Characterization and Optimization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Patient-Derived Organotypic Slices and Organoid Models of Glioblastoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
2.2. OSC
2.3. PDOs
2.4. PBMC Preparation
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Patient Cohort
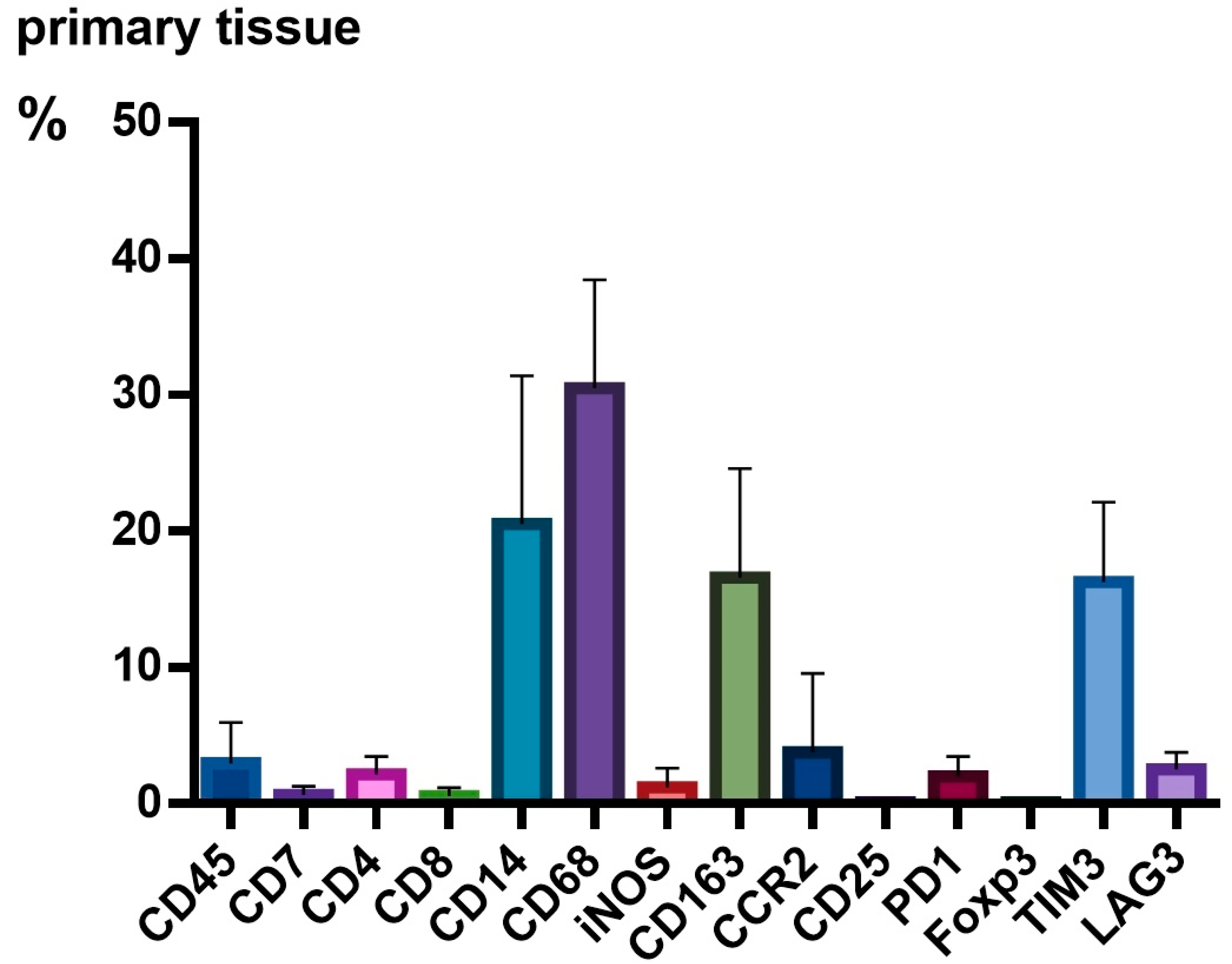
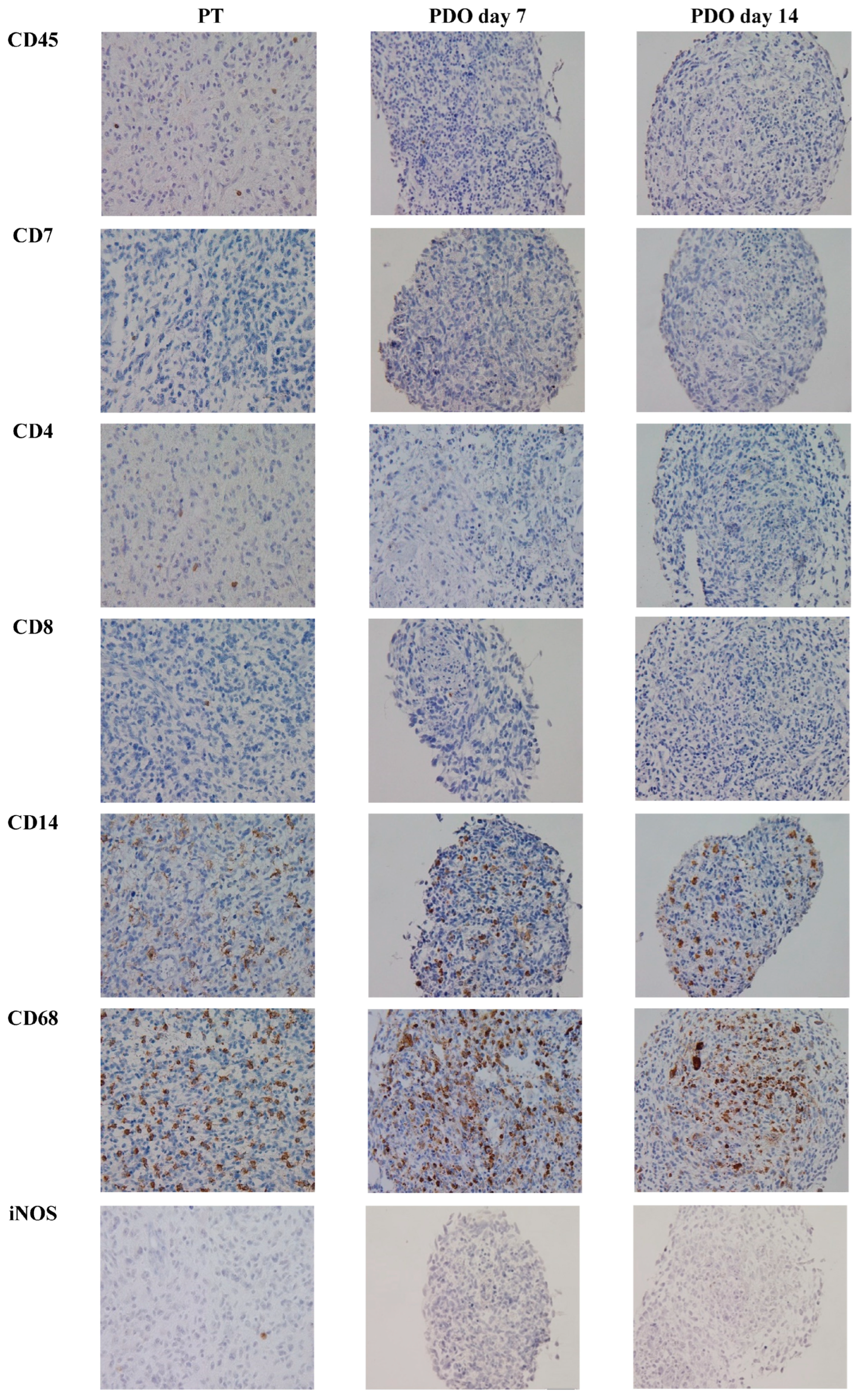
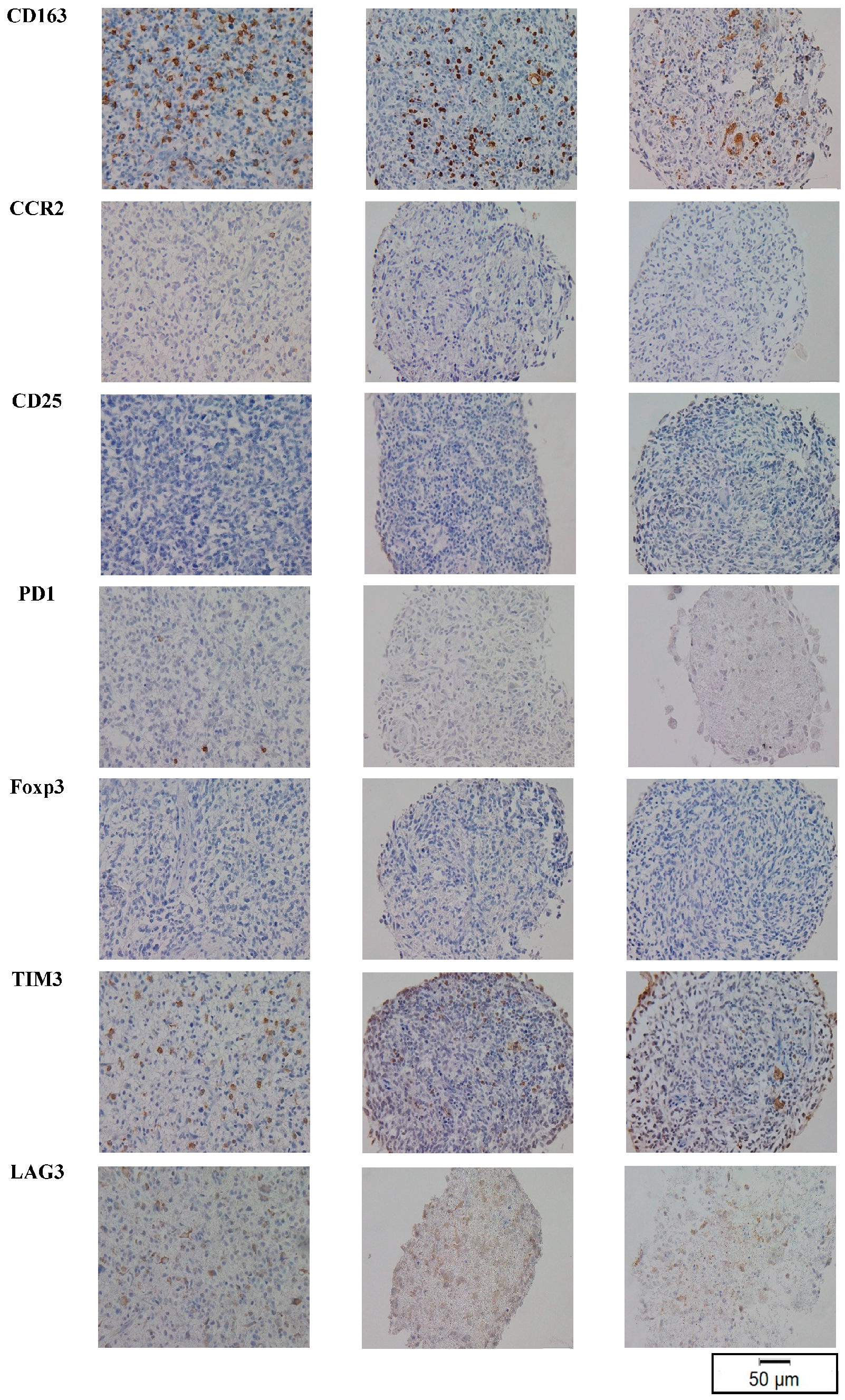
3.2. TME Expression in PT
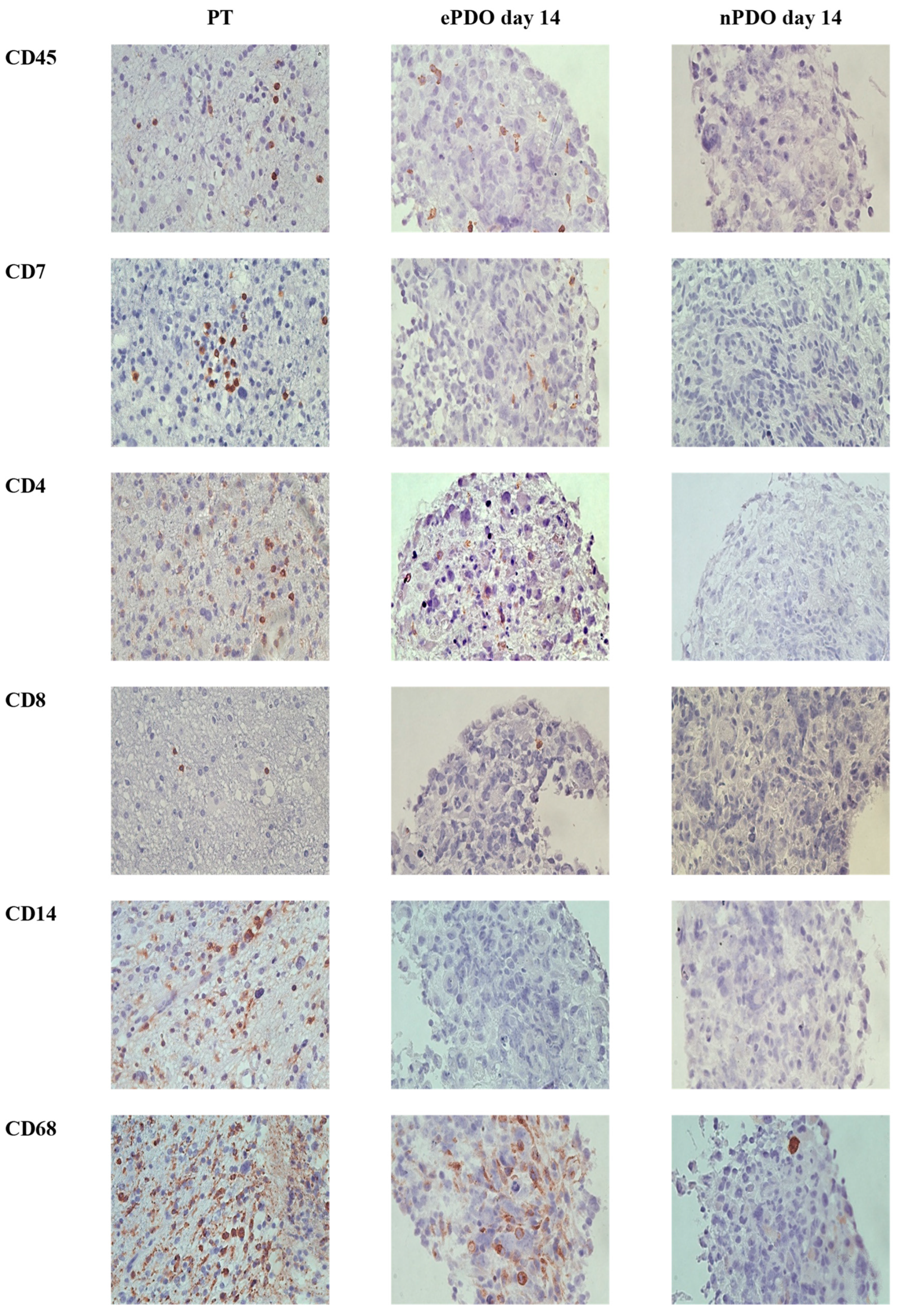
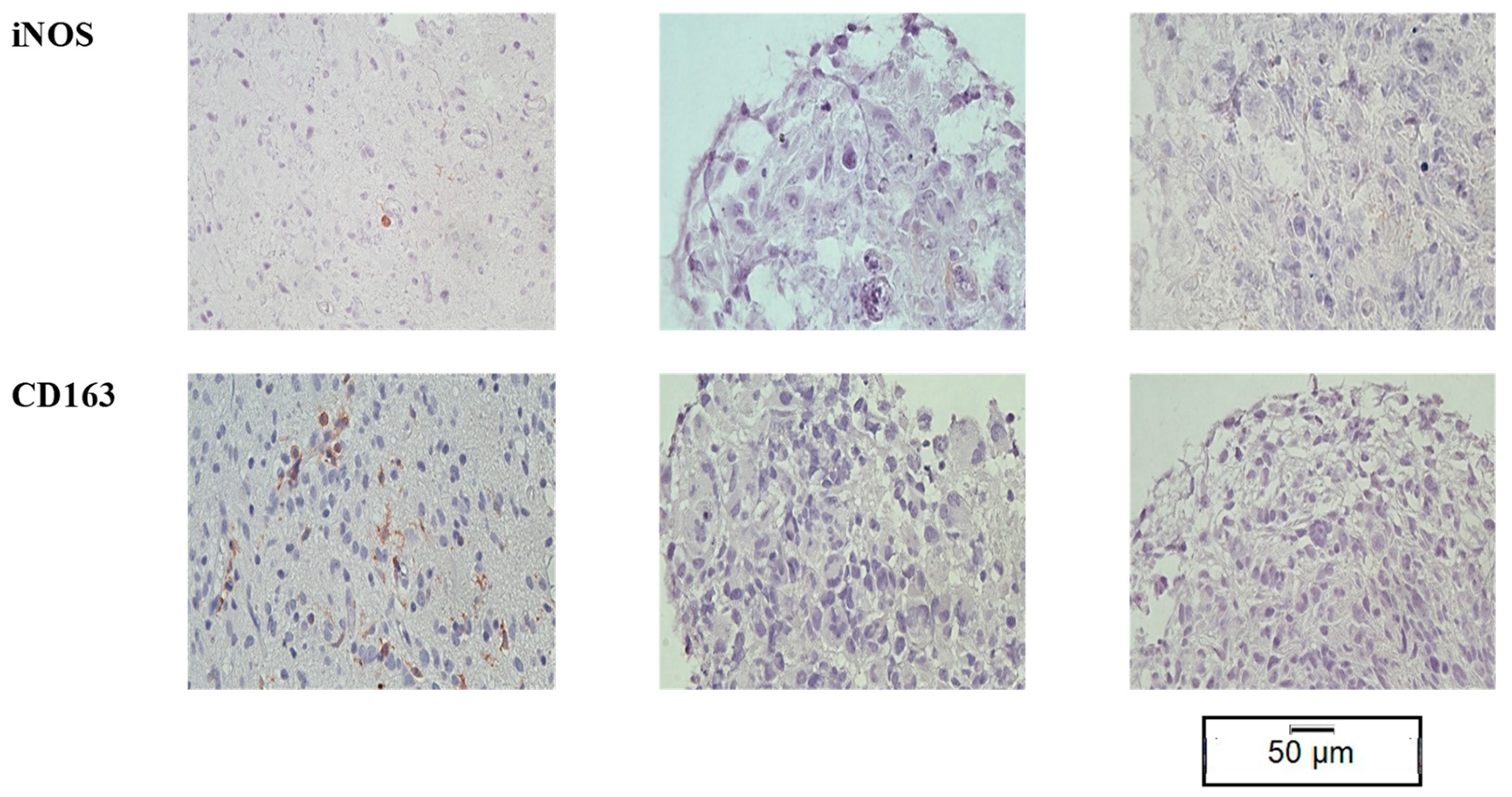
3.3. TME Expression in PDOs
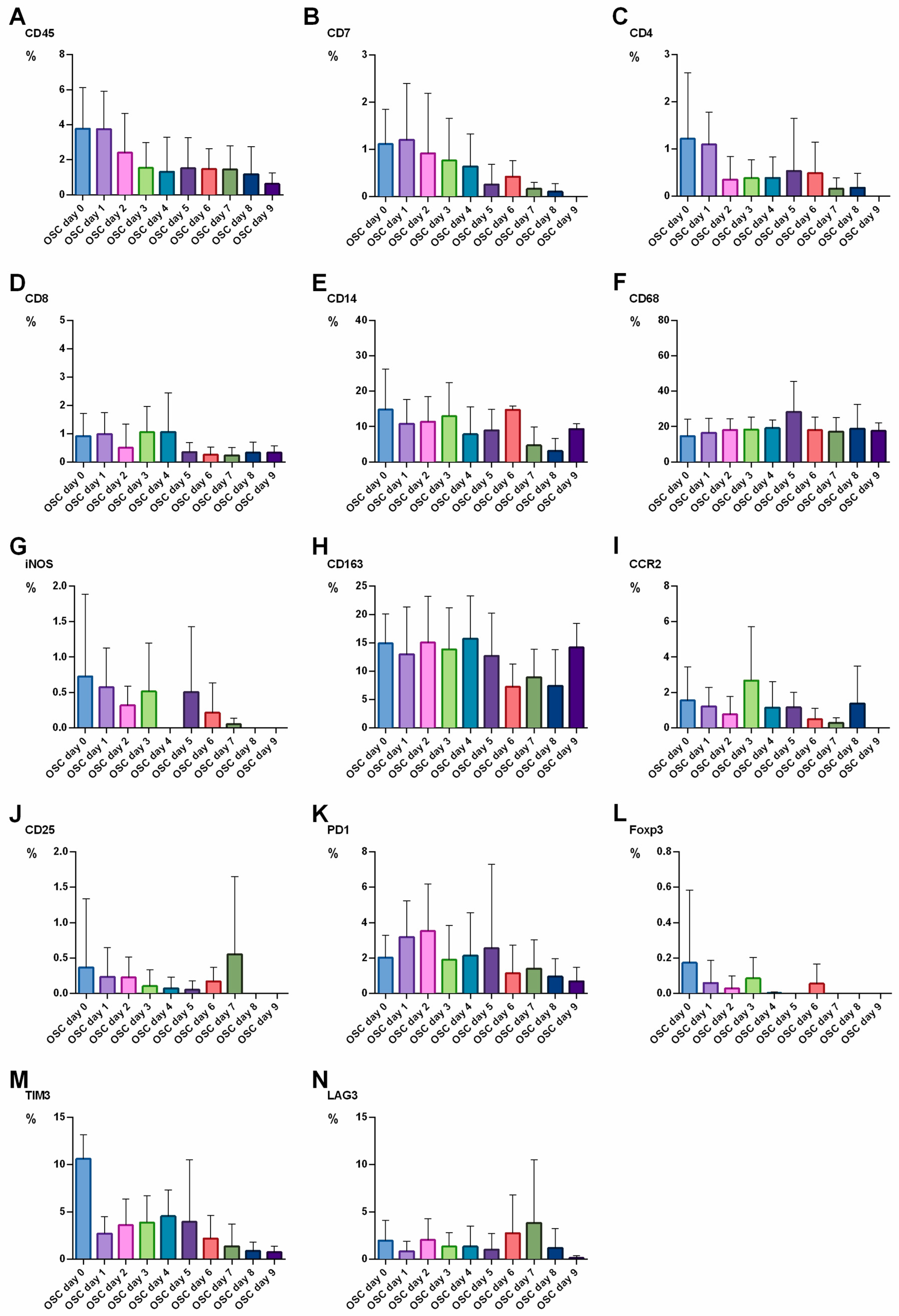
3.4. TME Expression in OSC
3.5. TME Expression in ePDOs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert Koch Institut. Zentrum Für Krebsregisterdaten. Available online: https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/DE/Home/homepage_node.html (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrlinger, U.; Tzaridis, T.; Mack, F.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schlegel, U.; Sabel, M.; Hau, P.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Krex, D.; Grauer, O.; et al. Lomustine-temozolomide combination therapy versus standard temozolomide therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CeTeG/NOA-09): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.A.; Elmore, K.B.; Mattei, T.A. The effects of alternating electric fields in glioblastoma: Current evidence on therapeutic mechanisms and clinical outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 2015, 38, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.J.; Ali, S.; Qadir, M.G.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. The role of bevacizumab in the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, C.G.; Yi, A.; Elramsisy, A.; Hu, J.; Mukherjee, D.; Irvin, D.K.; Yu, J.S.; Bannykh, S.I.; Black, K.L.; Nuño, M.; et al. Prognosis of patients with multifocal glioblastoma: A case-control study. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Andion, E.; Goodman, S.N.; Hidalgo, O.F.; Vanaclocha, V.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.L.; Pelloski, C.E. Diagnostic and prognostic molecular markers in common adult gliomas. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, H.; Borghaei, H.; Orlowski, R.; Subklewe, M.; Roboz, G.J.; Zugmaier, G.; Kufer, P.; Iskander, K.; Kantarjian, H.M. The BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) platform: Development and future potential of a targeted immuno-oncology therapy across tumor types. Cancer 2020, 126, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.D.; Suryadevara, C.M.; Gedeon, P.C.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Bigner, D.D.; Sampson, J.H. Intracerebral delivery of a third generation EGFRvIII-specific chimeric antigen receptor is efficacious against human glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Brawley, V.; Hegde, M.; Bielamowicz, K.; Kalra, M.; Landi, D.; Robertson, C.; Gray, T.L.; Diouf, O.; Wakefield, A.; et al. HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified Virus-Specific T Cells for Progressive Glioblastoma: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Badie, B.; Barish, M.E.; Weng, L.; Ostberg, J.R.; Chang, W.C.; Naranjo, A.; Starr, R.; Wagner, J.; Wright, C.; et al. Bioactivity and Safety of IL13Ralpha2-Redirected Chimeric Antigen Receptor CD8+ T Cells in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4062–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monie, D.D.; Bhandarkar, A.R.; Parney, I.F.; Correia, C.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Vile, R.G.; Li, H. Synthetic and systems biology principles in the design of programmable oncolytic virus immunotherapies for glioblastoma. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 50, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez-Ordonez, D.; Chagoya, G.; Salehani, A.; Atchley, T.J.; Laskay, N.M.; Parr, M.S.; Elsayed, G.A.; Mahavadi, A.K.; Rahm, S.P.; Friedman, G.K.; et al. Immunovirotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma and Other Malignant Gliomas. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 32, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henze, J.; Tacke, F.; Hardt, O.; Alves, F.; Al Rawashdeh, W. Enhancing the Efficacy of CAR T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Qiao, J.; Fu, Y.X. Immunotherapy and tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Gene modification strategies for next-generation CAR T cells against solid cancers. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorebrahim, M.; Melief, J.; de Coaña, Y.P.; Wickström, S.L.; Cid-Arregui, A.; Kiessling, R. Counteracting CAR T cell dysfunction. Oncogene 2021, 40, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, N.A.; Holland, E.C.; Gilbertson, R.; Glass, R.; Kettenmann, H. The brain tumor microenvironment. Glia 2012, 60, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguraman, R.; Parameswaran, S.; Kanwar, J.R.; Khetan, V.; Rishi, P.; Kanwar, R.K.; Krishnakumar, S. Evidence of Tumour Microenvironment and Stromal Cellular Components in Retinoblastoma. Ocul. Oncol. Pathol. 2019, 5, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, I.; Manic, G.; Coussens, L.M.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfiglioli, A.; Hambardzumyan, D. Macrophages and microglia: The cerberus of glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, S.; Rapp, C.; Dettling, S.; Herold-Mende, C. When Immune Cells Turn Bad-Tumor-Associated Microglia/Macrophages in Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungert, A.D.; Urbantat, R.M.; Jelgersma, C.; Bekele, B.M.; Mueller, S.; Mueller, A.; Felsenstein, M.; Dusatko, S.; Blank, A.; Ghori, A.; et al. Myeloid cell subpopulations compensate each other for Ccr2-deficiency in glioblastoma. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2023, 49, e12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Standing at the crossroads of immunobiology and neurobiology. Immunity 2009, 31, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sielska, M.; Przanowski, P.; Wylot, B.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Maleszewska, M.; Kijewska, M.; Zawadzka, M.; Kucharska, J.; Vinnakota, K.; Kettenmann, H.; et al. Distinct roles of CSF family cytokines in macrophage infiltration and activation in glioma progression and injury response. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanichapol, T.; Chutipongtanate, S.; Anurathapan, U.; Hongeng, S. Immune Escape Mechanisms and Future Prospects for Immunotherapy in Neuroblastoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1812535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Elahi, R.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. Solid Tumors Challenges and New Insights of CAR T Cell Engineering. Stem. Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navin, I.; Lam, M.T.; Parihar, R. Design and Implementation of NK Cell-Based Immunotherapy to Overcome the Solid Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, R.; Rivas, C.; Huynh, M.; Omer, B.; Lapteva, N.; Metelitsa, L.S.; Gottschalk, S.M.; Rooney, C.M. NK Cells Expressing a Chimeric Activating Receptor Eliminate MDSCs and Rescue Impaired CAR-T Cell Activity against Solid Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Moon, E.K. CAR T Cells for Solid Tumors: New Strategies for Finding, Infiltrating, and Surviving in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickl, V.; Schulz, E.; Salvador, E.; Trautmann, L.; Diener, L.; Kessler, A.F.; Monoranu, C.M.; Dehghani, F.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Löhr, M.; et al. Glioblastoma-Derived Three-Dimensional Ex Vivo Models to Evaluate Effects and Efficacy of Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields). Cancers 2022, 14, 5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, F.; Gaunitz, F.; Dehghani, F.; Renner, C.; Meixensberger, J.; Gutenberg, A.; Giese, A.; Schopow, K.; Hellwig, C.; Schäfer, M.; et al. Organotypic slice cultures of human glioblastoma reveal different susceptibilities to treatments. Neuro. Oncol. 2013, 15, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F.; Salinas, R.D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Nguyen, P.T.T.; Schnoll, J.G.; Wong, S.Z.H.; Thokala, R.; Sheikh, S.; Saxena, D.; Prokop, S.; et al. A Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Organoid Model and Biobank Recapitulates Inter- and Intra-tumoral Heterogeneity. Cell 2020, 180, 188–204.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Ming, G.-L.; Song, H. Generation and biobanking of patient-derived glioblastoma organoids and their application in CAR T cell testing. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 4000–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldheim, J.; Kessler, A.F.; Schmitt, D.; Wilczek, L.; Linsenmann, T.; Dahlmann, M.; Monoranu, C.M.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Hagemann, C.; Löhr, M. Expression of activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) is increased in astrocytomas of different WHO grades and correlates with survival of glioblastoma patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 8673–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabate-Soler, S.; Nickels, S.L.; Saraiva, C.; Berger, E.; Dubonyte, U.; Barmpa, K.; Lan, Y.J.; Kouno, T.; Jarazo, J.; Robertson, G.; et al. Microglia integration into human midbrain organoids leads to increased neuronal maturation and functionality. Glia 2022, 70, 1267–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.; Hau, A.-C.; Oudin, A.; Golebiewska, A.; Niclou, S.P. Glioblastoma Organoids: Pre-Clinical Applications and Challenges in the Context of Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 604121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Lesniak, M.S.; James, C.D.; Heimberger, A.B.; Chen, P. Context-Dependent Glioblastoma-Macrophage/Microglia Symbiosis and Associated Mechanisms. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | Sex | Age [Years] | Histology | KPS | Ki67 [%] | MGMT Promoter Methylation | MGMT Promoter Methylation [%] | IDH1 Mutation | IDH2 Mutation | ATRX Expression | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | m | 74 | GBM | 90 | 20 | no | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC |
| 2 | w | 55 | GBM | 80 | 20 | yes | 22 | 0 | 0 | 1 | nPDO |
| 3 | w | 56 | GBM | 70 | 25 | yes | 25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | nPDO |
| 4 | w | 59 | GBM | 90 | 30 | yes | 44 | 0 | 0 | 1 | nPDO |
| 5 | m | 74 | GBM | 80 | 20 | no | N/A | 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC, nPDO |
| 6 | m | 68 | GBM | 80 | 30 | yes | 24 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC, nPDO |
| 7 | w | 73 | GBM | 90 | 25 | yes | 57 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC, nPDO |
| 8 | m | 64 | GBM | 80 | 40 | no | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC, nPDO |
| 9 | m | 80 | GBM | 90 | 20 | no | N/A | 0 | 0 | 1 | nPDO |
| 10 | w | 69 | GBM | 90 | 25 | yes | 71 | 0 | 0 | 1 | nPDO |
| 11 | w | 64 | GBM | 90 | 20 | no | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ePDO |
| 12 | w | 70 | GBM | 80 | 50 | yes | 64 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ePDO |
| 13 | m | 33 | GBM | 100 | 20 | yes | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ePDO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nickl, V.; Eck, J.; Goedert, N.; Hübner, J.; Nerreter, T.; Hagemann, C.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Schulz, T.; Nickl, R.C.; Keßler, A.F.; et al. Characterization and Optimization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Patient-Derived Organotypic Slices and Organoid Models of Glioblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102698
Nickl V, Eck J, Goedert N, Hübner J, Nerreter T, Hagemann C, Ernestus R-I, Schulz T, Nickl RC, Keßler AF, et al. Characterization and Optimization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Patient-Derived Organotypic Slices and Organoid Models of Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102698
Chicago/Turabian StyleNickl, Vera, Juliana Eck, Nicolas Goedert, Julian Hübner, Thomas Nerreter, Carsten Hagemann, Ralf-Ingo Ernestus, Tim Schulz, Robert Carl Nickl, Almuth Friederike Keßler, and et al. 2023. "Characterization and Optimization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Patient-Derived Organotypic Slices and Organoid Models of Glioblastoma" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102698
APA StyleNickl, V., Eck, J., Goedert, N., Hübner, J., Nerreter, T., Hagemann, C., Ernestus, R.-I., Schulz, T., Nickl, R. C., Keßler, A. F., Löhr, M., Rosenwald, A., Breun, M., & Monoranu, C. M. (2023). Characterization and Optimization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Patient-Derived Organotypic Slices and Organoid Models of Glioblastoma. Cancers, 15(10), 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102698





