Crushed, Squeezed, or Pressed? How Extraction Methods Influence Sap Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Soil and Irrigation
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Sap Extraction Methods
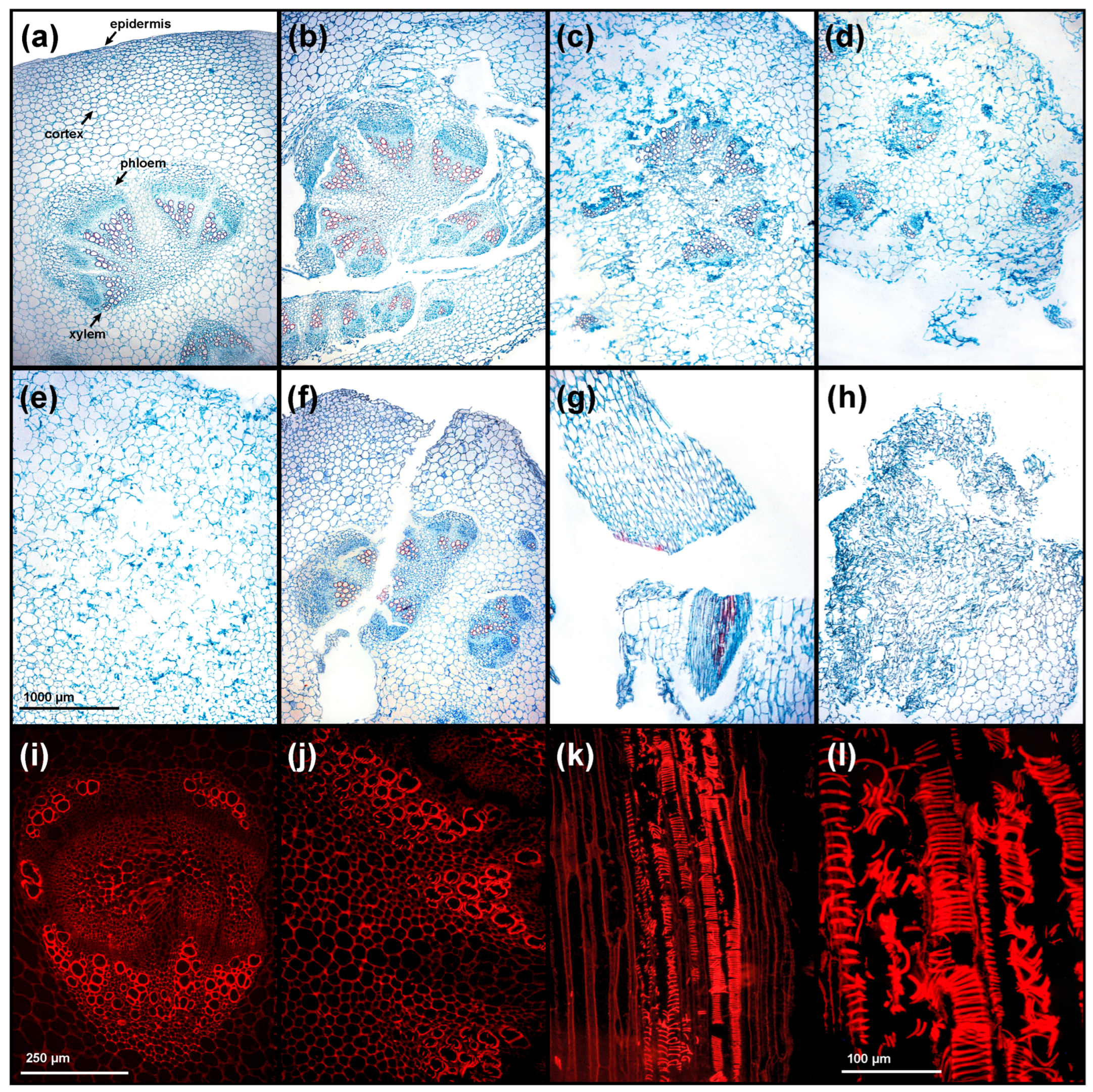
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Histological Characterization
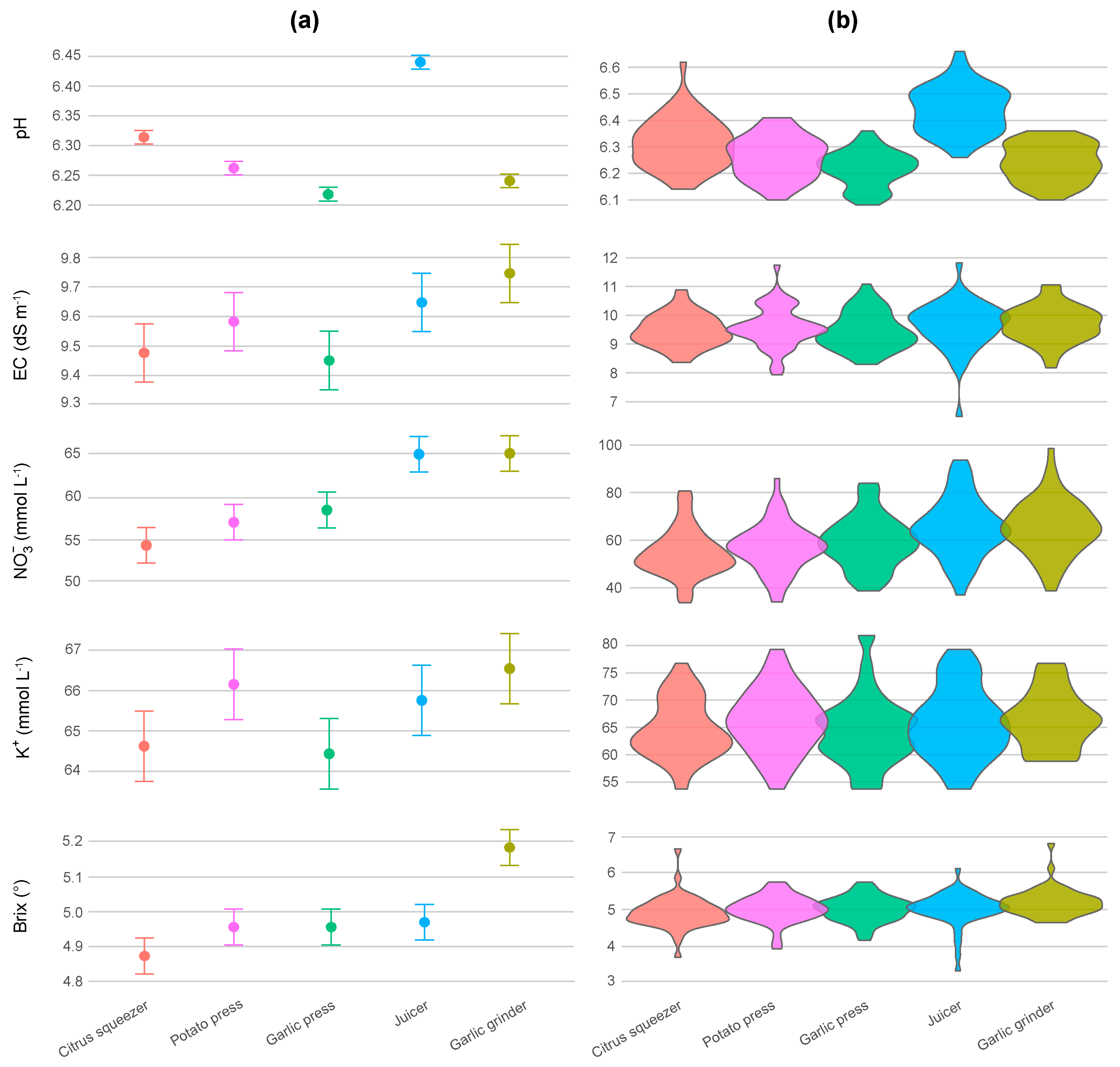
3.2. Sap Chemical Characterization
3.3. Sap Physical Characterization
3.4. Relationships Among Sap Traits
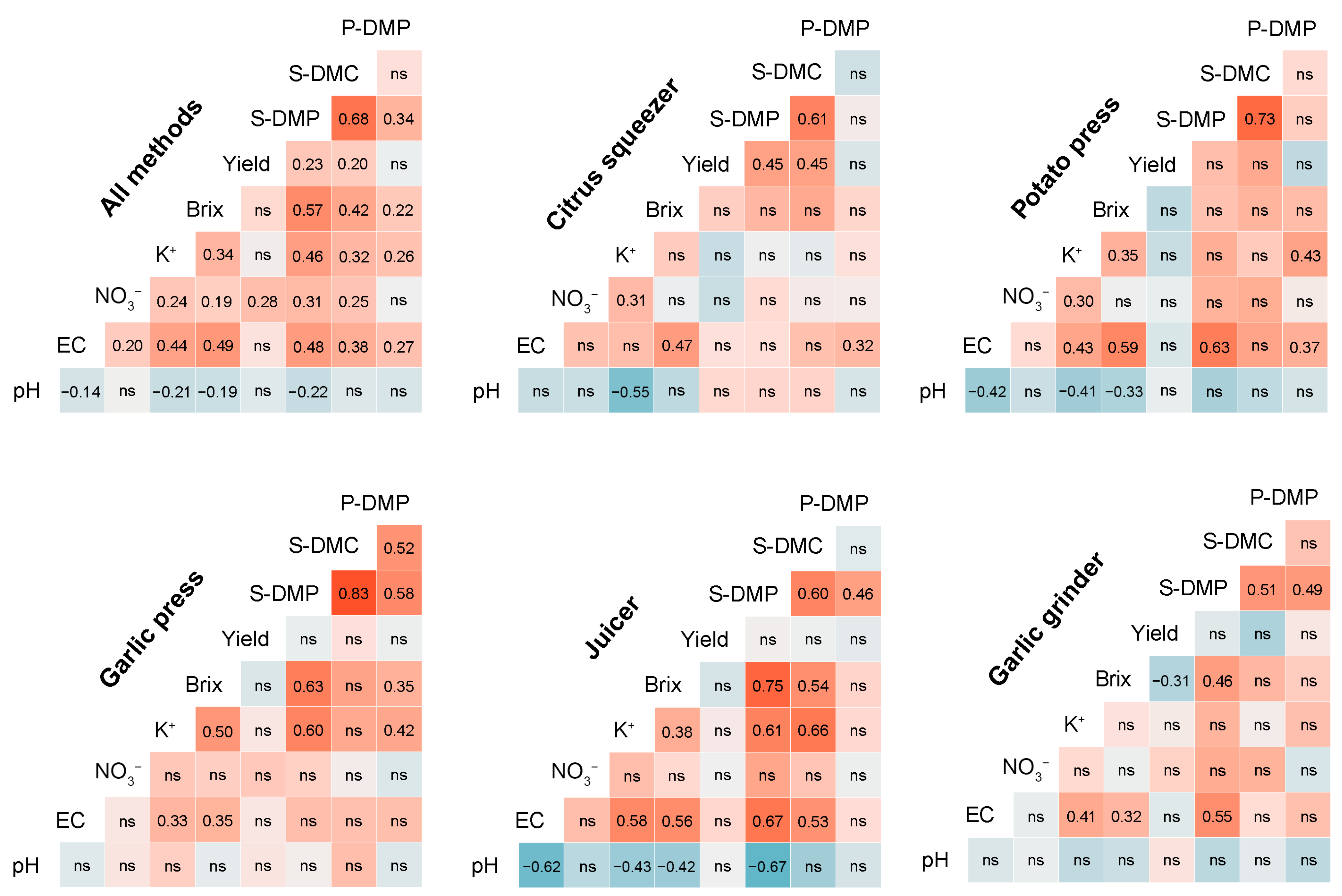
3.4.1. Exploratory Relationships
- Pairwise correlations
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
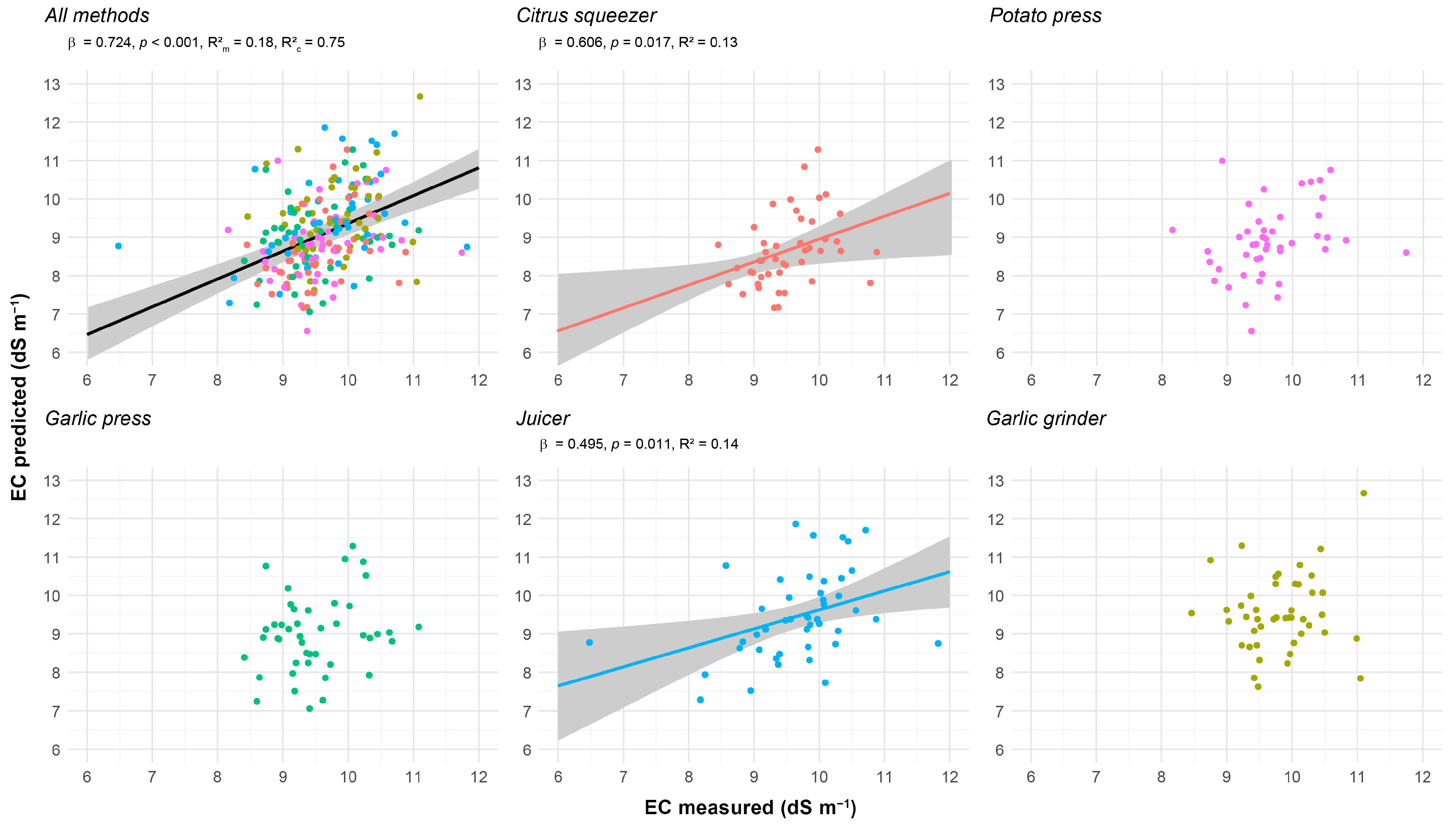
3.4.2. Modeled Relationships
- EC and ion concentrations
- K+ and °Bx
- Physical interactions
- S-DMP and Chemical Parameters
3.5. Temporal Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Extraction Method on Sap Chemical Profiles
4.2. Variability Among Extraction Methods
4.3. Variability Among Chemical Parameters
4.4. The Hidden Complexity Beyond Sap Yield
4.5. Sap Solids
4.6. What Is “Sap”, Really?
4.7. Could Sap EC Be Used as a Predictor of NO3− and K+ Concentrations?
4.8. Nutrient Relations
4.9. Tissue Moisture and Nutrients
4.10. Deriving Sap Sufficiency Thresholds Based on Nutrient Concentrations in Dry Tissue
4.11. Practical Implications
4.12. Was There Noise in the Findings and Dataset?
- Interpretation considerations for combined models
- b.
- Temporal effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| °Bx | Degrees Brix (soluble solids) |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BBCH | BBCH phenological scale |
| CIELab (L*, a*, b*) | CIELab color coordinates |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| EMM(s) | Estimated marginal mean(s) |
| ISE(s) | Ion-selective electrode(s) |
| K+ | Potassium (ion) |
| LMM(s) | Linear mixed-effects model(s) |
| LRT | Likelihood ratio test |
| MRML | Most recently matured leaves |
| NO3− | Nitrate (ion) |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| P-DMP | Petiole dry matter percentage |
| R2m/R2c | Marginal/conditional R-squared |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| S-DMC | Sap dry matter content |
| S-DMP | Sap dry matter percentage |
| SE | Standard error |
| Δ AIC | Change in AIC between models |
| ρ (rho) | Spearman correlation coefficient |
Appendix A

Appendix B
| Parameter | χ2 (EM) | p-Value | Replicate SD | Residual SD | Δ AIC | LRT p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 398.46 | <0.001 | 0.052 | 0.062 | 210.54 | <0.001 |
| EC | 16.89 | 0.002 | 0.547 | 0.408 | 8.51 | 0.002 |
| NO3− | 118.78 | <0.001 | 9.173 | 6.204 | 85.88 | <0.001 |
| K+ | 11.85 | 0.068 | 4.638 | 3.577 | 3.72 | 0.020 |
| °Bx | 27.26 | <0.001 | 0.172 | 0.313 | 18.00 | <0.001 |
| Method | L* (Lightness) | a* (Green-Red) | b* (Blue-Yellow) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus squeezer | 77.65 | −22.16 | 67.97 |
| Potato press | 81.57 | −22.97 | 70.81 |
| Garlic press | 81.57 | −22.97 | 70.81 |
| Juicer | 77.70 | −22.72 | 70.89 |
| Garlic grinder | 87.01 | −13.66 | 42.53 |
References
- Gallardo, M.; Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; Padilla, F.M.; Cedeño, J.; Thompson, R.B. Prescriptive-Corrective Irrigation and Macronutrient Management in Greenhouse Soil-Grown Tomato Using the VegSyst-DSS v2 Decision Support Tool. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, E.; Locatelli, G.; Bou, N.A.; Ferrarezi, R.S. Sap Analysis: A Powerful Tool for Monitoring Plant Nutrition. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahal, N.K.; Miguez, F.E.; Sawyer, J.E.; Dong, L.; Schnable, P.S.; Castellano, M.J. Stalk Sap Nitrate Test as a Potential Tool for Nitrogen Fertilizer Recommendations for Maize. Field Crops Res. 2024, 310, 109330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, I.G.; Hutsby, W. Development and Evaluation of Rapid Tests for the Estimation of Phosphate and Potassium in Plant Sap. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Errebhi, M. A Field Sap Test for Determining Petiole Nitrate-Nitrogen; University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.B.; Fernández Fernández, M.M.; Cánovas Fernández, G.; Gallardo, M. Aplicaciones Prácticas de Sistemas de Análisis Rápido de Nutrientes Para Mejorar El Manejo Del Nitrógeno En Cultivos de Invernadero. In Mejora en la Eficiencia del Uso de Agua y Fertilizantes en Agricultura; Gázquez, J.C., Ed.; Cajamar Caja Rural: Almería, Spain, 2018; pp. 181–202. ISBN 978-84-95531-88-9. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, J.; Lyons, D. Petiole Sap Nitrate is Better than Total Nitrogen in Dried Leaf for Indicating Nitrogen Status and Yield Responsiveness of Capsicum in Subtropical Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1994, 34, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; Gallardo, M.; Thompson, R.B.; Farneselli, M.; Padilla, F.M. Assessing Crop N Status of Fertigated Vegetable Crops Using Plant and Soil Monitoring Techniques. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 167, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremper, R.; Juhász, E.K.; Novák, T.; Kincses, I.; Sándor, Z.; Tállai, M.; Béni, Á.; Szabó, A.; Szarvas, S.; Balla Kovács, A. Assessment of Spring Oat Nitrogen Supply Based on Plant Sap Nitrate Concentration and SPAD Values. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.H.C.; Fratoni, M.M.J.; Fregonezi, G.A.d.F.; Takahashi, H.W. Nutritional Assessment of Potassium in Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) by Direct Reading of Fruit Sap. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltman, R.R. Sampling Considerations for Nitrate Quick Tests of Greenhouse-Grown Tomatoes. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1987, 112, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panique, E.; Kelling, K.A.; Schulte, E.E. Establishment of Potassium Tissue and Sap Critical Values; University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yosoff, S.F.; Mohamed, M.T.M.; Parvez, A.; Ahmad, S.H.; Ghazali, F.M.; Hassan, H. Production System and Harvesting Stage Influence on Nitrate Content and Quality of Butterhead Lettuce. Bragantia 2015, 74, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buajaila, F.; Cowan, J.S.; Inglis, D.; Carpenter-Boggs, L.; Miles, C. Tomato Growth, Yield, and Quality Response to Mixed Chemical–Organic Fertilizers and Grafting Treatments in a High Tunnel Environment. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2022, 102, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolem, C.A.; Van Mellis, V. Monitoring Nitrogen Nutrition in Cotton. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2010, 34, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmuth, G.J. Efficiency Ranges for Nitrate-Nitrogen and Potassium for Vegetable Petiole Sap Quick Tests. HortTechnology 1994, 4, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Smeal, D.; Arnold, R.N.; Gregory, E.J. Potato Nitrogen Management by Monitoring Petiole Nitrate Level. J. Plant Nutr. 1996, 19, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Miles, C.; Tao, H.; DeVetter, L. Evaluation of Real-Time Nutrient Analysis of Fertilized Raspberry Using Petiole Sap. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 918021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, C.; Pauletti, V.; Gervini de Menezes, F.O., Jr.; Mora, C. Diagnóstico de Nitrogênio Pelo Índice de Clorofila e Nitrato na Seiva para Cebola em Sistema de Semeadura Direta. Revista Thema 2022, 21, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Ci, B.; Feng, X.; Wen, S.; Lu, X.; He, Z.; Ma, F. Establishment of an NPK Nutrient Monitor System in Yield-Graded Cotton Petioles under Drip Irrigation. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; Padilla, F.M.; Gallardo, M.; Thompson, R.B. Effect of Cultivar on Measurements of Nitrate Concentration in Petiole Sap and Leaf N Content in Greenhouse Soil-Grown Cucumber, Melon, and Sweet Pepper Crops. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 320, 112200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Urushima, M.; Oi, S.; Toi, K.; Oka, J.; Inubushi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Wada, T. Diagnosis and Recommendation Integrated System by Sap Analysis for Horticultural Crops (Part 1): A Study on the Standardization of Preparing Samples for Analysis. Hort. J. 1998, 6, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajah, S. A Petiole Sap Test for Nitrate and Potassium in Sultana Grapevines. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1999, 5, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, D.; Gysi, C. Plant-Sap Analysis in Vegetables—A Tool to Decide on Nitrogen Top Dressing. Acta Hortic. 2001, 563, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, J.Z.; Ojodeagua, J.L. Manejo de La Fertirrigación Del Tomate de Invernadero En Suelo. In Manual de Producción de Tomate en Invernadero; Castellanos, J.Z., Ed.; Instituto de Tecnología Agrícola: Celaya, Mexico, 2009; pp. 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Llanderal, A.; García-Caparrós, P.; Contreras, J.I.; Segura, M.L.; Lao, M.T. Evaluation of the Nutrients Variability in Sap of Different Petiole Samples in Tomato Plant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.; Martins, M.J.; Sprey, L.; Maurício, A.; Rosa, C.; Faria, J.; Martins, M.B.; De Sousa, M.L.; Santos, R.; De Sousa, R.M.; et al. Analysis of Petiole Sap Nutrients Using Rapid and Standard Methods and Its Relation to Leaf Analysis of Fertilized Malus domestica cv. Gala. Horticulturae 2023, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.L.; Kubota, A.; Doerge, T.A.; Godin, R.E.; McCreary, T.W. Petiole Sap Nitrate Tests for Determining Nitrogen Status of Broccoli and Cauliflower. Veg. Res. 1996, 104, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Altland, J.E.; Gilliam, C.H.; Keever, G.J.; Sibley, J.L.; Fare, D.C. Rapid Determination of Nitrogen Status in Potted Pansy Production©. In Combined Proceedings-International Plant Propagators Society; International Plant Propagators’ Society (IPPS): Chipley, FL, USA, 2001; Volume 51, pp. 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- Roacho-Cortés, E.; Castellanos Ramos, J.Z.; Etchevers-Barra, J.D. Técnicas de Diagnóstico En Campo Para Determinar Nitrógeno En Maíz. Terra Latinoam. 2021, 39, e820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Mendoza, A.; De Alba Romenus, K.; León De La Rocha, J.F.; Narváez Ortiz, W.A.; Francisco Francisco, N. Ionic Sufficiency of the Nutrient Solution and Effects on the Total Soluble Solid’s Concentration in Mini Tomatoes. Nova Sci. 2022, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Benavides, A.D.; Garces-Varon, G.; Restrepo-Díaz, H. Foliar Cytokinins or Brassinosteroids Applications Influence the Rice Plant Acclimatization to Combined Heat Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 983276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa Cruz, J.; Calbucheo, D.; Valdebenito, S.; Vásquez, V.; Aguilar, M.; Peñaloza, P.; Allendes, H.; Vidal, K. Forgotten Science: How 1900s Studies Challenge the Current Research on Sap Analysis. Int. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2025, 18, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Eliason, R. Nutrient Management for Commercial Fruit & Vegetable Crops in Minnesota; University of Minnesota Extension Service: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2005; 40p. [Google Scholar]
- Schulbach, K.; Smith, R.; Hartz, T.K.; Jackson, L. Guide to Nitrogen Quick-Test for Vegetables with the “Cardy” Nitrate Meter; California Department of Food and Agriculture: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Havlin, J.L.; Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L.; Beaton, J.D. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers. An Introduction to Nutrient Management, 8th ed.; Pearson India: Tamil Nadu, India, 2017; 520p, ISBN 978-93-325-8603-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hartz, T.K.; Smith, R.; Schulbach, K.; LeStrange, M. On-Farm Nitrogen Tests Improve Fertilizer Efficiency, Protect Groundwater. Calif. Agric. 1994, 48, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Thompson, T.L.; Doerge, T.A.; Godin, R.E. A Petiole Sap Nitrate Test for Broccoli. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, J.Z.; Villalobos, S.; Delgado, J.A.; Muñoz-Ramos, J.; Sosa, A.; Vargas, P.; Lazcano, I.; Alvarez-Sanchez, E.; Enriquez, S.A. Use of Best Management Practices to Increase Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Protect Environmental Quality in a Broccoli-Corn Rotation of Central Mexico. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 1265–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, C.; Cialdella, L.; Ingels, R.; Jacquemyn, H.; Lievens, B. Cultivar-Dependent Effects of Plant-Beneficial Fungi on Plant Nutrient Composition and Feeding Damage by Nesidiocoris tenuis. Plant Soil 2023, 492, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studstill, D.W.; Simonne, E.H.; Hutchinson, C.M.; Hochmuth, R.; Dukes, M.D.; Davis, W.E. Petiole Sap Testing Sampling Procedures for Monitoring Pumpkin Nutritional Status. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2003, 34, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, J.Z. Nutrición de Cultivos Bajo Sistemas de Fertigación. Inf. Agronómicas 1999, 35, 5–11. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/258134428/Nutricion-de-cultivos-pdf (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Sonneveld, C.; De Bes, S.S. Relationship between Analytical Data of Plant Sap and Dried Material of Glasshouse Crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1983, 14, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastylianou, I. Diurnal Variation of Nitrate Concentration in Cereals Grown under Rainfed Mediterranean Conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1995, 26, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, P.; Molinos, C.; Alcántar-González, G.; Sandoval-Villa, M. Diagnóstico Nutrimental En Plantas. In Nutrición de Cultivos; Alcántar-González, G., Trejo-Téllez, L.I., Gómez-Merino, F.C., Eds.; Colegio de Postgraduados y Mundi-Prensa: Texcoco, Mexico, 2016; pp. 183–217. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/537956120/Nutricion-vegetal-1 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Delgado, J.A.; Follett, R.F. Sap Test to Determine Nitrate-nitrogen Concentrations in Aboveground Biomass of Winter Cover Crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadahía López, C. El Análisis de Savia Como Índice de Fertilización En Tomate. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Justes, E.; Meynard, J.M.; Mary, B.; Plénet, D. Diagnosis Using Stem Base Extract: JUBIL Method. In Diagnosis of the Nitrogen Status in Crops; Lemaire, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 163–187. ISBN 978-3-642-64506-8. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.M.J.; Maier, N.A. Use of Petiolar Sap Nitrate for Assessing Nitrogen Status of Irrigated Brussel Sprout Crops. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farneselli, M.; Simonne, E.H.; Studstill, D.W.; Tei, F. Washing and/or Cutting Petioles Reduces Nitrate Nitrogen and Potassium Sap Concentrations in Vegetables. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdebenito, S.; Rubio, A.; Moller, A.; Santa Cruz, J.; Castillo, P.; Providell, M.L.; Cáceres, C.; Calbucheo, D.; Hernández, I.; Peñaloza, P. Histological and Immunolabeling Techniques in Arabidopsis thaliana: A Practical Guide and Standardization Roadmap. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darricarrere, V.; Santa Cruz, J.; Calbucheo, D.; Valdebenito, S.; Providell, M.; Cisternas, M.; Muena, V.; Peñaloza, P. Storage-Induced Fruit Breakdown in Cryptocarya alba: Implications for the Conservation of a Keystone Mediterranean Recalcitrant Species. Plants 2025, 14, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; Grasso, R.; Gallardo, M.; Padilla, F.M.; De Souza, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Thompson, R.B. Sample Temperature Affects Measurement of Nitrate with a Rapid Analysis Ion Selective Electrode System Used for N Management of Vegetable Crops. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyński, K.; Kobus, Z.; Dziki, D. Effect of Press Construction on Yield and Quality of Apple Juice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, Z.; Nadulski, R.; Anifantis, A.S.; Santoro, F. Effect of Press Construction on Yield of Pressing and Selected Quality Characteristics of Apple Juice. ERDev 2018, 53, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Vázquez, F.A.; Sandoval-Rangel, A. Influencia del Acolchado y Gallinaza en Producción de Tomate Silvestre (Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme (Dunal)). Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2023, 10, e3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Mendoza, A.; De Alba-Romenus, K.; Francisco-Francisco, N. Relation between Soil Solution Composition and Petiole Cellular Extract of Crops in Western Mexico. Terra Latinoam. 2021, 39, e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Barco, F.A.; Zhiñin-Huachun, I.A.; Hernández-Pérez, R. Influencia de Bioestimulantes Sobre Caracteres Morfológicos y Agroquímicos del Banano (Musa AAA cv. Williams). Terra Latinoam. 2022, 40, e1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruener, C.E. Determination of Critical Y-Leaf-Potassium Concentrations across Reproductive Growth Stages for Direct-Seeded Delay-Flooded Rice. Master’s Thesis, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, W. Guía de Interpretación de Análisis de ECP. In Respuesta del Brócoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) Híbrido Fantástico a la Fertilización con Cinco Fuentes de Azufre Aplicadas a Dos Dosis, Mulaló, Cotopaxi; Sánchez Ayala, B.L., Ed.; UCE: Quito, Ecuador, 2013; Available online: https://www.dspace.uce.edu.ec/entities/publication/ffb7a914-2034-4383-b651-201fc6ea2f02 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Ankerman, D.; Large, R. Agronomy Handbook; Fall 2019 Edition; Midwest Laboratories: Omaha, NE, USA, 2019; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Billman, E.D.; Soder, K.J.; Horst, J.; Hafla, A.; Balk, K. Validation of Brix for Predicting Sugar Concentrations of Alfalfa and Orchardgrass. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2024, 40, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Nanayama, K.; Isobe, S.; Ozaki, K.; Miyagi, K.; Sumi, H.; Toume, Y.; Morine, S.; Ohta, H. Effect of Extraction Method on Yield and Quality of Citrus depressa Juice. Food. Sci. Technol. Int. 2007, 13, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Llanderal, A.; García-Caparrós, P.; Segura, M.L.; Contreras, J.I.; Lao, M.T. Nutritional Changes in Petiole Sap over Space and Time in a Tomato Crop Greenhouse. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, W.; Saritama, A.S. El Análisis Del Extracto Celular de La Planta de Banano Como Herramienta Para Identificar Potenciales Problemas de Producción. 2008. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/623804296/Washington-Padilla-El-Extracto-Celular-en-Banano (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Wilczyński, K.; Kobus, Z.; Guz, T. Analysis of Efficiency and Particles Size Distribution in Apple Juice Obtained with Different Methods. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2018, 63, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.M.J.; Maier, N.A. Determination of the Nitrogen Status of Irrigated Potato Crops: II. A Simple on Farm Quick Test for Nitrate-nitrogen in Petiole Sap. J. Plant Nutr. 1990, 13, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Tang, L.; Bélanger, G.; Zhu, Y.; Jeuffroy, M.-H. Forward New Paradigms for Crop Mineral Nutrition and Fertilization towards Sustainable Agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 125, 126248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappelis, A.J. Nature of Resistance to Diplodia Stalk Rot of Corn. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State College, Ames, IA, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gioia, F.; Simonne, E.H.; Gonnella, M.; Santamaria, P.; Gazula, A.; Sheppard, Z. Assessment of Ionic Interferences to Nitrate and Potassium Analyses with Ion-Selective Electrodes. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1750–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Pumarada, G.; Di Gioia, F. Assessing the Reliability of Portable Ion-Selective Electrodes Proposed for the on-Farm Management of Nutrient Solutions and Fertigation of Horticultural Crops. Acta Hortic. 2023, 1377, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareo-Benítez, I.; Yam-Tzec, J.A.; Ramírez-Seañez, A.R.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, J.O.; Hernández-Hernández, H. Application of Two Levels of Calcium Nitrate on Sap Nutrients, Growth and Yield of Persian Cucumber. Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosyst. 2024, 27, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinger, N.A. The Expressed Sap of Corn Plants as an Indicator of Nutrient Needs. J. Agric. Res. 1931, 43, 95–119. [Google Scholar]
- Chrudimsky, W.W. A Study of the Influence of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Concentrations. Master’s Thesis, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA, 1969. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/939759975/Chrumdimsky-1963-A-Study-of-the-Influence-of-Nitrogen-Phosphorous-and-Potassium-Concentrations?_gl=1*12vtab*_gcl_au*MTg0NDIzOTQ3OC4xNzYxNjc3MzkyLjE5OTEzOTk3My4xNzYxNjg0MTkxLjE3NjE2ODQxOTA (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Rangel-Lucio, J.A.; Alcántar González, G.; Castellanos, R.; García-Moya, E.; Trejo López, C.; Vaquera Huerta, H. Comparación de Dos Pruebas Para Diagnosticar Nitrógeno En Sorgo. Terra Latinoam. 2002, 20, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Peuke, A.D. Correlations in Concentrations, Xylem and Phloem Flows, and Partitioning of Elements and Ions in Intact Plants. A Summary and Statistical Re-Evaluation of Modelling Experiments in Ricinus communis. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.H.; Jinhui, W.; Li, X.; Hameed, M.K.; Manzoor, M.A.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Chang, L. Exploring the Role of Nitrogen and Potassium in Photosynthesis Implications for Sugar: Accumulation and Translocation in Horticultural Crops. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 327, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, S.C.; Baker, S. Correlation of Plant Sap Extracts of Nitrate-N and K with Dried Petiole Extracts. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–14 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Taurayi, S. An Investigation of Natuurboerdery (Natural Farming) Approach: A ZZ2 Case Study. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Santa Cruz, J.; Calbucheo, D.; Valdebenito, S.; Cortés, J.; Gautier, C.; Amín, A.; Hernández, I.; Allendes, H.; Peñaloza, P. Inter-Day Instability in Plant Sap Composition Undermines Single-Day Diagnostics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


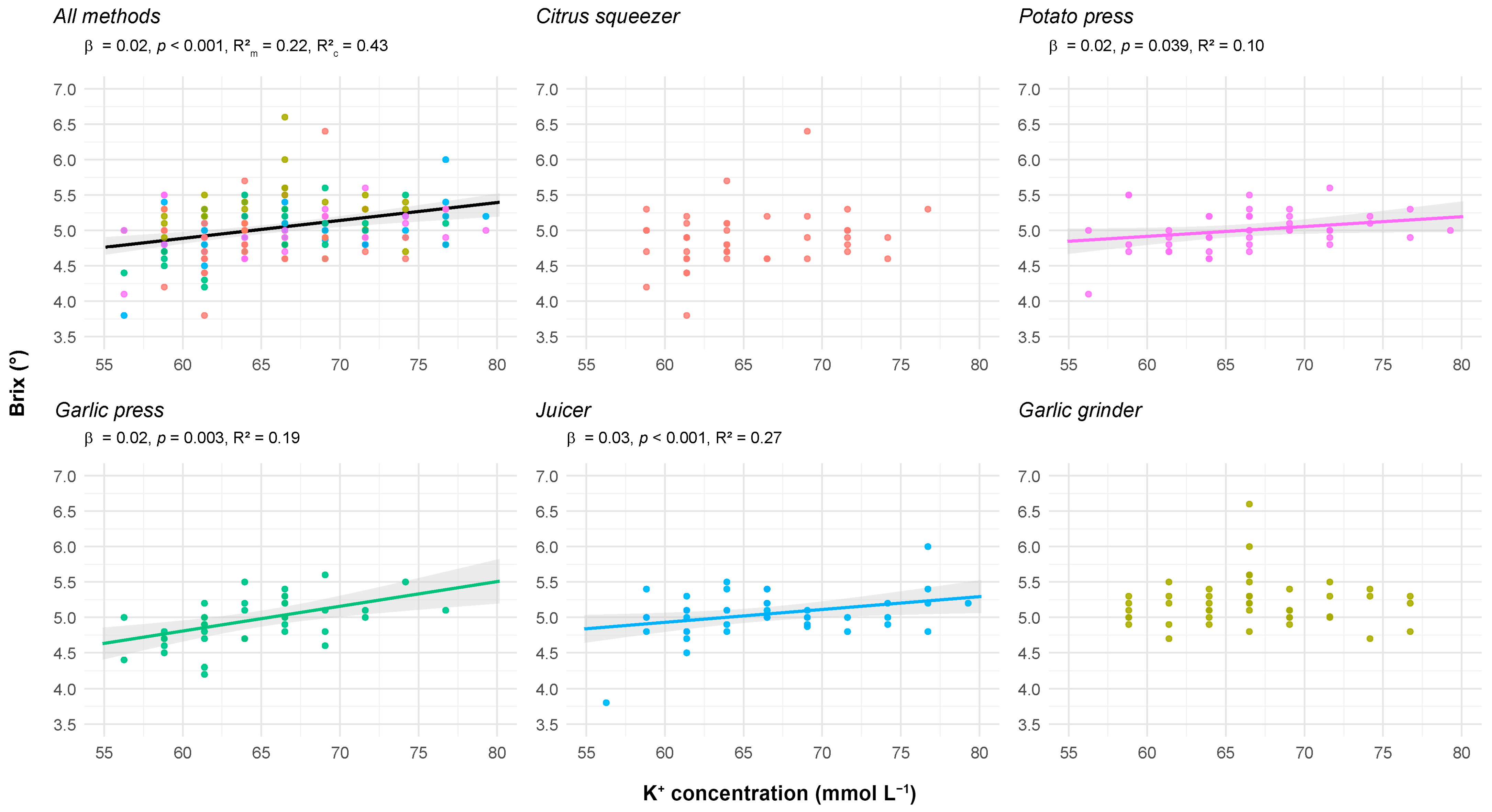

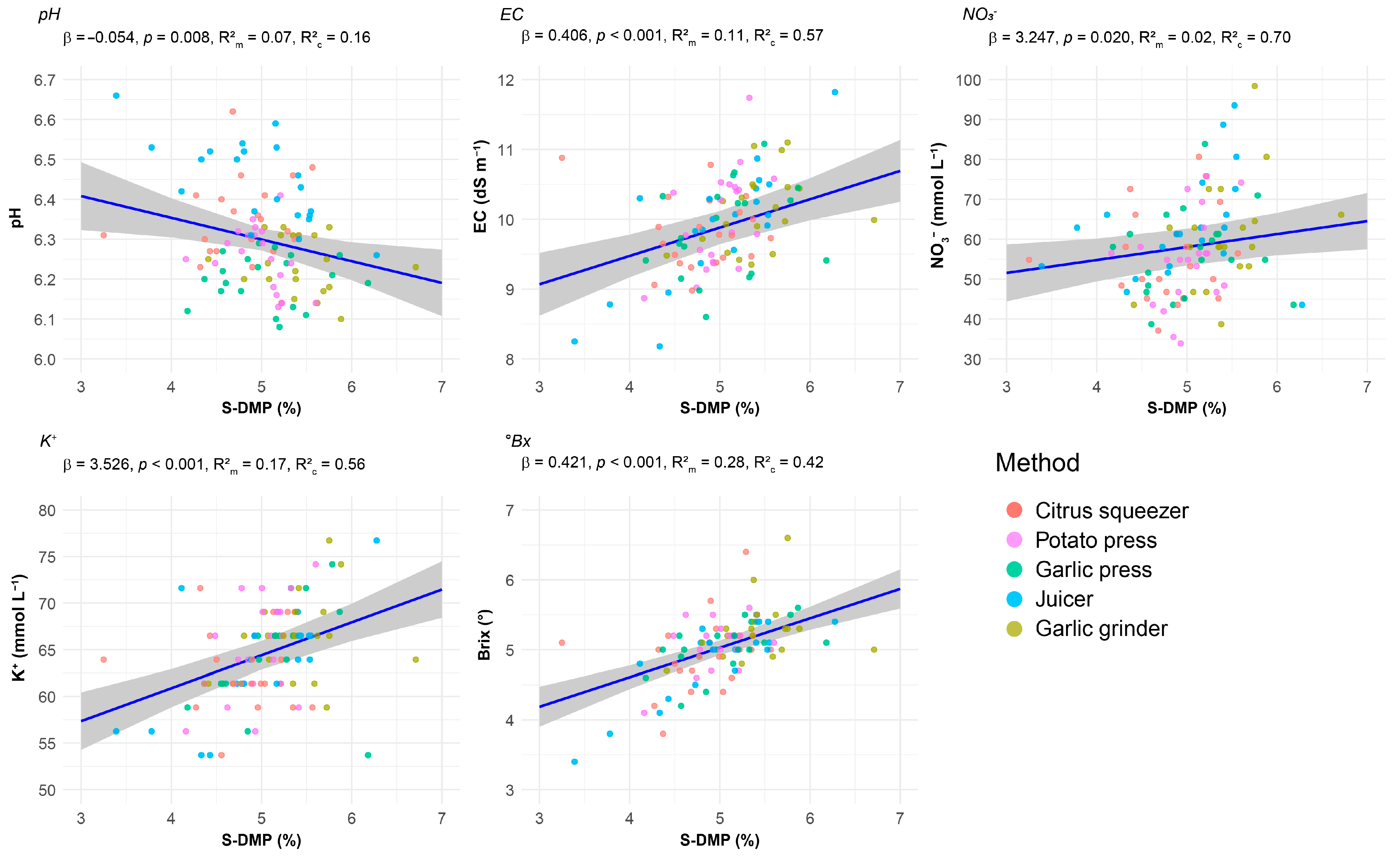
| Parameter | Method | EMM ± SE | SD | CI 95% | Range | CV (%) | Shapiro–Wilk | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Citrus squeezer | 6.31 ± 0.01 (c) | 0.09 | [6.29, 6.34] | [6.14, 6.62] | 1.48 (e) | 0.196 | 0.638 | 3.726 |
| Potato press | 6.26 ± 0.01 (b) | 0.08 | [6.24, 6.28] | [6.10, 6.41] | 1.22 (c) | 0.581 | 0.004 | 2.192 | |
| Garlic press | 6.22 ± 0.01 (a) | 0.07 | [6.20, 6.24] | [6.08, 6.36] | 1.06 (a) | 0.261 | −0.197 | 2.428 | |
| Juicer | 6.44 ± 0.01 (d) | 0.09 | [6.42, 6.47] | [6.26, 6.66] | 1.34 (d) | 0.562 | 0.181 | 2.523 | |
| Garlic grinder | 6.24 ± 0.01 (ab) | 0.07 | [6.22, 6.26] | [6.10, 6.36] | 1.12 (b) | 0.075 | −0.089 | 1.887 | |
| Mean | 6.29 ± 0.01 | 1.24 (A) | |||||||
| EC (dS m−1) | Citrus squeezer | 9.48 ± 0.10 (a) | 0.56 | [9.31, 9.64] | [8.36, 10.88] | 5.85 (a) | 0.729 | 0.355 | 2.885 |
| Potato press | 9.58 ± 0.10 (ab) | 0.71 | [9.38, 9.79] | [7.93, 11.74] | 7.35 (d) | 0.260 | 0.267 | 3.831 | |
| Garlic press | 9.45 ± 0.10 (a) | 0.64 | [9.27, 9.64] | [8.30, 11.08] | 6.69 (c) | 0.238 | 0.493 | 2.579 | |
| Juicer | 9.65 ± 0.10 (ab) | 0.84 | [9.40, 9.89] | [6.48, 11.82] | 8.41 (e) | 0.010 | −0.918 | 6.237 | |
| Garlic grinder | 9.74 ± 0.10 (b) | 0.63 | [9.56, 9.93] | [8.22, 11.10] | 6.33 (b) | 0.849 | −0.028 | 2.990 | |
| Mean | 9.58 ± 0.10 | 6.94 (B) | |||||||
| NO3− (mmol L−1) | Citrus squeezer | 54.67 ± 1.60 (a) | 10.05 | [51.75, 57.59] | [33.87, 80.65] | 18.05 (b) | 0.059 | 0.617 | 3.497 |
| Potato press | 56.65 ± 1.60 (ab) | 10.09 | [53.72, 59.58] | [33.87, 85.48] | 17.46 (a) | 0.427 | 0.203 | 3.634 | |
| Garlic press | 59.03 ± 1.60 (b) | 10.88 | [56.14, 62.53] | [38.71, 83.87] | 18.13 (b) | 0.292 | 0.331 | 2.799 | |
| Juicer | 65.22 ± 1.60 (c) | 12.45 | [61.61, 68.84] | [37.10, 93.55] | 18.81 (c) | 0.700 | 0.198 | 2.894 | |
| Garlic grinder | 65.26 ± 1.60 (c) | 11.58 | [61.89, 68.62] | [38.71, 98.39] | 17.49 (a) | 0.697 | 0.230 | 3.522 | |
| Mean | 60.17 ± 1.60 | 17.98 (C) | |||||||
| K+ (mmol L−1) | Citrus squeezer | 64.62 ± 0.87 (a) | 5.33 | [63.02, 66.22] | [53.71, 76.72] | 8.13 (b) | 0.028 | 0.297 | 2.581 |
| Potato press | 66.16 ± 0.87 (a) | 5.76 | [64.42, 67.89] | [53.71, 79.28] | 8.61 (c) | 0.616 | 0.083 | 2.661 | |
| Garlic press | 64.43 ± 0.87 (a) | 6.48 | [62.55, 66.49] | [53.71, 81.84] | 9.95 (e) | 0.025 | 0.706 | 3.709 | |
| Juicer | 65.76 ± 0.87 (a) | 6.47 | [63.81, 67.70] | [53.71, 79.28] | 9.75 (d) | 0.179 | 0.244 | 2.393 | |
| Garlic grinder | 66.50 ± 0.87 (a) | 5.14 | [64.95, 68.04] | [58.82, 76.73] | 7.56 (a) | 0.031 | 0.288 | 2.349 | |
| Mean | 65.50 ± 0.87 | 8.74 (B) | |||||||
| Bx (°) | Citrus squeezer | 4.87 ± 0.05 (a) | 0.39 | [4.76, 4.99] | [3.80, 6.40] | 7.75 (d) | <0.001 | 0.964 | 7.539 |
| Potato press | 4.96 ± 0.05 (a) | 0.32 | [4.84, 5.04] | [4.00, 5.60] | 6.42 (c) | 0.029 | −0.630 | 4.136 | |
| Garlic press | 4.96 ± 0.05 (a) | 0.30 | [4.86, 5.04] | [4.20, 5.60] | 6.04 (a) | 0.675 | −0.217 | 2.992 | |
| Juicer | 4.97 ± 0.05 (a) | 0.42 | [4.85, 5.09] | [3.40, 6.00] | 8.26 (e) | <0.001 | −1.385 | 6.994 | |
| Garlic grinder | 5.19 ± 0.05 (b) | 0.33 | [5.09, 5.28] | [4.70, 6.60] | 6.23 (b) | <0.001 | 1.723 | 8.303 | |
| Mean | 4.99 ± 0.05 | 6.94 (B) |
| Method | Yield (µL g−1) | S-DMP (%) | S-DMC (mg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus squeezer | 72.58 ± 8.02 (a) | 4.79 ± 0.12 (a) | 56.52 ± 1.77 (a) |
| Potato press | 138.91 ± 8.02 (b) | 5.00 ± 0.12 (ab) | 59.65 ± 1.77 (ab) |
| Garlic press | 234.63 ± 8.02 (c) | 5.04 ± 0.12 (ab) | 58.05 ± 1.77 (ab) |
| Juicer | 213.22 ± 8.02 (c) | 4.96 ± 0.12 (ab) | 60.76 ± 1.77 (ab) |
| Garlic grinder | 236.45 ± 8.02 (c) | 5.30 ± 0.12 (b) | 64.10 ± 1.77 (b) |
| Mean | 179.16 ± 5.46 | 5.02 ± 0.06 | 59.28 ± 1.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santa Cruz, J.; Calbucheo, D.; Valdebenito, S.; Cáceres, C.; Castillo, P.; Aguilar, M.; Hernández, I.; Allendes, H.; Vidal, K.; Peñaloza, P. Crushed, Squeezed, or Pressed? How Extraction Methods Influence Sap Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112572
Santa Cruz J, Calbucheo D, Valdebenito S, Cáceres C, Castillo P, Aguilar M, Hernández I, Allendes H, Vidal K, Peñaloza P. Crushed, Squeezed, or Pressed? How Extraction Methods Influence Sap Analysis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanta Cruz, Javier, Diego Calbucheo, Samuel Valdebenito, Camila Cáceres, Priscila Castillo, Marcelo Aguilar, Ignacia Hernández, Hernán Allendes, Kooichi Vidal, and Patricia Peñaloza. 2025. "Crushed, Squeezed, or Pressed? How Extraction Methods Influence Sap Analysis" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112572
APA StyleSanta Cruz, J., Calbucheo, D., Valdebenito, S., Cáceres, C., Castillo, P., Aguilar, M., Hernández, I., Allendes, H., Vidal, K., & Peñaloza, P. (2025). Crushed, Squeezed, or Pressed? How Extraction Methods Influence Sap Analysis. Agronomy, 15(11), 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112572







