Adipose Tissue Steroid Receptor RNA Activator 1 (SRA1) Expression Is Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Anthropometric Measurements
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Collection of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
2.4. Measurement of Metabolic Markers
2.5. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Detection of SRA1 and Inflammatory Markers by RT-qPCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
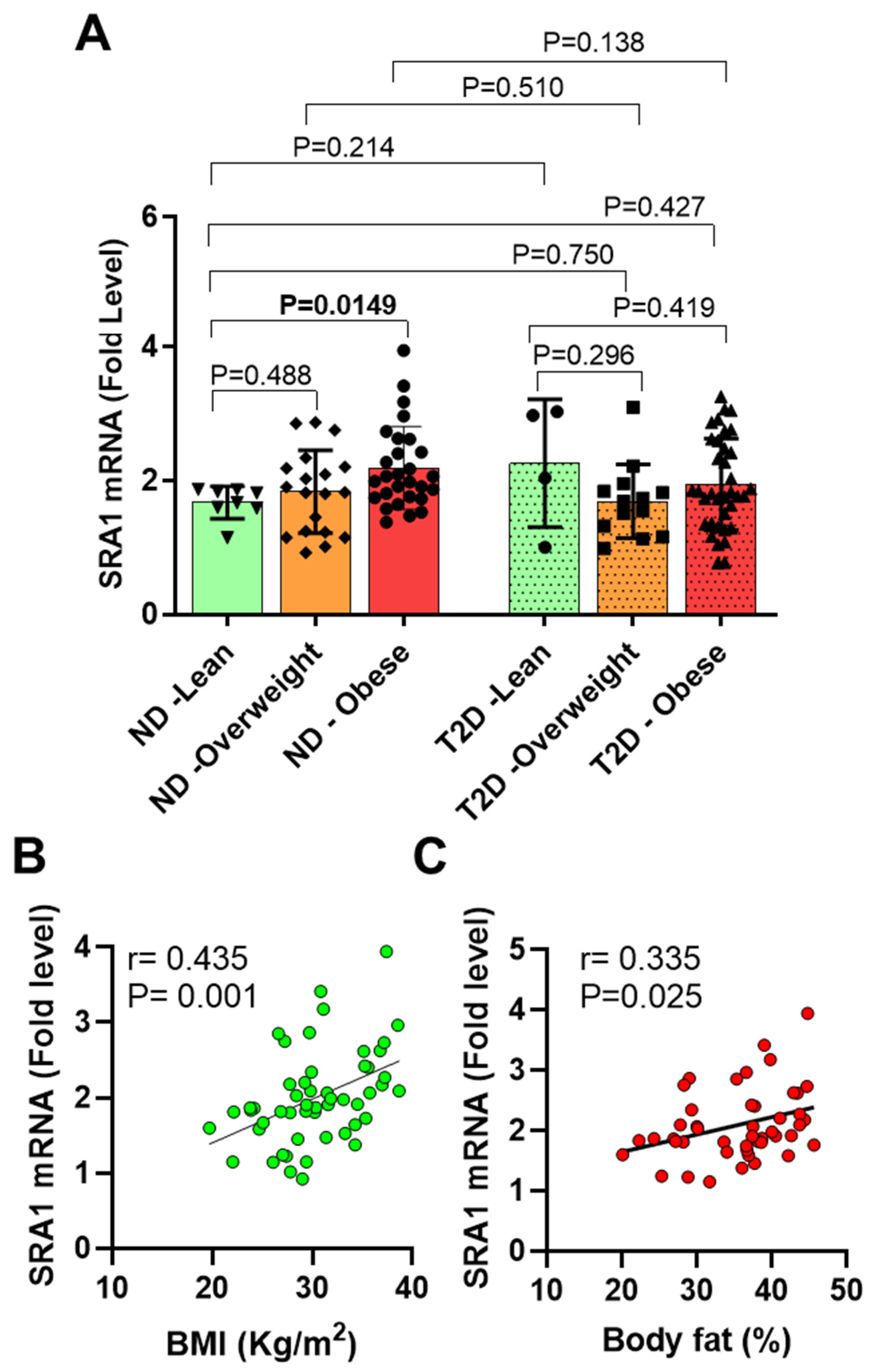
3.2. AT SRA1 Expression in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
3.3. Association of AT SRA1 Expression with Inflammatory Signatures
3.4. Analysis of the Indipenedent Associations between SRA1 and Immune Metabolic Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanz, R.B.; McKenna, N.J.; Onate, S.A.; Albrecht, U.; Wong, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; O’Malley, B.W. A steroid receptor coactivator, sra, functions as an rna and is present in an src-1 complex. Cell 1999, 97, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emberley, E.; Huang, G.-J.; Hamedani, M.K.; Czosnek, A.; Ali, D.; Grolla, A.; Lu, B.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C.; Leygue, E. Identification of new human coding steroid receptor rna activator isoforms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, F.; Zugck, C.; Rauch, G.J.; Ivandic, B.; Weichenhan, D.; Müller-Bardorff, M.; Meder, B.; Mokhtari, N.E.E.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Hetzer, R.; et al. Hbegf, sra1, and ik: Three cosegregating genes as determinants of cardiomyopathy. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubé, F.; Velasco, G.; Rollin, J.; Furling, D.; Francastel, C. Steroid receptor rna activator protein binds to and counteracts sra rna-mediated activation of myod and muscle differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colley, S.M.; Leedman, P.J. Steroid receptor rna activator—A nuclear receptor coregulator with multiple partners: Insights and challenges. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato, M.; Vicent, G.P. A new role for an old player: Steroid receptor rna activator (sra) represses hormone inducible genes. Transcription 2013, 4, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leygue, E. Steroid receptor rna activator (sra1): Unusual bifaceted gene products with suspected relevance to breast cancer. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2007, 5, e006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotan, L.D.; Cooper, C.; Darcan, Ş.; Carr, I.M.; Özen, S.; Yan, Y.; Hamedani, M.K.; Gürbüz, F.; Mengen, E.; Turan, İ.; et al. Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by inactivating mutations in sra1. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrino. 2016, 8, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Ma, J.; Wu, R.; Zhou, C.; Lin, J. Influence of ovarian endometrioma on expression of steroid receptor rna activator, estrogen receptors, vascular endothelial growth factor, and thrombospondin 1 in the surrounding ovarian tissues. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hao, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, N.; Bao, H.; Qu, Q. Peripheral blood leukocyte expression level of lncrna steroid receptor rna activator (sra) and its association with polycystic ovary syndrome: A case control study. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, G.; Schiltz, R.L.; Dilworth, F.J.; Di Padova, M.; Zhao, P.; Ogryzko, V.; Fuller-Pace, F.V.; Hoffman, E.P.; Tapscott, S.J.; Sartorelli, V. The rna helicases p68/p72 and the noncoding rna sra are coregulators of myod and skeletal muscle differentiation. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Yang, W.-H.; Gerin, I.; Hu, C.-D.; Hammer, G.D.; Koenig, R.J. Dax-1 and steroid receptor rna activator (sra) function as transcriptional coactivators for steroidogenic factor 1 in steroidogenesis. J. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 29, 1719–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, L.C.; Simon, S.L.; Parkes, A.; Leygue, E.; Dotzlaw, H.; Snell, L.; Troup, S.; Adeyinka, A.; Watson, P.H. Altered expression of estrogen receptor coregulators during human breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6266–6271. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.; Guo, J.; Yan, Y.; Chooniedass-Kothari, S.; Hube, F.; Hamedani, M.K.; Murphy, L.C.; Myal, Y.; Leygue, E. Increasing the relative expression of endogenous non-coding steroid receptor rna activator (sra) in human breast cancer cells using modified oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4518–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurisu, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ishii, J.; Matsumura, K.; Sugimura, K.; Nakatani, T.; Kawashima, H. Expression and function of human steroid receptor rna activator in prostate cancer cells: Role of endogenous hsra protein in androgen receptor-mediated transcription. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2006, 9, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanz, R.B.; Razani, B.; Goldberg, A.D.; O’Malley, B.W. Distinct rna motifs are important for coactivation of steroid hormone receptors by steroid receptor rna activator (sra). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16081–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leygue, E.; Dotzlaw, H.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C. Expression of the steroid receptor rna activator in human breast tumors. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4190–4193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gesta, S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Kahn, C.R. Developmental origin of fat: Tracking obesity to its source. Cell 2007, 131, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doria, A.; Patti, M.E.; Kahn, C.R. The emerging genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–c391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa Neto, J.C.; Calder, P.C.; Curi, R.; Newsholme, P.; Sethi, J.K.; Silveira, L.S. The immunometabolic roles of various fatty acids in macrophages and lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Aragón-Herrera, A.; Moraña-Fernández, S.; Anido-Varela, L.; Tarazón, E.; Roselló-Lletí, E.; Portolés, M.; Moscoso, I.; Gualillo, O.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; et al. Adipokines and inflammation: Focus on cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, M.; le Roux, C.W.; Docherty, N.G. Morbidity and mortality associated with obesity. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelan, S.M.; Burgess, D.J.; Yeazel, M.W.; Hellerstedt, W.L.; Griffin, J.M.; van Ryn, M. Impact of weight bias and stigma on quality of care and outcomes for patients with obesity. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arner, P. Resistin: Yet another adipokine tells us that men are not mice. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2203–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Thomas, R.; Kochumon, S.; Wilson, A.; Abu-Farha, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. Increased adipose tissue expression of interferon regulatory factor (irf)-5 in obesity: Association with metabolic inflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, N.R.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Expansion of the homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance to enable clinical trial outcome modeling through the interactive adjustment of physiology and treatment effects: Ihoma2. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochumon, S.; Al-Rashed, F.; Abu-Farha, M.; Devarajan, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Adipose tissue expression of ccl19 chemokine is positively associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Shihab, P.K.; Thomas, R.; Alghanim, M.; Hasan, A.; Sindhu, S.; Behbehani, K. Increased expression of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (irak)-1 is associated with adipose tissue inflammatory state in obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khadir, A.; Tiss, A.; Abubaker, J.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Khairi, I.; Cherian, P.; John, J.; Kavalakatt, S.; Warsame, S.; Al-Madhoun, A.; et al. Map kinase phosphatase dusp1 is overexpressed in obese humans and modulated by physical exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E71–E83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Mass, A.; Al-Ghawas, D.; Shareif, N.; Zghoul, N.; Melhem, M.; Hasan, A.; Al-Ghimlas, F.; Dermime, S.; Behbehani, K. Interaction of osteopontin with il-18 in obese individuals: Implications for insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, L.; Ye, L.; Zhang, D.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Xu, B. New insights into the long non-coding rna sra: Physiological functions and mechanisms of action. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sheng, L.; Miao, H.; Saunders, T.L.; MacDougald, O.A.; Koenig, R.J.; Xu, B. Sra gene knockout protects against diet-induced obesity and improves glucose tolerance*. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13000–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Gerin, I.; Miao, H.; Vu-Phan, D.; Johnson, C.N.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.W.; Cawthorn, W.P.; MacDougald, O.A.; Koenig, R.J. Multiple roles for the non-coding rna sra in regulation of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Yi, X.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Y. Integrated analysis of long noncoding rna and mrna expression profile in children with obesity by microarray analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, R.; Yu, N.; Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, H. Differentially expressed circulating lncrnas and mrna identified by microarray analysis in obese patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Han, X.; Wittfeldt, A.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Gan, L.-M.; Cao, H.; Liang, Z. Long non-coding rna anril regulates inflammatory responses as a novel component of nf-κb pathway. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Kerr, A.; Jiao, H.; Hon, C.C.; Rydén, M.; Dahlman, I.; Arner, P. Long non-coding rnas associated with metabolic traits in human white adipose tissue. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Gene Name | Assay ID | Gene Name | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRA1 | Hs00398296_g1 | IL1β | Hs01555410_m1 |
| CCL2 | Hs00234140_m1 | IL2 | Hs00174114_m1 |
| CCL3 | Hs04194942_s1 | IL5 | Hs01548712_g1 |
| CCL5 | Hs00982282_m1 | IL6 | Hs00985639_m1 |
| CCL7 | Hs00171147_m1 | IL8 | Hs00174103_m1 |
| CCL8 | Hs04187715_m1 | IL10 | Hs00961622_m1 |
| CCL11 | Hs00237013_m1 | IL12A | Hs01073447_m1 |
| CCL15 | Hs00361122_m1 | IL13 | Hs00174379_m1 |
| CCL18 | Hs00268113_m1 | IL18 | Hs01038788_m1 |
| CCL19 | Hs00171149_m1 | IL23A | Hs00900828_g1 |
| CCL20 | Hs01011368_m1 | IL33 | Hs00369211_m1 |
| CXCL9 | Hs00171065_m1 | IL1RL1 | Hs00545033_m1 |
| CXCL10 | Hs01124251_g1 | IL2RA | Hs00907779_m1 |
| CXCL11 | Hs04187682_g1 | CCR1 | Hs00928897_s1 |
| TNF-α | Hs01113624_g1 | CCR2 | Hs00704702_s1 |
| IFNβ | Hs01077958_s1 | CCR5 | Hs99999149_s1 |
| TGF-β | Hs00820148_g1 | GAPDH | Hs03929097_g1 |
| Total Participants (n = 108) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Diabetic (n = 55) | Diabetic (n = 53) | ||||||||||
| Lean | Overweight | Obese | Lean vs. Overweight | Lean vs. Obese | Lean | Overweight | Obese | Lean vs. Overweight | Lean vs. Obese | Non-Diabetic vs. Diabetic | |
| (n = 8) | (n = 19) | (n = 28) | (n = 4) | (n = 13) | (n = 36) | ||||||
| (p) | (p) | (p) | (p) | (p) | |||||||
| Age (years) | 42.00 (36.00–50.25) | 42.00 (35.00–52.00) | 46.50 (36.00–59.00) | 0.688 | 0.387 | 56 (49.75–57.75) | 54.00 (53.00–57.00) | 53.00 (46.00–58.00) | 0.608 | 0.557 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 61.00 (58.40–77.33) | 79.00 (70.20–88.00) | 91.75 (84.83–105.70) | 0.004 | <0.0001 | 68.85 (57.9–69.75) | 77.7 (72.5–85.25) | 93.50 (83.08–99.70) | 0.024 | 0.001 | 0.327 |
| Height (cm) | 1.66 (1.55–1.80) | 1.67 (1.59–1.76) | 1.65 (1.55–1.73) | 0.906 | 0.422 | 1.65 (1.538–1.665) | 1.66 (1.61–1.72) | 1.69 (1.58–1.73) | 0.461 | 0.223 | 0.784 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.81 (22.07–24.56) | 28.43 (27.26–29.4) | 35.20 (31.65–37.23) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 24.99 (24.28–25.59) | 28.2 (27.13–28.87) | 33.35 (31.47–35.56) | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.417 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 81.00 (77.00–97.00) | 96 (89–101.8) | 109.00 (99.00–117.00) | 0.014 | <0.0001 | 82 (76–87) | 98.00 (93.00–103.00) | 110 (104.5–114) | 0.024 | 0.005 | 0.052 |
| HIP circumference (cm) | 103.00 (91.50–105.00) | 103.50 (97.00–111.5) | 120.00 (109.50–125.00) | 0.324 | <0.0001 | 100.00 (93.00–106.00) | 104.00 (101.00–111.00) | 113.80 (110.00–120.80) | 0.273 | 0.015 | 0.768 |
| WHR | 0.82 (0.74–0.94) | 0.95 (0.82–1.02) | 0.91 (0.81–1.00) | 0.105 | 0.072 | 0.8172 (0.78–0.87) | 0.93 (0.90–1.01) | 0.9571 (0.8789–1.018) | 0.016 | 0.021 | 0.089 |
| Body fat (%) | 26.90 (22.30–36.70) | 30.9 (28.43–37.63) | 39.90 (36.78–43.63) | 0.074 | <0.0001 | 34.8 (27.70–36.50) | 30.7 (26.00–37.30) | 38 (32.2–41.85) | 0.938 | 0.181 | 0.984 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mM) | 4.90 (4.32–5.18) | 5.1 (4.9–5.43) | 5.20 (4.75–5.88) | 0.27 | 0.186 | 7.7 (5.65–9.953) | 8.72 (6.92–11.13) | 8.15 (6.6–10.03) | 0.362 | 0.471 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.62 (0.43–0.89) | 1.3 (0.64–1.65) | 1.05 (0.72–1.53) | 0.014 | 0.042 | 0.97 (0.47–1.88) | 1.79 (0.84–2.40) | 1.395 (1.113–1.818) | 0.225 | 0.131 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.35 (3.88–6.04) | 5 (4.48–5.42) | 4.75 (4.16–6.05) | 0.769 | 0.943 | 4.48 (3.8–6.54) | 4.09 (3.85–5.56) | 4.94 (4.1–5.745) | 0.544 | 0.701 | 0.314 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.59 (1.18–2.01) | 1.2 (1.08–1.36) | 1.16 (1.02–1.38) | 0.033 | 0.041 | 1.14 (0.97–1.3) | 1.03 (0.89–1.31) | 1.11 (0.95–1.36) | 0.671 | 0.835 | 0.096 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.55 (2.33–3.93) | 3.1 (2.6–3.7) | 3.25 (2.60–4.00) | 0.995 | 0.746 | 2.9 (2.38–4.63) | 2.3 (1.8–3.55) | 2.85 (2.275–3.75) | 0.202 | 0.686 | 0.069 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.50 (5.15–5.85) | 5.5 (5.18–5.73) | 5.83 (5.43–5.98) | 0.946 | 0.404 | 7.3 (5.90–8.70) | 7.7 (6.575–10.18) | 8.1 (7.35–9.175) | 0.544 | 0.367 | <0.0001 |
| Fasting insulin (mU/L) | 5.56 (5.04–11.51) | 6.08 (4.99–15.67) | 17.38 (7.32–34.58) | 0.448 | 0.015 | 13.37 (4.08–30.63) | 10.37 (6.277–17.16) | 17.15 (7.909–43.42) | 0.735 | 0.48 | 0.008 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.31 (1.00–2.53) | 1.351 (1.16–3.61) | 4.09 (1.89–10.91) | 0.419 | 0.01 | 5.53 (1.11–7.49) | 3.03 (2.59–6.01) | 5.74 (3.078–17.69) | 0.735 | 0.377 | <0.0001 |
| SRA1 mRNA(Fold level) | 1.74 (1.59–1.85) | 1.822 (1.23–2.20) | 2.03 (1.75–2.57) | 0.489 | 0.015 | 2.51 (1.26–3.01) | 1.69 (1.24–1.90) | 1.814 (1.35–2.567) | 0.296 | 0.419 | 0.373 |
| All Participants (n = 108) | Non-Diabetic (n = 55) | Diabetic (n = 53) | Lean (n = 12) | Overweight (n = 32) | Obese (n = 64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Age | 0.052 | 0.594 | 0.102 | 0.458 | 0.075 | 0.596 | 0.351 | 0.263 | 0.047 | 0.800 | −0.007 | 0.957 |
| Weight | 0.092 | 0.344 | 0.200 | 0.143 | 0.012 | 0.930 | 0.664 * | 0.018 | 0.154 | 0.399 | −0.136 | 0.285 |
| Height | −0.109 | 0.263 | −0.144 | 0.294 | −0.082 | 0.562 | 0.423 | 0.170 | 0.094 | 0.608 | −0.280 * | 0.025 |
| BMI | 0.221 * | 0.022 | 0.435 ** | 0.001 | 0.121 | 0.39 | 0.552 | 0.063 | 0.192 | 0.294 | 0.125 | 0.327 |
| PBF | 0.216 * | 0.044 | 0.335 * | 0.025 | 0.027 | 0.863 | −0.248 | 0.489 | −0.095 | 0.639 | 0.214 | 0.128 |
| Waist | 0.121 | 0.26 | 0.291 * | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.902 | 0.646 * | 0.043 | 0.077 | 0.698 | −0.084 | 0.559 |
| Hip | 0.156 | 0.141 | 0.157 | 0.287 | 0.15 | 0.343 | 0.334 | 0.345 | 0.176 | 0.371 | −0.026 | 0.855 |
| WHR | −0.004 | 0.974 | 0.163 | 0.274 | −0.081 | 0.612 | 0.309 | 0.385 | −0.053 | 0.791 | −0.036 | 0.804 |
| GLU | −0.025 | 0.797 | 0.075 | 0.586 | −0.088 | 0.535 | 0.249 | 0.436 | −0.138 | 0.46 | −0.058 | 0.646 |
| TGL | 0.007 | 0.94 | 0.200 | 0.143 | −0.097 | 0.495 | 0.063 | 0.846 | 0.075 | 0.690 | −0.076 | 0.548 |
| Chol | 0.004 | 0.971 | 0.023 | 0.866 | −0.043 | 0.762 | 0.042 | 0.897 | 0.028 | 0.882 | 0.005 | 0.967 |
| HDL | 0.073 | 0.459 | −0.015 | 0.913 | 0.164 | 0.249 | −0.427 | 0.167 | 0.082 | 0.661 | 0.183 | 0.151 |
| LDL | −0.017 | 0.863 | −0.042 | 0.760 | −0.006 | 0.965 | 0.074 | 0.819 | −0.093 | 0.619 | 0.014 | 0.914 |
| HbA1c | −0.163 | 0.096 | 0.164 | 0.235 | −0.349 * | 0.011 | 0.399 | 0.198 | −0.417 * | 0.022 | −0.214 | 0.089 |
| Insulin | 0.242 * | 0.026 | 0.44 ** | 0.005 | 0.065 | 0.673 | 0.009 | 0.979 | 0.277 | 0.162 | 0.179 | 0.229 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.235 * | 0.03 | 0.433 ** | 0.005 | 0.108 | 0.481 | 0.309 | 0.355 | 0.192 | 0.337 | 0.174 | 0.242 |
| All Participants (n = 108) | Non-Diabetic (n = 55) | Diabetic (n = 53) | Lean (n = 12) | Overweight (n = 32) | Obese (n = 64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| CCL2 | 0.234 * | 0.017 | 0.122 | 0.384 | 0.385 ** | 0.006 | 0.583 | 0.099 | −0.045 | 0.809 | 0.256 * | 0.043 |
| CCL3 | 0.091 | 0.366 | 0.298 * | 0.036 | 0.011 | 0.938 | 0.036 | 0.915 | 0.132 | 0.470 | −0.057 | 0.669 |
| CCL5 | 0.146 | 0.170 | 0.037 | 0.810 | 0.201 | 0.180 | 0.286 | 0.493 | −0.291 | 0.106 | 0.433 ** | 0.002 |
| CCL7 | 0.120 | 0.229 | 0.161 | 0.260 | 0.187 | 0.190 | 0.682 * | 0.021 | −0.106 | 0.583 | 0.019 | 0.882 |
| CCL8 | 0.262 * | 0.011 | 0.344 * | 0.021 | 0.202 | 0.169 | −0.033 | 0.932 | 0.041 | 0.839 | 0.294 * | 0.027 |
| CCL11 | 0.065 | 0.517 | 0.075 | 0.603 | 0.093 | 0.511 | 0.382 | 0.276 | −0.165 | 0.375 | 0.070 | 0.594 |
| CCL15 | −0.033 | 0.739 | −0.078 | 0.573 | 0.036 | 0.799 | −0.056 | 0.863 | −0.234 | 0.198 | 0.148 | 0.246 |
| CCL18 | 0.092 | 0.353 | 0.188 | 0.178 | 0.075 | 0.600 | −0.333 | 0.347 | 0.132 | 0.472 | 0.028 | 0.827 |
| CCL19 | −0.165 | 0.098 | −0.085 | 0.550 | −0.145 | 0.315 | −0.112 | 0.729 | −0.427 * | 0.017 | −0.101 | 0.446 |
| CCL20 | 0.037 | 0.711 | 0.039 | 0.783 | 0.066 | 0.643 | 0.491 | 0.150 | −0.233 | 0.208 | 0.034 | 0.791 |
| CXCL9 | 0.215 * | 0.029 | 0.069 | 0.618 | 0.379 ** | 0.008 | 0.264 | 0.433 | −0.215 | 0.245 | 0.408 ** | 0.001 |
| CXCL10 | 0.280 ** | 0.004 | 0.232 | 0.092 | 0.437 ** | 0.002 | 0.479 | 0.162 | −0.028 | 0.882 | 0.282 * | 0.028 |
| CXCL11 | 0.368 *** | <0.001 | 0.400 ** | 0.003 | 0.421 ** | 0.002 | 0.112 | 0.729 | 0.111 | 0.561 | 0.440 *** | <0.001 |
| TNF-α | 0.413 **** | <0.0001 | 0.317* | 0.030 | 0.505 *** | <0.001 | 0.810* | 0.015 | 0.001 | 0.995 | 0.504 **** | <0.0001 |
| IFNβ | 0.094 | 0.336 | −0.036 | 0.798 | 0.189 | 0.175 | −0.035 | 0.914 | −0.044 | 0.814 | 0.209 | 0.100 |
| TGF-β | 0.438 **** | <0.0001 | 0.514 **** | <0.0001 | 0.348 * | 0.014 | 0.321 | 0.365 | 0.317 | 0.082 | 0.430 ** | 0.001 |
| IL1β | 0.068 | 0.547 | 0.003 | 0.983 | 0.127 | 0.436 | 0.214 | 0.645 | −0.102 | 0.622 | 0.119 | 0.422 |
| IL2 | 0.021 | 0.834 | 0.093 | 0.510 | −0.002 | 0.991 | 0.098 | 0.762 | −0.160 | 0.390 | 0.077 | 0.550 |
| IL5 | 0.132 | 0.191 | −0.043 | 0.764 | 0.297 * | 0.040 | −0.145 | 0.670 | −0.141 | 0.483 | 0.264 * | 0.039 |
| IL6 | −0.089 | 0.378 | 0.033 | 0.820 | −0.145 | 0.309 | 0.033 | 0.932 | −0.294 | 0.115 | −0.023 | 0.861 |
| IL8 | −0.075 | 0.465 | −0.010 | 0.948 | −0.100 | 0.484 | −0.190 | 0.651 | −0.108 | 0.561 | −0.148 | 0.269 |
| IL10 | 0.152 | 0.129 | 0.226 | 0.107 | 0.163 | 0.264 | 0.667 * | 0.050 | 0.043 | 0.814 | 0.173 | 0.186 |
| IL12A | 0.051 | 0.641 | −0.036 | 0.822 | 0.126 | 0.404 | 0.321 | 0.482 | −0.216 | 0.270 | 0.070 | 0.621 |
| IL13 | 0.205 * | 0.044 | 0.310 * | 0.028 | 0.158 | 0.288 | 0.321 | 0.365 | 0.091 | 0.627 | 0.236 | 0.080 |
| IL18 | 0.371 *** | <0.001 | 0.547 **** | <0.0001 | 0.214 | 0.144 | 0.467 | 0.205 | 0.356 | 0.058 | 0.295 * | 0.021 |
| IL23A | 0.112 | 0.252 | 0.056 | 0.688 | 0.169 | 0.227 | −0.280 | 0.379 | −0.205 | 0.259 | 0.379 ** | 0.002 |
| IL33 | 0.056 | 0.572 | 0.011 | 0.940 | 0.087 | 0.534 | −0.098 | 0.762 | −0.026 | 0.888 | 0.134 | 0.298 |
| IL1RL1 | 0.034 | 0.748 | −0.024 | 0.872 | 0.129 | 0.382 | 0.000 | 1.000 | −0.231 | 0.219 | 0.163 | 0.226 |
| IL2RA | 0.197 * | 0.041 | −0.098 | 0.478 | 0.461 ** | 0.001 | −0.021 | 0.948 | −0.033 | 0.859 | 0.274 * | 0.028 |
| CCR1 | 0.258 ** | 0.009 | 0.246 | 0.082 | 0.299 * | 0.033 | 0.248 | 0.489 | −0.067 | 0.717 | 0.417 ** | 0.001 |
| CCR2 | 0.005 | 0.962 | −0.066 | 0.660 | 0.132 | 0.400 | 0.029 | 0.957 | −0.453 ** | 0.009 | 0.278 * | 0.046 |
| CCR5 | 0.134 | 0.176 | 0.144 | 0.301 | 0.260 | 0.071 | 0.430 | 0.214 | −0.227 | 0.227 | 0.194 | 0.129 |
| Multiple Regression Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All participants (n = 108) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.29 | p value < 0.0001 | |
| Predictor Variable | TGF-β | β value = 0.287 | p value = 0.004 | |
| IL18 | β value = 0.286 | p value = 0.004 | ||
| CXCL11 | β value = 0.237 | p value = 0.009 | ||
| Non-Diabetic (n = 55) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.41 | p value < 0.0001 | |
| Predictor Variable | TGF-β | β value = 0.419 | p value = 0.002 | |
| IL18 | β value = 0.326 | p value = 0.014 | ||
| Diabetic (n = 53) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.24 | p value = 0.0001 | |
| Predictor Variable | TNF-α | β value = 0.434 | p value = 0.001 | |
| IL2RA | β value = 0.259 | p value = 0.044 | ||
| Lean (n = 12) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.79 | p value = 0.002 | |
| Predictor Variable | TNF-α | β value = 0.90 | p value = 0.002 | |
| Overweight (n = 32) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.158 | p value = 0.014 | |
| Predictor Variable | CCR2 | β value = −0.430 | p value = 0.014 | |
| Obese (n = 64) | ANOVA | R2 = 0.33 | p value < 0.0001 | |
| Predictor Variable | TNF-α | β value = 0.412 | p value = 0.001 | |
| IL18 | β value = 0.311 | p value = 0.010 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kochumon, S.; Arefanian, H.; Sindhu, S.; Shenouda, S.; Thomas, R.; Al-Mulla, F.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Adipose Tissue Steroid Receptor RNA Activator 1 (SRA1) Expression Is Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102602
Kochumon S, Arefanian H, Sindhu S, Shenouda S, Thomas R, Al-Mulla F, Tuomilehto J, Ahmad R. Adipose Tissue Steroid Receptor RNA Activator 1 (SRA1) Expression Is Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102602
Chicago/Turabian StyleKochumon, Shihab, Hossein Arefanian, Sardar Sindhu, Steve Shenouda, Reeby Thomas, Fahd Al-Mulla, Jaakko Tuomilehto, and Rasheed Ahmad. 2021. "Adipose Tissue Steroid Receptor RNA Activator 1 (SRA1) Expression Is Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation" Cells 10, no. 10: 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102602
APA StyleKochumon, S., Arefanian, H., Sindhu, S., Shenouda, S., Thomas, R., Al-Mulla, F., Tuomilehto, J., & Ahmad, R. (2021). Adipose Tissue Steroid Receptor RNA Activator 1 (SRA1) Expression Is Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation. Cells, 10(10), 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102602










