An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
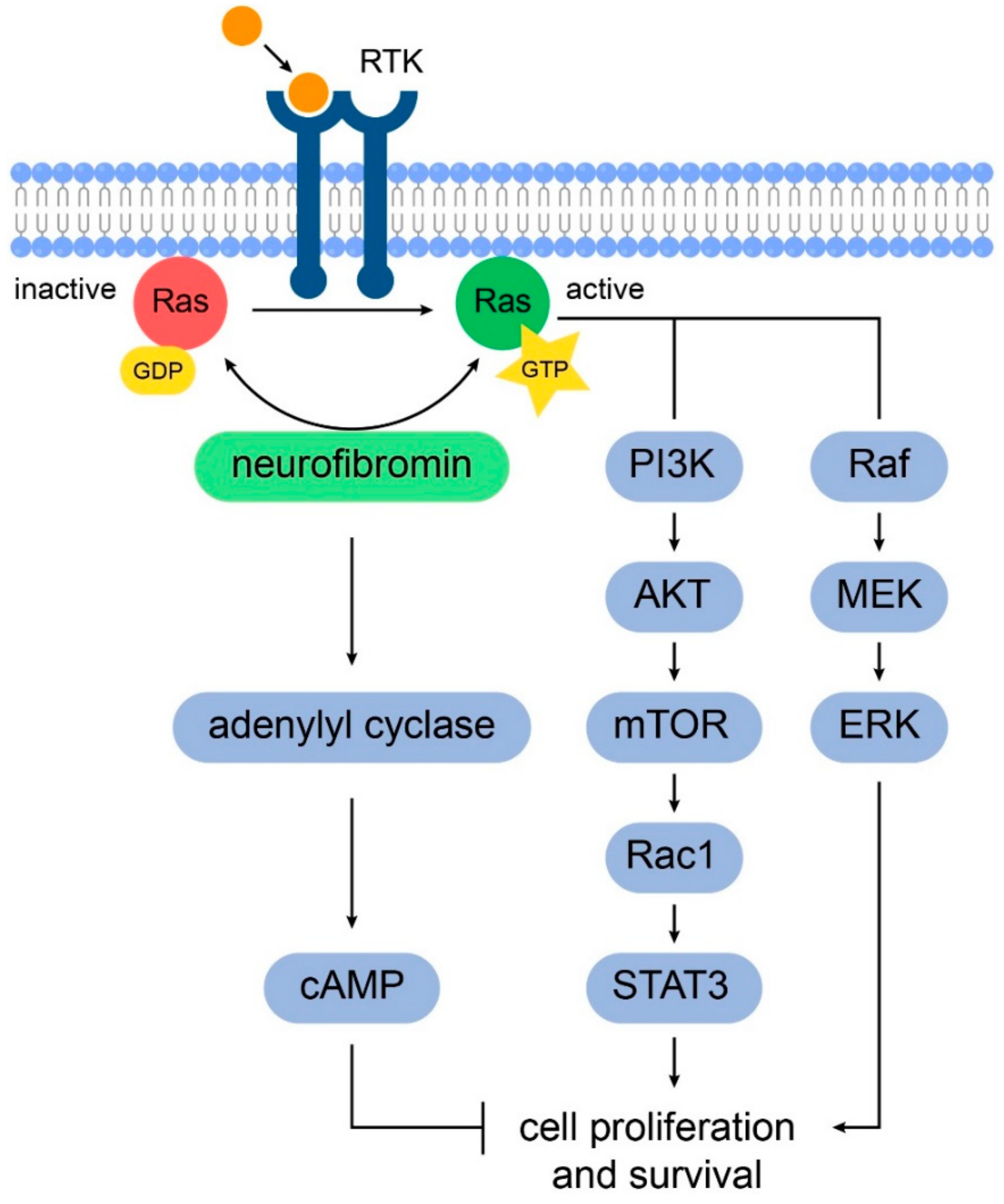
2. Gliomagenesis in Neurofibromatosis Type 1
3. Optic Pathway Gliomas
3.1. Genetic and Molecular Pathophysiology
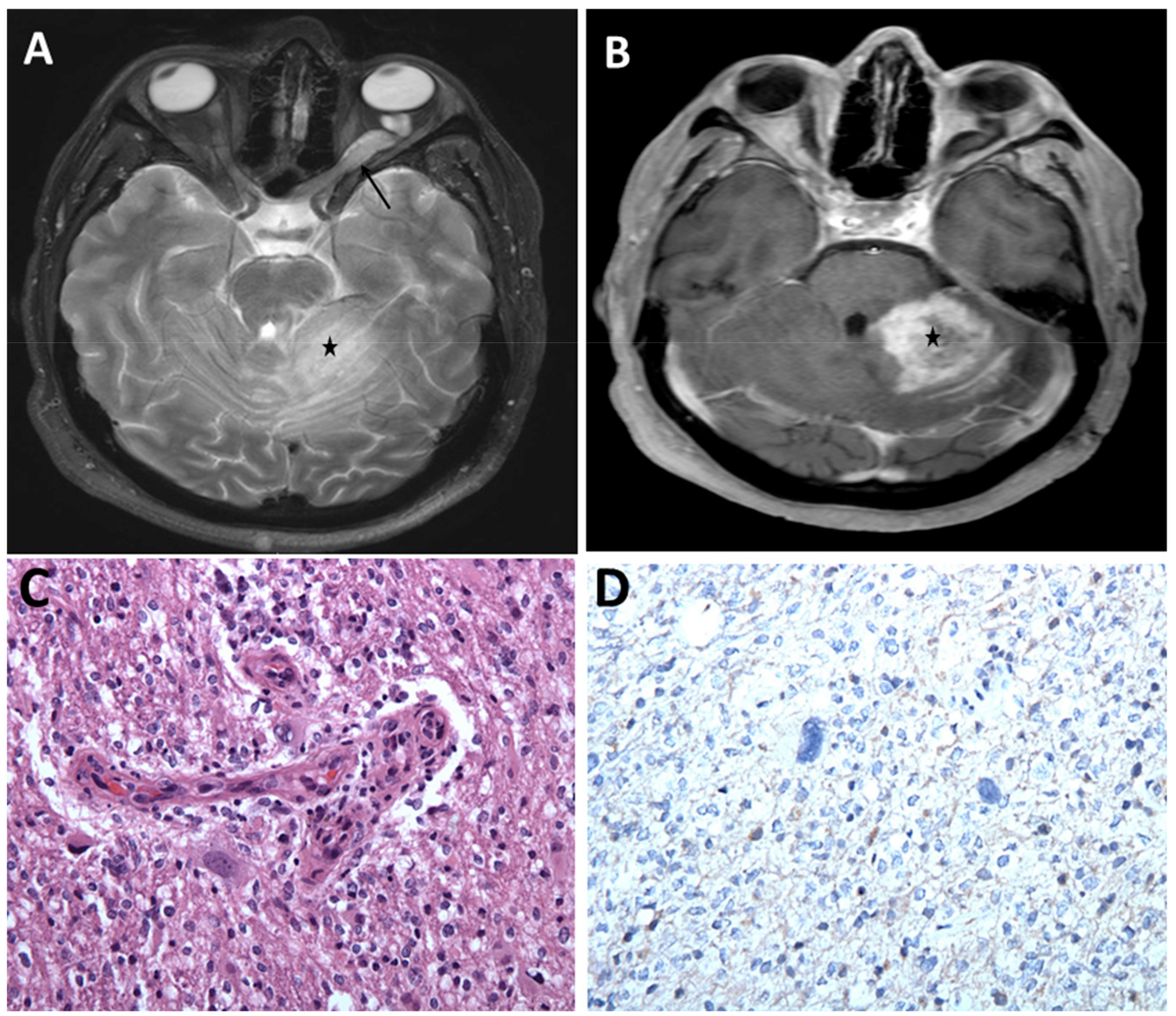
3.2. Clinical Presentation
3.3. Treatment
4. Non-Optic Pathway Intracranial Gliomas
5. Therapeutic Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huson, S.M.; Harper, P.S.; Compston, D.A.S. Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. A clinical and population study in south-east Wales. Brain 1988, 111, 1355–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.H.; Wood, D.L.; Collins, F.S. Identification of the Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Gene Product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.R.; Marchuk, D.A.; Andersen, L.B.; Letcher, R.; Odeh, H.M.; Saulino, A.M.; Fountain, J.W.; Brereton, A.; Nicholson, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; et al. Type 1 Neurofibromatosis Gene: Identification of a Large Transcript Disrupted in Three NF1 Patients. Science 1990, 249, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ars, E.; Kruyer, H.; Morell, M.; Pros, E.; Serra, E.; Ravella, A.; Estivill, X.; Lázaro, C. Recurrent Mutations in the NF1 Gene Are Common among Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Patients. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieley, M.B.; Stevenson, D.A.; Viskochil, D.H.; Tinkle, B.T.; Martin, L.J.; Schorry, E.K. Variable Expression of Neurofibromatosis 1 in Monozygotic Twins. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2011, 155, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojnueangnit, K.; Xie, J.; Gomes, A.; Sharp, A.; Callens, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cochran, M.; Abbott, M.-A.; Atkin, J.; et al. High Incidence of Noonan Syndrome Features Including Short Stature and Pulmonic Stenosis in Patients Carrying NF1 Missense Mutations Affecting p.Arg1809: Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasmant, E.; Sabbagh, A.; Spurlock, G.; Laurendeau, I.; Grillo, E.; Hamel, M.J.; Martin, L.; Barbarot, S.; Leheup, B.; Rodriguez, D.; et al. NF1 Microdeletions in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: From Genotype to Phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, E1506–E1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Montmain, G.; Ruano, E.; Upadhyaya, M.; Dudley, S.; Liskay, R.M.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Puisieux, A. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Gene as a Mutational Target in a Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cell Type. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrer-Sawatzki, H.; Mautner, V.-F.; Cooper, D.N. Emerging Genotype–Phenotype Relationships in Patients with Large NF1 Deletions. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 349–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, D.F.; Ponder, M.A.; Huson, S.M.; Ponder, B.A. An Analysis of Variation in Expression of Neurofibromatosis (NF) Type 1 (NF1): Evidence for Modifying Genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1993, 53, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, T.N.; Gutmann, D.H.; Fletcher, J.A.; Glover, T.W.; Collins, F.S.; Downward, J. Aberrant Regulation of Ras Proteins in Malignant Tumour Cells from Type 1 Neurofibromatosis Patients. Nature 1992, 356, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, N.; Miller, S.J. A RASopathy Gene Commonly Mutated in Cancer: The Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Tumour Suppressor. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, F.; Ho, I.; Tong, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; Nurnberg, P.; Zhong, Y. Effect of Neurofibromatosis Type I Mutations on a Novel Pathway for Adenylyl Cyclase Activation Requiring Neurofibromin and Ras. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bollag, G.; Clark, R.; Stevens, J.; Conroy, L.; Fults, D.; Ward, K.; Friedman, E.; Samowitz, W.; Robertson, M.; et al. Somatic Mutations in the Neurofibromatosis 1 Gene in Human Tumors. Cell 1992, 69, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Kluwe, L.; Spurlock, G.; Monem, B.; Majounie, E.; Mantripragada, K.; Ruggieri, M.; Chuzhanova, N.; Evans, D.G.; Ferner, R.; et al. Germline and Somatic NF1 Gene Mutation Spectrum in NF1-Associated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNSTs). Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listernick, R.; Charrow, J.; Gutmann, D.H. Intracranial Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 89, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listernick, R.; Louis, D.N.; Packer, R.J.; Gutmann, D.H. Optic Pathway Gliomas in Children with Neurofibromatosis 1: Consensus Statement from the Nf1 Optic Pathway Glioma Task Force. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 41, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, A.C.; Gutmann, D.H. Gliomas in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, B.R. Malignancy in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Oncologist 2000, 5, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, A.J.; Kieran, M.W.; Yao, X.; Cruz, L.; Ladner, J.; Quayle, K.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Irons, M.B.; Ullrich, N.J. Clinicopathologic Study of Glioblastoma in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A.; Listernick, R.; Charrow, J.; Goldman, S. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and High-Grade Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Yang, Q.; Friedman, J.M. Mortality in Neurofibromatosis 1: An Analysis Using U.S. Death Certificates. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szudek, J.; Birch, P.; Riccardi, V.M.; Evans, D.G.; Friedman, J.M. Associations of Clinical Features in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1). Genet. Epidemiol. 2000, 19, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, J.; Nijmeijer, R.; Brouwer, O.F.; Boon, M.; Fock, A.; Hoving, E.W.; Meijer, L.; den Dunnen, W.F.; Bont, E.S. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Associated Low Grade Gliomas: A Comparison with Sporadic Low Grade Gliomas. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Perry, A.; Gutmann, D.H.; O’Neill, B.P.; Leonard, J.; Bryant, S.; Giannini, C. Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Clinicopathologic Study of 100 Patients. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, F.; Ceccarelli, M.; Tala; Garofano, L.; Zhang, J.; Frattini, V.; Caruso, F.P.; Lewis, G.; Alfaro, K.D.; Bauchet, L.; et al. The Molecular Landscape of Glioma in Patients with Neurofibromatosis 1. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laycock-van Spyk, S.; Thomas, N.; Cooper, D.N.; Upadhyaya, M. Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Tumours: Their Somatic Mutational Spectrum and Pathogenesis. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 623–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations in Gliomas. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbink, H.J.; Taal, W.; van Marion, R.; Kros, J.M.; van Heuvel, I.; Bromberg, J.E.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Zonnenberg, C.B.; Postma, T.J.; Gijtenbeek, J.M.; et al. IDH1 Mutations in Low-Grade Astrocytomas Predict Survival but Not Response to Temozolomide. Neurology 2009, 73, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamo, J.-S.; Créange, A.; Kalifa, C.; Grill, J.; Rodriguez, D.; Doz, F.; Barbarot, S.; Zerah, M.; Sanson, M.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; et al. Prognostic Factors of CNS Tumours in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1)A Retrospective Study of 104 Patients. Brain 2003, 126, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.-Y.; Jones, D.T.W.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Quang, D.-A.K.; Tönjes, M.; et al. Driver Mutations in Histone H3.3 and Chromatin Remodelling Genes in Paediatric Glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koschmann, C.; Calinescu, A.A.; Nunez, F.J.; Mackay, A.; Fazal-Salom, J.; Thomas, D.; Mendez, F.; Kamran, N.; Dzaman, M.; Mulpuri, L.; et al. ATRX Loss Promotes Tumor Growth and Impairs Nonhomologous End Joining DNA Repair in Glioma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328ra28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, R.L.; Cox, K.E.; Jeitany, M.; Wakimoto, H.; Bryll, A.R.; Ganem, N.J.; Bersani, F.; Pineda, J.R.; Suvà, M.L.; Benes, C.H.; et al. Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres Renders Cancer Cells Hypersensitive to ATR Inhibitors. Science 2015, 347, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, K.B.; Arnold, M.A.; Pierson, C.R.; Choi, K.; Yeager, N.D.; Ratner, N.; Roberts, R.D.; Finlay, J.L.; Cripe, T.P. Immune Profiling of NF1-Associated Tumors Reveals Histologic Subtype Distinctions and Heterogeneity: Implications for Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82037–82048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.J.; Cullen, J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Langer, C.E.; Turner, M.C.; McKean-Cowdin, R.; Fisher, J.L.; Lupo, P.J.; Partap, S.; et al. Childhood Brain Tumor Epidemiology: A Brain Tumor Epidemiology Consortium Review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2716–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driever, P.H.; von Hornstein, S.; Pietsch, T.; Kortmann, R.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Emser, A.; Gnekow, A.K. Natural History and Management of Low-Grade Glioma in NF-1 Children. J. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 100, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xiong, H.; Han, Y.; Li, C.; Mai, S.; Huang, Z.; Ai, X.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, F.; Guo, Q. Identification of Mutation Regions on NF1 Responsible for High- and Low-Risk Development of Optic Pathway Glioma in Neurofibromatosis Type I. Front. Genet. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasaki, C.; Gao, F.; Gutmann, D.H. Commentary: Identification of Mutation Regions on NF1 Responsible for High- and Low-Risk Development of Optic Pathway Glioma in Neurofibromatosis Type I. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolcekova, A.; Nemethova, M.; Zatkova, A.; Hlinkova, K.; Pozgayova, S.; Hlavata, A.; Kadasi, L.; Durovcikova, D.; Gerinec, A.; Husakova, K.; et al. Clusterring of Mutations in the 5′ Tertile of the NF1 Gene in Slovak Patients with Optic Pathway Glioma. Neoplasma 2013, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, S.; Piro, R.M.; Waszak, S.M.; Kehrer-Sawatzki, H.; Friedrich, R.E.; Lassaletta, A.; Witt, O.; Korbel, J.O.; Lichter, P.; Schuhmann, M.U.; et al. No Correlation between NF1 Mutation Position and Risk of Optic Pathway Glioma in 77 Unrelated NF1 Patients. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczkowska, M.; Chen, Y.; Callens, T.; Gomes, A.; Sharp, A.; Johnson, S.; Hsiao, M.C.; Chen, Z.; Balasubramanian, M.; Barnett, C.P.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in NF1: Evidence for a More Severe Phenotype Associated with Missense Mutations Affecting NF1 Codons 844-848. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahsold, R.; Hoffmeyer, S.; Mischung, C.; Gille, C.; Ehlers, C.; Kücükceylan, N.; Abdel-Nour, M.; Gewies, A.; Peters, H.; Kaufmann, D.; et al. Minor Lesion Mutational Spectrum of the Entire NF1 Gene Does Not Explain Its High Mutability but Points to a Functional Domain Upstream of the GAP-Related Domain. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 790–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, J.J.; Schartner, J.M.; Badie, B. Microglia Function in Brain Tumors. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pong, W.W.; Higer, S.B.; Gianino, S.M.; Emnett, R.J.; Gutmann, D.H. Reduced Microglial CX3CR1 Expression Delays Neurofibromatosis-1 Glioma Formation. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Reilly, K.M. The Role of the Immune System in Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Nervous System Tumors. CNS Oncol. 2017, 6, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.J.; Loguidice, M.; Gutmann, D.H.; Listernick, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Ullrich, N.J.; Packer, R.J.; Tabori, U.; Hoffman, R.O.; Ardern-Holmes, S.L.; et al. Gender as a Disease Modifier in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Optic Pathway Glioma. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggs-Andrews, K.A.; Brown, J.A.; Gianino, S.M.; Rubin, J.B.; Wozniak, D.F.; Gutmann, D.H. Sex Is a Major Determinant of Neuronal Dysfunction in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilongo, G.; Moras, P.; Carollo, C.; Battistella, A.; Clementi, M.; Laverda, A.; Murgia, A. Spontaneous Partial Regression of Low-Grade Glioma in Children With Neurofibromatosis-1: A Real Possibility. J. Child Neurol. 1999, 14, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listernick, R.; Charrow, J.; Greenwald, M.; Mets, M. Natural History of Optic Pathway Tumors in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Longitudinal Study. J. Pediatr. 1994, 125, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcer, L.J.; Liu, G.T.; Heller, G.; Bilaniuk, L.; Volpe, N.J.; Galetta, S.L.; Molloy, P.T.; Phillips, P.C.; Janss, A.J.; Vaughn, S.; et al. Visual Loss in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Optic Pathway Gliomas: Relation to Tumor Location by Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 131, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagalingam, S.; Flaherty, M.; Billson, F.; North, K. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Optic Pathway Gliomas: Follow-up of 54 Patients. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyzyk, E.; Jóźwiak, S.; Roszkowski, M.; Schwartz, R.A. Optic Pathway Gliomas in Children With and Without Neurofibromatosis 1. J. Child Neurol. 2003, 18, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listernick, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Piersall, L.; Sharif, S.; Gutmann, D.H.; Charrow, J. Late-Onset Optic Pathway Tumors in Children with Neurofibromatosis 1. Neurology 2004, 63, 1944–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campen, C.J.; Gutmann, D.H. Optic Pathway Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 33, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.J.; Loguidice, M.; Gutmann, D.H.; Listernick, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Ullrich, N.J.; Packer, R.J.; Tabori, U.; Hoffman, R.O.; Ardern-Holmes, S.L.; et al. Visual Outcomes in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1–Associated Optic Pathway Glioma Following Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornreich, L.; Blaser, S.; Schwarz, M.; Shuper, A.; Vishne, T.H.; Cohen, I.J.; Faingold, R.; Michovitz, S.; Koplewitz, B.; Horev, G. Optic Pathway Glioma: Correlation of Imaging Findings with the Presence of Neurofibromatosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.J.; Avery, R.A.; Allen, J.C.; Ardern-Holmes, S.L.; Bilaniuk, L.T.; Ferner, R.E.; Gutmann, D.H.; Listernick, R.; Martin, S.; Ullrich, N.J.; et al. Functional Outcome Measures for NF1-Associated Optic Pathway Glioma Clinical Trials. Neurology 2013, 81, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, R.A.; Hwang, E.I.; Ishikawa, H.; Acosta, M.T.; Hutcheson, K.A.; Santos, D.; Zand, D.J.; Kilburn, L.B.; Rosenbaum, K.N.; Rood, B.R.; et al. Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography during Sedation in Young Children with Optic Pathway Gliomas. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimzadeh, B.; Piraino, D.C.; Albanese, G.; Cruciani, F.; Rahimi, S. Neurofibromatosis: An Update of Ophthalmic Characteristics and Applications of Optical Coherence Tomography. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Blank, P.; Fisher, M.J.; Gittleman, H.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Badve, C.; Berman, J.I. Validation of an Automated Tractography Method for the Optic Radiations as a Biomarker of Visual Acuity in Neurofibromatosis-Associated Optic Pathway Glioma. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.; Listernick, R.; Charrow, J.; Piersall, L.; Gutmann, D.H. Optic Pathway Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: The Effect of Presenting Symptoms on Outcome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2003, 122A, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, R.J.; Ater, J.; Allen, J.; Phillips, P.; Geyer, R.; Nicholson, H.S.; Jakacki, R.; Kurczynski, E.; Needle, M.; Finlay, J.; et al. Carboplatin and Vincristine Chemotherapy for Children with Newly Diagnosed Progressive Low-Grade Gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 86, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouffet, E.; Jakacki, R.; Goldman, S.; Hargrave, D.; Hawkins, C.; Shroff, M.; Hukin, J.; Bartels, U.; Foreman, N.; Kellie, S.; et al. Phase II Study of Weekly Vinblastine in Recurrent or Refractory Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellano, A.M.; Petrilli, A.S.; da Silva, N.S.; Silva, F.A.; Paiva, P.M.; Cavalheiro, S.; Bouffet, E. Single Agent Vinorelbine in Pediatric Patients with Progressive Optic Pathway Glioma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 121, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururangan, S.; Fisher, M.J.; Allen, J.C.; Herndon, J.E.; Quinn, J.A.; Reardon, D.A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Desjardins, A.; Phillips, P.C.; Watral, M.A.; et al. Temozolomide in Children with Progressive Low-Grade Glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2007, 9, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, R.A.; Hwang, E.I.; Jakacki, R.I.; Packer, R.J. Marked Recovery of Vision in Children with Optic Pathway Gliomas Treated with Bevacizumab. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin-Hajdu, E.; Décarie, J.C.; Marzouki, M.; Carret, A.S.; Ospina, L.H. Visual Acuity of Children Treated with Chemotherapy for Optic Pathway Gliomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via, P.D.; Opocher, E.; Pinello, M.L.; Calderone, M.; Viscardi, E.; Clementi, M.; Battistella, P.A.; Laverda, A.M.; Da Dalt, L.; Perilongo, G. Visual Outcome of a Cohort of Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Optic Pathway Glioma Followed by a Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Program. Neuro-Oncology 2007, 9, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Ferner, R.; Birch, J.M.; Gillespie, J.E.; Gattamaneni, H.R.; Baser, M.E.; Evans, D.G. Second Primary Tumors in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients Treated for Optic Glioma: Substantial Risks After Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2570–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Chen, Y.; Wong, F.L.; Hageman, L.; Smith, K.; Korf, B.; Cannon, A.; Leidy, D.J.; Paz, A.; Andress, J.E.; et al. Subsequent Neoplasms After a Primary Tumor in Individuals with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, N.J.; Robertson, R.; Kinnamon, D.D.; Scott, R.M.; Kieran, M.W.; Turner, C.D.; Chi, S.N.; Goumnerova, L.; Proctor, M.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Moyamoya Following Cranial Irradiation for Primary Brain Tumors in Children. Neurology 2007, 68, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listernick, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Liu, G.T.; Gutmann, D.H. Optic Pathway Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis-1: Controversies and Recommendations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karajannis, M.A.; Legault, G.; Fisher, M.J.; Milla, S.S.; Cohen, K.J.; Wisoff, J.H.; Harter, D.H.; Goldberg, J.D.; Hochman, T.; Merkelson, A.; et al. Phase II Study of Sorafenib in Children with Recurrent or Progressive Low-Grade Astrocytomas. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangusaro, J.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Young-Poussaint, T.; Wu, S.; Ligon, A.H.; Lindeman, N.; Banerjee, A.; Packer, R.J.; Kilburn, L.B.; Goldman, S.; et al. Selumetinib in Paediatric Patients with BRAF-Aberrant or Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Recurrent, Refractory, or Progressive Low-Grade Glioma: A Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, J.; Shah, A.C.; Sato, A.; Morris, S.M.; McKinstry, R.C.; Listernick, R.; Packer, R.J.; Fisher, M.J.; Gutmann, D.H. A Multi-Institutional Study of Brainstem Gliomas in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neurology 2017, 88, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, P.T.; Bilaniuk, L.T.; Vaughan, S.N.; Needle, M.N.; Liu, G.T.; Zackai, E.H.; Phillips, P.C. Brainstem Tumors in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neurology 1995, 45, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsgrove, D.N.; Brosnan-Cashman, J.A.; Giannini, C.; Raghunathan, A.; Jentoft, M.; Bettegowda, C.; Gokden, M.; Lin, D.; Yuan, M.; Lin, M.T.; et al. Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma -like Astrocytoma: A Neoplasm with a Distinct Phenotype and Frequent Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Association. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. USA Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc 2018, 31, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Crouse, N.R.; Emnett, R.J.; Gianino, S.M.; Gutmann, D.H. Neurofibromatosis-1 Regulates MTOR-Mediated Astrocyte Growth and Glioma Formation in a TSC/Rheb-Independent Manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15996–16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütt-Cabezas, M.; Karajannis, M.A.; Zagzag, D.; Shah, S.; Horkayne-Szakaly, I.; Rushing, E.J.; Cameron, J.D.; Jain, D.; Eberhart, C.G.; Raabe, E.H.; et al. Activation of MTORC1/MTORC2 Signaling in Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma and Pilocytic Astrocytoma Reveals MTOR as a Therapeutic Target. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhaiah, D.; Sridutt, B.S.; Thomas, B.; Vilanilam, G.C. Glioblastoma in Adults with Neurofibromatosis Type I: A Report of Two Cases. Neuropathology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, H.S.; Prados, M.D.; Wen, P.Y.; Mikkelsen, T.; Schiff, D.; Abrey, L.E.; Yung, W.K.; Paleologos, N.; Nicholas, M.K.; Jensen, R.; et al. Bevacizumab Alone and in Combination With Irinotecan in Recurrent Glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4733–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, J.T.; Reys, B.; Singh, P.; Pan, E. Brainstem Glioblastoma Multiforme in a Patient with NF1. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 4897–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibahara, I.; Sonoda, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Mayama, A.; Kanamori, M.; Saito, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Mashiyama, S.; Uenohara, H.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Glioblastoma in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients without IDH1, BRAF V600E, and TERT Promoter Mutations. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2018, 35, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.L.; Phong, C.; Pinarbasi, E.; Kogan, S.C.; Vandenberg, S.; Horvai, A.E.; Faddegon, B.A.; Fiedler, D.; Shokat, K.; Houseman, B.T.; et al. Dose-Dependent Effects of Focal Fractionated Irradiation on Secondary Malignant Neoplasms in Nf1 Mutant Mice. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Raedt, T.; Walton, Z.; Yecies, J.L.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Malone, C.F.; Maertens, O.; Jeong, S.M.; Bronson, R.T.; Lebleu, V.; et al. Exploiting Cancer Cell Vulnerabilities to Develop a Combination Therapy for Ras-Driven Tumors. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruin, E.C.; Cowell, C.; Warne, P.H.; Jiang, M.; Saunders, R.E.; Melnick, M.A.; Gettinger, S.; Walther, Z.; Wurtz, A.; Heynen, G.J.; et al. Reduced NF1 Expression Confers Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, M.; Huang, S.; Koster, J.; Ora, I.; Lakeman, A.; Caron, H.; Nijkamp, W.; Xie, J.; Callens, T.; Asgharzadeh, S.; et al. NF1 Is a Tumor Suppressor in Neuroblastoma That Determines Retinoic Acid Response and Disease Outcome. Cell 2010, 142, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, O.; Johnson, B.; Hollstein, P.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Messiaen, L.; Bronson, R.T.; McMahon, M.; Granter, S.; Flaherty, K.; et al. Elucidating Distinct Roles for NF1 in Melanomagenesis. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Mayes, P.A.; Eastman, S.; Shi, H.; Yadavilli, S.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Seestaller-Wehr, L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hopson, C.; et al. The BRAF and MEK Inhibitors Dabrafenib and Trametinib: Effects on Immune Function and in Combination with Immunomodulatory Antibodies Targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.H.; Loehr, A.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, J.; Henkemeyer, M.; Cashen, A. Haploinsufficiency for the Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) Tumor Suppressor Results in Increased Astrocyte Proliferation. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4450–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.J.R.; McCormick, F. The Molecular Pathology of Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauen, K.A. The RASopathies. Ann. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2013, 14, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K.; Yanai, N.; Fujita, M.; Harada, Y. Novel Mutations of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Gene in Small Cell Lung Cancers. Surg. Today 2003, 33, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.D.; Pfefferle, A.D.; Shen, L.; McNairn, A.J.; Cerami, E.G.; Fallon, B.L.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Southard, T.L.; Perou, C.M.; Schimenti, J.C. Comparative Oncogenomics Implicates the Neurofibromin 1 Gene (NF1) as a Breast Cancer Driver. Genetics 2012, 192, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Krisman, K.; Theobald, E.H.; Xu, J.; Akutagawa, J.; Lauchle, J.O.; Kogan, S.; Braun, B.S.; Shannon, K. Sustained MEK Inhibition Abrogates Myeloproliferative Disease in Nf1 Mutant Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, W.J.; Miller, S.J.; Jousma, E.; Wu, J.; Rizvi, T.A.; Brundage, M.E.; Eaves, D.; Widemann, B.; Kim, M.O.; Dombi, E.; et al. MEK Inhibition Exhibits Efficacy in Human and Mouse Neurofibromatosis Tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Croix, J.N.; Stevens, D.M.; Vignaux, G.; Uppuganti, S.; Perrien, D.S.; Yang, X.; Nyman, J.S.; Harth, E.; Elefteriou, F. Combined MEK Inhibition and BMP2 Treatment Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Healing in Nf1Osx -/- Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, A.; Toonen, J.A.; Cimino, P.J.; Gianino, S.M.; Gutmann, D.H. Akt- or MEK-Mediated MTOR Inhibition Suppresses Nf1 Optic Glioma Growth. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobbous, M.; Korf, B.R. Therapeutic Development in Neurofibromatosis. Neurofibromatosis Curr. Trends Futur. Dir. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.M.; Wolters, P.; Baldwin, A.; Dombi, E.; Fisher, M.J.; Weiss, B.D.; Kim, A.; O’Neill Blakeley, J.; Whitcomb, P.; Holmblad, M.; et al. SPRINT: Phase II Study of the MEK 1/2 Inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) and Inoperable Plexiform Neurofibromas (PN). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.F.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Giannini, C.; Rynearson, A.; Cen, L.; Hoesley, B.; Gilmer-Flynn, H.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Jenkins, S.; Long, J.; et al. PI3K/AKT Pathway Alterations Are Associated with Clinically Aggressive and Histologically Anaplastic Subsets of Pilocytic Astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.W.; Kocialkowski, S.; Liu, L.; Pearson, D.M.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Ichimura, K.; Collins, V.P. Tandem Duplication Producing a Novel Oncogenic BRAF Fusion Gene Defines the Majority of Pilocytic Astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, A.J.; Lang, S.S.; Boucher, K.L.; Madsen, P.J.; Slaunwhite, E.; Choudhari, N.; Kellet, M.; Storm, P.B.; Resnick, A.C. Paradoxical Activation and RAF Inhibitor Resistance of BRAF Protein Kinase Fusions Characterizing Pediatric Astrocytomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzin-Frankel, J. Cancer Immunotherapy. Science 2013, 342, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parney, I.F.; Hao, C.; Petruk, K.C. Glioma Immunology and Immunotherapy. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liechty, B.; Patel, S.; Weber, J.S.; Hollmann, T.J.; Snuderl, M.; Karajannis, M.A. Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression and Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and 2 Associated Tumors. J. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 138, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Bohanes, P.; Bisig, B.; Missiaglia, E.; Tsantoulis, P.; Coukos, G.; Montemurro, M.; Homicsko, K.; Michielin, O. Deep Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy of Metastatic Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor with CD274/PD-L1 Amplification. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoszczyk, S.; Rabkin, S.D. Prospect and Progress of Oncolytic Viruses for Treating Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Expert Opin. Orph. Drugs 2016, 4, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widemann, B.C.; Plotkin, S.R. Consensus for NF Clinical Trials: Recommendations of the REiNS Collaboration (Supplement II). Neurology 2016, 87, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, S.; Browder, V.; Bakker, A.C.; Blakeley, J.O.; Verma, S.K.; Wong, L.M.; Morris, J.A.; Bora, N. Delivering on the Vision of Bench to Bedside: A Rare Disease Funding Community Collaboration to Develop Effective Therapies for Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Tumors. BioRxiv 2019, 552976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variation | NF1-Glioma | LGm6 Sporadic Glioma | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Grade | Low Grade | High Grade | Low Grade | ||
| Grade IV | Grade III | Grade II | |||
| IDH Wild-Type | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| TERT | 47 | 12 | 43 | ||
| ATRX | 38 | 3 | 13 | 42 | 0 |
| CDNK2A | 58 | 19 | 59 | 46 | 17 |
| TP53 | 29 | 0 | 35 | 42 | 0 |
| PTEN | 12 | 0 | 54 | 38 | 0 |
| PIK3CA | 17 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 8 |
| NF1 | 88 | 91 | 22 | 50 | 8 |
| BRAF | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 15 |
| NF1 germline mutation | 92 | 91 | |||
| Drug | Target | Tumor | Phase | Age | Endpoints | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinblastine +/− Bevacizumab NCT02840409 | Cytotoxic/VEGF | LGG | II | 6 months to 18 years | Response rate, OS, PFS, visual outcome measures, OCT | Recruiting |
| Pegylated interferon NCT02343224 | Tumor microenvironment | PA or OPG | II | 3 to 18 years | Response rate | Recruiting |
| Pomalidomide NCT02415153 | Angiogenesis/immunomodulation | NF1-associated CNS tumors | I | 3 to 20 years | Toxicity, MTD | Active, not recruiting |
| Lenalidomide NCT01553149 | Angiogenesis/immunomodulation | PA or OPG | II | 0 to 21 years | Response rate | Active, not recruiting |
| Everolimus (RAD0001) NCT01158651 | mTOR | LGG | II | 1 to 21 years | Response rate | Active, not recruiting |
| Binimetinib (MEK162) NCT02285439 | MEK | LGG | I/II | 1 to 18 years | MTD, response rate | Recruiting |
| Binimetinib (MEK162) NCT01885195 | MEK | Solid tumors with NF1 mutation | II | Older than 18 years | Response rate | Completed (pending results) |
| Selumetinib NCT01089101 | MEK | LGG | I/II | 3 to 21 years | Safety, MTD, Response rate | Recruiting |
| Selumetinib (Selumetinib vs. carboplatin and vincristine) Randomized NCT03871257 | MEK | OPG | III | 2 to 21 years | Event-free survival ∗, visual acuity | Not yet recruiting |
| TAK-580 NCT03429803 | RAF (pan-RAF kinase inhibitor) | LGG | I/II | 1 to 18 years | Toxicity, MTD, 6-month PFS | Recruiting |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobbous, M.; Bernstock, J.D.; Coffee, E.; Friedman, G.K.; Metrock, L.K.; Chagoya, G.; Elsayed, G.; Nakano, I.; Hackney, J.R.; Korf, B.R.; et al. An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010114
Lobbous M, Bernstock JD, Coffee E, Friedman GK, Metrock LK, Chagoya G, Elsayed G, Nakano I, Hackney JR, Korf BR, et al. An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobbous, Mina, Joshua D. Bernstock, Elizabeth Coffee, Gregory K. Friedman, Laura K Metrock, Gustavo Chagoya, Galal Elsayed, Ichiro Nakano, James R. Hackney, Bruce R. Korf, and et al. 2020. "An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas" Cancers 12, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010114
APA StyleLobbous, M., Bernstock, J. D., Coffee, E., Friedman, G. K., Metrock, L. K., Chagoya, G., Elsayed, G., Nakano, I., Hackney, J. R., Korf, B. R., & Nabors, L. B. (2020). An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas. Cancers, 12(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010114




