Abstract
We conducted a two-year field experiment on winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from 2016–2018 to compare the effects of reducing nitrogen application rate in spring under three irrigation methods on grain yield (GY), water and nitrogen use efficiency in the North China Plain (NCP). Across the two years, GY of conventional irrigation (CI), micro-sprinkling irrigation (SI) and drip irrigation (DI) decreased by 6.35%, 9.84% and 6.83%, respectively, in the reduced nitrogen application rate (N45) than the recommended nitrogen application rate (N90). However, micro-irrigation (SI and DI) significantly increased GY relative to CI under the same nitrogen application rate, and no significant difference was observed in GY between SI and DI under N45, while SI obtained the highest GY under N90. The difference among different treatments in GY was mainly due to the variation in grain weight. The seasonal evapotranspiration (ET) in N45 was decreased more significantly than N90, and there was no significantly difference in ET among different irrigation methods under N45, but micro-irrigation significantly decreased the ET relative to CI under N90. Micro-irrigation significantly improved water use efficiency (WUE) compared to CI at the same nitrogen application rate. Under N45, compared with CI, WUE in SI and DI increased by 9.09% and 4.70%, respectively; however, the WUE increased by 15.9% and 7.23%, respectively, under N90. Reducing nitrogen application rate did not have a significant impact on WUE under CI, but it did have a substantial negative impact on SI and DI. Nitrogen accumulation in wheat plants at maturity (NAM) in N45 deceased significantly compared with N90 under the same irrigation method. Compared with CI under the same nitrogen application rate, micro-irrigation treatments significantly increased NAM, while SI was the largest. In comparison to N90, under three irrigation methods, N45 significantly increased nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency (NfUE). The highest NfUE was attained in SI, followed by DI, while CI was the lowest. Moreover, N45 significantly decreased soil NO3−-N accumulation (SNC) in three irrigation methods, and micro-irrigation significantly decreased the SNC in deep soil layers compared with CI when nitrogen is applied at the same level. Overall, micro-irrigation with a reduced nitrogen application rate in spring can achieve a relatively higher production of winter wheat while increasing the use efficiency of water and nitrogen and reducing soil NO3−-N leaching into deep soil layers in the NCP.
1. Introduction
North China Plain (NCP) is the main production base of winter wheat in China. The planting area of winter wheat reached 1752.8 × 104 hm2 in the NCP, which accounts for 71.5% and 79.7% of the national total planting area and output of winter wheat in China, respectively [1]. Therefore, it is crucial to guarantee the long-term production of winter wheat in this area. Although the annual precipitation is 500–950 mm in the NCP, it mainly concentrates in summer, and the lower precipitation during spring causes drought disasters of winter wheat [2]. The total water consumption for winter wheat production is 433 mm, 413 mm and 373 mm in dry, normal and wet years, respectively [3], and the most generally recognized method of meeting the water requirements of wheat cultivation in the NCP is irrigation. However, the extraction of groundwater for wheat growth and development in the NCP is responsible for around 70% of the need for irrigated water [4,5], and over-exploitation of groundwater had caused continuous ground settlement over the past four decades [6,7], resulting in this region becoming one of the deepest groundwater cones of depression on Earth [8]. Additionally, improper irrigation methods have increased the groundwater resource consumption and reduced the nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency (NfUE), leading to environmental degradation from water and nitrogen loss [9,10]. Therefore, it is of great significance for the NCP to reduce the nitrogen input and improve the water and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat.
Previous studies have reported that optimizing irrigation regimes to promote wheat root growth into deep soil layers and increase water utilization in deep soil is an important means to improve grain yield (GY) and water use efficiency (WUE) of winter wheat [11,12]. However, the unreasonable irrigation methods of wheat often reduce the water absorption from deep soil layers, and the conventional surface irrigation readily causes water and fertilizer to migrate out of the wheat’s main root zone, lowering WUE [7,13]. Currently, most farmers in the NCP use flooding irrigation to irrigate their winter wheat fields, and Xu et al. (2018) advocated that irrigation at the jointing and anthesis stages of wheat could achieve a higher GY and WUE [11]. The most common micro-irrigation techniques now applied in wheat production are surface drip irrigation and micro-sprinkling irrigation in the NCP. Studies have shown that micro-irrigation significantly improved crop yield and WUE by ensuring a water supply during the crucial growth stages of winter wheat through reducing the irrigation volume each time and increasing irrigation frequencies compared with the conventional irrigation practice [13,14]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that micro-irrigation simultaneously enhanced WUE and NfUE in wheat by co-locating water and nitrogen fertilizer applications with root distribution of winter wheat in the soil profile [14,15,16]. Previous studies also indicated that subjecting wheat to micro-irrigation could significantly increase leaf area index and chlorophyll content in leaf during grain filling, extend the leaf function period, enhance photosynthetic rate in plants, prevent premature senescence of wheat and increase grain weight and GY [17,18].
Nitrogen is one of the most important essential elements for crop growth [19]. Studies indicated that crops’ growth was highly impacted by the soil’s water conditions as well as the nitrogen application rate, and a suitable irrigation amount combined with nitrogen supply could boost the crops’ growth and increase GY [20,21]. Presently, the recommended nitrogen application rate for wheat production with a target of high yield and efficient resource utilization is 180–240 kg·ha−1 in the NCP, and it is divided into basal dressing and top dressing [22]. The prevailing nitrogen top dressing by farmers for winter wheat in this region is applied artificially combined with irrigation in spring, however, the inadvisable nitrogen application rate for winter wheat production has led to a lower NfUE [23], and the disposable top dressing accompanied by irrigation easily caused nitrogen to migrate out of the main root zone of wheat and leach into deeper soil layers [14]. Wu et al. (2008) [24] found that the reduction in nitrogen application rate for wheat greatly improved the NfUE while maintaining a higher yield. Even though an excessive nitrogen application rate may not have a major impact on crop yield, it can have a considerable impact on the amount of nitrogen residue in the soil after wheat harvest and decrease the use efficiency of nitrogen [25,26]. In particular, the rainy season comes soon after wheat harvest in the NCP, which easily exacerbates the residual nitrogen leaching into deeper soil layers. Therefore, the development of an optimized irrigation and fertilization regime is urgently needed to improve the GY, WUE and NfUE of winter wheat in the NCP. Furthermore, previous studies were focused on the physiological mechanism of micro-irrigation with water and nitrogen integration to achieve high yield and efficient utilization of water and nitrogen in wheat. However, there is insufficient research on the effect of reducing the nitrogen application rate under different irrigation methods on grain yield and water and nitrogen utilization in winter wheat. In this study, we hypothesized that, after increasing irrigation frequency and reducing nitrogen application rate, micro-irrigation with water and nitrogen integration could delay leaf senescence during grain filling and improve dry matter production post-anthesis so as to ensure grain yield, promote the absorption and utilization of soil water and nitrogen, increase nitrogen accumulation in plants and reduce the nitrate leaching to deep soil layers so as to increase WUE and NfUE. To confirm this hypothesis, a two-year field experiment was conducted to identify the effects of reducing nitrogen application rate under different irrigation methods on (1) grain yield and yield components of winter wheat, (2) leaf area index (LAI), chlorophyll content of flag leaf after anthesis and dry matter accumulation, (3) water and nitrogen utilization in winter wheat. We expect the research results to provide a theoretical basis and technical reference for high winter wheat yield and efficient utilization of water and nitrogen in the NCP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
At the experimental site of the China Agricultural University in Wuqiao County, Cangzhou City, Hebei Province (37°41′02″ N, 116°37′23″ E), an in situ field experiment was carried out from 2016 to 2018 throughout the winter wheat growing seasons. The altitude of the experimental site is 20 m. The field’s soil is a light loam consisting of 11.8% clay, 78.1% silt and 10.1% sand. In this two-year trial, summer maize was the previous crop before wheat. Mean bulk densities in 0–100 cm and 100–200 cm soil layers are both 1.43 g·cm−3. The soil total nitrogen, organic matter content, available phosphorus and potassium in the upper 40 cm of the soil layer before sowing were 0.95 g·kg−1, 11.7 g·kg−1, 104.4 mg·kg−1 and 29.2 mg·kg−1, respectively; soil pH was 7.5. The nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) content before sowing in the 0–100 cm soil layer was 18.6 mg·kg−1 and 12.7 mg·kg−1 in 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 winter wheat growing seasons. The total precipitation in the two wheat growing seasons was 95.5 mm and 185.6 mm, respectively. Figure 1 shows the climatic data in different months of the winter wheat growing season during this experiment.
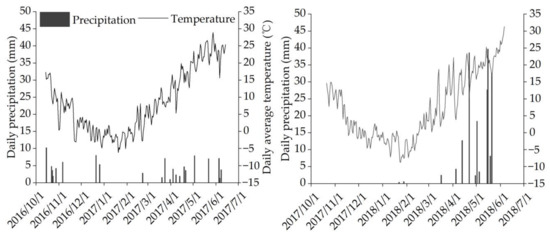
Figure 1.
Daily precipitation and average air temperature recorded during the growing seasons of winter wheat from 2016–2018 at the experiment site in this present study.
2.2. Experimental Design
In this experiment, conventional irrigation (CI), micro-sprinkling irrigation (SI) and drip irrigation (DI) were used over the two growing seasons of winter wheat. Wheat growth stages were recorded by the Zadoks scale [27]. Wheat was irrigated with 60 mm in each irrigation event and 120 mm of total irrigation during the jointing (Z31) and anthesis stages (Z61) in CI. SI and DI were carried out with 120 mm of total irrigation and 30 mm in each irrigation event at jointing (Z31), booting (Z45), anthesis (Z61) and filling stages (Z71). CI was carried out using PVC pipe, and SI and DI with hoses [14,28]. The length of the hoses for micro-irrigation treatments (SI and DI) was 30 m. The flow rate of micro-sprinkling hoses was 6.0 m3·h−1, and the sprinkling angle was 80°. The specific details of the layout of micro-sprinkling hose in this experiment field were according to Li et al. [14]. The distance between adjacent drip hoses was 30 cm, and the drip laterals had 30 cm emitter spacing and a flow rate of 2.0 L·h−1, with a worked pressure of 0.1 MPa. In this experiment, the irrigation water source is fresh water drawn from a well. Three replicates were used in the randomized complete block experimental design. Each experimental plot was 4 m × 30 m. Before sowing, 105 kg·ha−1 nitrogen, 120 kg·ha−1 P2O5 and 90 kg·ha−1 K2O were applied as base fertilizer. During the spring season of wheat growth, 45 kg·ha–1 nitrogen (N45) and 90 kg·ha–1 nitrogen (N90) were applied using urea (nitrogen content of 46.4%) as top dressing under different irrigation methods. For each irrigation event of SI and DI, a quarter of the top dressing urea was completely dissolved in a fertilization device and applied together with the irrigation, while all nitrogen was artificially spread over the field before irrigation at the jointing stage for CI. One of the most extensively grown varieties in the NCP, the high-yield winter wheat cultivar “Jimai22”, was utilized in the experiment. At a planting density of 540 plants per square meter, the wheat was sown on 14 October 2016 and 22 October 2017, and it was harvested on 14 June 2017 and 10 June 2018, respectively. No visible pests or diseases happened in the experimental field during the test period.
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Water Consumption and Use Efficiency
At sowing and maturity, soil samples were taken from 0 to 200 cm soil depth at 20 cm intervals with a soil corer. The soil water content (g·g−1) was measured using the oven-drying method. Some fresh soil samples were retained in each soil layer to determine soil NO3−-N content. The difference between the soil water storage (0–200 cm) at sowing and maturity was used to calculate the amount of soil water consumption. The soil water balance equation was used to determine the total seasonal evapotranspiration (ET) during the growth stage of winter wheat [29]:
where I (mm) is irrigation, P (mm) is precipitation recorded at the nearby meteorological station, SW (mm) is soil water consumption based on the difference between sowing and maturity, R is surface runoff, CR is capillary rise into the root zone and D is downward flux below the 200 cm soil layer. Due to the lower rainfall during wheat growing seasons in this region, deep soil layer and the large water holding capacity, plus the border of the experimental plots, runoff was rarely observed in the field and it was taken as zero. D can also be ignored in the NCP, including at the experimental site [30]. The soil water consumption percentage for 0–100 cm (SW1) and 100–200 cm (SW2) was the ratio of its water consumption volume to SW. The GY/ET ratio was used to calculate WUE.
ET = I + P ± SW − R + CR − D
2.3.2. Leaf Area Index (LAI) and Chlorophyll Content of Flag Leaves
At anthesis and grain filling stages (20 days after anthesis), the green leaf area of ten wheat plants was measured by a Li-3100 area meter (LI-COR, Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA) from each experimental plot to calculate the leaf area index (LAI) [13]. At these two stages, 20 flag leaf samples were randomly selected from each experimental plot to analyze the chlorophyll content (a + b). Flag leaf chlorophyll (a + b) content was extracted with 95% alcohol for 48 h in the dark, and the optical density (OD) of the alcohol extraction was measured at 649 and 665 nm using a UV-1800 Visible Ultraviolet Spectrophotometer, Shimadzu, Japan [14].
2.3.3. Dry Matter Accumulation (DM) and Grain Yield (GY)
Two 50 cm inner rows of wheat plants from each experimental plot were sampled at ground level at anthesis and maturity stages, then separated into grain and the rest. All samples were dried in an oven at 75 °C to a constant weight. Dry matter translocation (DMT) from the vegetative portions of the grain between anthesis and maturity was calculated as the difference between DM at anthesis and DM at maturity without grain. The contribution of DM pre-anthesis to grain was calculated from the ratio of DMT pre-anthesis to grain at maturity (DMR) [31], and the contribution ratio of DM post anthesis to grain was calculated as the difference by 100-DMR (DMPR). The ratio of grain to total above-ground DM at maturity is defined as the harvest index (HI). To determine spike number, spikes were counted in six 1 m center rows of each plot before harvest. Before harvest, 60 randomly picked spikes from each experimental plot were used to calculate the grain number. Wheat plants from a 3 m2 area in each plot were harvested and then threshed artificially to determine GY. Actual GY was reported on a 13% moisture basis. By weighing 1000 seeds from each sample and averaging the results of three replicates, the thousand grain weight (TGW) was determined.
2.3.4. Soil Nitrate Nitrogen (NO3−-N) Residue, Nitrogen Accumulation and Use
Soil NO3−-N contents were determined using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and soil samples were extracted with 0.01 mol·L−1 CaCl2 [32]. The calculation method for the accumulated amount of NO3−-N in the 0–200 cm soil profile is the sum of NO3−-N accumulation in each layer [33]. The Kjeldahl method was used to determine the total nitrogen content of plants [34]. According to Ruisi et al. (2016), nitrogen accumulation and use were calculated as follows [35]:
where NAM is the nitrogen accumulation in plants at maturity; DMM is dry matter accumulation of plants at maturity; NC is the nitrogen concentration in plants; NfUE is nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency; Nf is the applied amount of nitrogen fertilizer.
NAM = DMM × NC%,
NfUE = GY/Nf
2.4. Data Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2016 (Microsoft, Inc., Redmond, WA, USA) was used for data sorting, SPSS Statistics 22.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to analyze the data and the least significant difference test (p = 0.05) was used to compare the difference between different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates in this study. All figures in this paper were generated using Origin Pro 2019 (Origin Lab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Components
Grain yield (GY) clearly fell from 2017–2018 compared with 2016–2017, which was mostly as a result of a decline in spike number (SN) and thousand grain weight (TGW) (Table 1). However, the two-year study data revealed consistent outcomes. Across the two years, the GY under three irrigation methods was significantly lowered with a reduction in nitrogen application rate, which decreased by 6.35%, 9.84% and 6.83%, respectively, in N45 compared to N90. Under N45, there was no significant difference in GY between SI and DI, and they were both significantly higher than in CI. Under N90, GY in CI was significantly lower than that of DI, and SI yielded the highest GY when compared to those of CI and DI. Notably, there was no significant difference in GY among CIN90, SIN45 and DIN45. SN and grain number per spike (GN) among different treatments in the same year had no significant difference, while there was a large effect on TGW, and the difference in GY under different treatments was mainly caused by the change in TGW.

Table 1.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on grain yield (GY), spike number (SN), grain number per spike (GN) and thousand grain weight (TGW) of winter wheat.
3.2. Leaf Area Index (LAI) and Chlorophyll Content Flag Leaf
LAI of winter wheat at anthesis was obviously higher than at the grain filling stage, and it was obviously lower from 2017–2018 than that from 2016–2017 (Figure 2). The two years’ experimental results showed that LAI decreased in N45 compared with N90, but no significant difference was presented between N45 and N90 in micro-irrigation treatments in the first growing season. At the anthesis stage, the LAIs of SI and DI were significantly greater than in CI but did not differ significantly from each other under N45. However, irrigation methods had no significant impact on the LAI under N90. At the filling stage, N45 significantly reduced the LAI when compared to N90 under the same irrigation method. The LAI in SI and DI did not differ significantly, while LAI in micro-irrigation was significantly higher than that of CI under N45. Under N90, compared with CI, micro-irrigation significantly improved the LAI, and LAI in SI was significantly higher than that of DI.
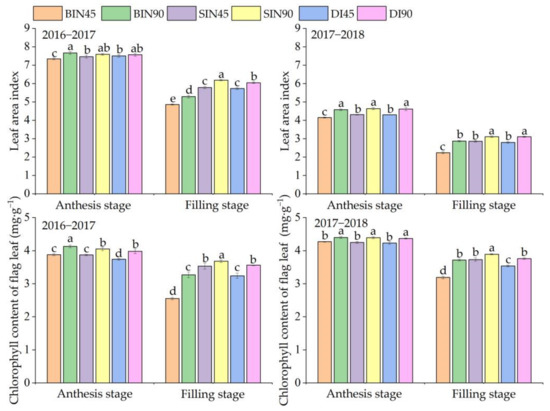
Figure 2.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on flag leaf chlorophyll content at anthesis and filling stages. Note: CI, conventional irrigation method; SI, micro-sprinkling irrigation method; DI, drip irrigation method; N45 indicates 45 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing; N90 indicates 90 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing. Values followed by the same letter within a column in each year are not significantly different at p < 0.05. Vertical bars represent standard errors. All the data are shown as the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
Chlorophyll content in flag leaf was obviously decreased when nitrogen application rate was reduced under the same irrigation method, but the results of chlorophyll content in different irrigation methods under the same nitrogen application rate were varied. At the anthesis stage, under N45, the two years’ results all showed that the chlorophyll content in CI and SI was not significantly different, while SI significantly improved the chlorophyll content compared to DI. Additionally, under N90, micro-irrigation significantly increased the chlorophyll content compared to CI, and no significant difference in the chlorophyll content was observed between SI and DI. At the filling stage, under N45, the two years’ data revealed that CI significantly decreased the chlorophyll content compared to micro-irrigation treatments, and SI had a much greater chlorophyll content than DI. Under N90, compared with micro-irrigation treatments, CI significantly decreased the chlorophyll content, and that of SI was significantly higher than that of DI; however, there was no significant difference between CI and DI from 2017–2018.
3.3. Dry Matter Accumulation and Translocation
Across the two years, dry matter accumulation (DM) at anthesis (DMA) in SI was not significantly impacted by reducing the nitrogen application rate, but it was significantly decreased in CI and DI when nitrogen application was reduced (Table 2). CI treatment significantly increased the DMA compared to SI and DI when nitrogen application was the same, and DMA in micro-irrigation treatments had no significant difference. Under N45, SI and DI significantly decreased DMA compared to CI from 2016–2017; however, no significant difference was observed in DMA between CI and SI from 2017–2018, nor between SI and DI, but DMA in CI was significantly higher than that in SI. At maturity, compared with N90, N45 significantly decreased the total DM (DMM) in both years under the same irrigation method, and under N90, DMM in CI was significantly decreased compared with those of DI and SI, and SI showed the highest DMM. However, compared to CI under N45, the DMM in micro-irrigation treatments was significantly improved, and that of SI was significantly higher than that of DI in the first growing season, while no significant difference was observed between SI and DI in the second year. The contribution ratio of pre-anthesis dry matter translocation to GY (DMR) was significantly higher for N45 than N90 in CI, and the reduction in nitrogen had no significant impact on DMR in SI and DI, but SI significantly decreased the DMR compared with DI. The contribution ratio of post-anthesis dry matter accumulation to grain (DMPR) in different treatments was in opposition to the DMR. In addition, CI significantly decreased harvest index (HI) compared to micro-irrigation treatments under the same nitrogen application rate, whereas SI and DI had no significant effect on HI. Under N45, no significant difference was observed in HI between DI and SI, however, that of DI was significantly lower than that of SI under N90.

Table 2.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on dry matter accumulation, translocation and harvest index of winter wheat.
3.4. Water Consumption and Utilization
As shown in Figure 3, the total seasonal evapotranspiration (ET) of winter wheat in N45 was significantly lower than that of N90 under the same irrigation method across the two years. The three irrigation methods had no significant effect on ET under N45. Under N90 in the 2016–2017 growing season of winter wheat, no significant difference in ET was observed between CI and DI and between DI and SI, but ET in SI was significantly lower than that in CI; however, CI significantly increased the ET compared with those of DI and SI from 2017–2018. Water use efficiency (WUE) was not significantly impacted by the reduction in nitrogen application rate under CI, but micro-irrigation treatments significantly decreased the WUE in N45 compared to N90. Micro-irrigation treatments significantly improved the WUE compared to CI under the same nitrogen application rate. WUE in SI and DI increased by 9.09% and 4.70%, respectively, compared with that of CI under N45; however, under N90, the WUE increased by 15.9% and 7.23%, respectively. However, WUE in DI was significantly lower than that of SI under the same nitrogen application rate, but SI and DI had no significant effect on WUE from 2017–2018. Under N90, the WUE variation in the various irrigation methods was consistent with the prior year.
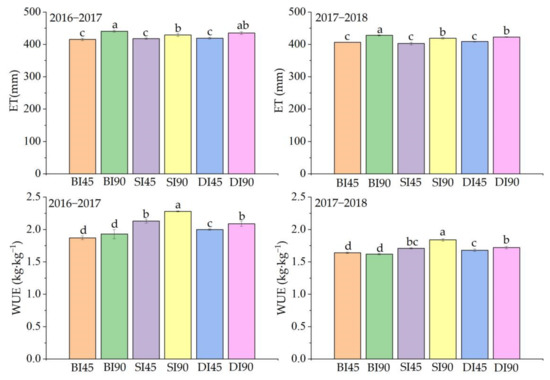
Figure 3.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on the seasonal evapotranspiration (ET) and water use efficiency (WUE) of winter wheat during the two seasons. Note: CI, conventional irrigation method; SI, micro-sprinkling irrigation method; DI, drip irrigation method; N45 indicates 45 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing; N90 indicates 90 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing. Values followed by the same letter within a column in each year are not significantly different at p < 0.05. Vertical bars represent standard errors. All the data are shown as the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
3.5. Soil Water Utilization
As shown in Table 3, across the two years, N90 treatments significantly increased soil water consumption (SW) as compared to those of N45 under three irrigation methods. However, under N45, there was no significant variation in SW among the three irrigation methods. Meanwhile, under N90, there was no significant variance in SW between SI and DI, and besides the DI, SW in SI declined significantly over the two years compared to CI. The two years of research indicated that the reduction in nitrogen application rate significantly decreased the soil water consumption from 0–100 cm (SW1), however, CI had a much higher SW1 than micro-irrigation treatments, and SW1 in SI was similar to that in DI. It is worth noting that, compared N90, N45 had no significant impact on the ratio of SW1 to SW in SI and DI, and CI significantly increased SW1 compared to SI and DI from 2016–2017, while there was no significant impact on SW1 under N90 among the three irrigation methods from 2017–2018. In addition, there was no significant difference in soil water consumption in the 100–200 cm soil profile (SW2) between N45 and N90 under SI, and the reduced nitrogen application rate treatments significantly decreased SW2 in the three irrigation methods. Under N45, there was no significant difference in SW2 between SI and DI in the two years, and they were both much higher than in CI. In comparison to CI, SW2 under N90 increased dramatically with SI and DI from 2016–2017, but the irrigation methods had no significant impact on SW2 from 2017–2018. Most notably, the SW2 to SW ratio in SI and DI was not significantly affected by the reduction in nitrogen application rate, and they significantly increased SW2 compared with CI from 2016–2017, while there was no significant impact on the ratio under N90 among the three irrigation methods from 2017–2018.

Table 3.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on soil water consumption of winter wheat during the two seasons.
3.6. Nitrogen Accumulation and Utilization in Plants
The variation in nitrogen accumulation in winter wheat at maturity (NAM) among different treatments was consistent between the two growing seasons (Figure 4). Compared with N90, NAM was decreased significantly in N45 under the same irrigation method. However, when nitrogen was applied at the same rate, NAM in SI significantly surpassed that of DI and CI, and CI obtained the lowest NAM. Across the two years, N45 significantly increased the nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency (NfUE) compared to N90 under the same irrigation method, but there were some changes in NfUE among the irrigation methods under the same nitrogen application rate. Under N45, CI significantly decreased the NfUE compared with DI from 2016–2017, whereas the NfUE in SI was significantly higher than that in DI. From 2017–2018, NfUE in CI was significantly lower than that of micro-irrigation treatments, and the NfUE in SI was similar to that of DI. SI had a much higher NfUE than DI and CI, and CI had the lowest NfUE under N90 in the two years.
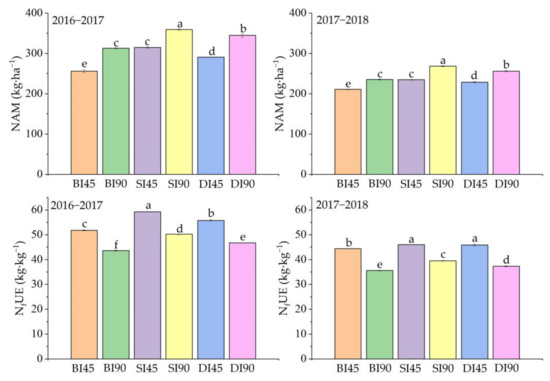
Figure 4.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on nitrogen accumulation at maturity (NAM) and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency (NfUE) of winter wheat during the two seasons. Note: CI, conventional irrigation method; SI, micro-sprinkling irrigation method; DI, drip irrigation method; N45 indicates 45 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing; N90 indicates 90 kg·ha−1 nitrogen was applied as top dressing. Values followed by the same letter within a column in each year are not significantly different at p < 0.05. Vertical bars represent standard errors. All the data are shown as the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
3.7. Soil Available Nitrogen Accumulation
Table 4 shows a similar variation in soil nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) accumulation at maturity in 0–200 cm soil depth (SNC) among different treatments from 2016–2017 and 2017–2018, that is, N45 significantly decreased the SNC compared to N90 under the same irrigation method, however, micro-irrigation significantly reduced the SNC compared to CI when nitrogen was applied at the same rate, and no significant difference in SNC was observed between SI and DI. Across the two years, N45 significantly decreased the NO3−-N residue from 0–100 cm (SNC1) under the same irrigation method, while there was no significant difference in SNC1 among different irrigation methods. In addition, the reduced nitrogen application rate had no significant impact on the ratio of NO3−-N residue of SNC1 to SNC under CI from 2016–2017 and, compared with N45, N90 significantly increased the ratio of NO3−-N residue of SNC1 to SNC under the same irrigation method. Under N45, there was no significant difference in the ratio of NO3−-N residue of SNC1 to SNC among the three irrigation methods from 2016–2017, but SI and DI significantly increased the ratio compared to CI under the same nitrogen application rate in the two growing seasons. N45 significantly decreased the NO3−-N residue in the 100–200 cm soil profile (SNC2) compared to N90, but under the same nitrogen application rate in the two years, CI significantly increased the SNC2 compared to micro-irrigation treatments, and no significant difference in SNC2 was observed between SI and DI. It was noted that the ratio of SNC2 to SNC in SI and DI was lower than that of CI under the same nitrogen application rate, and there was no significant difference in the ratio between SI and DI.

Table 4.
Effects of different irrigation methods and nitrogen application rates on soil NO3−-N accumulation of winter wheat at maturity.
4. Discussion
Spike number, grain number per spike and grain weight all affect wheat grain production. Numerous studies have shown that insufficient nitrogen application causes a significant decrease in GY of wheat, which mostly decreased the SN and GN but significantly increased grain weight [36,37,38]. However, in this study, nitrogen reduction under three irrigation methods had no significant impact on SN and GN, but significantly decreased the TGW, which led to a fall in wheat’s GY when compared to the recommended nitrogen application rate (Table 1). Tillering is an important phenological stage for winter wheat, and there is a close correlation between tillering in spring and spike development [39]. The number of tillers produced per plant has been found to be affected by limited nutrients [40]. Nitrogen deficiency has been recognized as an important nutrient factor to limit wheat tiller growth and development [41]. We considered that the excessive nitrogen reduction in earlier studies may have had a negative impact on the development of SN and GN in wheat, and the lower SN and GN were beneficial to the increase in grain weight. In our two-year study, the same nitrogen rate was applied under different treatments at sowing of wheat, and all treatments were applied with nitrogen in spring, therefore, the reduction in nitrogen did not have a negative impact on the SN and GN.
The flag leaf is one of the most important photosynthetic organs of wheat, and it is the basis for obtaining high grain weight and GY for wheat by delaying the leaf senescence and maintaining a higher LAI during the grain filling period [14,42,43]. However, an insufficient nitrogen application rate could easily lead to premature failure of wheat leaves, reducing wheat GY [32]. A prior study revealed that micro-irrigation could greatly increase the production of dry matter by delaying leaf senescence during grain filling, boosting the grain filling rate and raising wheat’s TGW and GY [18]. In this study, nitrogen reduction treatments significantly reduced GY under different irrigation methods, and GY in SI was significantly higher than that of DI and CI, and CI had the lowest GY (Table 1). Additionally, no significant difference in GY was found among CIN90, SIN45 and DIN45, and the greater TGW accounted for the increased GY in SI and DI under nitrogen reduction. According to Figure 2, compared to CI, SI and DI significantly increased the chlorophyll content at the grain filling stage while maintaining high levels of LAI under the same nitrogen application rate. Conversely, the chlorophyll content and LAI were significantly decreased when nitrogen was reduced under the same irrigation method, but they were still significantly higher in SI and DI than CIN90, which may be the reason why micro-irrigation treatments could significantly improve the TGW. In addition, nitrogen application during the post-anthesis of winter wheat could improve root activity and increase the photosynthetic rate of flag leaf during the grain filling period [44], which may account for the higher grain weight achieved by micro-irrigation treatments in this present study.
GY of wheat is directly related to dry matter production [45,46]. It is a promising way to improve the DMM and HI of wheat through optimizing irrigation and nitrogen application regime [11]. This study found that micro-irrigation significantly improved the DMM compared with CI under the same nitrogen application rate (Table 2). However, compared with N90, N45 significantly decreased the DMM under the same irrigation method, but micro-irrigation with nitrogen reduction showed a similar DMM to CI with the recommended nitrogen application rate, particularly in SI, which obtained the highest DMM and HI. In addition, grain growth depends on the photosynthesis during the grain filling period and the remobilization of pre-anthesis assimilates stored in vegetable organs to grain [47,48]. In this study, micro-irrigation significantly increased the DM post anthesis and increased the DMPR compared to CI under the same nitrogen application rate, which may be related to the higher chlorophyll content and LAI in the filling period in SI and DI (Figure 2).
Optimized irrigation practices are beneficial to improve the WUE of winter wheat [49,50], and insufficient nitrogen supply may lead to significantly decreased crop yield as well as WUE [32]. This study revealed that micro-irrigation greatly lowered ET when compared with the conventional farmer irrigation method and significantly enhanced wheat GY and WUE [14,51]. Furthermore, enhancing the water uptake and use from deeper soil profiles by the crop is a very promising strategy to increase the WUE and enhance wheat yield when irrigation is limited [12,52,53]. In this study, the ET in CI was significantly lower than in micro-irrigation methods under N90, especially in SI, which may be because SI and DI were beneficial to improving the micro-environment of the wheat canopy, and this favors reducing the ineffective evaporation of soil water in the field [46]. However, under N45, there was no significant change in ET among the various irrigation methods, and the study of this effect is ongoing. Compared with CI under the same nitrogen application rate, micro-irrigation significantly increased WUE of winter wheat, and WUE in SI was the highest. In this investigation, we also discovered that micro-irrigation altered water extraction of deep soil by winter wheat (Table 3, Figure 1). The water consumption of the 0–100 cm soil profile under the same irrigation method was significantly increased by SI and DI in the first growing season of winter wheat, but the deeper (100–200 cm) soil water consumption under N90 in the second year was not significantly different among the three irrigation methods, which may be related to the heavy rainfall during the filling period of winter wheat in this year (Figure 1). Therefore, we suppose that a small amount of micro-irrigation with two nitrogen application rates may have promoted the root to penetrate into the deep soil profile in this present study, and facilitated enhancing the acquisition capacity for deep soil water of winter wheat, thereby improving WUE.
Optimizing nitrogen application is an important means to improve GY and NfUE of wheat [32]. However, the nitrogen application rate has a great impact on the NfUE, as does the irrigation regime [16,36,54]. Increasing the irrigation volume usually increases nitrogen leaching, reducing soil’s available nitrogen accumulation in the root zone [14,55]. Previous studies showed that soil NO3−-N is easily leached into the deeper soil layer, especially after a large amount of irrigation for wheat, causing larger NO3−-N loss, which resulted in the decrease in NfUE [56,57]. Furthermore, improper agricultural production practices have had a serious impact on the eco-environment, and climate and environmental changes have social consequences affecting people [58]. In addition, the frequent occurrence of droughts over the last two decades has led to in rise in farmers’ concerns that field crop production will not be possible without irrigation. The warmer climate will also shorten the growing cycle of all crops [59]. In order to meet the growing demand from an increasing world population, there is a need to increase wheat production. Fertilization and irrigation have a great potential to enhance growth quality, grain yield and yield-related traits of wheat [60,61,62]. Nevertheless, previous studies found that because of the small irrigation volume and the divided nitrogen application, which encouraged wheat absorption and utilization, the NfUE in micro-irrigation treatments significantly improved when compared to conventional irrigation methods, and the soil NO3−-N residue was significantly reduced at maturity [13,14]. In this present study, micro-irrigation significantly improved the plants’ nitrogen accumulation at maturity when compared to CI at the same nitrogen application rate, and that of SI was the highest. However, under N45, the NfUE in micro-irrigation was significantly improved compared to CI (Figure 4), which was mainly due to the significant increase in GY of micro-irrigation treatments (Table 1). In addition, the residual NO3−-N of micro-irrigation treatments in the soil at maturity was significantly decreased compared to CI, which indicated that the micro-irrigation methods were conducive to reducing the residual amount of soil NO3−-N, and more nitrogen was absorbed and utilized by the crop (Table 4). In comparison to SI and DI, CI greatly enhanced the soil NO3−-N leaching into the deeper soil depth with the same nitrogen application rate, which is also one of the causes for the lowering of NfUE in CI. Furthermore, nitrogen deficit in wheat will stimulate root growth into the deep soil layers to increase nutrient absorption, according to Wang et al. (2014) [52]. In this study, the reason why micro-irrigation improved the WUE and NfUE compared to CI may be that it led to lower NO3−-N in the deeper soil layer than in CI from the jointing to booting stage of wheat, and this period is greatly critical for wheat root growth. However, more research will need to be carried out in the future on the effects of different nitrogen application rates on winter wheat root growth and their physiological mechanisms.
5. Conclusions
Compared with CI, using micro-irrigation with integrated water and N fertilizer, and with irrigation and nitrogen application at jointing, booting, anthesis and grain filling of winter wheat, could further reduce the nitrogen application rate and maintain the GY of winter wheat, and improve WUE and NfUE, particularly in SI. The reason for the higher GY, WUE and NfUE in micro-irrigation than in CI was because it delayed the leaf senescence during the grain filling period, improved the DM post anthesis and increased the use of water and nitrogen contained in deeper soil layers. Overall, using micro-irrigation technology with reduced nitrogen application rate can guarantee the output and improve the use efficiency of water and N fertilizer in the NCP.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.L. (Jinpeng Li), Y.Z. and Z.W.; Investigation, J.L. (Jinpeng Li); Data analysis, J.L. (Jinpeng Li); Writing—original draft preparation, J.L. (Jinpeng Li); Writing—review and editing, Y.Z., Y.S. and J.L. (Jincai Li); Funding acquisition, J.L. (Jinpeng Li) and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32001474, 31871563), and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-03).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yangyang Li, Yulei Zhu and Huihui Liu for guidance in revising this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Bureau of Statistic of China. China Statistical Year Book; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, P.J.; Huo, Z.G.; Wu, D.R.; Yang, J.Y. Crop drought identification index for winter wheat based on evapotranspiration in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 263, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Huang, F.; Li, B. Spatiotemporal patterns of water consumption and irrigation requirements of wheat-maize in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China and options of their reduction. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.S.; Ma, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Yan, P.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Effect of diversified crop rotations on groundwater levels and crop water productivity in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.S.; Zhang, M.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Recharge and groundwater use in the North China Plain for six irrigated crops for an eleven year period. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0115269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Lal, R.; Zhang, F.R.; Chen, X.H.; Niu, Z.G.; Han, L.; Song, W. Groundwater depletion by agricultural intensification in China’s HHH Plains, Since 1980s. Adv. Agron. 2016, 135, 59–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L.; Wang, G.Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sui, P.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Siddique, K.H.M. Reduced groundwater use and increased grain production by optimized irrigation scheduling in winter wheat–summer maize double cropping system—A 16-year field study in North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2022, 275, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.W.; Scanlon, B.R.; Shen, Y.J.; Reedy, R.C.; Long, D.; Liu, C.M. Impacts of varying agricultural intensification on crop yield and groundwater resources: Comparison of the North China Plain and US High Plains. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 044013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Hu, K.L.; Li, B.G.; Liu, H.T. Coupled simulation of soil water-heat- carbon nitrogen process and crop growth at soil-plant-atmosphere continuum system. Trans. CSAE. 2014, 30, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.L.; Xie, Y.H.; Gao, Z.Q.; Hong, J.P.; Li, L.; Meng, H.S.; Ma, H.M.; Jia, J.X. Year-round film mulching system with monitored fertilization management improve grain yield and water and nitrogen use efficiencies of winter wheat in the dryland of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 9524–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, Z.M. Improving water use efficiency and grain yield of winter wheat by optimizing irrigations in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xu, Y.Y.; Ma, X.C.; Ahmad, I.; Manzoor Jia, Q.M.; Akmal, M.; Hussain, Z.; Arif, M.; Cai, T.; Zhang, J.H.; et al. Deficit irrigation strategies to improve winter wheat productivity and regulating root growth under different planting patterns. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 219, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.X.; Lin, G.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Optimized micro-sprinkling irrigation scheduling improves grain yield by increasing the uptake and utilization of water and nitrogen during grain filling in winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Xu, X.X.; Lin, G.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Micro-irrigation improves grain yield and resource use efficiency by co-locating the roots and N-fertilizer distribution of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, C.S.; Song, W.Y.; Xu, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.N.; Gao, Y.M.; Wang, Z.M.; et al. Effects of micro-sprinkling with different irrigation amount on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.K.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, B.J.; Wang, D. Supplemental irrigation increases grain yield, water productivity, and nitrogen utilization efficiency by improving nitrogen nutrition status in winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.G.; Wang, D.; White, P.J. Photosynthesis and drymass production of winter wheat in response to micro-sprinkling irrigation. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Wang, Z.M.; Yao, C.S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.H. Micro-sprinkling irrigation simultaneously improves grain yield and protein concentration of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Crop J. 2021, 9, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, A.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Zhai, L.M.; Lei, B.K.; Ren, T.Z. An optimal regional nitrogen application threshold for wheat in the North China Plain considering yield and environmental effects. Field Crops Res. 2017, 207, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, N.M.; Abdel-Razek, M.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S.A.; Semida, W.M.; Leilah, A.A.A.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Ali, E.F.; Majrashi, A.; Rady, M.O.A. High nitrogen fertilization modulates morpho-physiological responses, yield, and water productivity of lowland rice under deficit irrigation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agami, R.A.; Alamri, S.A.M.; El-Mageed, T.A.A.; Abousekken, M.S.M.; Hashem, M. Role of exogenous nitrogen supply in alleviating the deficit irrigation stress in wheat plants. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Y.; Zain, M.; Mehmood, F.; Wang, G.S.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A.W. Effects of nitrogen application rate and irrigation regime on growth, yield, and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Yu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, Y. Nitrogen supply modulates nitrogen remobilization and nitrogen use of wheat under supplemental irrigation in the North China Plain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, Z.M. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer applications on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency under limited irrigation of winter wheat in North China Plain. J. Triticeae Crops 2008, 28, 1016–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.J.; Ge, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Luo, W.D.; Chang, J. Nitrate in groundwater of China: Sources and driving forces. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Z.; Shao, Y.H.; He, L.; Li, X.; Hou, G.G.; Li, S.N.; Feng, W.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Xie, Y.X. Optimizing nitrogen management to achieve high yield, high nitrogen efficiency and low nitrogen emission in winter wheat. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 6, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.G.; Yu, J.S.; White, P.J.; Gu, S.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, Q.F.; Shi, Y.; Wang, D. Effects of supplemental irrigation with micro-sprinkling hoses on water distribution in soil and grain yield of winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2014, 161, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Wang, Y.Z. Changes in evapotranspiration over irrigated winter wheat and maize in North China Plain over three decades. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liang, X.G.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.L.; Shen, S.; Zhou, S.L. Supplemental irrigation at tasseling optimizes water and nitrogen distribution for high-yield production in spring maize. Field Crops Res. 2017, 209, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, Z.W.; Man, J.G.; Ma, S.Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L. Tillage practices affect dry matter accumulation and grain yield in winter wheat in the North China Plain. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 160, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, Z.W. Water use and soil nitrate nitrogen changes under supplemental irrigation with nitrogen application rate in wheat field. Field Crops Res. 2015, 183, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, S.L. Soil nitrate n accumulation under different N-fertilizer rates in summer maize and its residual effects on subsequent winter wheat. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Dordas, C.A.; Sioulas, C. Dry matter and nitrogen accumulation, partitioning and retranslocation in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruisi, P.; Saia, S.; Badagliacca, G.; Amato, G.; Frenda, A.S.; Giambalvo, D.; Miceli, G.D. Long-term effects of no tillage treatment on soil N availability, N uptake, and 15N-fertilizer recovery of durum wheat differ in relation to crop sequence. Field Crops Res. 2016, 189, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.H.; Chen, Z.J.; Xiong, Y.W.; Huang, Q.Z.; Xu, X.; Huo, Z.L. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on grain yield, water and nitrogen dynamics and their use efficiency of spring wheat farmland in an arid agricultural watershed of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Palta, J.A.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X. Nitrogen fertilization improved water-use efficiency of winter wheat through increasing water use during vegetative rather than grain filling. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Han, M.M.; Pang, D.W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dong, H.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Jin, M.; Luo, Y.L.; Li, Y.; et al. Characteristics of lodging resistance of high-yield winter wheat as affected by nitrogen rate and irrigation managements. J. Integr. Agr. 2022, 20, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, D.; Andrade, F.H.; Goudriaan, J. Effects of phosphorus nutrition on tiller emergence in wheat. Plant Soil. 1999, 209, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longnecker, N.; Kirby, E.J.M.; Robson, A. Leaf emergence, tiller growth, and apical development of nitrogen-dificient spring wheat. Crop Sci. 1993, 33, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.X.; Dang, T.H.; Guo, S.L. Divergent responses of tiller and grain yield to fertilization and fallow precipitation: Insights from a 28-year long-term experiment in a semiarid winter wheat system. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, Z.W.; White, P.J. The effect of supplemental irrigation after jointing on leaf senescence and grain filling in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2013, 151, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Gao, Z.; Sun, X.N.; Bian, D.H.; Ren, J.H.; Yan, P.; Cui, Y.H. Increasing temperature during early spring increases winter wheat grain yield by advancing phenology and mitigating leaf senescence. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.D.; Li, J.C.; Wei, F.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G. Effects of nitrogen spraying on the post-anthesis stage of winter wheat under waterlogging stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Y.; Yu, Z.W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Luo, L.P.; Chu, P.F.; Guo, Z.J. Soil water use, grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in a long-term study of tillage practices and supplemental irrigation on the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, L.; Siosemardeh, A.; Sohrabi, Y.; Bahramnejad, B.; Hosseinpanahi, F. Dry matter remobilization and associated traits, grain yield stability, N utilization, and grain protein concentration in wheat cultivars under supplemental irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Han, K.; Gu, S.B.; Wang, D. Effects of supplemental irrigation on the accumulation, distribution and transportation of 13C-photosynthate, yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 214, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.W.; Yu, Z.W.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, Y. Effects of supplemental irrigation based on soil moisture levels on photosynthesis, dry matter accumulation, and remobilization in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Plant Product. Sci. 2017, 20, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.L.; Tao, H.B.; Tian, B.J.; Gao, Y.B.; Ren, J.H.; Wang, P. Limited-irrigation improves water use efficiency and soil reservoir capacity through regulating root and canopy growth of winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.M.; Zhang, M.; Yao, C.S.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Increasing seeding density under limited irrigation improves crop yield and water productivity of winter wheat by constructing a reasonable population architecture. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Mei, X.R.; Wang, J.D.; Huang, F.; Hao, W.P.; Li, B.G. Drip fertigation significantly increased crop yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency with respect to traditional irrigation and fertilization practices: A meta-analysis in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liu, W.X.; Li, Q.X.; Ma, D.Y.; Lu, H.F.; Feng, W.; Xie, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Guo, T.C. Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen regimes on root growth and its correlation with aboveground plant parts in high-yielding wheat under field conditions. Field Crops Res. 2014, 165, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.D.; Wang, G.S.; Liang, Y.P.; Duan, A.W. Root development and water uptake in winter wheat under different irrigation methods and scheduling for North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Z.W. Optimized border irrigation improved nitrogen accumulation, translocation of winter wheat and reduce soil nitrate nitrogen residue. Agronomy 2022, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lin, F.; Maucieri, C.; Zhang, Y.J. Efficient irrigation methods and optimal nitrogen dose to enhance wheat yield, inputs efficiency and economic benefits in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2022, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.T.; Cai, H.J.; Wang, X.i.Y.; Ma, C.G.; Lu, Y.J.; Ding, Y.B.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.F.; Saddique, Q. Exploring optimal irrigation and nitrogen fertilization in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system for improving crop yield and reducing water and nitrogen leaching. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Lu, Y.L.; YDing Yin, X.F.; Raza, S.; Tong, Y.A. Optimising nitrogen fertilisation: A key to improving nitrogen-use efficiency and minimising nitrate leaching losses in an intensive wheat/maize rotation (2008–2014). Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. 117 Mapping environmental and climate variations by GMT: A case of Zambia, Central Africa. Zemljište i biljka 2021, 70, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stričević, R.; Vujadinović-Mandić, M.; Đurović, N.; Lipovac, A. Application of two measures of adaptation to climate change for assessment on the yield of wheat, corn and sunflower by the aquacrop model. Zemljište i biljka 2021, 70, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubičić, N.; Popović, V.; Ćirić, V.; Kostić, M.; Ivošević, B.; Popović, D.; Pandžić, M.; El Musafah, S.; Janković, S. Multivariate interaction analysis of winter wheat grown in environment of limited soil conditions. Plants 2021, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubičić, N.; Popović, V.; Ivošević, B.; Rajičić, V.; Simić, D.; Kostić, M.; Pajić, M. Spike index stability of bread wheat grown on halomorphic soil. Selekcija i Semenarstvo 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, V.; Ljubičić, N.; Kostić, M.; Radulović, M.; Blagojević, D.; Ugrenovic, V.; Popovic, D.; Ivosevic, B. Genotype × environment interaction for wheat yield traits suitable for selection in different seed priming conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).