The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tissue Collection
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Double (Immuno)Fluorescence Staining
2.4. Quantification of Immunohistochemical Stainings
2.5. Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 Protein Analysis
2.7. Brain Proteome
2.8. TG2 Immunoprecipitation from Brain Homogenates
2.9. Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) and SWATH Acquisition MS of Brain Homogenates and TG2 Immunoprecipitates
2.10. Z-Test Statistical Analysis
2.11. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
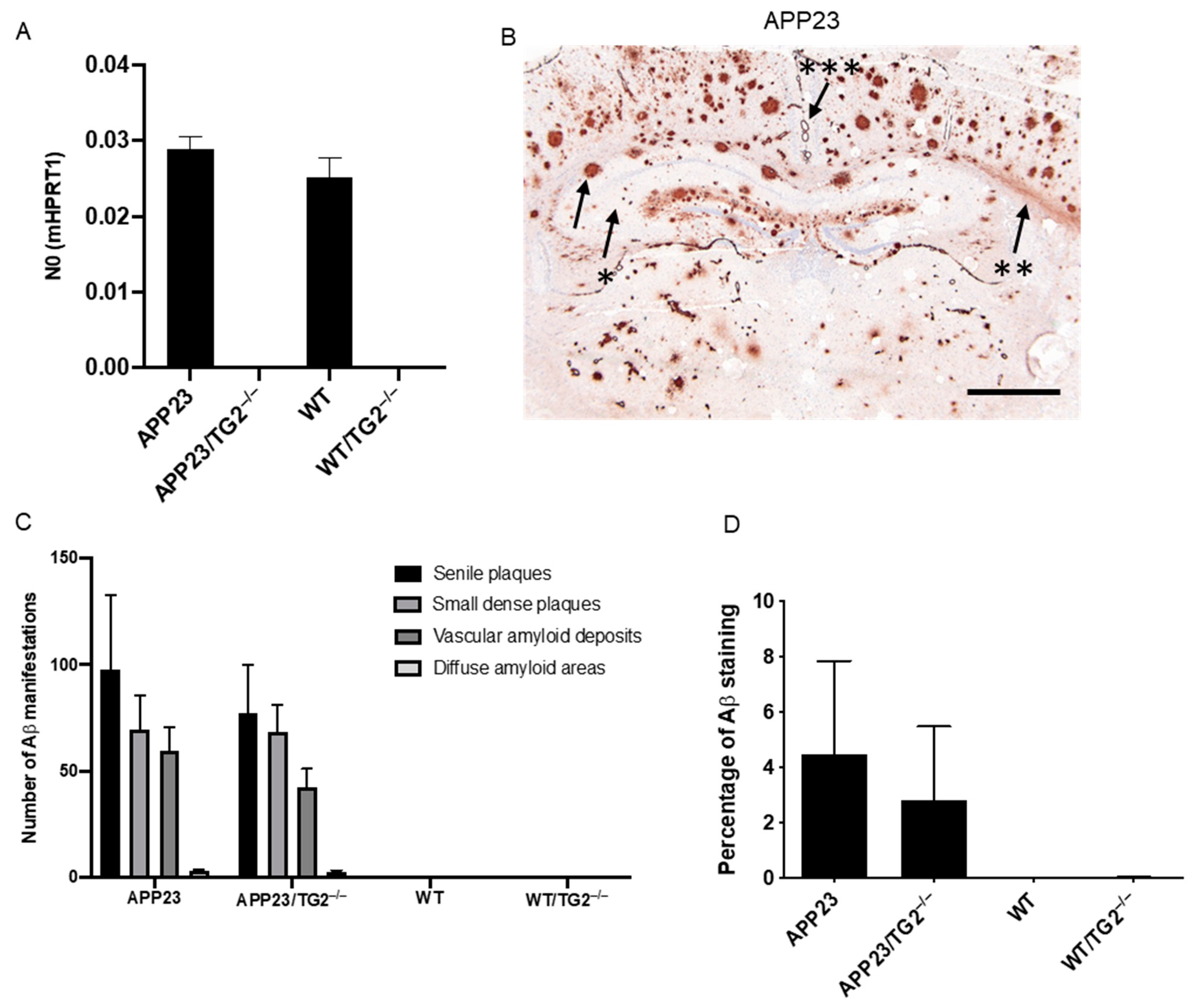
3.1. Distribution and Quantification of Aβ Pathology in APP23 and APP23/TG2−/− Mice Brain
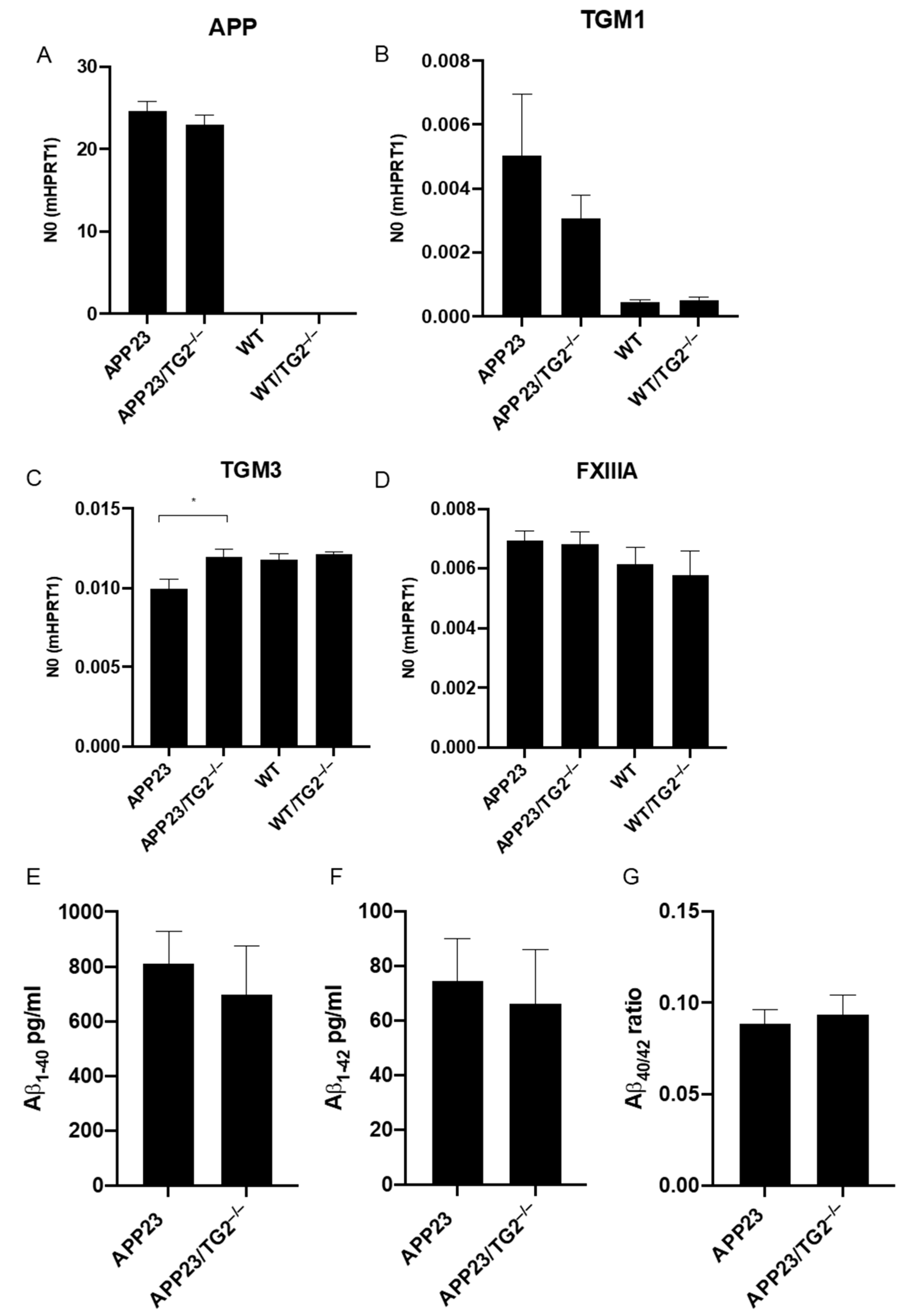
3.2. Analysis of mRNA of Human APP, Mouse TGM1, TGM3, TGM6 and FXIIIA and Soluble Brain Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 Levels, and Aβ40/42 Ratio in Mouse Brain Homogenates
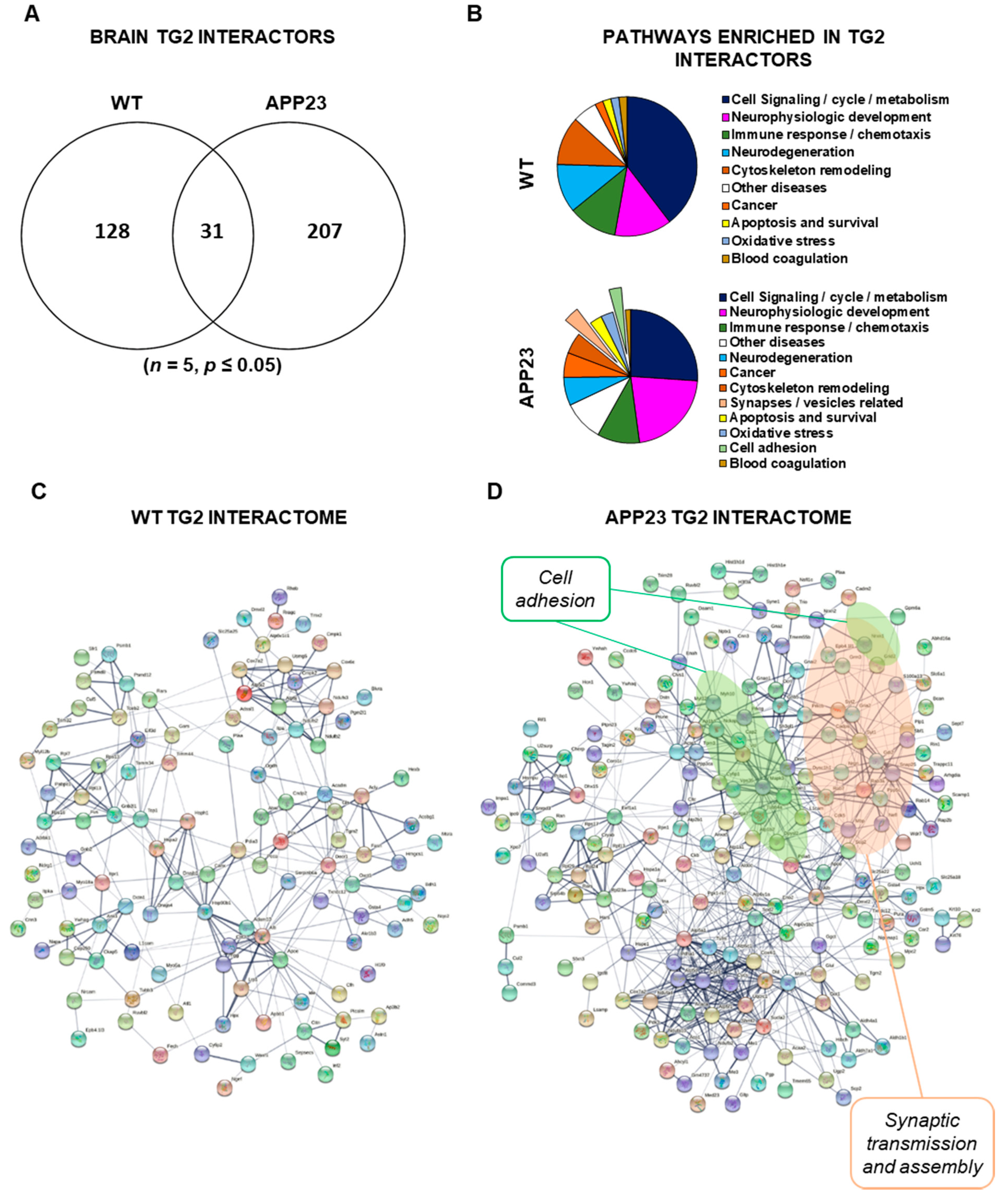
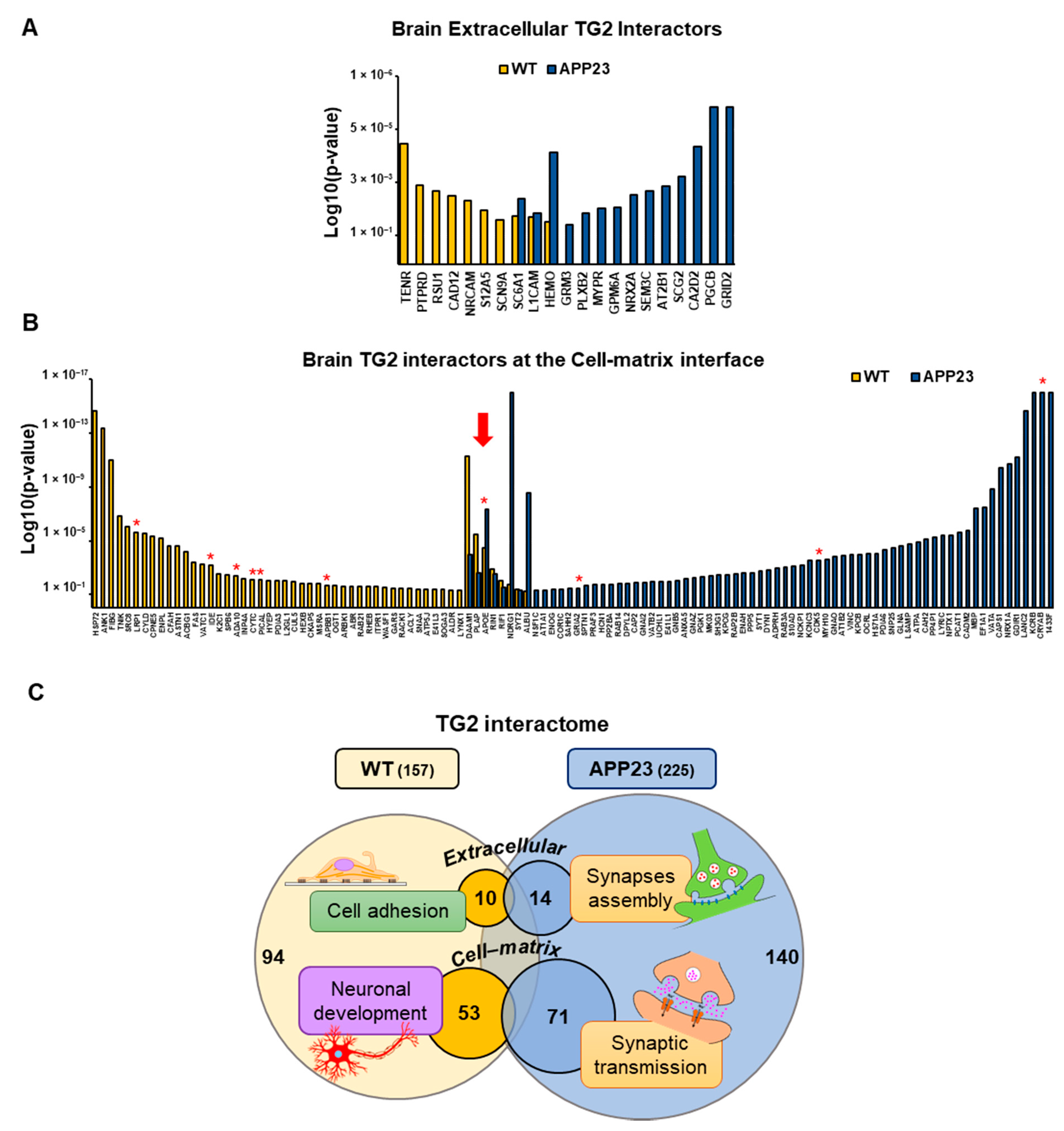
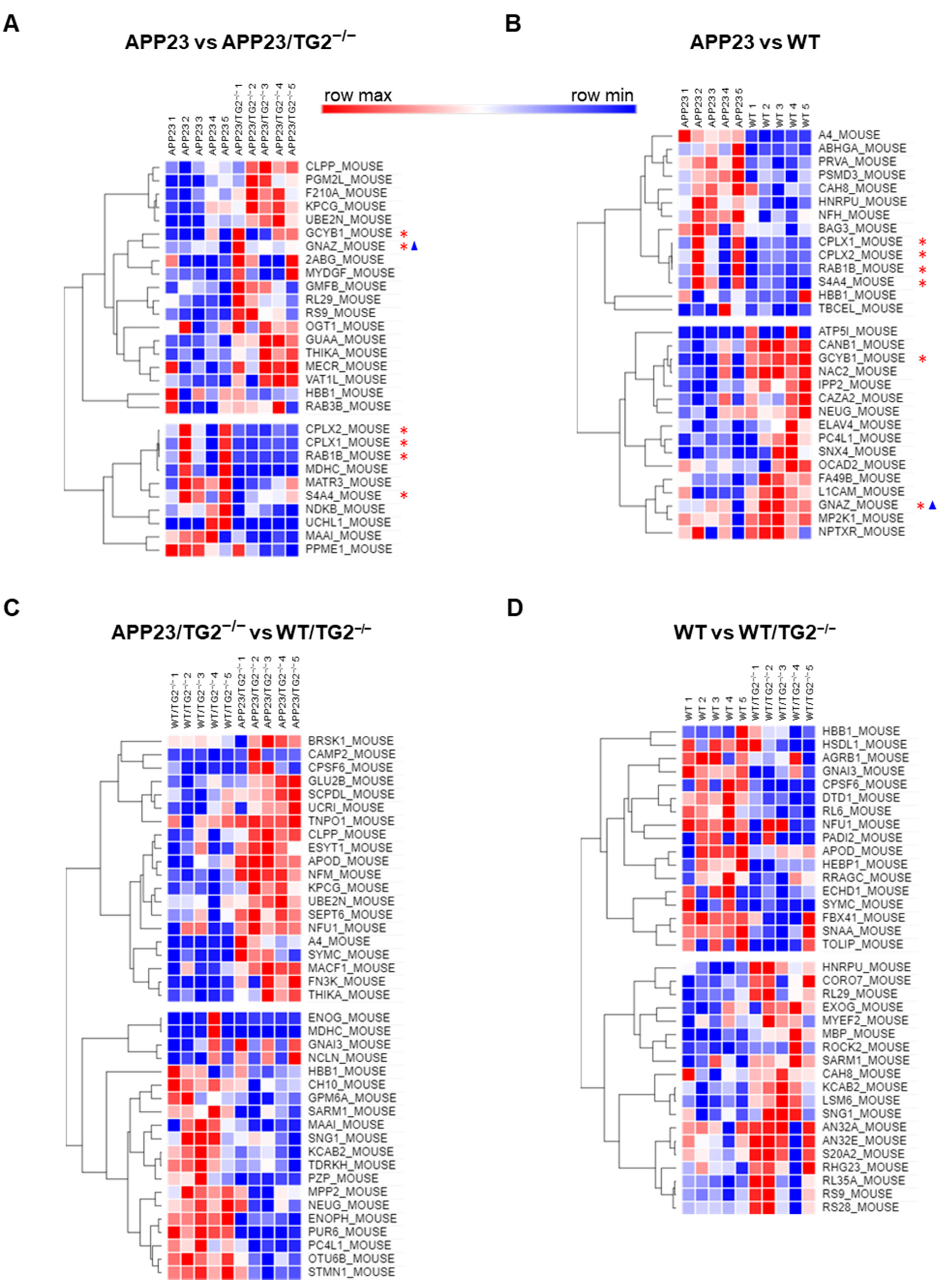
3.3. Quantitative Comparative Proteomics of TG2 Binding Partners
3.4. TG2+/+ and TG2−/− Brain Proteomes in APP23 Mouse Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J. Amyloid Protein and Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Am. 1991, 5, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1991, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian Hui Kwan, A.; Arfaie, S.; Therriault, J.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Gauthier, S. Lessons Learnt from the Second Generation of An-ti-Amyloid Monoclonal Antibodies Clinical Trials. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 49, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Corbett, A.; Ballard, C. Emerging treatments for Alzheimer’s disease for non-amyloid and non-tau targets. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrup, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Schenk, D.; Cacace, A.; DeSanti, S.; Fremeau, R.; Bhat, R.; Glicksman, M.; May, P.; Swerdlow, R.; et al. Beyond amyloid: Getting real about nonamyloid targets in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 452–458.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lendel, C. Extracellular protein components of amyloid plaques and their roles in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorand, L.; Graham, R.M. Transglutaminases: Crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsukawa, H.; Hitomi, K. Role of Transglutaminase 2 in Cell Death, Survival, and Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Grant, P.; Lee, J.H.; Pant, H.C.; Steinert, P.M. Differential Expression of Multiple Transglutaminases in Human Brain. Increased Expression and Cross-Linking by Transglutaminases 1 and 2 in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30715–30721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; Grunberg, S.C.; Bol, J.G.; van Dam, A.M.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Drukarch, B. Transglu-taminases and Transglutaminase-Catalyzed Cross-Links Colocalize with the Pathological Lesions in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.V.; Cox, T.M.; Lockhart, J.P.; Zinnerman, M.D.; Miller, M.L.; E Powers, R. Transglutaminase activity is increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain Res. 1997, 751, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, R.M.; Aschoff, A.; Niederwieser, G.; Heuberger, C.; Jirikowski, G. Cerebrospinal Fluid Tissue Transglutaminase as a Biochemical Marker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2002, 11, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nemes, Z.; Fesus, L.; Egerhazi, A.; Keszthelyi, A.; Degrell, I.M. N(Epsilon)(Gamma-Glutamyl)Lysine in Cerebrospinal Fluid Marks Alzheimer Type and Vascular Dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2001, 22, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Johnson, B.R.; Suri, D.E.; Martinez, J.; Bjornsson, T.D. Immunohistochemical demonstration of tissue transglutaminase in amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 96, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, S.M.; Johnson, G.V.W. Transglutaminase Catalyzes the Formation of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Insoluble, Alz-50-Reactive Polymers of τ? J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, S.M.; Johnson, G.V. Transglutaminase Facilitates the Formation of Polymers of the Beta-Amyloid Peptide. Brain Res. 1994, 651, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.W.; Condemi, E.; Tuchscherer, G.; Chiappe, D.; Mutter, M.; Vogel, H.; Moniatte, M.; Tsybin, Y. Tissue Transglutaminase-mediated Glutamine Deamidation of β-Amyloid Peptide Increases Peptide Solubility, Whereas Enzymatic Cross-linking and Peptide Fragmentation May Serve as Molecular Triggers for Rapid Peptide Aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12172–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; Otte-Holler, I.; van Triel, J.J.; Veerhuis, R.; Maat-Schieman, M.L.; Bu, G.; de Waal, R.M.; Verbeek, M.M. Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-1 Mediates Amyloid-Beta-Mediated Cell Death of Cerebrovascular Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.M.; Jongenelen, C.A.; Bol, J.G.J.M.; Drukarch, B. Interaction between Tissue Transglutaminase and Am-yloid-Beta: Protein- Protein Binding versus Enzymatic Crosslinking. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 592, 113578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, D.M.; Zhao, C.; Speier, A.C.; Woodard, G.A.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Walz, T. Transglutaminase Induces Protofibril-like Am-yloid Beta-Protein Assemblies That Are Protease-Resistant and Inhibit Long-Term Potentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16790–16800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, M.; Drukarch, B.; Hofstee, M.; Breve, J.; Jongenelen, C.A.; Bol, J.G.; Wilhelmus, M.M. Tissue Transglutami-nase-Catalysed Cross-Linking Induces Apolipoprotein E Multimers Inhibiting Apolipoprotein E’s Protective Effects towards Amyloid-Beta-Induced Toxicity. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, M.; van der Wildt, B.; Schul, E.; Bol, J.G.; van Duinen, S.G.; Drukarch, B.; Wilhelmus, M.M. Tissue Transglutaminase Colocalizes with Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boros, S.; Ahrman, E.; Wunderink, L.; Kamps, B.; de Jong, W.W.; Boelens, W.C.; Emanuelsson, C.S. Site-Specific Transami-dation and Deamidation of the Small Heat-Shock Protein Hsp20 by Tissue Transglutaminase. Proteins 2006, 62, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furini, G.; Schroeder, N.; Huang, L.; Boocock, D.; Scarpellini, A.; Coveney, C.; Tonoli, E.; Ramaswamy, R.; Ball, G.; Verderio, C.; et al. Proteomic Profiling Reveals the Transglutaminase-2 Externalization Pathway in Kidneys after Unilateral Ureteric Obstruction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 880–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuntas, S.; Rossin, F.; Marsella, C.; D’Eletto, M.; Diaz-Hidalgo, L.; Farrace, M.G.; Campanella, M.; Antonioli, M.; Fimia, G.M.; Piacentini, M. The transglutaminase type 2 and pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2 interplay in autophagy regulation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44941–44954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.M.; De Jager, M.; Smit, A.B.; Van Der Loo, R.J.; Drukarch, B. Catalytically active tissue transglutaminase colocalises with Aβ pathology in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturchler-Pierrat, C.; Abramowski, D.; Duke, M.; Wiederhold, K.-H.; Mistl, C.; Rothacher, S.; Ledermann, B.; Bürki, K.; Frey, P.; Paganetti, P.; et al. Two amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse models with Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13287–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laurenzi, V.; Melino, G. Gene Disruption of Tissue Transglutaminase. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.M.; Otte-Holler, I.; Wesseling, P.; De Waal, R.M.W.; Boelens, W.C.; Verbeek, M.M. Specific association of small heat shock proteins with the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2006, 32, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, D.; D’Hooge, R.; Staufenbiel, M.; Van Ginneken, C.; Van Meir, F.; De Deyn, P.P. Age-Dependent Cognitive Decline in the APP23 Model Precedes Amyloid Deposition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, D.H.; Vergoossen, D.L.E.; Huisman, E.; Lemstra, A.W.; Bank, N.B.; Berendse, H.W.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Foncke, E.M.; van de Berg, W. Distribution and Load of Amyloid-β Pathology in Parkinson Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burhan, I.; Furini, G.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Atobatele, A.G.; Scarpellini, A.; Schroeder, N.; Atkinson, J.; Maamra, M.; Nutter, F.H.; Watson, P.; et al. Interplay between transglutaminases and heparan sulphate in progressive renal scarring. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Tate, S.; Röst, H.; Selevsek, N.; Reiter, L.; Bonner, R.; Aebersold, R. Targeted Data Extraction of the MS/MS Spectra Generated by Data-Independent Acquisition: A New Concept for Consistent and Accurate Proteome Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, O111.016717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheadle, C.; Vawter, M.P.; Freed, W.J.; Becker, K.G. Analysis of Microarray Data Using Z Score Transformation. J. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 5, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, G.; Farrace, M.G.; Mastroberardino, P.G.; Viti, I.; Fimia, G.M.; Van, B.J.; Devreese, B.; Melino, G.; Molinaro, G.; Busceti, C.L.; et al. Transglutaminase 2 Ablation Leads to Defective Function of Mito-chondrial Respiratory Complex I Affecting Neuronal Vulnerability in Experimental Models of Extrapyramidal Disorders. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, N.; Staufenbiel, M.; Gomez-Mancilla, B. Proteomic 2-D DIGE Profiling of APP23 Transgenic Mice Brain from Pre-plaque and Plaque Phenotypes. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 13, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.; Rohe, M.; Mao, L.; Staufenbiel, M.; Zabel, C.; Klose, J. Impairment of Adolescent Hippocampal Plasticity in a Mouse Model for Alzheimer’s Disease Precedes Disease Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; de Jager, M.; Bakker, E.N.; Drukarch, B. Tissue Transglutaminase in Alzheimer’s Disease: Involvement in Pathogenesis and its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 42, S289–S303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.; Keppens, C.; De Deyn, P.P.; Van Dam, D. Late age increase in soluble amyloid-beta levels in the APP23 mouse model despite steady-state levels of amyloid-beta-producing proteins. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Park, H.H. Structural aspects of transglutaminase 2: Functional, structural, and regulatory diversity. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Cuevas, E.; Raymick, J.; Kanungo, J.; Sarkar, S. Downregulation of 14-3-3 Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; Boelens, W.C.; Otte-Holler, I.; Kamps, B.; de Waal, R.M.; Verbeek, M.M. Small Heat Shock Proteins Inhibit Amyloid-Beta Protein Aggregation and Cerebrovascular Amyloid-Beta Protein Toxicity. Brain Res. 2006, 1089, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenen, P.J.; Bloemendal, H.; de Jong, W.W. The Carboxy-Terminal Lysine of Alpha B-Crystallin Is an Amine-Donor Sub-strate for Tissue Transglutaminase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 205, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Murphy, L.J. Phosphorylation of transglutaminase 2 by PKA at Ser216 creates 14-3-3 binding sites. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eletto, M.; Farrace, M.G.; Falasca, L.; Reali, V.; Oliverio, S.; Melino, G.; Griffin, M.; Fimia, G.M.; Piacentini, M. Transglu-taminase 2 Is Involved in Autophagosome Maturation. Autophagy 2009, 5, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimiuk, M.; Sobiborowicz, A.; Tuzimek, A.; Deptała, A.; Czerw, A.; Badowska-Kozakiewicz, A.M. AB-Crystallin as a Promising Target in Pathological Conditions – A Review. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.-C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer Disease: Pathobiology and Tar-geting Strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; Otte-Holler, I.; Davis, J.; Van Nostrand, W.E.; de Waal, R.M.; Verbeek, M.M. Apolipoprotein E Genotype Regulates Amyloid-Beta Cytotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3621–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshchyns’Ka, I.; Sytnyk, V. Synaptic Cell Adhesion Molecules in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, R.L.; Kaartinen, M.; Nurminskaya, M.; Belkin, A.M.; Colak, G.; Johnson, G.V.; Mehta, K. Transglutaminase regulation of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 383–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunes-Medina, L.; Paciorkowski, A.; Nuzbrokh, Y.; Johnson, G.V.W. Depletion of transglutaminase 2 in neurons alters ex-pression of extracellular matrix and signal transduction genes and compromises cell viability. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 86, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furini, G.; Verderio, E.A. Spotlight on the Transglutaminase 2-Heparan Sulfate Interaction. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsepian, S.V.; Leary, V.B.O.; Zaborszky, L.; Ntziachristos, V.; Dolly, J.O. Synaptic Vesicle Cycle and Amyloid B: Biting the Hand That Feeds. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchiano, F.; Benfenati, F.; Valtorta, F.; Luini, A. Covalent modification of synapsin I by a tetanus toxin-activated transglutaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 4588–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Grosso Jasutkar, H.; Yan, R.; Woo, J.-M.; Lee, K.-W.; Im, J.-Y.; Junn, E.; Iismaa, S.E.; Mouradian, M.M. Transglu-taminase 2 Depletion Attenuates α-Synuclein Mediated Toxicity in Mice. Neuroscience 2020, 441, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.-S.; Lin, C.-J.; Wu, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-J. Tissue transglutaminase TG2 and mitochondrial function and dysfunction. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 1114–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.; Hu, Y.; Schultz, C.; Kandel, E.R.; Hawkins, R.D. Role of Guanylyl Cyclase and CGMP-Dependent Protein Kinase in Long-Term Potentiation. Nature 1994, 368, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfort, P.; Muñoz, M.-D.; Kosenko, E.; Felipo, V. Long-Term Potentiation in Hippocampus Involves Sequential Activation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase, cGMP-Dependent Protein Kinase, and cGMP-Degrading Phosphodiesterase. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10116–10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | TG2-Interactor Name | p-Value | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| TENR | Tenascin-R | 1.5 × 10−4 | WT |
| PTPRD | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase delta | 3.1 × 10−3 | WT |
| RSU1 | Ras suppressor protein 1 | 4.7 × 10−3 | WT |
| CAD12 | Cadherin-12 | 6.4 × 10−3 | WT |
| NRCAM | Neuronal cell adhesion molecule | 9.6 × 10−3 | WT |
| S12A5 | Solute carrier family 12 member 5 | 1.9 × 10−2 | WT |
| SCN9A | Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha | 3.8 × 10−2 | WT |
| SC6A1 | Sodium- and chloride-dependent GABA transporter 1 | 2.9 × 10−2/8.0 × 10−3 | WT/APP23 |
| L1CAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 | 3.2 × 10−2/2.4 × 10−2 | WT/APP23 |
| HEMO | Hemopexin | 4.5 × 10−2/2.8 × 10−4 | WT/APP23 |
| PGCB | Brevican core protein | 1.0 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| GRID2 | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, delta-2 | 1.0 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| CA2D2 | Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-2 | 1.8 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| SCG2 | Secretogranin-2 | 1.6 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| AT2B1 | Plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 1 | 3.2 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| SEM3C | Semaphorin-3C | 4.6 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| NRX2A | Neurexin-2 | 6.0 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| GPM6A | Neuronal membrane glycoprotein M6-a | 1.5 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| MYPR | Myelin proteolipid protein | 1.6 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| PLXB2 | Plexin-B2 | 2.4 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| GRM3 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 | 5.5 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| ID | TG2-Interactor Name | p-Value | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSP72 | Heat shock-related 70 kDa protein 2 | 2.4 × 10−15 | WT |
| ANK1 | Ankyrin-1 | 4.7 × 10−14 | WT |
| FIBG | Fibrinogen gamma chain | 1.0 × 10−11 | WT |
| TNIK | Traf2 and NCK-interacting protein kinase | 1.5 × 10−7 | WT |
| SRC8 | Src substrate cortactin | 9.4 × 10−7 | WT |
| LRP1 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 | 2.3 × 10−6 | WT |
| CYLD | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase CYLD | 2.9 × 10−6 | WT |
| CPNE5 | Copine-5 | 4.8 × 10−6 | WT |
| ENPL | Endoplasmin | 6.6 × 10−6 | WT |
| CFAH | Complement factor H | 2.5 × 10−5 | WT |
| ASTN1 | Astrotactin-1 | 2.6 × 10−5 | WT |
| ACBG1 | Long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase ACSBG1 | 6.9 × 10−5 | WT |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase | 4.2 × 10−4 | WT |
| VATC1 | V-type proton ATPase subunit C 1 | 5.3 × 10−4 | WT |
| IDE | Insulin-degrading enzyme | 6.8 × 10−4 | WT |
| K2C1 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | 2.9 × 10−3 | WT |
| SPB6 | Serpin B6 | 3.5 × 10−3 | WT |
| ADA10 | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10 | 4.2 × 10−3 | WT |
| INP4A | Type I inositol 3,4-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase | 6.9 × 10−3 | WT |
| CYTC | Cystatin-C | 7.7 × 10−3 | WT |
| PICAL | Phosphatidylinositol-binding clathrin assembly protein | 7.8 × 10−3 | WT |
| HYEP | Epoxide hydrolase 1 | 8.8 × 10−3 | WT |
| PDIA3 | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 | 1.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| L2GL1 | Lethal(2) giant larvae protein homolog 1 | 1.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| CUL5 | Cullin-5 | 1.1 × 10−2 | WT |
| HEXB | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta | 1.5 × 10−2 | WT |
| CKAP5 | Cytoskeleton-associated protein 5 | 1.5 × 10−2 | WT |
| MSRA | Mitochondrial peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase | 1.6 × 10−2 | WT |
| APBB1 | Amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein-binding family B member 1 | 2.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| OGT1 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine—peptide N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 110 kDa subunit | 2.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| ARBK1 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | 2.4 × 10−2 | WT |
| ABR | Active breakpoint cluster region-related protein | 2.5 × 10−2 | WT |
| RAB21 | Ras-related protein Rab-21 | 2.6 × 10−2 | WT |
| RHEB | GTP-binding protein Rheb | 2.7 × 10−2 | WT |
| ITPR1 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1 | 2.7 × 10−2 | WT |
| WASF1 | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein family member 1 | 2.8 × 10−2 | WT |
| GARS | Glycine—tRNA ligase | 3.5 × 10−2 | WT |
| RACK1 | Receptor of activated protein C kinase 1 | 3.5 × 10−2 | WT |
| ACLY | ATP-citrate synthase | 3.7 × 10−2 | WT |
| SNAA | Alpha-soluble NSF attachment protein | 3.8 × 10−2 | WT |
| ATP5J | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial | 4.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| E41L3 | Band 4.1-like protein 3 | 4.0 × 10−2 | WT |
| SOGA3 | Protein SOGA3 | 4.4 × 10−2 | WT |
| ALDR | Aldose reductase | 4.6 × 10−2 | WT |
| LYNX1 | Ly-6/neurotoxin-like protein 1 | 4.8 × 10−2 | WT |
| DAAM1 | Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1 | 5.1 × 10−12/1.1 × 10−4 | WT/APP23 |
| PLAP | Phospholipase A-2-activating protein | 3.2 × 10−6/2.6 × 10−3 | WT/APP23 |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E | 3.5 × 10−5/4.3 × 10−8 | WT/APP23 |
| RIN1 | Ras and Rab interactor 1 | 1.3 × 10−3/2.9 × 10−3 | WT/APP23 |
| RIF1 | Telomere-associated protein RIF1 | 9.7 × 10−3/2.8 × 10−2 | WT/APP23 |
| NDRG1 | Protein NDRG1 | 1.9 × 10−2/1.0 × 10−16 | WT/APP23 |
| SYT2 | Synaptotagmin-2 | 4.2 × 10−2/5.0 × 10−2 | WT/APP23 |
| ALBU | Serum albumin | 5.5 × 10−2/2.8 × 10−9 | WT/APP23 |
| KCRB | Creatine kinase B-type | 1.0 × 10−16 | APP23 |
| CRYAB | Alpha-crystallin B chain | 1.0 × 10−16 | APP23 |
| 1433F | 14-3-3 protein eta | 1.0 × 10−16 | APP23 |
| LANC2 | LanC-like protein 2 | 2.4 × 10−15 | APP23 |
| GDIR1 | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 | 6.8 × 10−12 | APP23 |
| NRX1A | Neurexin-1 | 2.1 × 10−11 | APP23 |
| CAPS1 | Calcium-dependent secretion activator 1 | 3.7 × 10−11 | APP23 |
| VATA | V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A | 1.4 × 10−9 | APP23 |
| EF1A1 | Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 | 3.5 × 10−8 | APP23 |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein | 3.7 × 10−8 | APP23 |
| CADM2 | Cell adhesion molecule 2 | 1.7 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| PCAT1 | Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 | 2.3 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| NPTX1 | Neuronal pentraxin-1 | 4.0 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| LYRIC | Protein LYRIC | 4.0 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| PP4P1 | Type 1 phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase | 5.7 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| CAH2 | Carbonic anhydrase 2 | 7.4 × 10−6 | APP23 |
| ATPA | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial | 1.3 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| LSAMP | Limbic system-associated membrane protein | 1.8 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| GLNA | Glutamine synthetase | 2.4 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| SNP25 | Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 | 3.6 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| PDIA6 | Protein disulfide-isomerase A6 | 5.1 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| HS71A | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A | 8.7 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| OCRL | Inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase OCRL-1 | 9.2 × 10−5 | APP23 |
| KPCB | Protein kinase C beta type | 1.0 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| VINC | Vinculin | 1.1 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| AT1B2 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-2 | 1.3 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| GNAO | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(o) subunit alpha | 1.4 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| MYH10 | Myosin-10 | 2.5 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| CDK5 | Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 | 3.0 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| KCNC3 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 3 | 3.1 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| NCKP1 | Nck-associated protein 1 | 6.6 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| S10AD | Protein S100-A13 | 8.5 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| RAB3A | Ras-related protein Rab-3A | 9.6 × 10−4 | APP23 |
| ADPRH | [Protein ADP-ribosylarginine] hydrolase | 1.1 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| DYN1 | Dynamin-1 | 1.4 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| SYT1 | Synaptotagmin-1 | 1.7 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| PPP5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | 2.3 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| ENAH | Protein enabled homolog | 2.4 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| RAP2B | Ras-related protein Rap-2b | 3.2 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| KPCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | 3.4 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| SH3G1 | Endophilin-A2 | 3.5 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| MK03 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | 4.2 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | 4.6 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| GNAZ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(z) subunit alpha | 5.2 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| ANXA5 | Annexin A5 | 6.8 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| GNB5 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-5 | 9.6 × 10−3 | APP23 |
| E41L1 | Band 4.1-like protein 1 | 1.1 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| UCHL1 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 | 1.1 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| VATB2 | V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform | 1.2 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | 1.2 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| CAP2 | Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 2 | 1.2 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| DPYL2 | Dihydropyrimidinase-related protein 2 | 1.5 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| RAB14 | Ras-related protein Rab-14 | 1.5 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| PP2BA | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit alpha isoform | 1.7 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| HCN1 | Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 | 1.8 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| PRAF3 | PRA1 family protein 3 | 1.8 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| SPTN1 | Spectrin alpha chain, non-erythrocytic 1 | 2.0 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| GRIA2 | Glutamate receptor 2 | 3.3 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| SAHH2 | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-like protein 1 | 3.8 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| COR1C | Coronin-1C | 4.2 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| ENOG | Gamma-enolase | 4.3 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| AT1A1 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1 | 4.7 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| NSF1C | NSFL1 cofactor p47 | 5.0 × 10−2 | APP23 |
| ID | Name | log2FC (APP23/WT) | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELAV4 | ELAV-like protein 4 | 3.93 | 0.55 |
| TBCEL | Tubulin-specific chaperone cofactor E-like protein | 2.84 | 0.56 |
| ATP5I | ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial | 2.56 | 0.60 |
| GCYB1 | Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-1 | 2.47 | 0.71 |
| SNX4 | Sorting nexin-4 | 2.34 | 0.58 |
| PSMD3 | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 3 | 1.31 | 0.68 |
| A4 | Amyloid beta A4 protein | 1.18 | 0.78 |
| CPLX2 | Complexin-2 | 1.09 | 0.58 |
| CPLX1 | Complexin-1 | 1.08 | 0.63 |
| RAB1B | Ras-related protein Rab-1B | 1.03 | 0.70 |
| BAG3 | BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 3 | 0.91 | 0.55 |
| CAH8 | Carbonic anhydrase-related protein | 0.76 | 0.67 |
| HBB1 | Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 | 0.70 | 0.56 |
| ABHGA | Protein ABHD16A | 0.60 | 0.65 |
| CAZA2 | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 | 0.57 | 0.65 |
| PRVA | Parvalbumin alpha | 0.47 | 0.68 |
| NFH | Neurofilament heavy polypeptide | 0.47 | 0.67 |
| HNRPU | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U | 0.41 | 0.55 |
| OCAD2 | OCIA domain-containing protein 2 | 0.38 | 0.63 |
| L1CAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 | 0.37 | 0.60 |
| FA49B | Protein FAM49B | 0.33 | 0.66 |
| IPP2 | Protein phosphatase inhibitor 2 | 0.33 | 0.63 |
| GNAZ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(z) subunit alpha | 0.32 | 0.56 |
| S4A4 | Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 | 0.28 | 0.56 |
| NEUG | Neurogranin | 0.28 | 0.55 |
| CANB1 | Calcineurin subunit B type 1 | 0.27 | 0.55 |
| NAC2 | Sodium/calcium exchanger 2 | −0.48 | 0.81 |
| MP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | −0.49 | 0.57 |
| NPTXR | Neuronal pentraxin receptor | −0.53 | 0.55 |
| PC4L1 | Purkinje cell protein 4-like protein 1 | −0.54 | 0.82 |
| ID | Name | log2FC (APP23/APP23 TG2−/−) | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| UCHL1 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 | 6.02 | 0.58 |
| MATR3 | Matrin-3 | 3.32 | 0.57 |
| MDHC | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | 1.78 | 0.55 |
| MAAI | Maleylacetoacetate isomerase | 1.59 | 0.70 |
| CPLX2 | Complexin-2 | 1.41 | 0.57 |
| S4A4 | Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 | 1.21 | 0.57 |
| CPLX1 | Complexin-1 | 1.16 | 0.59 |
| RAB1B | Ras-related protein Rab-1B | 1.01 | 0.71 |
| HBB1 | Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 | 0.77 | 0.66 |
| NDKB | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B | 0.43 | 0.72 |
| PPME1 | Protein phosphatase methylesterase 1 | 0.43 | 0.62 |
| GNAZ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(z) subunit alpha | −0.37 | 0.55 |
| OGT1 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine—peptide N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 110 kDa subunit | −0.45 | 0.55 |
| CLPP | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit, mitochondrial | −0.55 | 0.63 |
| F210A | Protein FAM210A | −0.56 | 0.67 |
| RL29 | 60S ribosomal protein L29 | −0.74 | 0.56 |
| KPCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | −0.94 | 0.72 |
| PGM2L | Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate synthase | −0.94 | 0.72 |
| UBE2N | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N | −1.00 | 0.79 |
| RS9 | 40S ribosomal protein S9 | −1.25 | 0.77 |
| MECR | Trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial | −1.48 | 0.56 |
| VAT1L | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog-like | −1.49 | 0.56 |
| RAB3B | Ras-related protein Rab-3B | −1.75 | 0.55 |
| GUAA | GMP synthase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] | −2.23 | 0.62 |
| GCYB1 | Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-1 | −2.39 | 0.56 |
| GMFB | Glia maturation factor beta | −2.57 | 0.58 |
| THIKA | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase A, peroxisomal | −2.97 | 0.64 |
| 2ABG | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 55 kDa regulatory subunit B gamma isoform | −3.43 | 0.61 |
| MYDGF | Myeloid-derived growth factor | −3.59 | 0.57 |
| ID | Name | log2FC (APP23 TG2−/−/WT TG2−/−) | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNAI3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(k) subunit alpha | 3.55 | 0.56 |
| MACF1 | Microtubule-actin crosslinking factor 1 | 3.46 | 0.57 |
| FN3K | Fructosamine-3-kinase | 3.18 | 0.78 |
| THIKA | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase A, peroxisomal | 3.08 | 0.62 |
| SYMC | Methionine—tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic | 3.06 | 0.62 |
| CPSF6 | Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 6 | 2.75 | 0.62 |
| NFU1 | NFU1 iron-sulfur cluster scaffold homolog, mitochondrial | 2.45 | 0.58 |
| ESYT1 | Extended synaptotagmin-1 | 2.40 | 0.71 |
| ENOG | Gamma-enolase | 2.07 | 0.60 |
| SEP6 | Septin-6 | 1.62 | 0.60 |
| CLPP | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit, mitochondrial | 1.49 | 0.88 |
| A4 | Amyloid beta A4 protein | 1.26 | 0.62 |
| NCLN | Nicalin | 0.92 | 0.55 |
| UCRI | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske, mitochondrial | 0.83 | 0.59 |
| NFM | Neurofilament medium polypeptide | 0.73 | 0.79 |
| UBE2N | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N | 0.68 | 0.65 |
| KPCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | 0.58 | 0.67 |
| CAMP2 | Calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 2 | 0.50 | 0.56 |
| APOD | Apolipoprotein D | 0.49 | 0.56 |
| BRSK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK1 | 0.46 | 0.67 |
| SCPDL | Saccharopine dehydrogenase-like oxidoreductase | 0.39 | 0.68 |
| TNPO1 | Transportin-1 | 0.36 | 0.56 |
| GLU2B | Glucosidase 2 subunit beta | 0.16 | 0.60 |
| STMN1 | Stathmin | −0.25 | 0.63 |
| GPM6A | Neuronal membrane glycoprotein M6-a | −0.30 | 0.57 |
| MPP2 | MAGUK p55 subfamily member 2 | −0.36 | 0.63 |
| NEUG | Neurogranin | −0.49 | 0.68 |
| OTU6B | OTU domain-containing protein 6B | −0.49 | 0.69 |
| PC4L1 | Purkinje cell protein 4-like protein 1 | −0.51 | 0.83 |
| CH10 | 10 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial | −0.56 | 0.64 |
| HBB1 | Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 | −0.60 | 0.71 |
| MDHC | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | −0.82 | 0.57 |
| SNG1 | Synaptogyrin-1 | −0.92 | 0.55 |
| KCAB2 | Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit beta-2 | −0.94 | 0.66 |
| MAAI | Maleylacetoacetate isomerase | −1.37 | 0.65 |
| TDRKH | Tudor and KH domain-containing protein | −1.66 | 0.57 |
| ENOPH | Enolase-phosphatase E1 | −2.11 | 0.60 |
| SARM1 | Sterile alpha and TIR motif-containing protein 1 | −2.21 | 0.62 |
| PZP | Pregnancy zone protein | −2.38 | 0.62 |
| PUR6 | Multifunctional protein ADE2 | −4.39 | 0.70 |
| ID | Name | log2FC (WT/WT TG2−/−) | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPSF6 | Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 6 | 3.76 | 0.68 |
| GNAI3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(k) subunit alpha | 3.75 | 0.55 |
| PADI2 | Protein-arginine deiminase type-2 | 3.59 | 0.59 |
| TOLIP | Toll-interacting protein | 3.53 | 0.61 |
| SYMC | Methionine—tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic | 3.46 | 0.60 |
| ECHD1 | Ethylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase | 2.54 | 0.60 |
| HSDL1 | Inactive hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like protein 1 | 2.50 | 0.55 |
| AGRB1 | Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 | 2.49 | 0.55 |
| NFU1 | NFU1 iron-sulfur cluster scaffold homolog, mitochondrial | 2.21 | 0.66 |
| FBX41 | F-box only protein 41 | 1.17 | 0.64 |
| APOD | Apolipoprotein D | 0.68 | 0.57 |
| SNAA | Alpha-soluble NSF attachment protein | 0.47 | 0.58 |
| HEBP1 | Heme-binding protein 1 | 0.27 | 0.56 |
| RRAGC | Ras-related GTP-binding protein C | 0.27 | 0.55 |
| DTD1 | D-tyrosyl-tRNA(Tyr) deacylase 1 | 0.23 | 0.68 |
| RL6 | 60S ribosomal protein L6 | 0.21 | 0.56 |
| CORO7 | Coronin-7 | −0.29 | 0.63 |
| AN32A | Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A | −0.35 | 0.64 |
| HNRPU | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U | −0.43 | 0.73 |
| CAH8 | Carbonic anhydrase-related protein | −0.47 | 0.55 |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein | −0.61 | 0.75 |
| HBB1 | Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 | −0.62 | 0.79 |
| MYEF2 | Myelin expression factor 2 | −0.63 | 0.57 |
| S20A2 | Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2 | −0.79 | 0.80 |
| KCAB2 | Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit beta-2 | −0.85 | 0.61 |
| RL35A | 60S ribosomal protein L35a | −0.94 | 0.55 |
| RS28 | 40S ribosomal protein S28 | −1.01 | 0.67 |
| LSM6 | U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm6 | −1.02 | 0.57 |
| RL29 | 60S ribosomal protein L29 | −1.03 | 0.78 |
| AN32E | Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member E | −1.03 | 0.61 |
| RS9 | 40S ribosomal protein S9 | −1.16 | 0.61 |
| SNG1 | Synaptogyrin-1 | −1.23 | 0.57 |
| SARM1 | Sterile alpha and TIR motif-containing protein 1 | −2.27 | 0.65 |
| EXOG | Nuclease EXOG, mitochondrial | −3.22 | 0.56 |
| RHG23 | Rho GTPase-activating protein 23 | −3.38 | 0.63 |
| ROCK2 | Rho-associated protein kinase 2 | −3.61 | 0.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilhelmus, M.M.M.; Tonoli, E.; Coveney, C.; Boocock, D.J.; Jongenelen, C.A.M.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Verderio, E.A.M.; Drukarch, B. The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030389
Wilhelmus MMM, Tonoli E, Coveney C, Boocock DJ, Jongenelen CAM, Brevé JJP, Verderio EAM, Drukarch B. The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells. 2022; 11(3):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030389
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilhelmus, Micha M. M., Elisa Tonoli, Clare Coveney, David J. Boocock, Cornelis A. M. Jongenelen, John J. P. Brevé, Elisabetta A. M. Verderio, and Benjamin Drukarch. 2022. "The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease" Cells 11, no. 3: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030389
APA StyleWilhelmus, M. M. M., Tonoli, E., Coveney, C., Boocock, D. J., Jongenelen, C. A. M., Brevé, J. J. P., Verderio, E. A. M., & Drukarch, B. (2022). The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells, 11(3), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030389








