In Vivo Thermal Ablation of Deep Intrahepatic Targets Using a Super-Convergent MRgHIFU Applicator and a Pseudo-Tumor Model
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol for In Vivo Experiment
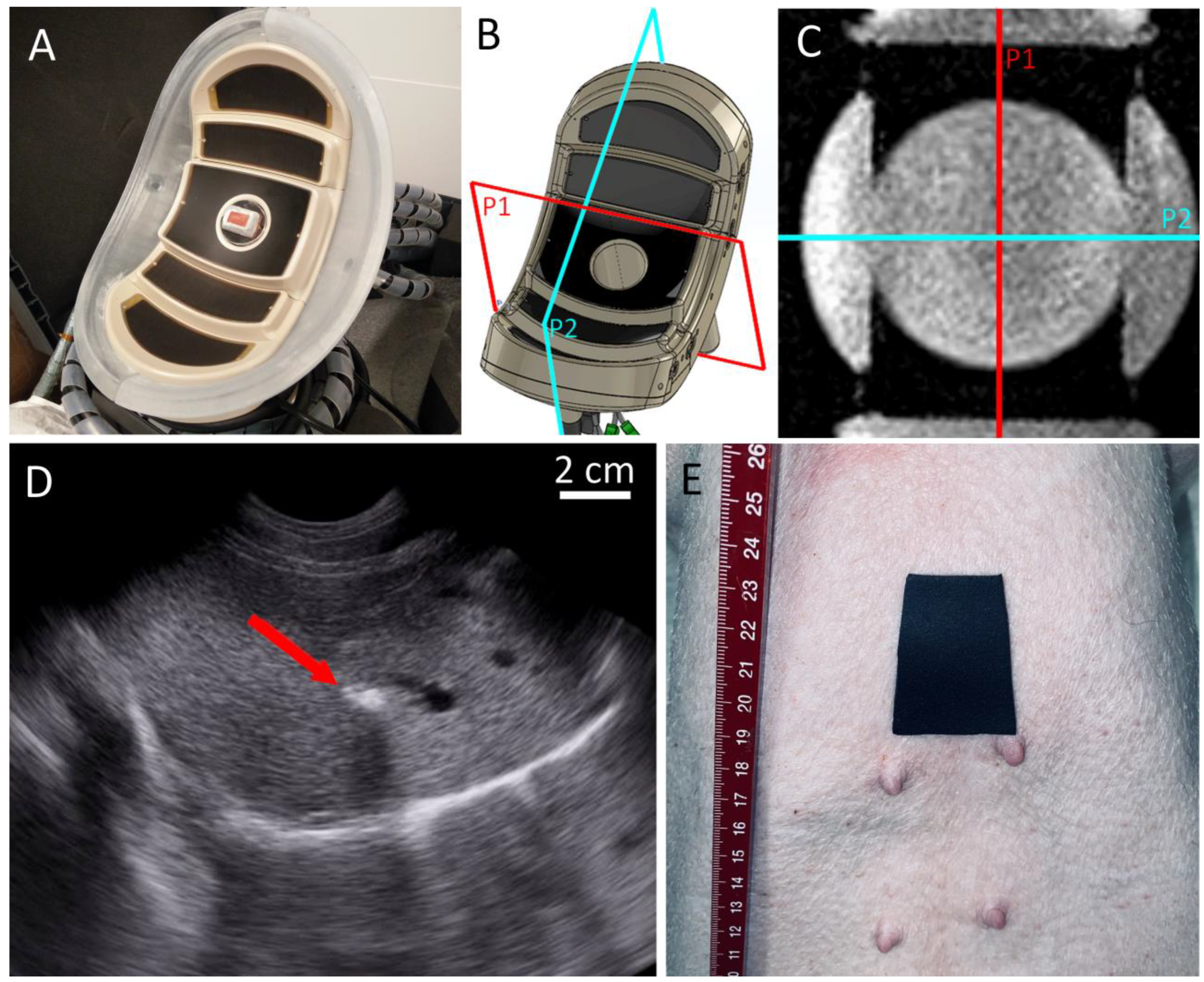
2.2. MR-Guided HIFU
2.3. Post-Treatment Follow-Up
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, J.; Victor, D.; 3rd Asham, E.H.; Burroughs, S.G.; Boktour, M.; Saharia, A.; Li, X.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Monsour, H.P., Jr. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2016, 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.; Frenette, C. Updates in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi, S.; Lepage, C.; Hatem, C.; Coatmeur, O.; Faivre, J.; Bouvier, A.M. Epidemiology and management of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrand, J.; Nilsson, H.; Stromberg, C.; Jonas, E.; Freedman, J. Colorectal cancer liver metastases—A population-based study on incidence, management and survival. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouquet, A.; Abdalla, E.K.; Kopetz, S.; Garrett, C.R.; Overman, M.J.; Eng, C.; Andreou, A.; Loyer, E.M.; Madoff, D.C.; Curley, S.A.; et al. High survival rate after two-stage resection of advanced colorectal liver metastases: Response-based selection and complete resection define outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackl, C.; Neumann, P.; Gerken, M.; Loss, M.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Schlitt, H.J. Treatment of colorectal liver metastases in Germany: A ten-year population-based analysis of 5772 cases of primary colorectal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Schulick, R.D.; Choti, M.A. Expanding criteria for resectability of colorectal liver metastases. Oncologist 2008, 13, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Schwartz, M.; Mazzaferro, V. Resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Singh, T.; Soni, S. Pre-operative Assessment of Ablation Margins for Variable Blood Perfusion Metrics in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Complex Breast Tumour Anatomy: Simulation Paradigms in Thermal Therapies. Comput. Meth Prog. Bio. 2021, 198, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivesgaard, K.; Larsen, L.P.; Sorensen, M.; Kramer, S.; Schlander, S.; Amanavicius, N.; Bharadwaz, A.; Tonner Nielsen, D.; Viborg Mortensen, F.; Morre Pedersen, E. Diagnostic accuracy of CE-CT, MRI and FDG PET/CT for detecting colorectal cancer liver metastases in patients considered eligible for hepatic resection and/or local ablation. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4735–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M. Incorporating vascular-stasis based blood perfusion to evaluate the thermal signatures of cell-death using modified Arrhenius equation with regeneration of living tissues during nanoparticle-assisted thermal therapy. Int. Commun. Heat. Mass. 2022, 135, 106046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Jimenez, J.; Esteban-Villarrubia, J.; Ferreiro-Monteagudo, R.; Carrato, A. Local Treatments in the Unresectable Patient with Colorectal Cancer Metastasis: A Review from the Point of View of the Medical Oncologist. Cancers 2021, 13, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chou, B.; Yalamanchili, A.; Lim, S.N.; Dawson, L.A.; Thomas, T.O. Local Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Role of MRI-Guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, B.X.; Long, H.Y. Ablative strategies for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chi, J.; Shi, D.; Wang, T.; Cui, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhai, B. Long-term results of percutaneous microwave ablation for colorectal liver metastases. HPB 2021, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, A.; Bhogal, R.H.; Fotiadis, N.; Mavroeidis, V.K. The Role of Ablative Techniques in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Indications and Outcomes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.H.; Zhu, Y.K.; Zou, X.M.; Zhou, H.D.; Li, R.H.; Zhong, J.H. Repeat hepatic resection versus percutaneous ablation for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Meta-analysis. BJS Open 2022, 6, zrac036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Jaraysa, Y.; Martin, S.S.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Savage, R.H.; Nour-Eldin, N.A.; Mehmedovic, A. A prospective randomized trial comparing microwave and radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver metastases using a dual ablation system horizontal line The Mira study. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2022, 9, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Wu, P.P.; Huang, B.; Kuang, M.; Qian, G.J. Microwave ablation is as effective as radiofrequency ablation for very-early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavriilidis, P.; Roberts, K.J.; de′Angelis, N.; Aldrighetti, L.; Sutcliffe, R.P. Recurrence and survival following microwave, radiofrequency ablation, and hepatic resection of colorectal liver metastases: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2021, 20, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Z.; Lu, F.; Ren, L.; Song, X.; Li, B.; Li, X. Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e29321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Collings, A.T.; Dirks, R.; Onkendi, E.; Nelson, D.; Ozair, A.; Miraflor, E.; Rahman, F.; Whiteside, J.; Shah, M.M.; et al. Surgical approach to microwave and radiofrequency liver ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastases less than 5 cm: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 3340–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Yu, M.; Zheng, M.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. Effects of radiofrequency ablation versus other ablating techniques on hepatocellular carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galanakis, N.; Kehagias, E.; Matthaiou, N.; Samonakis, D.; Tsetis, D. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency or microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Hepat. Oncol. 2018, 5, HEP07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orlacchio, A.; Bolacchi, F.; Chegai, F.; Bergamini, A.; Costanzo, E.; Del Giudice, C.; Angelico, M.; Simonetti, G. Comparative evaluation of percutaneous laser and radiofrequency ablation in patients with HCC smaller than 4 cm. Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.Z.; Li, J.L.; Xu, K.C. Percutaneous Cryoablation for Liver Cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2014, 2, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Bageacu, S.; Kaczmarek, D.; Lacroix, M.; Dubois, J.; Forest, J.; Porcheron, J. Cryosurgery for resectable and unresectable hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littrup, P.J.; Aoun, H.D.; Adam, B.; Krycia, M.; Prus, M.; Shields, A. Percutaneous cryoablation of hepatic tumors: Long-term experience of a large U.S. series. Abdom Radiol 2016, 41, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, G.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qu, J.; Lou, M.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Cryotherapy for cirrhosis-based hepatocellular carcinoma: A single center experience from 1595 treated cases. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Clark, T.W. Cryoablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21 (Suppl. 8), S187–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikbayeva, Z.; Tosi, D.; Balmassov, D.; Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Inglezakis, V. Application of Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials in Thermal Ablation Therapy of Cancer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.; Ma, R.H.; Zhu, L. Quantitative evaluation of effects of coupled temperature elevation, thermal damage, and enlarged porosity on nanoparticle migration in tumors during magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. Int. Commun. Heat. Mass. 2021, 126, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Bianchi, L.; De Landro, M.; Korganbayev, S.; Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P. Laser-induced optothermal response of gold nanoparticles: From a physical viewpoint to cancer treatment application. J. Biophotonics 2021, 14, e202000161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Q.; Kuang, L.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y. Effectiveness and safety of ultrasound-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for the treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Senneville, B.D.; Mougenot, C.; Quesson, B.; Dragonu, I.; Grenier, N.; Moonen, C.T. MR thermometry for monitoring tumor ablation. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroda, K. MR techniques for guiding high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatments. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, C.T.; Quesson, B.; Salomir, R.; Vimeux, F.C.; de Zwart, J.A.; van Vaals, J.J.; Grenier, N.; Palussiere, J. Thermal therapies in interventional MR imaging. Focused ultrasound. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2001, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, Y.; Calderon, A.; Watanabe, H.; Okamoto, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kuroda, K.; Suzuki, Y. A precise and fast temperature mapping using water proton chemical shift. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDannold, N. Quantitative MRI-based temperature mapping based on the proton resonant frequency shift: Review of validation studies. Int. J. Hyperth. 2005, 21, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.E.; Cho, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Han, J.Y. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation in hepatic and pancreatic cancer: Complications. Abdom. Imaging 2011, 36, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanter, M.; Pernot, M.; Aubry, J.F.; Montaldo, G.; Marquet, F.; Fink, M. Compensating for bone interfaces and respiratory motion in high-intensity focused ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2007, 23, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, S.H.; Ma, K.W.; She, W.H.; Chu, F.; Lau, V.; Lam, S.W.; Cheung, T.T.; Lo, C.M. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of liver tumors in difficult locations. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzidei, M.; Napoli, A.; Sandolo, F.; Marincola, B.C.; Di Martino, M.; Berloco, P.; Bosco, S.; Bezzi, M.; Catalano, C. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation in abdominal moving organs: A feasibility study in selected cases of pancreatic and liver cancer. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2014, 37, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auboiroux, V.; Dumont, E.; Petrusca, L.; Viallon, M.; Salomir, R. An MR-compliant phased-array HIFU transducer with augmented steering range, dedicated to abdominal thermotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 3563–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorton, O.; Guillemin, P.C.; Mori, N.; Crowe, L.A.; Boudabbous, S.; Terraz, S.; Becker, C.D.; Cattin, P.; Salomir, R.; Gui, L. Self-Scanned HIFU Ablation of Moving Tissue Using Real-Time Hybrid US-MR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auboiroux, V.; Petrusca, L.; Viallon, M.; Muller, A.; Terraz, S.; Breguet, R.; Montet, X.; Becker, C.D.; Salomir, R. Respiratory-gated MRgHIFU in upper abdomen using an MR-compatible in-bore digital camera. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 421726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Senneville, B.D.; Ries, M.; Maclair, G.; Moonen, C. MR-guided thermotherapy of abdominal organs using a robust PCA-based motion descriptor. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Z.B.; Chen, W.Z.; Zou, J.Z.; Bai, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, K.Q.; Jin, C.B.; Xie, F.L.; Su, H.B. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment with high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation combined with transcatheter arterial embolization. Radiology 2005, 235, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Murakami, T.; Mikami, K.; Onishi, H.; Tanigawa, N.; Marukawa, T.; Nakamura, H. A case of hepatocellular carcinoma treated by MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation with respiratory gating. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2006, 5, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bour, P.; Ozenne, V.; Marquet, F.; Denis de Senneville, B.; Dumont, E.; Quesson, B. Real-time 3D ultrasound based motion tracking for the treatment of mobile organs with MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diodato, A.; Cafarelli, A.; Schiappacasse, A.; Tognarelli, S.; Ciuti, G.; Menciassi, A. Motion compensation with skin contact control for high intensity focused ultrasound surgery in moving organs. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanel, L.A.; Nageotte, F.; Vappou, J.; Luo, J.; Cuvillon, L.; de Mathelin, M. Robotized High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) system for treatment of mobile organs using motion tracking by ultrasound imaging: An in vitro study. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2015, 2015, 2571–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Celicanin, Z.; Auboiroux, V.; Bieri, O.; Petrusca, L.; Santini, F.; Viallon, M.; Scheffler, K.; Salomir, R. Real-time method for motion-compensated MR thermometry and MRgHIFU treatment in abdominal organs. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celicanin, Z.; Manasseh, G.; Petrusca, L.; Scheffler, K.; Auboiroux, V.; Crowe, L.A.; Hyacinthe, J.N.; Natsuaki, Y.; Santini, F.; Becker, C.D.; et al. Hybrid ultrasound-MR guided HIFU treatment method with 3D motion compensation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2511–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Petrusca, L.; Auboiroux, V.; Valette, P.J.; Salomir, R.; Cotton, F. Management of respiratory motion in extracorporeal high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment in upper abdominal organs: Current status and perspectives. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2013, 36, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhang, D.; Gong, X.F. Influence of ribs on the nonlinear sound field of therapeutic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelat, P.; ter Haar, G.; Saffari, N. The optimization of acoustic fields for ablative therapies of tumours in the upper abdomen. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, L.; Jin, C.; Peng, S.; Yang, W.; Li, K.; Su, H.; Chen, W.; Bai, J.; et al. High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) therapy for local treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Role of partial rib resection. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 72, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomir, R.; Petrusca, L.; Auboiroux, V.; Muller, A.; Vargas, M.I.; Morel, D.R.; Goget, T.; Breguet, R.; Terraz, S.; Hopple, J.; et al. Magnetic resonance-guided shielding of prefocal acoustic obstacles in focused ultrasound therapy: Application to intercostal ablation in liver. Invest. Radiol. 2013, 48, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesson, B.; Merle, M.; Kohler, M.O.; Mougenot, C.; Roujol, S.; de Senneville, B.D.; Moonen, C.T. A method for MRI guidance of intercostal high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the liver. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Civale, J.; Clarke, R.; Rivens, I.; ter Haar, G. The use of a segmented transducer for rib sparing in HIFU treatments. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaekers, P.; Ries, M.; Moonen, C.T.; de Greef, M. Improved intercostal HIFU ablation using a phased array transducer based on Fermat′s spiral and Voronoi tessellation: A numerical evaluation. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1071–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorton, O.; Guillemin, P.C.; M′Rad, Y.; Peloso, A.; Boudabbous, S.; Charbonnier, C.; Holman, R.; Crowe, L.A.; Gui, L.; Poletti, P.A.; et al. A Novel Concept of a Phased-Array HIFU Transducer Optimized for MR-Guided Hepatic Ablation: Embodiment and First In-Vivo Studies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 899440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrusca, L.; Viallon, M.; Breguet, R.; Terraz, S.; Manasseh, G.; Auboiroux, V.; Goget, T.; Baboi, L.; Gross, P.; Sekins, K.M.; et al. An experimental model to investigate the targeting accuracy of MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation in liver. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viallon, M.; Petrusca, L.; Auboiroux, V.; Goget, T.; Baboi, L.; Becker, C.D.; Salomir, R. Experimental methods for improved spatial control of thermal lesions in magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1580–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Council of Radiation Protection (NCRP). National council of radiation protection & measurements report no.74: Biological effects of ultrasound: Mechanisms and clinical implications (report no. 74). Tech. Rep. NCRP 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Gedroyc, W.M. New clinical applications of magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 17, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Gedroyc, W.; Jolesz, F.A. Focused ultrasound as a local therapy for liver cancer. Cancer J. 2010, 16, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzidei, M.; Marincola, B.C.; Bezzi, M.; Brachetti, G.; Nudo, F.; Cortesi, E.; Berloco, P.; Catalano, C.; Napoli, A. Magnetic resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Preliminary experience for pain palliation and local tumor control. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorton, O.; Guillemin, P.; Holman, R.; Desgranges, S.; Gui, L.; Crowe, L.A.; Terraz, S.; Nastasi, A.; Lazeyras, F.; Contino-Pepin, C.; et al. Enhancement of HIFU thermal therapy in perfused tissue models using micron-sized FTAC-stabilized PFOB-core endovascular sonosensitizers. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Pig | Focal Point Coordinates along the Short Axis, Long Axis and Acoustic Axis of the Transducer [mm] |
|---|---|
| 1 | (0, 10, 2) |
| 2 | (0, −11, 7) |
| 3 | (2, 0, 7) |
| 4 | (0, 0, 1) |
| 5 | (0, 0, 0) |
| 6 | (0, −15, −7) |
| Grade | Evidence | Sub-Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No evidence of near-field thermal lesion | |
| 1 | Thermal lesion on the anterior surface of the bone facing the HIFU transducer | a: DCE MRI only b: necropsy-based visual evidence |
| 2 | Thermal lesion on the entire circumference of the bone | a: DCE MRI only b: necropsy-based visual evidence |
| 3 | Thermal lesion in the surrounding soft tissues juxtaposing the anterior surface of the bone facing the HIFU transducer | a: DCE MRI only b: necropsy-based visual evidence |
| 4 | Thermal lesion in the surrounding soft tissues anterior and posterior to the bone | a: DCE MRI only b: necropsy-based visual evidence |
| Pig | RF Ablation Size (mm3), from MR Images (along AP, LR and HF Axes) | Temperature Reached During HIFU Ablation (°C) | HIFU Ablation Longest Axis (mm) from MR Images; See Figure 6 and Figure 7 | HIFU Ablation Longest Axis (mm), from Gross Pathology; See Figure 6 and Figure 7 | Planned Center-to-Center Distance between the RF and MRgHIFU Ablations (mm), from MR Images | Center-to-Center Distance between the RF and MRgHIFU Ablations (mm), from Gross Pathology | Center-to-Center Distance between the RF and MRgHIFU Ablations (mm), from MR Images | Near-Field Side Effects Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.9 × 6.1 × 4.8 | 63 | - | - | 0 | - | - | 1a |
| 2 | 7.2 × 6.3 × 9.2 | 86 | 6.9 | - | 11.8 | - | 10.1 | 1a |
| 3 | 4.6 × 3.7 × 4.5 | 85 | 15.8 | 16.5 | 6.7 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 1a |
| 4 | 6.7 × 6.1 × 6.8 | 86 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 16.1 | 16.0 | 16.2 | 1a |
| 5 | 5.1 × 4.7 × 6.2 | 62 | 21.1 | 23.2 | 18.4 | 24.2 | 24.1 | 1a |
| 6 | 3.0 × 4.6 × 5.5 | 58 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 11.2 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 1b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorton, O.; Guillemin, P.C.; Peloso, A.; M’Rad, Y.; Crowe, L.A.; Koessler, T.; Poletti, P.-A.; Boudabbous, S.; Ricoeur, A.; Salomir, R. In Vivo Thermal Ablation of Deep Intrahepatic Targets Using a Super-Convergent MRgHIFU Applicator and a Pseudo-Tumor Model. Cancers 2023, 15, 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153961
Lorton O, Guillemin PC, Peloso A, M’Rad Y, Crowe LA, Koessler T, Poletti P-A, Boudabbous S, Ricoeur A, Salomir R. In Vivo Thermal Ablation of Deep Intrahepatic Targets Using a Super-Convergent MRgHIFU Applicator and a Pseudo-Tumor Model. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153961
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorton, Orane, Pauline Coralie Guillemin, Andrea Peloso, Yacine M’Rad, Lindsey Alexandra Crowe, Thibaud Koessler, Pierre-Alexandre Poletti, Sana Boudabbous, Alexis Ricoeur, and Rares Salomir. 2023. "In Vivo Thermal Ablation of Deep Intrahepatic Targets Using a Super-Convergent MRgHIFU Applicator and a Pseudo-Tumor Model" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153961
APA StyleLorton, O., Guillemin, P. C., Peloso, A., M’Rad, Y., Crowe, L. A., Koessler, T., Poletti, P.-A., Boudabbous, S., Ricoeur, A., & Salomir, R. (2023). In Vivo Thermal Ablation of Deep Intrahepatic Targets Using a Super-Convergent MRgHIFU Applicator and a Pseudo-Tumor Model. Cancers, 15(15), 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153961







