, A. How a small nuclear war would transform the entire planet. Nature 2020, 579, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, N.; Gong, K.; Liu, Y.S. Characteristics of Turbulent Aeolian Sand Movement Over Straw Checkerboard Barriers and Formation Mechanisms of Their Internal Erosion Form. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6907–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.H.; Huang, N.; He, W. Turbulence burst over four micro-topographies in the wind tunnel. Catena 2017, 148, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, G.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhu, W. Investigation on very large scale motions (VLSMs) and their influence in a dust storm. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013, 56, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronzo, D.M.; Valentine, G.A.; Dellino, P.; de Tullio, M.D. Numerical analysis of the effect of topography on deposition from dilute pyroclastic density currents. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 300, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, N.; Nagai, T.; Murayama, T.; Adachi, A.; Murayama, Y. Volcanic ash transport from mount asama to the Tokyo metropolitan area influenced by large-scale local wind circulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1248–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.T.; Li, X.P.; Fang, S.; Dong, X.W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.J.; Nibert, M.; Buty, D.; Alberge, A. Validation and sensitivity study of Micro-SWIFT SPRAY against wind tunnel experiments for air dispersion modeling with both heterogeneous topography and complex building layouts. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 222, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yang, X.H.; Huo, W.; Ali, M.; Zheng, X.Q.; Zhou, C.L.; He, Q. A continuously weighing, high frequency sand trap: Wind tunnel and field evaluations. Geomorphology 2017, 293, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boor, B.E.; Siegel, J.A.; Novoselac, A. Monolayer and Multilayer Particle Deposits on Hard Surfaces: Literature Review and Implications for Particle Resuspension in the Indoor Environment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, B.; Dhaniyala, S.; Ahmadi, G. Particle resuspension from surfaces: Overview of theoretical models and experimental data. Dev. Surf. Contam. Clean. Types Contam. Contam. Resou. 2017, 9, 55–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, S.T.; Armand, P.; Tinarelli, G.; Duchenne, C.; Nibart, M. Validation of a Lagrangian particle dispersion model with wind tunnel and field experiments in urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, A.; Henry, F.S.; Butler, J.P. Particle Transport and Deposition: Basic Physics of Particle Kinetics. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1437–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.M. An overview of particulate dry deposition: Measuring methods, deposition velocity and controlling factors. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Huang, N. Numerical simulation of the falling snow deposition over complex terrain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 980–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Pan, S.Z.; Shen, Z.T.; Song, Y.A.; Jin, Y.L.; Wu, W.M.; Hou, D.Y. Microplastics undergo accelerated vertical migration in sand soil due to small size and wet-dry cycles. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.; Avouac, J.P.; Ayoub, F.; Ewing, R.C.; Vriend, N.; Heggy, E. Comparing dune migration measured from remote sensing with sand flux prediction based on weather data and model, a test case in Qatar. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 497, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Teng, Z.J.; Huang, N.; Guo, L.; Shao, Y.P. Surface renewal as a significant mechanism for dust emission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15517–15528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wang, C.; Pan, X.Y. Simulation of aeolian sand saltation with rotational motion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, H.C.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J.; He, W. Effects of Shape and Rotation of Sand Particles in Saltation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13462–13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X. Mechanics of Wind-Blown Sand Movements; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raupach, M.R.; Lu, H. Representation of land-surface processes in aeolian transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figgis, B.; Ennaoui, A.; Ahzi, S.; Rémond, Y. Review of PV soiling particle mechanics in desert environments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockie, J.M. The mathematics of atmospheric dispersion modeling. Siam Rev. 2011, 53, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Huang, N. The effect of mountain wind on the falling snow deposition. In Proceedings of the 15th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics (15ACFM), Kuching, Malaysia, 21–23 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, S.E.; Harman, I.N.; Finnigan, J.J. The Wind in the Willows: Flows in Forest Canopies in Complex Terrain. In Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics; Davis, S.H., Moin, P., Eds.; Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics; Palo Alto: Singapore, 2012; Volume 44, pp. 479–504. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, D. Aeolian deposition of dust over hills: The effect of dust grain size on the deposition pattern. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulidis, A.P.; Takemi, T.; Iguchi, M.; Renfrew, I.A. Orographic effects on the transport and deposition of volcanic ash: A case study of Mount Sakurajima, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9332–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eychenne, J.; Rust, A.C.; Cashman, K.V.; Wobrock, W. Distal Enhanced Sedimentation from Volcanic Plumes: Insights From the Secondary Mass Maxima in the 1992 Mount Spurr Fallout Deposits. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 7679–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, N.; Shao, Y.-P.; Zheng, X.-J. A Review on Modeling and Monitoring of Dust Dry Deposition. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Zufall, M.J.; Dai, W.P.; Davidson, C.I. Dry deposition of particles to wave surfaces: II. Wind tunnel experiments. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4283–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufall, M.J.; Dai, W.P.; Davidson, C.I.; Etyemezian, V. Dry deposition of particles to wave surfaces: I. Mathematical modeling. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Khlystov, A. Investigation of Ultrafine Particle Deposition to Vegetation Branches in a Wind Tunnel. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.T.; Kinnersley, R.P. A computational and wind tunnel study of particle dry deposition in complex topography. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Storelvmo, T.; Karydis, V.A.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T.; He, C.L.; Leung, D.M. Mineral dust aerosol impacts on global climate and climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, S.F.L.; Gilbert, J.S.; Folch, A.; Phillips, J.C.; Cai, X.M. An example of enhanced tephra deposition driven by topographically induced atmospheric turbulence. Bull. Volcanol. 2015, 77, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouet, B.; Dawson, P.; Ohminato, T.; Martini, M.; Saccorotti, G.; Giudicepietro, F.; De Luca, G.; Milana, G.; Scarpa, R. Source mechanisms of explosions at Stromboli Volcano, Italy, determined from moment-tensor inversions of very-long-period data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushi, E.; Stockie, J.M. An inverse Gaussian plume approach for estimating atmospheric pollutant emissions from multiple point sources. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaele, L.; Glabeke, G.; van Beeck, J. Wind-sand tunnel experiment on the windblown sand transport and sedimentation over a two-dimensional sinusoidal hill. Wind Struct. 2023, 36, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, T.; Herget, J. Obstacle-Reynolds-number based analysis of local scour at submerged cylinders. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, H.C.; Xin, G.W.; Huang, N.; Shi, G.T.; Zhang, J. Wind-Tunnel Studies on Sand Sedimentation around Wind-Break Walls of Lanxin High-Speed Railway II and Its Prevention. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, Y. Mastersizer 2000 laser particle size analyzer and its applications. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 2007, 30, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Callesen, I.; Keck, H.; Andersen, T.J. Particle size distribution in soils and marine sediments by laser diffraction using Malvern Mastersizer 2000-method uncertainty including the effect of hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thölén, A. Character of Adhesion Strain Fields at Contacts between Spheres of Different Materials. In Tribology Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 7, pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.B.; Wang, H.T.; Zhang, X.H.; Ayrault, M. Height profile of particle concentration in an aeolian saltating cloud: A wind tunnel investigation by PIV MSD. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.S.; Gu, M. Wind tunnel tests and numerical simulations of wind pressures on buildings in staggered arrangement. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Z.S.; Huang, N. A Snow Distribution Model Based on Snowfall and Snow Drifting Simulations in Mountain Area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 7193–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Löwe, H.; Ryser, M.; Raderschall, N. Inhomogeneous precipitation distribution and snow transport in steep terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Jia, S.M. A simulation of a large-scale drifting snowstorm in the turbulent boundary layer. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 3841–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulidis, A.P.; Biass, S.; Bagheri, G.; Takemi, T.; Iguchi, M. Atmospheric vertical velocity—A crucial component in understanding proximal deposition of volcanic ash. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 566, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cases | Mountain Model | Wind Speed/m·s−1 | Reo | Feeding Height/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-5 | Flat | 5 | 0.5 | |
| F-10 | Flat | 10 | 0.4 | |
| A-5 | Model A 1 | 5 | 246.91 | 0.5 |
| A-10 | Model A 1 | 10 | 493.83 | 0.4 |
| B-5 | Model B 2 | 5 | 1234.57 | 0.5 |
| B-10 | Model B 2 | 10 | 2469.14 | 0.4 |
| AB-5 | Combination model AB 3 | 5 | 1481.48 | 0.5 |
| AB-10 | Combination model AB 3 | 10 | 2962.96 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dun, H.; Gong, K.; Shi, L.; Huang, N. Experimental Study of Particle Transport and Deposition Distribution over Complex Terrains Based on Spherical Alumina. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121756
Liu Y, Zhang J, Dun H, Gong K, Shi L, Huang N. Experimental Study of Particle Transport and Deposition Distribution over Complex Terrains Based on Spherical Alumina. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(12):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121756
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yusheng, Jie Zhang, Hongchao Dun, Kang Gong, Li Shi, and Ning Huang. 2023. "Experimental Study of Particle Transport and Deposition Distribution over Complex Terrains Based on Spherical Alumina" Atmosphere 14, no. 12: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121756
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, J., Dun, H., Gong, K., Shi, L., & Huang, N. (2023). Experimental Study of Particle Transport and Deposition Distribution over Complex Terrains Based on Spherical Alumina. Atmosphere, 14(12), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121756








