Interactive Effects of Mulching Width and Irrigation Management on Cotton Growth and Dynamic Changes in Soil Factors in Arid Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
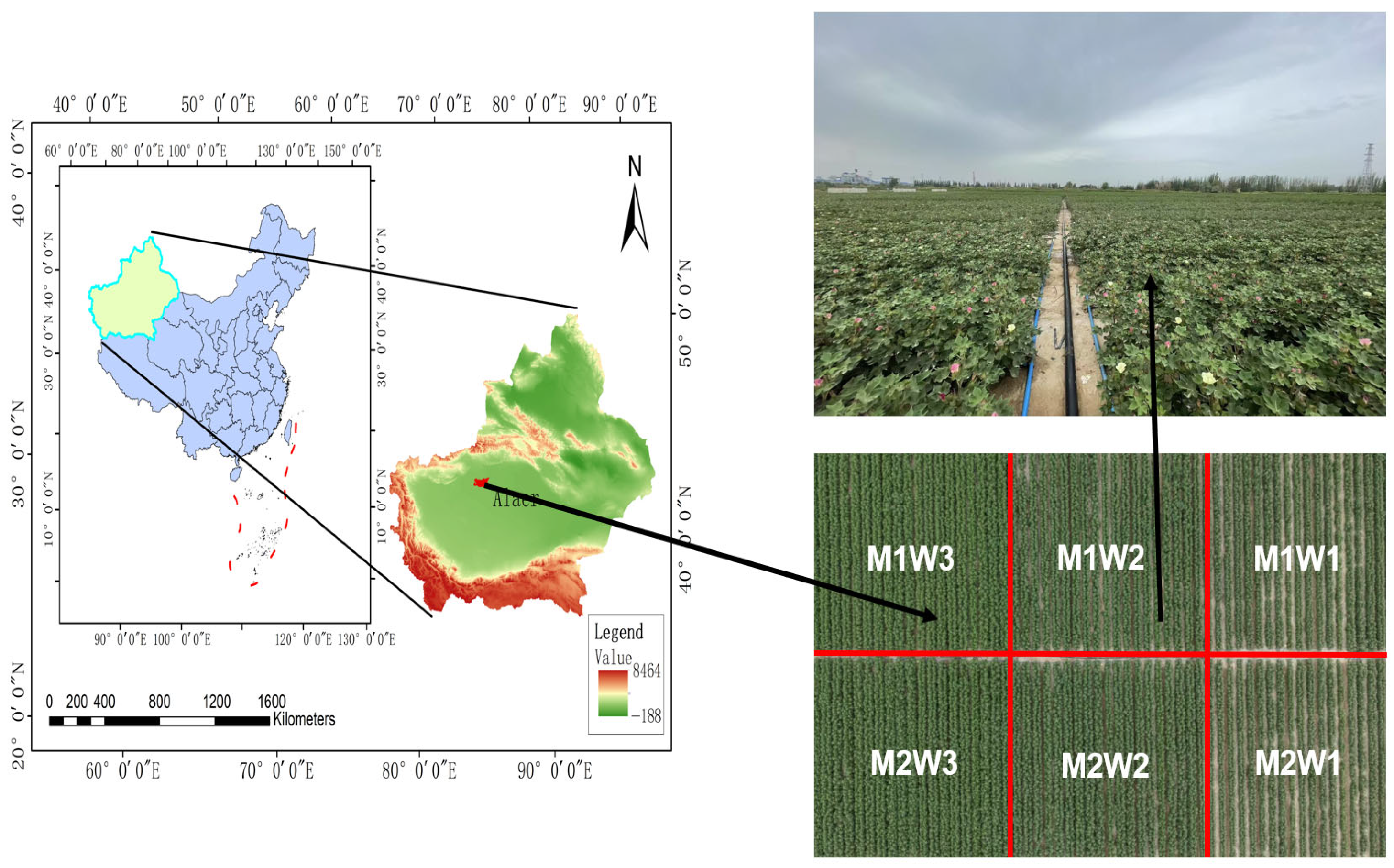
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Area
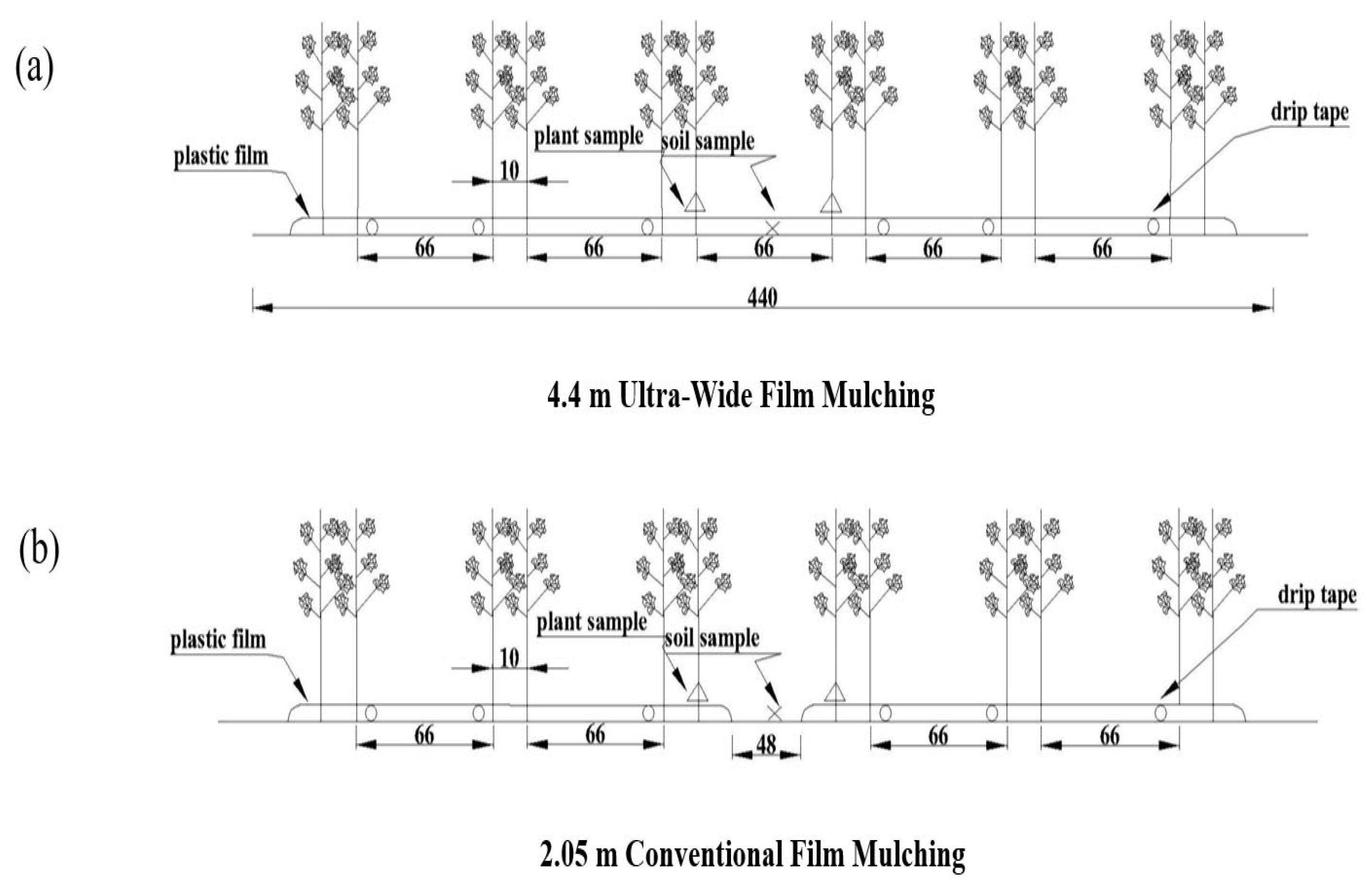
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Moisture Content
2.3.2. Soil Electrical Conductivity
2.3.3. Soil Temperature
2.3.4. Plant Dry Matter Accumulation
2.3.5. Cotton Root Distribution
2.3.6. Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms
2.3.7. Crop Water Consumption
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results Analysis
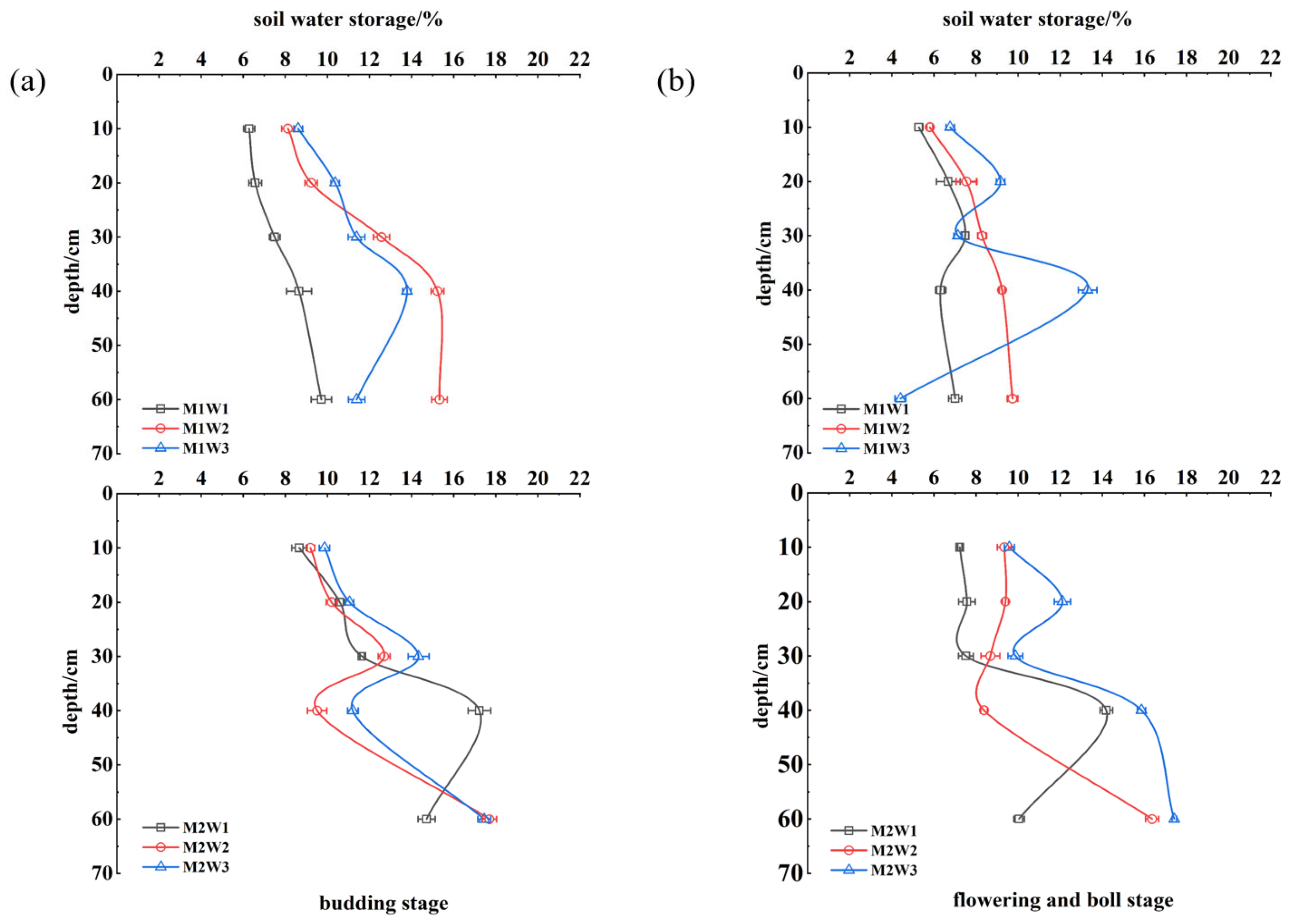
3.1. Vertical Distribution of Soil Moisture Content Under Different Treatments
3.2. Vertical Distribution of Soil Electrical Conductivity Under Different Treatments
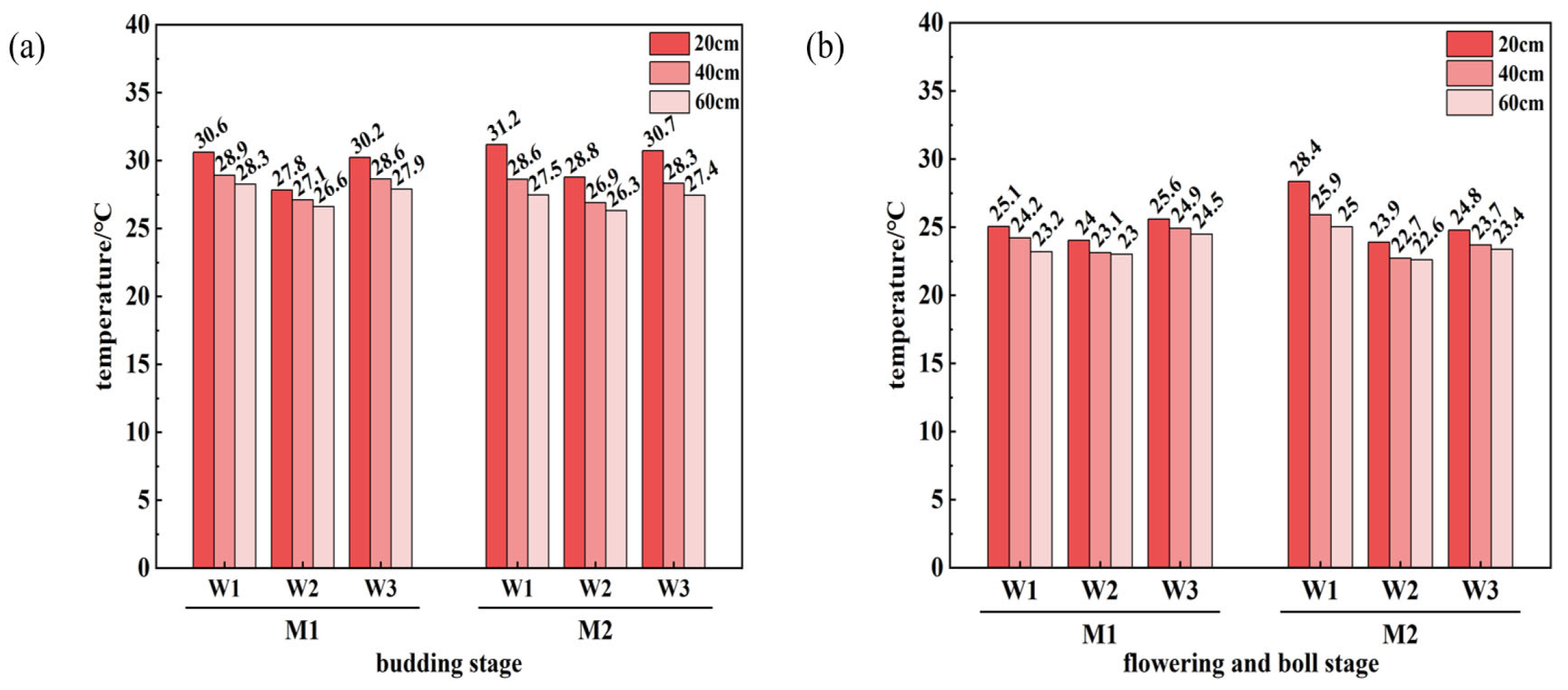
3.3. Variations in Soil Temperature Under Different Treatments
3.4. Root Distribution of Cotton Under Different Treatments
3.5. Effects of Different Treatments on Cotton Dry Matter Accumulation
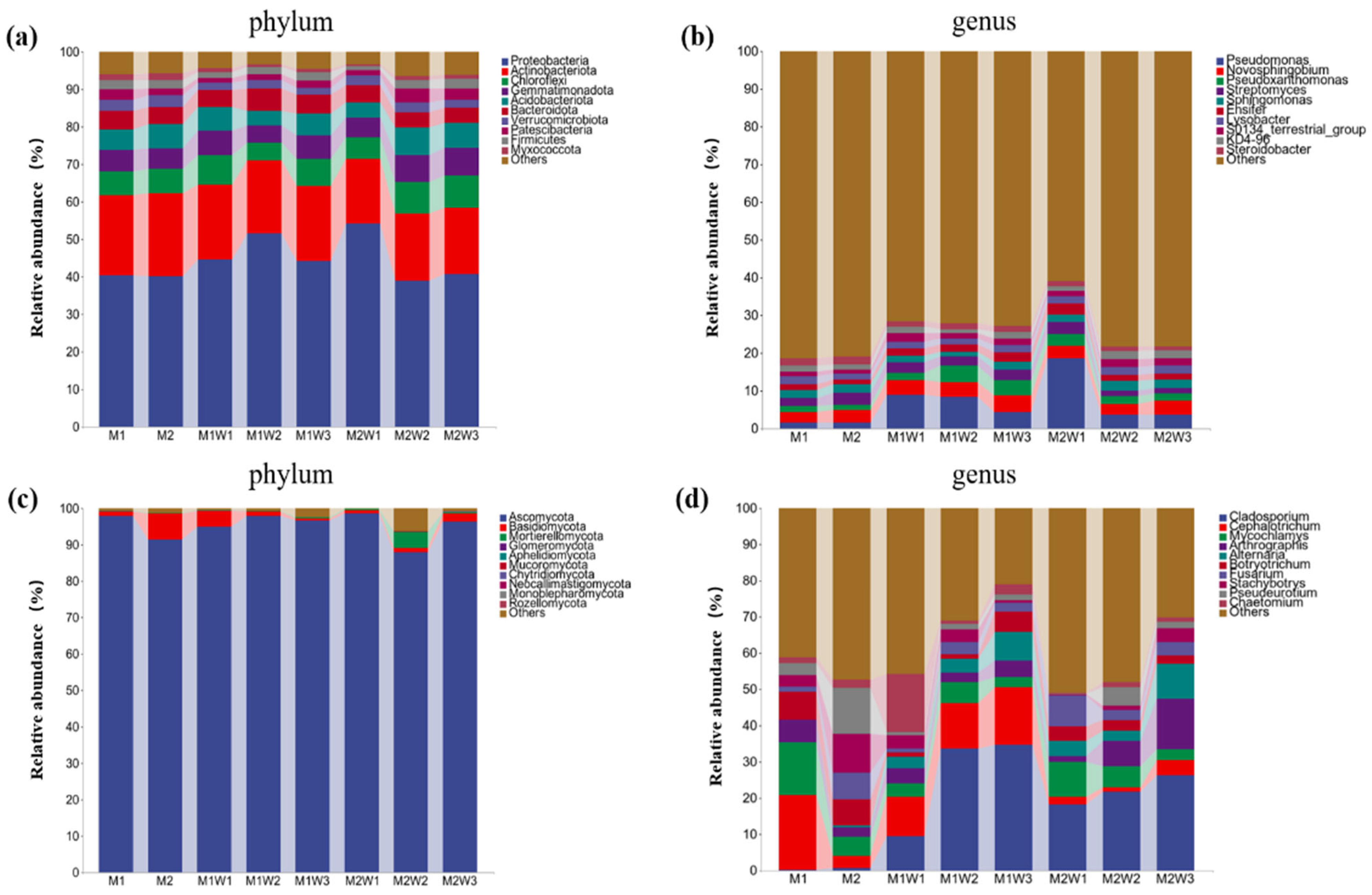
3.6. Effects of Different Treatments on the Composition of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities
3.7. Effects of Different Treatments on the Alpha Diversity of Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms
3.8. Effects of Different Treatments on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial β-Diversity
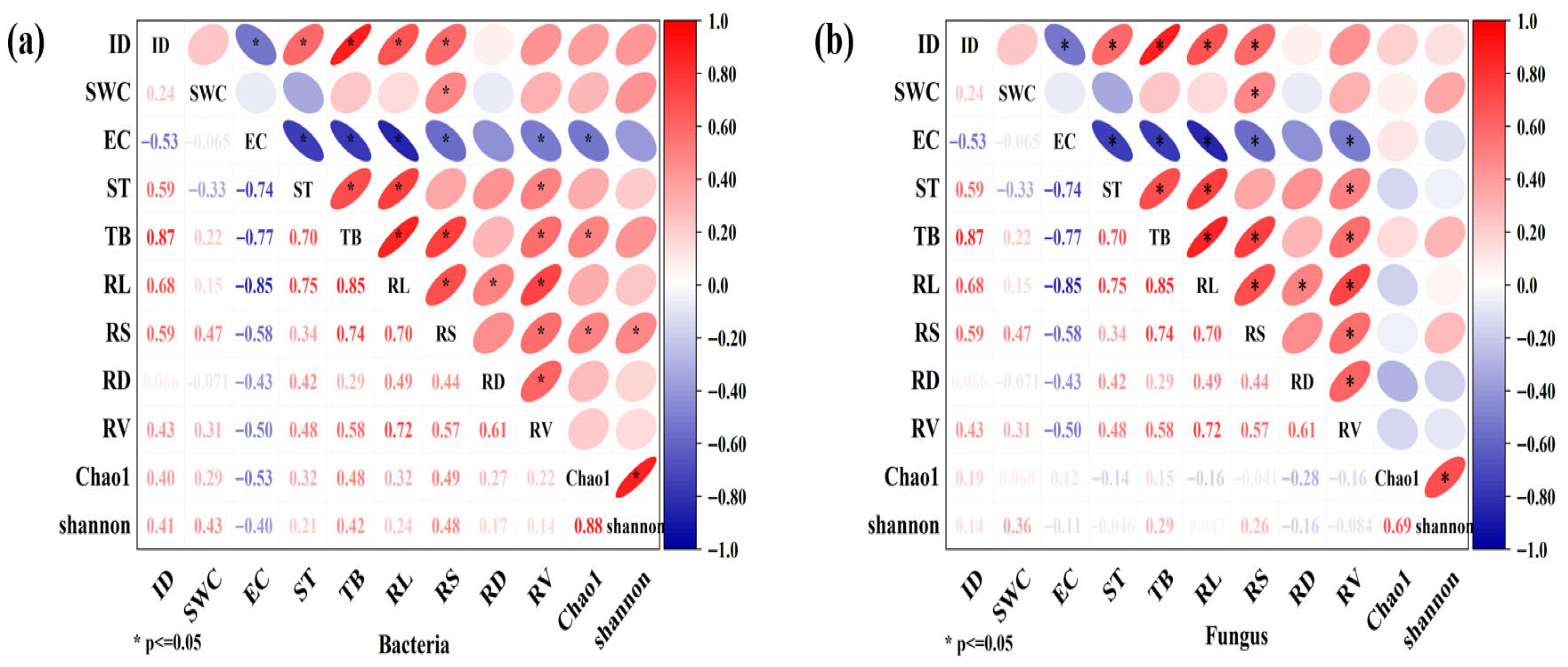
3.9. The Correlation Analysis of Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Water, Temperature, and Salinity
4.2. The Effect of Different Treatments on Cotton Growth
4.3. Soil Environmental Factors and Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities
4.4. Limitations and Future Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Announcement from the National Bureau of Statistics on Cotton Production in 2024. China Information Daily, 2024-12-25. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202412/t20241227_1957916.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Li, G. Study on the Effects of Water Regulation Under Mulched Drip Irrigation on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield Formation Mechanisms of Machine-Harvested Cotton. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Ürümqi, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, S.; Zuo, Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Water Use Efficiency and Economic Benefits of Typical Mulched Drip-Irrigated Cotton Planting Patterns in Xinjiang. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Experimental Study of Farmland Environment and Maize Growth Under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Bao, X.; Sun, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; et al. Optimizing root system architecture to improve cotton drought tolerance and minimize yield loss during mild drought stress. Field Crops Res. 2024, 308, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, P.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, W. Optimizing water and nitrogen management can enhance nitrogen heterogeneity and stimulate root foraging. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Research on the Ratio of Soil Salt Accumulation to Leaching and Its Control Techniques Under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Ph.D. Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Ma, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q. Spatial Variability of Soil Water and Salt under Micro-Scale Drip Irrigation in Mulched Cotton Fields. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 585–593. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Shi, X. Effects of Irrigation Amount on Soil Water and Salt Distribution Characteristics and Winter Wheat Yield in Semi-Arid Regions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 317, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Chen, S. Response and Simulation Study of Soil Water-Salt Transport and Crop Growth under Deficit Drip Irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, V.K.; Singh, C.B.; Sidhu, A.S.; Thind, S.S. Irrigation, tillage and mulching effects on soybean yield and water productivity in relation to soil texture. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shi, J.; Song, R.; Li, W.; Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, W. Experimental Study on the Effects of Mulched Drip Irrigation on Maize Growth and Soil Temperature at Seedling Stage. J. Water Sav. Irrig. 2016, 09, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, B. Experimental Demonstration of Supporting Cultivation Technology for Ultra-Wide Film Mulching in Cotton. J. Xinjiang Agric. Reclam. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Šimůnek, J.; Shi, H.; Yan, J.; Peng, Z.; Gong, X. Spatial distribution of soil water, soil temperature, and plant roots in a drip-irrigated intercropping field with plastic mulch. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 83, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, G.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W. Effect of irrigation methods on root growth, root-shoot ratio and yield components of cotton by regulating the growth redundancy of root and shoot. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yan, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Guo, S.; Jiang, S.; Duan, J. Research Progress on the Influence of Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Medicinal Plants on Quality Formation and Their Mechanisms of Action. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 52, 4064–4073. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Kravchenko, A.N.; Cupples, A.; Guber, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Philip, R.G.; Blagodatskaya, E. Composition and metabolism of microbial communities in soil pores. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, E.D.; McBride, S.G.; Bahram, M.; Strickland, M.S. Global patterns in the growth potential of soil bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Huang, Y.; Hungate, B.A.; Manzoni, S.; Frey, S.D.; Schmidt, M.W.; Reichstein, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Ciais, P.; Jiang, L.; et al. Microbial carbon use efficiency promotes global soil carbon storage. Nature 2023, 618, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Bezemer, T.M.; de Vries, F.T.; van Bodegom, P.M. Trade-offs in soil microbial functions and soil health in agroecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2024, 39, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y. Enhancing nitrogen fertilizer productivity in cotton fields in southern Xinjiang by improving the soil microen-vironment through water and nitrogen management. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 312, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, D.; Wei, B.; Yang, Y. Dual roles of microbes in mediating soil carbon dynamics in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, K.; Auffret, M.D.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Hopkins, D.W.; Prosser, J.I.; Singh, B.K.; Subke, J.; Wookey, P.A.; Agren, G.I.; Sebastià, M.; et al. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration rates enhanced by microbial community response. Nature 2014, 513, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Different Mulching Widths on Cotton Growth, Yield, and Quality. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Study on the Impact of Two Mulching Widths on Cotton Growth Environment and Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Ürümqi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X. High-Yield Cultivation Technology for Machine-Picked Cotton with Ultra-Wide Film Mulching. J. Rural Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yin, F.; Guo, L.; Wen, Y.; Song, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z. Ultra-wide film mulching with moderate irrigation water salinity enhances cotton growth under drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. Field Crops Res. 2024, 315, 109485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Gao, F.; Ning, H.; Han, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X. The Effects of Different Planting Patterns and Irrigation Quotas on Cotton Growth and Yield. J. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 42, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Analysis and Research on the Impact of Two Film Widths on the Growth Environment and Traits of Cotton. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Ürümqi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F. Effects of Drip Irrigation with Spring Irrigation on Soil Water-Heat-Salt Distribution and Cotton Growth in Mulched Fields in Southern Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Effects of Irrigation Quotas Under Different Planting Patterns on Root-Shoot Growth and Yield of Mechanically Harvested Cotton in Southern Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Wen, T.; Yang, W.; Tang, F. Effects of Mepiquat Chloride and Sodium Nitroprusside on Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activities and Bacterial Communities in Cotton Seedlings. Cotton Sci. 2023, 35, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.E.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory, C.J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Pang, N.; Gui, H.; Dong, Q.; Ruan, K.; Song, M.; Zhang, X. Effects of Different Mechanically Harvested Cotton Planting Patterns and Planting Densities on Soil Hydrothermal Conditions and Yield in Cotton Fields. J. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wan, S.; Chen, G.; Han, Y.; Lei, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, S.; Mao, T.; Feng, L.; Wang, G.; et al. Effects of irrigation regime on soil hydrothermal microenvironment, cotton biomass, and yield under non-film drip irrigation system in cotton fields in southern Xinjiang, China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 198, 116738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Guo, M.; Jia, W.; Kong, C.; Wang, C.; He, X. The Effects of Irrigation Gradient and Mulching Combination Patterns on the Transpiration and Evaporation Dynamics in Drip-Irrigated Cotton Fields. Res. Agric. Arid Reg. 2024, 42, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Cao, H.; He, Z.; Ding, B.; Li, Z. Effects of Surface-Subsurface Relay Drip Irrigation Leaching on Soil Water and Salt Transport and Cotton Yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, B. Study on the Spatiotemporal Migration Patterns and Regulation of Soil Water-Heat-Salt in Winter-Free Spring-Irrigated Cotton Fields in Southern Xinjiang. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, Z. Impact of Various Mulching Widths on the Cotton Farmland Environment. J. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 60, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Lv, T.; Zong, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T. Effects of drip tape modes on soil hydrothermal conditions and cotton yield (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under machine-harvest patterns. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadras, V.O.; Calderni, D.F. Crop Physiology Applications for Genetic Improvement and Agronomy Preface. In Crop Physiology: Applications for Genetic Improvement and Agronomy; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. XIII–XIV. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Tang, Q.; Cui, J.; Tian, L.; Guo, R.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, T. Deficit irrigation combined with a high planting density optimizes root and soil water–nitrogen distribution to enhance cotton productivity in arid regions. Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q. Investigation of Cotton Water Uptake and Utilization Responses to Water and Salt Stress Based on Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Techniques. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Ning, H.; Han, Q.; Liu, H.; Feng, Q. Effects of Different Irrigation Regimes on Soil Water-Salt Distribution and Crop Growth in Cotton Fields of Southern Xinjiang. Xinjiang J. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 42, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J. Study on the Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil and Microbial Characteristics of Safflower During Flowering Under Different Irrigation Patterns in Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Cao, J.; Su, H. The Effects of Mulching Cultivation on Soil Enzyme Activity, Soil Microorganisms, and Yield of Rainfed Potato. J. Southwest Agric. 2018, 31, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ye, X.; Han, B.; Zhng, X.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of three soil microbial activity measurement methods under different irrigation methods. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 4084–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Yadav, A.N.; Saxena, R.; Paul, D.; Tomar, R.S. Biodiversity of pesticides degrading microbial communities and their environmental impact. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Archana; Uniyal, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Chapter 8—Pseudomonas for sustainable agricultural ecosystem. In Microbial Syntrophy-Mediated Eco-Enterprising; Pratap Singh, R., Manchanda, G., Bhattacharjee, K., Panosyan, H., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, M.; Ma, Z.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.; Liang, J.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, D.; et al. Fusarium diversity associated with diseased cereals in China, with an updated phylogenomic assessment of the genus. Stud. Mycol. 2023, 104, 87–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, T.; Wang, B. The Genus Cladosporium: A Prospective Producer of Natural Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; He, S.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Weng, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Ma, J. Influences of irrigation amount on the rhizospheric microorganism composition and carbon dioxide flux of maize crops. Geoderma 2019, 343, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhenan ZhangÅgren, G.I.; Wang, F. Effects of Different Sprinkler Irrigation Treatments on Water Consumption Characteristics and Soil Microbial Properties of Purple Alfalfa. Water Resour. Plan. Des. 2021, 08, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Qin, H.; Zhu, C.; Tian, W.; Zhu, X. Research Progress on the Mechanisms by Which Soil Microorganisms Influence Soil Health. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 17, 331–347. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Q. Analysis of microbial community diversity based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2021, 61, 1044–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wang, G. Soil moisture influences wheat yield by affecting root growth and the composition of microbial communities under drip fertigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Salinity-induced variations in wheat biomass are regulated by the Na+: K+ ratio, root exudates, and keystone species. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, E. Experimental study on simultaneous heat-water-salt migration of bare soil subjected to evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yu, P.; Shen, J.; Lambers, H. Do rhizosphere microbiomes match root functional traits? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2025, 40, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Soil Layer /cm | Total N /(mg·g−1) | Alkali Hydrolyzable Nitrogen/ (mg·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus/ (mg·kg−1) | Available Potassium/ (mg·kg−1) | Organic Matter/ (g·kg−1) | K+/g·kg−3 | Ca2+/g·kg−3 | Mg2+/g·kg−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 1.75 | 55.51 | 16.16 | 167.65 | 6.03 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| 20–40 | 1.65 | 74.14 | 26.05 | 187.55 | 5.60 | 0.10 | 1.21 | 0.05 |
| 40–60 | 0.85 | 47.18 | 2.73 | 117.64 | 2.49 | 0.16 | 2.29 | 0.05 |
| 60–80 | 0.67 | 25.81 | 2.58 | 110.58 | 2.19 | 0.15 | 2.31 | 0.02 |
| 80–100 | 0.68 | 31.16 | 2.16 | 93.09 | 2.49 | 0.10 | 1.18 | 0.10 |
| Mulching Width | Irrigation Treatment | Budding Stage | Flowering and Boll Stage | Boll Opening Stage | Full Growth Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET /mm | ET /mm | ET /mm | ET /mm | ETC/mm | ||
| M1 | W1 | 11.74 | 224.36 | 49.09 | 285.19 | 325.54 |
| W2 | 18.70 | 255.11 | 90.2 | 364.13 | 406.92 | |
| W3 | 20.52 | 340.30 | 75.51 | 436.33 | 488.30 | |
| M2 | W1 | 14.56 | 239.81 | 49.22 | 303.58 | 325.54 |
| W2 | 24.72 | 225.28 | 126.98 | 376.98 | 406.92 | |
| W3 | 14.15 | 364.13 | 68.71 | 446.99 | 488.30 | |
| Mulching Width | Irrigation Depth/mm | Length/cm | Surface Area/cm2 | Diameter/mm | Volume/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 2091.48 c | 181.64 b | 4.65 b | 2.62 d | |
| M1 | W2 | 2619.87 ab | 240.29 a | 5.71 ab | 4.20 ab |
| W3 | 2532.38 ab | 224.84 a | 7.43 a | 3.67 bc | |
| W1 | 2415.72 b | 222.47 ab | 5.79 ab | 3.46 c | |
| M2 | W2 | 2625.28 ab | 257.52 a | 748 a | 4.03 bc |
| W3 | 2761.53 a | 246.34 a | 8.09 a | 4.77 ab | |
| M | * | * | ns | ** | |
| W | ** | ** | * | ** | |
| M×W | ns | ns | ns | * | |
| Mulching Width | Irrigation Depth/mm | Length/cm | Surface Area/cm2 | Diameter/mm | Volume/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 2453.22 c | 234.17 d | 5.73 b | 4.22 b | |
| M1 | W2 | 2735.30 c | 260.88 c | 6.41 b | 4.40 ab |
| W3 | 3604.22 ab | 275.48 bc | 7.31 ab | 4.98 ab | |
| W1 | 3223.34 b | 258.10 c | 8.40 a | 4.34 ab | |
| M2 | W2 | 3642.47 ab | 300.33 a | 8.05 a | 5.43 a |
| W3 | 3996.16 a | 284.77 ab | 7.18 ab | 5.20 a | |
| M | ** | ** | ** | * | |
| W | ** | ** | ns | ns | |
| M×W | ns | ns | * | ns | |
| Group | Bacterial | Fungal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| M1 | 0.04 | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.02 |
| M2 | 0.13 | 0.05 | −0.18 | 0.00 |
| M1W1 | 0.02 | −0.05 | −0.22 | −0.01 |
| M1W2 | 0.20 | −0.01 | −0.02 | 0.21 |
| M1W3 | −0.06 | −0.13 | −0.04 | −0.09 |
| M2W1 | −0.08 | −0.12 | −0.18 | −0.04 |
| M2W2 | −0.13 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.00 |
| M2W3 | −0.11 | 0.15 | 0.31 | −0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Yang, G.; Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Ning, H. Interactive Effects of Mulching Width and Irrigation Management on Cotton Growth and Dynamic Changes in Soil Factors in Arid Regions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081964
Li N, Yang G, Song Y, Wang W, Zhang X, Liu H, Ning H. Interactive Effects of Mulching Width and Irrigation Management on Cotton Growth and Dynamic Changes in Soil Factors in Arid Regions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081964
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Nanfang, Guang Yang, Yinping Song, Wenzhi Wang, Xianbo Zhang, Hao Liu, and Huifeng Ning. 2025. "Interactive Effects of Mulching Width and Irrigation Management on Cotton Growth and Dynamic Changes in Soil Factors in Arid Regions" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081964
APA StyleLi, N., Yang, G., Song, Y., Wang, W., Zhang, X., Liu, H., & Ning, H. (2025). Interactive Effects of Mulching Width and Irrigation Management on Cotton Growth and Dynamic Changes in Soil Factors in Arid Regions. Agronomy, 15(8), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081964







