The Proportional Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Based on Daily Precipitation in Huai River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
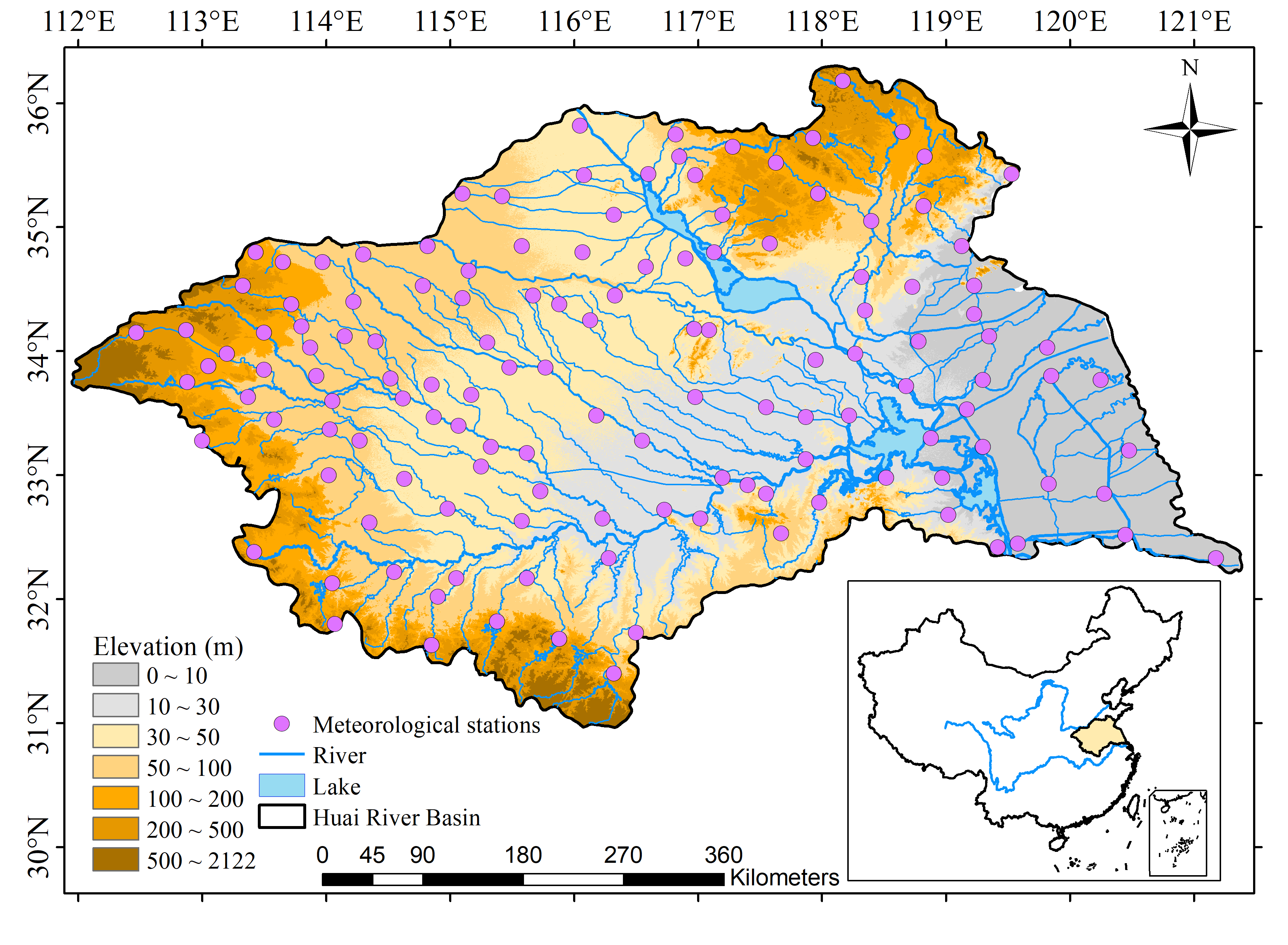
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Definitions of Wet and Dry Seasons
2.4. Different Grades of Precipitation Intensity
2.5. Precipitation Extremes
2.6. Copula Method
3. Results
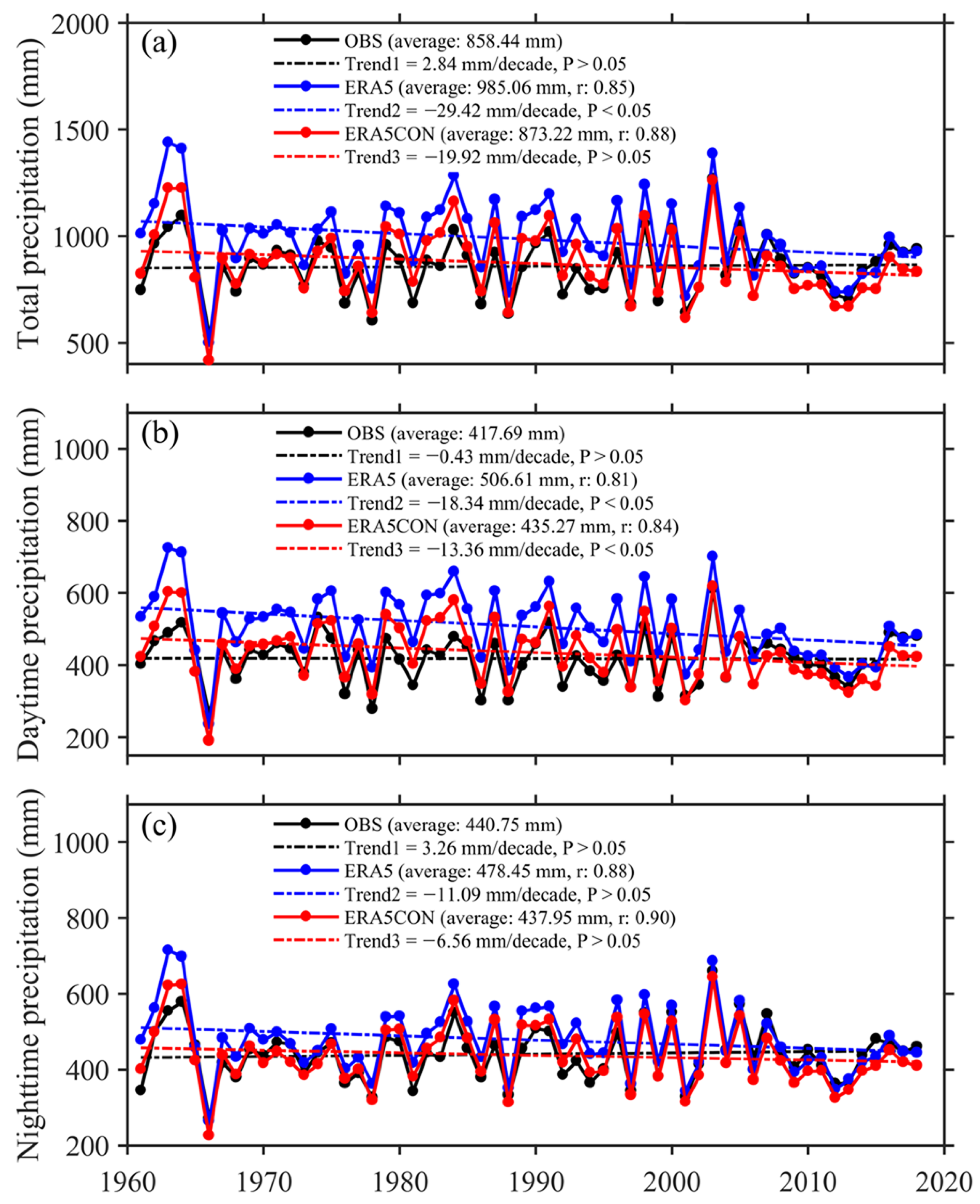
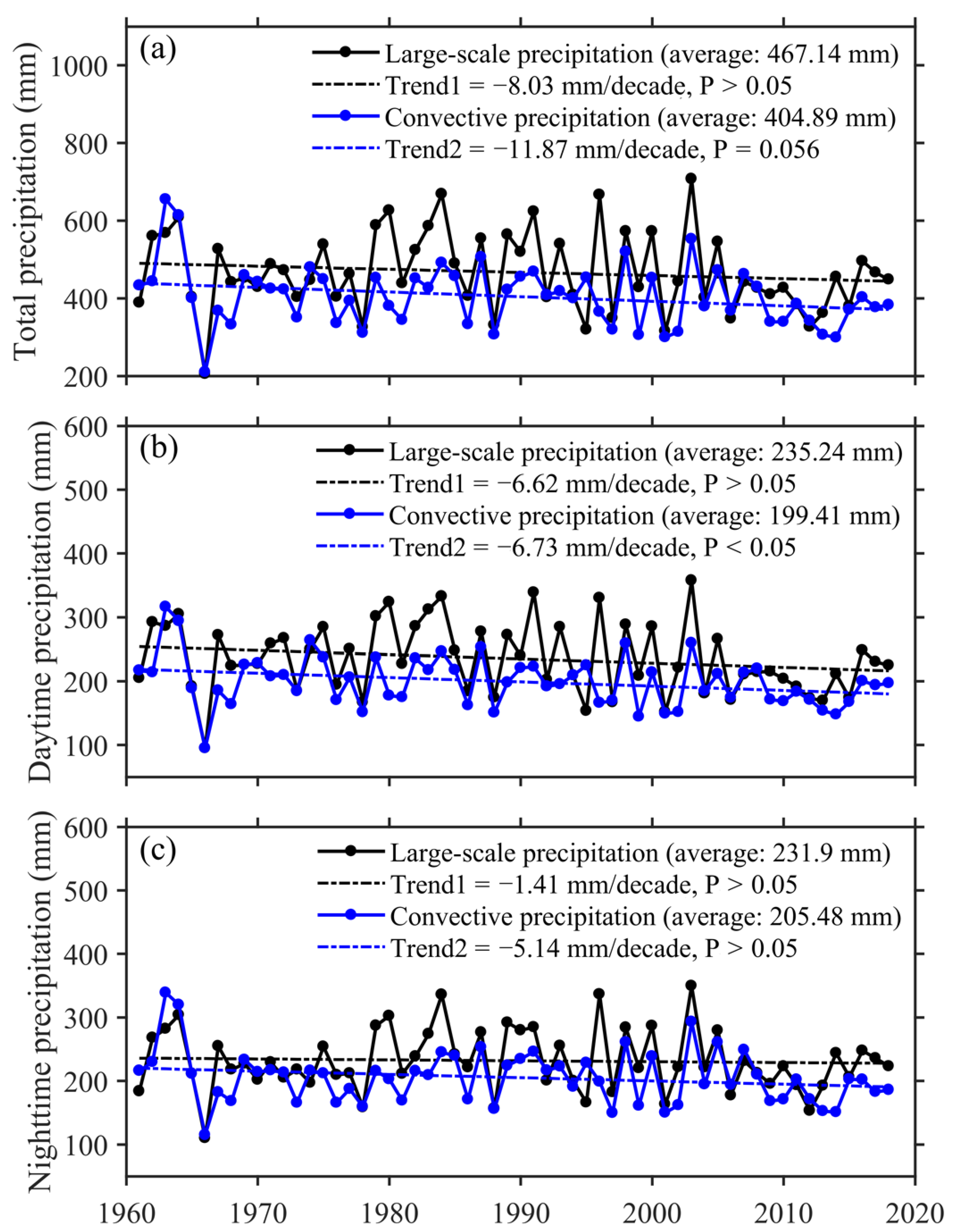
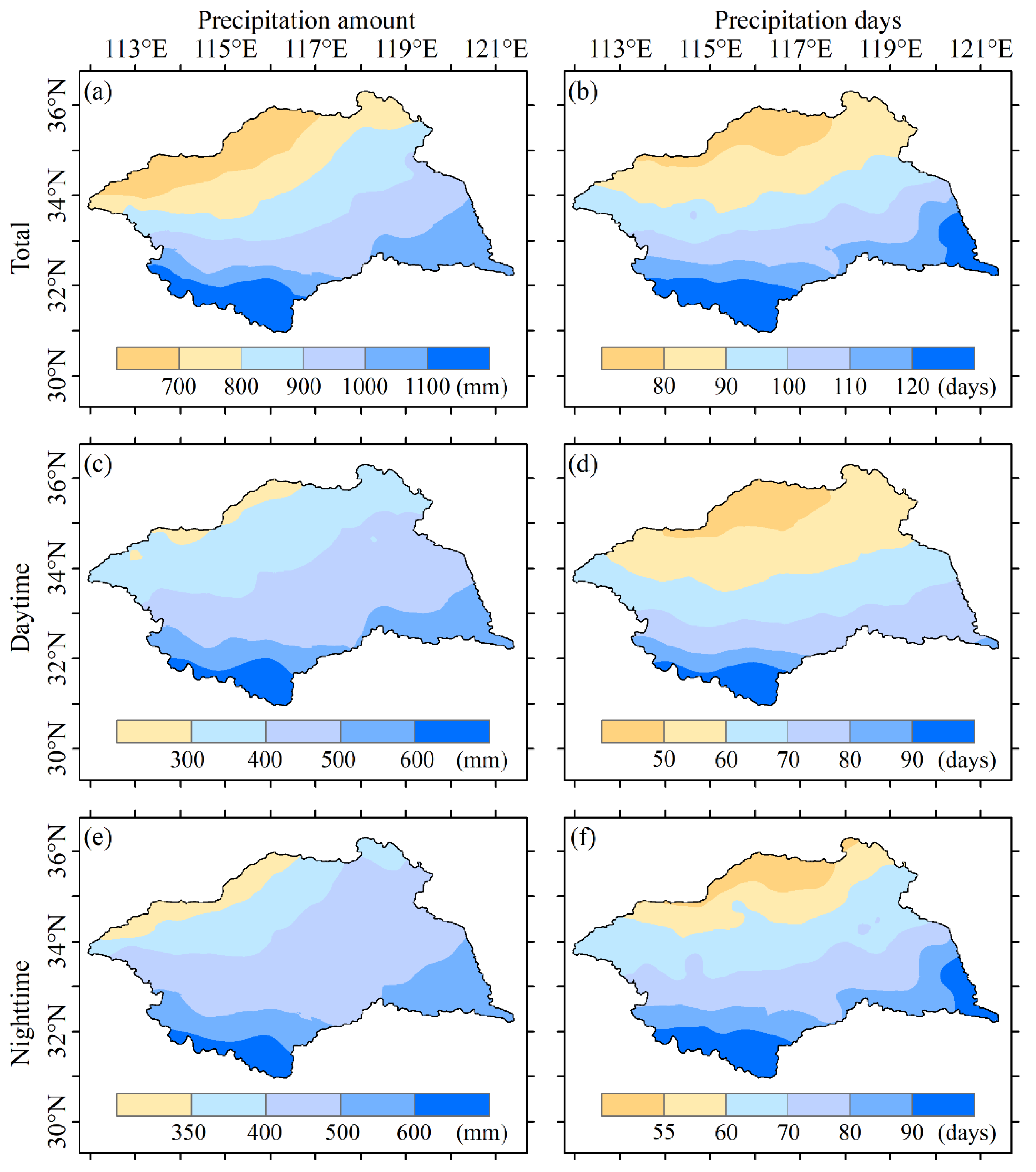
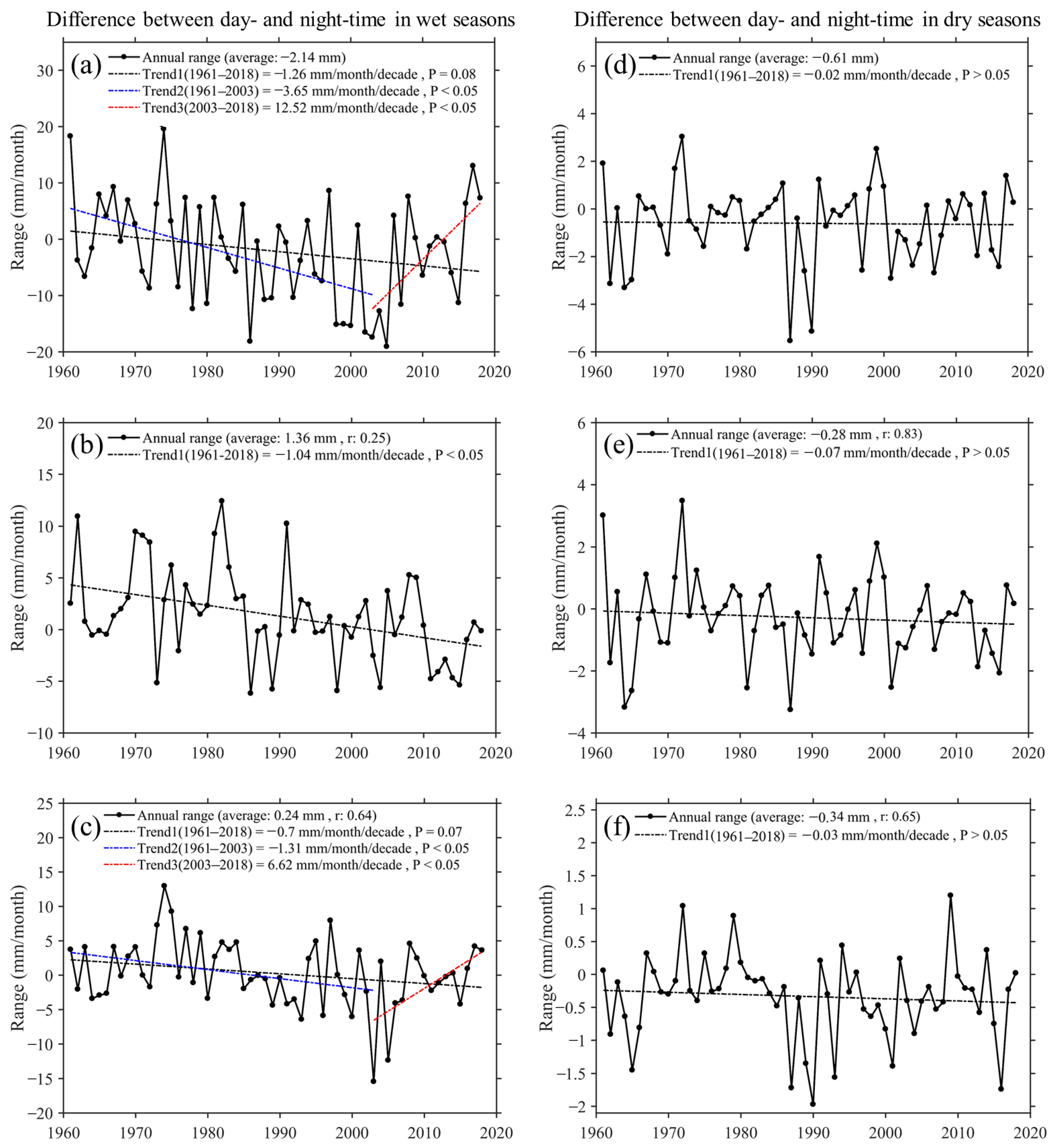
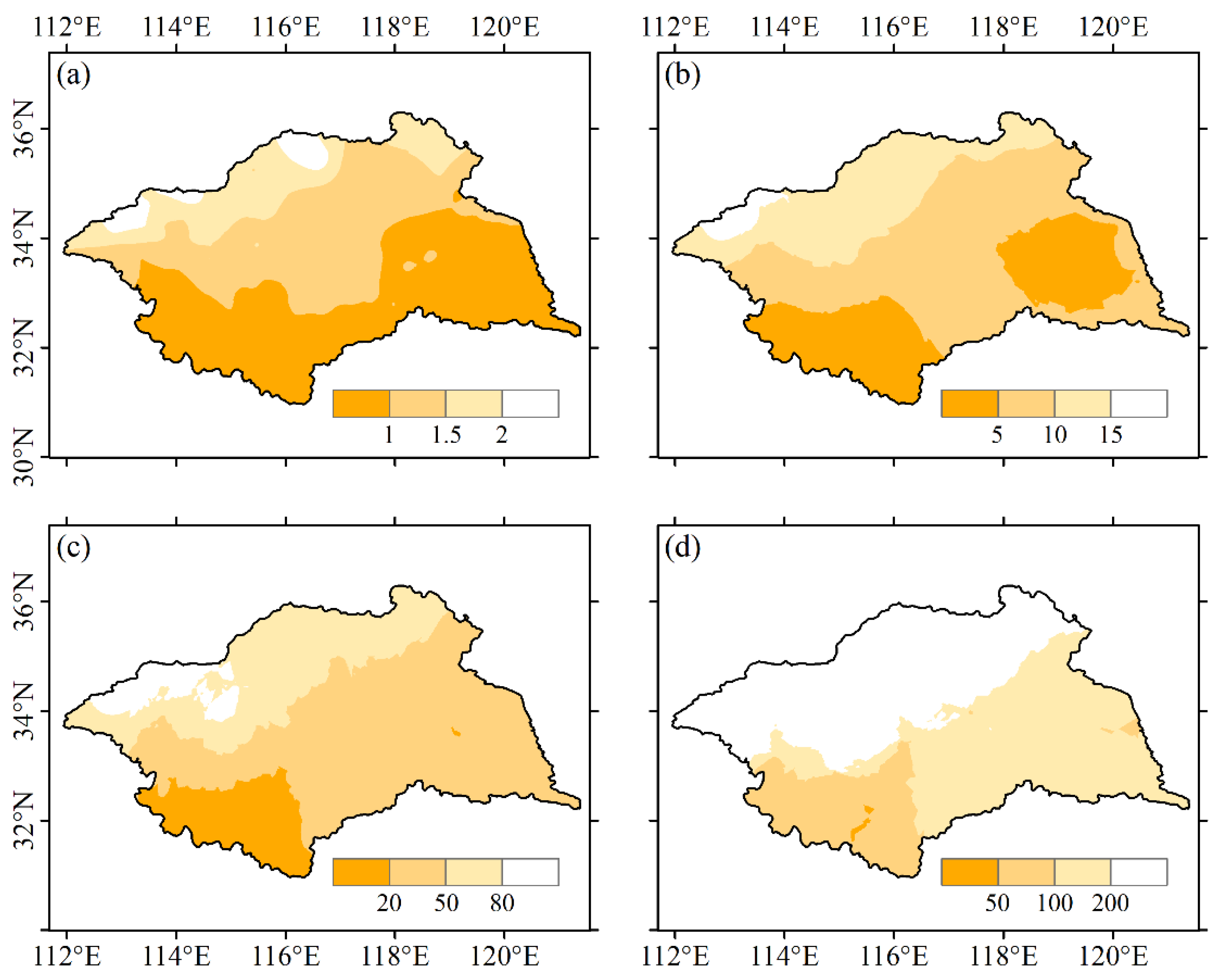
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Annual and Seasonal Precipitation
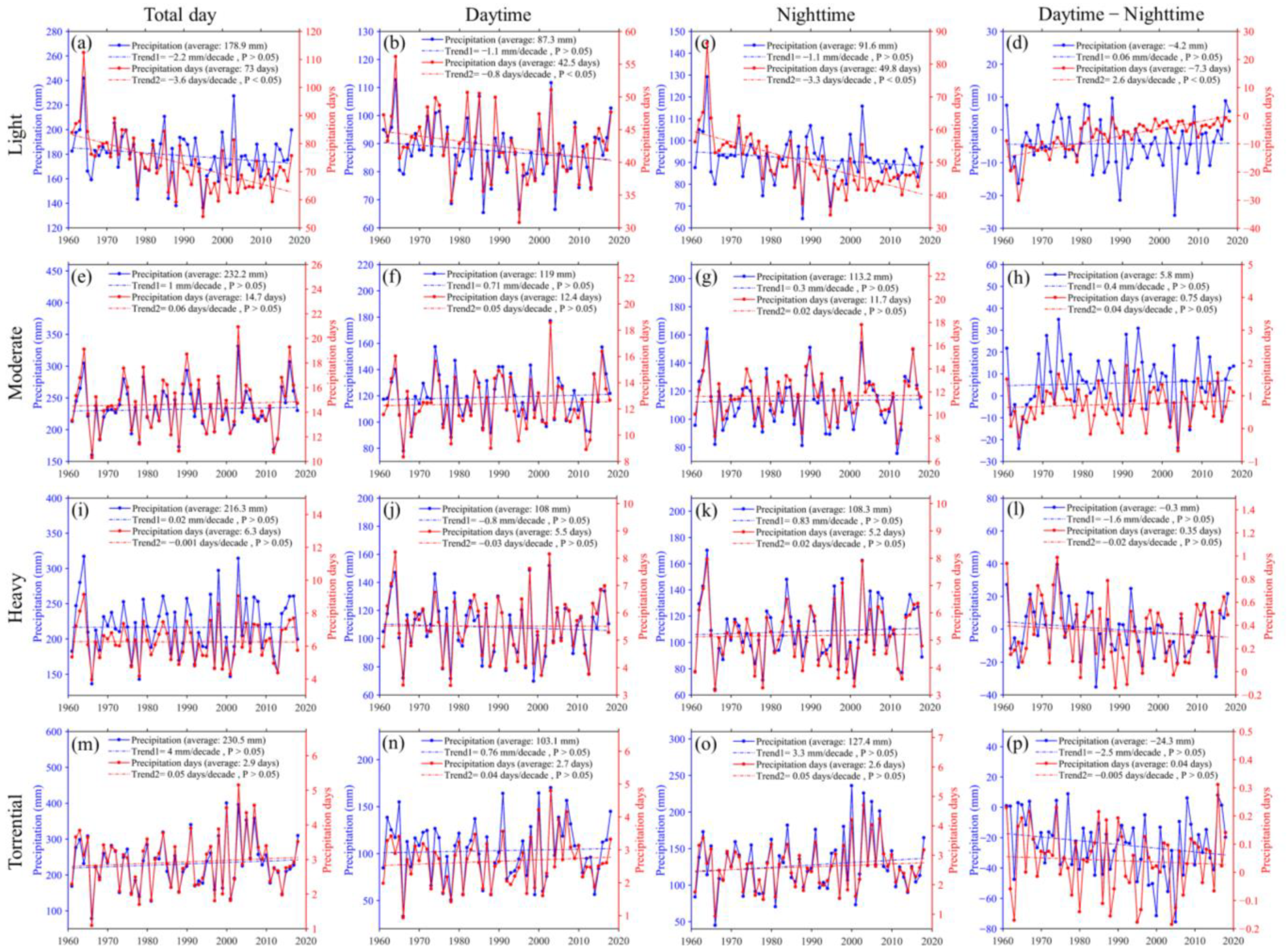
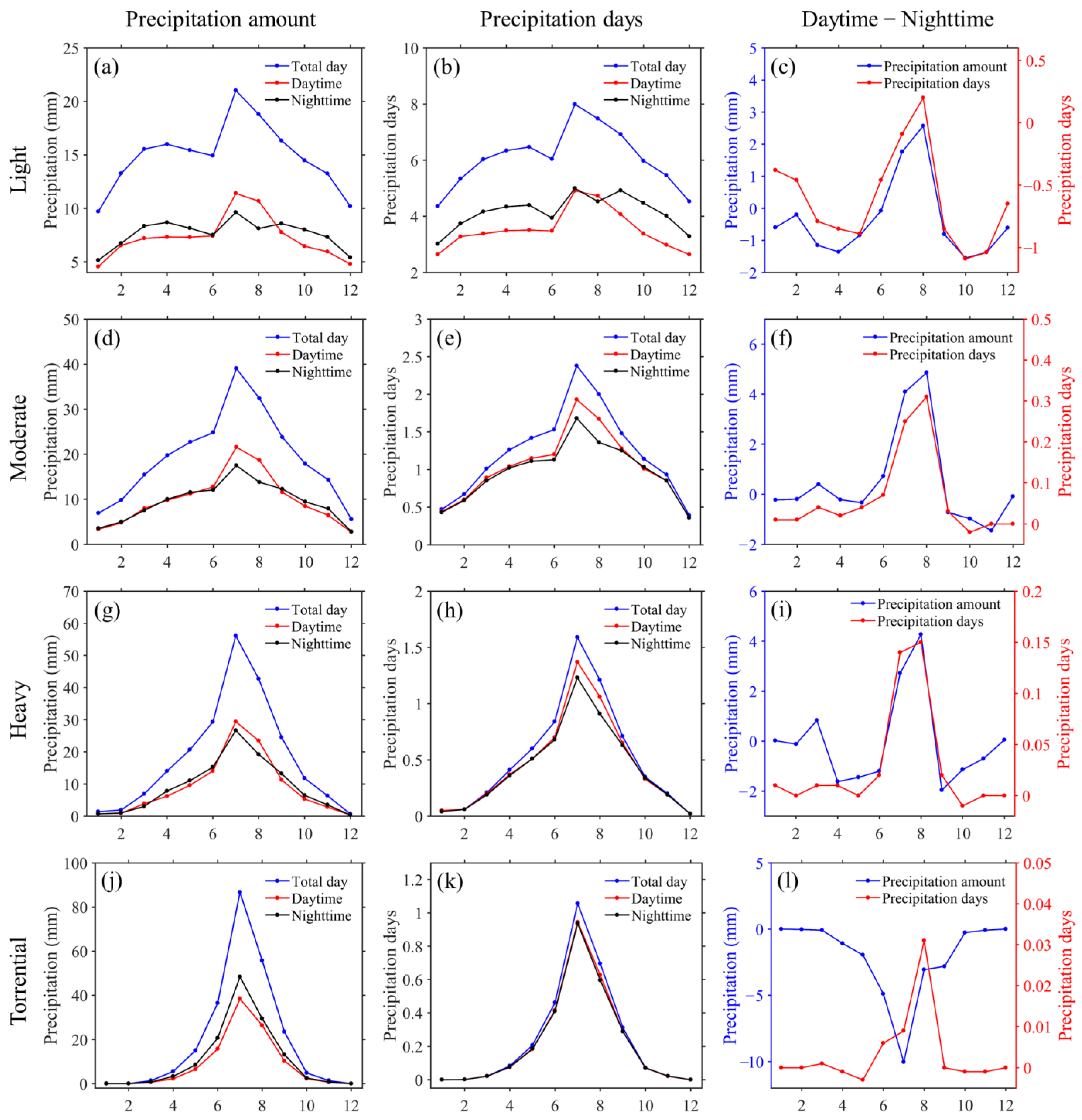
3.2. Characteristics of Precipitation at Different Grades
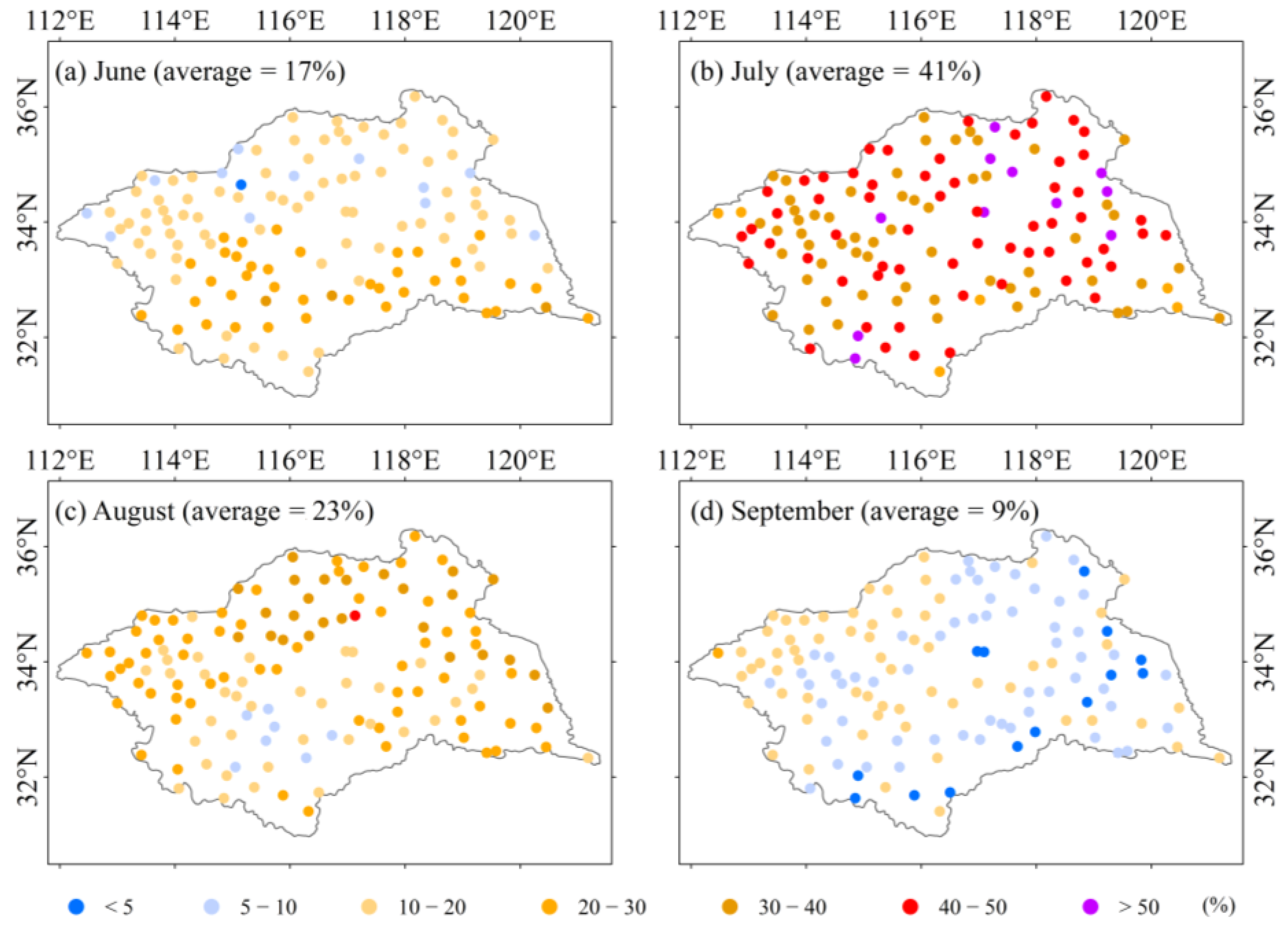
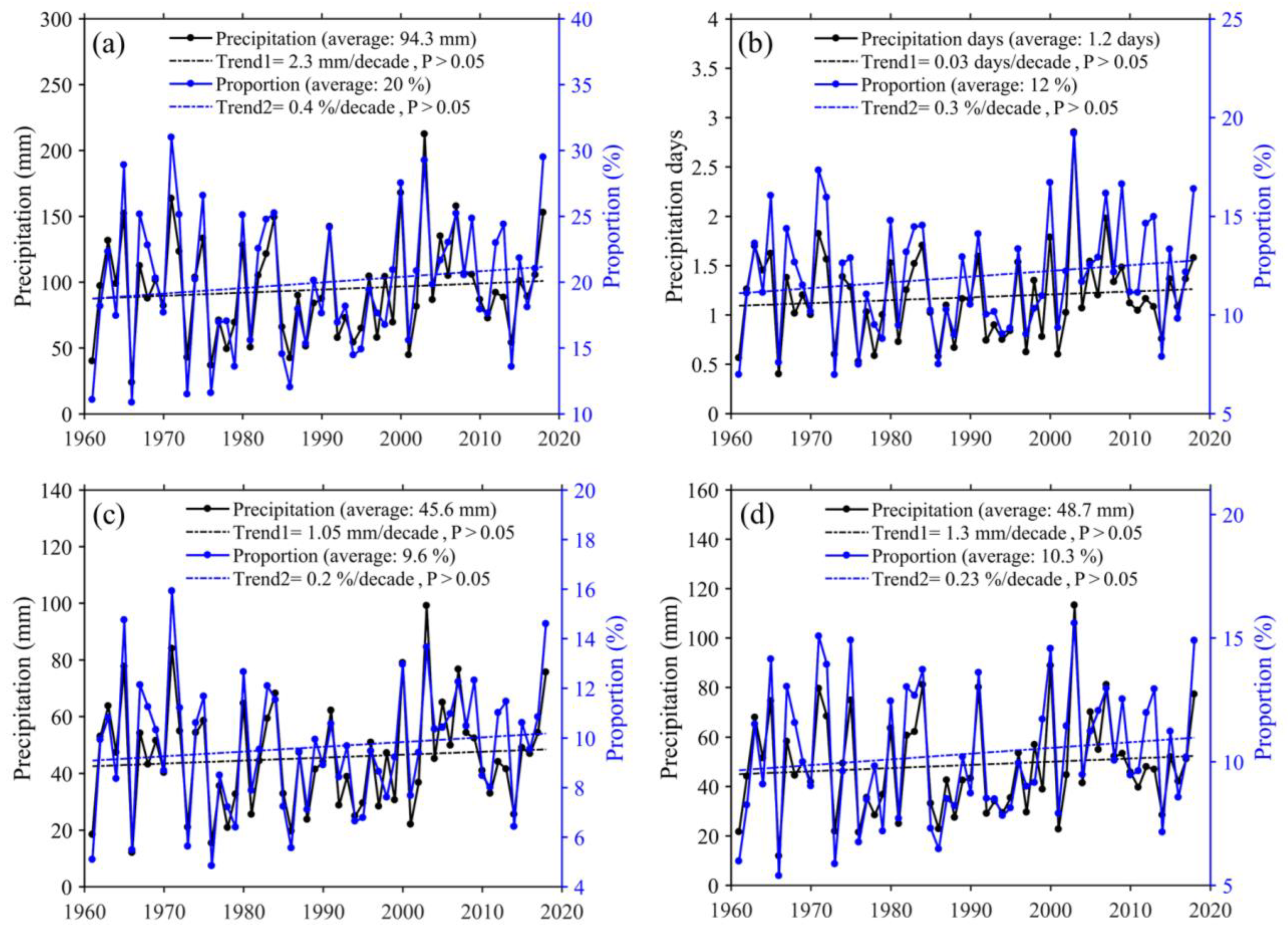
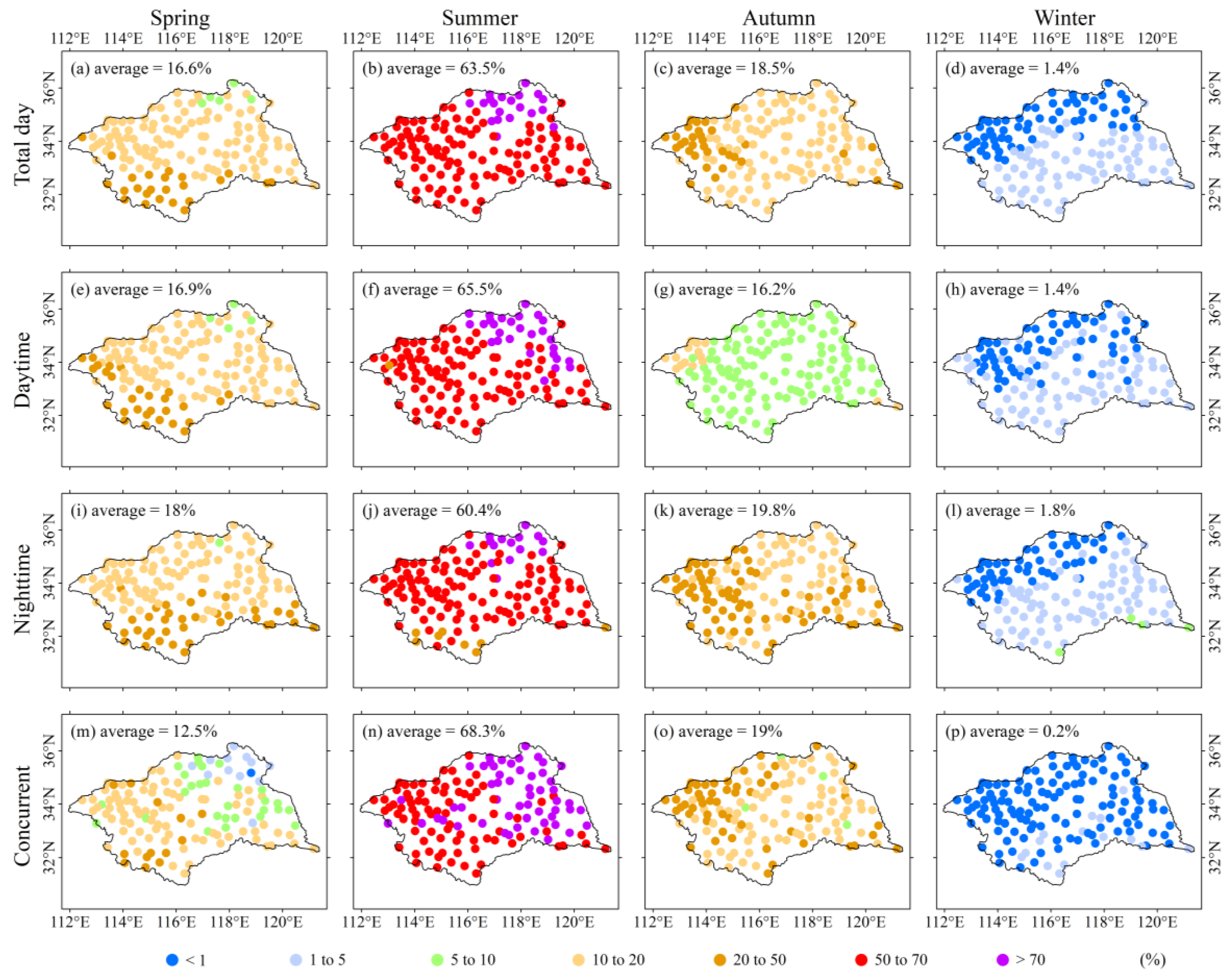
3.3. Proportions of Sub-Daily Precipitation under Extreme Precipitation Conditions
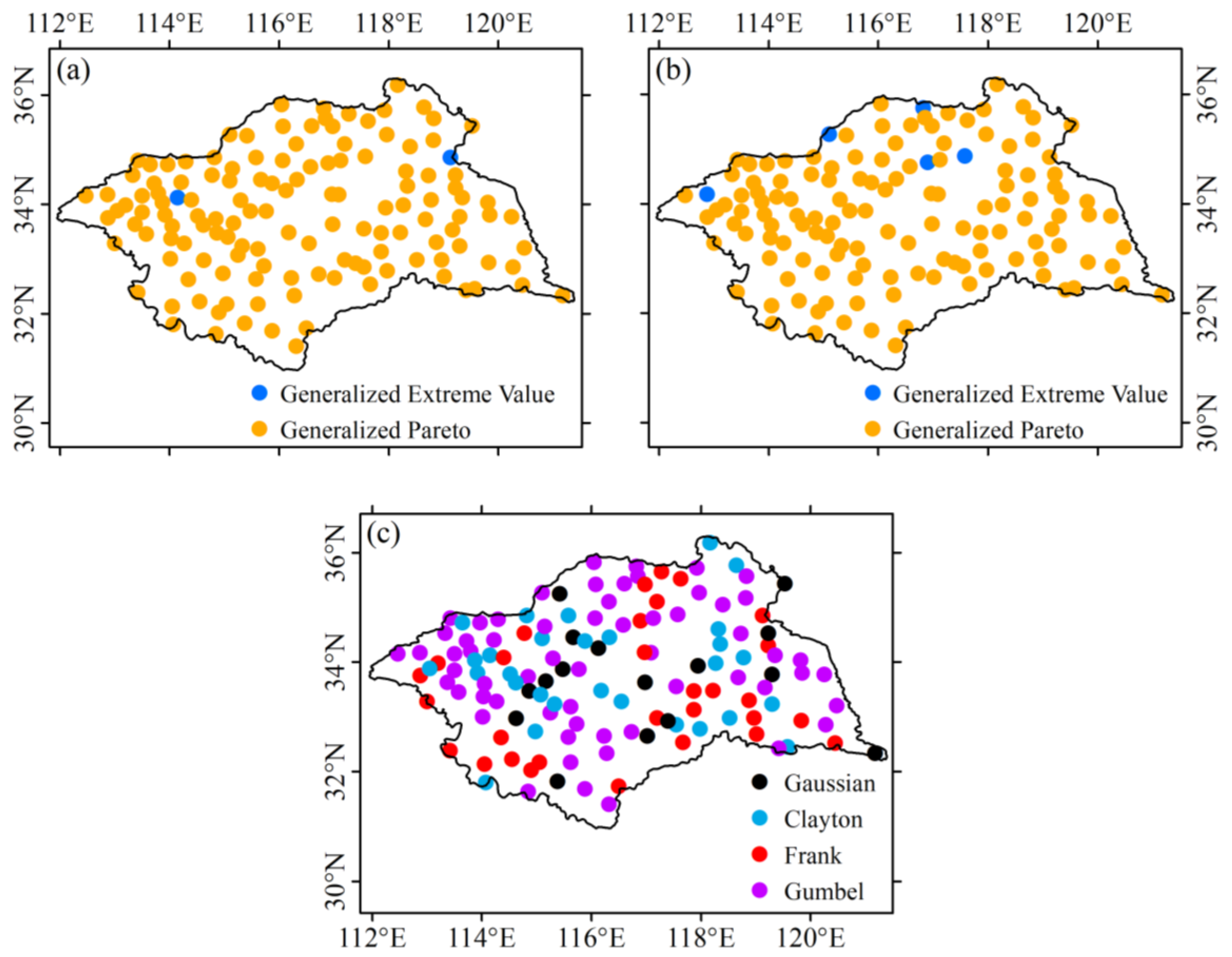
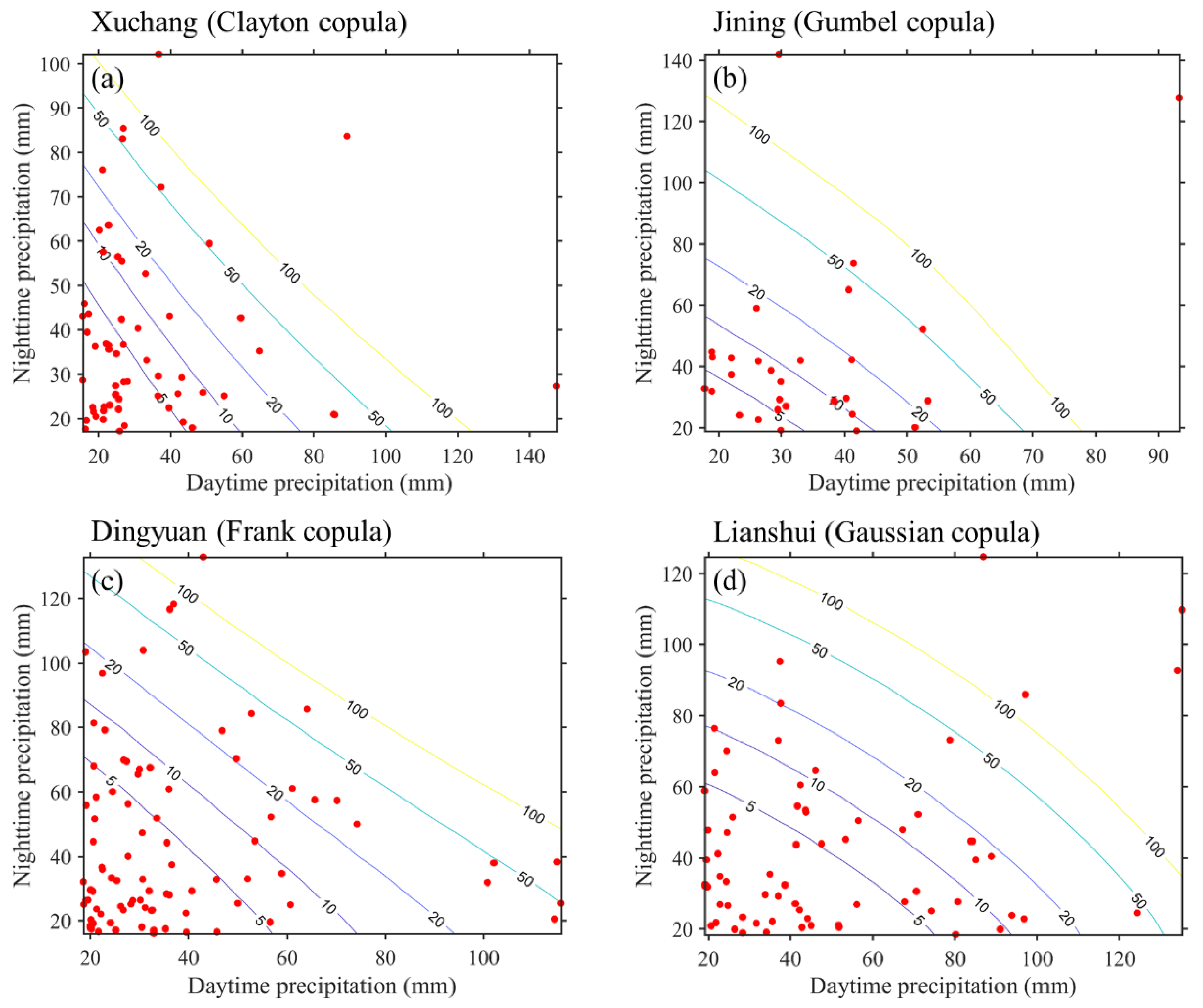
3.4. The Return Periods of CEDNP Events
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koutsoyiannis, D. Revisiting the global hydrological cycle: Is it intensifying? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3899–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, T.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Projecting the future of rainfall extremes: Better classic than trendy. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, K. Contrasting daytime and nighttime precipitation variability between observations and eight reanalysis products from 1979 to 2014 in China. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6443–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J.; Yuan, W.; Duan, Z. Mapping diurnal cycles of precipitation over China through clustering. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, P.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Iliopoulou, T.; Papanicolaou, P. A global-scale investigation of stochastic similarities in marginal distribution and dependence structure of key hydrological-cycle processes. Hydrology 2021, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, T. Diurnal cycle of summer rainfall in Shandong of eastern China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Gao, L.; Zuo, X.; Zhong, F. Statistical analyses of spatial and temporal variabilities in total, daytime, and nighttime precipitation indices and of extreme dry/wet association with large-scale circulations of southwest China, 1961–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 219, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Evaluation of the latest satellite–gauge precipitation products and their hydrologic applications over the huaihe river basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X. Effect of heteroscedasticity treatment in residual error models on model calibration and prediction uncertainty estimation. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yu, R.; Li, J. Changes in the diurnal cycles of precipitation over eastern China in the past 40 years. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 30, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, K.; Ohta, T.; Aida, K.; Tamakawa, K.; Im, M.S. Diurnal pattern of rainfall in cambodia: Its regional characteristics and local circulation. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Takano, S.; Kusaka, H. Nighttime precipitation induced by a synoptic-scale convergence in the central tibetan plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sha, W.; Iwasaki, T.; Ueno, K. Diurnal variation of rainfall in the yangtze river valley during the spring-summer transition from trmm measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D0610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, R.; Li, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, T. Why nocturnal long-duration rainfall presents an eastward-delayed diurnal phase of rainfall down the yangtze river valley. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, S. Diurnal cycles of mei-yu rainfall simulated over eastern China: Sensitivity to cumulus convective parameterization. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, R.; Chen, H.; Dai, A.; Pan, Y. Summer precipitation frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle over China: A comparison of satellite data with rain gauge observations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3997–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, J. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Fetzer, E.; Wong, S.; Lambrigtsen, B. Rapid decadal convective precipitation increase over eurasia during the last three decades of the 20th century. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Sun, Q.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Duan, Q. Linkage between hourly precipitation events and atmospheric temperature changes over China during the warm season. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, K.; Wu, G.; Shi, C. Performance of trmm product in quantifying frequency and intensity of precipitation during daytime and nighttime across China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Lan, C.W.; Chung, C.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Lee, C.J. Increase in the range between wet and dry season precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiong, C.; Yongguang, Z.; Xiaoling, Z.; Peijun, Z.H.U. Distribution and diurnal variation of warm-season short-duration heavy rainfall in relation to the mcss in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2013, 27, 868–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Nan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H. Using cygnss data to map flood inundation during the 2021 extreme precipitation in henan province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, C. Characteristics of concurrent precipitation and wind speed extremes in China. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 32, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Feng, L. Raindrop size distribution and microphysical characteristics of a great rainstorm in 2016 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, A.; Kan, M.; Dong, X.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, S. Characteristics of hourly extreme precipitation along the yangtze river basin, China during warm season. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Cheung, H.-N.; Liu, F.; Cheng, J.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, G.; Dong, W. The longest 2020 meiyu season over the past 60 years: Subseasonal perspective and its predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.-L.; Li, M.; Bao, X.; Sun, J. On the diurnal cycle of heavy rainfall over the sichuan basin during 10–18 august 2020. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cui, H.; Ge, Q. Assessment of potential risks induced by increasing extreme precipitation under climate change. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 2059–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnant, C.; Gori, A.; Sebastian, A.; Bedient, P.B.; Ensor, K.B. Characterizing spatiotemporal trends in extreme precipitation in southeast texas. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 1597–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhou, B.; You, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, S. Observed changes in heat waves with different severities in China during 1961–2015. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakouchak, A.; Cheng, L.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Farahmand, A. Global warming and changes in risk of concurrent climate extremes: Insights from the 2014 california drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 41, 8847–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; You, Q.; Chen, C.; Xie, W.; Ye, Z.; Li, X.; He, Q. Decrease in light precipitation events in huai river eco-economic corridor, a climate transitional zone in eastern China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Luo, G.; Chen, C. Water requirement of summer maize at different growth stages and the spatiotemporal characteristics of agricultural drought in the huaihe river basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 136, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pan, S.; Cao, L.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W. Changes in extreme climate events in eastern China during 1960–2013: A case study of the huaihe river basin. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, R.; Wen, Q. Hydrological drought regimes of the huai river basin, China: Probabilistic behavior, causes and implications. Water 2019, 11, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The era5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, L.E.; Catto, J.L.; Stephenson, D.B.; Dunstone, N.J. Compound precipitation and wind extremes over europe and their relationship to extratropical cyclones. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2021, 33, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mao, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, L.; Xiao, B. Population exposure to compound droughts and heatwaves in the observations and era5 reanalysis data in the gan river basin, China. Land 2021, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinita, M.J.; Richardson, M.; Teixeira, J.; Miranda, P.M.A. Global mean frequency increases of daily and sub-daily heavy precipitation in era5. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 074035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Henderson, M. Where have all the showers gone? Regional declines in light precipitation events in China, 1960–2000. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Sun, A.; Ren, F.; Liu, X.; Gao, B.; Zhang, Q. Changes of climate extremes in China. Clim. Chang. 1999, 42, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, C. Substantial decrease in concurrent meteorological droughts and consecutive cold events in huai river basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 6065–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, A. Random variables, joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetika 1973, 9, 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, M.; Ragno, E.; AghaKouchak, A. Multivariate copula analysis toolbox (mvcat): Describing dependence and underlying uncertainty using a bayesian framework. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5166–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, M.; Moftakhari, H.; Gupta, H.V.; Ragno, E.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Sanders, B.; Matthew, R.; AghaKouchak, A. Multihazard scenarios for analysis of compound extreme events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5470–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, Q.; Mao, G.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Yu, J. Flash drought characteristics by different severities in humid subtropical basins: A case study in the gan river basin, China. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 7337–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, G.; Wang, S.; You, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Change in the heatwave statistical characteristics over China during the climate warming slowdown. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Sun, Q.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Y. Joint analysis of changes in temperature and precipitation on the loess plateau during the period 1961–2011. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 3221–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, M. Copula-based drought risk assessment combined with an integrated index in the wei river basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Ziegler, A.D.; Searchinger, T.D.; Yang, L.; Chen, A.; Ju, K.; Piao, S.; Li, L.; Ciais, P.; Chen, D. A reversal in global terrestrial stilling and its implications for wind energy production. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Xu, N.; Yang, F.; Xu, K. Evaluation of spatial-temporal variation performance of era5 precipitation data in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Huang, A.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, H.; Fang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Cai, S. Characteristics of the precipitation diurnal variation and underlying mechanisms over jiangsu, eastern China, during warm season. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 703071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; He, R.; Zhang, J. Non-stationary frequency analysis of annual extreme rainfall volume and intensity using archimedean copulas: A case study in eastern China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaoui, Z.K.; Bardossy, A. Modeling short duration extreme precipitation patterns using copula and generalized maximum pseudo-likelihood estimation with censoring. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 84, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; Hu, W.; Zhu, B.; Wang, P.; Wei, Y. Exploring the climatic impacts on residential electricity consumption in Jiangsu, China. Energy Policy 2020, 140, 111398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

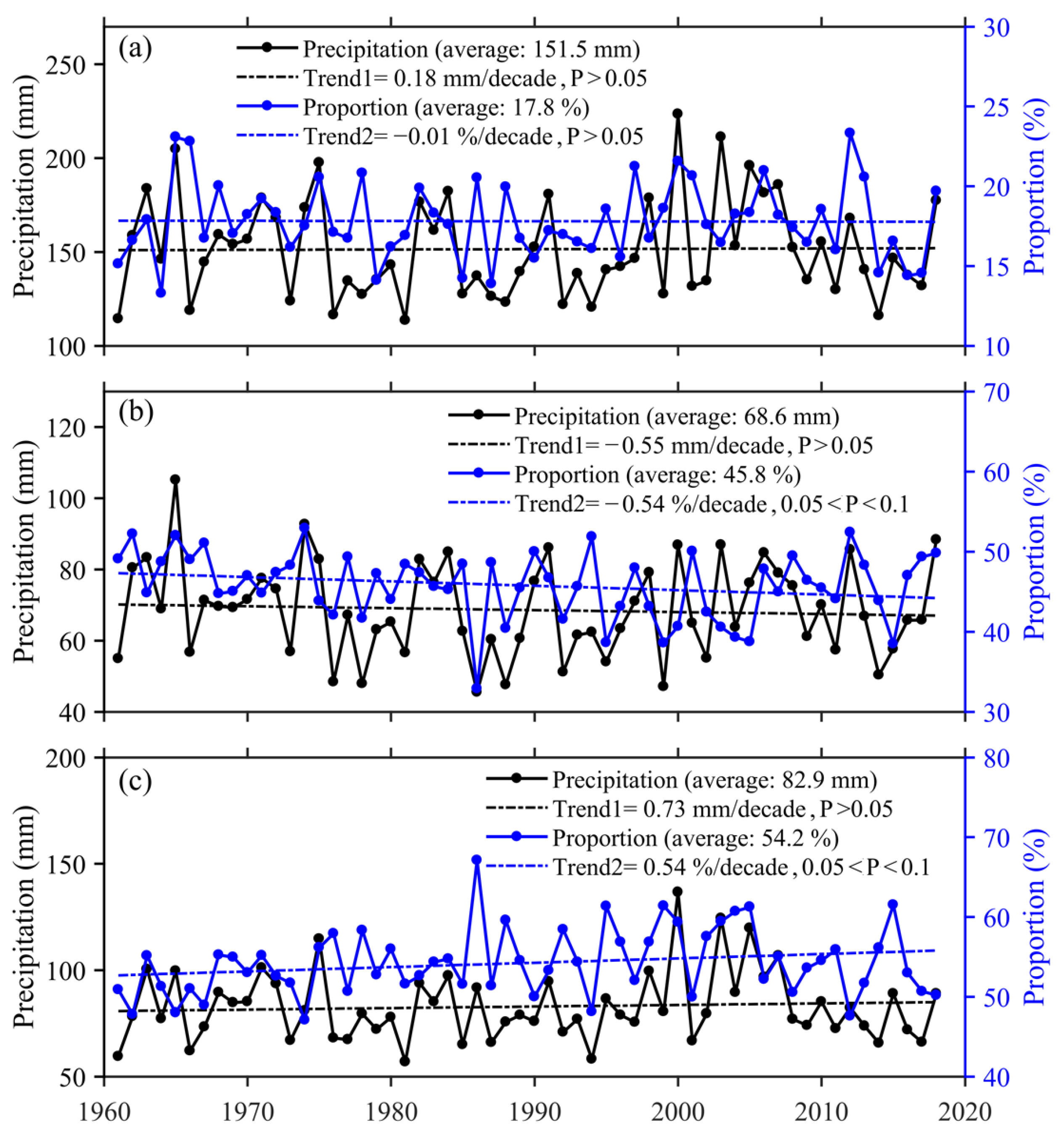

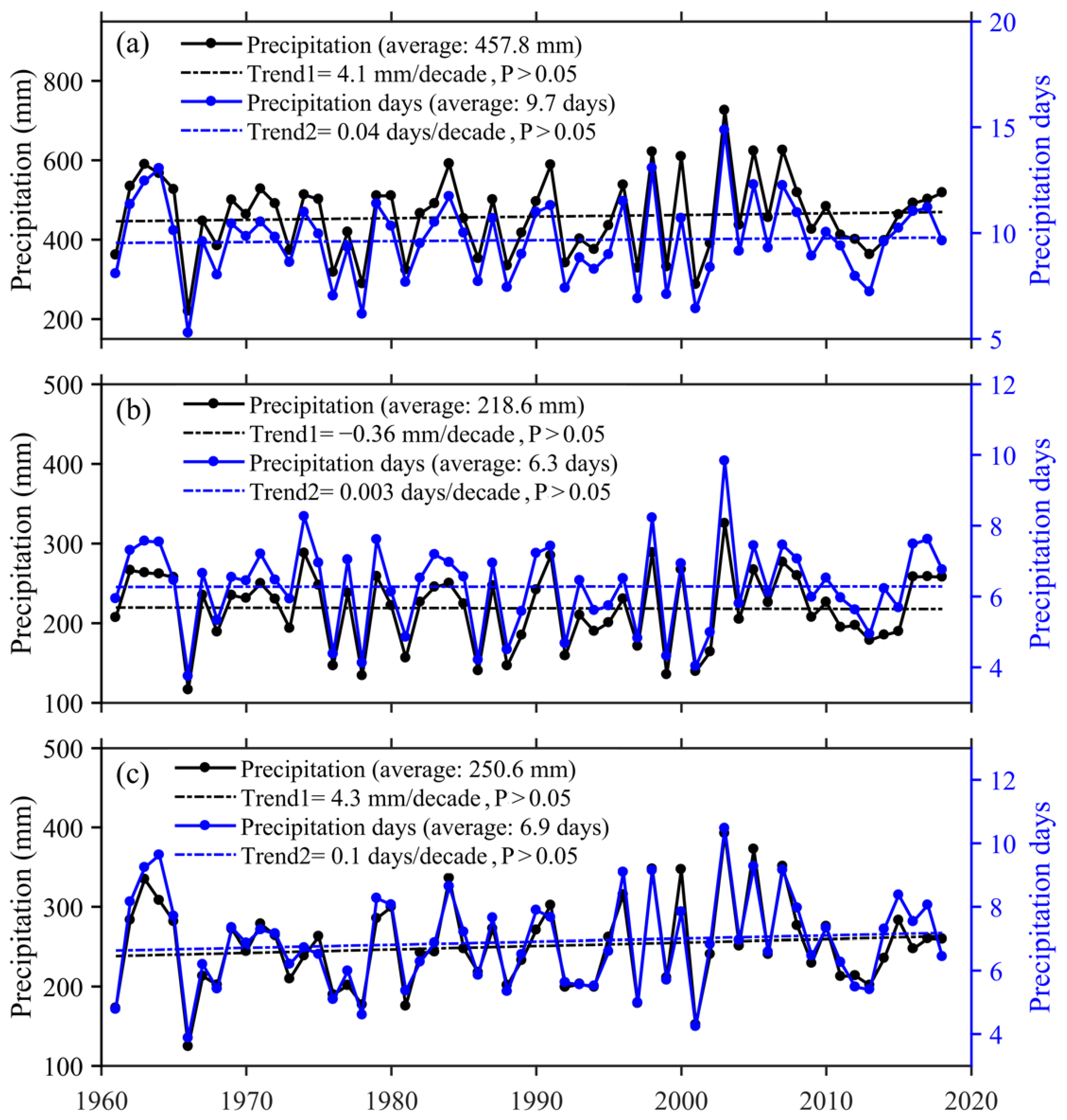
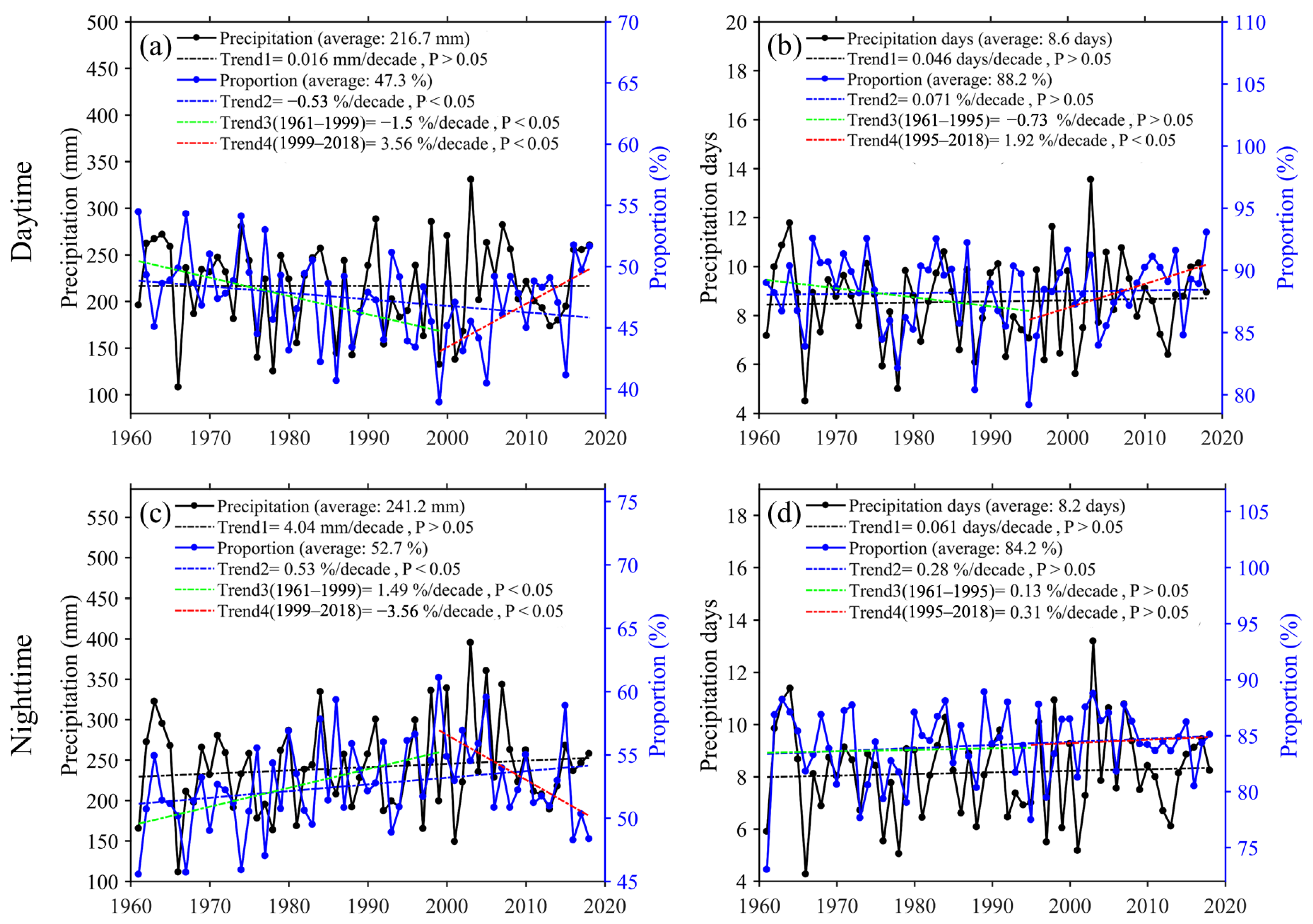
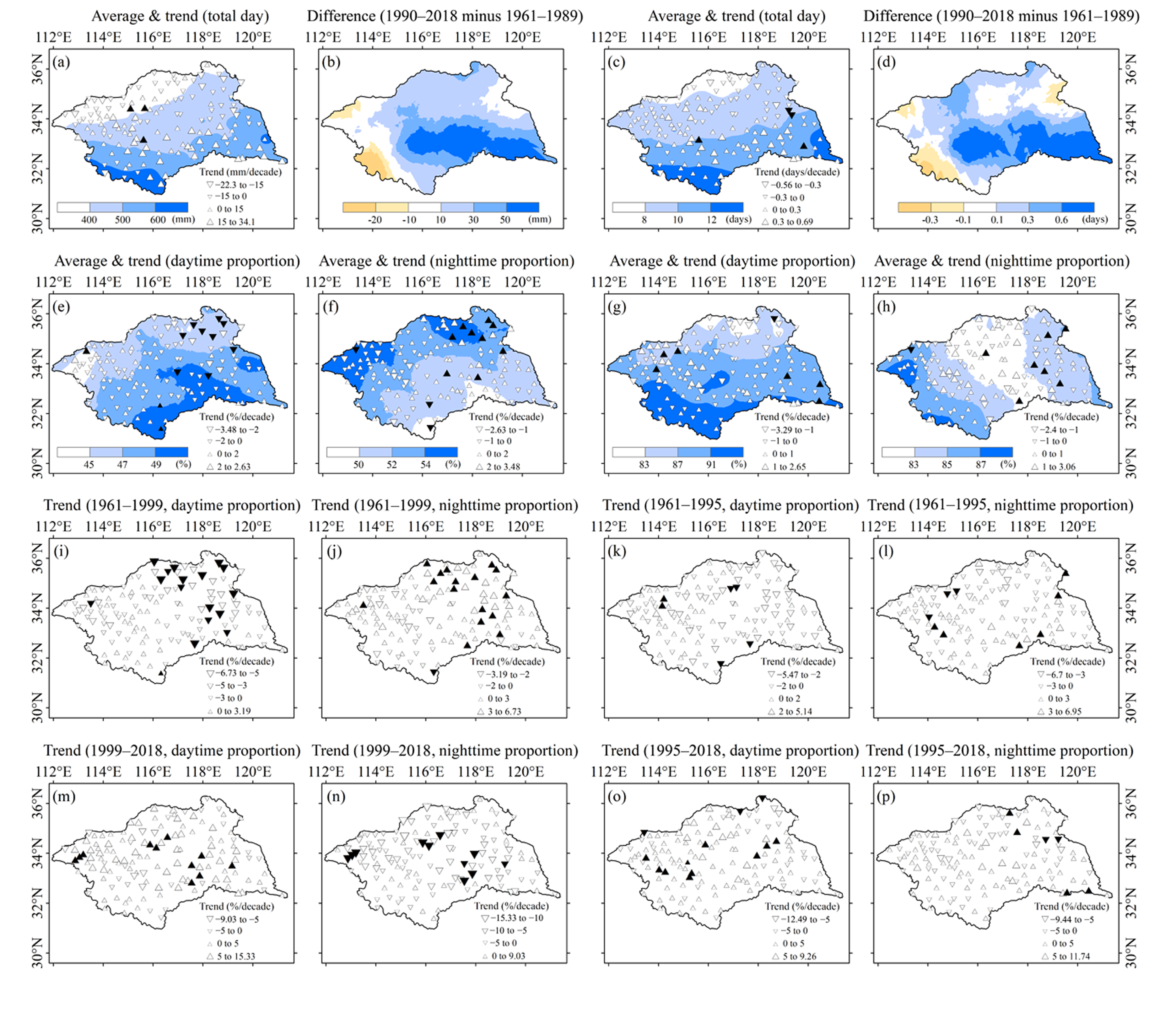

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Shen, L.; Ju, Q.; Zhou, T.; Xia, P. The Proportional Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Based on Daily Precipitation in Huai River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081287
Zhu Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Chen C, Shen L, Ju Q, Zhou T, Xia P. The Proportional Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Based on Daily Precipitation in Huai River Basin, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081287
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ying, Xiaoli Liu, Yuqing Zhang, Changchun Chen, Liucheng Shen, Qin Ju, Ting Zhou, and Ping Xia. 2022. "The Proportional Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Based on Daily Precipitation in Huai River Basin, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081287
APA StyleZhu, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, C., Shen, L., Ju, Q., Zhou, T., & Xia, P. (2022). The Proportional Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Based on Daily Precipitation in Huai River Basin, China. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081287






