Preparation of Phenolic Epoxy-Based Electronic Packaging Materials with High Thermal Conductivity by Creating an Interfacial Heat Conduction Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of EMCs
2.3. Characterization of EMCs
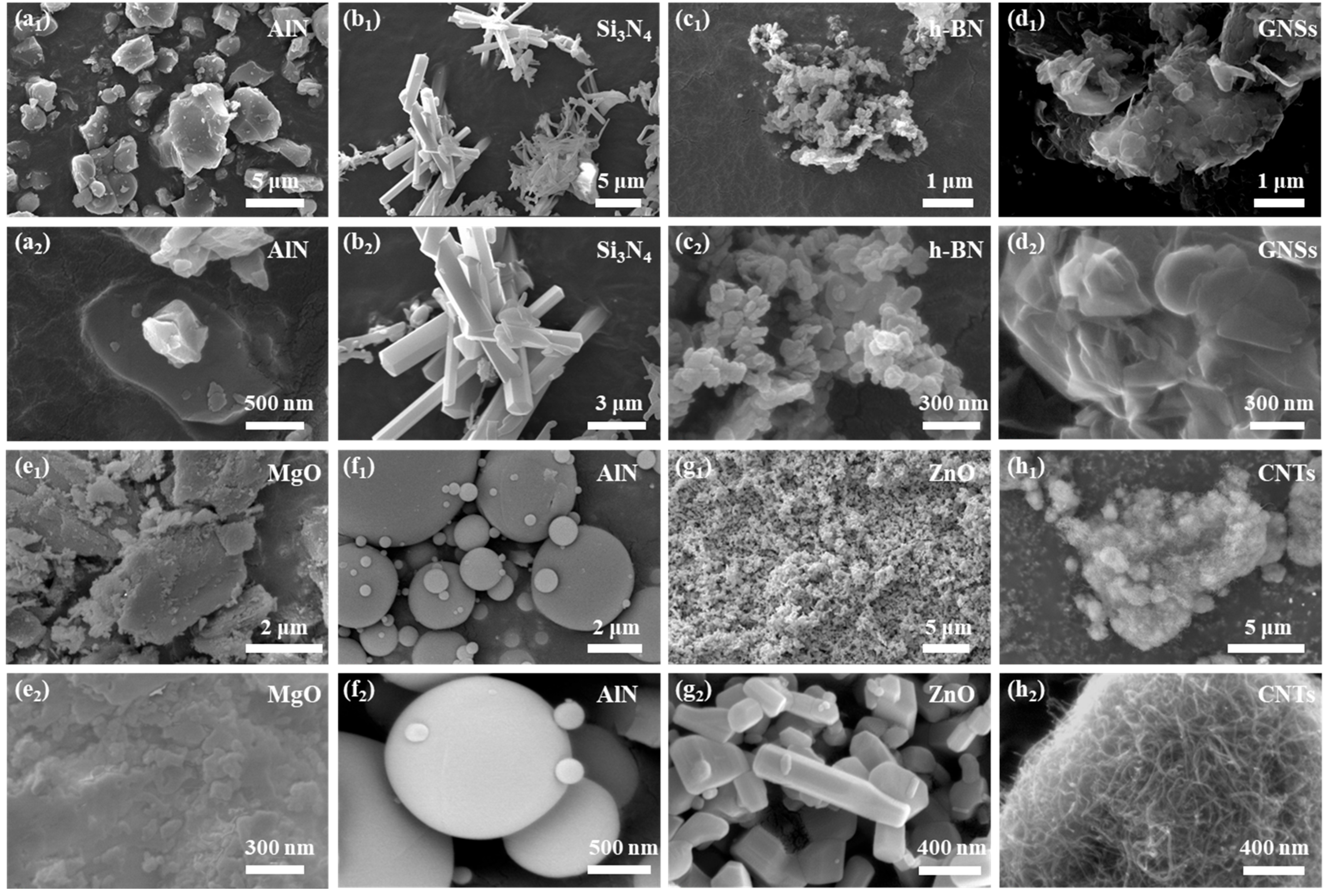
2.3.1. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
2.3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.3.3. TCT-S2 Thermal Conductivity Test
2.3.4. Water Evaporation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. λ Values of EMCs with Different Inorganic Fillers
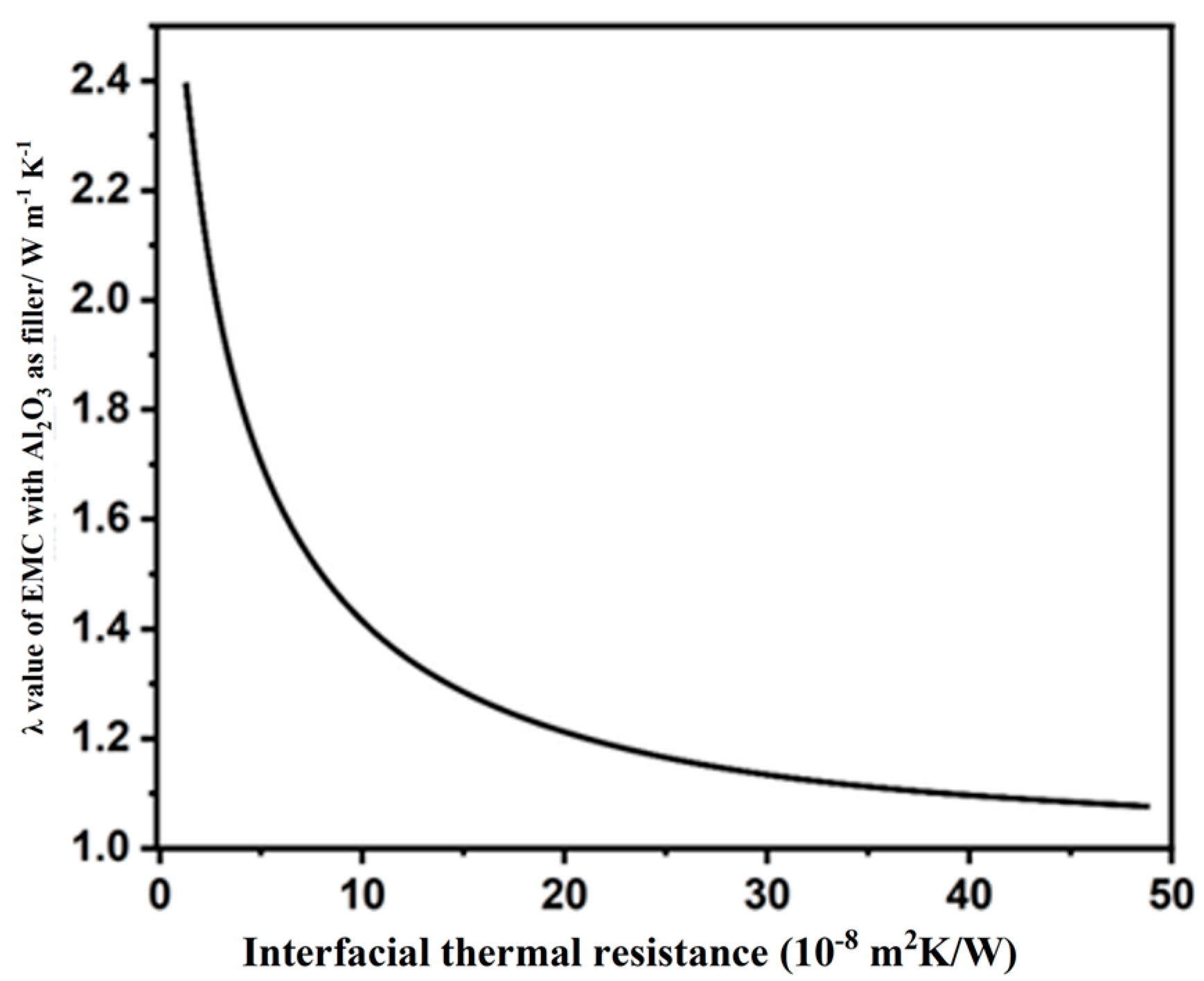
3.2. ITR Between the EP Matrix and Inorganic Filler
- (I).
- The morphology and structure of inorganic fillers have a significant impact on their λ values. The theoretical λ values of the added inorganic fillers are calculated or measured by assuming a state of perfect crystalline structures, while the actual inorganic fillers utilized in this study were amorphous particles, which have λ values lower than those of perfect crystals.
- (II).
- The ITR between the EP matrix and inorganic fillers significantly influences the overall TC of the prepared EMCs.
3.3. λ Values of EMCs with Fillers and CNTS
Characterization of the Molecular Chain Structure
3.4. Topographic Characterization of Filler Surfaces
3.5. Surface Morphology and Elemental Distribution of EMCs
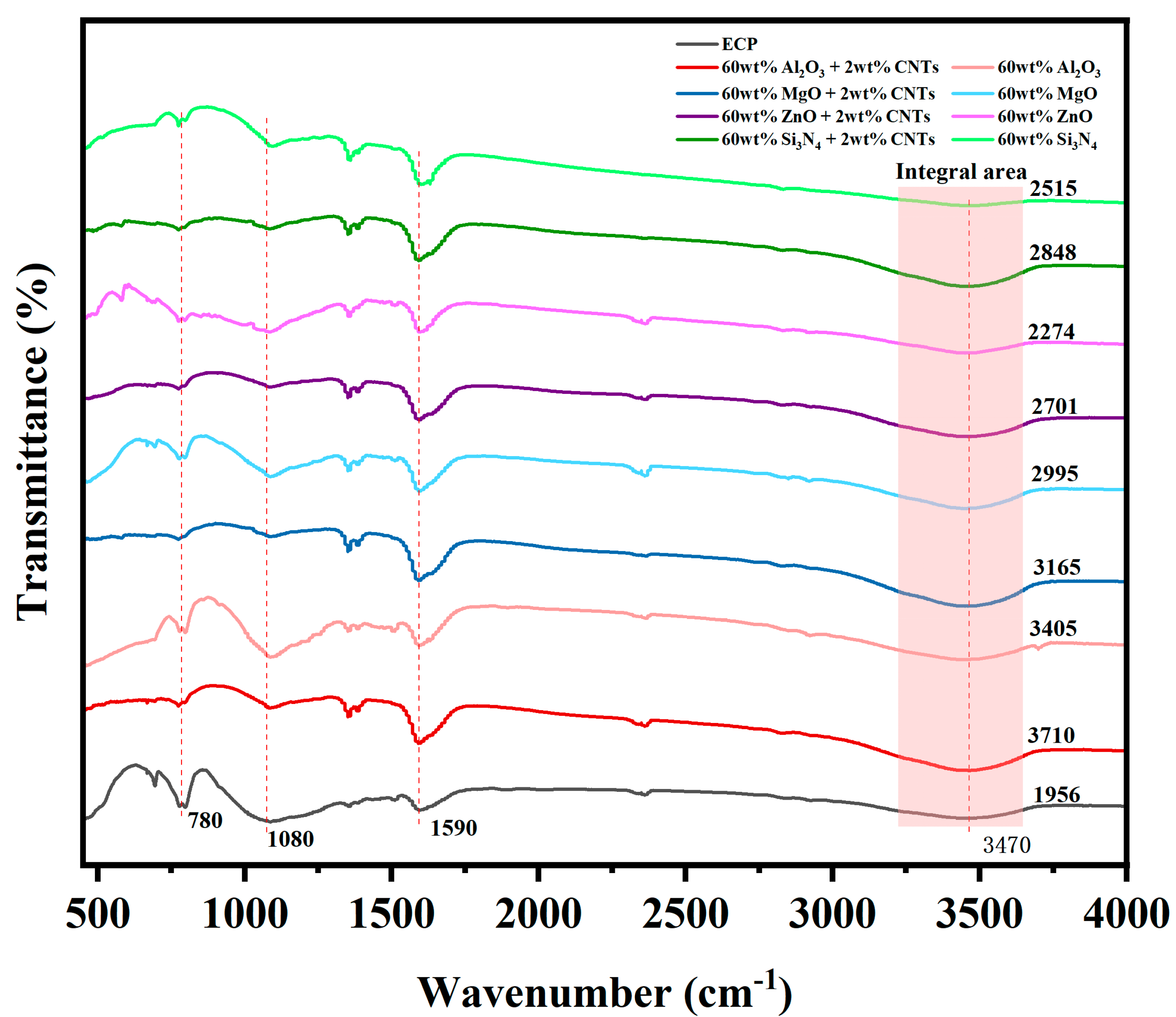
3.6. FT-IR of EMCs
3.7. Thermal Conductive Testing of EMCs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Yao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chi, Q. High thermal conductivity and low dielectric loss of three-dimensional boron nitride nanosheets/epoxy composites. Compos. Commun. 2024, 50, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; Chen, C.; Wan, X.; Mu, Y. Functional Zwitterionic Polyurethanes as Gate Dielectrics for Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 11, 2400578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Xiang, L.; Tang, B.; Shi, S.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Sun, K.; Fan, R.; et al. Highly thermally conductive and negative permittivity epoxy composites by constructing the carbon fiber/carbon networks. Compos. Commun. 2023, 39, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. Enhanced thermal conductivities of epoxy nanocomposites via incorporating in-situ fabricated hetero-structured SiC-BNNS fillers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 187, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Gu, J. Low dielectric constant and highly intrinsic thermal conductivity fluorine-containing epoxy resins with ordered liquid crystal structures. SusMat 2023, 3, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Cheng, H.-M.; Kang, F. Two-dimensional materials for thermal management applications. Joule 2018, 2, 442–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.-J.; Li, G.; Yao, Y.-M.; Zeng, X.-L.; Zhu, P.-L.; Sun, R. Recent advances in polymer-based electronic packaging materials. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procter, P.; Solc, J. Improved thermal conductivity in microelectronic encapsulants. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1991, 14, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Bollampally, R.S. Thermal conductivity; elastic modulus, and coefficient of thermal expansion of polymer composites filled with ceramic particles for electronic packaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Bollampally, R.S. Comparative study of thermally conductive fillers for use in liquid encapsulants for electronic packaging. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 1999, 22, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Bae, J.-W.; Choi, I.-D.; Kim, Y.-S. Thermally conductive EMC (epoxy molding compound) for microelectronic encapsulation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, W.A.L.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Soong, Y.-C.; Chan, Y.-N.; Chiou, K.-C.; Lee, T.-M.; Cheng, C.-C.; Chiu, C.-W. Enhanced thermal conductivity of epoxy composites filled with Al2O3/boron nitride hybrids for underfill encapsulation materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wan, S.; Niu, M.; Li, M.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xuan, W.; Yue, M.; Cao, W.; Wang, Q. Oriented Three-Dimensional Skeletons Assembled by Si3N4 Nanowires/AlN Particles as Fillers for Improving Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isarn, I.; Gamardella, F.; Fernàndez-Francos, X.; Serra, À.; Ferrando, F. Thermal conductive composites prepared by addition of several ceramic fillers to thermally cationic curing cycloaliphatic epoxy resins. Polymers 2019, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-X.; He, Z.-X.; Mo, D.-C.; Lu, S.-S. Thermal conductivity enhancement with different fillers for epoxy resin adhesives. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 66, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Du, L.; Chen, B. Thermal conductivity of polymer-based composites: Fundamentals and applications. Progress. Polym. Sci. 2016, 59, 41–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Song, B.; Jiang, Z.; Lee, E.M.Y.; Huberman, S.; Gleason, K.K.; Chen, G. Molecular engineered conjugated polymer with high thermal conductivity. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Hierarchically hydrogen-bonded graphene/polymer interfaces with drastically enhanced interfacial thermal conductance. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3656–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, C.; Ye, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, X.; Mai, Y.-W. Advances on thermally conductive epoxy-based composites as electronic packaging underfill materials—A review. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2201023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P. A recipe for strength. Nature 1999, 399, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourie, O.; Wagner, H.D. Transmission electron microscopy observations of fracture of single-wall carbon nanotubes under axial tension. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3527–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Shi, L.; Majumdar, A.; McEuen, P.L. Thermal transport measurements of individual multiwalled nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumanek, B.; Janas, D. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube networks: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 7397–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22007-2:2022; Plastics—Determination of Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusivity—Part 2: Transient Plane Heat Source (Hot Disc) Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Li, Y.; Xiong, T.; Xu, C.; Qian, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J. Al2O3/h-BN/epoxy based electronic packaging material with high thermal conductivity and flame retardancy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ruan, K.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Gu, J. Factors affecting thermal conductivities of the polymers and polymer composites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Izman, S.; Uday, M.B.; Omar, M.F. Review on grain size effects on thermal conductivity in ZnO thermoelectric materials. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Bai, H.; Sajgalik, P.; Jiang, D. High thermal conductivity silicon nitride ceramics prepared by pressureless sintering with ternary sintering additives. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2019, 16, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Bai, S.-L.; Wong, C.P. “White graphene”—Hexagonal boron nitride based polymeric composites and their application in thermal management. Compos. Commun. 2016, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Koh, Y.R.; Mamun, A.; Shi, J.; Bai, T.; Huynh, K.; Yates, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, R.; Lee, E.; et al. Experimental observation of high intrinsic thermal conductivity of AlN. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2020, 4, 044602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Feng, Y.; Qin, M.; Gao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, F.; Feng, W. Stress controllability in thermal and electrical conductivity of 3D elastic graphene-crosslinked carbon nanotube sponge/polyimide nanocomposite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liang, C.; Zhao, X.; Gan, B.; Qiu, H.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.-Y. Highly thermally conductive flame-retardant epoxy nanocomposites with reduced ignitability and excellent electrical conductivities. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. Thermal conductivity of polymers and their nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Keblinski, P.; Schelling, P.K. Kapitza conductance of silicon–amorphous polyethylene interfaces by molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2009, 79, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, X.; Guo, Q.; Yao, Z. Improvement of thermal conductivities for epoxy composites via incorporating poly (vinyl benzal)-coated h-BN fillers and solvent-assisted dispersion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18635–18643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.-W.; Birringer, R.; Clarke, D.R.; Gleiter, H. Effective thermal conductivity of particulate composites with interfacial thermal resistance. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 6692–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Zhou, X.; Shi, D.; Hu, G.-H.; Xie, X. Novel micro-nano epoxy composites for electronic packaging application: Balance of thermal conductivity and processability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 209, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Youn, J.R. Influence of dispersion states of carbon nanotubes on physical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Carbon 2005, 43, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Fina, A. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 914–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.; Bao, Y.; Huang, J.; Fei, X.; Li, X.; Wei, W. Development of molding compounds based on epoxy resin/aromatic amine/benzoxazine for high-temperature electronic packaging applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.-C.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Chiang, J.-C.; Ho, K.-K.; Chou, T.-Y.; Xie, X.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chang, L.-H.; Hsieh, C.-K. Thermally conductive and electrically insulating epoxy nanocomposites with thermally reduced graphene oxide–silica hybrid nanosheets. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5863–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yin, H. Hybrid fillers of hexagonal and cubic boron nitride in epoxy composites for thermal management applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7388–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Gnanaprakasam, P.; Emmanuel, R.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Saravanan, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mimusops elengi, Linn. for enhanced antibacterial activity against multi drug resistant clinical isolates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.; Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Russo, S.; Longo, P.; Mariconda, A. Self-Healing Ability of Poly(PEGMA-5-UPy) Evaluated by Thermomechanical Analysis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2200500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Pan, L. Effect of functionalization on thermal conductivity of hexagonal boron nitride/epoxy composites. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 219, 124844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dang, J.; Xie, C. Thermal conductivity epoxy resin composites filled with boron nitride. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Yu, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Feng, L. A graphite nanoplatelet/epoxy composite with high dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity. Carbon 2013, 55, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Drzal, L.T.; Qin, Y.; Huang, Z. Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Yin, L.-J.; Zhong, S.-L.; Feng, Q.-K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xu, H.-P.; Liang, T.; Dang, Z.-M. A processable high thermal conductivity epoxy composites with multi-scale particles for high-frequency electrical insulation. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Teng, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-W.; Liao, S.-H.; Huang, Y.-L.; Tien, H.-W.; Lee, T.-M.; Chiou, K.-C. Effect of functionalized carbon nanotubes on the thermal conductivity of epoxy composites. Carbon 2010, 48, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.-C.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Lu, C.-H.; Yang, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Yen, M.-Y.; Chiou, K.-C.; Lee, T.-M. Thermal conductivity and structure of non-covalent functionalized graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 5107–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, G.; Yang, N.; Qin, L.; Grami, M.E.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Qu, X. Preparation and characterization of surface modified boron nitride epoxy composites with enhanced thermal conductivity. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 44282–44290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reagent Name | Manufacturer | Purity |
|---|---|---|
| Linear phenolic resin | Shandong Shengquan New Material Co., Ltd. (Jinan, China) | CP |
| Triphenylphosphine | Shandong Shengquan New Material Co., Ltd. (Jinan, China) | CP |
| Fused silica micro powder | Shandong Shengquan New Material Co., Ltd. (Jinan, China) | AR |
| o-cresol epoxy resin | Sinopec Baling Petrochemical Co., Ltd. (Yueyang, China) | CP |
| Carbon nanosheets (GNSs) | Anhui Zesheng Technology Co., Ltd. (Anqing, China) | CP |
| Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) | Tianjin Hiens Optronics Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) | CP |
| Aluminum nitride (AlN) | Dongguan Zhan Yang Materials Co., Ltd. (Dongguan, China) | CP |
| Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) | Anhui Senrise Technology Co., Ltd. (Anqing, China) | CP |
| Magnesium oxide (MgO) | Chengdu Huaxia Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China) | CP |
| Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) | Jiangsu Lianrui New Materials Co., Ltd. (Lianyungang, China) | CP |
| Zinc oxide (ZnO) | Fushi New Material Technology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) | CP |
| Silicon nitride (Si3N4) | Chengdu Dianchun Technology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China) | CP |
| Materials | Quality/g |
|---|---|
| Phenolic resin | 100 |
| o-cresol Epoxy resin | 200 |
| Triphenylphosphine | 0.9 |
| Fused silica micro powder | 700 |
| Filler | Theoretical λ Values (W m−1∙K−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 10–30 | [26] |
| MgO | 40 | [27] |
| ZnO | 30 | [28] |
| Si3N4 | 180 | [29] |
| h-BN | 250–380 | [30] |
| AlN | 320 | [31] |
| Entry | Filler | Filler Contents | λ Values (W m−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | N/A | 0.36 |
| 2 | Al2O3 | 90 wt.% | 1.19 |
| 3 | AlN | 90 wt.% | 0.82 |
| 4 | Si3N4 | 90 wt.% | 0.67 |
| 5 | Al2O3 | 60 wt.% | 0.67 |
| 6 | AlN | 60 wt.% | 0.44 |
| 7 | Si3N4 | 60 wt.% | 0.86 |
| 8 | MgO | 60 wt.% | 0.49 |
| 9 | ZnO | 60 wt.% | 0.76 |
| 10 | h-BN | 60 wt.% | 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of Phenolic Epoxy-Based Electronic Packaging Materials with High Thermal Conductivity by Creating an Interfacial Heat Conduction Network. Polymers 2025, 17, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111507
Ye M, Jiang J, Zhao L, Zhu H, Wang J, Sun Z, Zhang D, Li M, Zhang Y. Preparation of Phenolic Epoxy-Based Electronic Packaging Materials with High Thermal Conductivity by Creating an Interfacial Heat Conduction Network. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111507
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Minghao, Jing Jiang, Lin Zhao, Hongyu Zhu, Junjie Wang, Zicai Sun, Dewei Zhang, Ming Li, and Yagang Zhang. 2025. "Preparation of Phenolic Epoxy-Based Electronic Packaging Materials with High Thermal Conductivity by Creating an Interfacial Heat Conduction Network" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111507
APA StyleYe, M., Jiang, J., Zhao, L., Zhu, H., Wang, J., Sun, Z., Zhang, D., Li, M., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Preparation of Phenolic Epoxy-Based Electronic Packaging Materials with High Thermal Conductivity by Creating an Interfacial Heat Conduction Network. Polymers, 17(11), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111507








