Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Maize Planting in Hunan Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
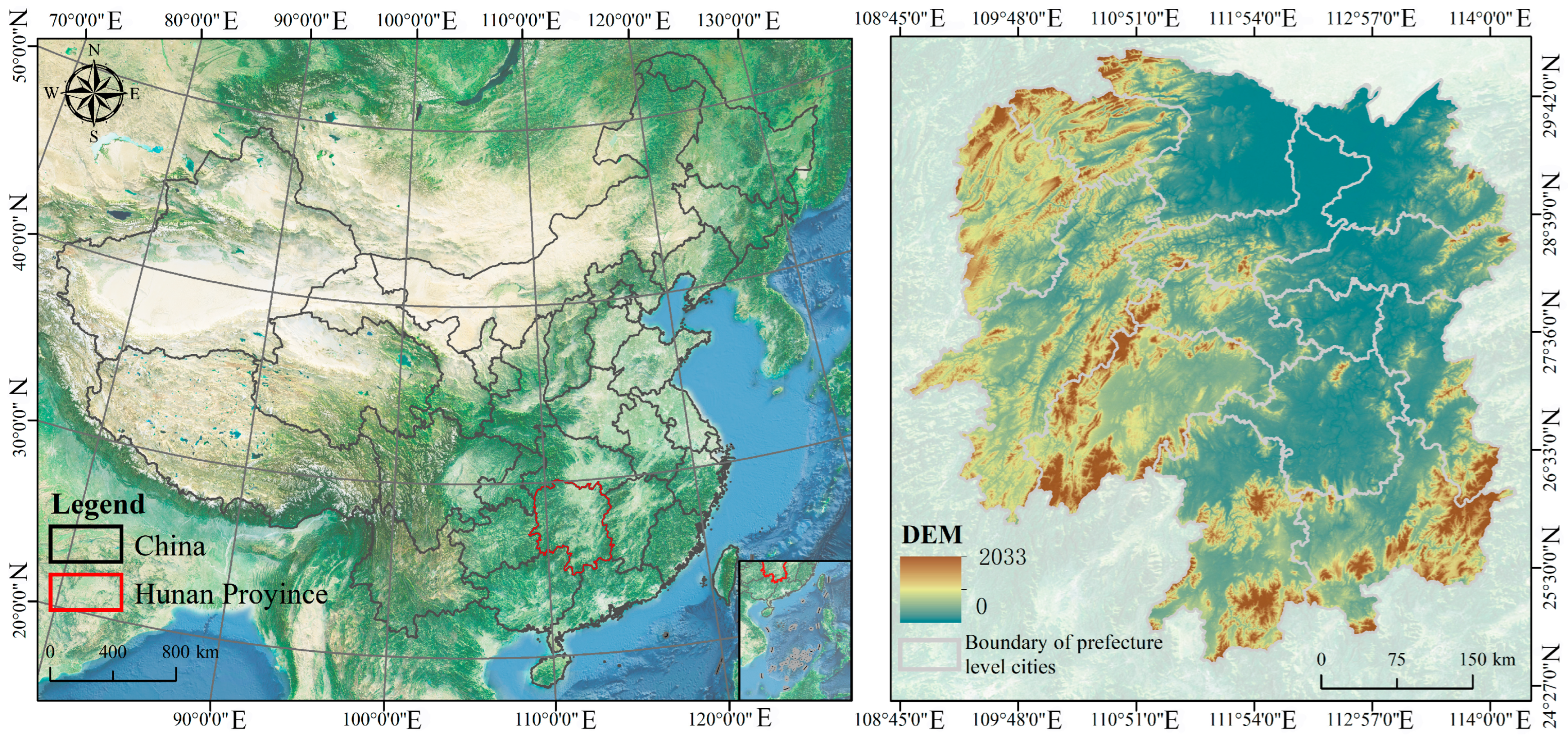
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
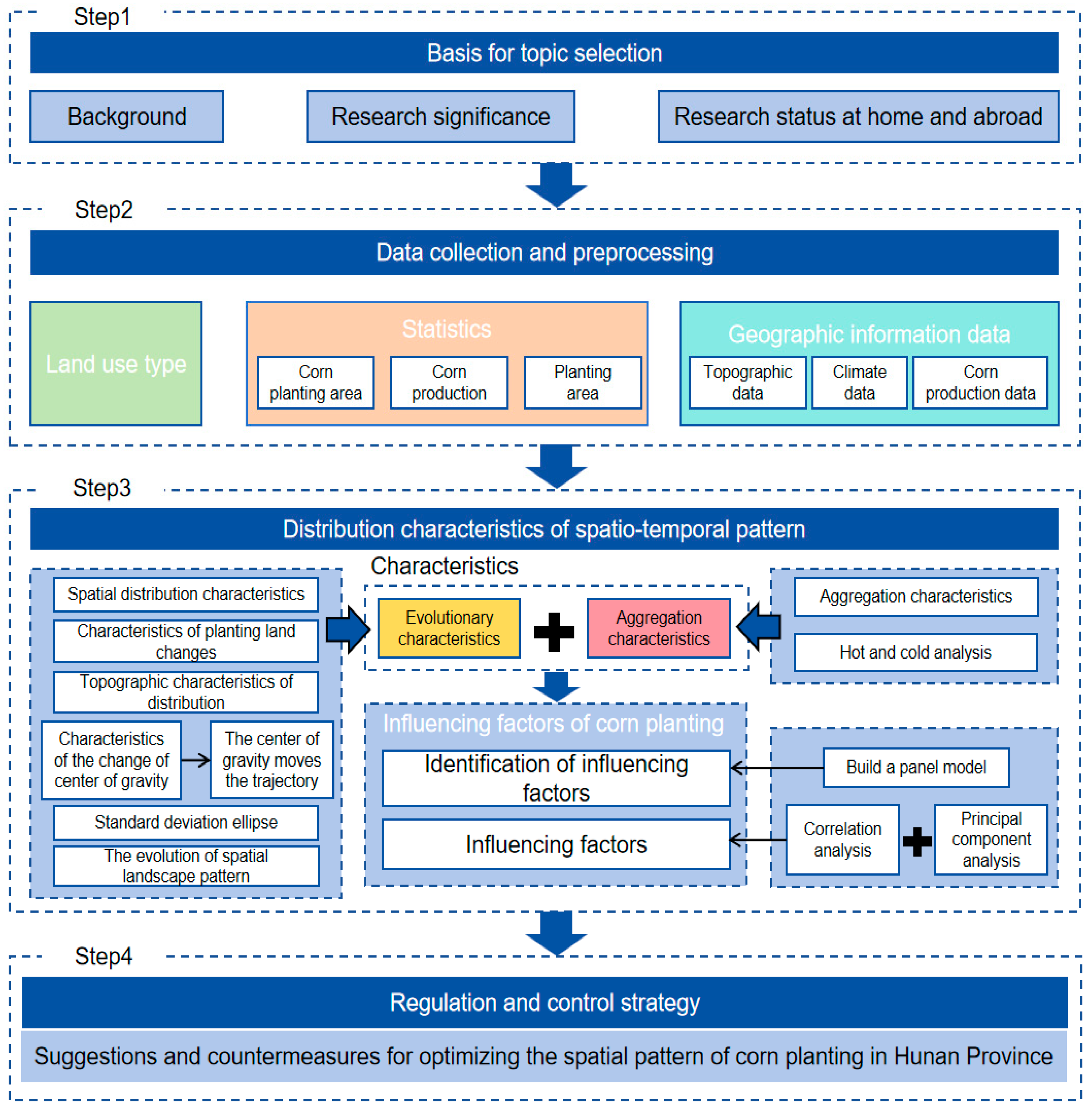
2.2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Research Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Evolution Characteristics of Maize Planting Spatial Pattern
3.1.1. Overview of Maize Planting in Hunan Province
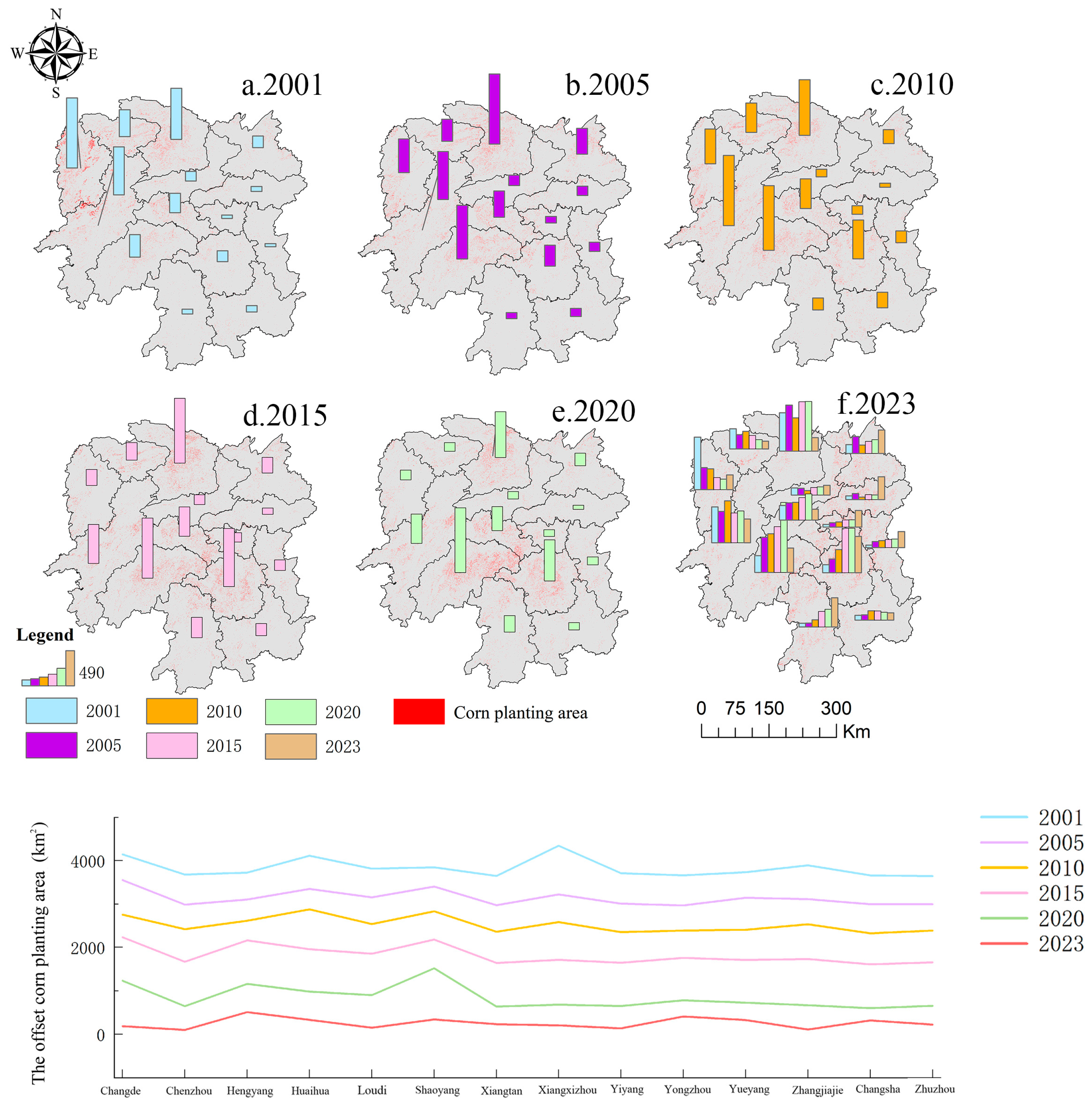
3.1.2. Characteristics of Change in Maize Planting Area
3.1.3. Topographic Distribution Characteristics of Maize Planting
3.1.4. The Standard Deviation Ellipse and Center of Gravity Shift in Maize Planting
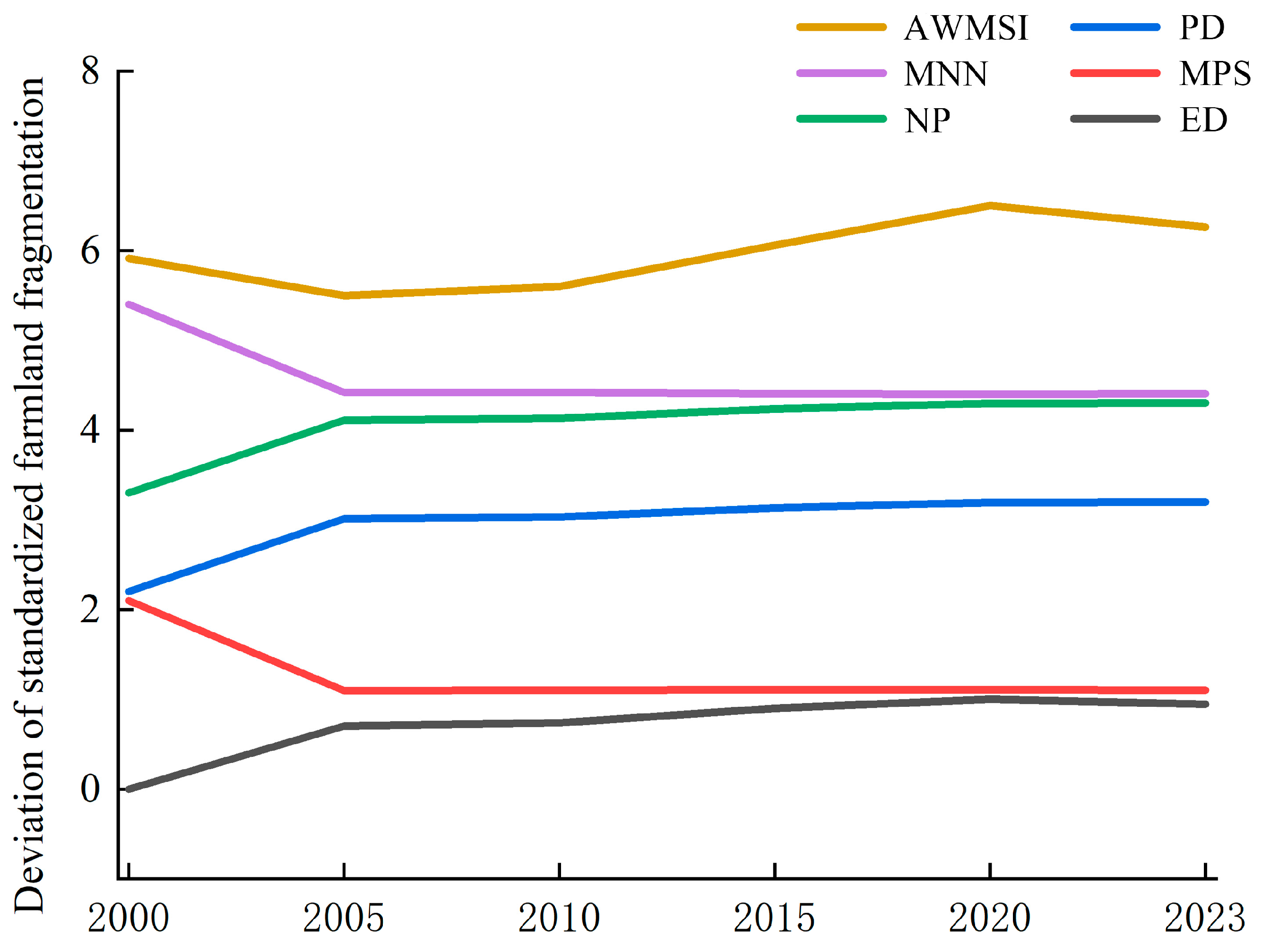
3.1.5. Changes in the Landscape Pattern of Maize Planting
3.2. Analysis of Planting Space Agglomeration Characteristics
3.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
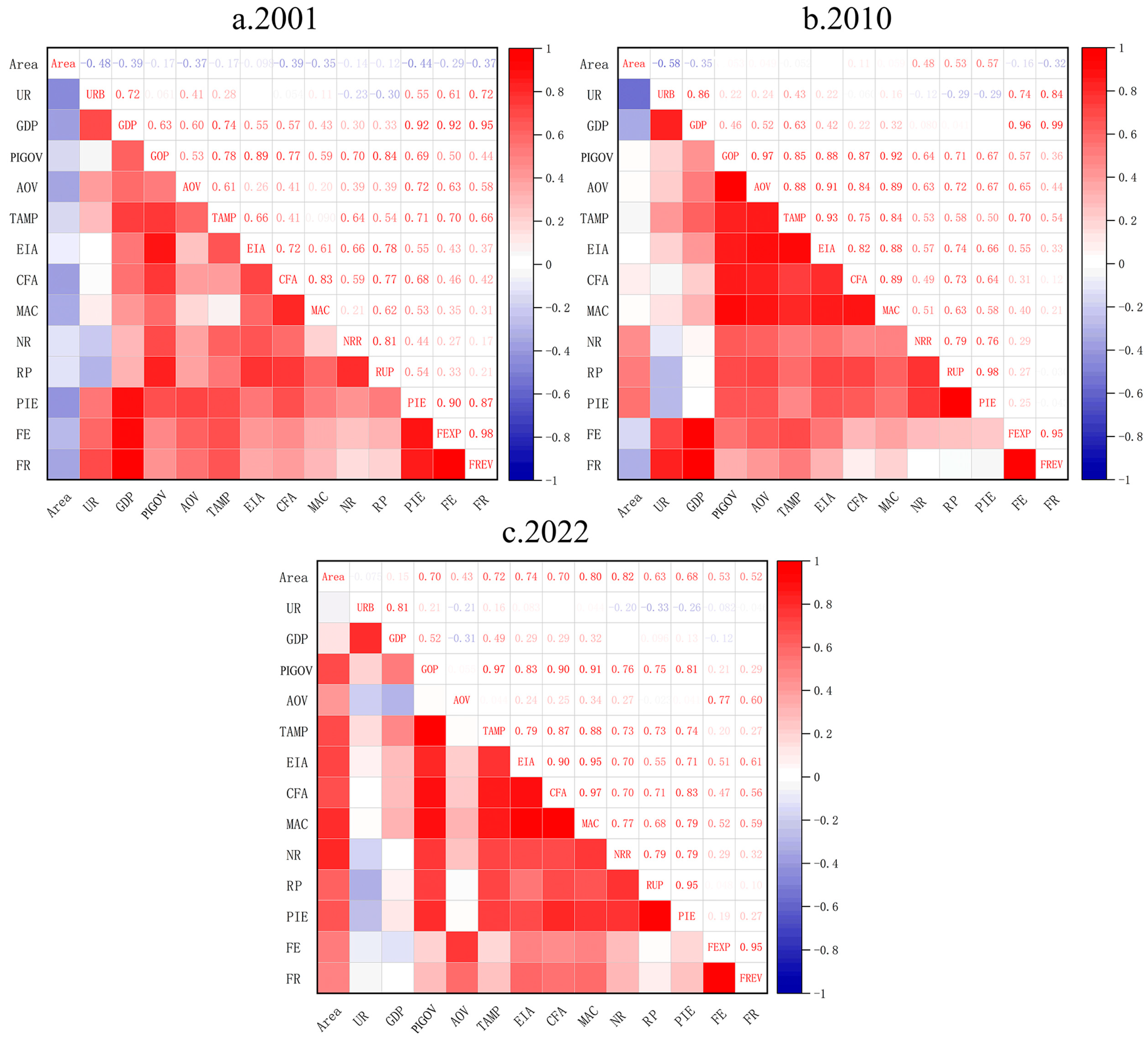
3.3.1. Influencing Factors Panel Analysis
3.3.2. Analysis of Driving Factors of Crop Production Pattern Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Deciphering the 2023 Maize Planting Decline in Hunan’s Core Regions
4.2. Discussion on Influencing Factors
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
4.4. Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. World Food and Agriculture—Statistical Yearbook 2021; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Pei, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Soil organic carbon depletion in global Mollisols regions and restoration by management practices: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhou, G.; Lü, X.; Zhou, M. Climatic suitability and spatial distribution for summer maize cultivation in China at 1.5 and 2.0 °C global warming. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y. How global warming alters future maize yield and water use efficiency in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 160, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillerberg, T.; Tian, D. Changes in crop failures and their predictions with agroclimatic conditions: Analysis based on earth observations and machine learning over global croplands. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 340, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Xie, R.; Wang, K.; Ming, B.; Liu, G.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Quantifying maize grain yield losses caused by climate change based on extensive field data across China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G. Spatial-temporal Pattern Evolution and Matching Analysis of Maize Production and Consumption in China. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, B.G.; Messina, J.P.; Lin, Z.; Snapp, S.S. Crop climate suitability mapping on the cloud: A geovisualization application for sustainable agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpoti, K.; Kabo-bah, A.T.; Zwart, S.J. Agricultural land suitability analysis: State-of-the-art and outlooks for integration of climate change analysis. Agric. Syst. 2019, 173, 172–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-J.; Wu, W.-B.; Yang, P.; Zhou, Q.-B.; Chen, Z.-X. Recent Progresses in Monitoring Crop Spatial Patterns by Using Remote Sensing Technologies. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2010, 43, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, J.A.; Müller, C.; Minoli, S.; Elliott, J.; Folberth, C.; Gardner, C.; Hank, T.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Jägermeyr, J.; Jones, C.D.; et al. Agricultural breadbaskets shift poleward given adaptive farmer behavior under climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guga, S.; Bole, Y.; Riao, D.; Bilige, S.; Wei, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z.; Liu, X. The challenge of chilling injury amid shifting maize planting boundaries: A case study of Northeast China. Agric. Syst. 2025, 222, 104166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q.-Z.; Zhou, H. Empirical Analysis of Corn Spatial Distribution Variation in China. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. National-scale 10 m annual maize maps for China and the contiguous United States using a robust index from Sentinel-2 time series. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 221, 109018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Du, L. A dynamic correction method for the influence of SAR observation incidence angle based on the corn crop phenology information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 46, 2909–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Peng, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y. Planting suitability of China’s main grain crops under future climate change. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, D.; Bai, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, D. Future projection for climate suitability of summer maize in the North China Plain. Agriculture 2022, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, R.; Shrestha, S.; Mohanasundaram, S.; Loc, H.H. Climate change-induced drought and implications on maize cultivation area in the upper Nan River Basin, Thailand. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 628–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhang, J.; Meng, L. Assessing the Spatial–Temporal Pattern of Spring Maize Drought in Northeast China Using an Optimised Remote Sensing Index. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lyu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Liu, L.; Song, K. Maize yield estimation in Northeast China’s black soil region using a deep learning model with attention mechanism and remote sensing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wan, W.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Lv, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z. Study on climate suitability for maize and technical implementation strategies under conservation tillage in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 249, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Wu, B. Spatial-temporal characteristics of spring maize drought in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water 2023, 15, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Yang, B.; Shen, Y.; Yue, S.; Li, S. Carbon footprint, yield and economic performance assessment of different mulching strategies in a semi-arid spring maize system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; You, L.; Tang, H. Spatiotemporal changes of maize sown area and yield in Northeast China between 1980 and 2010 using spatial production allocation model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Hannaford, J.; Su, Z.; Barker, L.; Qu, Y. Drought risk assessment of spring maize based on APSIM crop model in Liaoning province, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 45, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, F.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Tong, Z.; Liu, X. Assessment of waterlogging hazard during maize growth stage in the Songliao plain based on daily scale SPEI and SMAI. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 304, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Wang, H.-N.; Han, X.-D.; Zhen, F.-T. Comparative advantage and the spatial distribution of China’s corn producing areas: Based on the data of 18 provinces from 1996 to 2015. Res. Agric. Mod. 2017, 38, 921–929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Niu, H. Spatio-temporal variations in the areas suitable for the cultivation of rice and maize in China under future climate scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B. Study on Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Winter Wheat Planting in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.-J.; Wang, W.-B.; Cao, Y.-Q.; Sun, X.-G.; Song, S.-H.; Wang, C.-L.; Zhang, L.-J. Response of Physiological Characteristics of Different Drought-tolerant Soybean Varieties to Different Rainfall Climatic Conditions. Soybean Sci. 2018, 37, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Cai, S.-S.; Wang, W.; Ding, J.-L.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.-M.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Path Analysis on Black Soil Fertility via Soybean Yield and Quality. Soybean Sci. 2021, 40, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Cui, Y.; Meng, L.; Wu, D.; Qian, L.; Bao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, H. Effects of terrain on soybean yields in rolling hilly black soil areas. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Deng, F. Mapping Maize Cultivated Area Combining MODIS EVI Time Series and the Spatial Variations of Phenology over Huanghuaihai Plain. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounsevell, M.-D.; Pedroli, B.; Erb, K.-H.; Gramberger, M.; Busck, A.-G.; Haberl, H.; Kristensen, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lavorel, S.; Lindner, M. Challenges for land system science. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; McLaughlin, N.-B.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, A. Effects of tillage practices on environment, energy, and economy of maize production in Northeast China. Agric. Syst. 2024, 215, 103872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Yin, M.; Zhou, C. Effects of different ridge-furrow mulching systems on yield and water use efficiency of summer maize in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.V.; Aditya, K.S.; Anbukkani, P.; Kumar, P.; Kar, A. Spatial Diversity in Indian Wheat and its Determinants. Agric. Econ. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, H. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Carbon Emission Efficiency and Influencing Factors in the Five Major Maize Producing Areas of China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Jian, D.; Long, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y. Evolution characteristics and mechanism of major crops production patterns in Guangxi. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 2322–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Grain Production Resilience in China. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.-R.; Zhang, J.-Y. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of production of major oil crops in China from 2000 to 2020. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 37, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wen, Q.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Driving Factors of Grain Production in Jiangsu Province. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; He, X. Influencing Factors and Optimization Countermeasures of Spatial and Temporal Evolution Patterns of Soybean Production in China. Soybean Sci. 2024, 43, 782–792. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S. Study on spatial-temporal changes and influencing factors of grain crops in rocky desertification area of Southwest China. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2024, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.-X.; Pei, T.-T.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Q.-Q.; Xie, B.-P.; Wu, H.-W. Spatial-Temporal Variation and Driving Factors of Grassland NDVI in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 2001 to 2020. Acta Agric. Sin. 2022, 30, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Chu, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.-H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wang, T.-W.; Cai, C.-F. Spatial heterogeneity and determinants of soybean yield in Northeast China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Chen, X.; Shi, L. On factors influencing the acreage of staple crops in China: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2024, 42, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Dong, X.; Peng, H.; Liu, H.; Yu, Z. Production efficiency of soybean—Maize relay strip intercropping system and influencing factors—Based on the questionnaire of Huang—Huai—Hai, Southwest and Northwest China. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. 2024, 39, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Song, N. Evolution of Crop Planting Structure in Traditional Agricultural Areas and Its Influence Factors: A Case Study in Alar Reclamation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; Ladet, S.; Coqué, N.; Gibon, A. Agricultural land-use change and its drivers in mountain landscapes: A case study in the Pyrenees. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 114, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.J. Evolution Path Analysis of Economic Gravity Center and Air Pollutants Gravity Center in Shaanxi Province. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 361, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, D.; He, W.; Xia, J.; Jin, H.; Lou, Y. Spatio-temporal distribution and evolution characteristics of slope farmland resources in Yunnan from 1980 to 2015. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, Y. Research on the temporal and spatial changes of crop planting landscape and fragmentation—Taking Yutian county in Tangshan as an example. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2021, 46, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z. On Potential and Model of Rural Residential Lands Consolidation Based on Cold-Hot Spot Analysis. J. Southwest China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 47, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Tan, X.; Tan, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Evolution of Crop Planting Structure in Traditional Agricultural Areas and Its Influence Factors: A Case Study in Hunan Province. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Xiao, M.; Liu, Z. Spatio-temporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Landscape Fragmentation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2025, 34, 461–473. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.; Deng, Y.; Hai, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, W. Characterization of spatio-temporal evolution of grain production and identification of its heterogeneity drivers in Sichuan Province based on Geodetector and GWR models. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1561910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L. A Study on the Spatial and Temporal Variation of Crop Cultivation Scale and Driving Forces in Zhejiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Shen, Y.; Stricevic, R.; Pei, H.; Sun, H.; Amiri, E.; Rio, S. Evaluation of the FAO AquaCrop model for winter wheat on the North China Plain under deficit irrigation from field experiment to regional yield simulation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
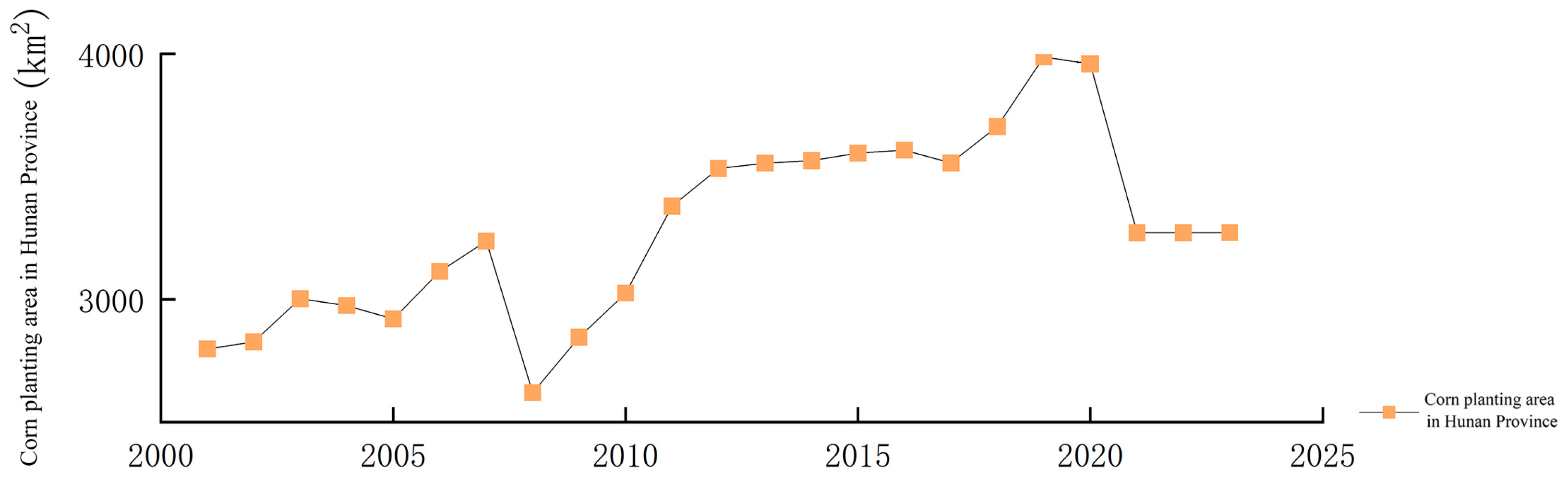
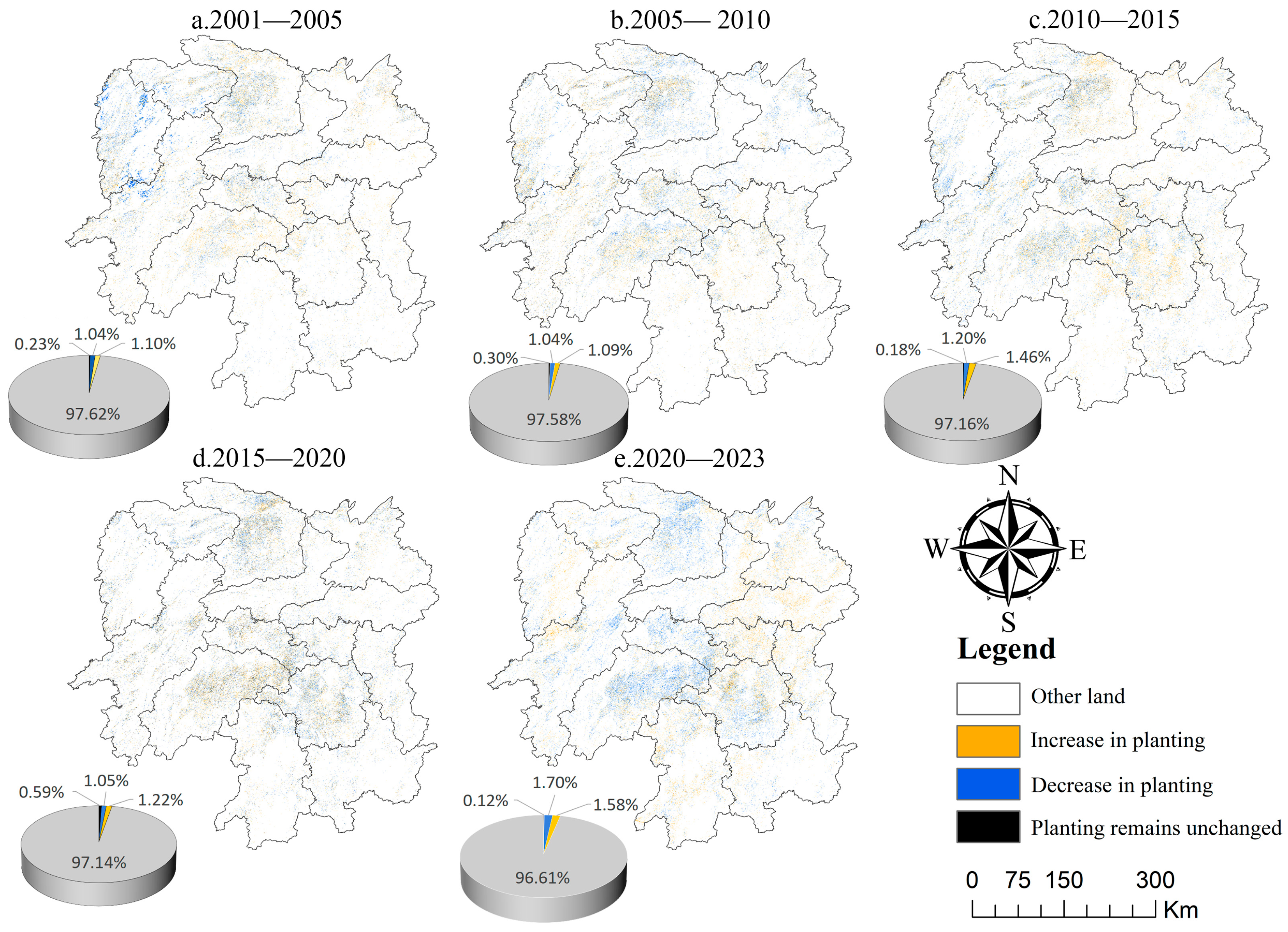
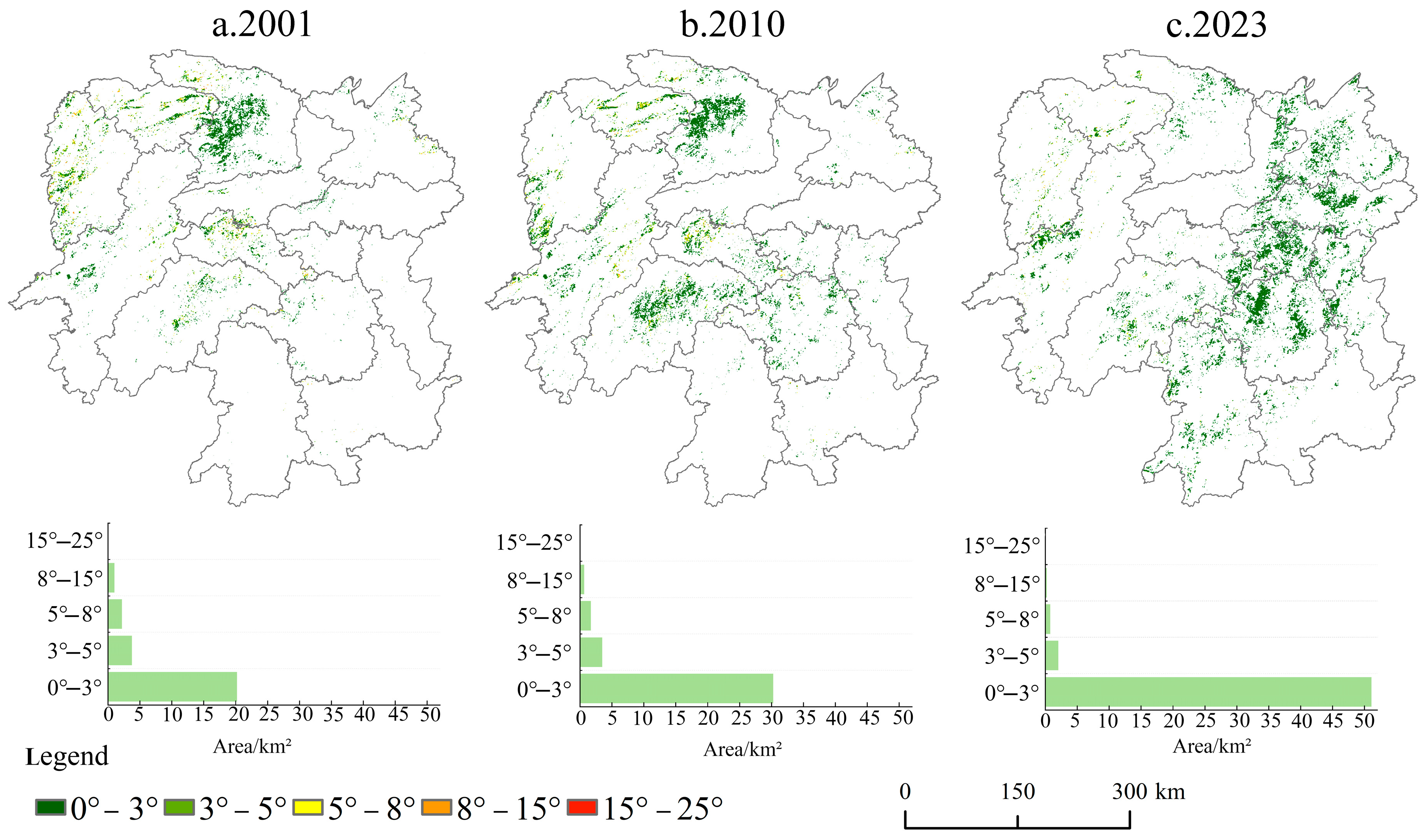


| Year | Planting Area (km2) | Year | The Planting Area Has Increased | The Planting Area Is Reduced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In 2001 | 2798.35 | 2001–2005 | 2408.97 | 2286.61 |
| In 2005 | 2920.71 | 2005–2010 | 2380.06 | 2274.74 |
| In 2010 | 3026.03 | 2010–2015 | 3194.80 | 2624.59 |
| In 2015 | 3596.24 | 2015–2020 | 2661.47 | 2296.55 |
| In 2020 | 3959.11 | 2020–2023 | 3059.27 | 3282.63 |
| In 2023 | 3272.56 |
| Year | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Place | Timing Stage | Distance Traveled (km) | Direction of Movement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 111.293247 | 28.165704 | Loudi City | 2001–2005 | 16.88 | Southeast |
| 2005 | 111.432507 | 28.07655 | Loudi City | 2005–2010 | 30.43 | Southwest |
| 2010 | 111.382724 | 27.806423 | Loudi City | 2010–2015 | 30.20 | Southeast |
| 2015 | 111.68896 | 27.786867 | Loudi City | 2015–2020 | 5.88 | Southeast |
| 2020 | 111.713857 | 27.738761 | Loudi City | 2020–2023 | 24.35 | Southeast |
| 2023 | 111.956328 | 27.695455 | Loudi City | 2001–2023 | 83.53 | Southeast |
| Evaluation Elements | Index | In 2001 | In 2005 | In 2010 | In 2015 | In 2020 | In 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area edge indicator | ED (km/km2) | 0.7689 | 3.1729 | 3.2908 | 3.8564 | 4.1928 | 4.0228 |
| MPS (km2/patch) | 50.0672 | 3.2185 | 3.2517 | 3.4806 | 3.6028 | 3.3761 | |
| Convergence indicators | PD (patch) | 0.0257 | 0.4116 | 0.4227 | 0.4709 | 0.4997 | 0.5021 |
| NP (patch/km2) | 5474 | 87,281 | 89,632 | 99,851 | 106,038 | 106,479 | |
| MNN (m) | 2582.748 | 577.179 | 572.9158 | 544.4744 | 536.6999 | 541.6392 | |
| Shape indicators | AWMSI (%) | 1.1922 | 1.156 | 1.1649 | 1.2053 | 1.244 | 1.2231 |
| 2001 | Commonality (Common Factor Variance) | 2010 | Commonality (Common Factor Variance) | 2022 | Commonality (Common Factor Variance) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Factor | Load Factor | Load Factor | |||||||
| Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 | Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 | Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 | ||||
| UR | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 0.89 | −0.01 | −0.51 | 0.93 |
| GDP | 0.89 | 0.42 | 0.97 | 0.58 | 0.8 | 0.97 | 0.3 | −0.68 | 0.92 |
| PIGOV | 0.87 | −0.38 | 0.91 | 0.95 | −0.1 | 0.92 | 0.93 | −0.33 | 0.98 |
| AOV | 0.69 | 0.23 | 0.6 | 0.97 | −0.05 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 0.8 | 0.74 |
| TAMP | 0.82 | 0.05 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.9 | −0.32 | 0.91 |
| EIA | 0.78 | −0.44 | 0.8 | 0.94 | −0.11 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.05 | 0.87 |
| CFA | 0.79 | −0.37 | 0.9 | 0.83 | −0.32 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0 | 0.93 |
| MCA | 0.6 | −0.3 | 0.98 | 0.88 | −0.17 | 0.8 | 0.98 | 0.04 | 0.98 |
| NR | 0.62 | −0.55 | 0.86 | 0.66 | −0.41 | 0.61 | 0.83 | 0.03 | 0.79 |
| RP | 0.72 | −0.65 | 0.94 | 0.76 | −0.55 | 0.88 | 0.78 | −0.2 | 0.93 |
| PIE | 0.94 | 0.24 | 0.94 | 0.7 | −0.55 | 0.8 | 0.87 | −0.13 | 0.92 |
| FE | 0.83 | 0.46 | 0.9 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.48 | 0.76 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhu, L.; Gong, K.; Zhan, S. Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Maize Planting in Hunan Province. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102339
Xiao Q, Li X, Ma J, Zhu L, Gong K, Zhan S. Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Maize Planting in Hunan Province. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102339
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Qinhao, Xigui Li, Jingyi Ma, Liangwei Zhu, Kequan Gong, and Siting Zhan. 2025. "Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Maize Planting in Hunan Province" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102339
APA StyleXiao, Q., Li, X., Ma, J., Zhu, L., Gong, K., & Zhan, S. (2025). Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Maize Planting in Hunan Province. Agronomy, 15(10), 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102339





