Retrospective Modeling of NO2 and PM10 Concentrations over the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France), 1990–2010—Performance Evaluation, Exposure Assessment and Correlation between Pollutants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Period and Population
2.2. Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling
2.2.1. The SIRANE Model
2.2.2. Emissions
2.2.3. Background Concentrations
2.3. Assessment Approach
2.3.1. Concentration Measurements
2.3.2. Subjects Exposure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Background Concentration Data on 2010 Simulations
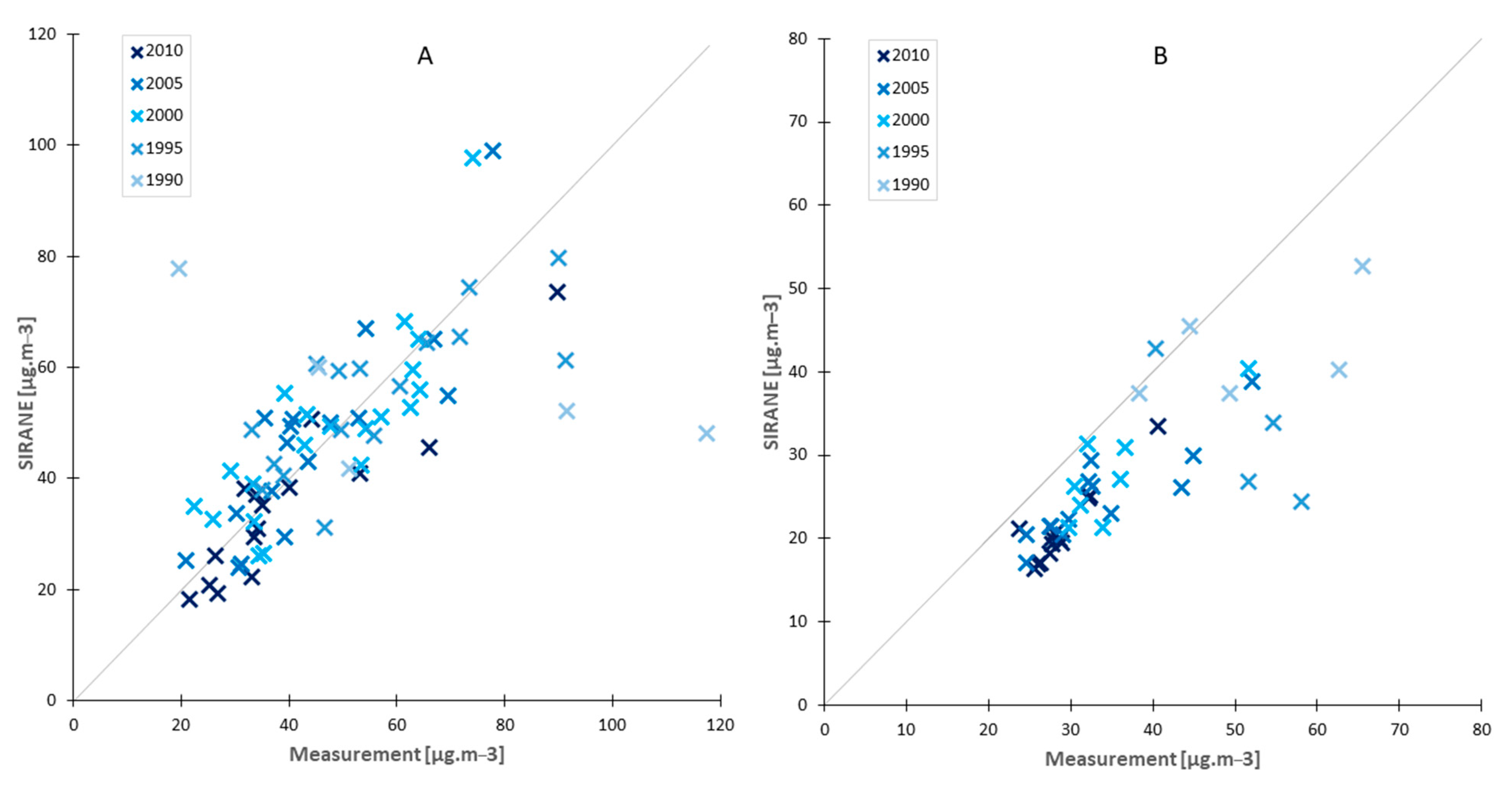
3.2. Comparison of Simulated Concentrations with Historical Annual Measurements
3.3. Historical Trend in Annual PM10 and NO2 Concentrations
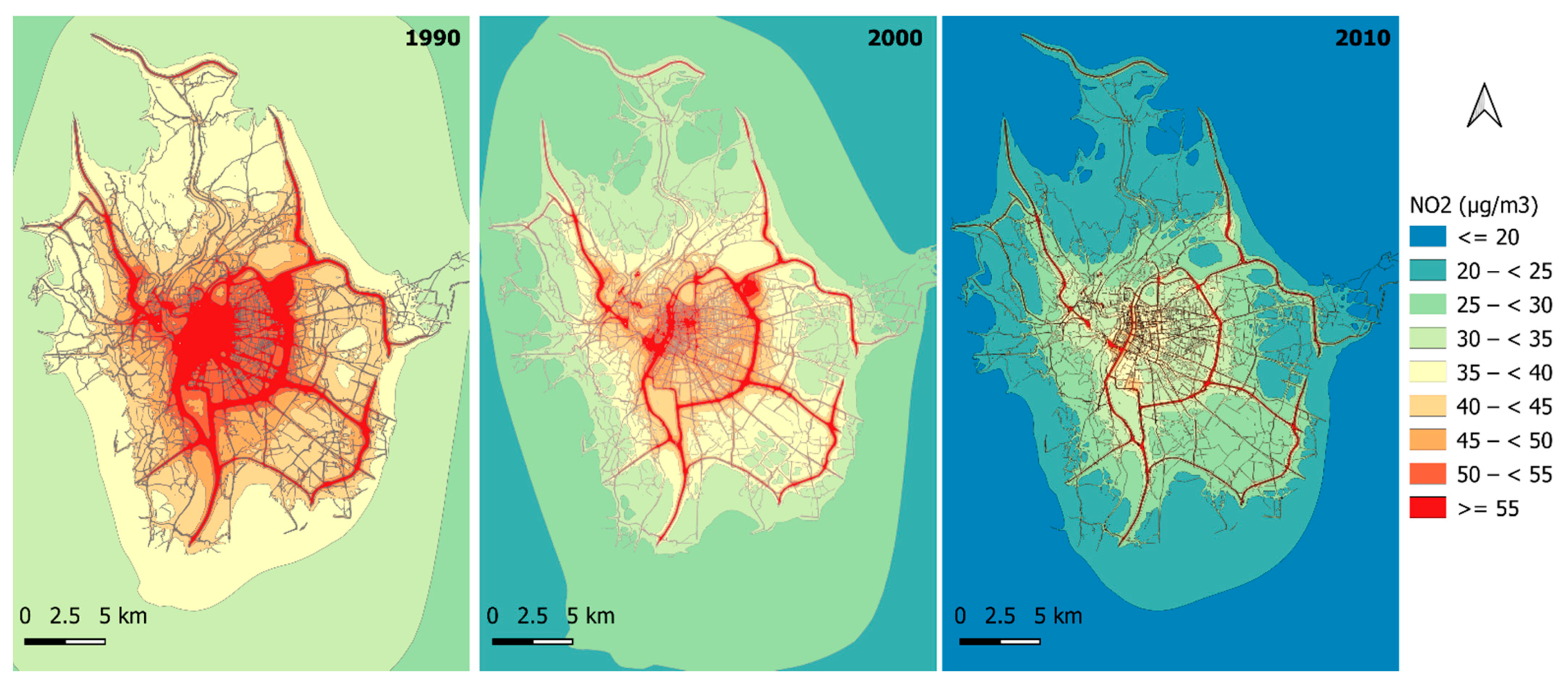
3.3.1. Over the Study Domain
3.3.2. PM10 and NO2 Concentrations at the Study Subjects’ Address of Residence
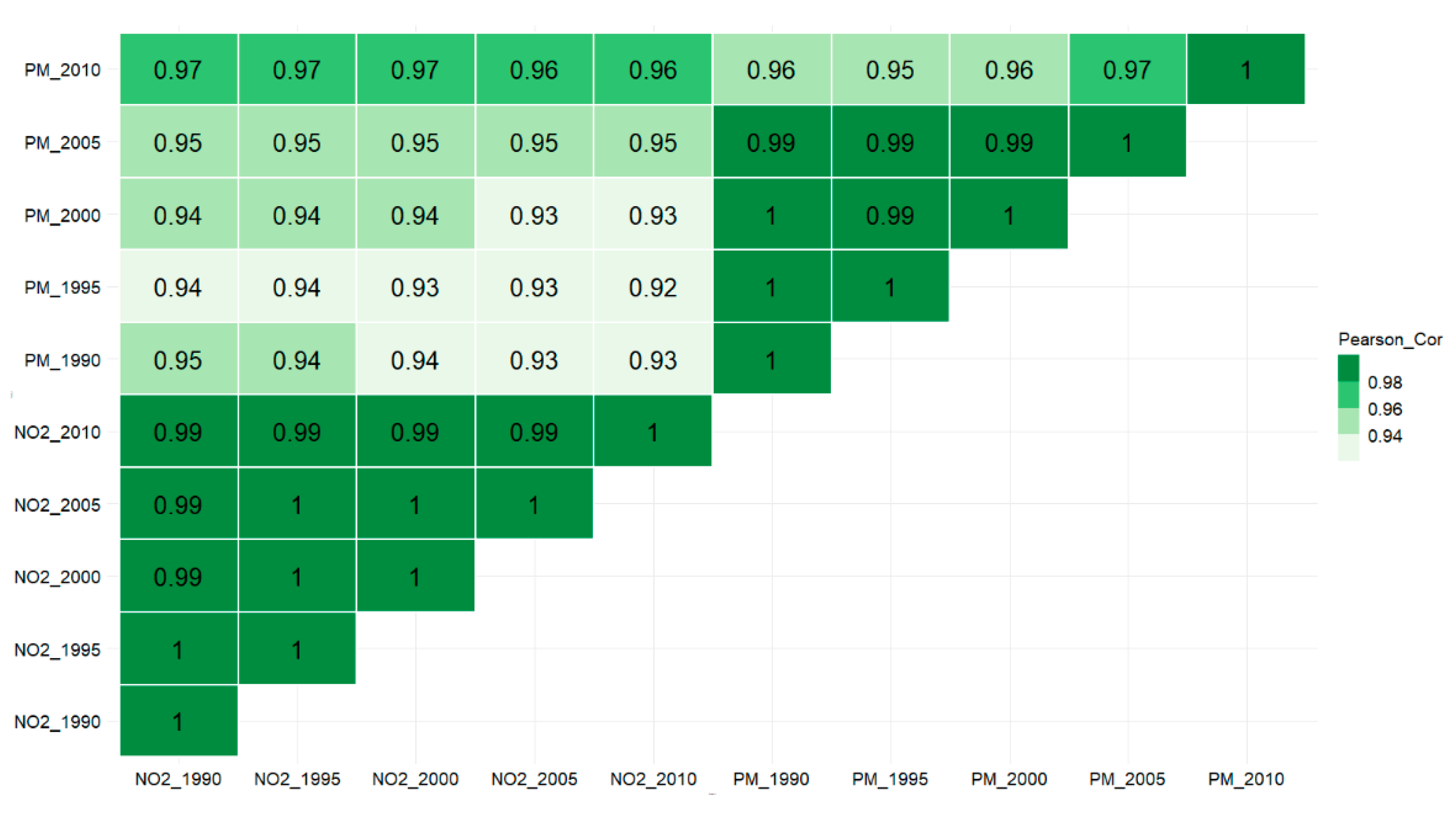
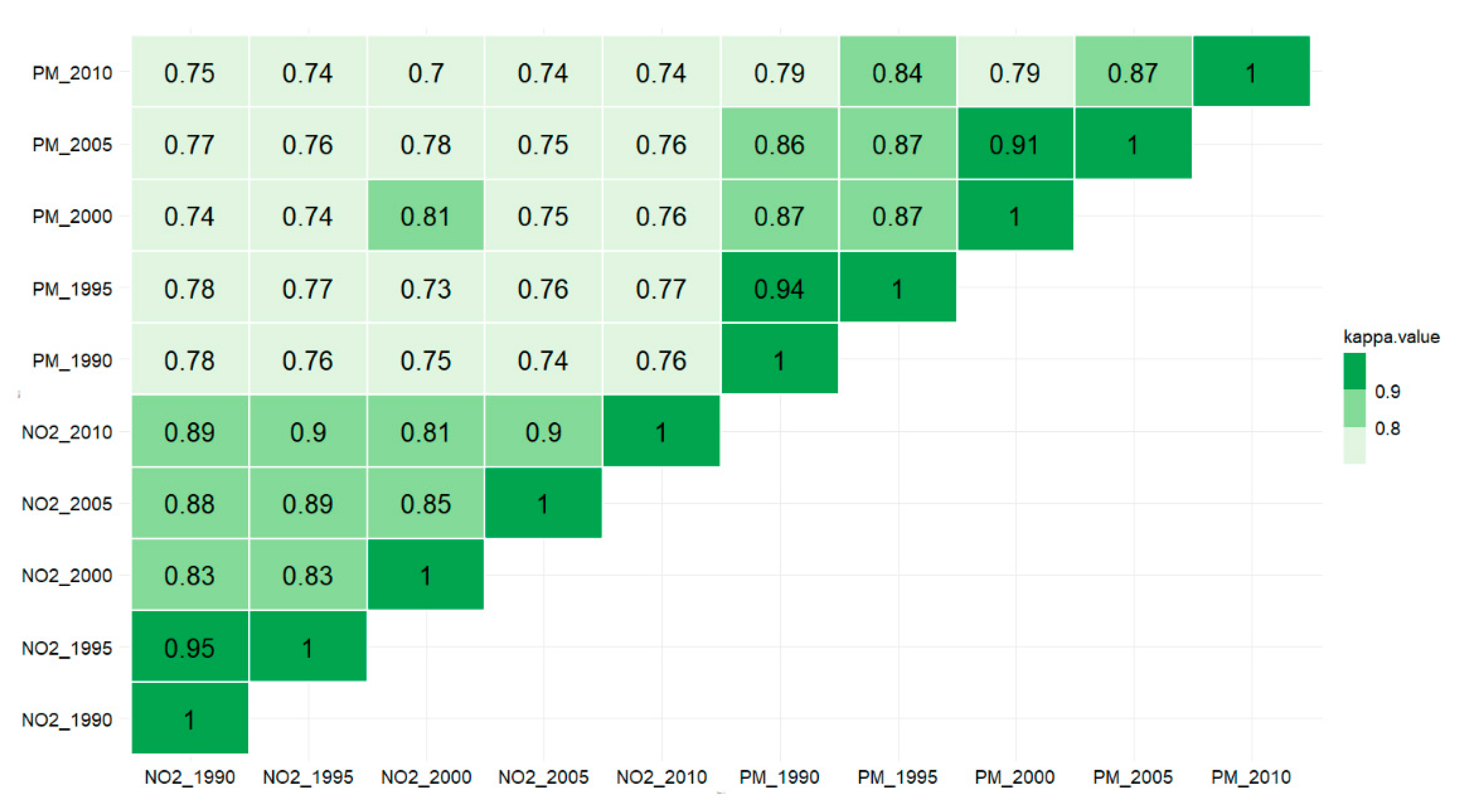
3.3.3. Correlation of Subject’s Exposure over Years
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lallukka, T.; Millear, A.; Pain, A.; Cortinovis, M.; Giussani, G. GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators Global, Regional, and National Life Expectancy, All-Cause Mortality, and Cause-Specific Mortality for 249 Causes of Death, 1980-2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Cardiovascular Disease Burden from Ambient Air Pollution in Europe Reassessed Using Novel Hazard Ratio Functions. Eur. Heart. J. 2019, 40, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.A.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Loomis, D.; Straif, K. International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group Carcinogenicity of Diesel-Engine and Gasoline-Engine Exhausts and Some Nitroarenes. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K.; et al. The Carcinogenicity of Outdoor Air Pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forastiere, F.; Renzi, M.; Cesaroni, G.; Stafoggia, M.; Rodopolou, S.; Vienneau, D.; Andersen, Z.; De Hoogh, K.; Klompmaker, J.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Low-Level Air Pollution and Natural Cause Mortality in Rome: Comparison of Results Based on European Wide and Local Land Use Regression Models within the ELAPSE Project. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Brook, J.R.; Brook, R.D.; Oiamo, T.H.; Luginaah, I.; Peters, P.A.; Spence, J.D. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Carotid Plaque Burden in a Canadian City With Low-Level Ambient Pollution. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e013400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Rodopolou, S.; de Hoogh, K.; Ljungman, P.; Samoli, E.; Hoek, G.; Bellander, T.; Peters, S.; Pershagen, G.; et al. Low-Level Air Pollution and Incidence of Asthma among Adults: Pooled Analysis of 2 European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodonos, A.; Awad, Y.A.; Schwartz, J. The Concentration-Response between Long-Term PM2.5 Exposure and Mortality; A Meta-Regression Approach. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Rodopolou, S.; de Hoogh, K.; Ljungman, P.; Samoli, E.; Hoek, G.; Bellander, T.; Peters, A.; Pershagen, G. Low-Level Air Pollution and Incidence of Acute Coronary Events: Pooled Analysis of 6 European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Davis, J.; Bina, W.F. Ambient Air Pollution Is Associated with the Increased Incidence of Breast Cancer in US. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2012, 22, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamra, G.B.; Laden, F.; Cohen, A.J.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Brauer, M.; Loomis, D. Lung Cancer and Exposure to Nitrogen Dioxide and Traffic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hystad, P.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Goldberg, M.S.; Crouse, D.L.; Johnson, K. Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and the Risk of Developing Breast Cancer among Women in Eight Canadian Provinces: A Case–Control Study. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Beyea, J.; Bonner, M.R.; Han, D.; Vena, J.E.; Rogerson, P.; Vito, D.; Muti, P.; Trevisan, M.; Edge, S.B.; et al. Exposure to Traffic Emissions throughout Life and Risk of Breast Cancer: The Western New York Exposures and Breast Cancer (WEB) Study. Cancer Causes Control 2007, 18, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Hvidberg, M.; Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Sorensen, M.; Hansen, J.; Loft, S.; Overvad, K.; Tjonneland, A. Air Pollution from Traffic and Cancer Incidence: A Danish Cohort Study. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Krewski, D.; Diver, W.R.; Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Jerrett, M.; Marshall, J.D.; Gapstur, S.M. Ambient Air Pollution and Cancer Mortality in the Cancer Prevention Study II. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A Review of Land-Use Regression Models to Assess Spatial Variation of Outdoor Air Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Puel, C.; Duclaux, O.; Perkins, R.J. Simulations of Atmospheric Pollution in Greater Lyon an Example of the Use of Nested Models. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5147–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basagana, X.; Aguilera, I.; Rivera, M.; Agis, D.; Foraster, M.; Marrugat, J.; Elosua, R.; Kuenzli, N. Measurement Error in Epidemiologic Studies of Air Pollution Based on Land-Use Regression Models. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordioli, M.; Ranzi, A.; De Leo, G.A.; Lauriola, P. A Review of Exposure Assessment Methods in Epidemiological Studies on Incinerators. J. Environ. Public Health 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadou, A.; Praud, D.; Coudon, T.; Danjou, A.M.N.; Faure, E.; Leffondré, K.; Le Romancer, M.; Severi, G.; Salizzoni, P.; Mancini, F.R.; et al. Chronic Long-Term Exposure to Cadmium Air Pollution and Breast Cancer Risk in the French E3N Cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel-Chapelon, F. Cohort Profile: The French E3N Cohort Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudon, T.; Hourani, H.; Nguyen, C.; Faure, E.; Mancini, F.R.; Fervers, B.; Salizzoni, P. Assessment of Long-Term Exposure to Airborne Dioxin and Cadmium Concentrations in the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France). Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Cierco, F.-X.; Perkins, R. The Model SIRANE for Atmospheric Urban Pollutant Dispersion; Part I, Presentation of the Model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Perkins, R.J. Parametric Laws to Model Urban Pollutant Dispersion with a Street Network Approach. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Perkins, R.J.; Salizzoni, P. Flow in a Street Canyon for Any External Wind Direction. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2008, 126, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Perkins, R.J. Flow and Dispersion in Street Intersections. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2981–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L.; Mejean, P. Street Canyon Ventilation and Atmospheric Turbulence. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5056–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H. ES Books: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Air Pollution. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/es00151a602 (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Salem, N.B.; Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Lamaison, G.; Soulhac, L. Modelling Pollutant Dispersion in a Street Network. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 155, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, M.; Salizzoni, P.; Robins, A.; Soulhac, L. Evaluation of a Neighbourhood Scale, Street Network Dispersion Model through Comparison with Wind Tunnel Data. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2012, 37, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Nguyen, C.V.; Volta, P.; Salizzoni, P. The Model SIRANE for Atmospheric Urban Pollutant Dispersion. PART III: Validation against NO2 Yearly Concentration Measurements in a Large Urban Agglomeration. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Didier, D.; Rios, I. The Model SIRANE for Atmospheric Urban Pollutant Dispersion; PART II, Validation of the Model on a Real Case Study. Atmos. Environ 2012, 49, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Charvolin-Volta, P.; Clerico, M.; Nguyen, C.V.; Pognant, F.; Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P. Urban Air Quality and Meteorology on Opposite Sides of the Alps: The Lyon and Torino Case Studies. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dėdelė, A.; Miškinytė, A. The Statistical Evaluation and Comparison of ADMS-Urban Model for the Prediction of Nitrogen Dioxide with Air Quality Monitoring Network. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambini, P.; Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L.; Corti, A. H13-216 Air quality modelling system for traffic scenario analysis in florence: Model validation and identification of critical issues. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Paris, France, 1–4 June 2010; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Tchepel, O.; Costa, A.M.; Martins, H.; Ferreira, J.; Monteiro, A.; Miranda, A.I.; Borrego, C. Determination of Background Concentrations for Air Quality Models Using Spectral Analysis and Filtering of Monitoring Data. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda Rojas, A.L.; Venegas, L.E. Upgrade of the DAUMOD Atmospheric Dispersion Model to Estimate Urban Background NO2 Concentrations. Atmos. Res. 2013, 120–121, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.D.; Brandt, J.; Hvidberg, M.; Frydendall, J.; Christensen, J.H. Assimilation of OMI NO2 Retrievals into the Limited-Area Chemistry-Transport Model DEHM (V2009.0) with a 3-D OI Algorithm. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Khvorostyanov, D.; Beekmann, M.; Blond, N.; Colette, A.; Coll, I.; Curci, G.; Foret, G.; Hodzic, A.; et al. CHIMERE 2013: A Model for Regional Atmospheric Composition Modelling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 981–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Air Quality Guidelines. Global Update 2005. Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/environment-and-health/Housing-and-health/publications/pre-2009/air-quality-guidelines.-global-update-2005.-particulate-matter,-ozone,-nitrogen-dioxide-and-sulfur-dioxide (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Datzmann, T.; Markevych, I.; Trautmann, F.; Heinrich, J.; Schmitt, J.; Tesch, F. Outdoor Air Pollution, Green Space, and Cancer Incidence in Saxony: A Semi-Individual Cohort Study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reding, K.W.; Young, M.T.; Szpiro, A.A.; Han, C.J.; DeRoo, L.A.; Weinberg, C.; Kaufman, J.D.; Sandler, D.P. Breast Cancer Risk in Relation to Ambient Air Pollution Exposure at Residences in the Sister Study Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1907–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.J.; O’Brien, K.M.; Niehoff, N.M.; Carroll, R.; Sandler, D.P. Metallic Air Pollutants and Breast Cancer Risk in a Nationwide Cohort Study. Epidemiology 2019, 30, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.J.; Garrett, J.M. Understanding Interobserver Agreement: The Kappa Statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, C.V. Assimilation de Données et Couplage d’échelles Pour La Simulation de La Dispersion Atmosphérique En Milieu Urbain. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Ecole Doctorale MEGA, Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sally Liu, L.-J.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Keidel, D.; Gemperli, A.; Ineichen, A.; Hazenkamp-von Arx, M.; Bayer-Oglesby, L.; Rochat, T.; Künzli, N.; Ackermann-Liebrich, U.; et al. Long-Term Exposure Models for Traffic Related NO2 across Geographically Diverse Areas over Separate Years. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanosky, J.D.; Paciorek, C.J.; Laden, F.; Hart, J.E.; Puett, R.C.; Liao, D.; Suh, H.H. Spatio-Temporal Modeling of Particulate Air Pollution in the Conterminous United States Using Geographic and Meteorological Predictors. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Sørensen, M.; Geels, C.; Ketzel, M.; Khan, J.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Brandt, J.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Long-Term Residential Exposure to PM2.5, PM10, Black Carbon, NO2, and Ozone and Mortality in a Danish Cohort. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentayeb, M.; Stempfelet, M.; Wagner, V.; Zins, M.; Bonenfant, S.; Songeur, C.; Sanchez, O.; Rosso, A.; Brulfert, G.; Rios, I.; et al. Retrospective Modeling Outdoor Air Pollution at a Fine Spatial Scale in France, 1989–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, E.; Bernard, J.; Hulin, A.; Virga, J.; Dugay, F.; Charles, M.-A.; Cheminat, M.; Cortinovis, J.; Ducroz, F.; Laborie, A.; et al. Air Pollution Modeling and Exposure Assessment during Pregnancy in the French Longitudinal Study of Children (ELFE). Atmos. Environ. 2019, 205, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, C.; Badaloni, C.; Mataloni, F.; Bolignano, A.; Bucci, S.; Cesaroni, G.; Sozzi, R.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F. Mortality and Morbidity in a Population Exposed to Multiple Sources of Air Pollution: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Air Dispersion Models. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Background Data from the St Exupery Location | Number of Stations | R² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured concentrations | 15 | 33.5 (14.5) | 39.7 (18) | 18.3% | 0.82 |
| Simulated concentrations | 35.2 (14.5) | 15.7% | 0.82 |
| Background Data from the St Exupery Location | Number of Stations | R² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured concentrations | 13 | 30.1 (4.6) | 28.9 (4.2) | 4.8% | 0.85 |
| Simulated concentrations | 21.0 (4.6) | 27.7% | 0.84 |
| Years | Number of Stations | R² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 5 | 56.0 (13.9) | 65.0 (39.0) | 90.4% | 0.41 |
| 1995 | 16 | 55.0 (13.3) | 56.0 (18.2) | 15.8% | 0.59 |
| 2000 | 20 | 48.9 (16.6) | 47.1 (15.1) | 19.2% | 0.67 |
| 2005 | 17 | 47.2 (18.8) | 44.6 (15.3) | 17.3% | 0.75 |
| 2010 | 15 | 35.2 (14.5) | 39.7 (18) | 15.7% | 0.82 |
| Years | Number of Stations | R² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 5 | 42.6 (6.5) | 52.1 (11.7) | 16.8% | 0.33 |
| 1995 | 4 | 32.0 (8.3) | 51.2 (7.67) | 37.5% | 0.75 |
| 2000 | 8 | 27.9 (6.4) | 35.2 (7.1) | 21.0% | 0.71 |
| 2005 | 13 | 24.9 (5.6) | 33.5 (8.4) | 24.9% | 0.76 |
| 2010 | 13 | 21.0 (4.6) | 28.9 (4.2) | 27.7% | 0.84 |
| Years | |
|---|---|
| 2005 | −0.28 |
| 2010 | −0.37 |
| NO2 | PM10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Annual Concentration (µg/m3) (SD) | Proportion of Study Area above WHO Recommendation | Mean Annual Concentration (µg/m3) (SD) | Proportion of Study Area above WHO Recommendation | |
| 1990 | 37.8 (11.1) | 26.5% | 33.8 (2.3) | 100% |
| 1995 | 36.0 (11.5) | 22.9% | 26.9 (2.5) | 100% |
| 2000 | 30.7 (9.6) | 11.7% | 21.9 (2.8) | 95.1% |
| 2005 | 28.2 (9.7) | 9.0% | 20.8 (2.6) | 50.9% |
| 2010 | 21.8 (7.1) | 2.2% | 17.5 (2.0) | 7.7% |
| NO2 | PM10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Min–Max) Concentrations at Subject Adresses | Proportion of Subject Exposed above WHO Recommendation | Median (Min–Max) Concentrations at Subject Adresses | Proportion of Subject Exposed above WHO Recommendation | |
| 1990 | 51.0 (29.5–102.4) | 79% | 36.3 (32.2–53.0) | 100% |
| 1995 | 49.6 (27.8–105.6) | 76% | 29.6 (25.3–50.8) | 100% |
| 2000 | 43.1 (24.1–90.5) | 59% | 25.1 (20.0–46.0) | 100% |
| 2005 | 40.2 (21.7–84.2) | 51% | 23.7 (19.2–40.8) | 93% |
| 2010 | 31.6 (16.5–62.1) | 16% | 20.0 (16.0–29.5) | 50% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coudon, T.; Nguyen, C.V.; Volta, P.; Grassot, L.; Couvidat, F.; Soulhac, L.; Gulliver, J.; Mancini, F.R.; Fervers, B.; Salizzoni, P. Retrospective Modeling of NO2 and PM10 Concentrations over the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France), 1990–2010—Performance Evaluation, Exposure Assessment and Correlation between Pollutants. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020239
Coudon T, Nguyen CV, Volta P, Grassot L, Couvidat F, Soulhac L, Gulliver J, Mancini FR, Fervers B, Salizzoni P. Retrospective Modeling of NO2 and PM10 Concentrations over the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France), 1990–2010—Performance Evaluation, Exposure Assessment and Correlation between Pollutants. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoudon, Thomas, Chi Vuong Nguyen, Perrine Volta, Lény Grassot, Florian Couvidat, Lionel Soulhac, John Gulliver, Francesca Romana Mancini, Béatrice Fervers, and Pietro Salizzoni. 2021. "Retrospective Modeling of NO2 and PM10 Concentrations over the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France), 1990–2010—Performance Evaluation, Exposure Assessment and Correlation between Pollutants" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020239
APA StyleCoudon, T., Nguyen, C. V., Volta, P., Grassot, L., Couvidat, F., Soulhac, L., Gulliver, J., Mancini, F. R., Fervers, B., & Salizzoni, P. (2021). Retrospective Modeling of NO2 and PM10 Concentrations over the Lyon Metropolitan Area (France), 1990–2010—Performance Evaluation, Exposure Assessment and Correlation between Pollutants. Atmosphere, 12(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020239







