Evaluation of High-Resolution Crop Model Meteorological Forcing Datasets at Regional Scale: Air Temperature and Precipitation over Major Land Areas of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Datasets Introduction
2.2. Evaluation Method
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Air Temperature
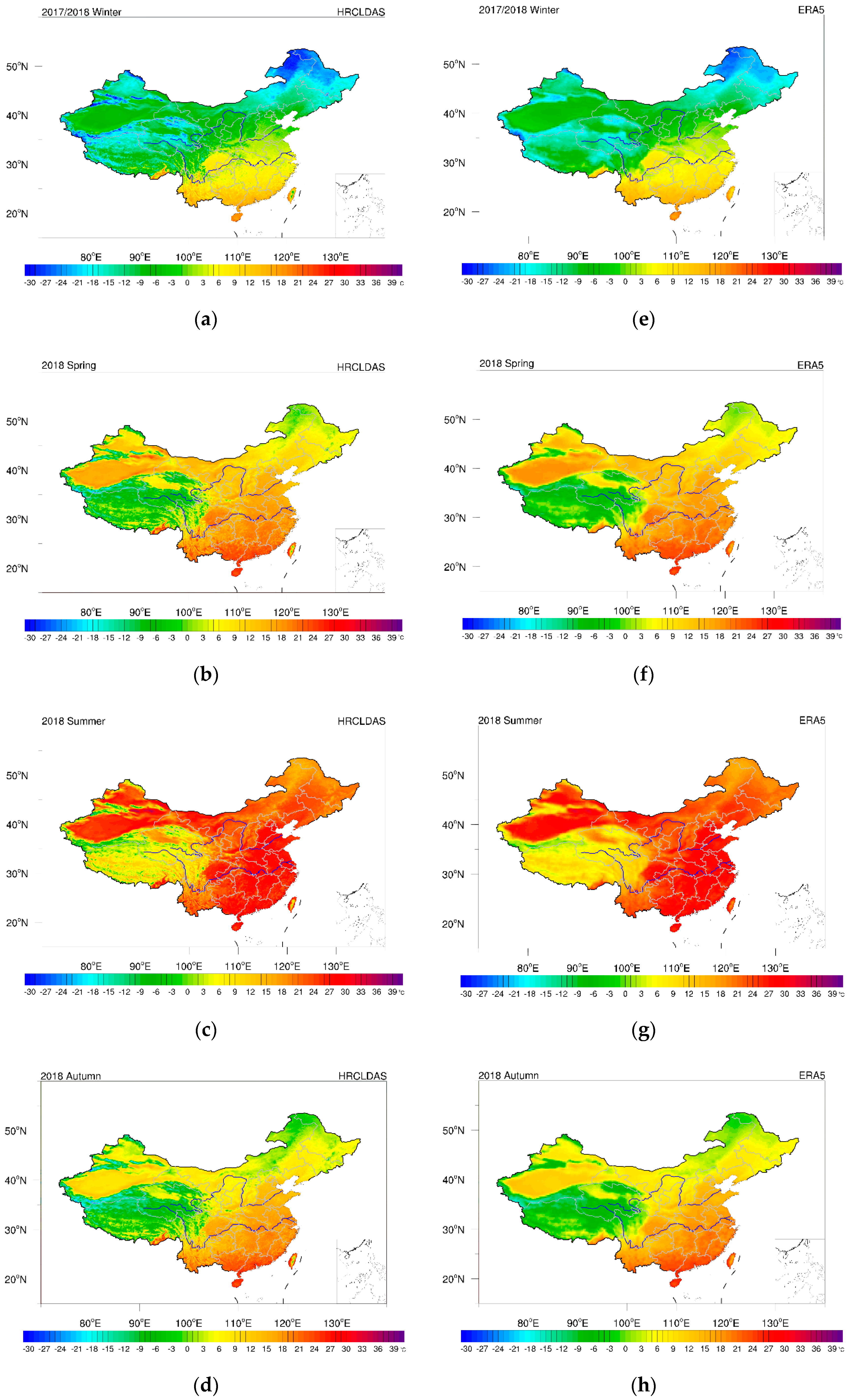
3.1.1. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Air Temperature
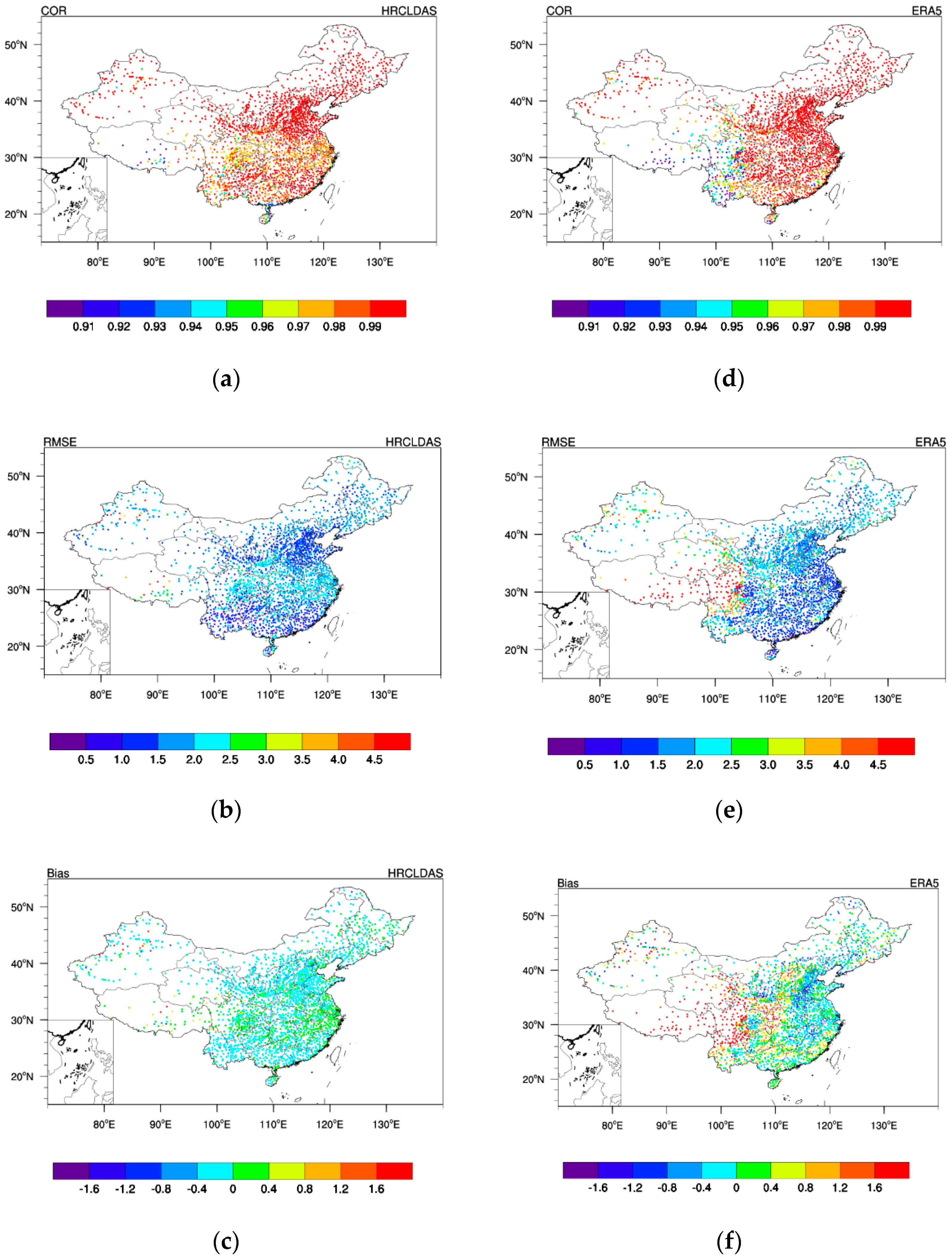
3.1.2. Evaluation of Air Temperature on Each Station
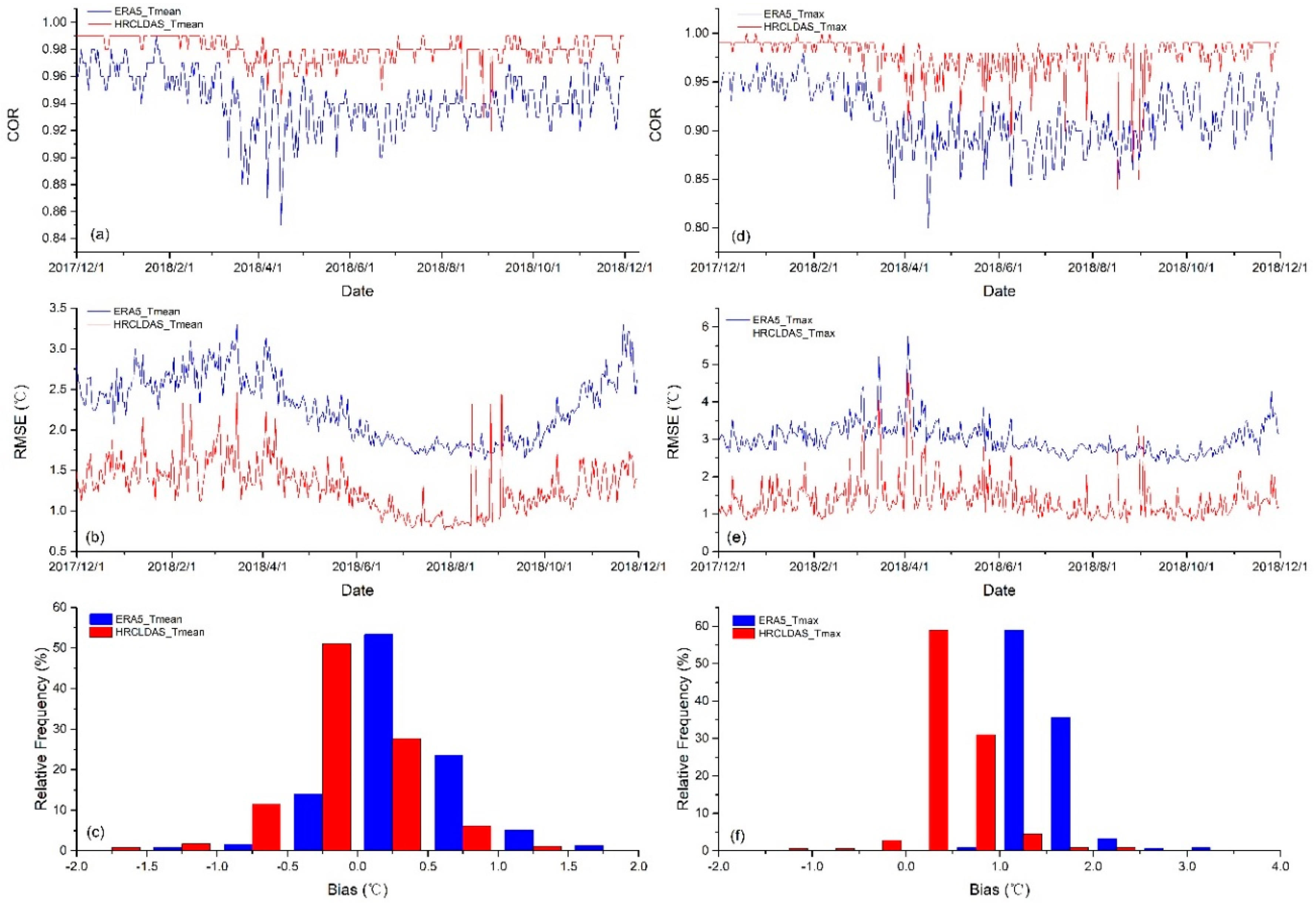
3.1.3. Evaluation of Air Temperature in Daily Time Series
3.1.4. Evaluation of Air Temperature at Different Altitudes
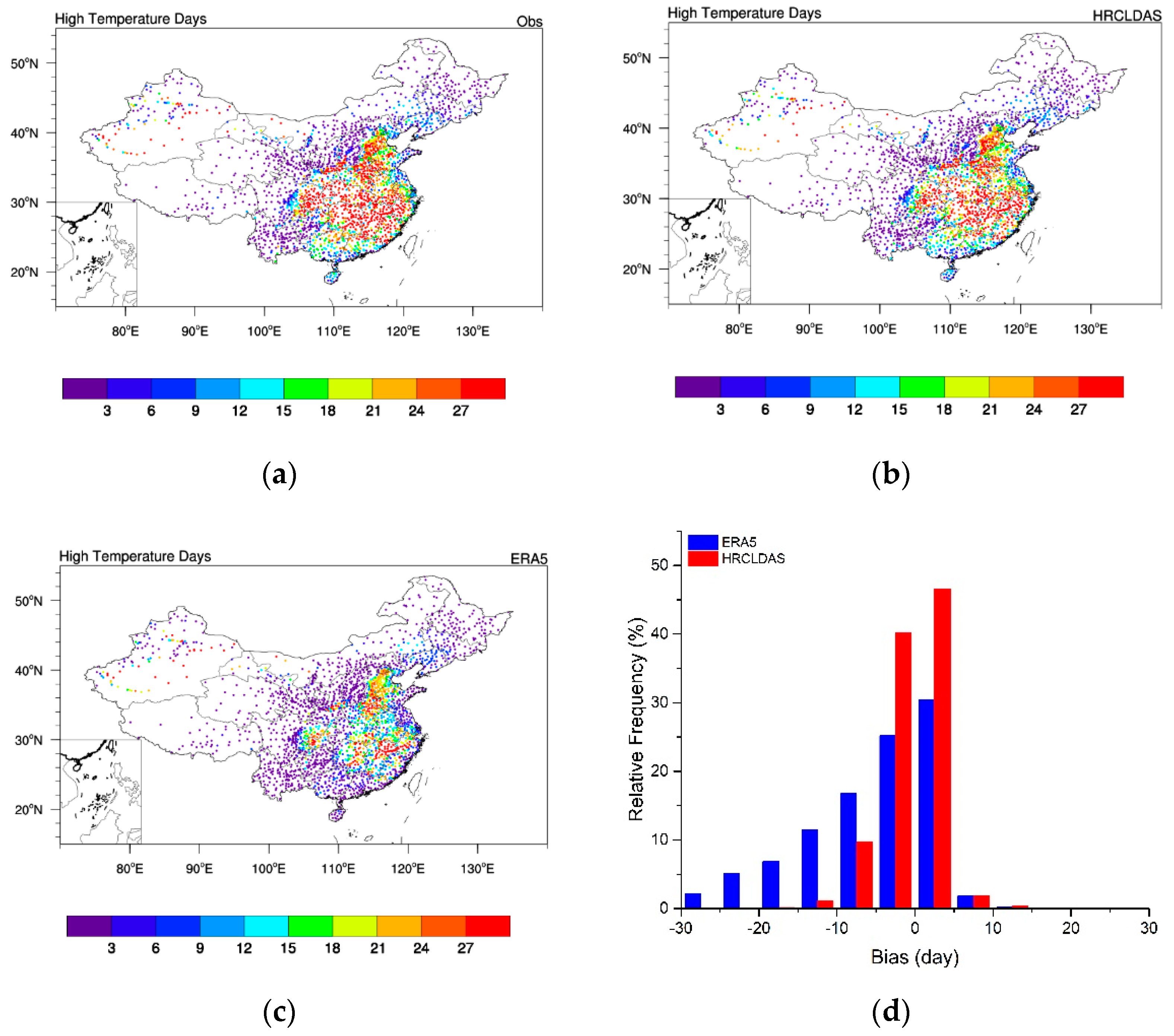
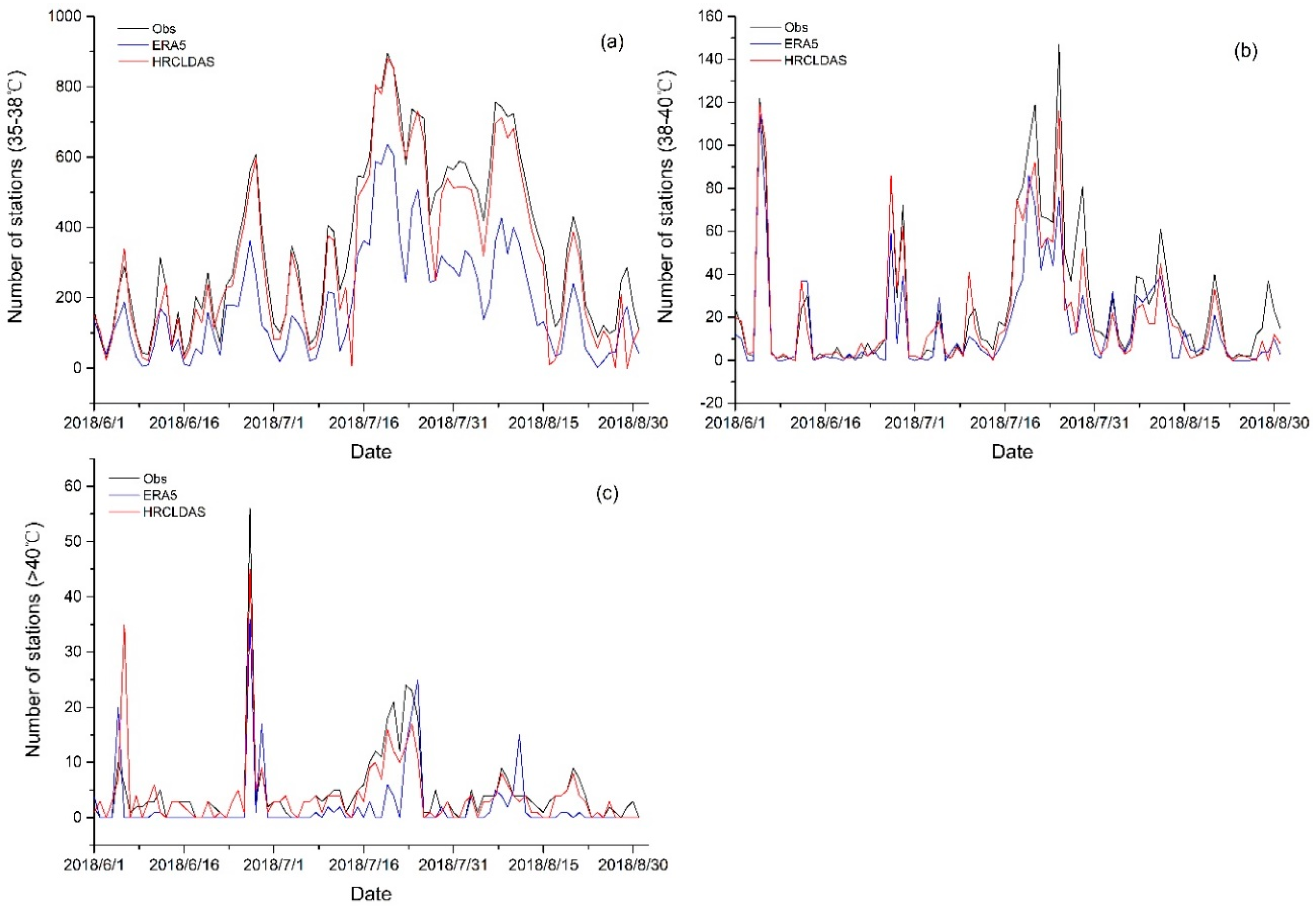
3.1.5. Evaluation of High Temperature
3.2. Evaluation of Precipitation
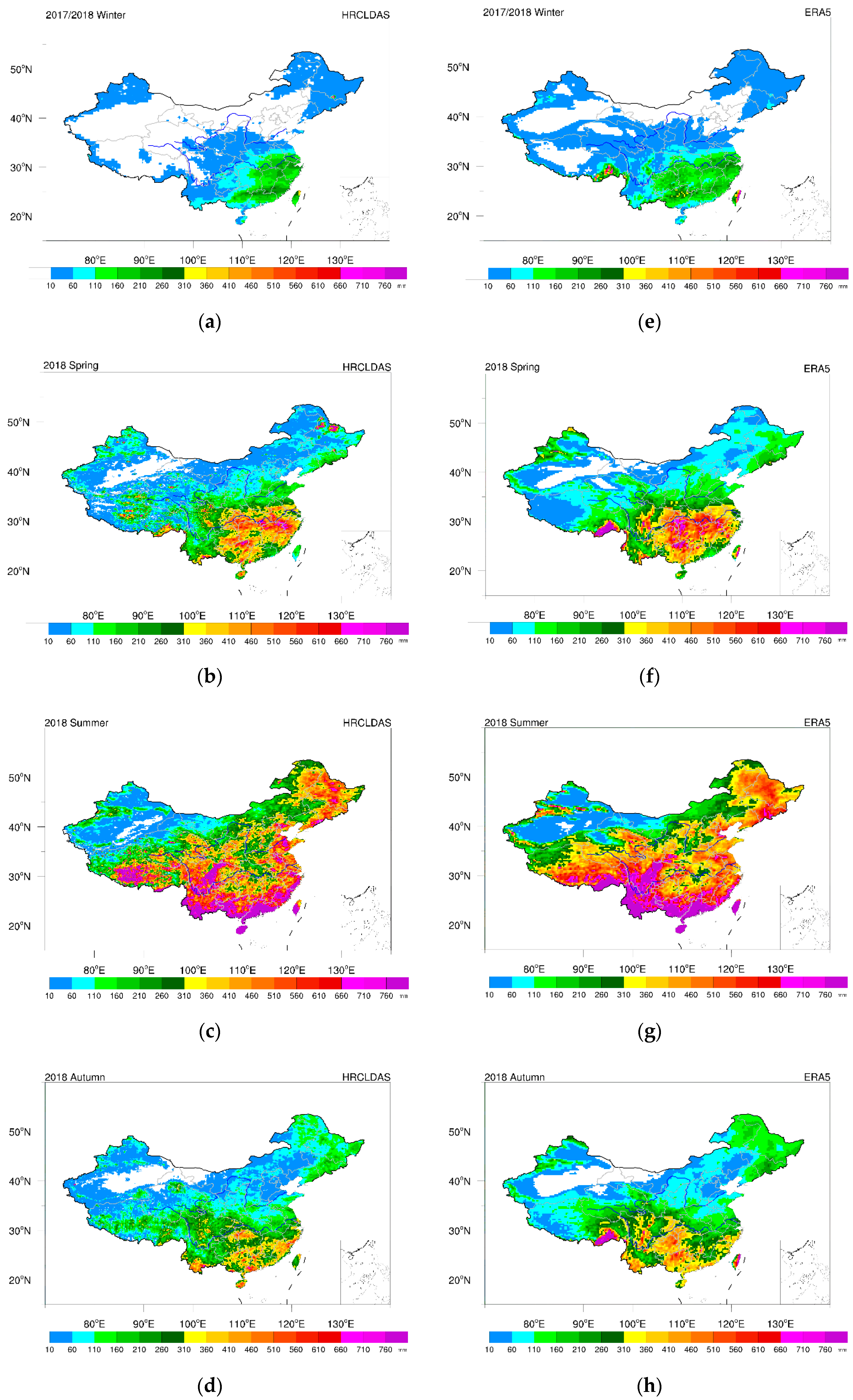
3.2.1. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Precipitation
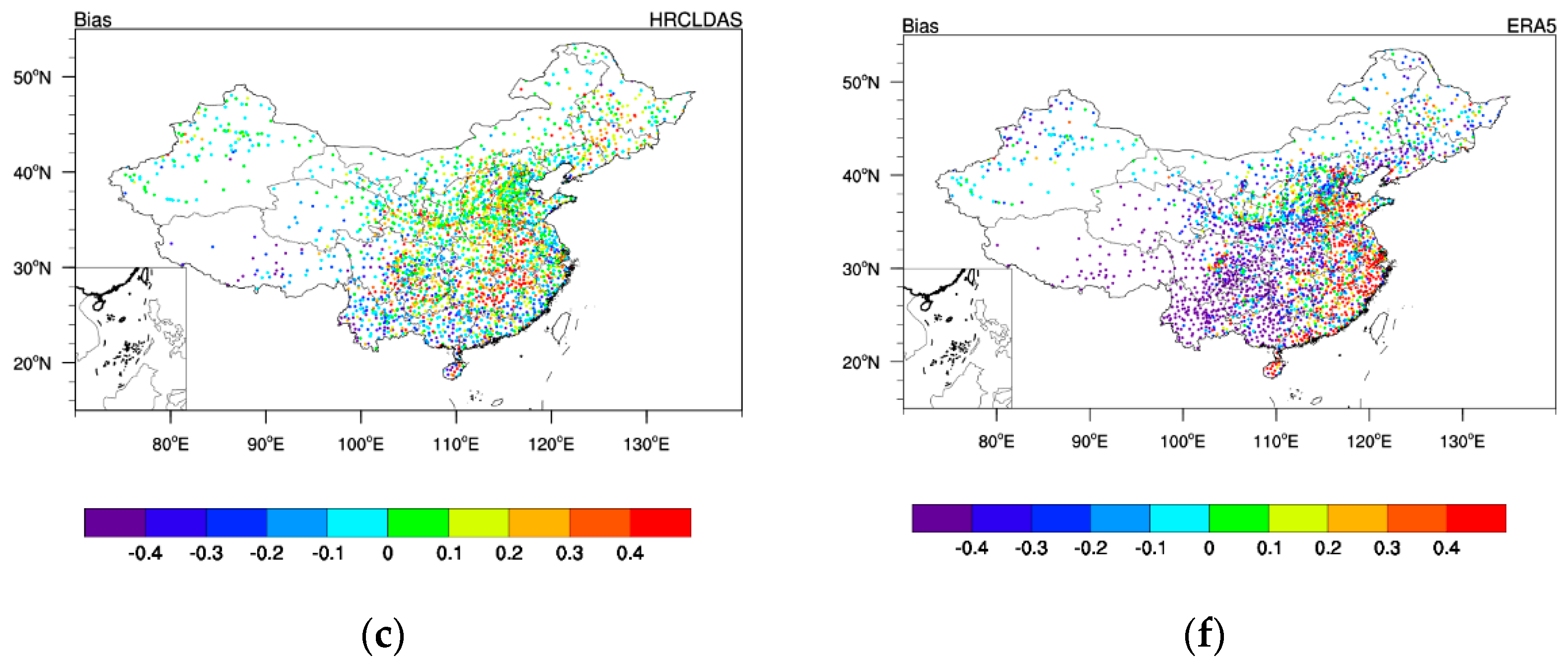
3.2.2. Evaluation of Precipitation on Each Station
3.2.3. Evaluation of Precipitation in Time Series
3.2.4. Evaluation of Precipitation at Different Altitudes
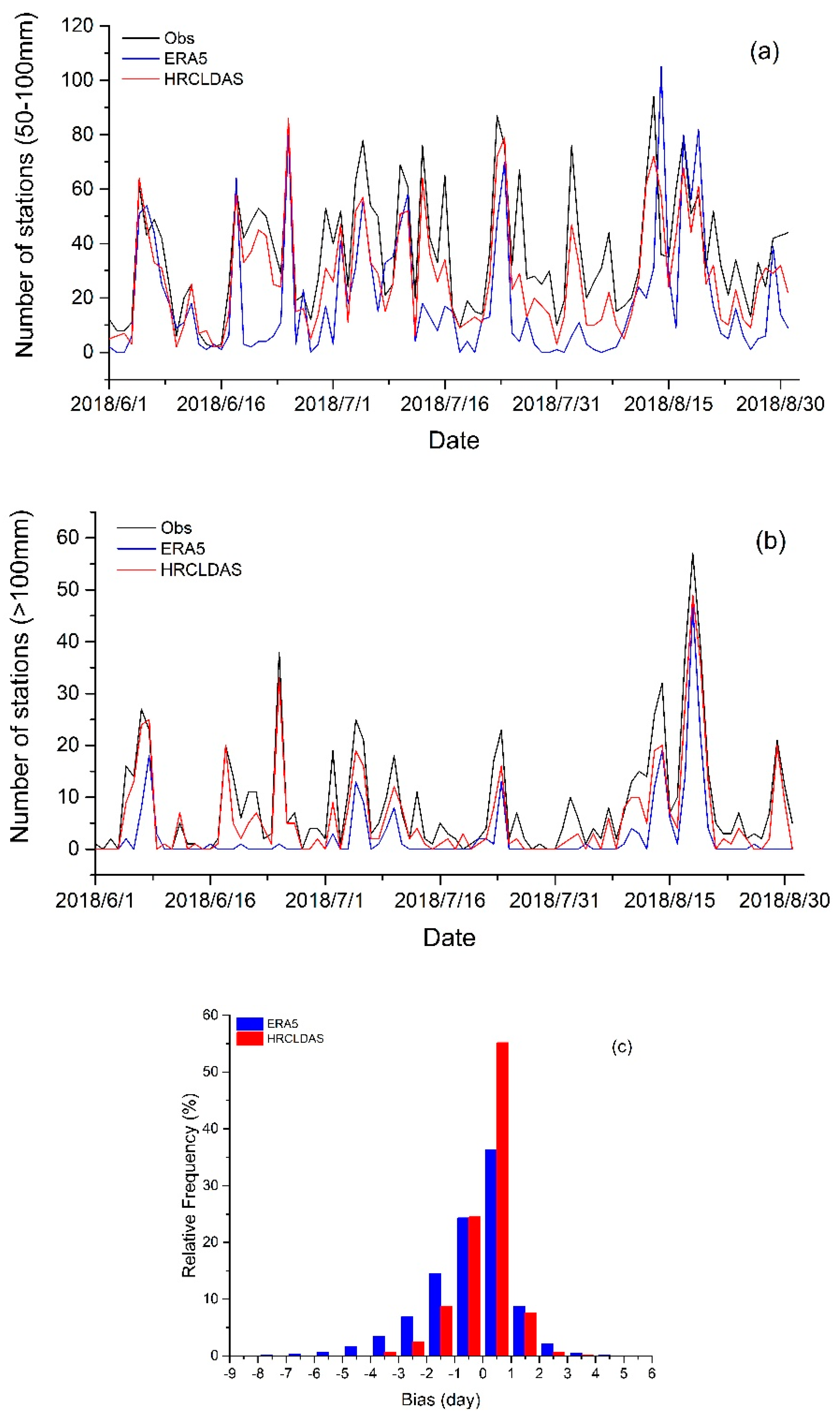
3.2.5. Evaluation of Rainstorm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; Song, X. Evaluation of optimal irrigation scheduling and groundwater recharge at representative sites in the North China Plain with SWAP model and field experiments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, C.J.; Green, P. Global Water Resources: Vulnerability from Climate Change and Population Growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, M.P.; Charchousi, D.; Spanoudaki, K.; Karali, A.; Varotsos, K.V.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Markou, M.; Loizidou, M. Agricultural Water Vulnerability under Climate Change in Cyprus. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Tank, A.M.G.K.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global Observed Changes in Daily Climate Extremes of Temperature and Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Singh, D.N.; Mankin, J.S.; Horton, D.E.; Swain, D.L.; Touma, D.; Charland, A.; Liu, Y.J.; Haugen, M.; Tsiang, M.; et al. Quantifying The Influence of Global Warming on Unprecedented Extreme Climate Events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4881–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easterling, D.R.; Evans, J.L.; Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Kunkel, K.E.; Ambenje, P. Observed Variability and Trends in Extreme Climate Events: A Brief Review. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, E.T.; John, T.F.; Thodore, G.S. Attribution of Climate Extreme Events. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 725–730. [Google Scholar]
- Lassa, J.; Teng, P.; Caballero, A.M.; Shrestha, M.R. Emergency Food Reserve Policy and Practice under Disaster and Extreme Climate Events. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, A.R. On Detecting Ecological Impacts of Extreme Climate Events and Why It Matters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2017, 372, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesselaar, M.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Impacts of Climate Change and Remote Natural Catastrophes on EU Flood Insurance Markets: An Analysis of Soft and Hard Reinsurance Markets for Flood Coverage. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentsch, A.; Kreyling, J.; Beierkuhnlein, C. A new generation of climate-change experiments: Events, not trends. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, B.C.; Shi, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, M.J.; Sun, S. Evaluation of CLDAS and GLDAS datasets for Near-surface Air Temperature over major land areas of China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.A.; Xuan, Y.Q. Impact of Precipitation Pre-Processing Methods on Hydrological Model Performance using High-Resolution Gridded Dataset. Water 2020, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boegh, E.; Thorsen, M.; Butts, M.B.; Hansen, S.; Christiansen, J.S.; Abrahamsen, P.; Hasager, C.B.; Jensen, N.O.; van der Keur, P.; Refsgaard, J.C.; et al. Incorporating remote sensing data in physically based distributed agro-hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, E.P.; Wood, A.W.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Nijssen, B. A long-term hydrologically-based data set of land surface fluxes and states for the conterminous united states. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3237–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Wang, W.; Wright, J.S.; Li, C.W.; Han, M.L.; Li, Y.S. Evaluation of multiple forcing data sets for precipitation and shortwave radiation over major land areas of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5805–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Liu, J.Z. Monthly and annual validation of TRMM Mulitisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) products in the Caspian Sea Region for the period 1999–2003. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; Volume 2, pp. 3696–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Comparison of versions 6 and 7 3-hourly TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) research products. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Shi, C.X.; Xu, B.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.P.; Liang, X. Development and Evaluation of Hourly and Kilometer Resolution Retrospective and RealTime Surface Meteorological Blended Forcing Dataset (SMBFD) in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; He, J.H.; Qi, L. A review on applicability evaluation of four reanalysis datasets in China. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2011, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.B.; Fu, C.B.; Ke, Z.J.; Guo, W.D. Global atmosphere reanalysis datasets: Current status and recent advances. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 25, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Dorigo, W.; Balsamo, G.; Munoz-Sabater, J.; Rosnay, P.; Isaksen, L.; Brocca, L.; Jeu, R.; Wagner, W. Monitoring multi-decadal satellite earth observation of soil moisture products through land surface reanalyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.X.; Pan, Y.; Gu, J.X.; Xu, B.; Han, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Jiang, Z.W. A review of multi-source meteorological data fusion products. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2019, 77, 774–783. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.L.; Hao, Z.C.; Shi, C.X.; Li, Y.H.; Meng, J. Regional and global land data assimilation systems: Innovations, challenges, and prospects. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thépaut, J.N.; Dee, D.P.; Engelen, R.; Pinty, B. The Copernicus programme and its climate change service. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1591–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.C.; Wiscombe, W.; Jayaweera, K. Numerically stable algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple scattering and emitting layered media. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.X.; Xie, Z.H.; Qian, H.; Liang, M.L.; Yang, X.C. China land soil moisture EnKF data assimilation based on satellite remote sensing data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, M.; Hólm, E.V.; Isaksen, L.; Fisher, M. The evolution of the ECMWF hybrid data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, L.; Bonavita, M.; Buizza, R.; Fisher, M.; Haseler, J.; Leutbecher, M.; Raynaud, L. Ensemble of Data Assimilations at ECMWF. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/10125 (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Kim, J.B.; So, J.M.; Bae, D.H. Global Warming Impacts on Severe Drought Characteristics in Asia Monsoon Region. Water 2020, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.; Yu, H.P.; Guan, X.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Guo, R.X. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.T.; Huang, J.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Wang, X. Long-term trends of dust events over Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2010. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warscher, M.; Wagner, S.; Marke, T.; Laux, P.; Smiatek, G.; Strasser, U.; Kunstmann, H. A 5 km Resolution Regional Climate Simulation for Central Europe: Performance in High Mountain Areas and Seasonal, Regional and Elevation-Dependent Variations. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Datasets | NAWS 1 Observations | HRCLDAS 2 | ERA5 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data type | point | grid | grid |
| Spatial coverage | over major land areas of China | 70–140° E; 15–60° N | global |
| Spatial resolution | more than 2400 stations | 1 km | 31 km |
| Temporal coverage | from 2008 to present | from 2015 to present | from 1979 to present |
| Temporal resolution | daily | hourly | hourly |
| Download lag | 1 day | 1 h | 5 days |
| Altitude (m) | COR | RMSE (°C) | Bias (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRCLDAS | ERA5 | HRCLDAS | ERA5 | HRCLDAS | ERA5 | ||
| Tmean | Alt ≤ 1000 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1.61 | 1.66 | −0.06 | 0.05 |
| 1000 < Alt ≤ 2000 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.49 | 2.19 | −0.15 | 0.50 | |
| 2000 < Alt ≤ 4000 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.79 | 4.63 | 0.03 | 3.15 | |
| Alt < 4000 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 2.79 | 4.91 | 0.61 | 3.43 | |
| Tmax | Alt ≤ 1000 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.40 | 2.19 | 0.48 | 1.10 |
| 1000 < Alt ≤ 2000 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.53 | 2.88 | 0.58 | 1.83 | |
| 2000 < Alt ≤ 4000 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 2.11 | 6.02 | 0.94 | 4.85 | |
| Alt < 4000 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 3.39 | 6.10 | 1.46 | 4.83 | |
| Altitude (m) | COR | RMSE (mm) | Bias (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRCLDAS | ERA5 | HRCLDAS | ERA5 | HRCLDAS | ERA5 | |
| Alt ≤ 1000 | 0.94 | 0.66 | 3.03 | 6.94 | 0.06 | −0.16 |
| 1000 < Alt ≤ 2000 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 2.27 | 4.75 | 0.01 | −0.44 |
| 2000 < Alt ≤ 4000 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 4.39 | −0.06 | −0.75 |
| Alt > 4000 | 0.85 | 0.57 | 2.29 | 3.76 | −0.3 | −0.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Xiao, C.; Ai, W. Evaluation of High-Resolution Crop Model Meteorological Forcing Datasets at Regional Scale: Air Temperature and Precipitation over Major Land Areas of China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091011
Wang Q, Li W, Xiao C, Ai W. Evaluation of High-Resolution Crop Model Meteorological Forcing Datasets at Regional Scale: Air Temperature and Precipitation over Major Land Areas of China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091011
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiuling, Wei Li, Chan Xiao, and Wanxiu Ai. 2020. "Evaluation of High-Resolution Crop Model Meteorological Forcing Datasets at Regional Scale: Air Temperature and Precipitation over Major Land Areas of China" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091011
APA StyleWang, Q., Li, W., Xiao, C., & Ai, W. (2020). Evaluation of High-Resolution Crop Model Meteorological Forcing Datasets at Regional Scale: Air Temperature and Precipitation over Major Land Areas of China. Atmosphere, 11(9), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091011




