ADAM17 Activity and IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-6 Trans-Signaling and ADAM17 in Inflammation
2.1.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.1.2. Acute Inflammation
2.1.3. Sepsis
2.1.4. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
2.1.5. Lung Pathophysiology: Emphysema, Asthma, and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
2.2. IL-6 Trans-Signaling and ADAM17 in Cancer
2.2.1. Colorectal Cancer
2.2.2. Pancreatic Cancer
2.2.3. Liver Cancer
2.2.4. Lung Cancer
3. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM | a disintegrin and metalloprotease |
| AOM | azoxymethane |
| APC | adenomatous polyposis coli protein |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DSS | dextransulfate sodium |
| EAE | experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| FDA | US food and drug administration |
| FoxP3 | forkhead box protein 3 |
| FRMD | FERM domain containing protein, identical to iTAP |
| Gp130 | glycoprotein 130 kDa |
| IECs | intestinal epithelial cells |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-6R | Interleukin-6 receptor |
| iRhom | inactive rhomboid protease |
| iTAP | iRhom Tail-Associated Protein identical to FRMD8 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| Kras | oncogene first identified in Kirsten RAt Sarcoma virus |
| MAP | mitogen-activated protein |
| mTOR | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NFκB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer |
| Notch | cell signaling receptor present in most animals |
| PTPN | tyrosine phosphatase |
| RANK | Receptor Activator of NFκB |
| RANKL | ligand of RANK |
| ROSA26 | reverse oriented splice acceptor, Clone 26 |
| SHP2 | protein-tyrosine phosphatase shp2 |
| SOCS | suppressor of cytokine signaling |
| Src | proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| WHO | world health organization |
| YAP | proto-oncogene yes associated protein. |
References
- Jones, S.A.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S. Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 Trans-Signaling via the Soluble IL-6 Receptor: Importance for the Pro-Inflammatory Activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, F.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Moroishi, T.; De Jong, P.R.; Krawczyk, M.; Grebbin, B.M.; Luo, H.; Xu, R.H.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Schweiger, C.; Wang, K.; et al. YAP–IL-6ST autoregulatory loop activated on APC loss controls colonic tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Wu, L.W.; Grivennikov, S.I.; De Jong, P.R.; Lian, I.; Yu, F.X.; Wang, K.; Ho, S.B.; Boland, B.S.; Chang, J.T.; et al. A gp130–Src–YAP module links inflammation to epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 519, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhlmann-Laeisz, C.; Lang, S.; Chalaris, A.; Krzysztof, P.; Enge, S.; Eichler, J.; Klingmüller, U.; Samuel, M.; Ernst, M.; Rose-John, S.; et al. Forced Dimerization of gp130 Leads to Constitutive STAT3 Activation, Cytokine-independent Growth, and Blockade of Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 2986–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 family cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mülberg, J.; Schooltink, H.; Stoyan, T.; Günther, M.; Graeve, L.; Buse, G.; Mackiewicz, A.; Heinrich, P.C.; Rose-John, S. The soluble interleukin-6 receptor is generated by shedding. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, I.; Schwarz, J.; Lücke, K.; Schumacher, N.; Schumacher, V.; Schmidt, S.; Rabe, B.; Saftig, P.; Donners, M.; Rose-John, S.; et al. Adam17 controls IL-6 signaling by cleavage of the murine IL-6Rα from the cell surface of leukocytes during inflammatory responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, N.; Meyer, D.; Mauermann, A.; Von Der Heyde, J.; Wolf, J.; Schwarz, J.; Knittler, K.; Murphy, G.; Michalek, M.; Garbers, C.; et al. Shedding of Endogenous Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL-6R) Is Governed by A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) Proteases while a Full-length IL-6R Isoform Localizes to Circulating Microvesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26059–26071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S.; Heinrich, P.C. Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: Generation and biological function. Biochem. J. 1994, 300, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro-and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, P.; Boll, I.; Rothaug, M.; Schumacher, N.; Schmidt, F.; Wichert, R.; Schneppenheim, J.; Lokau, J.; Pickhinke, U.; Koudelka, T.; et al. Meprin Metalloproteases Generate Biologically Active Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor to Induce Trans-Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbers, C.; Jänner, N.; Chalaris, A.; Moss, M.L.; Floss, D.M.; Meyer, D.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Species Specificity of ADAM10 and ADAM17 Proteins in Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Trans-signaling and Novel Role of ADAM10 in Inducible IL-6 Receptor Shedding. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14804–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riethmueller, S.; Ehlers, J.C.; Lokau, J.; Düsterhöft, S.; Knittler, K.; Dombrowsky, G.; Grötzinger, J.; Rabe, B.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Cleavage Site Localization Differentially Controls Interleukin-6 Receptor Proteolysis by ADAM10 and ADAM17. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethmueller, S.; Somasundaram, P.; Ehlers, J.C.; Hung, C.W.; Flynn, C.M.; Lokau, J.; Agthe, M.; Düsterhöft, S.; Zhu, Y.; Grötzinger, J.; et al. Proteolytic origin of the soluble human IL-6R in vivo and a decisive role of n-glycosylation. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Blinn, G.; Solem, F.; Fischer, M.; Zum Büschenfelde, K.H.M.; Rose-John, S. In vivo and in vitro activities of the gp130-stimulating designer cytokine Hyper-IL-6. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. IL-6 pathway in the liver: From physiopathology to therapy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jostock, T.; Müllberg, J.; Özbek, S.; Atreya, R.; Blinn, G.; Voltz, N.; Fischer, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Rose-John, S. Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignaling responses. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Heink, S.; Korn, T.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, A. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Reinheimer, T.M.; Wege, H.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Different Soluble Forms of the Interleukin-6 Family Signal Transducer gp130 Fine-tune the Blockade of Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16186–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S. The interleukin 6 pathway and atherosclerosis. Lancet 2012, 380, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Monhasery, N.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Lokau, J.; Baran, P.; Nowell, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The interleukin-6 receptor Asp358Ala single nucleotide polymorphism rs2228145 confers increased proteolytic conversion rates by ADAM proteases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Garbers, Y.; Flynn, C.M.; Waetzig, G.H.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Krone, W.; Berthold, H.K.; Laudes, M.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. The IL-6-neutralizing sIL-6R-sgp130 buffer system is disturbed in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.C.; Freitag, D.F.; Cutler, A.J.; Howson, J.M.M.; Rainbow, D.B.; Smyth, D.J.; Kaptoge, S.; Clarke, P.; Boreham, C.; Coulson, R.M.; et al. Functional IL6R 358Ala Allele Impairs Classical IL-6 Receptor Signaling and Influences Risk of Diverse Inflammatory Diseases. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IL6R Genetics Consortium Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar, N.; Butterworth, A.S.; Freitag, D.F.; Gregson, J.; Willeit, P.; Gorman, D.N.; Gao, P.; Saleheen, D.; Rendon, A.; et al. Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 2012, 379, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Interleukin-6 Receptor Mendelian Randomisation Analysis (IL6R MR) Consortium; Sarwar, N.; Butterworth, A.S.; Freitag, D.F.; Gregson, J.; Willeit, P.; Gorman, D.N.; Gao, P.; Saleheen, D.; Rendon, A.; et al. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: A mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Parisinos, C.A.; Serghiou, S.; Katsoulis, M.; George, M.J.; Patel, R.S.; Hemingway, H.; Hingorani, A.D. Variation in Interleukin 6 Receptor Gene Associates with Risk of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, E.; Clement, M.; Lareyre, F.; Sweeting, M.; Raffort, J.; Grenier, C.; Finigan, A.; Harrison, J.; Peters, J.E.; Sun, B.B.; et al. Interleukin-6 receptor signaling and abdominal aortic aneurysm growth rates. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, M.; Baumann, H.; Freer, G.; Freudenberg, M.; Lamers, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Zinkernagel, R.; Bluethmann, H.; Köhler, G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature 1994, 368, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, V.; Balena, R.; Fattori, E.; Markatos, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ciliberto, G.; Rodan, G.; Costantini, F. Interleukin-6 deficient mice are protected from bone loss caused by estrogen depletion. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, E.; Cappelletti, M.; Costa, P.; Sellitto, C.; Cantoni, L.; Carelli, M.; Faggioni, R.; Fantuzzi, G.; Ghezzi, P.; Poli, V. Defective inflammatory response in interleukin 6-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suematsu, S.; Matsuda, T.; Aozasa, K.; Akira, S.; Nakano, N.; Ohno, S.; Miyazaki, J.; Yamamura, K.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. IgG1 plasmacytosis in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7547–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suematsu, S.; Matsusaka, T.; Matsuda, T.; Ohno, S.; Miyazaki, J.; Yamamura, K.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. Generation of plasmacytomas with the chromosomal translocation t (12;15) in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Jacobs, S.; Ehlers, M.; Vollmer, P.; Müllberg, J.; Wolf, E.; Brem, G.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Rose-John, S. The function of the soluble interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor in vivo: Sensitization of human soluble IL-6 receptor transgenic mice towards IL-6 and prolongation of the plasma half-life of IL-6. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Goldschmitt, J.; Odenthal, M.; Peschel, C.; Fattori, E.; Ciliberto, G.; Dienes, H.P.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Rose-John, S. Extramedullary Expansion of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in Interleukin (IL)-6–sIL-6R Double Transgenic Mice. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrman, J.M.; Patel, N.; Timans, J.C.; Kastelein, R.A. Functional Replacement of Cytokine Receptor Extracellular Domains by Leucine Zippers. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30386–30391. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Scherger, A.K.; Al-Maarri, M.; Maurer, H.C.; Schick, M.; Maurer, S.; Ollinger, R.; Gonzalez-Menendez, I.; Martella, M.; Thaler, M.; Pechloff, K.; et al. Activated gp130 signaling selectively targets b cell differentiation to induce mature lymphoma and plasmacytoma. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.A.; Rauch, C.T.; Kozlosky, C.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Slack, J.L.; Wolfson, M.F.; Castner, B.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Reddy, P.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 1997, 385, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, M.L.; Jin, S.L.; Milla, M.E.; Bickett, D.M.; Burkhart, W.; Carter, H.L.; Chen, W.J.; Clay, W.C.; Didsbury, J.R.; Hassler, D.; et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-alpha. Nature 1997, 385, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschon, J.J. An Essential Role for Ectodomain Shedding in Mammalian Development. Science 1998, 282, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, V.; Schuster, B.; Schütze, S.; Bussmeyer, I.; Ludwig, A.; Hundhausen, C.; Sadowski, T.; Saftig, P.; Hartmann, D.; Kallen, K.J.; et al. Cellular Cholesterol Depletion Triggers Shedding of the Human Interleukin-6 Receptor by ADAM10 and ADAM17 (TACE). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38829–38839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. ADAM17: A molecular switch to control inflammation and tissue regeneration. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunke, F.; Rose-John, S. The shedding protease adam17: Physiology and pathophysiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1864, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, K.; Kimura, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Takaishi, H.; Okada, Y.; Toyama, Y.; Blobel, C.P. Cutting Edge: TNF-α-Converting Enzyme (TACE/ADAM17) Inactivation in Mouse Myeloid Cells Prevents Lethality from Endotoxin Shock. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2686–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalaris, A.; Adam, N.; Sina, C.; Rosenstiel, P.; Lehmann-Koch, J.; Schirmacher, P.; Hartmann, D.; Cichy, J.; Gavrilova, O.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Critical role of the disintegrin metalloprotease ADAM17 for intestinal inflammation and regeneration in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulloo, I.; Muliyil, S.; Freeman, M. The molecular, cellular and pathophysiological roles of iRhom pseudoproteases. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adrain, C.; Freeman, M. New lives for old: Evolution of pseudoenzyme function illustrated by iRhoms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Lang, P.A.; Maretzky, T.; Hamada, K.; Ohishi, K.; Maney, S.K.; Berger, T.; Murthy, A.; Duncan, G.; Xu, H.C.; et al. iRhom2 regulation of TACE controls TNF-mediated protection against Listeria and responses to LPS. Science 2012, 335, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, U.; Grieve, A.G.; Meng, Y.; Sieber, B.; Cowley, S.A.; Freeman, M. FRMD8 promotes inflammatory and growth factor signalling by stabilising the iRhom/ADAM17 sheddase complex. Elife 2018, 7, e35012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomidi, I.; Burbridge, E.; Cavadas, M.; Sullivan, G.; Collis, B.; Naegele, H.; Clancy, D.; Brezinova, J.; Hu, T.; Bileck, A.; et al. Itap, a novel irhom interactor, controls tnf secretion by policing the stability of irhom/tace. Elife 2018, 7, e35032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.; Kordowski, F.; Büch, J.; Maretzky, T.; Evers, A.; Andrä, J.; Düsterhöft, S.; Michalek, M.; Lorenzen, I.; Somasundaram, P.; et al. Phosphatidylserine exposure is required for ADAM17 sheddase function. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalaris, A.; Rabe, B.; Paliga, K.; Lange, H.; Laskay, T.; Fielding, C.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Apoptosis is a natural stimulus of IL6R shedding and contributes to the proinflammatory trans-signaling function of neutrophils. Blood 2007, 110, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, E.B.; Horton, J.L.; Hilliard, B.; Liu, T.S.; Chen, Y. IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Roles of IL-6 in the activation and differentiation of autoreactive T cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6480–6486. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, Y.; Sakoda, S.; Bernard, C.C.; Fujimura, H.; Saeki, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Yanagihara, T. IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis provoked by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Int. Immunol. 1998, 10, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, H.P.; Frei, K.; Kopf, M.; Lassmann, H.; Fontana, A.; Eugster, H. IL-6-deficient mice resist myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, S.; Saeki, Y.; Mima, T.; Sasai, M.; Nishioka, K.; Nomura, S.; Kopf, M.; Katada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Suemura, M.; et al. Interleukin 6 plays a key role in the development of antigen-induced arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8222–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonzi, T.; Fattori, E.; Lazzaro, D.; Costa, P.; Probert, L.; Kollias, G.; De Benedetti, F.; Poli, V.; Ciliberto, G. Interleukin 6 Is Required for the Development of Collagen-induced Arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladel, C.H.; Blum, C.; Dreher, A.; Reifenberg, K.; Kopf, M.; Kaufmann, S.H. Lethal tuberculosis in interleukin-6-deficient mutant mice. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 4843–4849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McFarland-Mancini, M.M.; Funk, H.M.; Paluch, A.M.; Zhou, M.; Giridhar, P.V.; Mercer, C.A.; Kozma, S.C.; Drew, A.F. Differences in Wound Healing in Mice with Deficiency of IL-6 versus IL-6 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 7219–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoge, J.; Yan, I.; Jänner, N.; Schumacher, V.; Chalaris, A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Engel, D.R.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Mittrücker, H.W. IL-6 controls the innate immune response against listeria monocytogenes via classical IL-6 signaling. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, S.M.; Wilkinson, T.S.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Jones, S.; Horiuchi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Rose-John, S.; Fuller, G.M.; Topley, N.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Orchestrate a Temporal Switch in the Pattern of Leukocyte Recruitment Seen during Acute Inflammation. Immunity 2001, 14, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabe, B.; Chalaris, A.; May, U.; Waetzig, G.H.; Seegert, D.; Williams, A.S.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Transgenic blockade of interleukin 6 transsignaling abrogates inflammation. Blood 2008, 111, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraakman, M.J.; Kammoun, H.L.; Allen, T.L.; Deswaerte, V.; Henstridge, D.C.; Estevez, E.; Matthews, V.B.; Neill, B.; White, D.A.; Murphy, A.J.; et al. Blocking IL-6 trans-Signaling Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Macrophage Recruitment but Does Not Improve Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desgeorges, A.; Gabay, C.; Silacci, P.; Novick, D.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Grau, G.; Dayer, J.M.; Vischer, T.; Guerne, P.A. Concentrations and origins of soluble interleukin 6 receptor-alpha in serum and synovial fluid. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Braune, J.; Weyer, U.; Hobusch, C.; Mauer, J.; Brüning, J.C.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. IL-6 Regulates M2 Polarization and Local Proliferation of Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2927–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, J.; Chaurasia, B.; Goldau, J.; Vogt, M.C.; Ruud, J.; Nguyen, K.D.; Theurich, S.; Hausen, A.C.; Schmitz, J.; Brönneke, H.S.; et al. Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganci, A.; Eigenbrod, T.; Krug, N.; De Sanctis, G.T.; Hausding, M.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Haddad, E.B.; Schmitt, E.; Bopp, T.; Kallen, K.J.; et al. The IL-6R alpha chain controls lung CD4+ CD25+ Treg development and function during allergic airway inflammation in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, R.M.; Jenkins, B.J.; Grail, D.; Williams, A.S.; Fielding, C.A.; Parker, C.R.; Ernst, M.; Topley, N.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 trans-signaling via STAT3 directs T cell infiltration in acute inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veldhoen, M.; Hocking, R.J.; Atkins, C.J.; Locksley, R.M.; Stockinger, B. Tgfbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 2006, 24, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.J.; Maini, R.N.; Feldmann, M.; Kalden, J.R.; Antoni, C.; Smolen, J.S.; Leeb, B.; Breedveld, F.C.; Macfarlane, J.D.; Bijl, H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1994, 344, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, G.E.; Maennel, D.N. TNF inhibition and sepsis—Sounding a cautionary note. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1193–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M. Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 2012, 119, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, A.; Hirano, T.; Hishitani, Y.; Tanaka, T. Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, M.A.; Williams, A.S.; Carty, S.A.; Scheller, J.; Hayes, A.J.; Jones, G.W.; Richards, P.J.; Slinn, S.; Ernst, M.; Jenkins, B.J.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of IL-6 trans signaling counteracts STAT3 control of experimental inflammatory arthritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Hu, X. The JAK/STAT pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: Pathogenic or protective? Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G.; Smith, M.D. The Jak-STAT pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burmester, G.R.; Lin, Y.; Patel, R.; van Adelsberg, J.; Mangan, E.K.; Graham, N.M.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Bauer, D.; Ignacio Vargas, J.; Lee, E.B. Efficacy and safety of sarilumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (monarch): A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group phase iii trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis 2017, 76, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Emery, P.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; Dikranian, A.; Alten, R.; Pavelka, K.; Klearman, M.; Musselman, D.; Agarwal, S.; Green, J.; et al. Tocilizumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (ADACTA): A randomised, double-blind, controlled phase 4 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, T.K.; Talbot, E.S.; Scherle, P.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Rapid inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling and Stat3 activation mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11107–11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, N.; Zhang, T.; Fong, S.L.; Lim, C.P.; Cao, X. Repression of Stat3 activity by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Oncogene 1998, 17, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebbutt, N.C.; Giraud, A.S.; Inglese, M.; Jenkins, B.; Waring, P.; Clay, F.J.; Malki, S.; Alderman, B.M.; Grail, D.; Hollande, F.; et al. Reciprocal regulation of gastrointestinal homeostasis by SHP2 and STAT-mediated trefoil gene activation in gp130 mutant mice. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, T.; Ishihara, K.; Kamimura, D.; Ikushima, H.; Ohtani, T.; Hirota, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Park, S.J.; Saeki, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; et al. A Point Mutation of Tyr-759 in Interleukin 6 Family Cytokine Receptor Subunit gp130 Causes Autoimmune Arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, S.E.; De Souza, D.; Fabri, L.J.; Corbin, J.; Willson, T.A.; Zhang, J.G.; Silva, A.; Asimakis, M.; Farley, A.; Nash, A.D.; et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 preferentially binds to the shp-2-binding site on the shared cytokine receptor subunit gp130. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6493–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Weissenbach, M.; Haan, S.; Heinrich, P.C.; Schaper, F. SOCS3 Exerts Its Inhibitory Function on Interleukin-6 Signal Transduction through the SHP2 Recruitment Site of gp130. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12848–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shouda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hanada, T.; Wakioka, T.; Oishi, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Komiya, S.; Kosai, K.I.; Hanakawa, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Induction of the cytokine signal regulator SOCS3/CIS3 as a therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Invest. 2001, 108, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Moriya, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Ohsugi, Y. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces the proliferation of synovial fibroblastic cells in the presence of soluble IL-6 receptor. Rheumatology 1995, 34, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, A.; Scaletta, N.; Ji, J.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Rheumatoid arthritis synoviocyte survival is dependent on Stat3. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6610–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Miyaura, C.; Tanaka, S.; Yamada, Y.; Koishihara, Y.; Ohsugi, Y.; Kumaki, K.; Taga, T. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor triggers osteoclast formation by interleukin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11924–11928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, N. Interleukin (IL)-6 induction of osteoclast differentiation depends on IL-6 receptors expressed on osteoblastic cells but not on osteoclast progenitors. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotake, S.; Sato, K.; Kim, K.J.; Takahashi, N.; Udagawa, N.; Nakamura, I.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kishimoto, T.; Suda, T.; Kashiwazaki, S. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, P.; Persson, E.; Conaway, H.H.; Lerner, U.H. IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M stimulate bone resorption and regulate the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and receptor activator of NF-kappa B in mouse calvariae. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3353–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, H.; Luo, T.; Liu, D.; Du, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Han, X.; Yang, K.; Guo, J.; et al. Combination of IL-6 and sIL-6R differentially regulate varying levels of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-kappab, ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowell, M.A.; Richards, P.J.; Horiuchi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Rose-John, S.; Topley, N.; Williams, A.S.; Jones, S.A. Soluble IL-6 receptor governs IL-6 activity in experimental arthritis: Blockade of arthritis severity by soluble glycoprotein130. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3202–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.J.; Nowell, M.A.; Horiuchi, S.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Fielding, C.A.; Grau, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ehrmann, M.; Williams, A.S.; Topley, N.; et al. Functional characterization of a soluble gp130 isoform and its therapeutic capacity in an experimental model of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, C.D.; Akama-Garren, E.H.; Stein, E.A.; Petralia, J.D.; Ruiz, P.J.; Edalati, A.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Robinson, W.H. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issuree, P.D.A.; Maretzky, T.; McIlwain, D.R.; Monette, S.; Qing, X.; Lang, P.A.; Swendeman, S.L.; Park-Min, K.H.; Binder, N.; Kalliolias, G.D.; et al. iRHOM2 is a critical pathogenic mediator of inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLoughlin, R.M.; Witowski, J.; Robson, R.L.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Hurst, S.M.; Williams, A.S.; Williams, J.D.; Rose-John, S.; Jones, S.A.; Topley, N. Interplay between IFN-gamma and IL-6 signaling governs neutrophil trafficking and apoptosis during acute inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, C.A.; McLoughlin, R.M.; McLeod, L.; Colmont, C.S.; Najdovska, M.; Grail, D.; Ernst, M.; Jones, S.A.; Topley, N.; Jenkins, B.J. IL-6 regulates neutrophil trafficking during acute inflammation via STAT3. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.; Sironi, M.; Toniatti, C.; Polentarutti, N.; Fruscella, P.; Ghezzi, P.; Faggioni, R.; Luini, W.; Van Hinsbergh, V.; Sozzani, S.; et al. Role of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor in Induction of Chemokines and Leukocyte Recruitment. Immunity 1997, 6, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, N.; Schmidt, S.; Schwarz, J.; Dohr, D.; Lokau, J.; Scheller, J.; Garbers, C.; Chalaris, A.; Rose-John, S.; Rabe, B. Circulating Soluble IL-6R but Not ADAM17 Activation Drives Mononuclear Cell Migration in Tissue Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3705–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, C.A.; Jones, G.W.; McLoughlin, R.M.; McLeod, L.; Hammond, V.J.; Uceda, J.; Williams, A.S.; Lambie, M.; Foster, T.L.; Liao, C.T.; et al. Interleukin-6 signaling drives fibrosis in unresolved inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twohig, J.P.; Cardus Figueras, A.; Andrews, R.; Wiede, F.; Cossins, B.C.; Derrac Soria, A.; Lewis, M.J.; Townsend, M.J.; Millrine, D.; Li, J.; et al. Activation of naive CD4+ T cells re-tunes stat1 signaling to deliver unique cytokine responses in memory CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhill, C.J.; Rose-John, S.; Lissilaa, R.; Ferlin, W.; Ernst, M.; Hertzog, P.J.; Mansell, A.; Jenkins, B.J. IL-6 trans-signaling modulates TLR4-dependent inflammatory responses via STAT3. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhausen, T.; Tschernig, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; van Griensven, M.; Vonberg, R.P.; Dorsch, M.; Mueller-Heine, A.; Chalaris, A.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; et al. Selective blockade of interleukin-6 trans-signaling improves survival in a murine polymicrobial sepsis model. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and Stat3 Are Required for Survival of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Development of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arndt, P.G.; Strahan, B.; Wang, Y.; Long, C.; Horiuchi, K.; Walcheck, B. Leukocyte ADAM17 Regulates Acute Pulmonary Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, A.; Zhao, Z.; Northoff, B.H.; Sass, K.; Herbst, A.; Kohlmaier, A.; Chalaris, A.; Wolfrum, C.; Weber, C.; Steffens, S.; et al. Adam17 Deficiency Promotes Atherosclerosis by Enhanced TNFR2 Signaling in Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, H.K.; Johnson, T.J.; Seelig, D.M.; Walcheck, B. Targeting ADAM17 in leukocytes increases neutrophil recruitment and reduces bacterial spread during polymicrobial sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, H.K.; Long, C.; Bahaie, N.S.; Walcheck, B. Regulation of cxcr2 expression and function by a disintegrin and metalloprotease-17 (ADAM17). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zarbock, A.; Gomez, I.; Wilson, C.L.; Lefort, C.T.; Stadtmann, A.; Bell, B.; Huang, L.C.; Ley, K.; Raines, E.W. ADAM17-dependent shedding limits early neutrophil influx but does not alter early monocyte recruitment to inflammatory sites. Blood 2011, 118, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, T.K.; Schaefer, B.C.; Hildeman, D.; Bender, J.; Mitchell, T.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. Activation-Induced Inhibition of Interleukin 6–Mediated T Cell Survival and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Yoshida, N.; Takeda, J.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Stat3 activation is responsible for IL-6-dependent T cell proliferation through preventing apoptosis: Generation and characterization of T cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4652–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Mudter, J.; Finotto, S.; Müllberg, J.; Jostock, T.; Wirtz, S.; Schütz, M.; Bartsch, B.; Holtmann, M.; Becker, C.; et al. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: Evidence in Crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina, K.; Itoh, J.; Fukushima, K.; Kusugami, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kyokane, K.; Imada, A.; Binion, D.G.; Musso, A.; West, G.A.; et al. Resistance of Crohn’s disease T cells to multiple apoptotic signals is associated with a Bcl-2/Bax mucosal imbalance. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Rose-John, S.; Suzuki, A.; Hara, T.; Tomiyasu, N.; Handa, K.; Tsuruta, O.; Funabashi, H.; Scheller, J.; et al. STAT3 activation via interleukin 6 trans-signalling contributes to ileitis in SAMP1/Yit mice. Gut 2006, 55, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Takazoe, M.; Fukuda, Y.; Hibi, T.; Kusugami, K.; Andoh, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamamura, T.; Azuma, J.; Nishimoto, N.; et al. A pilot randomized trial of a human anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in active Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, A.I.; Mazioti, A.; Kiropoulos, T.; Tsilioni, I.; Koutsokera, A.; Tanou, K.; Nikoulis, D.J.; Georgoulias, P.; Zakynthinos, E.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; et al. Systemic and airway inflammation and the presence of emphysema in patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruwanpura, S.M.; McLeod, L.; Miller, A.; Jones, J.; Bozinovski, S.; Vlahos, R.; Ernst, M.; Armes, J.; Bardin, P.G.; Anderson, G.P.; et al. Interleukin-6 promotes pulmonary emphysema associated with apoptosis in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwanpura, S.M.; McLeod, L.; Dousha, L.F.; Seow, H.J.; Alhayyani, S.; Tate, M.D.; Deswaerte, V.; Brooks, G.D.; Bozinovski, S.; MacDonald, M.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the IL-6 trans-signaling/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 axis in pulmonary emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevnikar, Z.; Östling, J.; Ax, E.; Calvén, J.; Thörn, K.; Israelsson, E.; Oberg, L.; Singhania, A.; Lau, L.C.; Ward, J.A.; et al. Epithelial IL-6 trans-signaling defines a new asthma phenotype with increased airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiris, S.A.; Tomos, I.P.; Karakatsani, A.; Spathis, A.; Korbila, I.; Analitis, A.; Kolilekas, L.; Kagouridis, K.; Loukides, S.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. High levels of IL-6 and IL-8 characterize early-on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis acute exacerbations. Cytokine 2018, 102, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza, M.; Schneider, D.J.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Coote, J.; Shaw, S.; Corrigan, R.; Molina, J.G.; Alcorn, J.L.; Galas, D.; Gelinas, R.; et al. Interleukin-6 contributes to inflammation and remodeling in a model of adenosine mediated lung injury. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Tasaka, S.; Inoue, K.I.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Yamada, W.; Shiraishi, Y.; Hasegawa, N.; Fujishima, S.; et al. Role of Interleukin-6 in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Inflammatory Changes in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.T.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Melicoff, E.; Le, T.T.T.; Weng, T.; Chen, N.Y.; Pedroza, M.; Zhou, Y.; Davies, J.; Philip, K.; et al. Blockade of IL-6 Trans Signaling Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3755–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza, M.; Le, T.T.; Lewis, K.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; To, S.; George, A.T.; Blackburn, M.R.; Tweardy, D.J.; Agarwal, S.K. Stat-3 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis through epithelial injury and fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, Y.P.; Scaffidi, A.K.; Misso, N.L.; Keerthisingam, C.; McAnulty, R.J.; Laurent, G.J.; Mutsaers, S.E.; Thompson, P.J.; Knight, D.A. Fibroblasts Isolated from Normal Lungs and Those with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Differ in Interleukin-6/gp130-Mediated Cell Signaling and Proliferation. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pechkovsky, D.V.; Prele, C.M.; Wong, J.; Hogaboam, C.M.; McAnulty, R.J.; Laurent, G.J.; Zhang, S.S.M.; Selman, M.; Mutsaers, S.E.; Knight, D.A. STAT3-Mediated Signaling Dysregulates Lung Fibroblast-Myofibroblast Activation and Differentiation in UIP/IPF. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A.; Balkwill, F. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Goldschmitt, J.; Peschel, C.; Brakenhoff, J.P.G.; Kallen, K.J.; Wollmer, A.; Grötzinger, J.; Rose-John, S. A bioactive designer cytokine for human hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuyama, K.; Sata, M.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 trans-signaling in inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.; Fantini, M.; Schramm, C.; Lehr, H.; Wirtz, S.; Burg, J.; Strand, S.; Kiesslich, R.; Huber, S.; Galle, P.; et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 2004, 21, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Wirtz, S.; Nikolaev, A.; Lehr, H.A.; Galle, P.R.; Rose-John, S.; Neurath, M.F. IL-6 signaling promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Hara, T.; Mitsuyama, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsuruta, O.; Sata, M.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Kado, S.; Takada, T. Essential roles of IL-6 trans-signaling in colonic epithelial cells, induced by the IL-6/soluble-IL-6 receptor derived from lamina propria macrophages, on the development of colitis-associated premalignant cancer in a murine model. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollrath, J.; Phesse, T.J.; Von Burstin, V.A.; Putoczki, T.; Bennecke, M.; Bateman, T.; Nebelsiek, T.; Lundgren-May, T.; Canli, O.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. gp130-Mediated Stat3 Activation in Enterocytes Regulates Cell Survival and Cell-Cycle Progression during Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spehlmann, M.E.; Manthey, C.F.; Dann, S.M.; Hanson, E.; Sandhu, S.S.; Liu, L.Y.; Abdelmalak, F.K.; Diamanti, M.A.; Retzlaff, K.; Scheller, J.; et al. Trp53 deficiency protects against acute intestinal inflammation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsa, S.; Paul, M.C.; Cardone, C.; Holcmann, M.; Amberg, N.; Pathria, P.; Diamanti, M.A.; Linder, M.; Timelthaler, G.; Dienes, H.P.; et al. EGFR in Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells Promotes Development of Colorectal Cancer in Mice and Associates with Outcomes of Patients. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebouissou, S.; Amessou, M.; Couchy, G.; Poussin, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Pilati, C.; Izard, T.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130 in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours. Nature 2009, 457, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Mori, H. Multistep carcinogenesis of the colon in Apcmin/+ mouse. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Schumacher, N.; Schwarz, J.; Tangermann, S.; Kenner, L.; Schlederer, M.; Sibilia, M.; Linder, M.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; Knösel, T.; et al. ADAM17 is required for EGF-R–induced intestinal tumors via IL-6 trans-signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1205–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilia, M.; Kroismayr, R.; Lichtenberger, B.M.; Natarajan, A.; Hecking, M.; Holcmann, M. The epidermal growth factor receptor: From development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 2007, 75, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emburgh, B.O.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesina, M.; Kurkowski, M.U.; Ludes, K.; Rose-John, S.; Treiber, M.; Klöppel, G.; Yoshimura, A.; Reindl, W.; Sipos, B.; Akira, S.; et al. Stat3/Socs3 Activation by IL-6 Transsignaling Promotes Progression of Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Development of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cressman, D.E.; Greenbaum, L.E.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Ciliberto, G.; Furth, E.E.; Poli, V.; Taub, R. Liver Failure and Defective Hepatocyte Regeneration in Interleukin-6-Deficient Mice. Science 1996, 274, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Blinn, G.; Jostock, T.; Schirmacher, P.; Büschenfelde, K.M.Z.; Galle, P.R.; Rose–John, S. Combined interleukin 6 and soluble interleukin 6 receptor accelerates murine liver regeneration. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmacher, P.; Peters, M.; Ciliberto, G.; Blessing, M.; Lotz, J.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Rose-John, S. Hepatocellular Hyperplasia, Plasmacytoma Formation, and Extramedullary Hematopoiesis in Interleukin (IL)-6/Soluble IL-6 Receptor Double-Transgenic Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maione, D.; Di Carlo, E.; Li, W.; Musiani, P.; Modesti, A.; Peters, M.; Rose-John, S.; Della Rocca, C.; Tripodi, M.; Lazzaro, D.; et al. Coexpression of IL-6 and soluble IL-6R causes nodular regenerative hyperplasia and adenomas of the liver. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5588–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Kamata, H.; Luo, J.L.; Leffert, H.; Karin, M. Ikkbeta couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 2005, 121, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugler, W.E.; Sakurai, T.; Kim, S.; Maeda, S.; Kim, K.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Karin, M. Gender Disparity in Liver Cancer Due to Sex Differences in MyD88-Dependent IL-6 Production. Science 2007, 317, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergmann, J.; Muller, M.; Baumann, N.; Reichert, M.; Heneweer, C.; Bolik, J.; Lucke, K.; Gruber, S.; Carambia, A.; Boretius, S.; et al. IL-6 trans-signaling is essential for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2017, 65, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.D.; McLeod, L.; Alhayyani, S.; Miller, A.; Russell, P.A.; Ferlin, W.; Rose-John, S.; Ruwanpura, S.; Jenkins, B. IL-6 trans-signaling promotes KRAS-driven lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.I.; Alhayyani, S.; McLeod, L.; Yu, L.; Alanazi, M.; Deswaerte, V.; Tang, K.; Jarde, T.; Smith, J.A.; Prodanovic, Z.; et al. ADAM17 selectively activates the IL-6 trans-signaling/erk mapk axis in kras-addicted lung cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Derynck, R. Direct activation of tace-mediated ectodomain shedding by p38 map kinase regulates egf receptor-dependent cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2009, 37, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.I.; McLeod, L.; Yu, L.; Ebi, H.; Ruwanpura, S.; Sagi, I.; Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J. The ADAM17 protease promotes tobacco smoke carcinogen-induced lung tumourigenesis. Carcinogenesis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuett, H.; Oestreich, R.; Waetzig, G.H.; Annema, W.; Luchtefeld, M.; Hillmer, A.; Bavendiek, U.; Von Felden, J.; Divchev, D.; Kempf, T.; et al. Transsignaling of Interleukin-6 Crucially Contributes to Atherosclerosis in Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Neuhöfer, P.; Song, L.; Rabe, B.; Lesina, M.; Kurkowski, M.U.; Treiber, M.; Wartmann, T.; Regnér, S.; Thorlacius, H.; et al. IL-6 trans-signaling promotes pancreatitis-associated lung injury and lethality. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linardou, H.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Kanaloupiti, D.; Siannis, F.; Bafaloukos, D.; Kosmidis, P.; Papadimitriou, C.A.; Murray, S. Assessment of somatic k-RAS mutations as a mechanism associated with resistance to EGFR-targeted agents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, N.P.; Foukakis, T.; De Petris, L.; Bergh, J. The importance of molecular markers for diagnosis and selection of targeted treatments in patients with cancer. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 545–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Vernieri, C.; Siravegna, G.; Mennitto, A.; Berenato, R.; Perrone, F.; Gloghini, A.; Tamborini, E.; Lonardi, S.; Morano, F.; et al. Heterogeneity of acquired resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
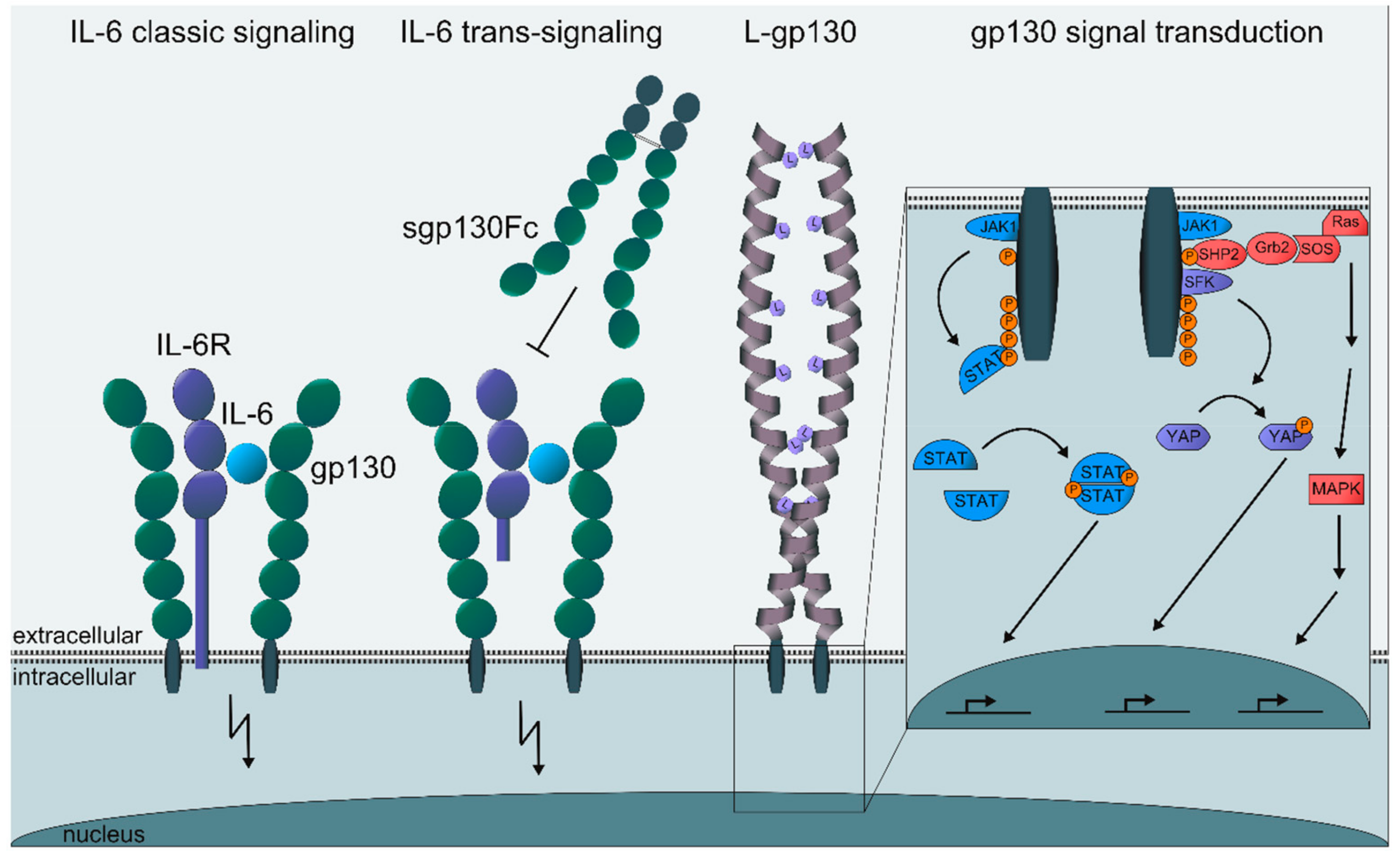
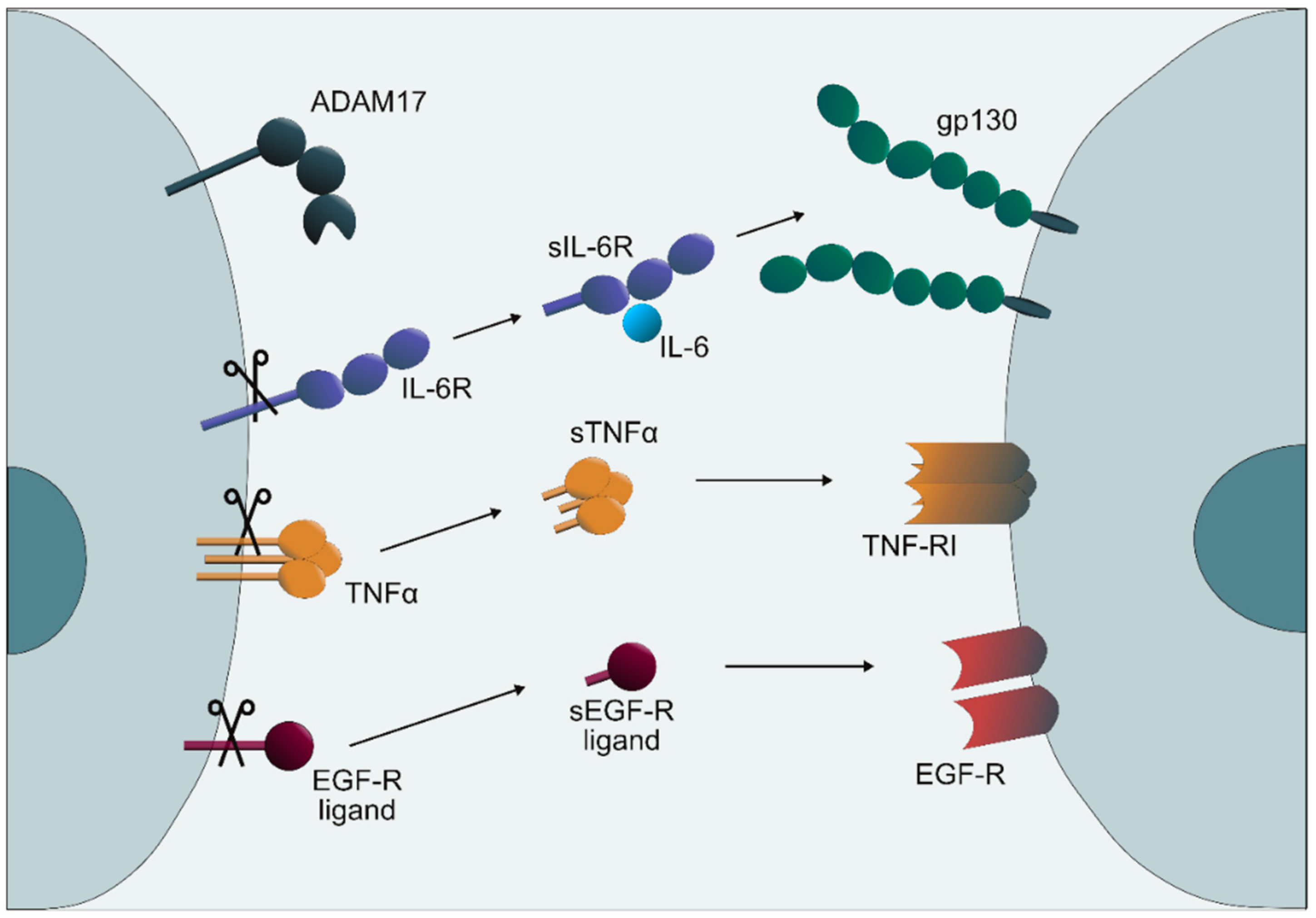
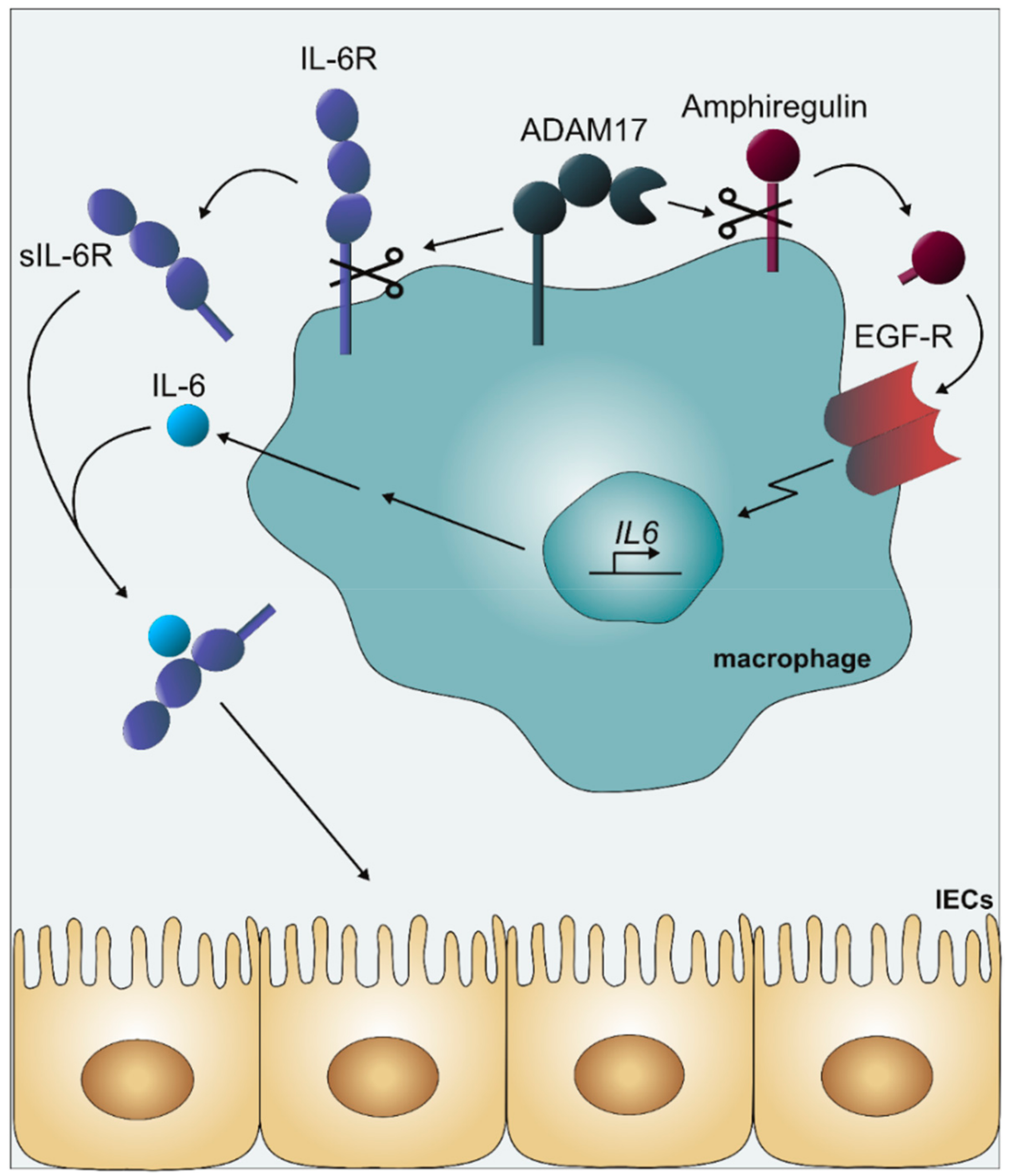
| Disease Model | Outcome of the Study |
|---|---|
| Intestinal inflammation [118,138] | Suppression of colitis activity |
| Acute inflammation [54,64,65] | Blockade of inflammatory processes |
| Atherosclerosis [159] | Regression of advanced atherosclerosis |
| Rheumatoid arthritis [79,98,99] | Improvement of established arthritis |
| Sepsis [108,109] | Up to 100% survival in different sepsis models |
| Pancreatitis-lung failure [160] | 100% survival of severe acute pancreatitis |
| Lung emphysema [124] | Improvement by blockade of alveolar cell apoptosis |
| Abdominal aortic aneurism [30] | Improved survival in two animal models |
| Colon cancer [110,136,137,138,144] | Blockade of tumor formation |
| Pancreatic cancer [147] | Inhibition of pancreatic neoplasia progression |
| Liver cancer [154] | Protection from tumor formation |
| Lung cancer [156,158] | Amelioration of lung cancer pathogenesis |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schumacher, N.; Rose-John, S. ADAM17 Activity and IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111736
Schumacher N, Rose-John S. ADAM17 Activity and IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111736
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchumacher, Neele, and Stefan Rose-John. 2019. "ADAM17 Activity and IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111736
APA StyleSchumacher, N., & Rose-John, S. (2019). ADAM17 Activity and IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers, 11(11), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111736





