Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Distant Recurrence in Invasive Breast Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Data: A Cross-Institutional Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Development and Testing Using ImaGene
2.2. Validation Using ImaGene
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
3.2. Model Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redig, A.J.; McAllister, S.S. Breast cancer as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Poznak, C.; Somerfield, M.R.; Bast, R.C.; Cristofanilli, M.; Goetz, M.P.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hicks, D.G.; Hill, E.G.; Liu, M.C.; Lucas, W.; et al. Use of Biomarkers to Guide Decisions on Systemic Therapy for Women With Metastatic Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, M.T.; Tin, S.T.; Elwood, J.M. Prognostic models for breast cancer: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, E.; Cheng, S.H.; Dressman, H.; Pittman, J.; Tsou, M.H.; Horng, C.F.; Bild, A.; Iversen, E.S.; Liao, M.; Chen, C.M.; et al. Gene expression predictors of breast cancer outcomes. Lancet 2003, 361, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, E.G.; Garvelink, M.M.; Haes, J.C.J.M.D.; Hoeven, J.J.M.V.D.; Smets, E.M.A.; Pieterse, A.H.; Stiggelbout, A.M. Predicting and Communicating the Risk of Recurrence and Death in Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review of Risk Prediction Models. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zheng, S.; Yang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Y.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of distant metastasis at initial diagnosis: A population-based study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5329–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S. Breast cancer subtypes predict the preferential site of distant metastases: A SEER based study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27990–27996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, G.P.; Massagué, J. Cancer Metastasis: Building a Framework. Cell 2006, 127, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howlader, N.; Cronin, K.A.; Kurian, A.W.; Andridge, R. Differences in Breast Cancer Survival by Molecular Subtypes in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, H.-Y.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, J.-Y.; Li, F.-Y.; He, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.-G. The Clinicopathological Features and Survival Outcomes of Different Histological Subtypes in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polyak, K. Heterogeneity in breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3786–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selli, C.; Sims, A.H. Neoadjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer as a Model for Translational Research. Breast Cancer 2019, 13, 1178223419829072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Mao, X. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.M.; Mankoff, D.A.; Joe, B.N. Imaging Neoadjuvant Therapy Response in Breast Cancer. Radiology 2017, 285, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi-Naini, A.; Sannachi, L.; Tadayyon, H.; Tran, W.T.; Slodkowska, E.; Trudeau, M.; Gandhi, S.; Pritchard, K.; Kolios, M.C.; Czarnota, G.J. Chemotherapy-Response Monitoring of Breast Cancer Patients Using Quantitative Ultrasound-Based Intra-Tumour Heterogeneities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossuyt, V.; Spring, L. Pathologic evaluation of response to neoadjuvant therapy drives treatment changes and improves long-term outcomes for breast cancer patients. Breast J. 2020, 26, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, E.; Bossuyt, V.; Viale, G.; Cameron, D.; Badve, S.; Denkert, C.; MacGrogan, G.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Boughey, J.; Curigliano, G.; et al. Standardization of pathologic evaluation and reporting of postneoadjuvant specimens in clinical trials of breast cancer: Recommendations from an international working group. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Minckwitz, G.; Untch, M.; Blohmer, J.U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Eiermann, W.; Hilfrich, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anampa, J.; Makower, D.; Sparano, J.A. Progress in adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: An overview. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flatley, M.J.; Dodwell, D.J. Adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Surgery 2019, 37, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, A.I.; Varley, K.E.; Welm, A.L. The lingering mysteries of metastatic recurrence in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Ping, M. Targeting breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Basic. Clin. Res. 2015, 9, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Albain, K.S.; Barlow, W.E.; Shak, S.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Livingston, R.B.; Yeh, I.T.; Ravdin, P.; Bugarini, R.; Baehner, F.L.; Davidson, N.E.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of the 21-gene recurrence score assay in postmenopausal women with node-positive, oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer on chemotherapy: A retrospective analysis of a randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, M.C.; Bryson, A.; Weinberger, M.; Dusetzina, S.B.; Dinan, M.A.; Reeder-Hayes, K.; Wheeler, S.B. Oncologists’ Barriers and Facilitators for Oncotype dx Use: Qualitative Study. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2016, 32, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iles, K.; Roberson, M.L.; Spanheimer, P.; Gallagher, K.; Ollila, D.W.; Strassle, P.D.; Downs-Canner, S. The impact of age and nodal status on variations in oncotype DX testing and adjuvant treatment. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; Olson, J.A.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy Guided by a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osareh, A.; Shadgar, B. Machine learning techniques to diagnose breast cancer. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Symposium on Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, Ankara, Turkey, 20–22 April 2010; pp. 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Amrane, M.; Oukid, S.; Gagaoua, I.; Ensari, T. Breast cancer classification using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 Electric Electronics, Computer Science, Biomedical Engineerings’ Meeting (EBBT), Istanbul, Turkey, 18–19 April 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Khosla, A.; Gargeya, R.; Irshad, H.; Andrew, H.B. Deep Learning for Identifying Metastatic Breast Cancer. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.05718. [Google Scholar]
- Ganggayah, M.D.; Taib, N.A.; Har, Y.C.; Lio, P.; Dhillon, S.K. Predicting factors for survival of breast cancer patients using machine learning techniques. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Ding, W.; Ye, B.; Cheng, C.; Shao, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H. Crosstalk of disulfidptosis-related subtypes, establishment of a prognostic signature and immune infiltration characteristics in bladder cancer based on a machine learning survival framework. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1180404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Xie, J.; Zheng, S.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Tian, W.; Deng, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, C.W.; et al. Leveraging diverse cell-death patterns to predict the prognosis and drug sensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer patients after surgery. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 107, 106936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Luo, X.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Tian, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xie, X. Advances in artificial intelligence to predict cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1076883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutros, C.; Mazouni, C.; Lerebours, F.; Stevens, D.; Lei, X.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Delaloge, S. A preoperative nomogram to predict the risk of synchronous distant metastases at diagnosis of primary breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, C.; Périer, C.; Prague, M.; Bellera, C.; MacGrogan, G.; Saut, O.; Benzekry, S. Machine Learning and Mechanistic Modeling for Prediction of Metastatic Relapse in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform 2020, 4, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-E.; Wen, C.-N.; Lai, P.-Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Sun, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lu, J.-J. Predicting breast cancer metastasis by using serum biomarkers and clinicopathological data with machine learning technologies. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 128, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.; Gill, S.; Ismail, Z.; Forkert, N.D. Building machine learning models without sharing patient data: A simulation-based analysis of distributed learning by ensembling. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020, 106, 103424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dluhoš, P.; Schwarz, D.; Cahn, W.; van Haren, N.; Kahn, R.; Španiel, F.; Horáček, J.; Kašpárek, T.; Schnack, H. Multi-center machine learning in imaging psychiatry: A meta-model approach. NeuroImage 2017, 155, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhadia, S.S.; Tyagi, A.; Venkataraman, V.; Mukherjee, P.; Prasad, P.; Gevaert, O.; Nagaraj, S.H. ImaGene: A web-based software platform for tumor radiogenomic evaluation and reporting. Bioinform. Adv. 2022, 2, vbac079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Harowicz, M.R.; Grimm, L.J.; Kim, C.E.; Ghate, S.V.; Walsh, R.; Mazurowski, M.A. A machine learning approach to radiogenomics of breast cancer: A study of 922 subjects and 529 DCE-MRI features. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Symmans, W.F.; Peintinger, F.; Hatzis, C.; Rajan, R.; Kuerer, H.; Valero, V.; Assad, L.; Poniecka, A.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korde, L.A.; Somerfield, M.R.; Carey, L.A.; Crews, J.R.; Denduluri, N.; Hwang, E.S.; Khan, S.A.; Loibl, S.; Morris, E.A.; Perez, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Endocrine Therapy, and Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1485–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viale, G.; Fusco, N. Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment—How to assess residual disease. Breast 2022, 62, S25–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M.K. Does adjuvant therapy reduce postmetastatic survival? Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valagussa, P.; Tess, J.D.; Rossi, A.; Tancini, G.; Banfi, A.; Bonadonna, G. Adjuvant CMF effect on site of first recurrence, and appropriate follow-up intervals, in operable breast cancer with positive axillary nodes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1981, 1, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, D.; Eckel, R.; Bauerfeind, I.; Baier, B.; Beck, T.; Braun, M.; Ettl, J.; Hamann, U.; Kiechle, M.; Mahner, S.; et al. Improved systemic treatment for early breast cancer improves cure rates, modifies metastatic pattern and shortens post-metastatic survival: 35-year results from the Munich Cancer Registry. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castro, L.; Chávez, M.; Duflot, P.; Bleret, V.; Martin, A.G.; Zobel, M.; Nateqi, J.; Lin, S.; Pazos-Arias, J.J.; Del Fiol, G.; et al. Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Breast Cancer Recurrence Using Structured and Unstructured Sources from Electronic Health Records. Cancers 2023, 15, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.J.; Hou, M.F.; Chang, H.T.; Chiu, C.C.; Lee, H.H.; Yeh, S.J.; Shi, H.Y. Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Recurrence within 10 Years after Breast Cancer Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Luo, Y. Prediction of breast cancer distant recurrence using natural language processing and knowledge-guided convolutional neural network. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 110, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khene, Z.-E.; Bigot, P.; Doumerc, N.; Ouzaid, I.; Boissier, R.; Nouhaud, F.-X.; Albiges, L.; Bernhard, J.-C.; Ingels, A.; Borchiellini, D.; et al. Application of Machine Learning Models to Predict Recurrence After Surgical Resection of Nonmetastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 6, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Noda, K.; Yoshida, K. The application of machine learning for predicting recurrence in patients with early-stage endometrial cancer: A pilot study. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2020, 64, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourou, K.; Exarchos, T.P.; Exarchos, K.P.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Fotiadis, D.I. Machine learning applications in cancer prognosis and prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Duchesnay, É. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]

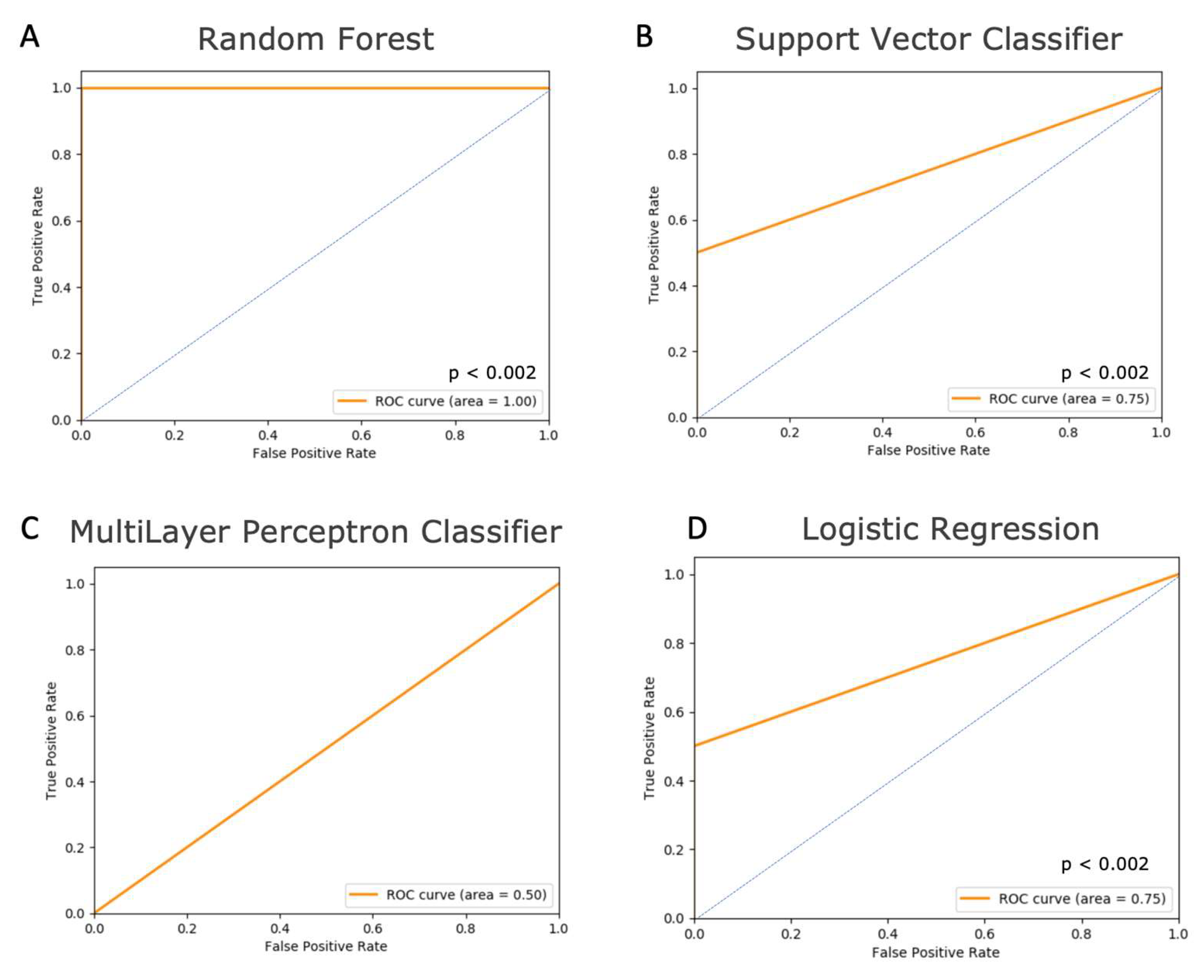
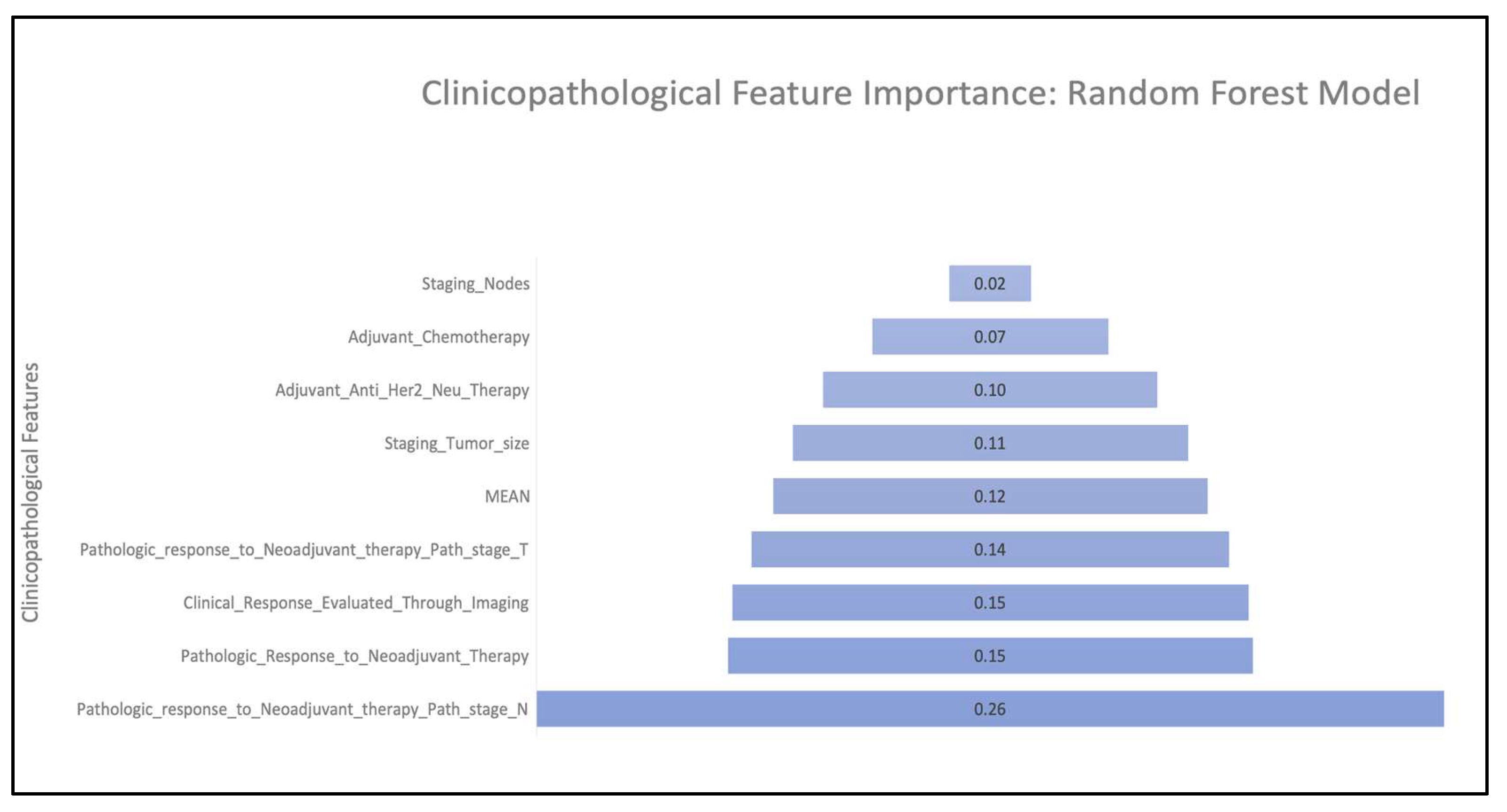

| Models | AUC | R2 | RMSE:Stdev |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Support Vector Classifier | 0.75 | 0.43 | 0.75 |
| Multilayer Perceptron Classifier | 0.5 | −0.41 | 1.19 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.75 | 0.4 | 0.77 |
| Model | AUC | R2 | RMSE:Stdev |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 0.75 | 0.33 | 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukhadia, S.S.; Muller, K.E.; Workman, A.A.; Nagaraj, S.H. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Distant Recurrence in Invasive Breast Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Data: A Cross-Institutional Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153960
Sukhadia SS, Muller KE, Workman AA, Nagaraj SH. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Distant Recurrence in Invasive Breast Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Data: A Cross-Institutional Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153960
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukhadia, Shrey S., Kristen E. Muller, Adrienne A. Workman, and Shivashankar H. Nagaraj. 2023. "Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Distant Recurrence in Invasive Breast Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Data: A Cross-Institutional Study" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153960
APA StyleSukhadia, S. S., Muller, K. E., Workman, A. A., & Nagaraj, S. H. (2023). Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Distant Recurrence in Invasive Breast Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Data: A Cross-Institutional Study. Cancers, 15(15), 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153960






