Identification of Carrot Expansin Gene Family and Its Regulation of Carrot Growth and Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Extraction of Total RNA and Synthesis of cDNA
2.3. Identification of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
2.4. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
2.5. Protein Properties and Sequence Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
2.6. Chromosomal Localization, Collinearity and Selection Pressure Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
2.7. Cis-Acting Element Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
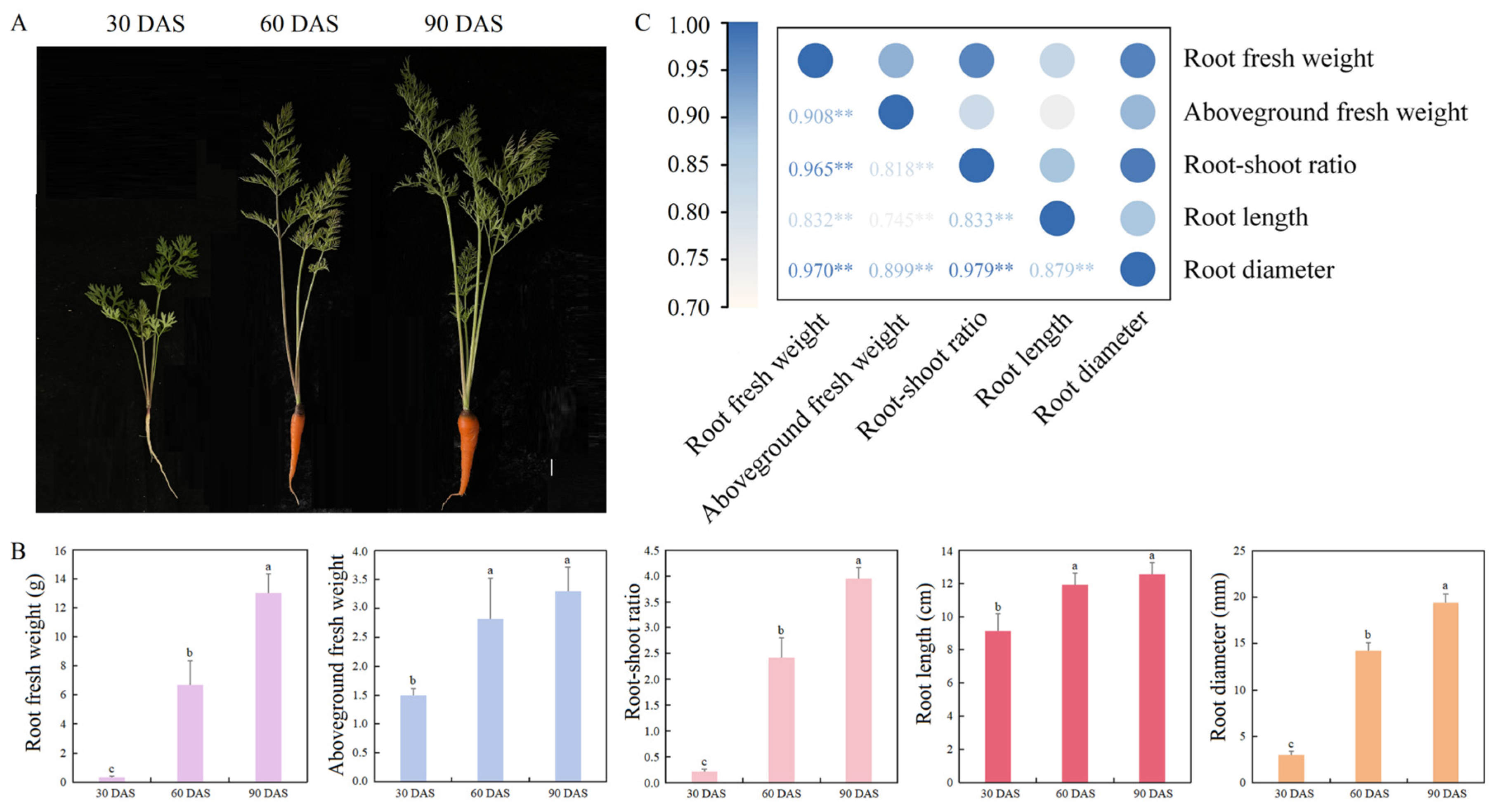
2.8. Measurement of Agronomic Characters and Correlation Analysis
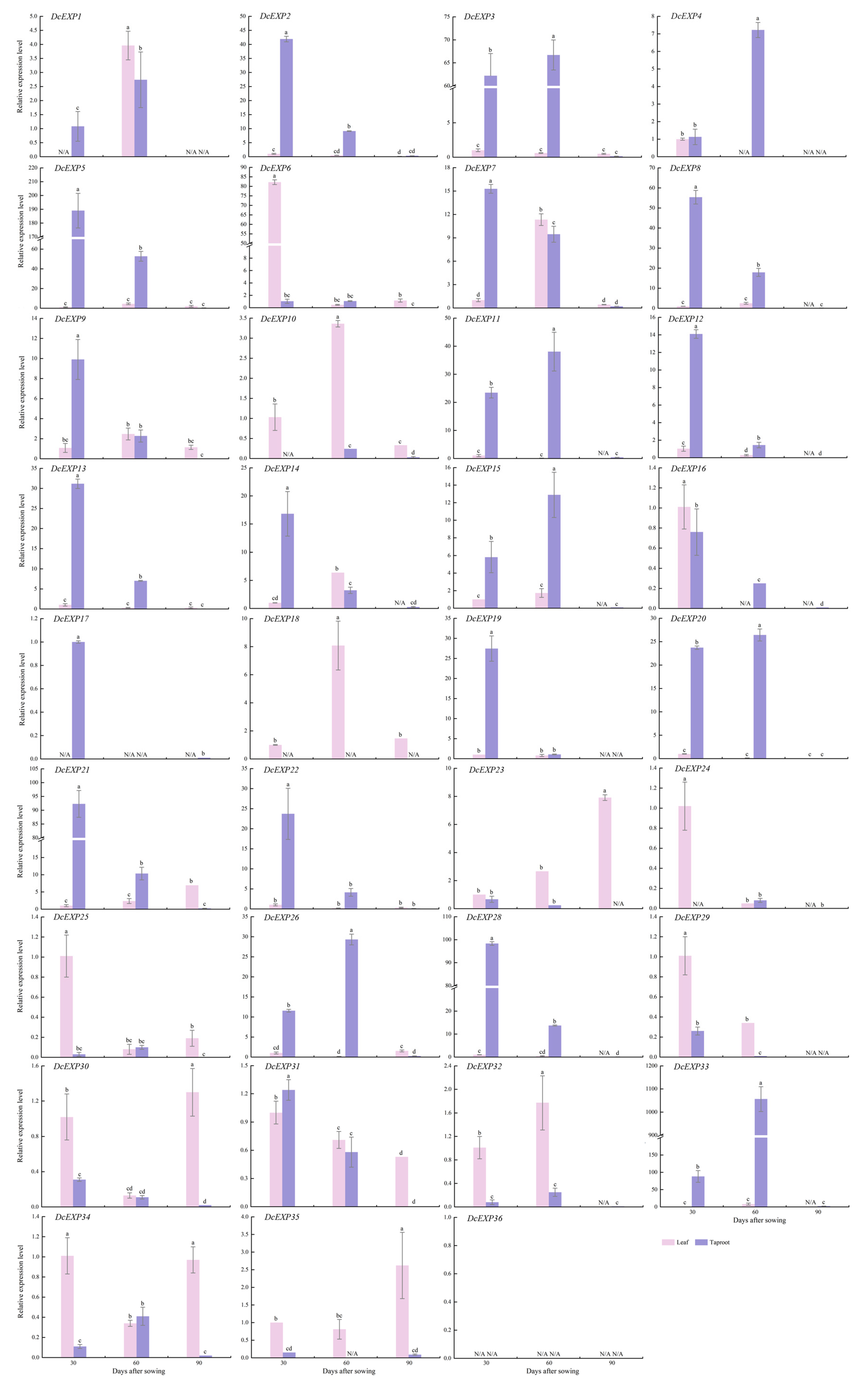
2.9. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
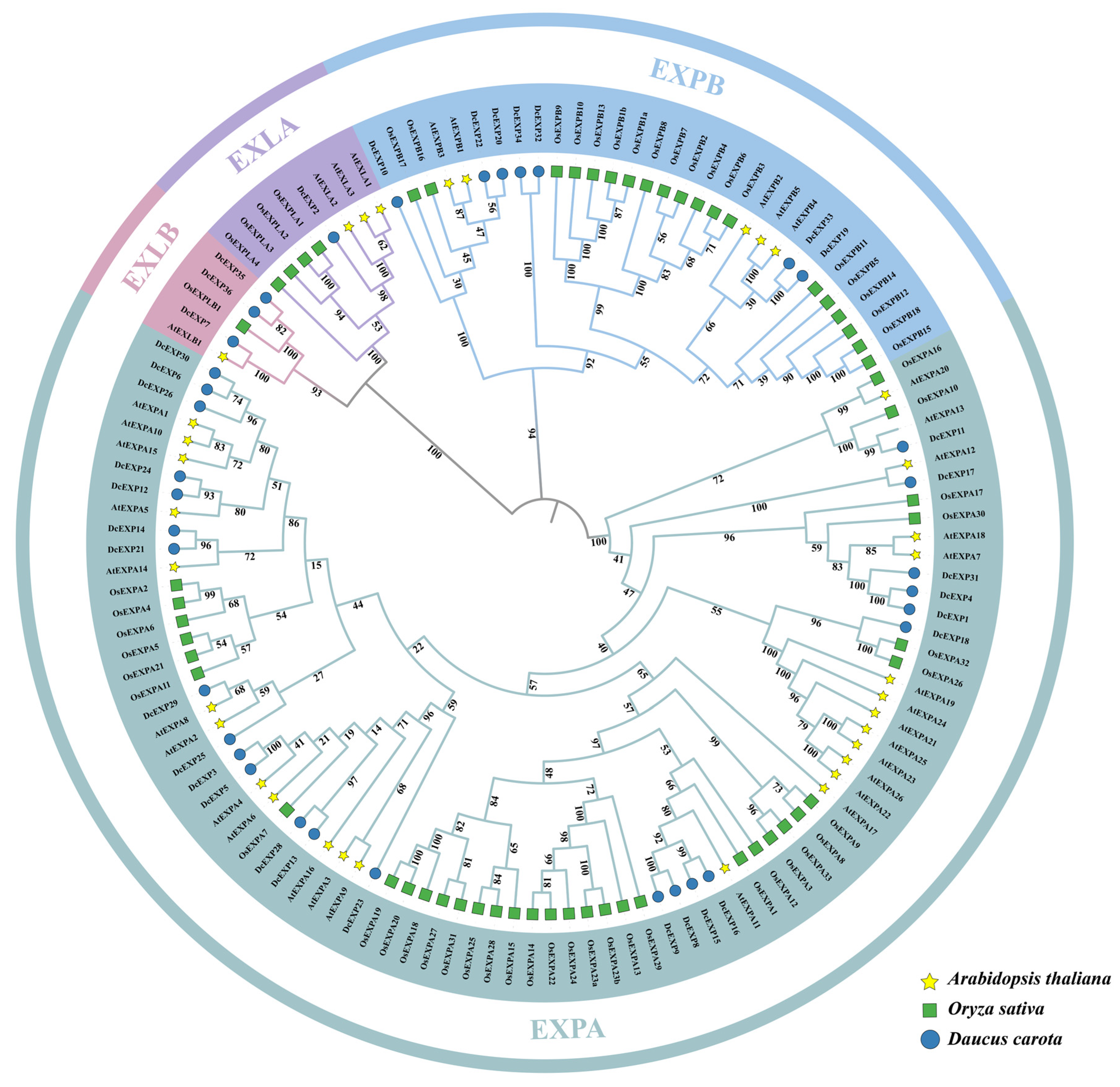
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
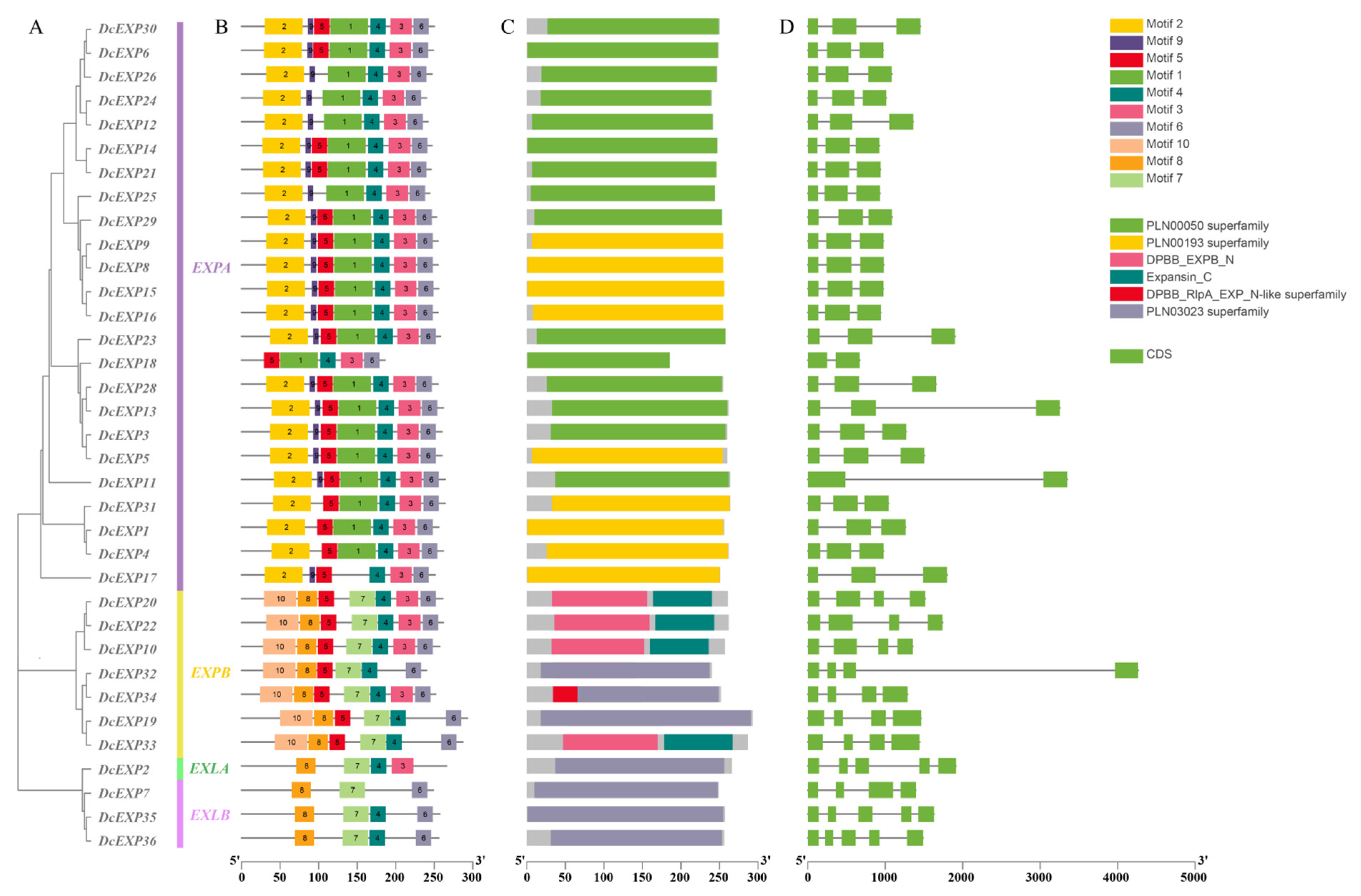
3.3. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
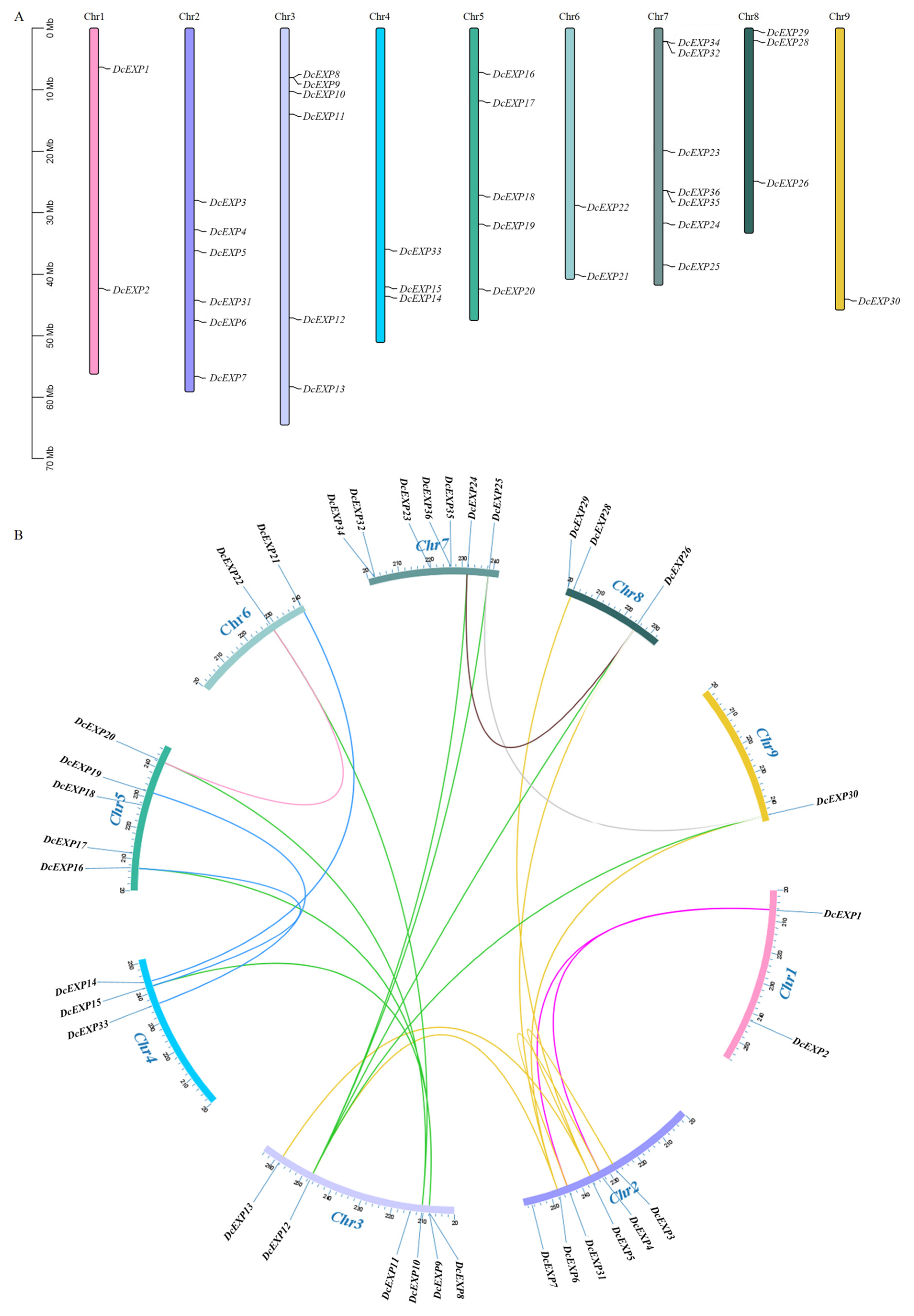
3.4. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
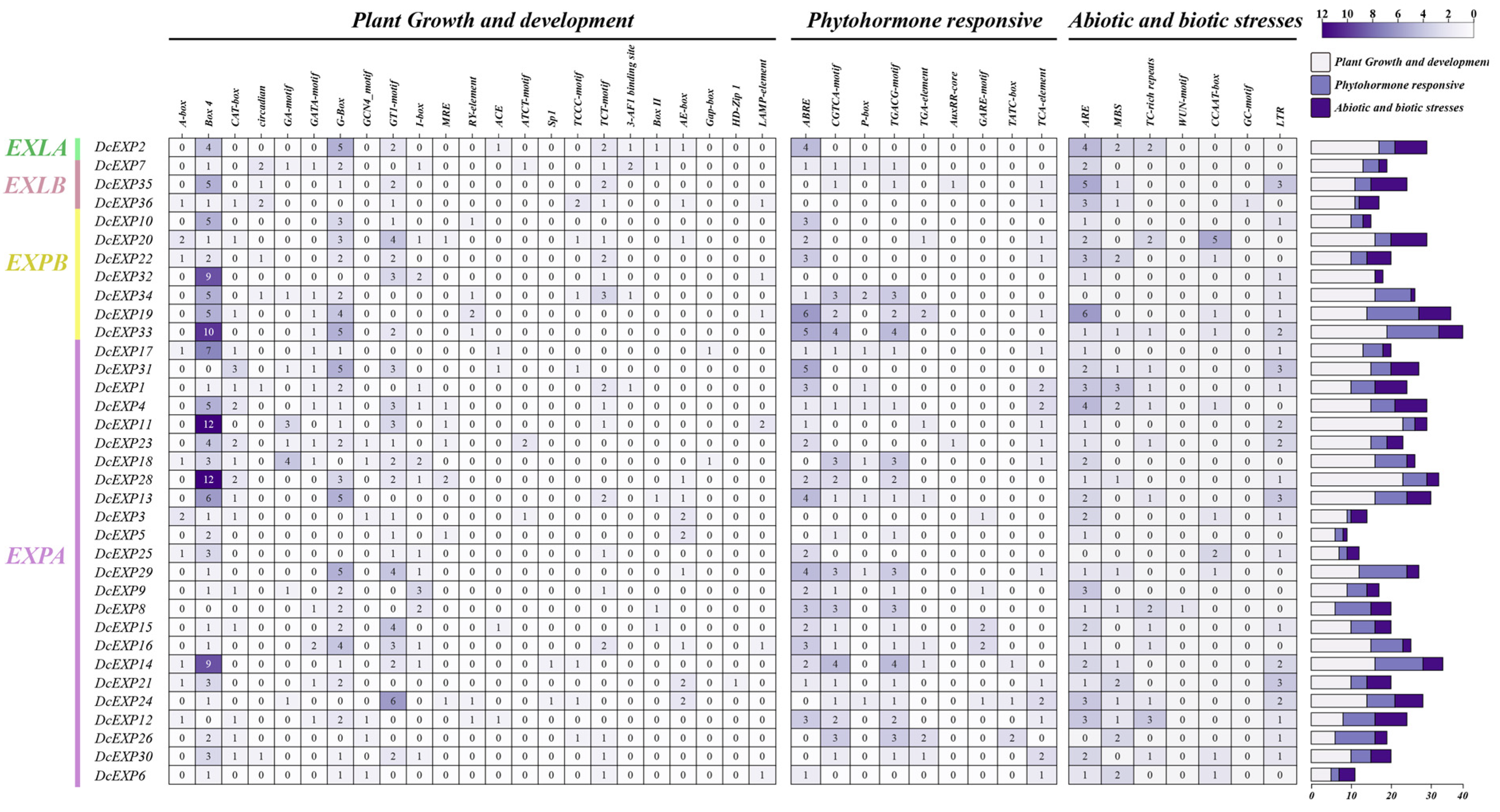
3.5. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis of the Carrot DcEXP Gene Family
3.6. Agronomic Characters and Correlation Analysis of Carrot at Different Growth and Development Stages
3.7. Temporal and Spatial Expression Pattern Analysis of DcEXP Genes in Carrot
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandenburg, W.A. Possible relationships between wild and cultivated carrots (Daucus carota L.) in the Netherlands. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1981, 29, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, F.; Hou, X.L.; Wang, G.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Tan, G.F.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Khadr, A.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in research on the carrot, animportant root vegetable in the Apiaceae family. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Jia, X.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: Novel insights into the hormonal control of carrot root development revealed by a high-throughput transcriptome. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, F.; Wang, G.L.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Genome-wide identification, expansion, and evolution analysis of homeobox genes and their expression profiles during root development in carrot. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2018, 18, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Luo, Q.; Li, T.; Meng, P.H.; Pu, Y.T.; Liu, J.X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Tan, G.F.; Xiong, A.S. Origin, evolution, breeding, and omics of Apiaceae: A family of vegetables and medicinal plants. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen-Mason, S.; Durachko, D.M.; Cosgrove, D.J. Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Meeley, R.B.; Cosgrove, D.J. Analysis and expression of the alpha-expansin and beta-expansin gene families in maize. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabirzhanova, I.B.; Sabirzhanov, B.E.; Chemeris, A.V.; Veselov, D.S.; Kudoyarova, G.R. Fast changes in expression of expansin gene and leaf extensibility in osmotically stressed maize plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.T.; Kende, H. Tissue localization of expansins in deepwater rice. Plant J. 1998, 15, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Takano, T.; Akita, S. Expression of alpha-expansin genes in young seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 2000, 211, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Song, R.; Li, X.; Shi, J. Overexpression of two cambium-abundant Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) α-expansin genes ClEXPA1 and ClEXPA2 affect growth and development in transgenic tobacco and increase the amount of cellulose in stem cell walls. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.T.; Cosgrove, D.J. Altered expression of expansin modulates leaf growth and pedicel abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9783–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.T.; Cosgrove, D.J. Regulation of root hair initiation and expansin gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, N.; Song, W. Soybean (Glycine max) expansin gene superfamily origins: Segmental and tandem duplication events followed by divergent selection among subfamilies. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Santo, S.; Vannozzi, A.; Tornielli, G.B.; Fasoli, M.; Venturini, L.; Pezzotti, M.; Zenoni, S. Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals grapevine-specific structural and functional characteristics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sansebastiano, G.P.; Fornaciari, S.; Barozzi, F.; Piro, G.; Arru, L. New insights on plant cell elongation: A role for acetylcholine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4565–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá, C.; Rose, J.K.; Bennett, A.B. Auxin regulation and spatial localization of an endo-1,4-beta-D-glucanase and a xyloglucan endotransglycosylase in expanding tomato hypocotyls. Plant J. 1997, 12, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caderas, D.; Muster, M.; Vogler, H.; Mandel, T.; Rose, J.K.; McQueen-Mason, S.; Kuhlemeier, C. Limited correlation between expansin gene expression and elongation growth rate. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arru, L.; Rognoni, S.; Poggi, A.; Loreti, E. Effect of sugars on auxin-mediated LeEXPA2 gene expression. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 55, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, J.; Carey, R.E.; Cosgrove, D.J. Genome histories clarify evolution of the expansin superfamily: New insights from the poplar genome and pine ESTs. J. Plant Res. 2006, 119, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, K.; Kanehisa, M. A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics 1992, 14, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kende, H. Expression of alpha-expansin and expansin-like genes in deepwater rice. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Enzymes and other agents that enhance cell wall extensibility. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 391–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. New genes and new biological roles for expansins. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, J.; Lee, Y.; Carey, R.E.; dePamphilis, C.; Cosgrove, D.J. Use of genomic history to improve phylogeny and understanding of births and deaths in a gene family. Plant J. 2005, 44, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Plant expansins: Diversity and interactions with plant cell walls. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, Y.; Cho, H.T.; Kende, H. Regulation of expansin gene expression affects growth and development in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Bourdais, G.; Reidy, B.; Bencivenni, C.; Massonneau, A.; Condamine, P.; Rolland, G.; Conéjéro, G.; Rogowsky, P.; Tardieu, F. Association of specific expansins with growth in maize leaves is maintained under environmental, genetic, and developmental sources of variation. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Yan, X.; Liao, H. A soybean β-expansin gene GmEXPB2 intrinsically involved in root system architecture responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J. 2011, 66, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Que, F.; Wang, G.L.; Hao, J.N.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics provide insights into the importance of expansins during root development in carrot. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, D.; Kende, H. Expansins: Ever-expanding numbers and functions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Tian, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Comparison of nine reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR in roots and leaves during five developmental stages in carrot (Daucus carota L.). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotech. 2016, 91, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in realtime RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Lin, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yao, W.; Li, Y. Origin, evolution, and diversification of the expansin family in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Marowa, P.; Kong, Y. Genome-wide identification of the expansin gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, B. Genome-wide identification and characterization of maize expansin genes expressed in endosperm. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Darley, C.P.; Ongaro, V.; Fleming, A.; Schipper, O.; Baldauf, S.L.; McQueen-Mason, S. Plant expansins are a complex multigene family with an ancient evolutionary origin. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollet, J.C.; Leroux, C.; Dardelle, F.; Lehner, A. Cell wall composition, biosynthesis and remodeling during pollen tube growth. Plants 2013, 2, 107–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Xu, J. Bioinformatics analysis of the expansin gene family in rice. Hereditas 2014, 36, 809–820. [Google Scholar]
- Lecharny, A.; Boudet, N.; Gy, I.; Aubourg, S.; Kreis, M. Introns in, introns out in plant gene families: A genomic approach of the dynamics of gene structure. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2003, 3, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ding, H. Genomic location and expression analysis of expansin gene family reveals the evolutionary and functional significance in Triticum aestivum. Genes Genom. 2016, 38, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Muthusamy, M.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, M.J.; Lee, S.I. Brassica rapa expansin-like B1 gene (BrEXLB1) regulate growth and development in transgenic Arabidopsis and elicits response to abiotic stresses. J. Plant. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lyu, T.; Xu, L.; Hu, Z.; Xiong, X.; Liu, T.; Cao, J. Complex molecular evolution and expression of expansin gene families in three basic diploid species of Brassica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Hong, J.K.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, M.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.I. Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals Brassica rapa-specific evolutionary dynamics upon whole genome triplication. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.; Purugganan, M. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeau, J.H.; Sankoff, D. Comparable rates of gene loss and functional divergence after genome duplications early in vertebrate evolution. Genetics 1997, 147, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, J.; Cosgrove, D. The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, D.K.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, S.K.; Choi, Y.D.; Lee, J.S. Expression of an expansin gene is correlated with root elongation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, E.; Di Mambro, R.; Dello Ioio, R.; Costantino, P.; Sabatini, S. Acidic cell elongation drives cell differentiation in the Arabidopsis root. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e99134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boron, A.K.; Van Loock, B.; Suslov, D.; Markakis, M.N.; Verbelen, J.P.; Vissenberg, K. Over-expression of AtEXLA2 alters etiolated arabidopsis hypocotyl growth. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, P.Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.R.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Li, X.J.; Luo, Q.; Tan, G.F.; Wang, G.L.; et al. Telomere-to-telomere carrot (Daucus carota) genome assembly reveals carotenoid characteristics. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.R.; Zhang, R.R.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, J.H.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.J.; Xu, Z.S.; et al. Carotene hydroxylase DcCYP97A3 affects carotenoid metabolic flow and taproot color by influencing the conversion of α-carotene to lutein in carrot. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coe, K.; Bostan, H.; Rolling, W.; Turner-Hissong, S.; Macko-Podgórni, A.; Senalik, D.; Liu, S.; Seth, R.; Curaba, J.; Mengist, M.F.; et al. Population genomics identifies genetic signatures of carrot domestication and improvement and uncovers the origin of high-carotenoid orange carrots. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | Chromosome Location | gDNA Length (bp) | Amino Acid Length (aa) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DcEXP1 | DCAR_100846 | Chr1: 6,339,073–6,340,335 | 1263 | 256 | 28.19 | 9.46 | −0.02 |
| DcEXP2 | DCAR_103393 | Chr1: 42,300,842–42,302,755 | 1914 | 266 | 28.40 | 8.84 | 0.08 |
| DcEXP3 | DCAR_206001 | Chr2: 27,997,411–27,998,682 | 1272 | 260 | 28.11 | 9.65 | −0.08 |
| DcEXP4 | DCAR_206376 | Chr2: 32,762,836–32,763,816 | 981 | 262 | 28.88 | 9.46 | −0.05 |
| DcEXP5 | DCAR_206704 | Chr2: 36,196,798–36,198,305 | 1508 | 260 | 28.14 | 9.92 | −0.04 |
| DcEXP6 | DCAR_208090 | Chr2: 47,500,356–47,501,332 | 977 | 249 | 26.42 | 8.63 | −0.14 |
| DcEXP7 | DCAR_209418 | Chr2: 56,592,221–56,593,616 | 1396 | 249 | 27.65 | 6.37 | −0.17 |
| DcEXP8 | DCAR_310739 | Chr3: 8,031,000–8,031,983 | 984 | 255 | 27.55 | 9.51 | −0.01 |
| DcEXP9 | DCAR_310740 | Chr3: 8,040,221–8,041,199 | 979 | 255 | 27.59 | 9.43 | 0.01 |
| DcEXP10 | DCAR_310999 | Chr3: 10,333,932–10,335,287 | 1356 | 257 | 27.79 | 5.32 | 0.02 |
| DcEXP11 | DCAR_311357 | Chr3: 14,013,746–14,017,096 | 3351 | 264 | 28.67 | 7.53 | −0.08 |
| DcEXP12 | DCAR_312580 | Chr3: 47,099,297–47,100,658 | 1362 | 242 | 26.36 | 9.60 | −0.12 |
| DcEXP13 | DCAR_313707 | Chr3: 58,306,829–58,310,084 | 3256 | 262 | 28.35 | 9.62 | −0.02 |
| DcEXP14 | DCAR_417312 | Chr4: 43,592,653–43,593,579 | 927 | 247 | 26.57 | 9.32 | −0.12 |
| DcEXP15 | DCAR_417091 | Chr4: 42,059,527–42,060,504 | 978 | 256 | 27.38 | 9.22 | −0.01 |
| DcEXP16 | DCAR_519135 | Chr5: 7,163,308–7,164,252 | 945 | 255 | 27.13 | 8.53 | 0.01 |
| DcEXP17 | DCAR_519597 | Chr5: 11,841,355–11,843,154 | 1800 | 251 | 27.87 | 9.67 | −0.16 |
| DcEXP18 | DCAR_520240 | Chr5: 27,149,749–27,150,419 | 671 | 186 | 20.60 | 8.85 | −0.49 |
| DcEXP19 | DCAR_520709 | Chr5: 31,877,033–31,878,497 | 1465 | 293 | 31.36 | 6.37 | 0.01 |
| DcEXP20 | DCAR_521959 | Chr5: 42,405,577–42,407,092 | 1516 | 261 | 28.19 | 9.20 | −0.08 |
| DcEXP21 | DCAR_626607 | Chr6: 40,060,705–40,061,644 | 940 | 246 | 26.54 | 9.39 | −0.04 |
| DcEXP22 | DCAR_625076 | Chr6: 28,787,956–28,789,696 | 1741 | 262 | 28.29 | 9.04 | −0.08 |
| DcEXP23 | DCAR_728217 | Chr7: 19,885,069–19,886,970 | 1902 | 258 | 28.24 | 8.03 | −0.19 |
| DcEXP24 | DCAR_729133 | Chr7: 31,691,116–31,692,131 | 1016 | 240 | 25.61 | 8.13 | 0.00 |
| DcEXP25 | DCAR_729937 | Chr7: 38,481,461–38,482,393 | 933 | 244 | 26.07 | 6.27 | −0.07 |
| DcEXP26 | DCAR_832117 | Chr8: 24,892,236–24,893,322 | 1087 | 247 | 26.48 | 9.02 | −0.18 |
| DcEXP28 | DCAR_830574 | Chr8: 2,025,127–2,026,785 | 1659 | 255 | 27.68 | 9.31 | −0.14 |
| DcEXP29 | DCAR_830374 | Chr8: 402,868–403,956 | 1089 | 253 | 27.23 | 8.72 | −0.19 |
| DcEXP30 | DCAR_935972 | Chr9: 44,050,963–44,052,416 | 1454 | 250 | 26.58 | 9.03 | −0.15 |
| DcEXP31 | DCAR_207623 | Chr2: 44,225,282–44,226,327 | 1046 | 264 | 29.08 | 9.27 | 0.00 |
| DcEXP32 | DCAR_726983 | Chr7: 2,203,016–2,207,281 | 4266 | 240 | 25.40 | 8.09 | −0.07 |
| DcEXP33 | DCAR_416279 | Chr4: 35,958,787–35,960,231 | 1445 | 287 | 30.75 | 6.44 | −0.09 |
| DcEXP34 | DCAR_726980 | Chr7: 2,137,458–2,138,746 | 1289 | 252 | 26.88 | 4.91 | −0.16 |
| DcEXP35 | DCAR_728680 | Chr7: 26,399,400–26,401,031 | 1632 | 257 | 27.60 | 4.89 | −0.10 |
| DcEXP36 | DCAR_728679 | Chr7: 26,395,737–26,397,225 | 1489 | 256 | 27.65 | 7.99 | −0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.-R.; Wang, Y.-H.; Tao, J.-P.; Zhou, J.-H.; Zhang, N.; Peng, X.-F.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, X.; Sun, Y.-J.; Tan, G.-F.; et al. Identification of Carrot Expansin Gene Family and Its Regulation of Carrot Growth and Development. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102338
Zhang R-R, Wang Y-H, Tao J-P, Zhou J-H, Zhang N, Peng X-F, Zhang L, Xiang X, Sun Y-J, Tan G-F, et al. Identification of Carrot Expansin Gene Family and Its Regulation of Carrot Growth and Development. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102338
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rong-Rong, Ya-Hui Wang, Jian-Ping Tao, Jian-Hua Zhou, Nan Zhang, Xue-Feng Peng, Li Zhang, Xiaoe Xiang, Yu-Jie Sun, Guo-Fei Tan, and et al. 2025. "Identification of Carrot Expansin Gene Family and Its Regulation of Carrot Growth and Development" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102338
APA StyleZhang, R.-R., Wang, Y.-H., Tao, J.-P., Zhou, J.-H., Zhang, N., Peng, X.-F., Zhang, L., Xiang, X., Sun, Y.-J., Tan, G.-F., & Xiong, A.-S. (2025). Identification of Carrot Expansin Gene Family and Its Regulation of Carrot Growth and Development. Agronomy, 15(10), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102338







