Figure 1.
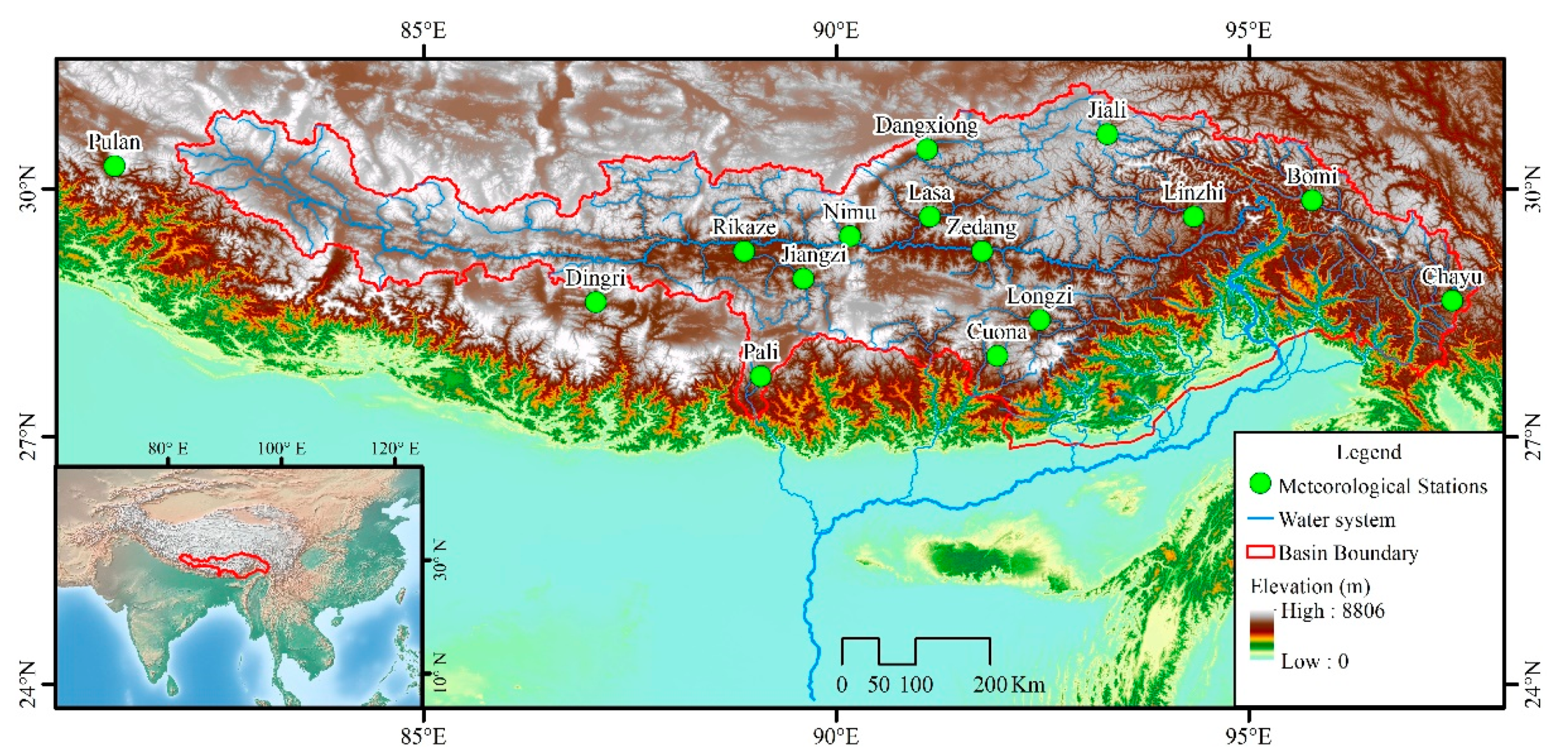
Location of the study area and the meteorological stations.
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and the meteorological stations.
Figure 2.
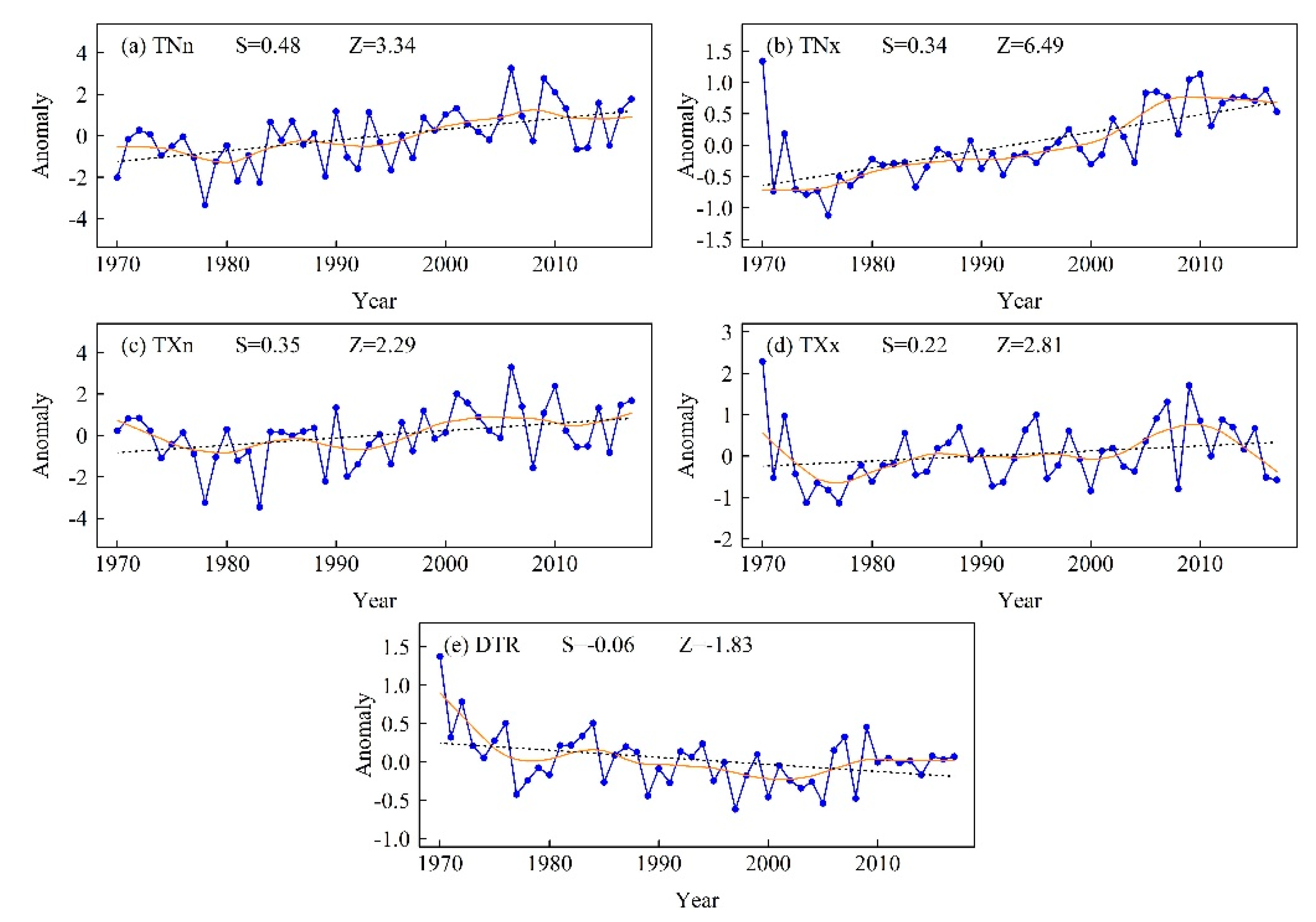
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TNn, (b) TNx, (c) TXn, (d) TXx, and (e) DTR during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 2.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TNn, (b) TNx, (c) TXn, (d) TXx, and (e) DTR during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 3.
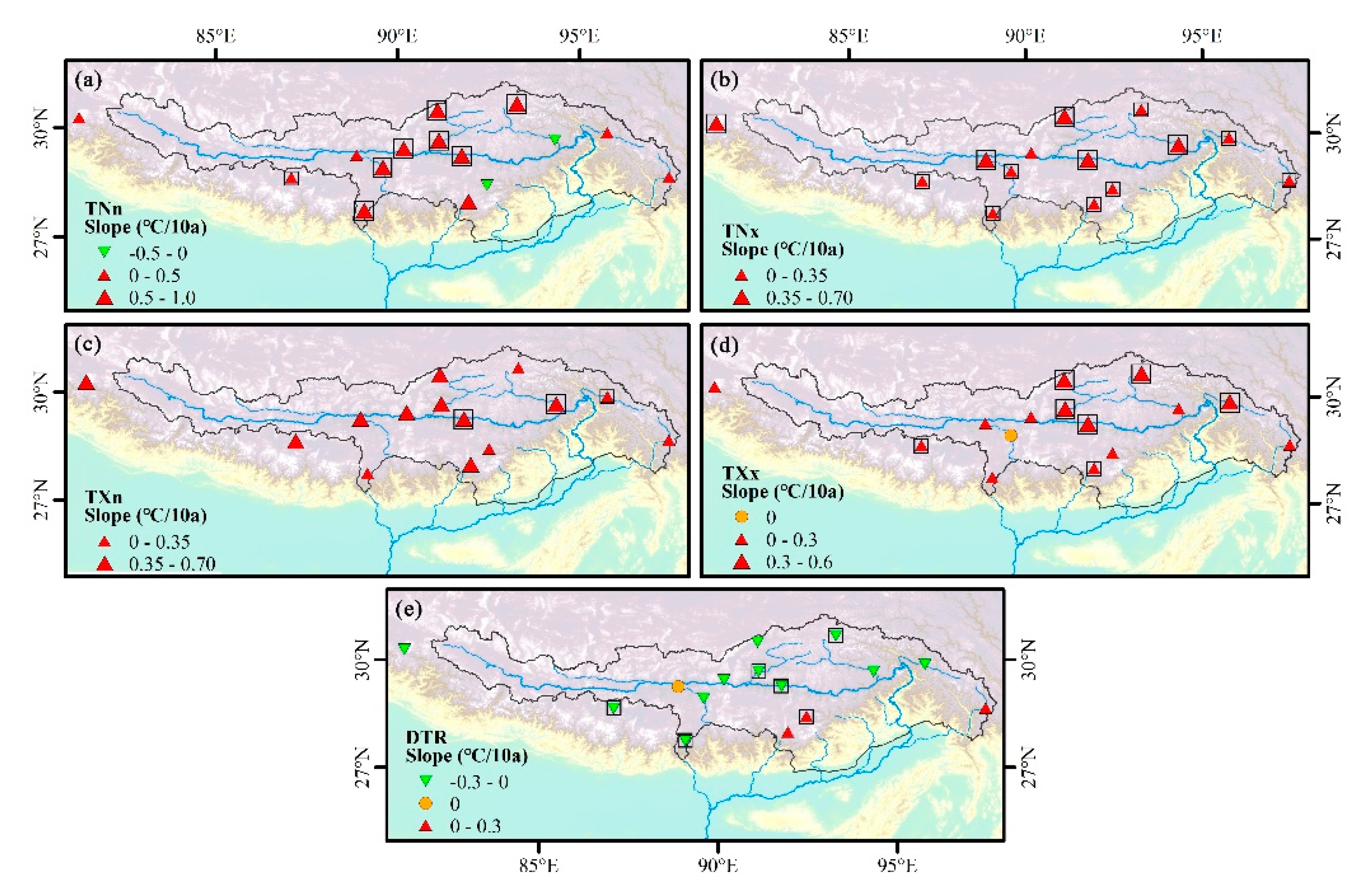
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TNn, (b) TNx, (c) TXn, (d) TXx, and (e) DTR during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TNn, (b) TNx, (c) TXn, (d) TXx, and (e) DTR during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 4.
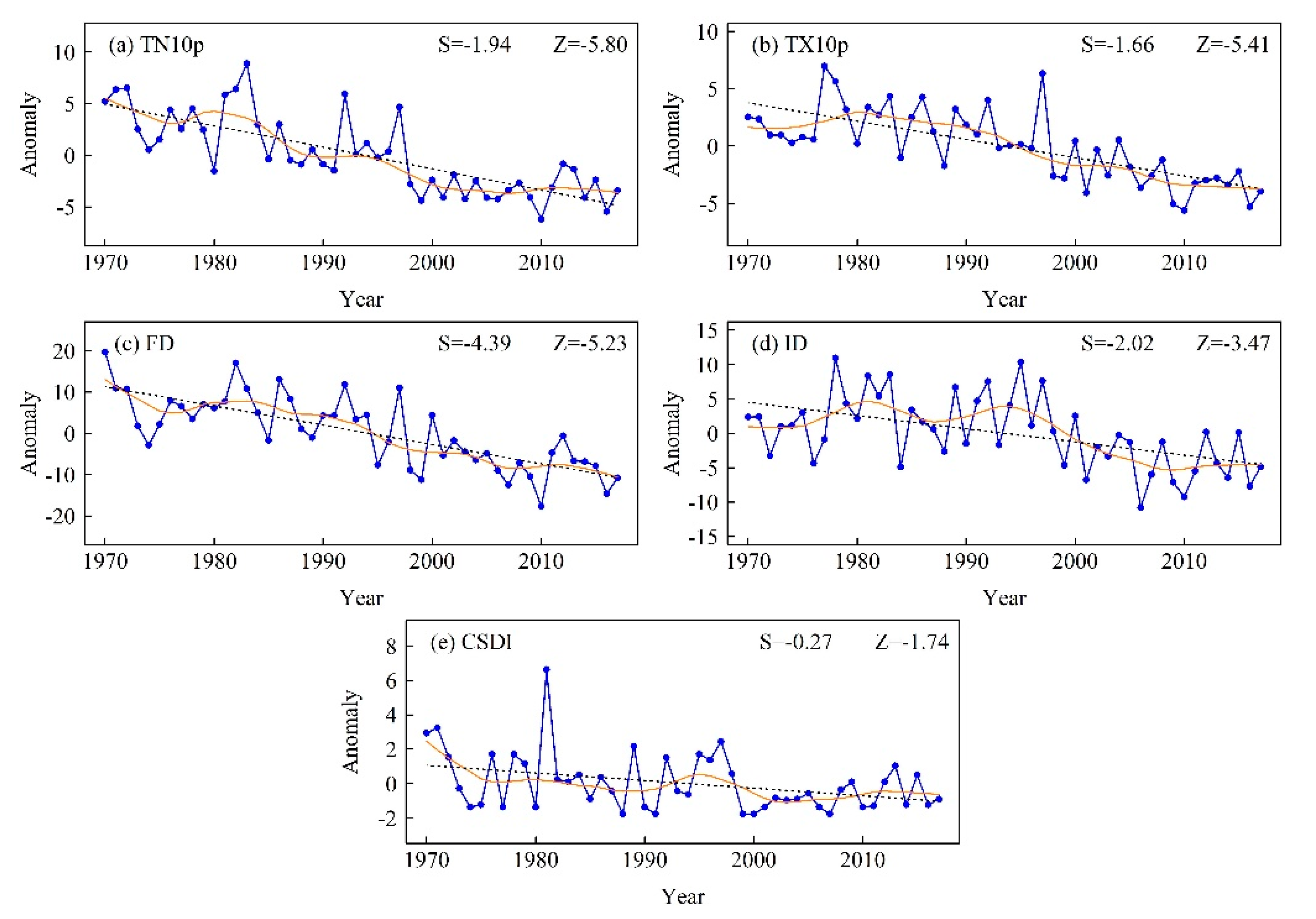
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TN10p, (b) TX10p, (c) FD, (d) ID, and (e) CSDI during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 4.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TN10p, (b) TX10p, (c) FD, (d) ID, and (e) CSDI during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
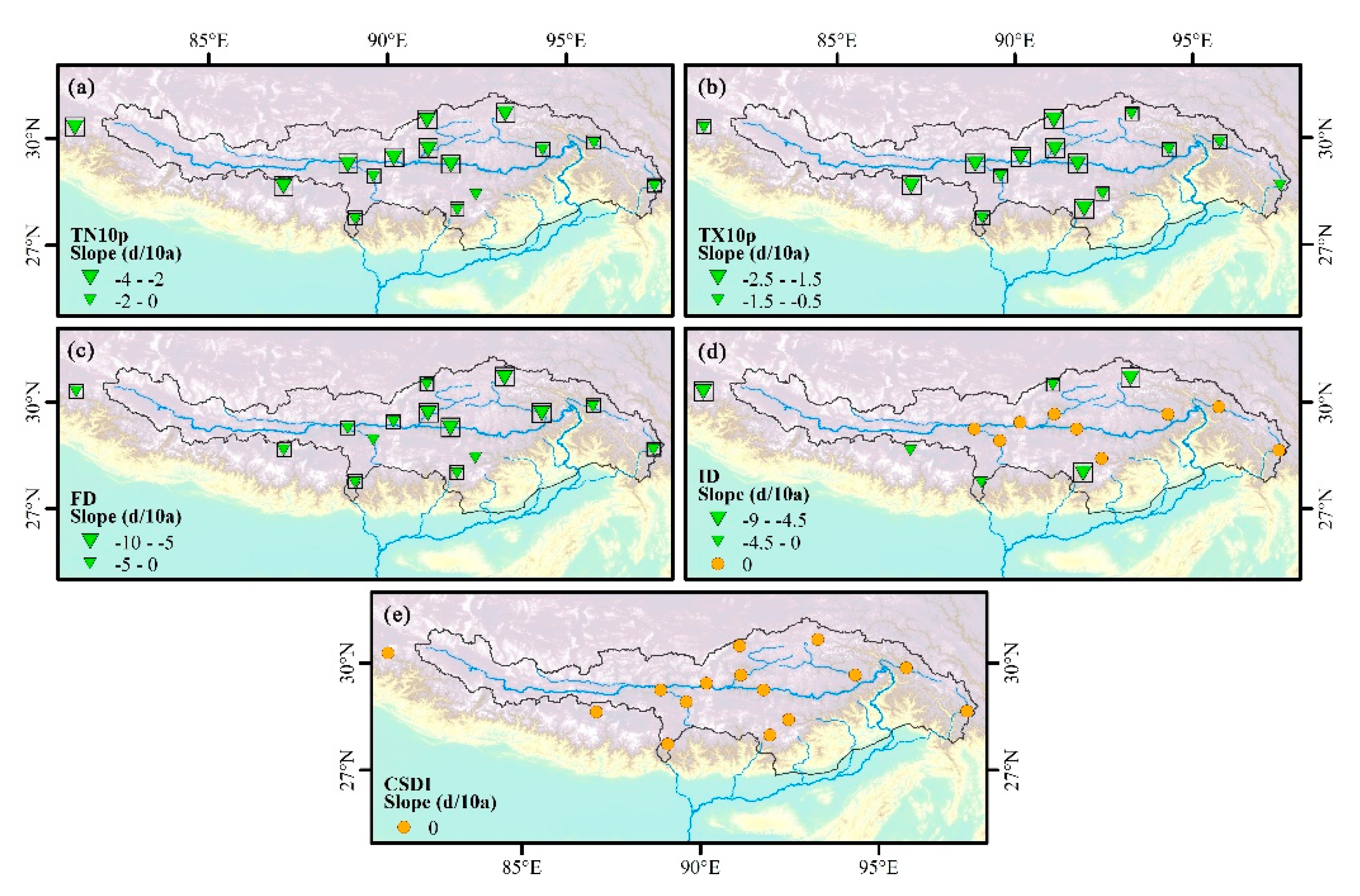
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TN10p, (b) TX10p, (c) FD, (d) ID, and (e) CSDI during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TN10p, (b) TX10p, (c) FD, (d) ID, and (e) CSDI during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
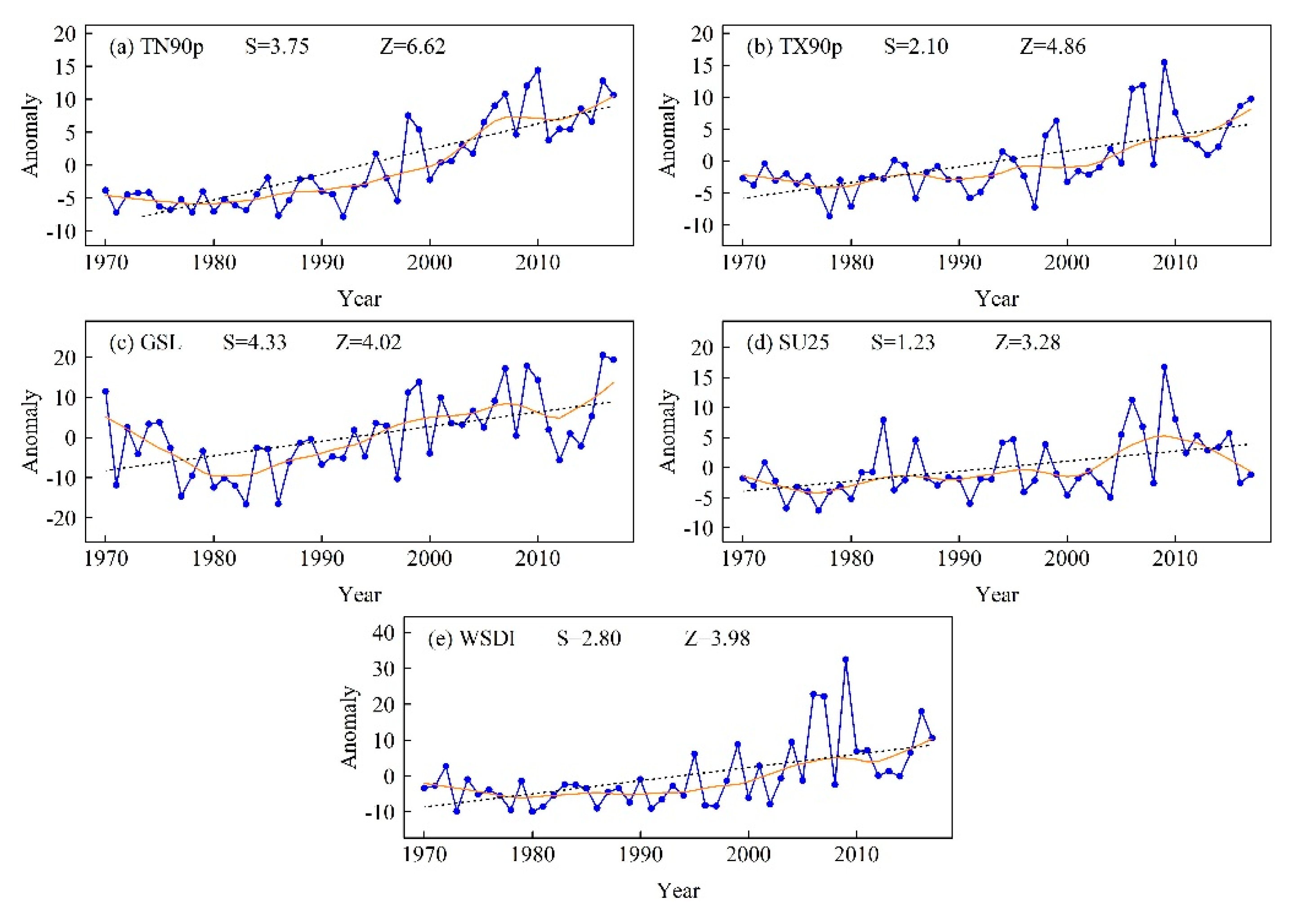
Figure 6.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TN90p, (b) TX90p, (c) GSL, (d) SU25, and (e) WSDI during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 6.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) TN90p, (b) TX90p, (c) GSL, (d) SU25, and (e) WSDI during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
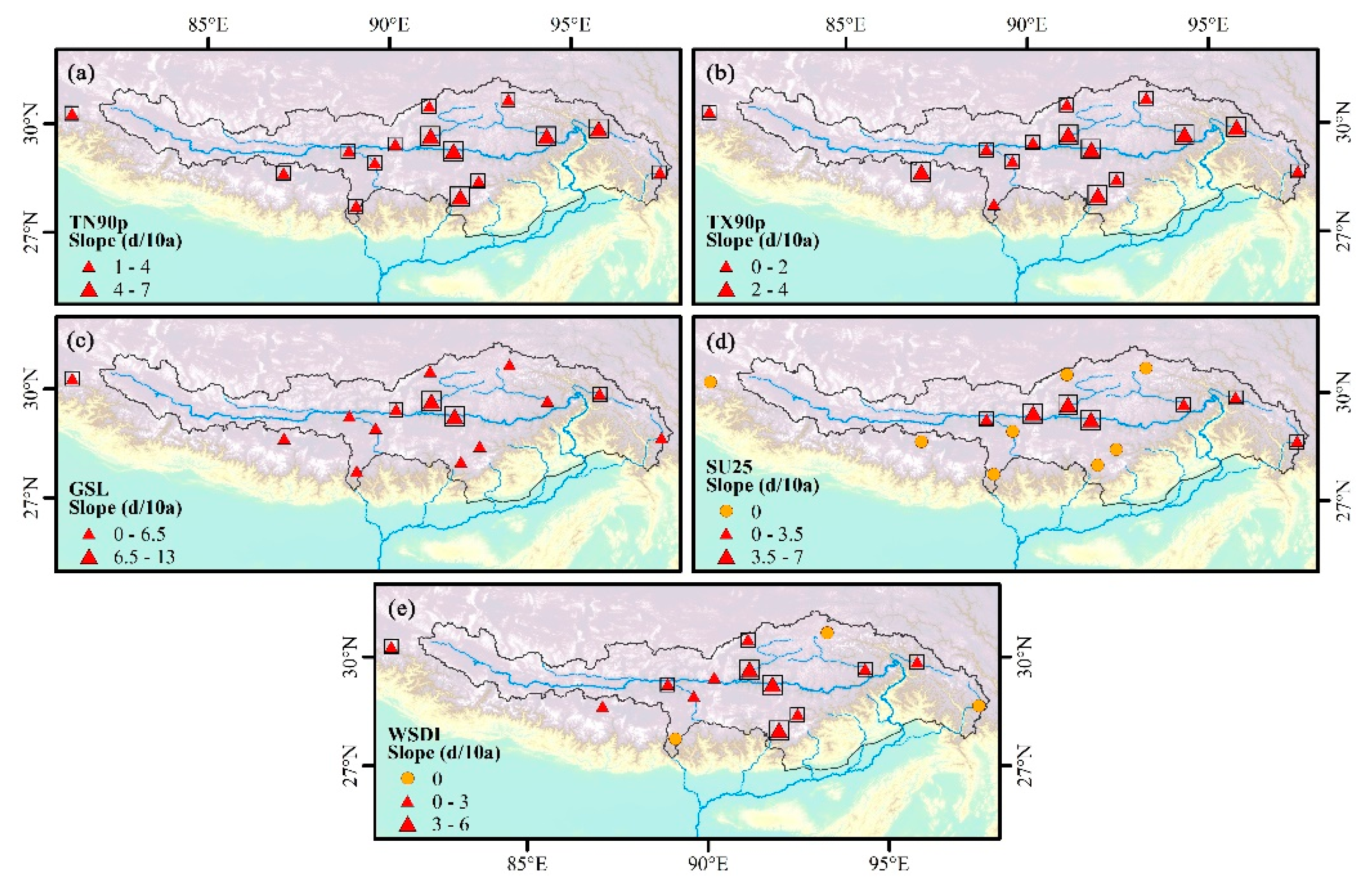
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TN90p, (b) TX90p, (c) GSL, (d) SU25, and (e) WSDI during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) TN90p, (b) TX90p, (c) GSL, (d) SU25, and (e) WSDI during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
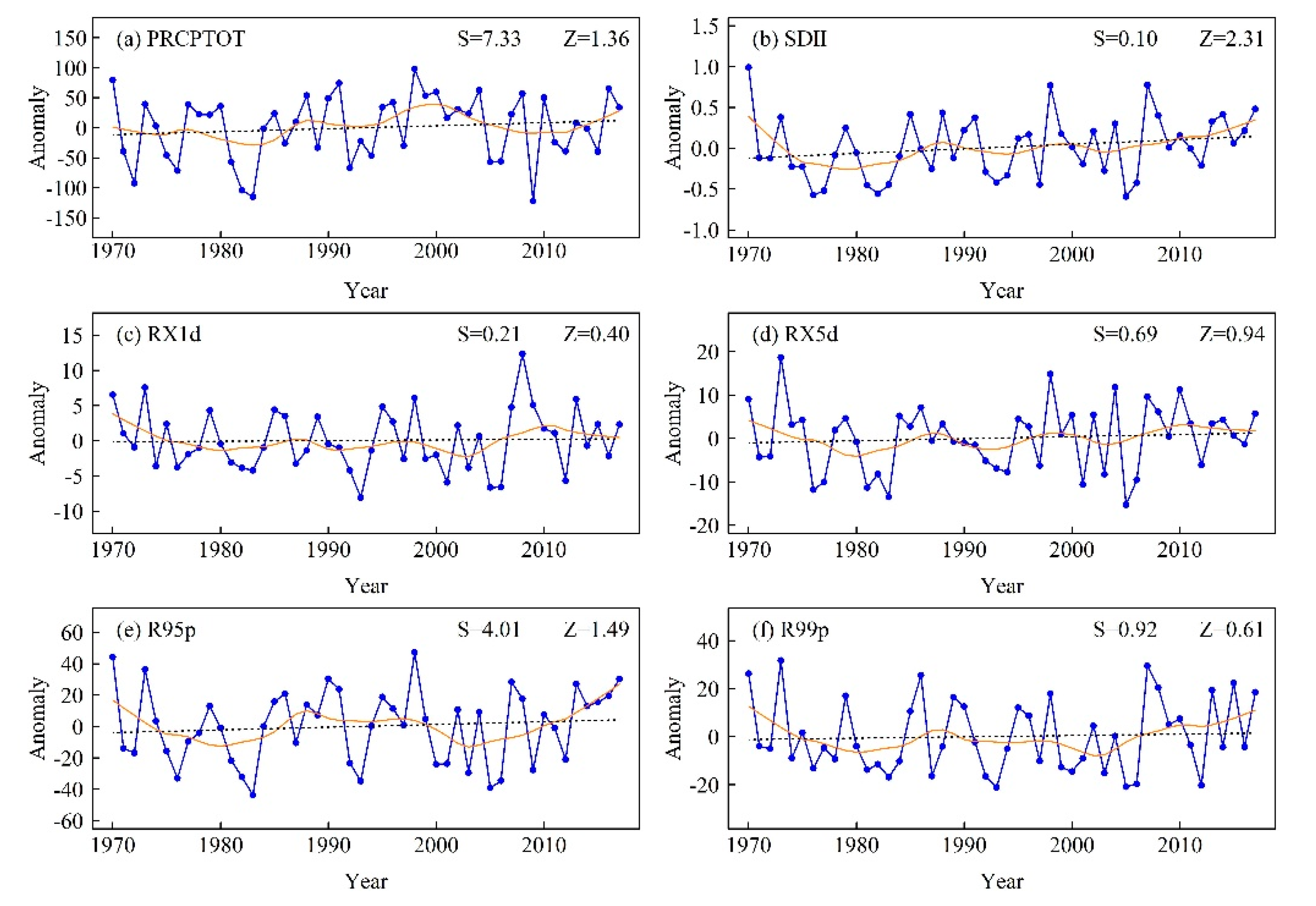
Figure 8.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) PRCPTOT, (b) SDII, (c) RX1d, (d) RX5d, (e) R95p, and (f) R99p during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 8.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) PRCPTOT, (b) SDII, (c) RX1d, (d) RX5d, (e) R95p, and (f) R99p during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
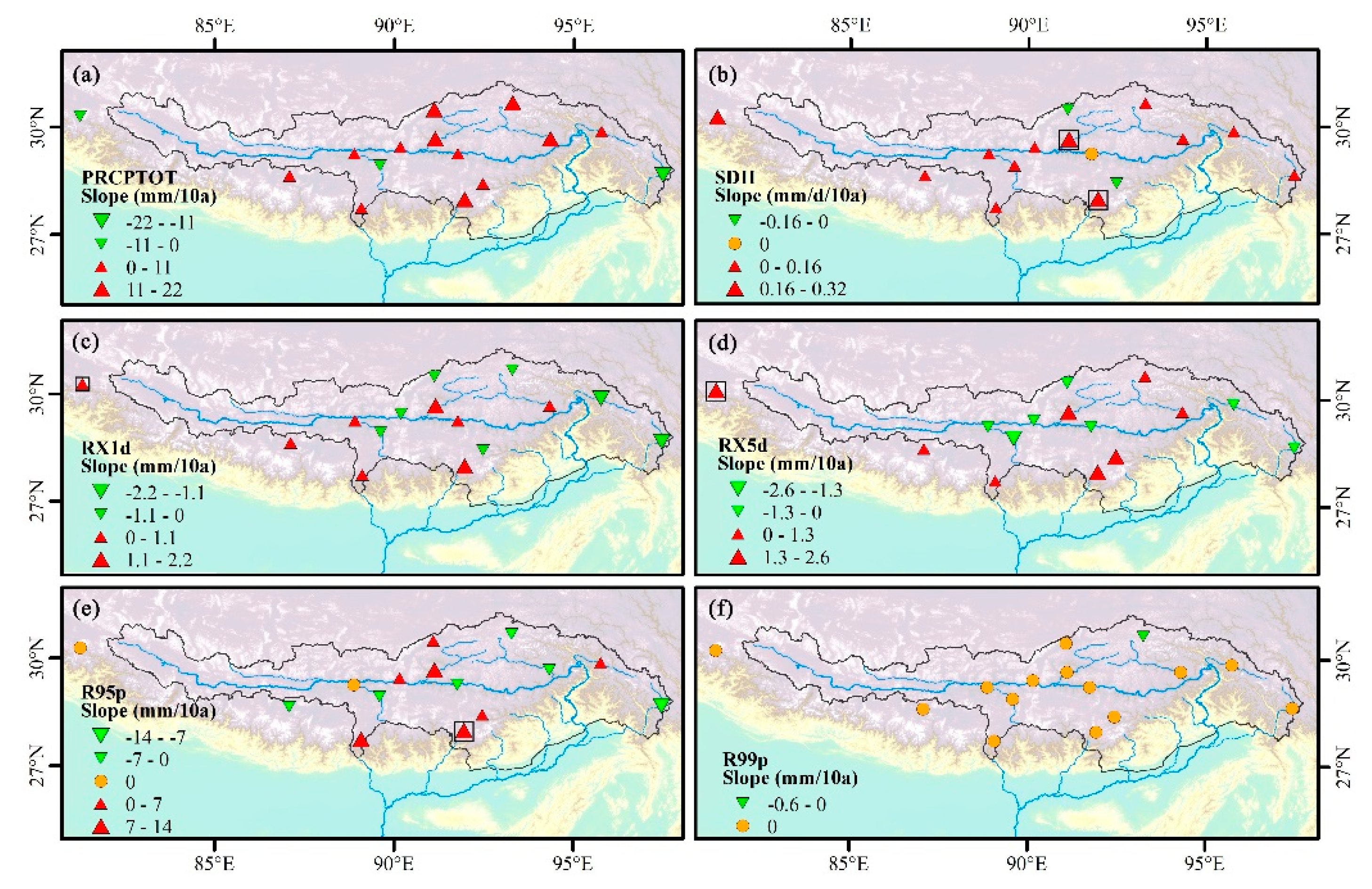
Figure 9.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) PRCPTOT, (b) SDII, (c) RX1d, (d) RX5d, (e) R95p, and (f) R99p during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 9.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) PRCPTOT, (b) SDII, (c) RX1d, (d) RX5d, (e) R95p, and (f) R99p during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
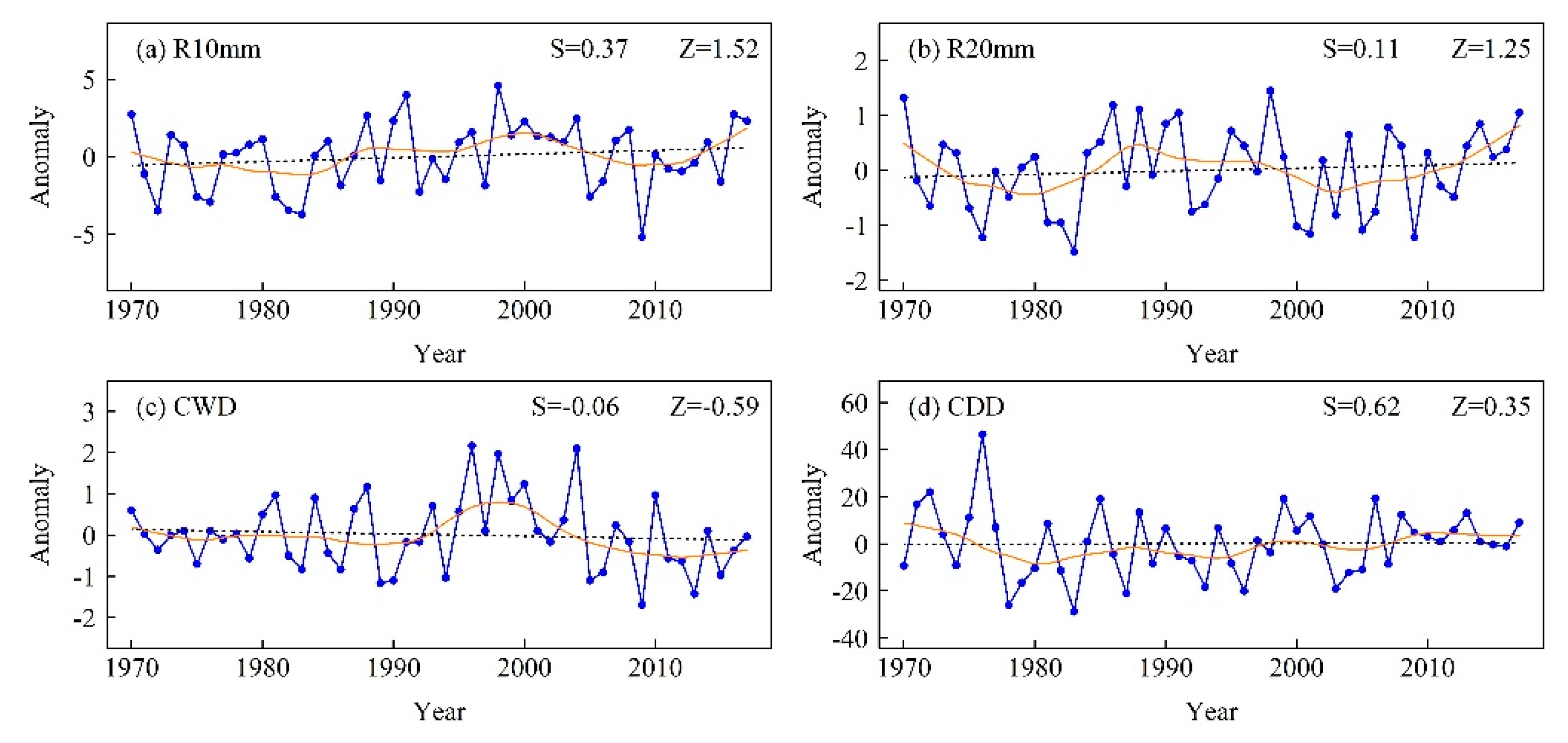
Figure 10.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) R10mm, (b) R20mm, (c) CWD, and (d) CDD during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
Figure 10.
Regionally averaged anomaly series of (a) R10mm, (b) R20mm, (c) CWD, and (d) CDD during 1970–2017. The black dashed line is the linear trend and the solid orange line from Locally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing (LOESS). Z is the Mann–Kendall test statistic and S is the Sen’s slope.
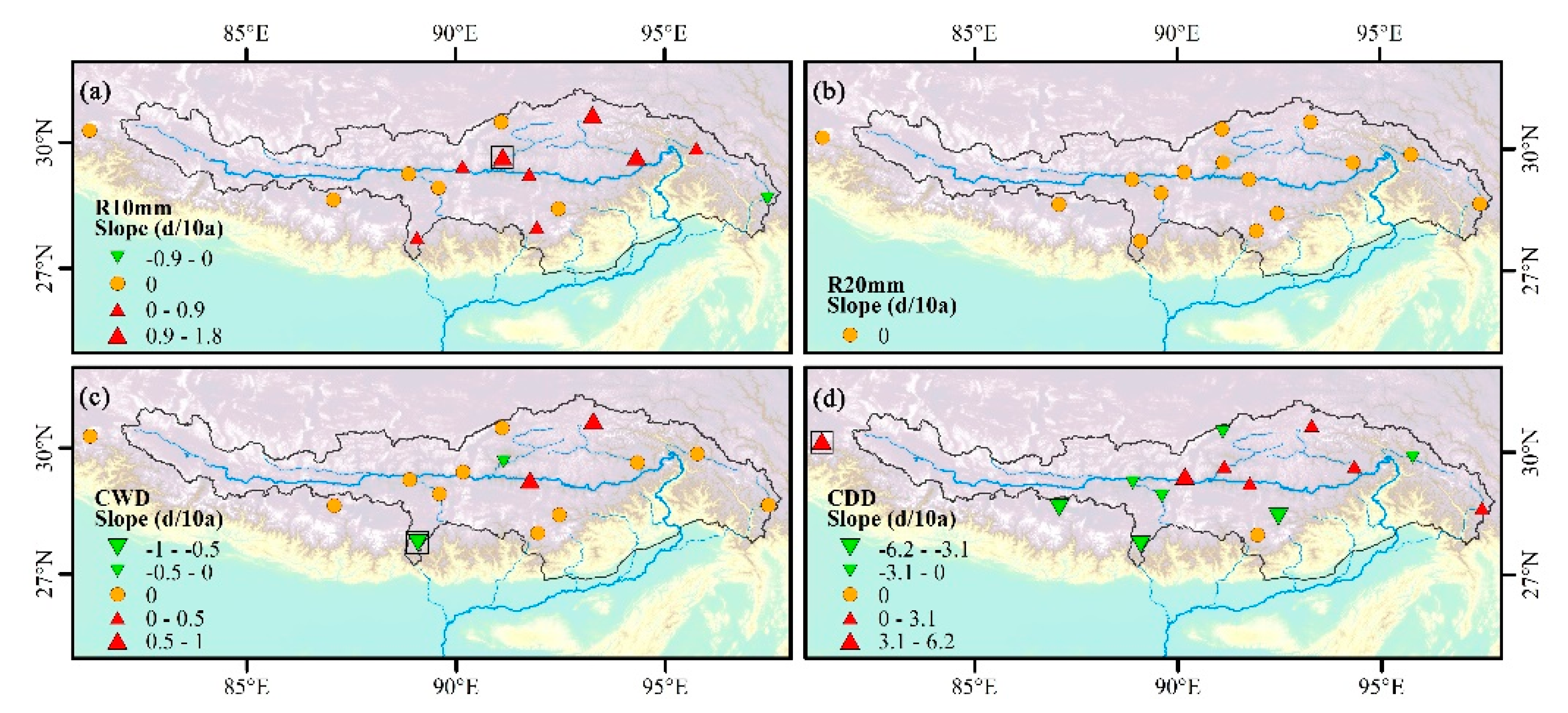
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) R10mm, (b) R20mm, (c) CWD, and (d) CDD during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of change trends for (a) R10mm, (b) R20mm, (c) CWD, and (d) CDD during 1970–2017. Positive/negative trends are shown as up/down triangles. Triangle size is proportional to the magnitude of the trend. Trends significant at the 0.05 level are shown by a black box.
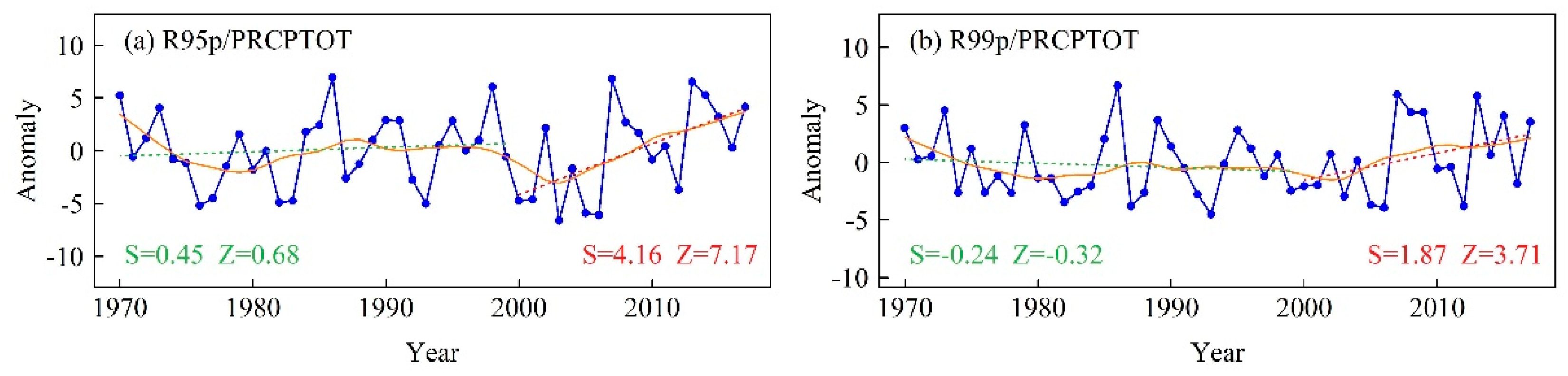
Figure 12.
(a) Ratio of very wet day precipitation (R95p) to total precipitation; (b) ratio of extremely wet day precipitation (R99p) to total precipitation. Green dashed line is the linear trend during 1970–1999, and the red dashed line is the linear trend during 2000–2017.
Figure 12.
(a) Ratio of very wet day precipitation (R95p) to total precipitation; (b) ratio of extremely wet day precipitation (R99p) to total precipitation. Green dashed line is the linear trend during 1970–1999, and the red dashed line is the linear trend during 2000–2017.
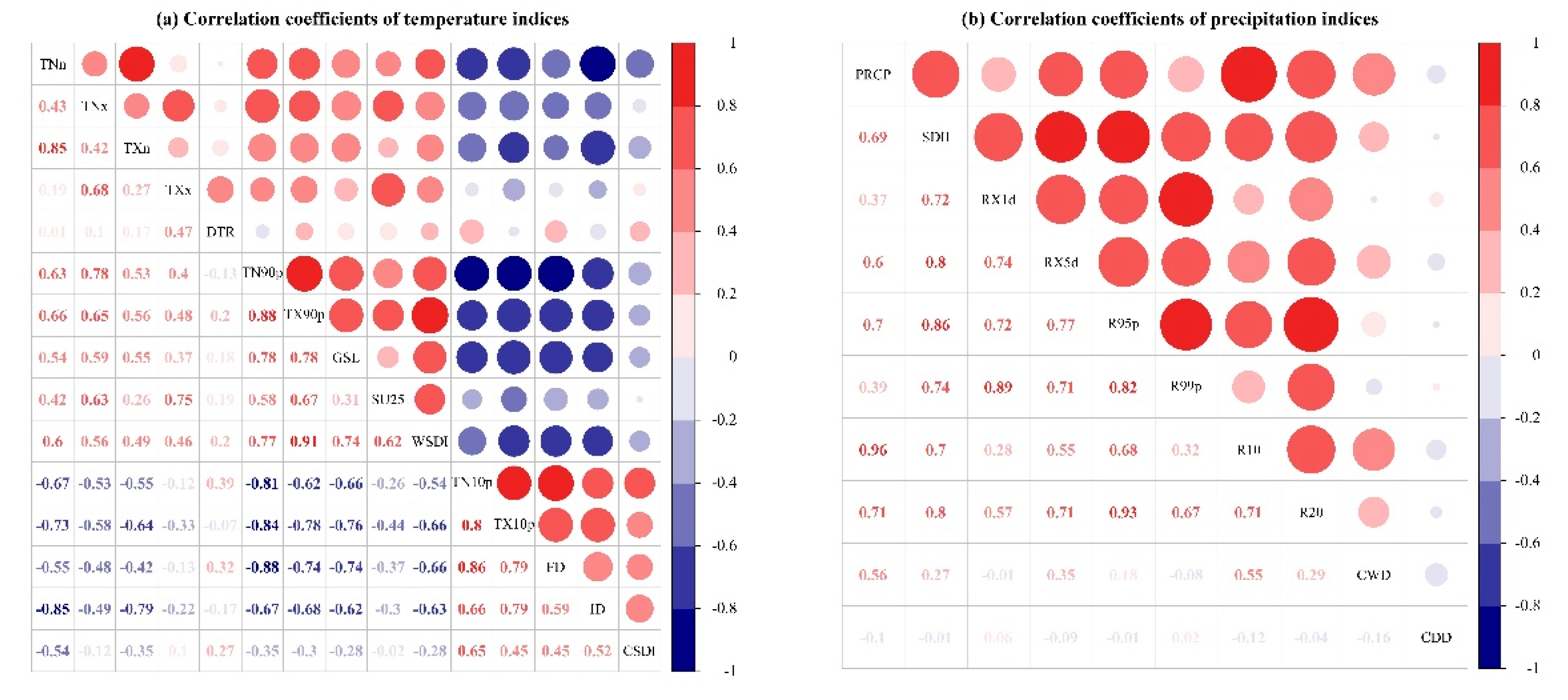
Figure 13.
Pearson correlation analysis of (a) temperature and (b) precipitation indices.
Figure 13.
Pearson correlation analysis of (a) temperature and (b) precipitation indices.
Table 1.
Meteorological stations used in this study.
Table 1.
Meteorological stations used in this study.
| ID | Station | Lat (° N) | Lon (° E) | Elevation (m) | Study Periods |
|---|
| 55437 | Pulan | 30.28 | 81.25 | 4900 | 1973–2017 |
| 55493 | Dangxiong | 30.48 | 91.1 | 4200 | 1970–2017 |
| 55578 | Rikaze | 29.25 | 88.88 | 3836 | 1970–2017 |
| 55585 | Nimu | 29.43 | 90.16 | 3809 | 1973–2017 |
| 55591 | Lasa | 29.66 | 91.13 | 3648 | 1970–2017 |
| 55598 | Zedang | 29.25 | 91.76 | 3551 | 1970–2017 |
| 55664 | Dingri | 28.63 | 87.08 | 4300 | 1970–2017 |
| 55680 | Jiangzi | 28.91 | 89.6 | 4040 | 1970–2017 |
| 55690 | Cuona | 27.98 | 91.95 | 4280 | 1970–2017 |
| 55696 | Longzi | 28.41 | 92.46 | 3860 | 1970–2017 |
| 55773 | Pali | 27.73 | 89.08 | 4300 | 1970–2017 |
| 56202 | Jiali | 30.66 | 93.28 | 4488 | 1970–2017 |
| 56227 | Bomi | 29.86 | 95.76 | 2736 | 1970–2017 |
| 56312 | Linzhi | 29.66 | 94.33 | 2991 | 1970–2017 |
| 56434 | Chayu | 28.65 | 97.46 | 2327 | 1970–2017 |
Table 2.
Definition of the 15 temperature extreme indices used in this study.
Table 2.
Definition of the 15 temperature extreme indices used in this study.
| Classification | Abbreviation | Index | Definition | Units |
|---|
| Absolute indices and DTR | TNn | Minimum Tmin | Annual lowest TN | °C |
| TNx | Maximum Tmin | Annual highest TN | °C |
| TXn | Minimum Tmax | Annual lowest TX | °C |
| TXx | Maximum Tmax | Annual highest TX | °C |
| DTR | Diurnal temperature range | Annual mean difference between TX and TN | °C |
| Cooling indices | TN10p | Cold nights | Percentage of days when TN < 10th percentile of 1971–2000 | d |
| TX10p | Cold days | Percentage of days when TX < 10th percentile of 1971–2000 | d |
| FD | Frost days | Annual count when TN < 0 °C | d |
| ID | Ice days | Annual count when TX < 0 °C | d |
| CSDI | Cold spell duration indicator | Annual count of days with at least 6 consecutive days when TN < 10th percentile | d |
| Warming indices | TN90p | Warm nights | Percentage of days when TN > 90th percentile of 1971–2000 | d |
| TX90p | Warm days | Percentage of days when TX > 90th percentile of 1971–2000 | d |
| GSL | Growing season length | Annual count between the first span of at least 6 days with daily mean temperature >5 °C after winter and the first span after summer of 6 days with a daily mean temperature < 5 °C | d |
| SU25 | Summer days | Annual count when TX > 5 °C | d |
| WSDI | Warm spell duration indicator | Annual count of days with at least 6 consecutive days when TX > 90th percentile | d |
Table 3.
Definition of the 10 precipitation extreme indices used in this study.
Table 3.
Definition of the 10 precipitation extreme indices used in this study.
| Classification | Abbreviation | Index | Definition | Units |
|---|
| PRCPTOT and intensity indices | PRCPTOT | Wet day precipitation | Annual total precipitation in wet days | mm |
| SDII | Simple daily intensity index | Average precipitation on wet days | mm/d |
| RX1d | Maximum 1-d precipitation amount | Annual maximum 1-day precipitation | mm |
| RX5d | Maximum 5-d precipitation amount | Annual maximum consecutive 5-day precipitation | mm |
| R95p | Very wet day precipitation | Annual total precipitation when RR >95th percentile of 1971–2000 daily precipitation | mm |
| R99p | Extremely wet day precipitation | Annual total precipitation when RR > 99th percentile of 1971–2000 daily precipitation | mm |
| Frequency indices | R10mm | Number of heavy precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR > 10 mm | d |
| R20mm | Number of very heavy precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR > 20 mm | d |
| Duration indices | CWD | Consecutive wet days | Maximum number of consecutive days with RR > 1 mm | d |
| CDD | Consecutive dry days | Maximum number of consecutive days with RR < 1 mm | d |
Table 4.
Trends per decade, change range, and percentage of stations with positive, negative, and no trend for regional indices of temperature extremes.
Table 4.
Trends per decade, change range, and percentage of stations with positive, negative, and no trend for regional indices of temperature extremes.
| Index | Regional Trends | Range | Positive Trend (Significant) | Negative Trend (Significant) | No Trend |
|---|
| TNn | 0.48 | −0.14 to 0.91 | 87% (60%) | 13% (0%) | 0% |
| TNx | 0.34 | 0.18 to 0.70 | 100% (93%) | 0% (0%) | 0% |
| TXn | 0.35 | 0.05 to 0.60 | 100% (87%) | 0% (0%) | 0% |
| TXx | 0.22 | 0.00 to 0.57 | 93% (47%) | 0% (0%) | 7% |
| DTR | −0.06 | −0.27 to 0.17 | 20% (7%) | 73% (33%) | 7% |
| TN10p | −1.94 | −3.64 to −0.03 | 0% (0%) | 100% (93%) | 0% |
| TX10p | −1.66 | −2.14 to −0.55 | 0% (0%) | 100% (93%) | 0% |
| FD | −4.39 | −9.64 to −0.83 | 0% (0%) | 100% (87%) | 0% |
| ID | −2.02 | −8.66 to 0.00 | 0% (0%) | 67% (27%) | 33% |
| CSDI | −0.27 | 0.00 | 0% (0%) | 0% (0%) | 100% |
| TN90p | 3.75 | 1.94 to 6.22 | 100% (100%) | 0% (0%) | 0% |
| TX90p | 2.10 | 0.25 to 3.41 | 100% (93%) | 0% (0%) | 0% |
| GSL | 4.33 | 0.04 to 12.34 | 100% (27%) | 0% (0%) | 0% |
| SU25 | 1.23 | 0.00 to 6.46 | 47% (47%) | 0% (0%) | 53% |
| WSDI | 2.80 | 0.00 to 5.00 | 80% (60%) | 0% (0%) | 20% |
Table 5.
Trends per decade, change range, and percentage of stations with positive, negative, and no trend in regional precipitation extreme indices.
Table 5.
Trends per decade, change range, and percentage of stations with positive, negative, and no trend in regional precipitation extreme indices.
| Index | Regional Trends | Range | Positive Trend (Significant) | Negative Trend (Significant) | No Trend |
|---|
| PRCPTOT | 7.33 | −17.80 to 20.27 | 80% (0%) | 20% (0%) | 0% |
| SDII | 0.10 | −0.10 to 0.31 | 80% (13%) | 13% (0%) | 7% |
| RX1d | 0.21 | −2.06 to 1.80 | 53% (7%) | 47% (0%) | 0% |
| RX5d | 0.69 | −1.77 to 2.44 | 53% (7%) | 47% (0%) | 0% |
| R95p | 4.01 | −9.24 to 13.27 | 47% (7%) | 40% (0%) | 13% |
| R99p | 0.92 | −0.60 to 0.00 | 0% (0%) | 7% (0%) | 93% |
| R10mm | 0.37 | −0.85 to 1.26 | 53% (7%) | 7% (0%) | 40% |
| R20mm | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0% (0%) | 0% (0%) | 100% |
| CWD | −0.06 | −0.84 to 0.59 | 13% (0%) | 13% (7%) | 73% |
| CDD | 0.62 | −6.10 to 5.87 | 47% (7%) | 47% (0%) | 7% |
Table 6.
Pettitt’s test results of the temperature and precipitation extreme indices.
Table 6.
Pettitt’s test results of the temperature and precipitation extreme indices.
| Index | Change Year | U * | p | Index | Change Year | U * | p |
|---|
| TNn | 1997 | 387 | <0.01 | SU25 | 2004 | 316 | 0.01 |
| TNx | 1995 | 459 | <0.01 | WSDI | 1997 | 438 | <0.01 |
| TXn | 1997 | 295 | 0.02 | PRCPTOT | 1987 | 154 | 0.57 |
| TXx | 1992 | 208 | 0.20 | SDII | 2006 | 206 | 0.21 |
| DTR | 1988 | 279 | 0.03 | RX1d | 2006 | 161 | 0.50 |
| TN10p | 1997 | 548 | <0.01 | RX5d | 2006 | 151 | 0.60 |
| TX10p | 1997 | 522 | <0.01 | R95p | 2006 | 143 | 0.67 |
| FD | 1997 | 503 | <0.01 | R99p | 2006 | 175 | 0.39 |
| ID | 1998 | 434 | <0.01 | R10mm | 1987 | 192 | 0.28 |
| CSDI | 1998 | 268 | 0.04 | R20mm | 1983 | 157 | 0.54 |
| TN90p | 1997 | 546 | <0.01 | CWD | 2004 | 207 | 0.21 |
| TX90p | 1997 | 466 | <0.01 | CDD | 1977 | 138 | 0.73 |
| GSL | 1997 | 407 | <0.01 | | | | |
Table 7.
Trends of temperature and precipitation indices from this study and other sources.
Table 7.
Trends of temperature and precipitation indices from this study and other sources.
| Indices | The YTRB | TP and Its Surroundings | Eastern and Central TP | Western TP | Three-River Headwaters | Southwestern China | China |
|---|
| TNn | 0.48 | 1.04 | - | 0.63 | 0.49 | 0.29 | 0.58 |
| TNx | 0.34 | 0.36 | - | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.28 |
| TXn | 0.35 | 0.10 | - | 0.67 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.32 |
| TXx | 0.22 | 0.30 | - | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| DTR | −0.06 | - | −0.20 | −0.20 | −0.11 | −0.18 | - |
| TN10p | −1.94 | - | −2.38 | −4.92 | −4.63 | −0.37 | −2.00 |
| TX10p | −1.66 | - | −0.85 | −2.84 | −2.47 | −0.13 | −0.80 |
| FD | −4.39 | −4.06 | −4.32 | −5.69 | −4.28 | −0.29 | −3.90 |
| ID | −2.02 | −2.03 | −2.46 | −7.74 | −4.68 | −0.09 | −2.10 |
| CSDI | −0.27 | - | - | −2.55 | - | - | −0.80 |
| TN90p | 3.75 | - | 2.54 | 4.00 | 4.30 | 0.36 | 3.30 |
| TX90p | 2.10 | - | 1.26 | 3.43 | 3.05 | 0.22 | 1.70 |
| GSL | 4.33 | - | 4.25 | 4.35 | 3.94 | 0.12 | 3.40 |
| SU25 | 1.23 | 2.59 | - | 0.42 | 1.20 | - | 1.90 |
| WSDI | 2.80 | - | - | 3.31 | - | - | 3.00 |
| PRCPTOT | 7.33 | 6.98 | 6.66 | 0.47 | 8.33 | 0.03 | 0.30 |
| SDII | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.70 |
| RX1d | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.37 | −0.16 | 0.05 | - |
| RX5d | 0.69 | 0.50 | −0.08 | 1.25 | −0.44 | 0.03 | - |
| R95p | 4.01 | 3.24 | 1.28 | 0.48 | 3.83 | 0.04 | 2.10 |
| R99p | 0.92 | 1.96 | 1.09 | 0.41 | 1.90 | 0.05 | - |
| R10mm | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.00 | - |
| R20mm | 0.11 | 0.07 | - | - | 0.04 | 0.00 | - |
| CWD | −0.06 | −0.02 | −0.07 | 0.17 | −0.16 | −0.08 | 0.20 |
| CDD | 0.62 | −0.87 | −4.64 | 0.52 | −2.06 | −0.05 | −3.50 |
Table 8.
Correlation coefficients between extreme precipitation indices and the East Asian summer monsoon index (EASMI) and South Asian summer monsoon index (SASMI).
Table 8.
Correlation coefficients between extreme precipitation indices and the East Asian summer monsoon index (EASMI) and South Asian summer monsoon index (SASMI).
| Indices | PRCPTOT | SDII | RX1d | RX5d | R95p | R99p | R10mm | R20mm | CWD | CDD |
|---|
| EASMI | −0.32 | −0.28 | −0.25 | −0.19 | −0.23 | −0.25 | −0.31 | −0.27 | −0.30 | 0.28 |
| SASMI | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.14 |