Characterizing the Relationship between Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs), DNA Methylation Quantitative Trait Loci (mQTLs), and Breast Cancer Risk Variants
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
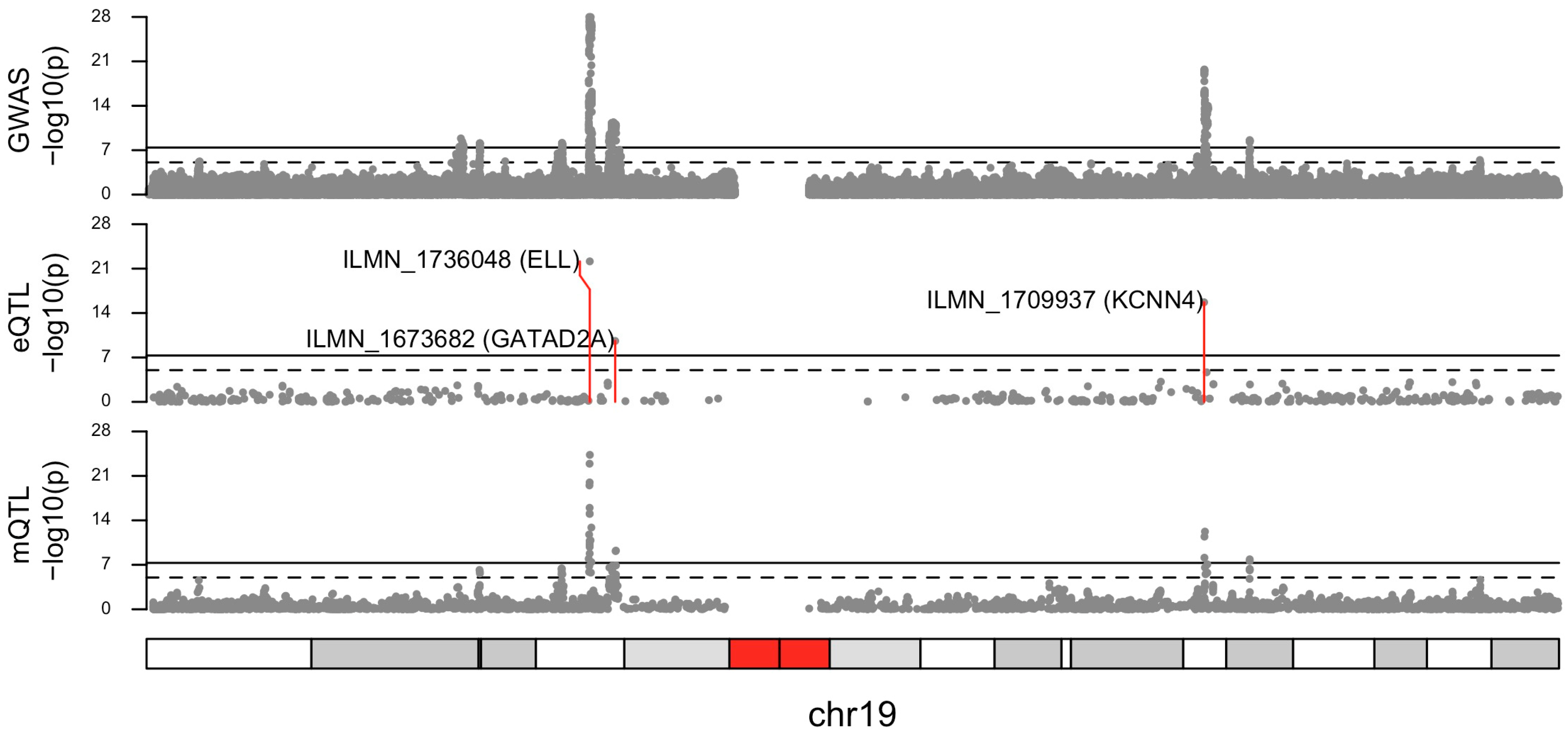
2.1. Pleiotropic Associations—165 DNAm Sites and Eight Genes Associated with Breast Cancer Risk
2.2. Larger eQTL Dataset
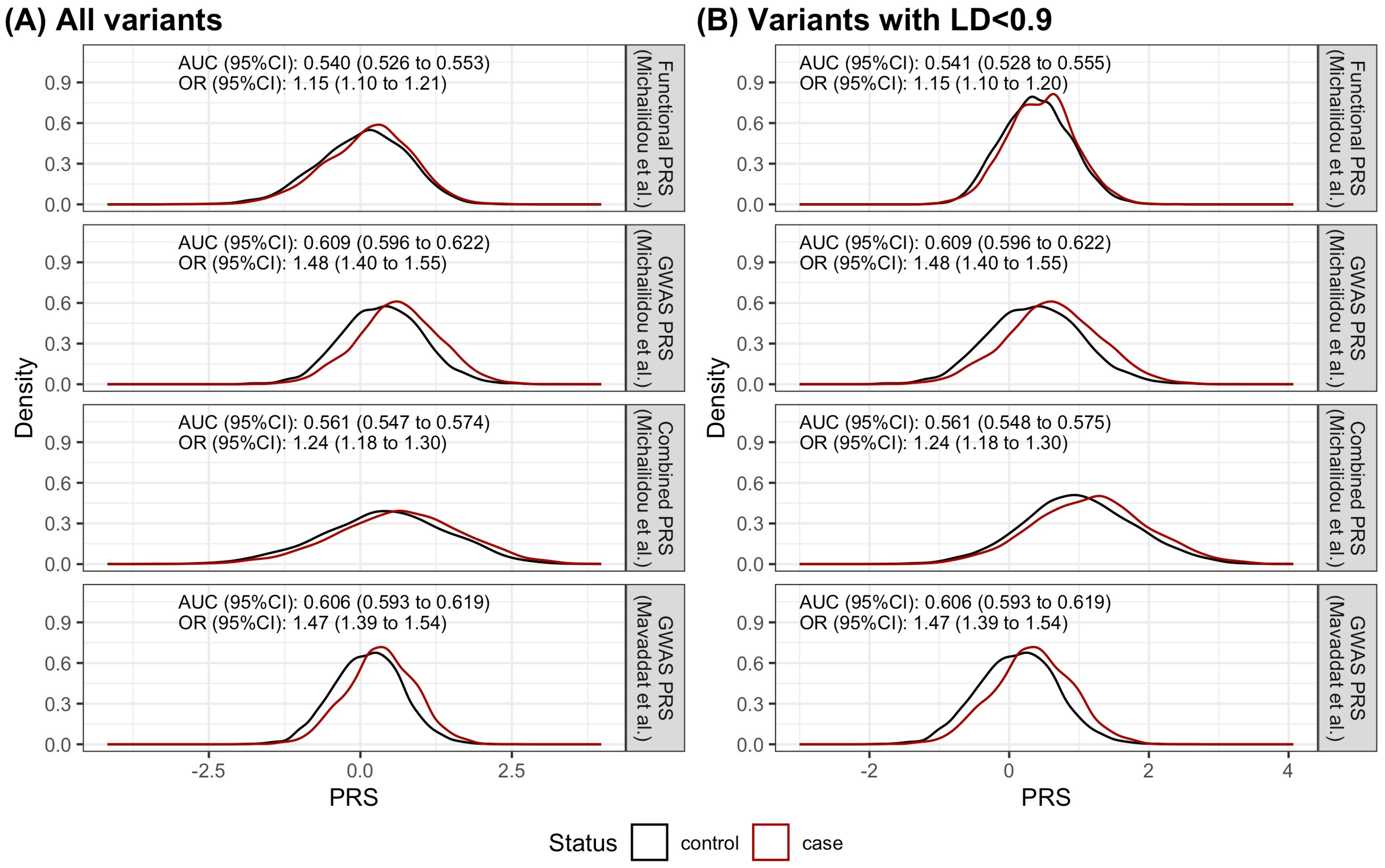
2.3. The Performance of the Functional PRS Was Inferior to the GWAS PRS
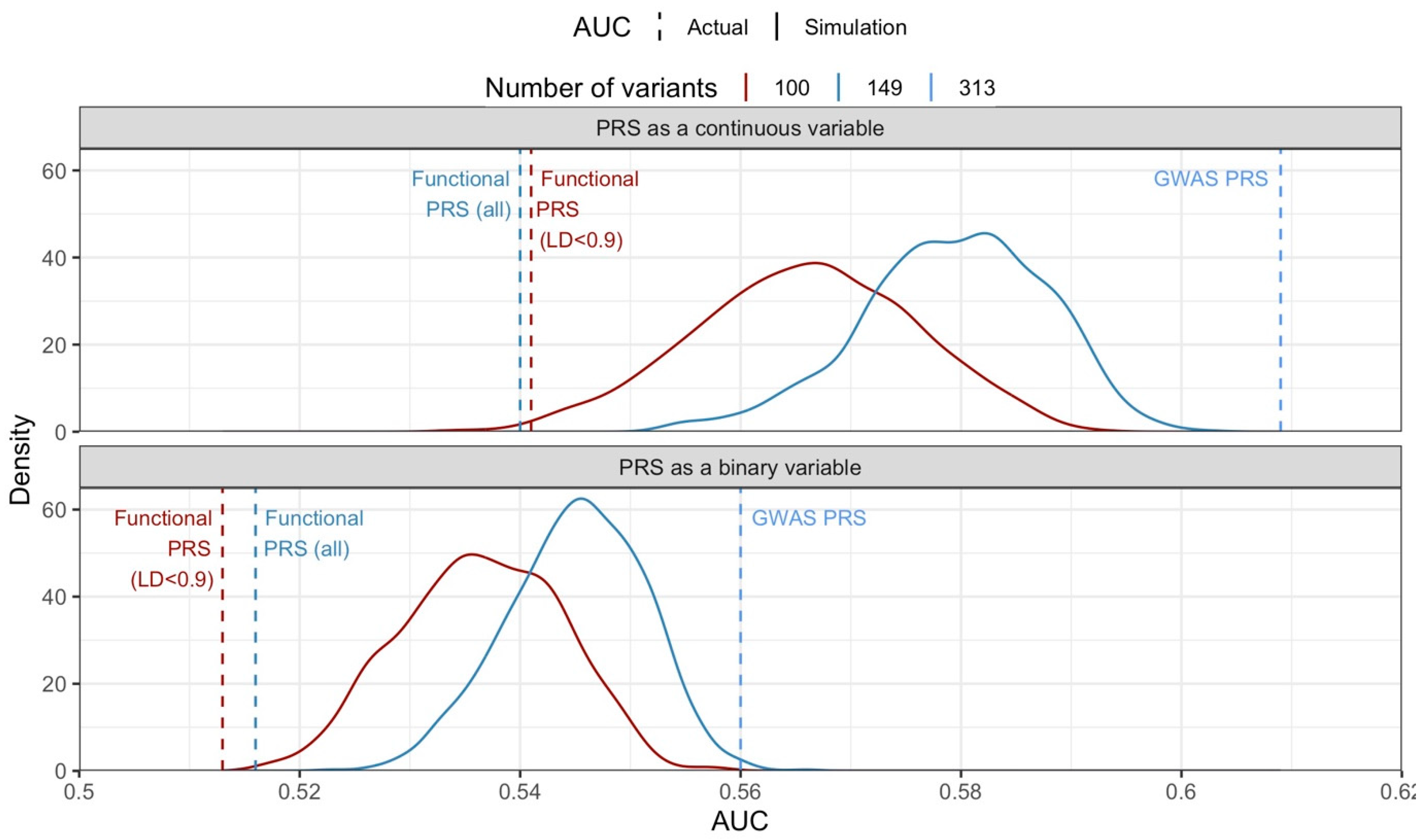
2.4. The Discriminatory Ability of the Functional PRS Was Worse Than the GWAS PRS
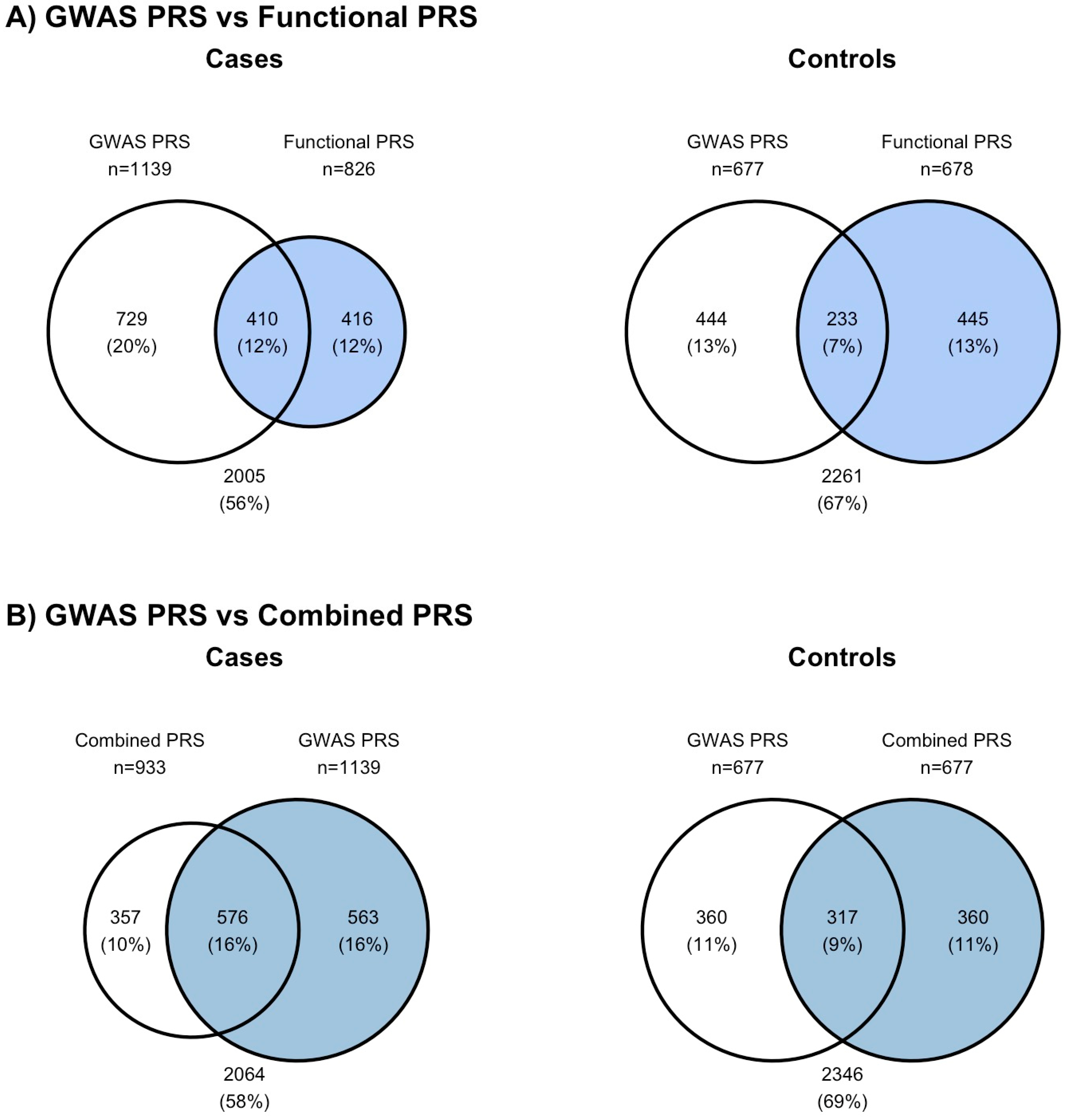
2.5. Performance of PRS Was Not Dependent on Weights Used; However, Different Individuals Were Identified as High Risk
2.6. Individuals Identified as High Risk by PRS
2.7. The Validation of the Findings from the Case–Control Study in a Prospective Cohort
2.8. The Discriminatory Ability of the PRS Derived from Blood, Adipose, and Breast Tissues of the 46 Variants in Our Case–Control Dataset
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Summary Data-Based Mendelian Randomization (SMR)
4.2. Selection of Functional Variants for Breast Cancer PRS Construction
4.3. Polygenic Risk Score (PRS)
4.4. The Performance of the Functional PRS in a Case–Control Study
4.5. Cases—Singapore Breast Cancer Cohort (SGBCC)
4.6. Controls—Singapore Multi-Ethnic Cohort Phase 2 (MEC2) Study
4.7. DNA Isolation and Genotyping
4.8. Performance Assessment of PRS
4.9. Simulation Study to Address Imbalance in Number of Variants in Each PRS
4.10. The Validation of the Findings from the Case–Control Study in a Prospective Cohort
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Easton, D.F.; Pooley, K.A.; Dunning, A.M.; Pharoah, P.D.; Thompson, D.; Ballinger, D.G.; Struewing, J.P.; Morrison, J.; Field, H.; Luben, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies novel breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature 2007, 447, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ahearn, T.U.; Lecarpentier, J.; Barnes, D.; Beesley, J.; Qi, G.; Jiang, X.; O’Mara, T.A.; Zhao, N.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 32 novel breast cancer susceptibility loci from overall and subtype-specific analyses. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, K.; Lindstrom, S.; Dennis, J.; Beesley, J.; Hui, S.; Kar, S.; Lemacon, A.; Soucy, P.; Glubb, D.; Rostamianfar, A.; et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature 2017, 551, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, Y.; Roger, J.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Hirst, G.L.; Swigart, L.B.; Huntsman, S.; Hu, D.; Nierenberg, J.L.; Middha, P.; et al. Development and testing of a polygenic risk score for breast cancer aggressiveness. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavaddat, N.; Michailidou, K.; Dennis, J.; Lush, M.; Fachal, L.; Lee, A.; Tyrer, J.P.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, Q.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Polygenic Risk Scores for Prediction of Breast Cancer and Breast Cancer Subtypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakeman, I.M.M.; Schmidt, M.K.; van Asperen, C.J.; Devilee, P. Breast Cancer Susceptibility—Towards Individualised Risk Prediction. Curr. Genet. Med. Rep. 2019, 7, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.D.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S. The Post-GWAS Era: From Association to Function. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, Y.G.; Farnham, P.J. Making sense of GWAS: Using epigenomics and genome engineering to understand the functional relevance of SNPs in non-coding regions of the human genome. Epigenet. Chromatin 2015, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Gamez, E.; Trynka, G. From GWAS to Function: Using Functional Genomics to Identify the Mechanisms Underlying Complex Diseases. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, A.J.; Thompson, W.K.; Pham, P.; Torkamani, A.; Roddey, J.C.; Sullivan, P.F.; Kelsoe, J.R.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Furberg, H.; The Tobacco and Genetics Consortium; et al. All SNPs are not created equal: Genome-wide association studies reveal a consistent pattern of enrichment among functionally annotated SNPs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, T.; Zheng, Z.; Lloyd-Jones, L.R.; Marioni, R.E.; Martin, N.G.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. Integrative analysis of omics summary data reveals putative mechanisms underlying complex traits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Yu, W. Mendelian randomization analysis identified genes pleiotropically associated with central corneal thickness. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Feng, B.; Lu, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, L. Mendelian randomization analysis identified genes pleiotropically associated with the risk and prognosis of COVID-19. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Jing, H.; Meng, Q.; Yang, J. Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS and mQTL data identified novel pleiotropic DNA methylation loci for neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 97, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahed, H.; Feng, X.; Sheikh, M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Ginsburg, O.; Shiels, M.S.; Robbins, H.A. Age at diagnosis for lung, colon, breast and prostate cancers: An international comparative study. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 154, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosa, U.; Claringbould, A.; Westra, H.J.; Bonder, M.J.; Deelen, P.; Zeng, B.; Kirsten, H.; Saha, A.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Yazar, S.; et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBL-EBI: The Home for Big Data in Biology. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/eqtl/ (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Liming Liang’s Faculty Website. Available online: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/liming-liang/software/eqtl/ (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Ferreira, M.A.; Gamazon, E.R.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Aittomaki, K.; Andrulis, I.L.; Anton-Culver, H.; Arason, A.; Arndt, V.; Aronson, K.J.; Arun, B.K.; et al. Genome-wide association and transcriptome studies identify target genes and risk loci for breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhao, H. A review of post-GWAS prioritization approaches. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantor, R.M.; Lange, K.; Sinsheimer, J.S. Prioritizing GWAS results: A review of statistical methods and recommendations for their application. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, N.J.; Old, R. The illusion of polygenic disease risk prediction. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1705–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Schmidtke, J.; Krawczak, M.; Caliebe, A. Clinical utility of polygenic risk scores: A critical 2023 appraisal. J. Community Genet. 2023, 14, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.M.; Vassos, E. Polygenic risk scores: From research tools to clinical instruments. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxim, L.D.; Niebo, R.; Utell, M.J. Screening tests: A review with examples. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, L.R.; Holloway, A.; McRae, A.; Yang, J.; Small, K.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, B.; Bakshi, A.; Metspalu, A.; Dermitzakis, M.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.K.; Tan, M.M.; Mavaddat, N.; Tai, M.C.; Mariapun, S.; Li, J.; Ho, P.J.; Dennis, J.; Tyrer, J.P.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. European polygenic risk score for prediction of breast cancer shows similar performance in Asian women. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, P.J.; Lin, A.F.; Arendt, L.M.; Klebba, I.; Jones, A.D.; Rudnick, J.A.; DiMeo, T.A.; Gilmore, H.; Jefferson, D.M.; Graham, R.A.; et al. Mapping the cellular and molecular heterogeneity of normal and malignant breast tissues and cultured cell lines. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, E.; Gorrie-Stone, T.J.; Smart, M.C.; Burrage, J.; Hughes, A.; Bao, Y.; Kumari, M.; Schalkwyk, L.C.; Mill, J. Leveraging DNA-Methylation Quantitative-Trait Loci to Characterize the Relationship between Methylomic Variation, Gene Expression, and Complex Traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, T.A.; Chanock, S.J.; Machiela, M.J. LDlinkR: An R Package for Rapidly Calculating Linkage Disequilibrium Statistics in Diverse Populations. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gel, B.; Serra, E. karyoploteR: An R/Bioconductor package to plot customizable genomes displaying arbitrary data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3088–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.J.; Yeoh, Y.S.; Miao, H.; Lim, S.H.; Tan, E.Y.; Tan, B.K.T.; Tan, V.K.M.; Tan, S.M.; Yong, W.S.; Wong, F.Y.; et al. Cohort profile: The Singapore Breast Cancer Cohort (SGBCC), a multi-center breast cancer cohort for evaluation of phenotypic risk factors and genetic markers. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.H.X.; Tan, L.W.L.; Sim, X.; Tai, E.S.; Lee, J.J.; Chia, K.S.; van Dam, R.M. Cohort Profile: The Singapore Multi-Ethnic Cohort (MEC) study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 699–699j. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankin, J.H.; Stram, D.O.; Arakawa, K.; Park, S.; Low, S.H.; Lee, H.P.; Yu, M.C. Singapore Chinese Health Study: Development, validation, and calibration of the quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Nutr. Cancer 2001, 39, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorajoo, R.; Chang, X.; Gurung, R.L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Beckman, K.B.; Adams-Haduch, J.; Yiamunaa, M.; Liu, S.; et al. Loci for human leukocyte telomere length in the Singaporean Chinese population and trans-ethnic genetic studies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case–Control Study | Prospective Cohort Study | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRS | Weights | n | AUC (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | Sensitivity * | Specificity * | n | AUC (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | Sensitivity * | Specificity * |
| Continuous | |||||||||||
| GWAS PRS | Mavaddat et al. [5] | 313 | 0.606 (0.593 to 0.619) | 1.47 (1.39 to 1.54) | 0.688 | 0.469 | 290 | 0.592 (0.564 to 0.621) | 1.42 (1.29 to 1.57) | 0.324 | 0.820 |
| Functional PRS | Michailidou et al. [3] | 149 | 0.540 (0.526 to 0.553) | 1.15 (1.10 to 1.21) | 0.651 | 0.417 | 146 | 0.568 (0.541 to 0.596) | 1.28 (1.16 to 1.41) | 0.688 | 0.422 |
| GWAS PRS | Michailidou et al. | 313 | 0.609 (0.596 to 0.622) | 1.48 (1.40 to 1.55) | 0.578 | 0.581 | 290 | 0.595 (0.567 to 0.623) | 1.43 (1.29 to 1.57) | 0.655 | 0.490 |
| Combined PRS | Michailidou et al. | 457 | 0.561 (0.547 to 0.574) | 1.24 (1.18 to 1.30) | 0.522 | 0.572 | 431 | 0.603 (0.575 to 0.630) | 1.44 (1.30 to 1.59) | 0.648 | 0.531 |
| Functional PRS, LD < 0.9 | Michailidou et al. | 100 | 0.541 (0.528 to 0.555) | 1.15 (1.10 to 1.20) | 0.390 | 0.680 | 98 | 0.564 (0.537 to 0.592) | 1.25 (1.13 to 1.38) | 0.643 | 0.485 |
| Combined PRS, LD < 0.9 | Michailidou et al. | 401 | 0.561 (0.548 to 0.575) | 1.24 (1.18 to 1.30) | 0.489 | 0.615 | 376 | 0.597 (0.569 to 0.624) | 1.42 (1.29 to 1.57) | 0.690 | 0.471 |
| Binary ^ | |||||||||||
| GWAS PRS | Mavaddat et al. | 313 | 0.560 (0.550 to 0.570) | 1.88 (1.69 to 2.10) | 0.320 | 0.8 | 290 | 0.565 (0.543 to 0.588) | 1.98 (1.60 to 2.44) | 0.331 | 0.8 |
| Functional PRS | Michailidou et al. | 149 | 0.516 (0.506 to 0.525) | 1.21 (1.07 to 1.35) | 0.232 | 0.8 | 146 | 0.538 (0.516 to 0.560) | 1.53 (1.23 to 1.90) | 0.276 | 0.8 |
| GWAS PRS | Michailidou et al. | 313 | 0.560 (0.550 to 0.570) | 1.88 (1.68 to 2.10) | 0.320 | 0.8 | 290 | 0.558 (0.536 to 0.581) | 1.85 (1.50 to 2.29) | 0.317 | 0.8 |
| Combined PRS | Michailidou et al. | 457 | 0.531 (0.521 to 0.541) | 1.42 (1.27 to 1.59) | 0.262 | 0.8 | 431 | 0.551 (0.529 to 0.574) | 1.73 (1.40 to 2.15) | 0.302 | 0.8 |
| Functional PRS, LD < 0.9 | Michailidou et al. | 100 | 0.513 (0.504 to 0.523) | 1.17 (1.04 to 1.31) | 0.227 | 0.8 | 98 | 0.531 (0.510 to 0.552) | 1.42 (1.14 to 1.77) | 0.262 | 0.8 |
| Combined PRS, LD < 0.9 | Michailidou et al. | 401 | 0.531 (0.522 to 0.541) | 1.43 (1.27 to 1.60) | 0.263 | 0.8 | 376 | 0.550 (0.528 to 0.572) | 1.71 (1.38 to 2.12) | 0.300 | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, P.J.; Khng, A.; Tan, B.K.-T.; Khor, C.C.; Tan, E.Y.; Lim, G.H.; Yuan, J.-M.; Tan, S.-M.; Chang, X.; Tan, V.K.M.; et al. Characterizing the Relationship between Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs), DNA Methylation Quantitative Trait Loci (mQTLs), and Breast Cancer Risk Variants. Cancers 2024, 16, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112072
Ho PJ, Khng A, Tan BK-T, Khor CC, Tan EY, Lim GH, Yuan J-M, Tan S-M, Chang X, Tan VKM, et al. Characterizing the Relationship between Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs), DNA Methylation Quantitative Trait Loci (mQTLs), and Breast Cancer Risk Variants. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112072
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Peh Joo, Alexis Khng, Benita Kiat-Tee Tan, Chiea Chuen Khor, Ern Yu Tan, Geok Hoon Lim, Jian-Min Yuan, Su-Ming Tan, Xuling Chang, Veronique Kiak Mien Tan, and et al. 2024. "Characterizing the Relationship between Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs), DNA Methylation Quantitative Trait Loci (mQTLs), and Breast Cancer Risk Variants" Cancers 16, no. 11: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112072
APA StyleHo, P. J., Khng, A., Tan, B. K.-T., Khor, C. C., Tan, E. Y., Lim, G. H., Yuan, J.-M., Tan, S.-M., Chang, X., Tan, V. K. M., Sim, X., Dorajoo, R., Koh, W.-P., Hartman, M., & Li, J. (2024). Characterizing the Relationship between Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs), DNA Methylation Quantitative Trait Loci (mQTLs), and Breast Cancer Risk Variants. Cancers, 16(11), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112072








