Advancing Research on Overlooked Invertebrates in Biological Control: A Case Study of Local Hoverflies and Wolf Spiders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Collection and Rearing of Wolf Spiders
2.2. Collection and Rearing of Hoverflies
2.3. Chemical Formulations
2.4. Acute Toxicity Bioassays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Wolf Spiders
3.2. Hoverflies
3.3. Comparisons Between Wolf Spiders and Hoverflies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altieri, M.A. The Ecological Role of Biodiversity in Agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.G. Ecosystem Services and Agriculture: Tradeoffs and Synergies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, D.K.; Jedlicka, J.A.; Bothwell, S.G.; Moreno, C.R. Effects of Natural Enemy Biodiversity on the Suppression of Arthropod Herbivores in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; Bueno, A.d.F. Conservation Biological Control Using Selective Insecticides—A Valuable Tool for IPM. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffeler, M.; Sunderland, K.D. Composition, Abundance and Pest Control Potential of Spider Communities in Agroecosystems: A Comparison of European and US Studies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 95, 579–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekár, S. Spiders (Araneae) in the Pesticide World: An Ecotoxicological Review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkhofer, K.; Gavish-Regev, E.; Endlweber, K.; Lubin, Y.D.; Von Berg, K.; Wise, D.H.; Scheu, S. Cursorial Spiders Retard Initial Aphid Population Growth at Low Densities in Winter Wheat. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, H.; Simon, S.; Sauphanor, B.; Capowiez, Y. The Role of Natural Enemies on the Population Dynamics of the Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea Passerini (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Organic Apple Orchards in South-Eastern France. Biol. Control 2010, 55, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, M.D.; Jepson, P.C.; Luna, J.M. Hoverfly Oviposition Response to Aphids in Broccoli Fields. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 122, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemptinne, J.L.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Doucet, J.L.; Petersen, J.E. Optimal Foraging by Hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae) and Ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Mechanisms. Eur. J. Entomol. 1993, 90, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, J.V.; Nelson, E.H.; Daane, K.M.; Mills, N.J. Growth, Development and Consumption by Four Syrphid Species Associated with the Lettuce Aphid, Nasonovia ribisnigri, in California. Biol. Control 2011, 58, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekas, A.; De Craecker, I.; Boonen, S.; Wäckers, F.L.; Moerkens, R. One Stone; Two Birds: Concurrent Pest Control and Pollination Services Provided by Aphidophagous Hoverflies. Biol. Control 2020, 149, 104328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oystaeyen, A.; Tuyttens, E.; Boonen, S.; De Smedt, L.; Bellinkx, S.; Wäckers, F.; Pekas, A. Dual Purpose: Predatory Hoverflies Pollinate Strawberry Crops and Protect Them against the Strawberry Aphid, Chaetospihon fragaefolii. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss, A.M.; Jensen, A.S.; Schreiber, A.; Pike, K.S.; Snyder, W.E. Comparison of Predator and Pest Communities in Washington Potato Fields Treated with Broad-Spectrum, Selective, or Organic Insecticides. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.V.A.; Potin, D.M.; Torres, J.B.; Silva Torres, C.S.A. Selective Insecticides Secure Natural Enemies Action in Cotton Pest Management. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, L.; Knapp, R.A.; McDougall, R.; Overton, K.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Umina, P.A. Acute Toxicity Effects of Pesticides on Beneficial Organisms—Dispelling Myths for a More Sustainable Use of Chemicals in Agricultural Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, R.A.; Mata, L.; McDougall, R.; Yang, Q.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Umina, P.A. Acute Toxicity Effects of Pesticides on Predatory Snout Mites (Trombidiformes: Bdellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Ward, S.E.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Umina, P.A. Lethal Impacts of Insecticides and Miticides on Three Agriculturally Important Aphid Parasitoids. Biol. Control 2023, 178, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Bigler, F.; Bogenschütz, H.; Boller, E.; Brun, J.; Calis, J.N.M.; Chiverton, P.; Coremans-Pelseneer, J.; Duso, C.; Lewis, G.B.; et al. Results of the Fifth Joint Pesticide Testing Programme Carried out by the IOBC/WPRS-Working Group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms”. Entomophaga 1991, 36, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Bigler, F.; Bogenschütz, H.; Boller, E.; Brun, J.; Calis, J.N.M.; Coremans-Pelseneer, J.; Duso, C.; Grove, A.; Heimbach, U.; et al. Results of the Sixth Joint Pesticide Testing Programme of the IOBC/WPRS-Working Group «pesticides and Beneficial Organisms». Entomophaga 1994, 39, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, G.; Hassan, S.A.; Baillod, M.; Bakker, F.; Bigler, F.; Blümel, S.; Bogenschütz, H.; Boller, E.; Bromand, B.; Brun, J.; et al. Results of the Seventh Joint Pesticide Testing Programme Carried out by the IOBC/WPRS-Working Group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms”. BioControl 1999, 44, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinter, A.; Poehling, H.M. Side-effects of Insecticides on Two Erigonid Spider Species. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1995, 74, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques Martins, C.A.; Azpiazu, C.; Bosch, J.; Burgio, G.; Dindo, M.L.; Francati, S.; Sommaggio, D.; Sgolastra, F. Different Sensitivity of Flower-Visiting Diptera to a Neonicotinoid Insecticide: Expanding the Base for a Multiple-Species Risk Assessment Approach. Insects 2024, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, J.; de Clercq, P.; Tirry, L. Side Effects of Pesticides on the Larvae of the Hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus in the Laboratory. Phytoparasitica 2011, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, B.; van den Berg, J.H.J.; Leopold, A.; Jagers, G.A.J.M.; Everts, J.W. A Method for Testing the Toxicity of Residues of Pesticides on a Standardized Substrate to Erigonid and Linyphiid Spiders. J. Appl. Entomol. 1990, 109, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duso, C.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Pozzebon, A. Improving the Compatibility of Pesticides and Predatory Mites: Recent Findings on Physiological and Ecological Selectivity. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 39, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, M.H.; Gurr, G.M.; Frampton, C.M. Adult and Larval Hoverfly Communities and Their Parasitoid Fauna in Wheat in New South Wales, Australia. New Zeal. Entomol. 2001, 24, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.R.; Finch, J.T.D.; Young, A.D.; Spooner-Hart, R.N.; Outim, S.K.M.; Cook, J.M. Species Diversity in Bee Flies and Hover Flies (Diptera: Bombyliidae and Syrphidae) in the Horticultural Environments of the Blue Mountains, Australia. Austral Entomol. 2020, 59, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, R.; Kristiansen, P.; Latty, T.; Jones, J.; Rader, R. Pollination Service Delivery Is Complex: Urban Garden Crop Yields Are Best Explained by Local Canopy Cover and Garden Scale Plant Species Richness. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, P.; Reid, C.; Young, A.D.; Threlfall, C.G.; Latty, T. If You Plant It, They Will Come: Quantifying Attractiveness of Exotic Plants for Winter-Active Flower Visitors in Community Gardens. Urban Ecosyst. 2020, 23, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öberg, S.; Ekbom, B. Recolonisation and Distribution of Spiders and Carabids in Cereal Fields after Spring Sowing. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2006, 149, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.; Hebron, W.M.; Raven, R.J.; Zalucki, M.P.; Hassan, E. Spider Fauna of Soybean Crops in South-East Queensland and Their Potential as Predators of Helicoverpa Spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Aust. J. Entomol. 2004, 43, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, M.E.A.; Hardwick, S.; Scholz, B.C.G.; Annells, A.J.; Ward, A.; Grundy, P.R.; Harden, S. Evidence of a Latitudinal Gradient in Spider Diversity in Australian Cotton. Austral Ecol. 2009, 34, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, D.; Whitehouse, M.E.A.; Hulugalle, N.R.; Taylor, P.W. Influence of Crop Management and Environmental Factors on Wolf Spider Assemblages (Araneae: Lycosidae) in an Australian Cotton Cropping System. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, R.; Schmidt, O.; Keller, M.A. Detection of Predators within Brassica Crops: A Search for Predators of Diamondback Moth (Plutella xylostella) and Other Important Pests. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, J.M. Spiders (Araneae) of Irrigated Pasture with and without Shelterbelt of Native Records of the South Australian Museum Monograph Series No. 7 Invertebrate Biodiversity And. Rec. S. Aust. Mus. Monogr. Ser. 2003, 7, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, R.; Keller, M.A.; Schmidt, O.; Framenau, V.W. Molecular Identification of Wolf Spiders (Araneae: Lycosidae) by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction. Biol. Control 2007, 40, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Framenau, V.W. The Wolf Spider Genus Venatrix Roewer: New Species, Synonymies and Generic Transfers (Araneae, Lycosidae). Rec. West. Aust. Mus. 2006, 23, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschokke, S.; Herberstein, M.E. Laboratory Methods for Maintaining and Studying Web-Building Spiders. J. Arachnol. 2005, 33, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, P.; Whitlock, R. A Naturalist’s Guide to the Insects of Australia, 2nd ed.; John Beaufoy Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2022; ISBN 9781913679262. [Google Scholar]
- Soleyman-Nezhadiyan, E. The Ecology of Mebngyna Viridíceps and Símosyrphus Grandícornis (Diptera: Syrphidae) and Their Impact on Populations of the Rose Aphid, Macrosípharn rosoo. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, R.; Mata, L.; Ward, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Umina, P.A. Assessing the Sub-Lethal Impacts of Insecticides on Aphid Parasitoids through Laboratory-Based Studies. Austral Entomol. 2024, 63, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.M.K.; Weeks, A.R.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Umina, P.A. Does Bdellodes lapidaria (Acari: Bdellidae) Have a Role in Biological Control of the Springtail Pest, Sminthurus viridis (Collembola: Sminthuridae) in South-Eastern Australia? Biol. Control 2011, 58, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.J.; Rothman, K.J.; Carlin, J.B.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.N.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Tests, P Values, Confidence Intervals, and Power: A Guide to Misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akol, A.M.; Sithanantham, S.; Njagi, P.G.N.; Varela, A.; Mueke, J.M. Relative Safety of Sprays of Two Neem Insecticides to Diadegma mollipla (Holmgren), a Parasitoid of the Diamondback Moth: Effects on Adult Longevity and Foraging Behaviour. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Katayama, H.; Saito, T. Effect of Insecticides on the Mortalities of Three Whitefly Parasitoid Species, Eretmocerus mundus, Eretmocerus eremicus and Encarsia formosa (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2011, 46, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, J.F.; Dunley, J.E.; Doerr, M.D.; Beers, E.H. Effect of Pesticides on Colpoclypeus florus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) and Trichogramma platneri (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), Parasitoids of Leafrollers in Washington. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, E.L.; Bueno, A.F.; Bueno, R.C.O.F. Pesticide Selectivity for the Insect Egg Parasitoid Telenomus remus. BioControl 2010, 55, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.X.; Irungu, R.W.; Dean, D.A.; Harris, M.K. Impacts of Spinosad and λ-Cyhalothrin on Spider Communities in Cabbage Fields in South Texas. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Isaia, M.; Pekár, S.; Riess, K.; Scherf, G.; Schäfer, R.B.; Entling, M.H. Sensitivity of Spiders from Different Ecosystems to Lambda-Cyhalothrin: Effects of Phylogeny and Climate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.G. Pesticide Susceptibility of Two Coccinellids (Stethorus punctum picipes and Harmonia axyridis) Important in Biological Control of Mites and Aphids in Washington Hops. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2003, 13, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubos, C.R.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Holdcraft, R.; Mason, K.S.; Isaacs, R. Relative Toxicity and Residual Activity of Insecticides Used in Blueberry Pest Management: Mortality of Natural Enemies. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, G.; Baldessari, M.; Maines, R.; Duso, C. Side-Effects of Pesticides on the Predatory Bug Orius laevigatus (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) in the Laboratory. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2005, 15, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, L.; Picanço, M.C.; Rosado, J.F.; Silva, G.A.; Crespo, A.L.B.; Pereira, E.J.G.; Martins, J.C. Conservation of Natural Enemies in Brassica Crops: Comparative Selectivity of Insecticides in the Management of Brevicoryne brassicae (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Aphididae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2009, 44, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, S.; Garcia, P.; Soares, A.O. Effects of Pirimicarb, Buprofezin and Pymetrozine on Survival, Development and Reproduction of Coccinella undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2008, 18, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehoff, B.; Poehling, H.M. Population Dynamics of Aphids and Syrphid Larvae in Winter Wheat Treated with Different Rates of Pirimicarb. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 52, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.A.; van Leeuwen, T.; Tirry, L.; de Clercq, P. Toxicity of Selected Insecticides to the Two-Spot Ladybird Adalia bipunctata. Phytoparasitica 2009, 37, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzini, D.T.; Koch, R.L. Compatibility of Flonicamid and a Formulated Mixture of Pyrethrins and Azadirachtin with Predators for Soybean Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Management. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, J.; Tirry, L.; de Clercq, P. Susceptibility of Cocooned Pupae and Adults of the Parasitoid Microplitis Mediator to Selected Insecticides. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, H.G.; Ha, P.J.; Lim, U.T.; Lee, J.H. Toxicities of 26 Pesticides against 10 Biological Control Species. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The Sublethal Effects of Pesticides on Beneficial Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.J.; Beers, E.H.; Shearer, P.W.; Unruh, T.R.; Amarasekare, K.G. Comparative Analysis of Pesticide Effects on Natural Enemies in Western Orchards: A Synthesis of Laboratory Bioassay Data. Biol. Control 2016, 102, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviter, H.; Muth, F. Do Novel Insecticides Pose a Threat to Beneficial Insects? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, T.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Sublethal Toxicity, Transgenerational Effects, and Transcriptome Expression of the Neonicotinoid Pesticide Cycloxaprid on Demographic Fitness of Coccinella septempunctata. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantedeschi, R.; Grützmacher, A.D.; Pazini, J.d.B.; Bueno, F.A.; Machado, L.L. Selectivity of Pesticides Registered for Soybean Crop on Telenomus podisi and Trissolcus basalis. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2018, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, J.T.; Bueno, A.d.F.; Neves, P.M.O.J.; da Silva, D.M.; Pomari-Fernandes, A.; Favetti, B.M. Selectivity of Different Biological Products to the Egg Parasitoid Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2018, 62, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: An Overview of Their Biocidal Activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, E.; Zaritsky, A.; Dahan, E.; Barak, Z.; Sinai, R.; Manasherob, R.; Khamraev, A.; Troitskaya, E.; Dubitsky, A.; Berezina, N.; et al. Extended Screening by PCR for Seven Cry-Group Genes from Field-Collected Strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4883–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossentine, J.; Robertson, M.; Xu, D. Biological Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis in Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, D.J. Selective mortality of parasitoids and predators of Myzus persicae on collards treated with malathion, carbaryl, or Bacillus thuringiensis. Ent. Exp. Appl. 1983, 34, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hu, D.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y. Communal Rearing Induces High Predatory Capacity in a Solitary Wolf Spider and Its Potential in Pest Control. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, S.; Thyselius, M.; Holden, M.; Nordström, K. Rearing and Long-Term Maintenance of Eristalis tenax Hoverflies for Research Studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, K. An Efficient Breeding Method for Eupeodes corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae), a Pollinator and Insect Natural Enemy in Facility-Horticulture Crops. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, I.; Perez-Bañón, C.; Rojo, S. Life Cycle, Population Parameters, and Predation Rate of the Hover Fly Eupeodes corollae Fed on the Aphid Myzus persicae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, F.; Karimpour, Y.; Aramideh, S.; Gilasian, E. Investigation on Some Biological Characteristics of Eupeodes corollae (Dip.: Syrphidae) on Aphis pomi (Hom: Aphididae) in Vitro. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 432–435. [Google Scholar]
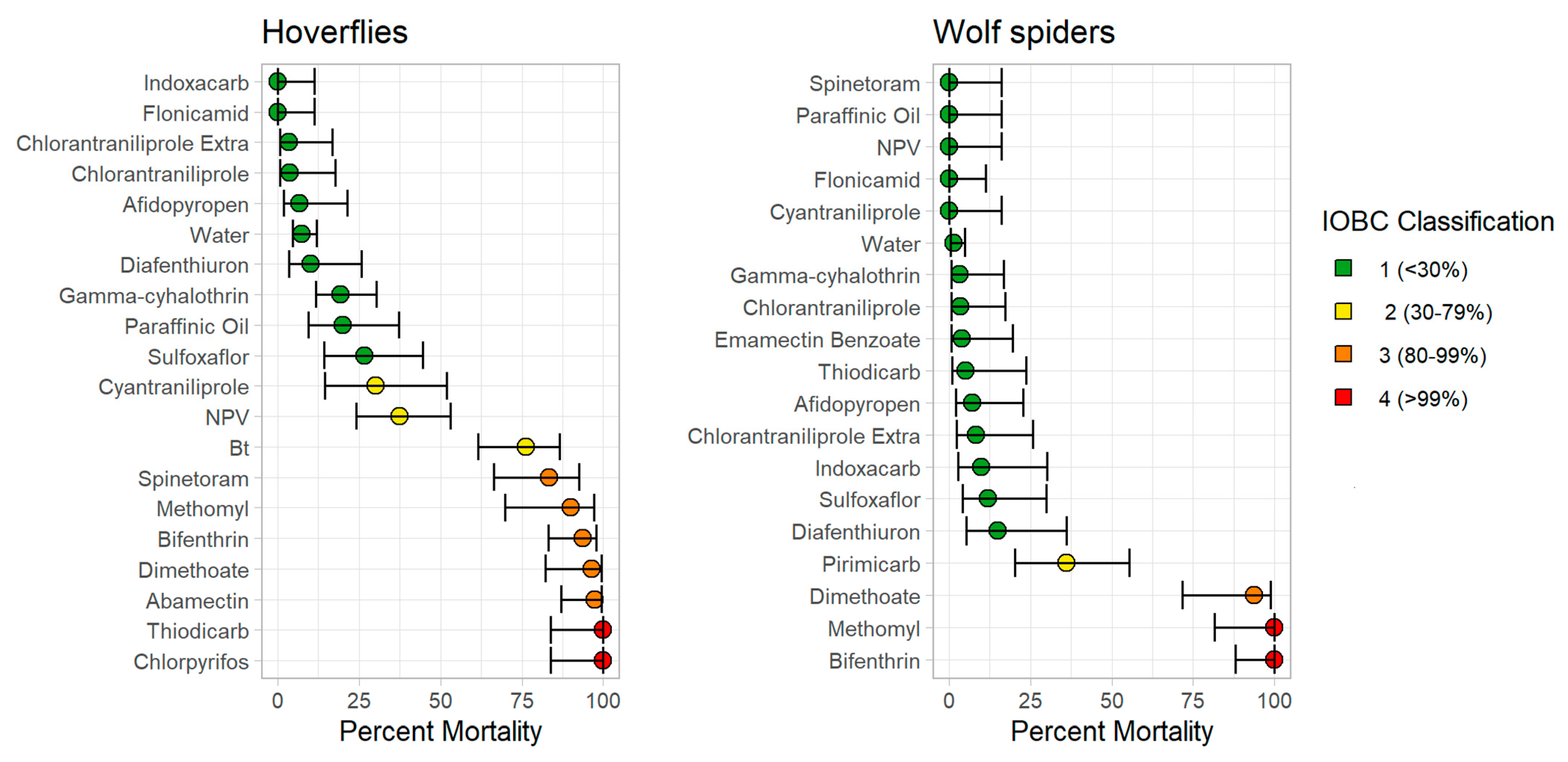
| Mode of Action (MoA) Group | Active Ingredient (a.i.) | Product Name (Distributer) | Formulation (g a.i./kg or mL a.i./L) | Rate Tested (g or mL a.i./ha) | Hoverflies (Melangyna sp.) | Wolf Spiders (Venatrix spp.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent Mortality (95% CIs) | IOBC Classification | N | Percent Mortality (95% CIs) | IOBC Classification | N | |||||
| NA | Water | NA | NA | NA | 7.46 (4.57–11.95) ab | NA | 201 | 1.36 (0.37–4.82) a | NA | 147 |
| Carbamates | Methomyl | Methomyl 225 (Nufarm) | 225 | 450 | 90.00 (69.9–97.21) cd | 3 | 20 | 100.00 (81.57–100.00) c | 4 | 17 |
| Pirimicarb | Pirimor WG (Syngenta) | 500 | 500 | - | - | - | 36.00 (20.25–55.48) b | 2 | 25 | |
| Thiodicarb | Larvin 375 (Bayer) | 375 | 281.25 | 100.00 (83.89–100.00) d | 4 | 20 | 5.00 (0.89–23.61) ab | 1 | 20 | |
| Organophosphates | Chlorpyrifos | Lorsban 500 EC (Corteva) | 500 | 750 | 100.00 (83.89–100.00) d | 4 | 20 | - | - | - |
| Dimethoate | Dimethoate 400 (ADAMA) | 400 | 320 | 96.43 (82.29–99.37) cd | 3 | 28 | 93.75 (71.67–98.89) c | 3 | 16 | |
| Pyrethroids | Bifenthrin | Talstar 250 EC (FMC) | 250 | 80 | 93.75 (83.16–97.85) cd | 3 | 48 | 100.00 (87.94–100.00) c | 4 | 28 |
| Gamma-cyhalothrin | Trojan (FMC) | 150 | 4.5 | 19.40 (11.71–30.42) b | 1 | 67 | 3.33 (0.59–16.67) a | 1 | 30 | |
| Sulfoximines | Sulfoxaflor | Transform WG (Corteva) | 500 | 50 | 26.67 (14.18–44.45) b | 1 | 30 | 12.00 (4.17–29.96) ab | 1 | 25 |
| Spinosyns | Spinetoram | Success Neo (Corteva) | 500 | 50 | 83.33 (66.44–92.66) cd | 3 | 30 | 0.00 (0.00–16.11) a | 1 | 20 |
| Avermectins | Abamectin | Vantal Upgrade 36 (FMC) | 36 | 5.4 | 97.50 (87.12–99.56) d | 3 | 40 | - | - | - |
| Emamectin Benzoate | Affirm (Syngenta) | 17 | 5.1 | - | - | - | 4.00 (0.71–19.54) a | 1 | 25 | |
| Pyropenes | Afidopyropen | Versys (BASF) | 100 | 5 | 6.67 (1.85–21.32) a | 1 | 30 | 7.14 (1.98–22.65) ab | 1 | 28 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) subsp. kurstaki | DiPel DF (Sumitomo) | 280 | 3285.7 | 76.19 (61.47–86.52) c | 2 | 42 | - | - | - |
| Diafenthiuron | Diafenthiuron | Pegasus (Syngenta) | 500 | 300 | 10.00 (3.46–25.62) ab | 1 | 30 | 15.00 (5.24–36.04) ab | 1 | 20 |
| Oxadiazines | Indoxacarb | Steward EC (FMC) | 150 | 60 | 0.00 (0.00–11.35) a | 1 | 30 | 10.00 (2.79–30.1) ab | 1 | 20 |
| Diamides | Chlorantraniliprole | Altacor (FMC) | 350 | 15 | 3.57 (0.63–17.71) a | 1 | 28 | 3.45 (0.61–17.18) a | 1 | 29 |
| Chlorantraniliprole Extra | Altacor (FMC) | 350 | 30 | 3.33 (0.59–16.67) a | 1 | 30 | 8.33 (2.32–25.85) ab | 1 | 24 | |
| Cyantraniliprole | Exirel (FMC) | 100 | 15 | 30.00 (14.55–51.9) b | 2 | 20 | 0.00 (0.00–16.11) a | 1 | 20 | |
| Flonicamid | Flonicamid | MainMan (ISK) | 500 | 50 | 0.00 (0.00–11.35) a | 1 | 30 | 0.00 (0.00–11.35) a | 1 | 30 |
| Baculoviruses | Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus (NPV) | NearNPV (AgBiTech) | 7.5 × 109 | 100 | 37.50 (24.22–52.97) b | 2 | 40 | 0.00 (0.00–16.11) a | 1 | 20 |
| NA | Paraffinic Oil | Canopy (FMC) | 778 | 1584 | 20.00 (9.51–37.31) ab | 1 | 30 | 0.00 (0.00–16.11) a | 1 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knapp, R.A.; McDougall, R.; Umina, P.A. Advancing Research on Overlooked Invertebrates in Biological Control: A Case Study of Local Hoverflies and Wolf Spiders. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051203
Knapp RA, McDougall R, Umina PA. Advancing Research on Overlooked Invertebrates in Biological Control: A Case Study of Local Hoverflies and Wolf Spiders. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051203
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnapp, Rosemary A., Robert McDougall, and Paul A. Umina. 2025. "Advancing Research on Overlooked Invertebrates in Biological Control: A Case Study of Local Hoverflies and Wolf Spiders" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051203
APA StyleKnapp, R. A., McDougall, R., & Umina, P. A. (2025). Advancing Research on Overlooked Invertebrates in Biological Control: A Case Study of Local Hoverflies and Wolf Spiders. Agronomy, 15(5), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051203







