Thermal Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Properties of Composite Sheets Composed of Dry Processed Core–Shell Structured Fillers and Silicone Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
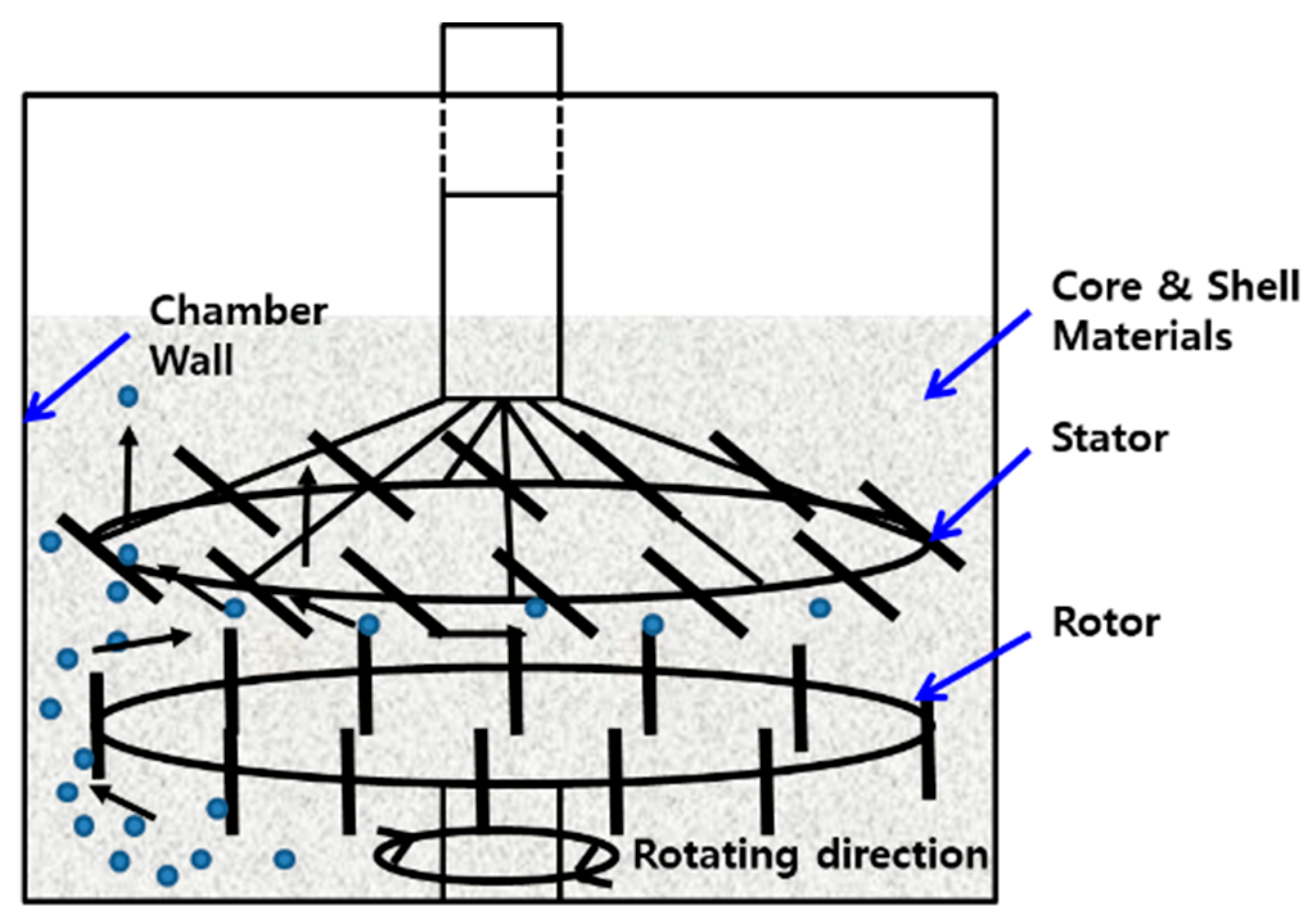
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
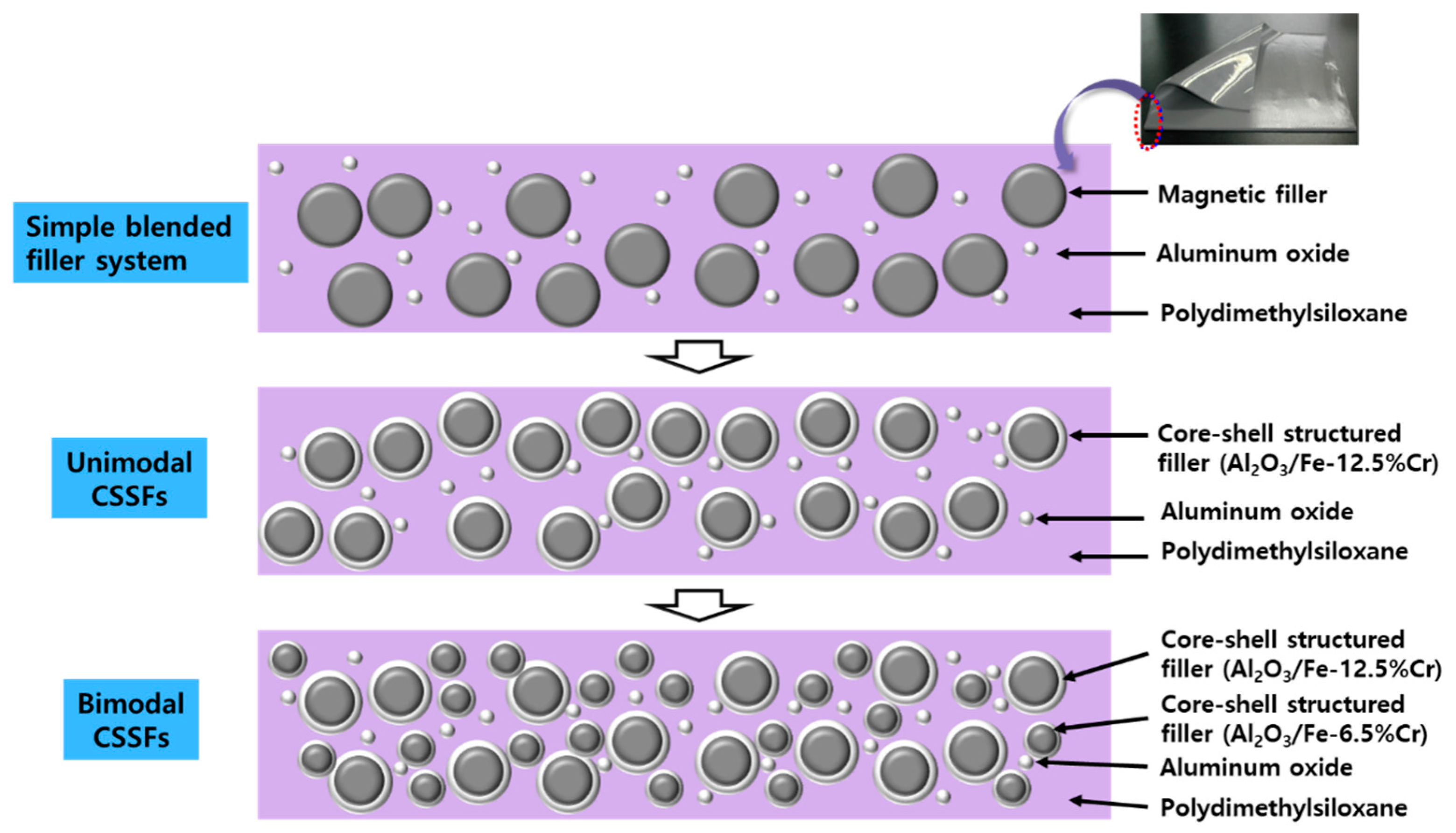
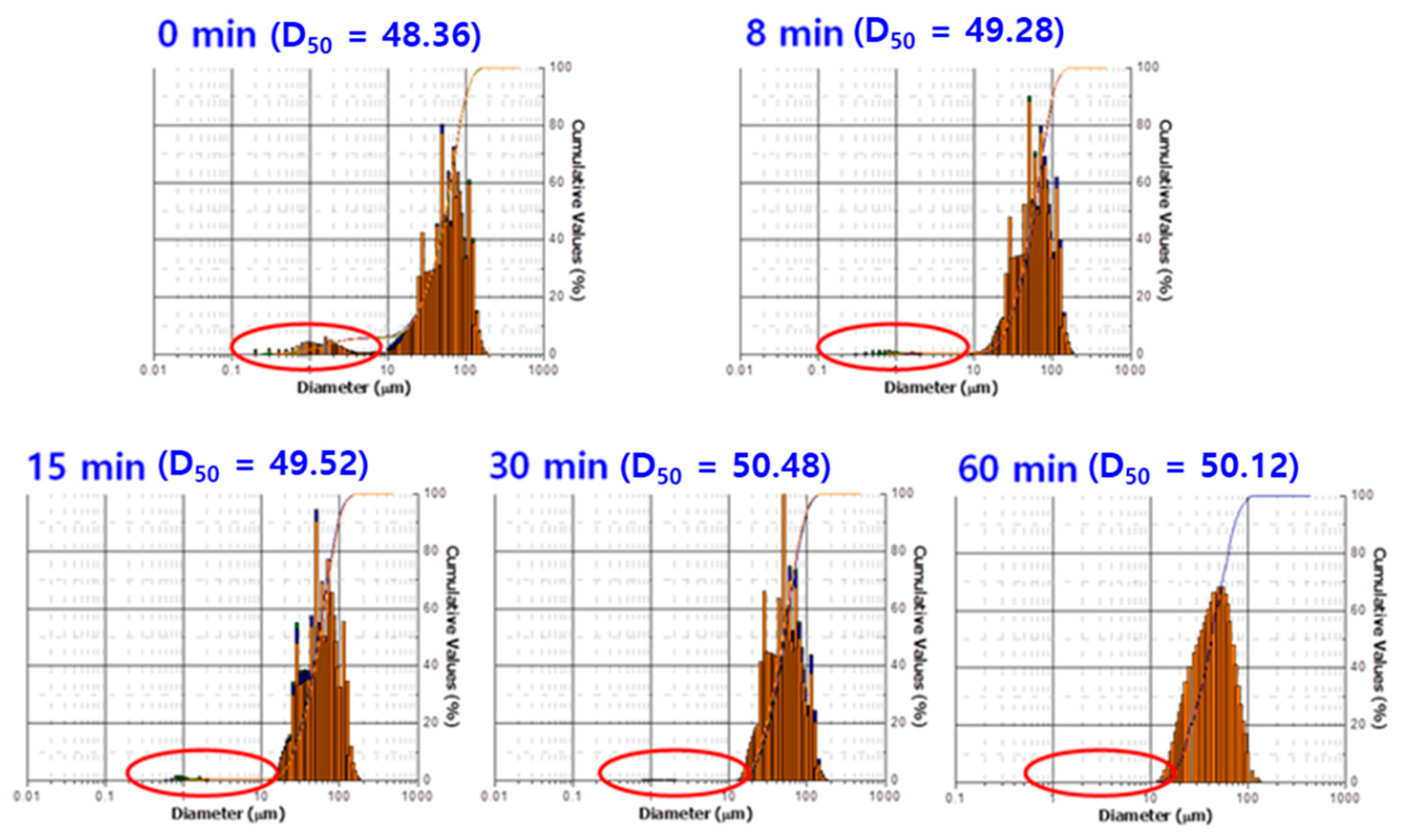
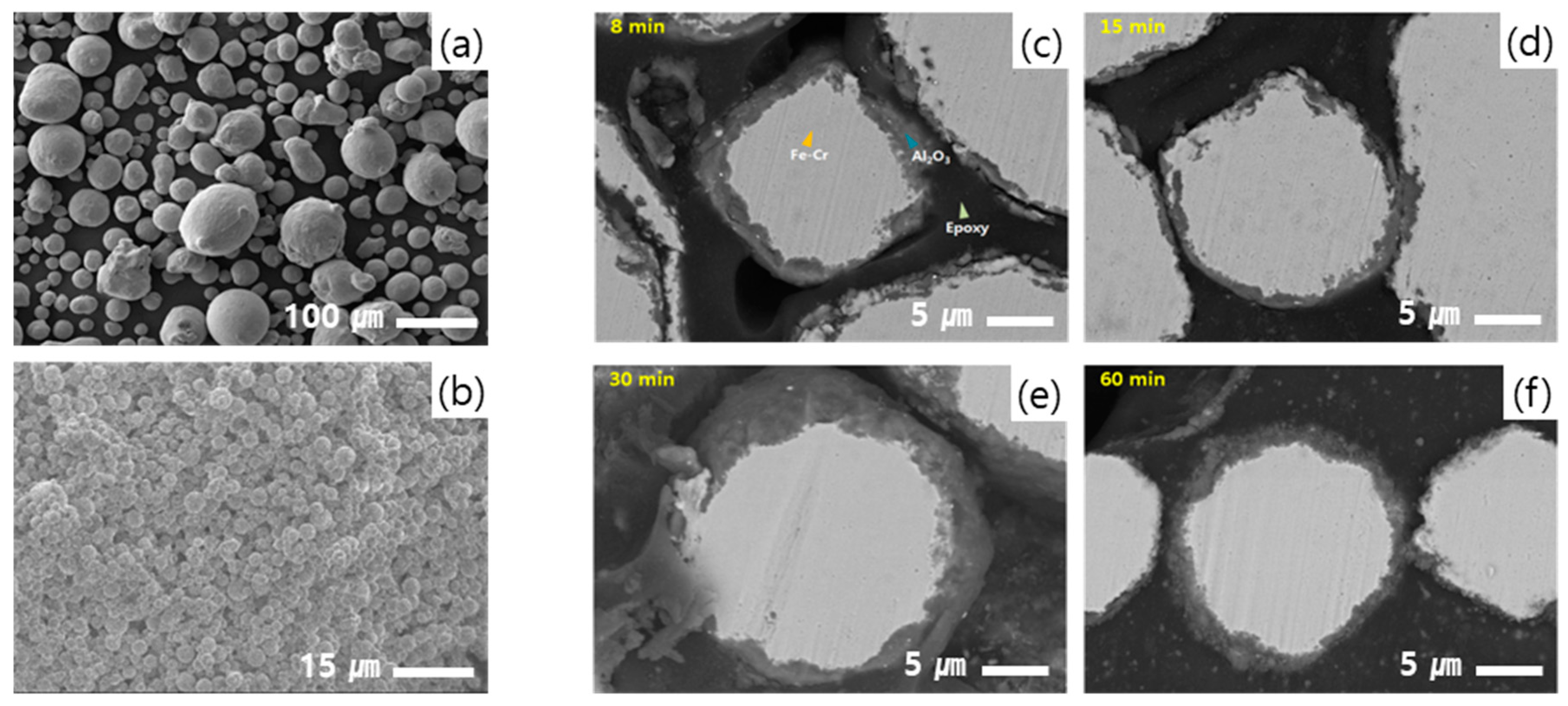
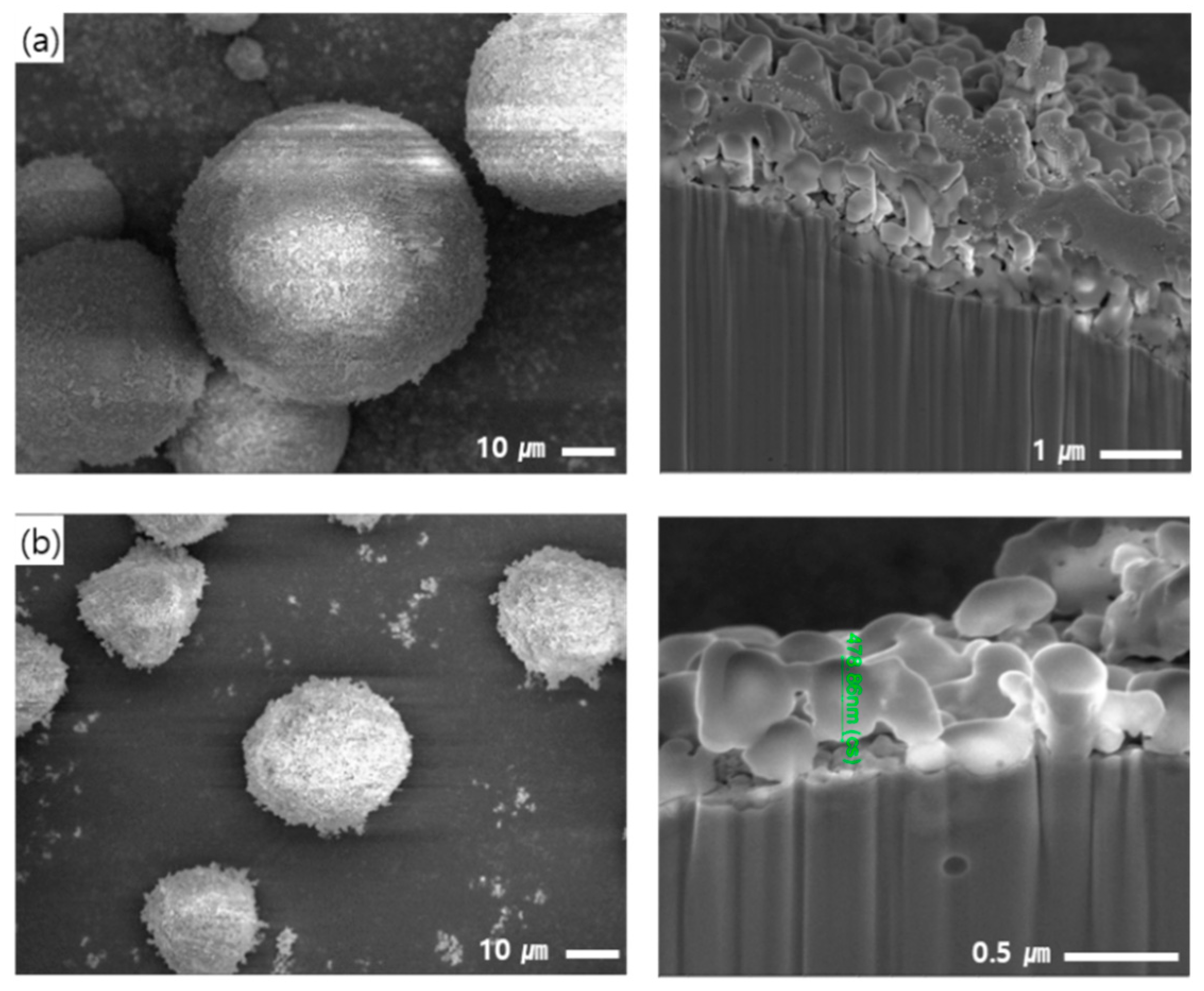
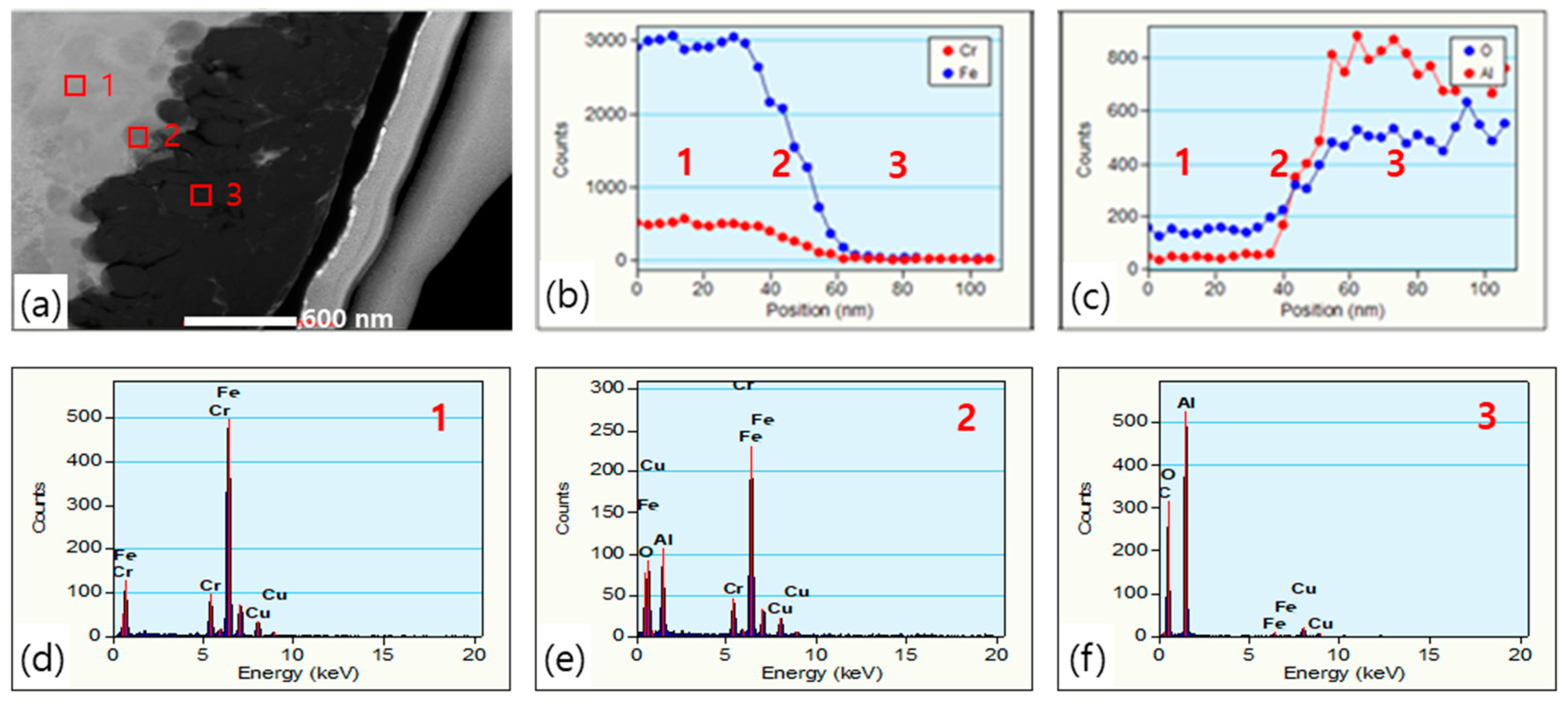
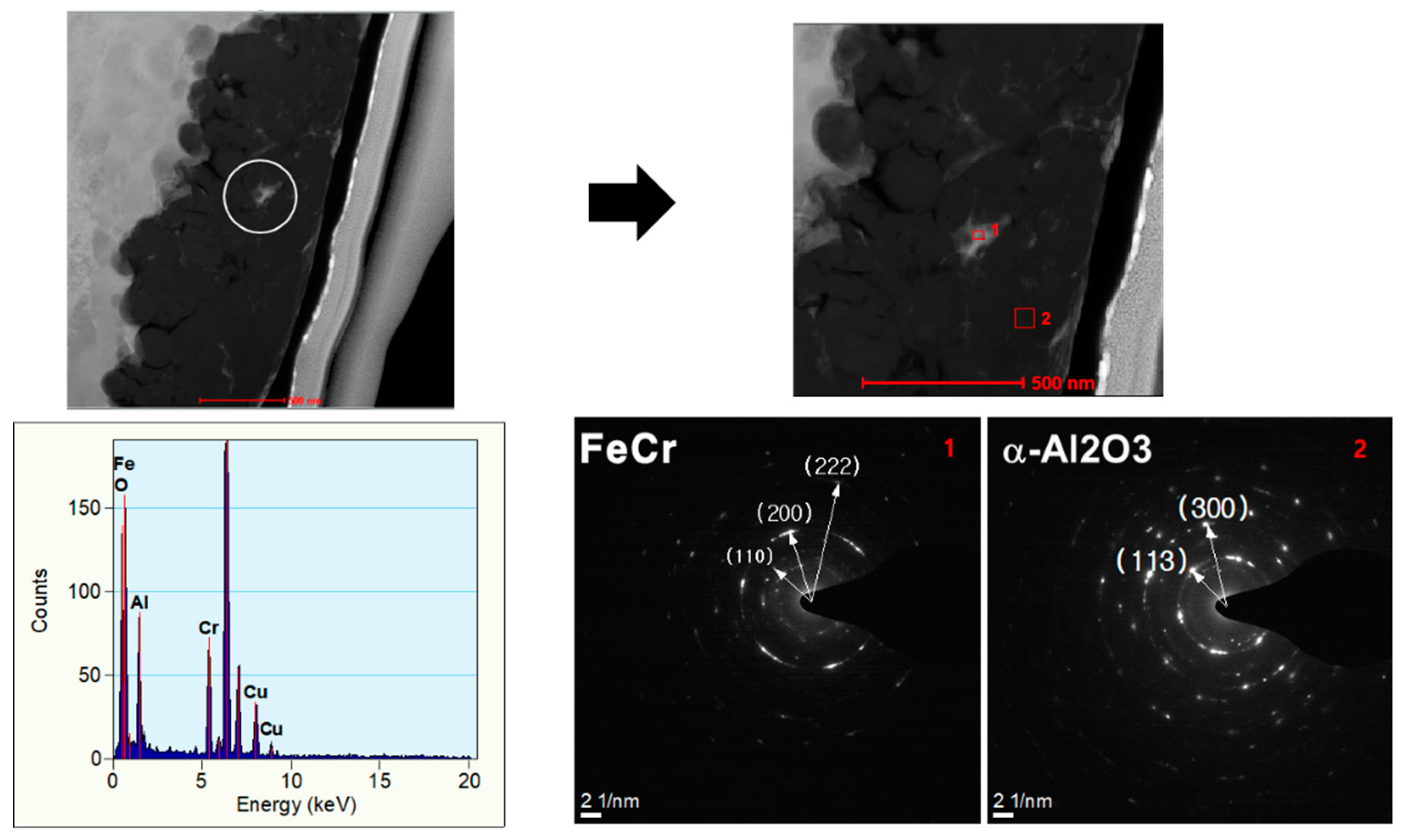
3.1. Characterization of Core–Shell Structured Fillers (CSSFs)
3.2. Characterization of Dual-Functional Sheets (DFSs)
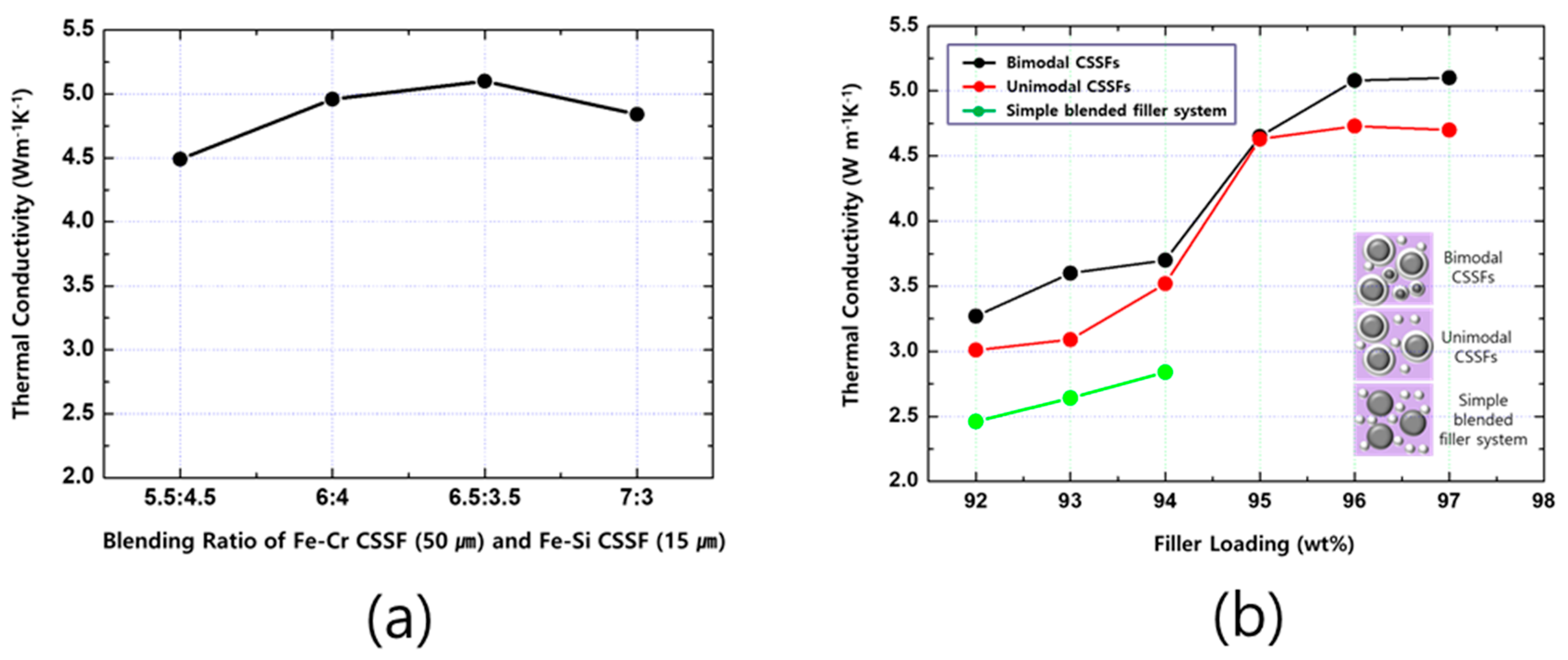
3.2.1. Thermal Conductivity (TC)
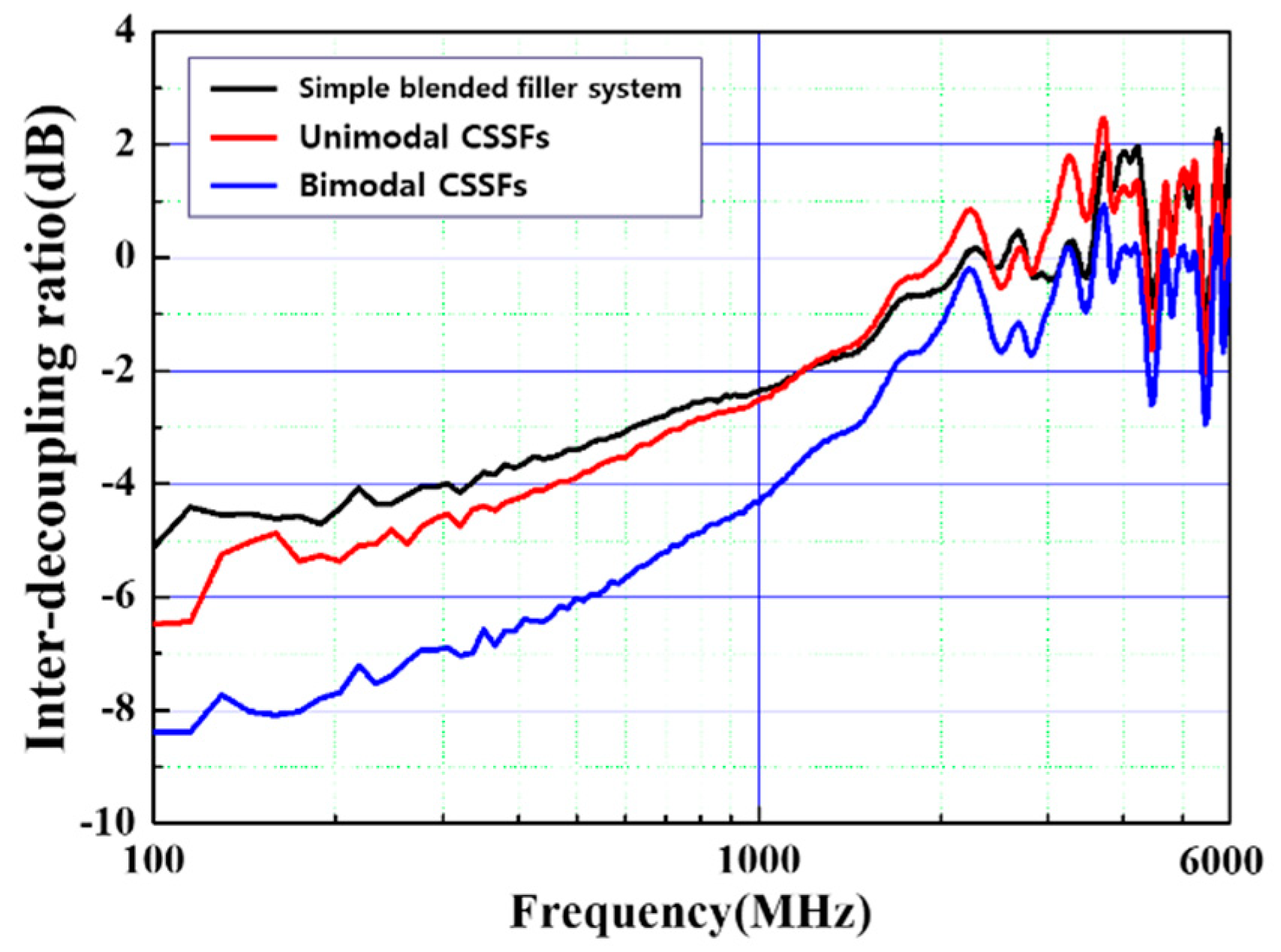
3.2.2. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Property
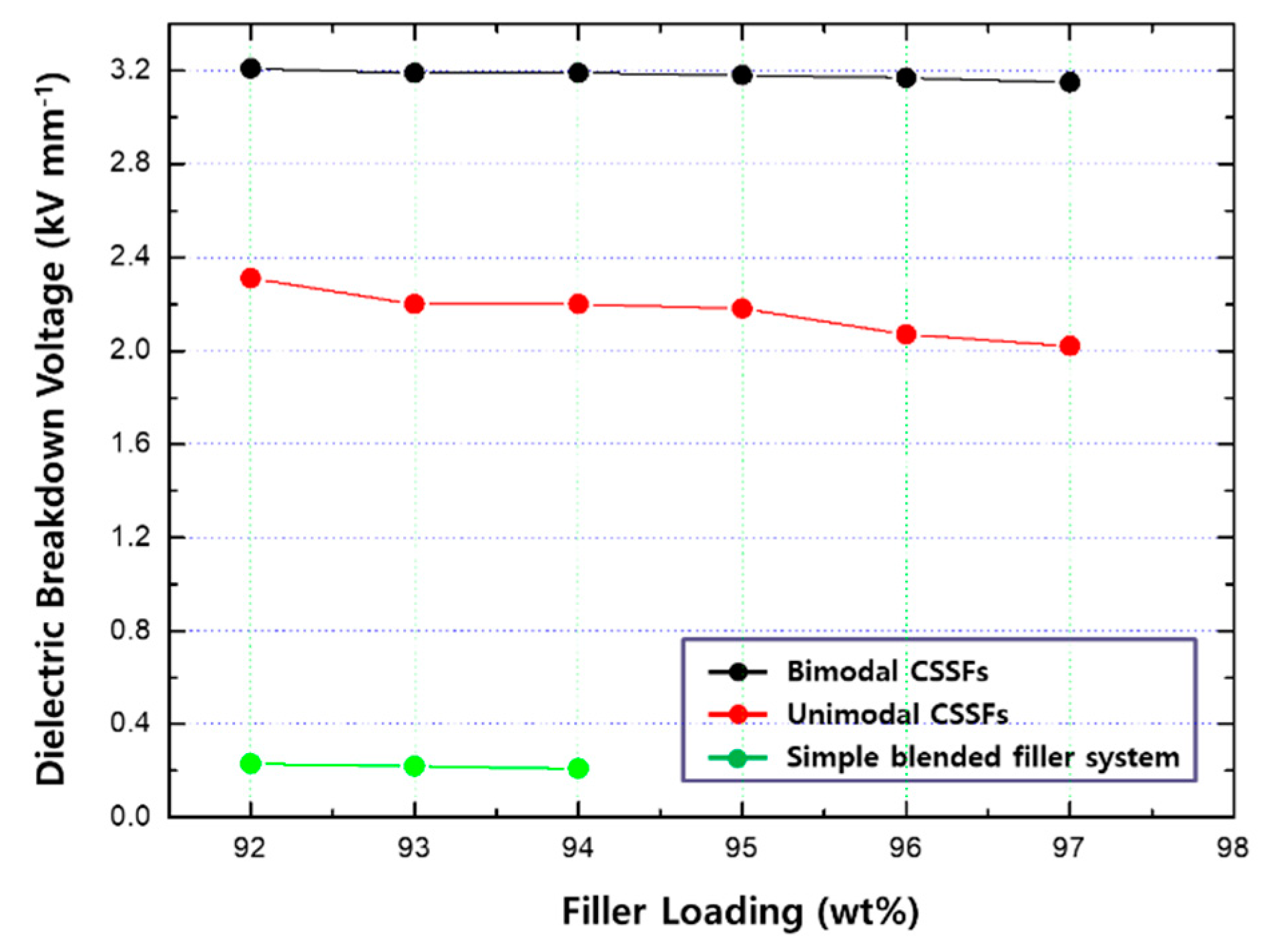
3.2.3. Dielectric Breakdown Voltage (BDV)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sambyal, P.; Noh, S.J.; Hong, J.P.; Kim, W.N.; Iqbal, A.; Hwang, S.S.; Hong, S.M.; Koo, J.M. FeSiAl/metal core shell hybrid composite with high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 172, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheling, P.K.; Shi, I.; Goodson, K.E. Managing heat for electronics. Mater. Today 2005, 8, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otiaba, K.C.; Ekere, N.N.; Bhatti, R.S.; Mallik, S.; Alam, M.O.; Amalu, E.H. Thermal interface materials for automotive electronic control unit: Trends, technology and R&D challenges. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 2031–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Lee, C.C.; Lai, Y.S. High-powered thermal gel degradation evaluation on board-level HFCBGA subjected to reliability tests. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Song, D.; Li, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, D.; Ren, P. Synergistic effect of graphene nanosheets and carbonyl iron-nickel alloy hybrid filler on electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal conductivity of cyanate ester composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Moucka, R.; Sedlacik, M.; Babayan, V.; Pavlinek, V. Enhancement of radio-absorbing properties and thermal conductivity of polysiloxane-based magnetorheological elastomers by the alignment of filler particles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, K.S. Thermal conductivity of thermally conductive composites consisting of core-shell particles with nanostructured shell layers. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Reddy, P. Role of electron-phonon coupling in thermal conductance of metal-nonmetal interfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4768–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Su, J.; Wen, Q.; Luo, F.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W. Enhanced dielectric and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of FeSiAl/Al2O3 ceramics by plasma spraying. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 651, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, A.; Gaska, K. Functional composites with core-shell fillers: Ⅰ. Particle synthesis and thermal conductivity measurements. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7779–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, I.L.; Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Byon, C. Effect of thermal contact resistance on the thermal conductivity of core-shell nanoparticle polymer composites. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 102, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, P.I.; Hudson, T.S. New high-density packings of similarly sized binary spheres. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 115, 19037–19040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojac, T.; Kosec, M. Mechanochemical synthesis of complex ceramic oxides. In High-Energy Ball Milling; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Volume 6, pp. 113–148. [Google Scholar]
- Senna, M.; Billik, P.; Yermakov, A.Y.; Skratek, M.; Caplovicova, M.; Micusik, M.; Coplovic, L.; Bujdos, M.; Nosko, M. Synthesis and magnetic properties of CuAlO2 from high-energy ball-milled Cu2O and Al2O3 mixture. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, H.; Tang, N.; Wu, X.; Du, Y. Highly stable alumina-coated iron nanocomposites synthesized by wet chemistry method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5170–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsfield, H.T. The strength of asphalt mixtures. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1934, 53, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, D.R. Density and packing in an aggregate of mixed spheres. J. Appl. Phys. 1949, 20, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ueno, S.; Hiraguchi, K. Improvement in flowability, oxidation resistance and water wettability of graphite powders by TiO2 coating. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 104, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Thermal conductivity of three-component composites of core-shell particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agari, Y.; Ueda, A.; Tanaka, M.; Nagai, S. Thermal conductivity of a polymer filled with particles in the wide range from low to super-high volume content. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1990, 40, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, K.H. FeCoNi coated glass fibers in composite sheets for electromagnetic absorption and shielding behaviors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 415, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, K.H. FeCoNi-coated glass fabric/polycarbonate composite sheets for electromagnetic absorption and shielding. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Kono, T.; Kawamura, M.; Nakajima, Y. Magnetic properties of FeCr system alloys in direct and alternating field. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 1993, 40, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.F.; Deng, C.R.; Shi, Y.; Chow, Y.S.; Gang, T.B. Microstructure and soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe-Si powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J.-Z.; Lei, J.; Li, Z.M. Highly thermal conductive, anisotropically heat-transferred, mechanically flexible composite film by assembly of boron nitride nanosheets for thermal management. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 180, 107569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fang, J.; Ma, J.; Huang, R.; Chai, S.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Achieving a collapsible, strong, and highly thermally conductive film based on oriented functionalized boron nitride nanosheets and cellulose nanofiber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30035–30045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, Y.; Chatterjee, D.; Bose, S. Core—Multishell heterostructure with excellent heat dissipation for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30762–30773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Qu, B.; Huang, Y.; Chu, D. Colossal permittivity in percolative ceramic/metal dielectric composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Composition (wt %) | Filler wt % | Filler vol % | Porosity 1 (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-12.5%Cr | Fe-6.5%Si | Al2O3 | PDMS | Total | |||||
| Bimodal CSSFs | BM1 | 56.81 | 30.59 | 4.60 | 8 | 100 | 92 | 63.27 | 0.08 |
| BM2 | 57.43 | 30.92 | 4.65 | 7 | 100 | 93 | 66.56 | 0.10 | |
| BM3 | 58.05 | 31.25 | 4.70 | 6 | 100 | 94 | 70.12 | 0.09 | |
| BM4 | 58.66 | 31.59 | 4.75 | 5 | 100 | 95 | 73.99 | 0.12 | |
| BM5 | 59.28 | 31.92 | 4.80 | 4 | 100 | 96 | 78.24 | 0.15 | |
| BM6 | 59.90 | 32.25 | 4.85 | 3 | 100 | 97 | 82.89 | 0.28 | |
| Unimodal CSSFs | UM1 | 87.40 | - | 4.60 | 8 | 100 | 92 | 62.01 | 0.13 |
| UM2 | 88.35 | - | 4.65 | 7 | 100 | 93 | 65.34 | 0.15 | |
| UM3 | 89.30 | - | 4.70 | 6 | 100 | 94 | 68.92 | 0.16 | |
| UM4 | 90.25 | - | 4.75 | 5 | 100 | 95 | 72.95 | 0.24 | |
| UM5 | 91.20 | - | 4.80 | 4 | 100 | 96 | 77.30 | 0.28 | |
| UM6 | 92.15 | - | 4.85 | 3 | 100 | 97 | 82.11 | 0.35 | |
| Simple blended filler system | SB1 | 87.40 | - | 4.60 | 8 | 100 | 92 | 54.97 | 0.14 |
| SB2 | 88.35 | - | 4.65 | 7 | 100 | 93 | 58.11 | 0.16 | |
| SB3 | 89.30 | - | 4.70 | 6 | 100 | 94 | 61.56 | 0.23 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Suh, S.-J. Thermal Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Properties of Composite Sheets Composed of Dry Processed Core–Shell Structured Fillers and Silicone Polymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102318
Choi H-S, Park J-W, Lee K-S, Kim S-W, Suh S-J. Thermal Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Properties of Composite Sheets Composed of Dry Processed Core–Shell Structured Fillers and Silicone Polymers. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102318
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyun-Seok, Ji-Won Park, Kyung-Sub Lee, Sang-Woo Kim, and Su-Jeong Suh. 2020. "Thermal Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Properties of Composite Sheets Composed of Dry Processed Core–Shell Structured Fillers and Silicone Polymers" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102318
APA StyleChoi, H.-S., Park, J.-W., Lee, K.-S., Kim, S.-W., & Suh, S.-J. (2020). Thermal Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Absorbing Properties of Composite Sheets Composed of Dry Processed Core–Shell Structured Fillers and Silicone Polymers. Polymers, 12(10), 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102318






