Quantification of Regional Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Its Temporal Evolution: Insights from Identification of the Impacts of Meteorological Conditions and Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. O3 and Meteorological Data Sets
2.2. Identification of the Impacts from Local, Non-Local and Meteorological Factors on O3
2.3. Determination of Relationships between O3 and Meteorological Factors
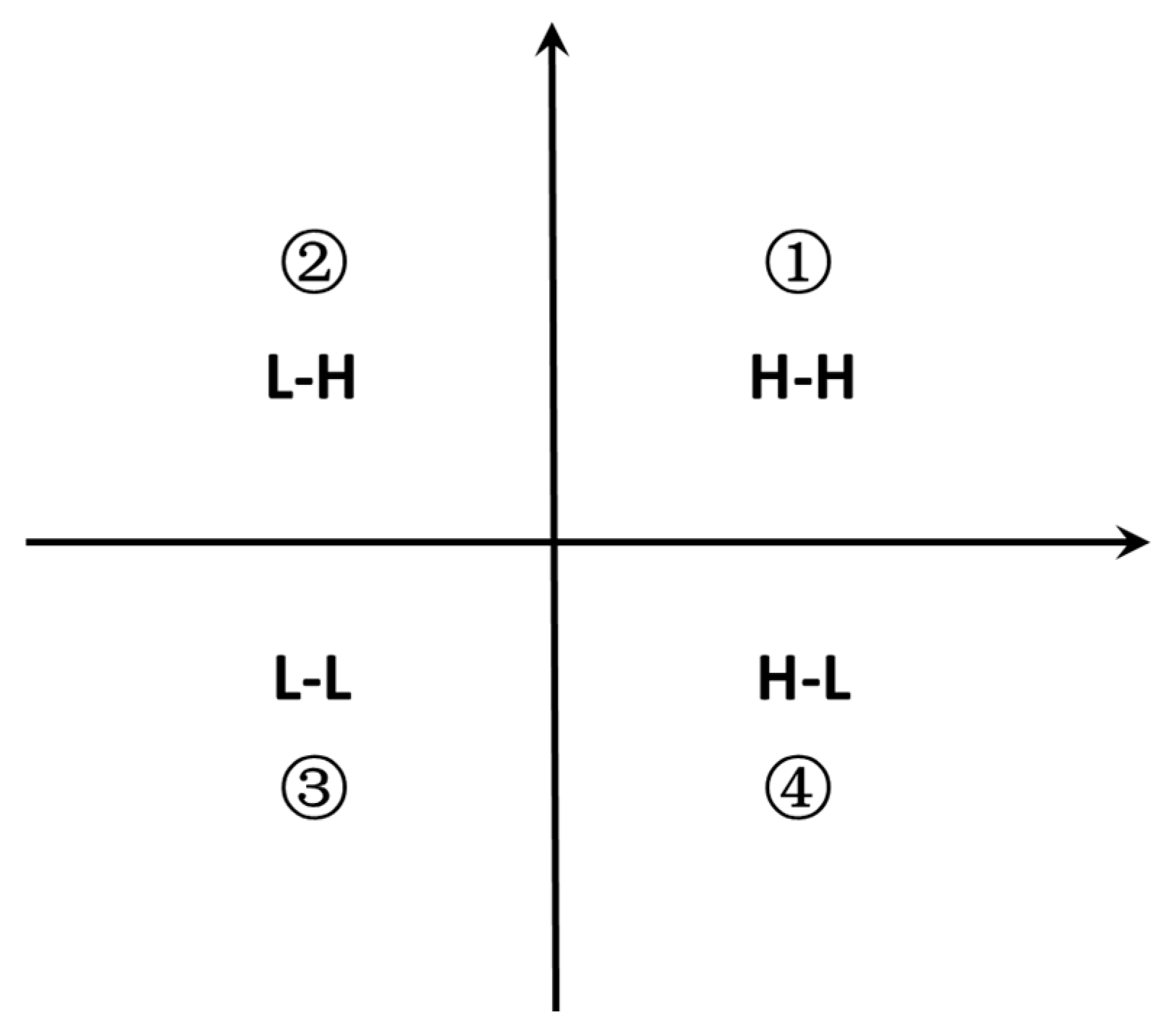
2.4. Calculation of Degree of Aggregation Dispersion of Stations with Similar O3 Levels
3. Results
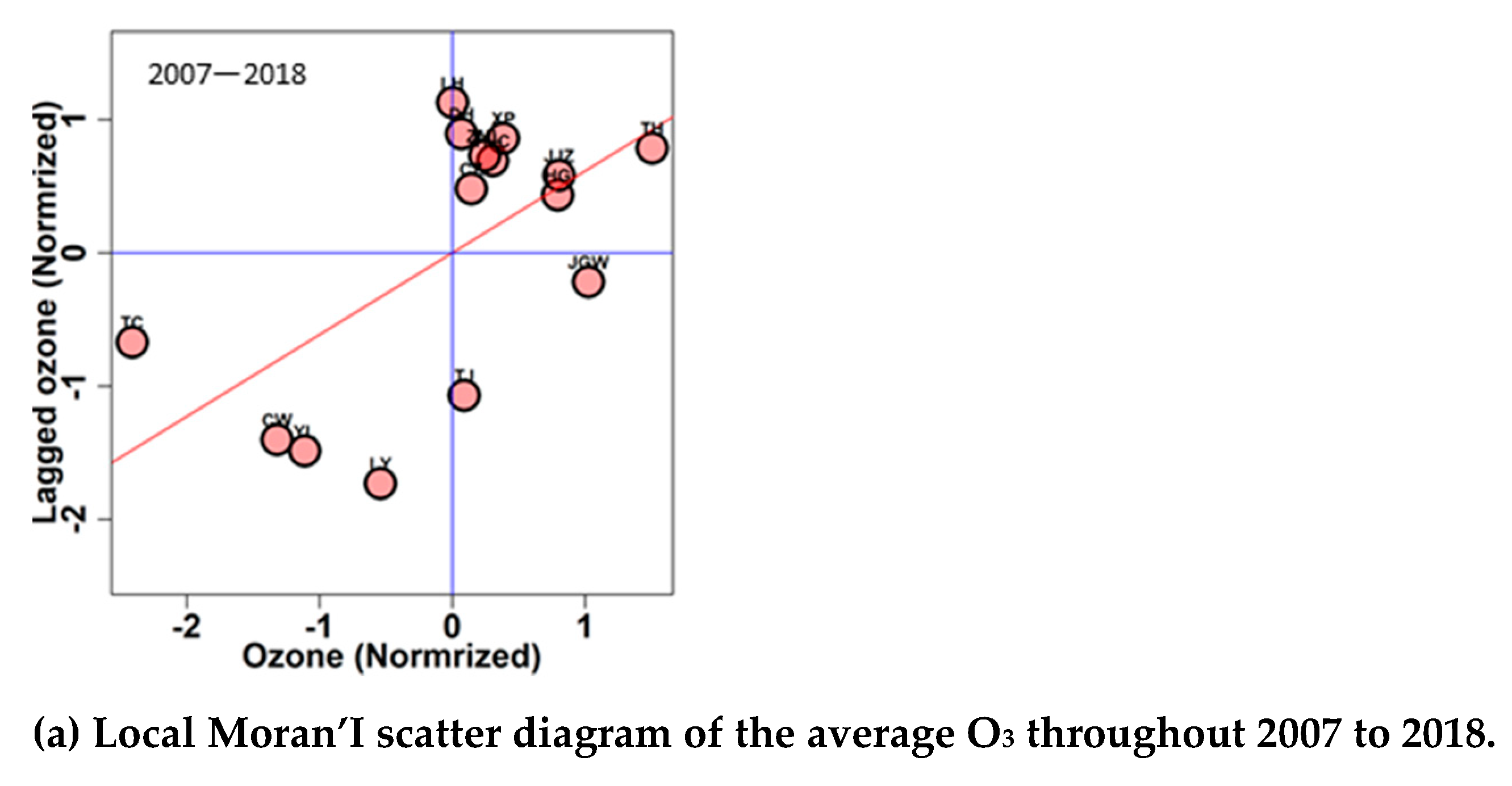
3.1. Aggregation of Stations with Similar O3 Concentrations over Different Time Scales
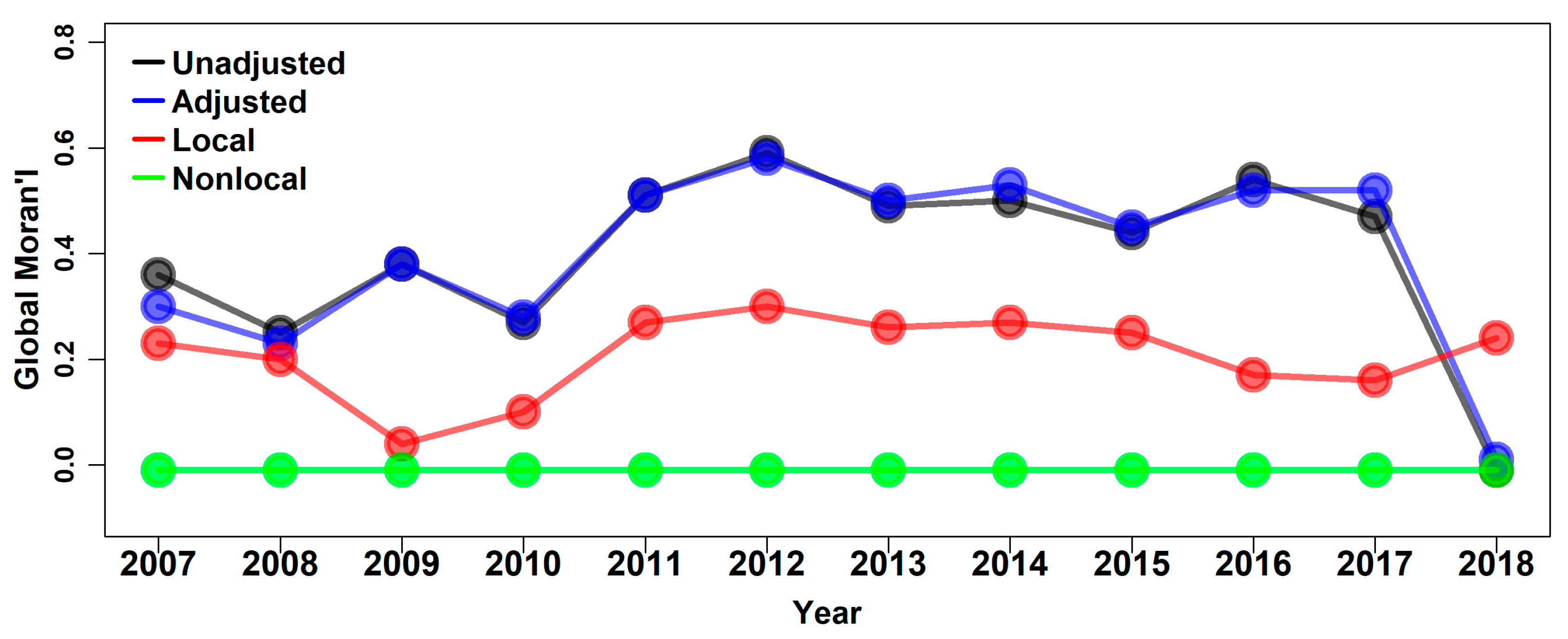
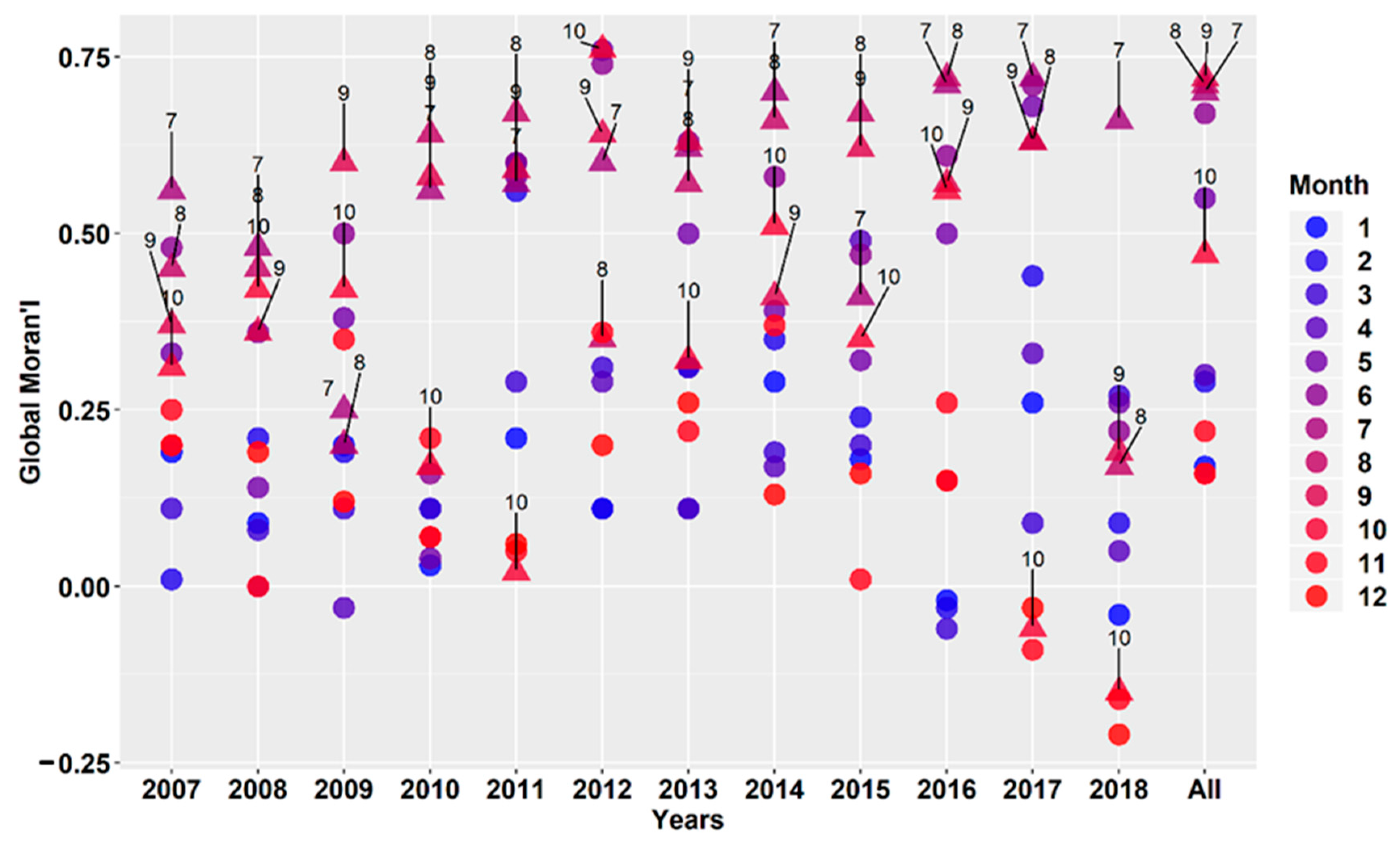
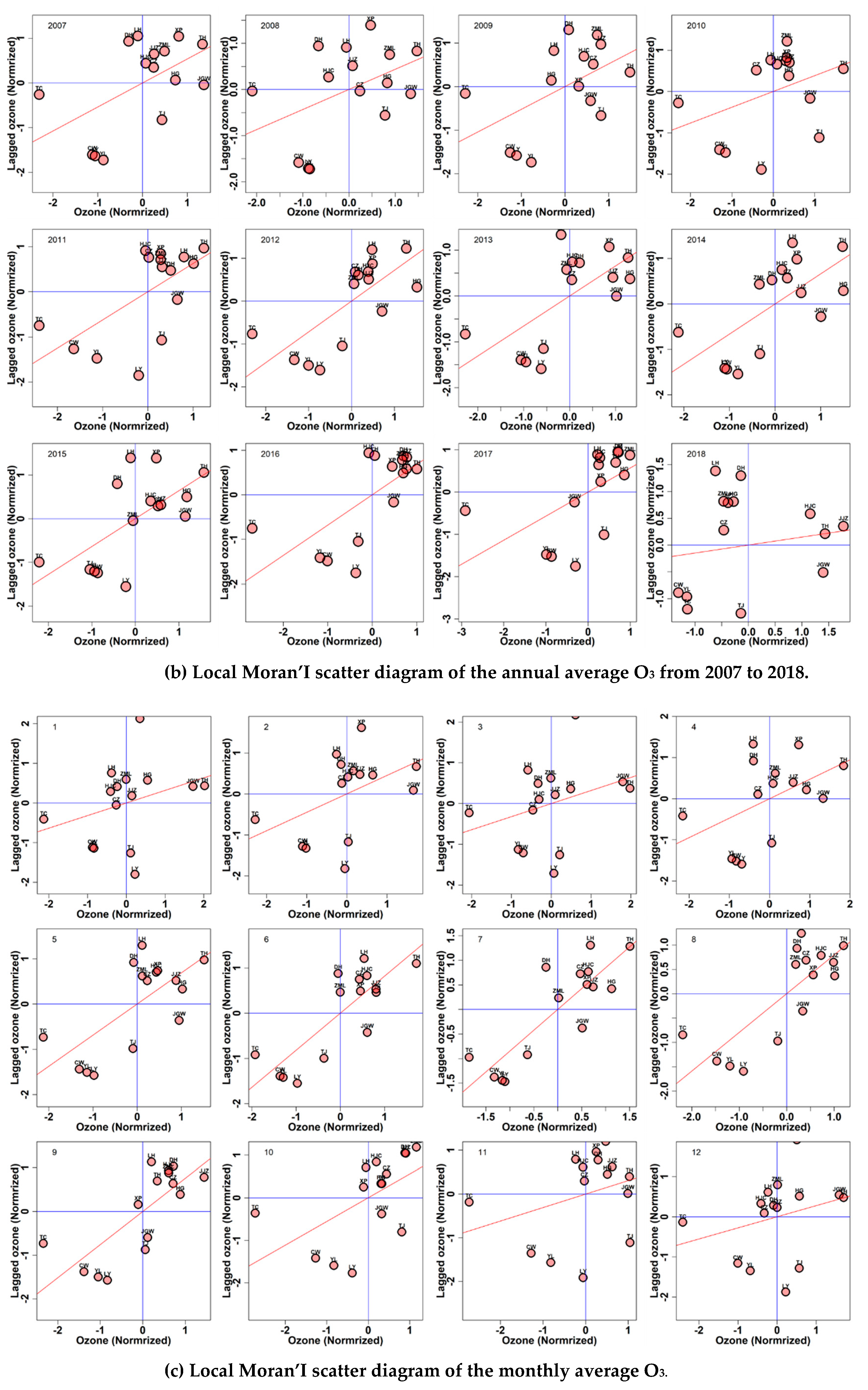
3.1.1. Global Moran’s I on Different Time Scales
3.1.2. GM on Different Time Scales
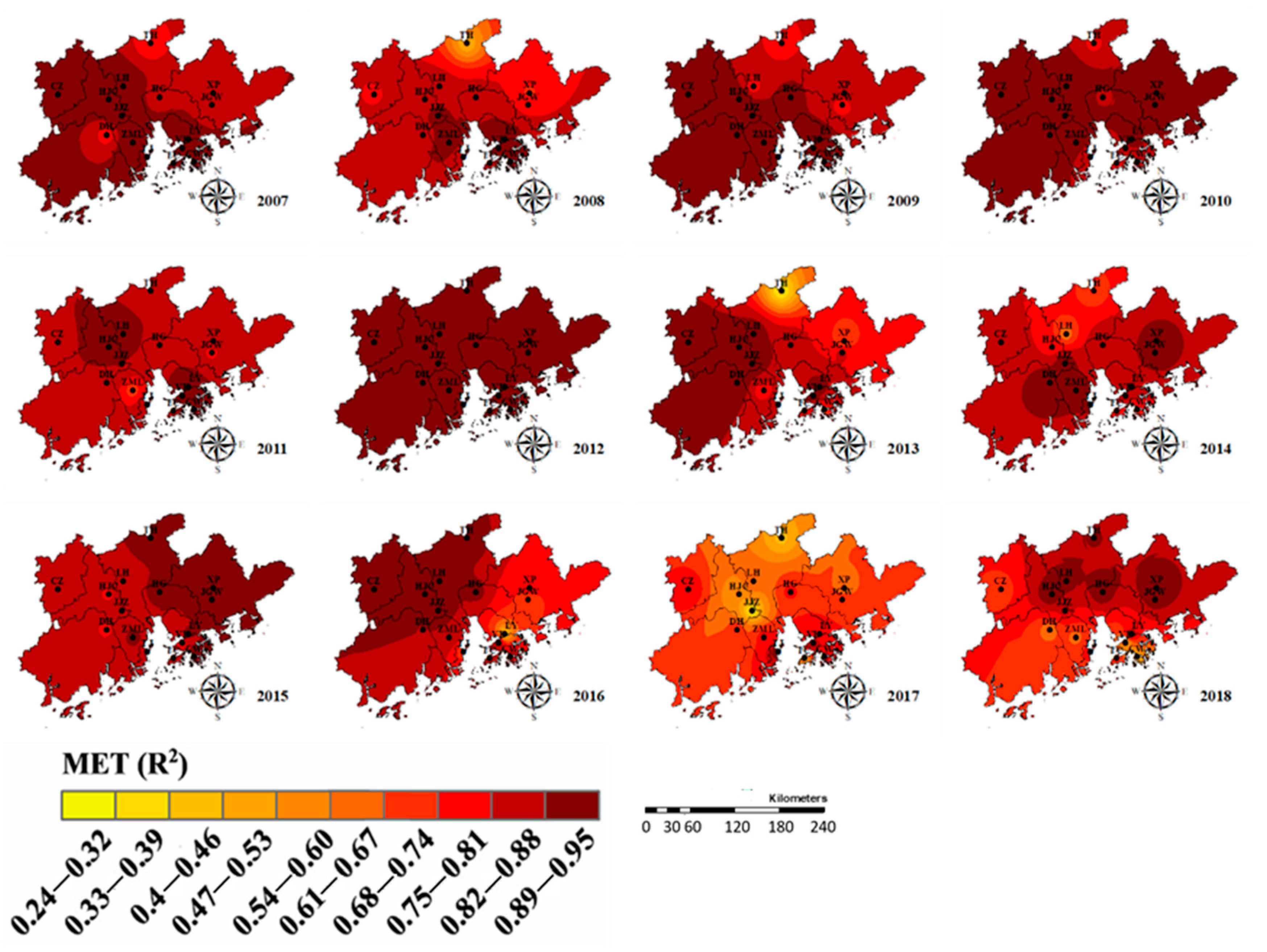
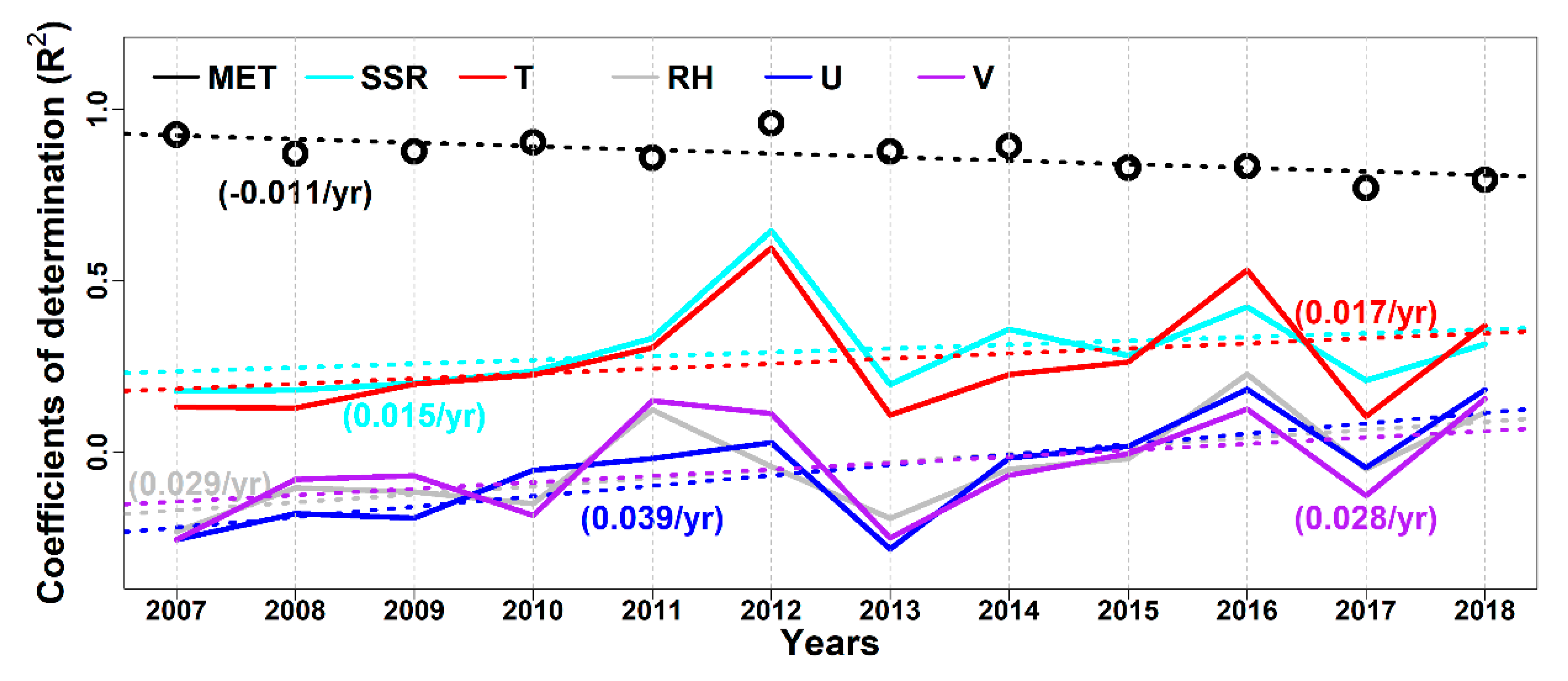
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Meteorological Conditions-O3 Correlations and Its Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ou, J.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Ye, X.; Wu, Y.; Yin, X. Evolution of anthropogenic air pollutant emissions in Guangdong Province, China, from 2006 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11701–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Lyu, X.; Cheng, H.; Ling, Z.; Louie, P.; Simpson, I.; Meinardi, S.; Blake, D. Long-term O3–precursor relationships in Hong Kong: Field observation and model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10919–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report on the State of Guangdong Provinccal Environment of 2019. Available online: http://gdee.gd.gov.cn/attachment/0/397/397371/3048134.pdf. (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Stevenson, D.S.; Young, P.J.; Naik, V.; Lamarque, J.; Shindell, D.; Voulgarakis, A.; Skeie, R.; Dalsoren, S.; Myhre, G.; Berntsen, T. Tropospheric ozone changes, radiative forcing and attribution to emissions in the Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Model Intercomparison Project (ACCMIP). Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 3063–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Balashov, N.; Witte, J.; Coetzee, J.; Thouret, V.; Posny, F. Tropospheric ozone increases over the southern Africa region: Bellwether for rapid growth in Southern Hemisphere pollution? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 9855–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzuca, G.; Ren, X.; Loughner, C.; Estes, M.; Crawford, J.; Pickering, K.; Weinheimer, A.; Dickerson, R. Ozone Production and Its Sensitivity to NOx and VOCs: Results from the DIS-COVER-AQ Field Experiment, Houston 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14463–14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Horowitz, L.W.; Munger, J.; Heikes, B.G.; Dickerson, R.; Artz, R.; Keene, W.C. Seasonal transition from NOx- to hydrocarbon-limited conditions for ozone production over the eastern United States in September. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1995, 100, 9315–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; An, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, R.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Lou, S.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Q.; et al. Source apportionment of surface ozone in the Yangtze River Delta, China in the summer of 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Holloway, T. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument: Ozone Sensitivity over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7229–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xie, S. Spatial Distribution of Ozone Formation in China Derived from Emissions of Speciated Volatile Organic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2574–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Ling, Z.; Wang, Y.; Louie, P.; Luk, C. Spatiotemporal variation of ozone precursors and ozone formation in Hong Kong: Grid field measurement and modelling study. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 569, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Fan, S.; Chen, W.; Chang, M.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Z.; Fan, Q. Photochemical indicators of ozone sensitivity: Application in the Pearl River Delta, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.; Wang, B. Ground-level ozone in the Pearl River Delta and the roles of VOC and NOx in its pro-duction. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Shao, M.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Guo, H.; Louie, P.K.K. Ambient Ozone Control in a Photochemically Active Region: Short-Term Despiking or Long-Term Attainment? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lyu, X.; Deng, X.; Huang, X.; Jiang, F.; Ding, A. Aggravating O3 pollution due to NOx emission control in eastern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 677, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.; Chiu, C.; Yu, H. Influences of ambient air pollutants and meteorological conditions on ozone variations in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 29, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Stauffer, R.; Thompson, A.; Knepp, T.; Pippin, M. Surface ozone at a coastal suburban site in 2009 and 2010: Relationships to chemical and meteorological processes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shao, M.; Che, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Streets, D. Speciated VOC Emission Inventory and Spatial Patterns of Ozone Formation Potential in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8580–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneman, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Mulholland, J.; Russell, A. Responses in Ozone and Its Production Efficiency Attributable to Recent and Future Emissions Changes in the Eastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13797–13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Ojha, N.; Pozzer, A.; Mar, K.; Beig, G.; Lelieveld, J.; Gunthe, S. WRF-Chem simulated surface ozone over south Asia during the pre-monsoon: Effects of emission inventories and chemical mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 14393–14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, C.; Munyan, J.; Bailey, C.; Kotsakis, A.; Sagona, J.; Esperanza, A.; Pusede, S. On the effect of upwind emission controls on ozone in Sequoia National Park. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 17061–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Episode study of fine particle and ozone during the CAPUM-YRD over Yangtze River Delta of China: Characteristics and source attribution. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, K.; Fung, J.H.; Zheng, J.; Zhong, L.; Louie, P. Ozone source apportionment (OSAT) to differentiate local regional and super-regional source contributions in the Pearl River Delta region, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemball-Cook, S.; Parrish, D.; Ryerson, T.; Nopmongcol, U.; Johnson, J.; Tai, E.; Yarwood, G. Contributions of regional transport and local sources to ozone exceedances in Houston and Dallas: Comparison of results from a photochemical grid model to aircraft and surface measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, A.; Fung, J.; Ma, H.; Tse, Y. Systematic evaluation of ozone control policies using an Ozone Source Apportionment method. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, J.; Reidmiller, D.; Jaffe, D. Causes of high O in the lower free troposphere over the Pacific Northwest as observed at the Mt. Bachelor Observatory. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5302–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Lin, X.; Louie, P.; Chen, D.; Bian, Y. Quantitative impacts of meteorology and precursor emission changes on the long-term trend of ambient ozone over the Pearl River Delta, China, and implications for ozone control strategy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 12901–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifko, F.J. Isoprene emissions and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6121–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folberth, G.; Hauglustaine, D.; Lathière, J.; Brocheton, F. Impact of biogenic hydrocarbons on tropospheric chemistry: Results from a global chemistry-climate model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, P.; Wooldridge, P.; Millet, D.; McKay, M.; Goldstein, A.; Cohen, R. Observations of total peroxy nitrates and aldehydes: Measurement interpretation and inference of OH radical concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2007, 7, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Paulot, F.; Mao, J.; Yantosca, R.M. Positive but variable sensitivity of August surface ozone to large-scale warming in the southeast United States. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xu, Y. Effects of Relative Humidity on Ozone and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from the Photooxidation of Benzene and Ethylbenzene. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavassalis, S.C.; Murphy, J.G. Understanding ozone-meteorology correlations: A role for dry deposition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Youn, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, H. Extensive spatio-temporal analyses of surface ozone and related meteorological variables in South Korea for 1999–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 14, 1191–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Swall, L.; Cox, W.; Davis, J.M. Interannual variation in meteorologically adjusted ozone levels in the eastern United States: A comparison of two approaches. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.T.; Zalewsky, E.; Zurbenko, I. Determining Temporal and Spatial Variations in Ozone Air Quality. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 45, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, T.; Zurbenko, G. Detecting and Tracking Changes in Ozone Air Quality. Air Waste 1994, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanchus, M.; Rao, S.; Zurbenko, I. Evaluating the effectiveness of ozone management efforts in the presence of mete-orological variability. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1998, 48, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskridge, E.; Ku, Y.; Rao, T.; Porter, S.; Zurbenko, G. Separating Different Scales of Motion in Time Series of Meteorological Variables. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaum, B.; Rao, T.; Zurbenko, G. Moderating the Influence of Meteorological Conditions on Ambient Ozone Concentrations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, E.; Comrie, A. Extending the Kolmogorov–Zurbenko Filter: Application to Ozone, Particulate Matter, and Meteor-ological Trends. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, W.; Xia, J. Using Semivariogram and Moran’s I Techniques to Evaluate Spatial Distribution of Soil Micro-nutrients. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, N.; Li, H.; Sun, F.; Zhou, D.; Li, G. Combining Geostatistics with Moran’s I Analysis for Mapping Soil Heavy Metals in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Xu, W.; Ledwith, V. Use of local Moran’s I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 398, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report on the State of Guangdong Provinccal Environment of 2017. Available online: http://gdee.gd.gov.cn/protect/P0201806/P020180620/P020180620631772750308.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- China Meteorological Data Service Center. 2019. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Sillman, S.; Samson, P. Impact of temperature on oxidant photochemistry in urban, polluted rural and remote environments. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1995, 100, 11497–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszyna, K.; Luria, M.; Meagher, J. The correlation of temperature and rural ozone levels in southeastern U.S.A. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 3011–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Washenfelder, R.; Roberts, J.; Mielke, L.; Osthoff, H.; Tsai, C.; Pikelnaya, O.; Stutz, J.; Veres, P.; Cochran, A.; et al. Vertically Resolved Measurements of Nighttime Radical Reservoirs in Los Angeles and Their Contribution to the Urban Radical Budget. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10965–10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wei, W.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y. Association between the Emission Rate and Temperature for Chemical Pollutants in Building Materials: General Correlation and Understanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8540–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormeño, E.; Gentner, D.; Fares, S.; Karlik, J.; Park, J.; Goldstein, A. Sesquiterpenoid Emissions from Agricultural Crops: Correlations to Monoterpenoid Emissions an–d Leaf Terpene Content. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3758–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, T.; Louie, P.; Luk, C.W.; Blake, D.; Xu, Z. Increasing External Effects Negate Local Efforts to Control Ozone Air Pollution: A Case Study of Hong Kong and Implications for Other Chinese Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10769–10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Station | Full Name | City | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Environmental Background |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | Central/Western | Hong Kong | 114.15 | 22.28 | Residential/Commercial |
| CZ | Chengzhong | Zhaoqing | 112.47 | 23.05 | Residential/Commercial |
| DH | Donghu | Jiangmen | 113.08 | 22.59 | Urban |
| HG | Haogang | Dongguan | 113.73 | 23.03 | Residential/Commercial |
| HJC | Huijingcheng | Foshan | 113.10 | 23.00 | Residential/Commercial |
| JGW | Jinguowan | Huizhou | 114.38 | 22.93 | Residential |
| JJZ | Jinjuzui | Foshan | 113.26 | 22.81 | Suburban |
| LH | Luhu | Guangzhou | 113.28 | 23.15 | Urban |
| LY | Liyuan | Shenzhen | 114.09 | 22.55 | Urban |
| TC | Tung Chung | Hong Kong | 113.91 | 22.27 | Residential |
| TH | Tianhu | Guangzhou | 113.62 | 23.65 | Rural |
| TJ | Tangjia | Zhuhai | 113.58 | 22.34 | Commercial/Industrial |
| XP | Xiapu | Huizhou | 114.40 | 23.07 | Commercial |
| YL | Yuen Long | Hong Kong | 114.02 | 22.44 | Residential |
| ZML | Zimaling | Zhongshan | 113.40 | 22.50 | Residential/Commercial |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Xie, D.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Jia, W. Quantification of Regional Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Its Temporal Evolution: Insights from Identification of the Impacts of Meteorological Conditions and Emissions. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020279
Yang L, Xie D, Yuan Z, Huang Z, Wu H, Han J, Liu L, Jia W. Quantification of Regional Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Its Temporal Evolution: Insights from Identification of the Impacts of Meteorological Conditions and Emissions. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020279
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Leifeng, Danping Xie, Zibing Yuan, Zhijiong Huang, Haibo Wu, Jinglei Han, Lijun Liu, and Wenchao Jia. 2021. "Quantification of Regional Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Its Temporal Evolution: Insights from Identification of the Impacts of Meteorological Conditions and Emissions" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020279
APA StyleYang, L., Xie, D., Yuan, Z., Huang, Z., Wu, H., Han, J., Liu, L., & Jia, W. (2021). Quantification of Regional Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Its Temporal Evolution: Insights from Identification of the Impacts of Meteorological Conditions and Emissions. Atmosphere, 12(2), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020279







