Leveraging Wearable Sensors for the Identification and Prediction of Defensive Pessimism Personality Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
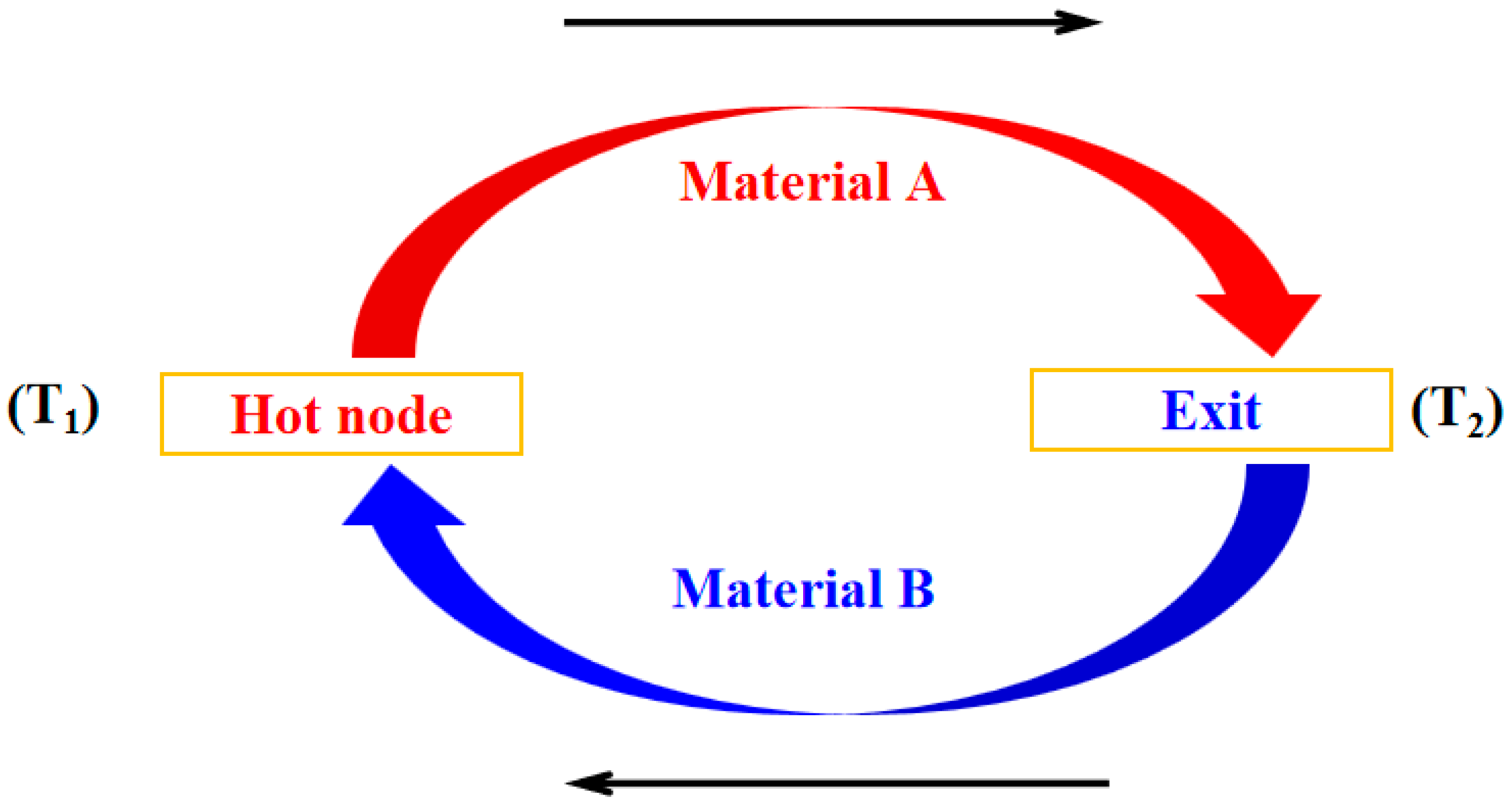
2.1. Temperature Sensor
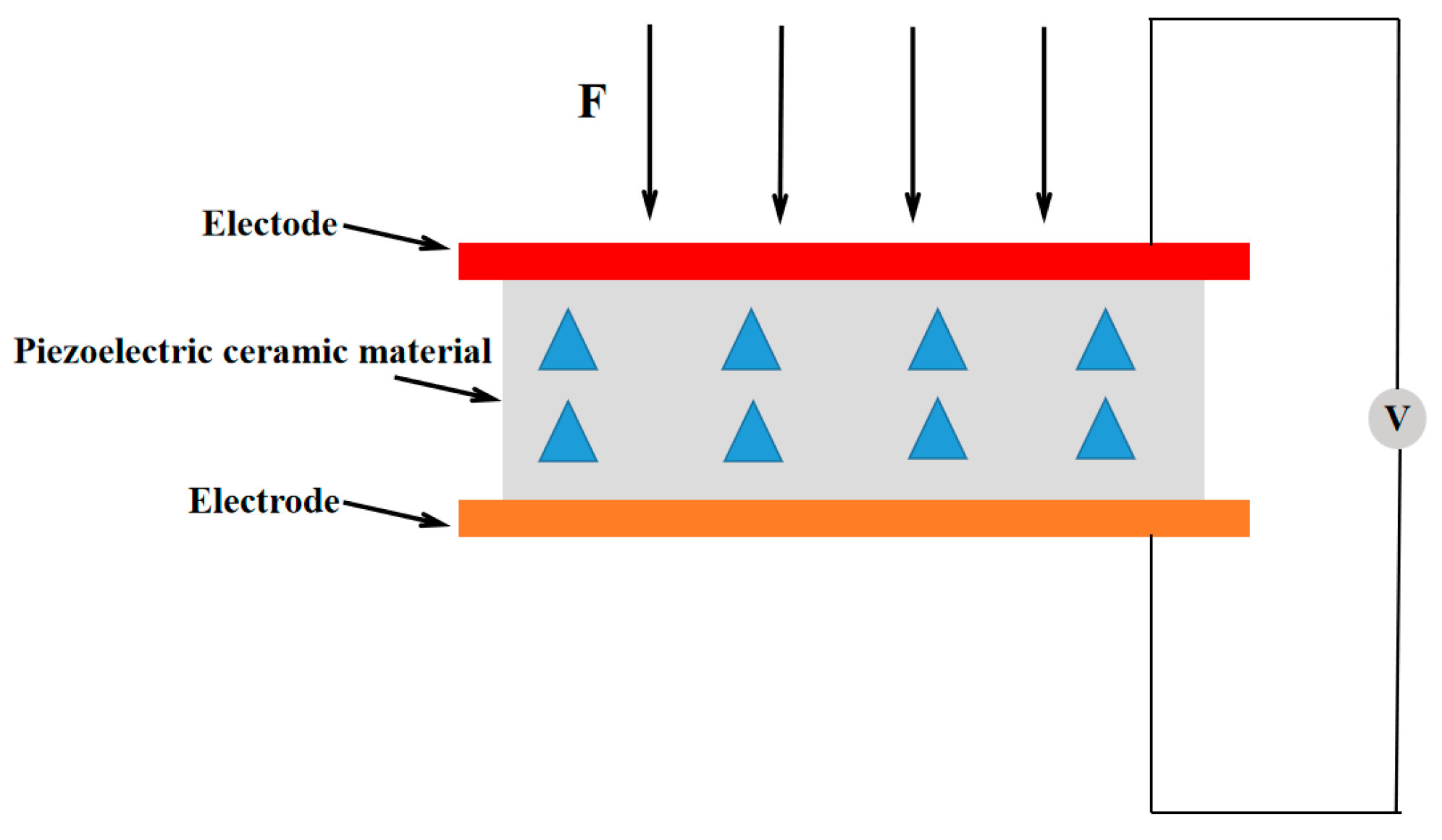
2.2. Piezoelectric Voltage Sensor
3. Design and Preparation of Samples
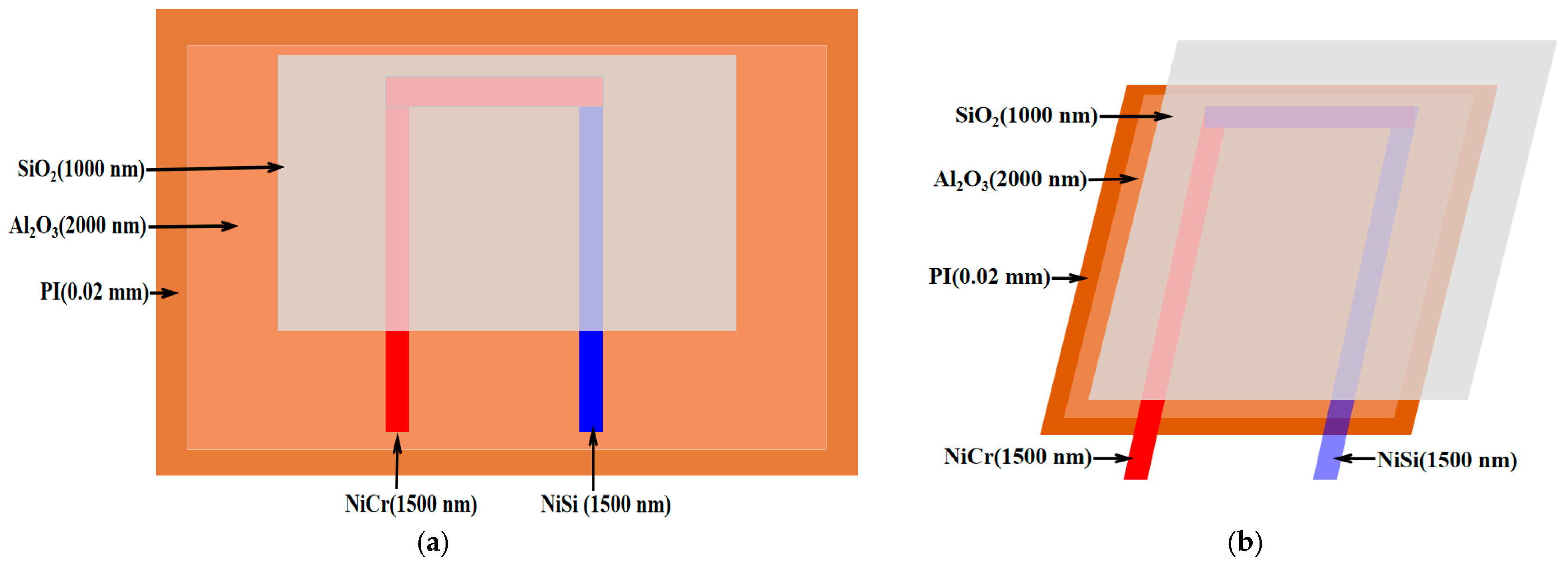
3.1. NiCr/NiSi Alloy Thin-Film Temperature Sensor
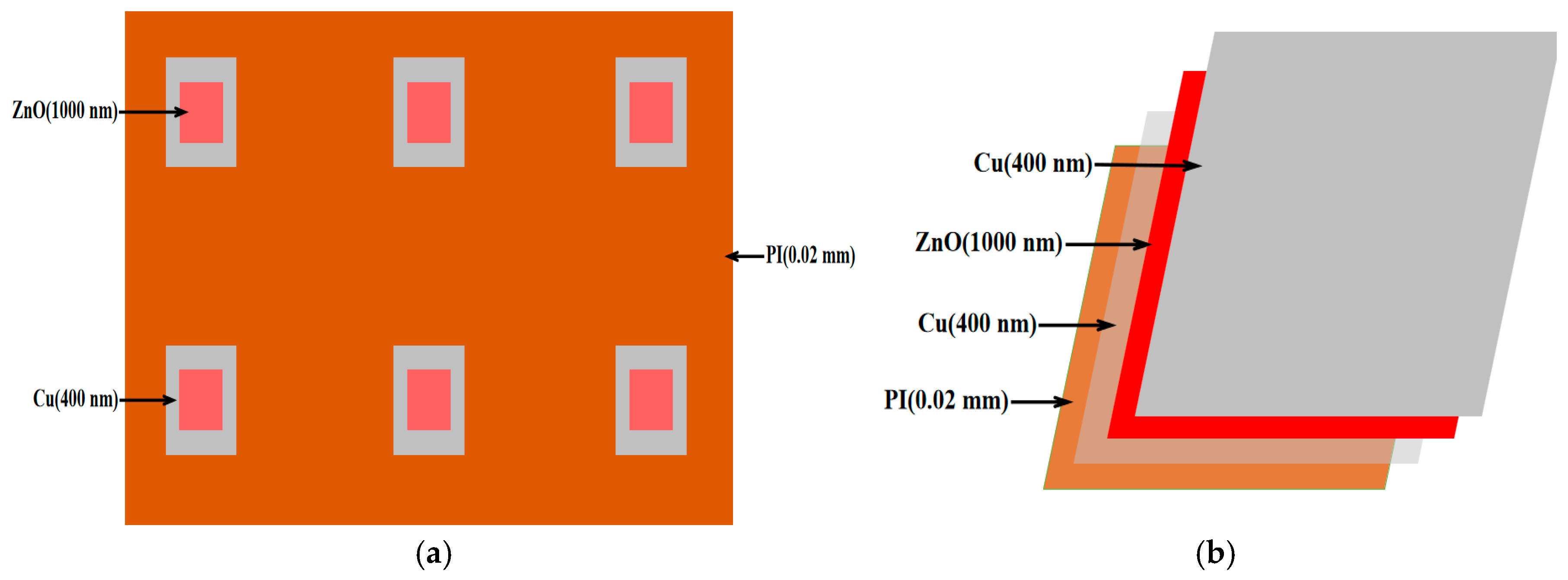
3.2. Flexible Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor
4. Temperature Static Calibration Experiment
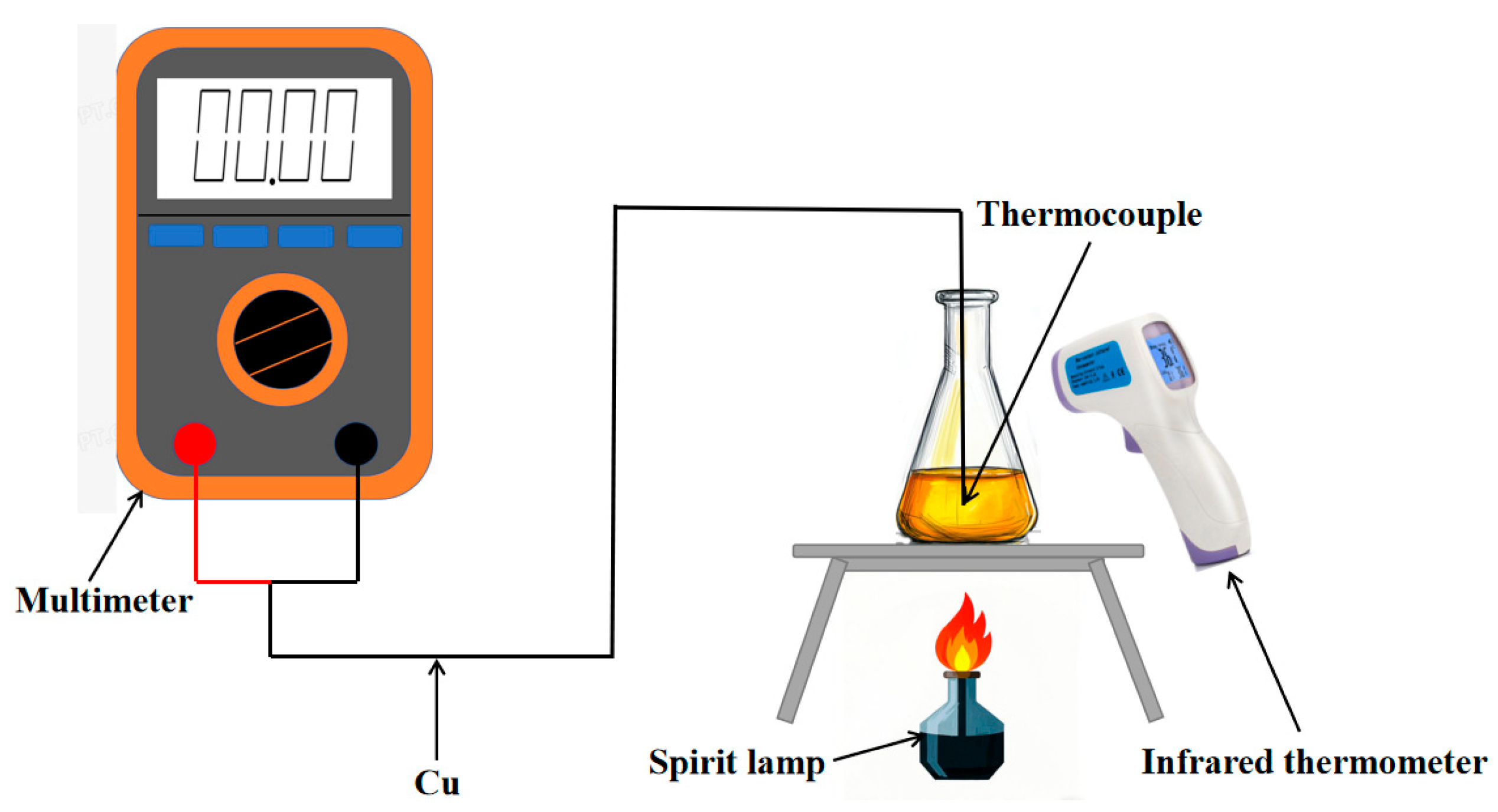
4.1. Construction of Experimental Platform
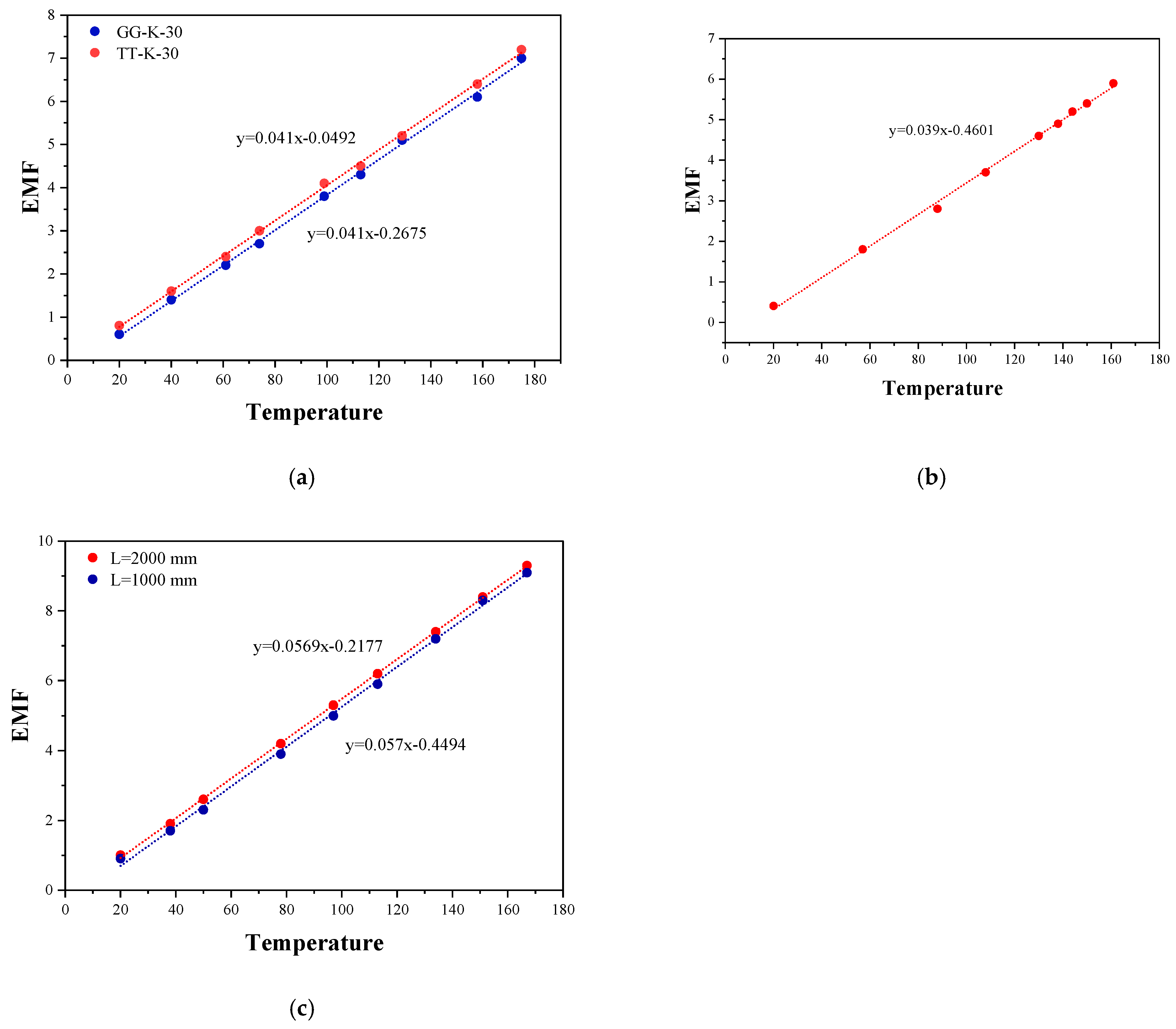
4.2. Static Calibration Result of Thermocouple
4.2.1. Feasibility Analysis
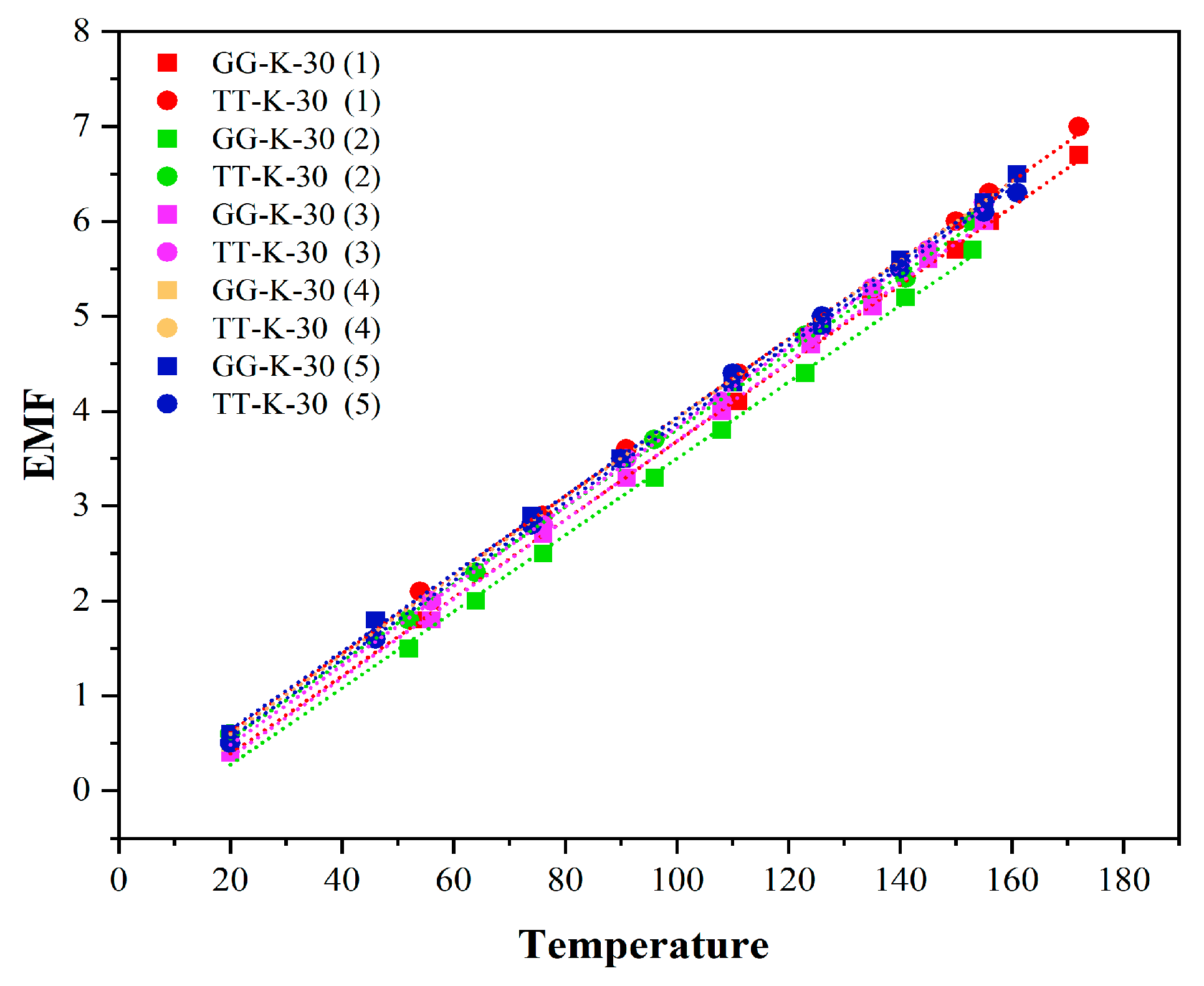
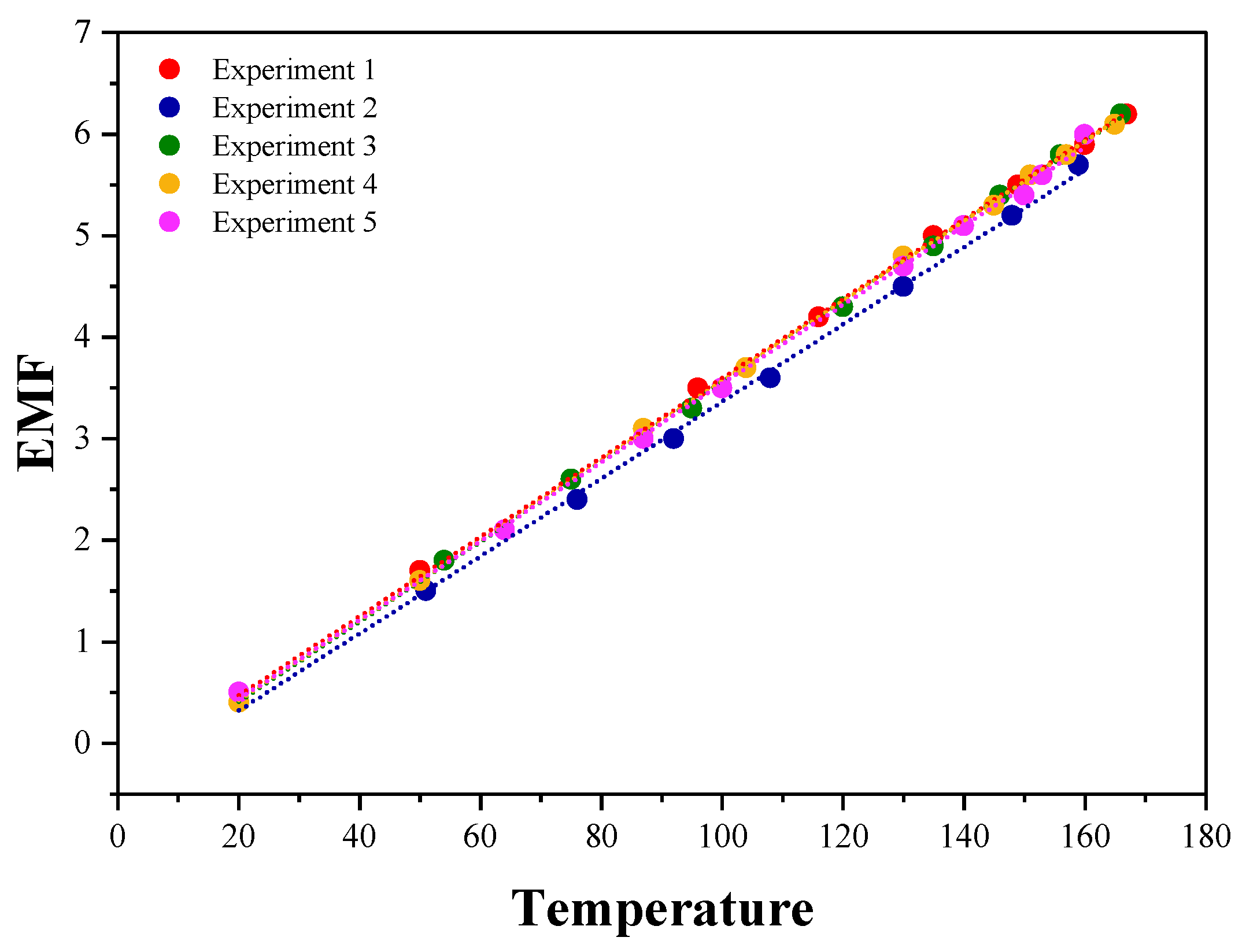
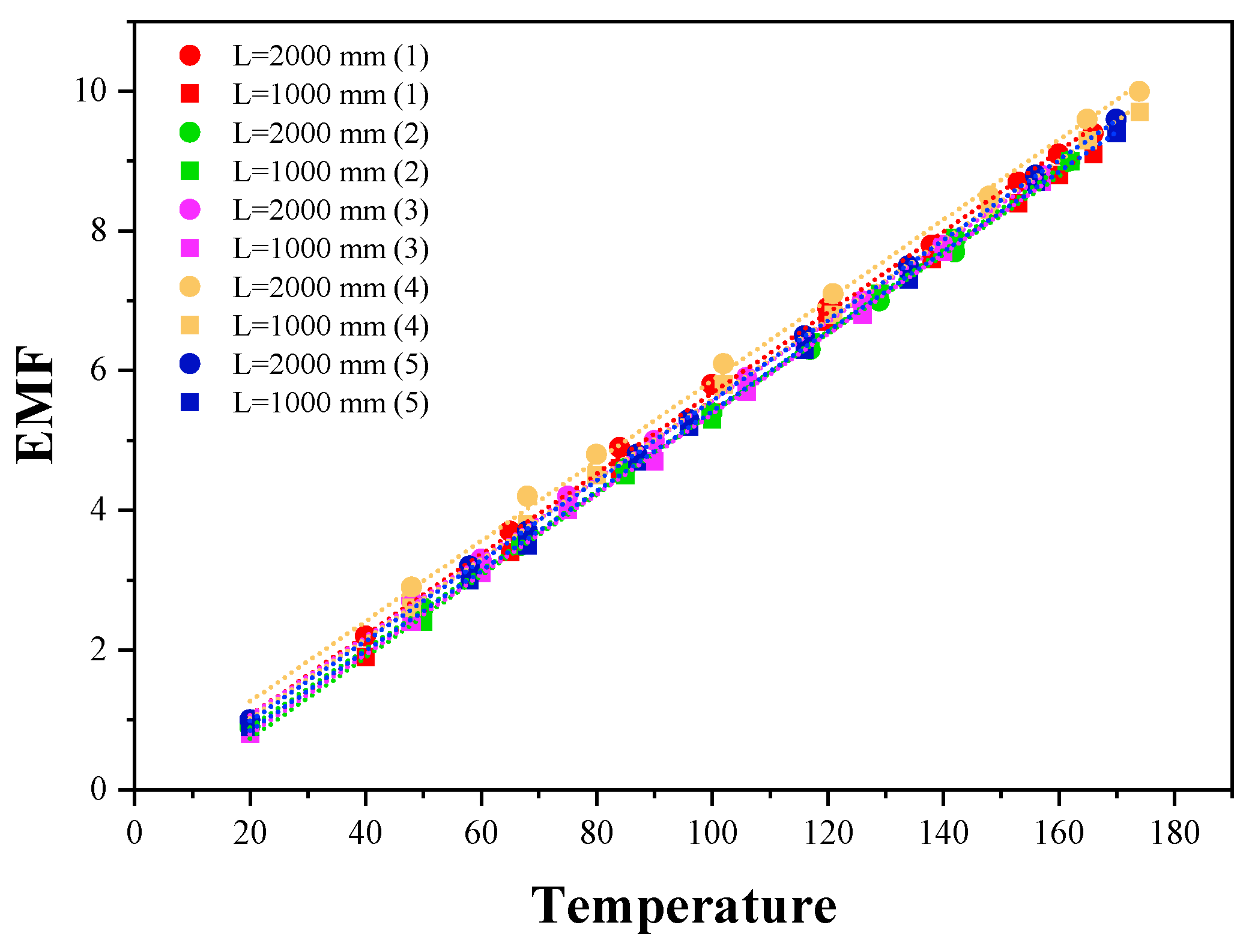
4.2.2. Consistency Analysis
K-Type Thermocouple
T-Type Thermocouple
E-Type Thermocouple
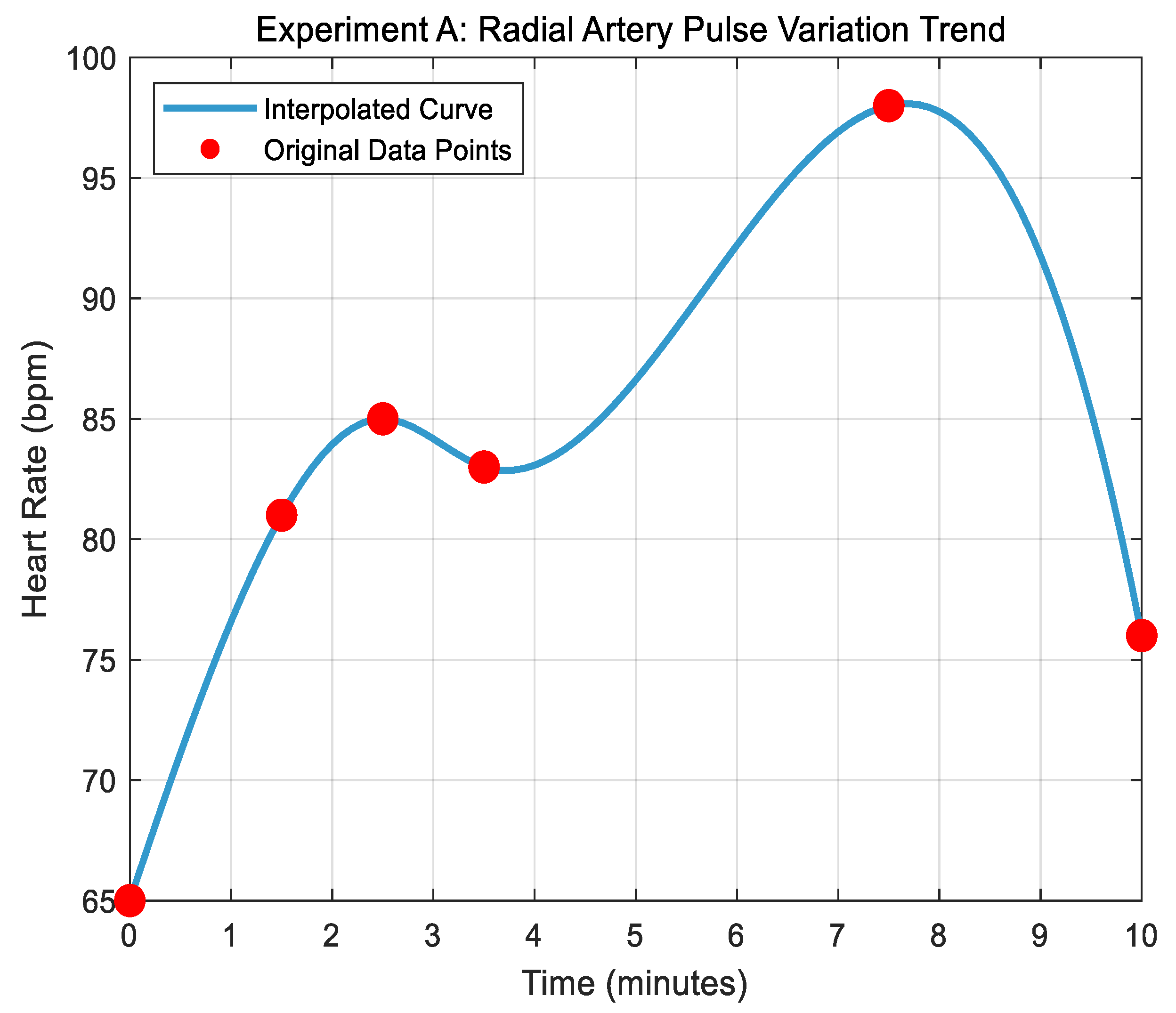
5. Radial Artery Frequency Test Experiment
5.1. Performance Test of Flexible Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor
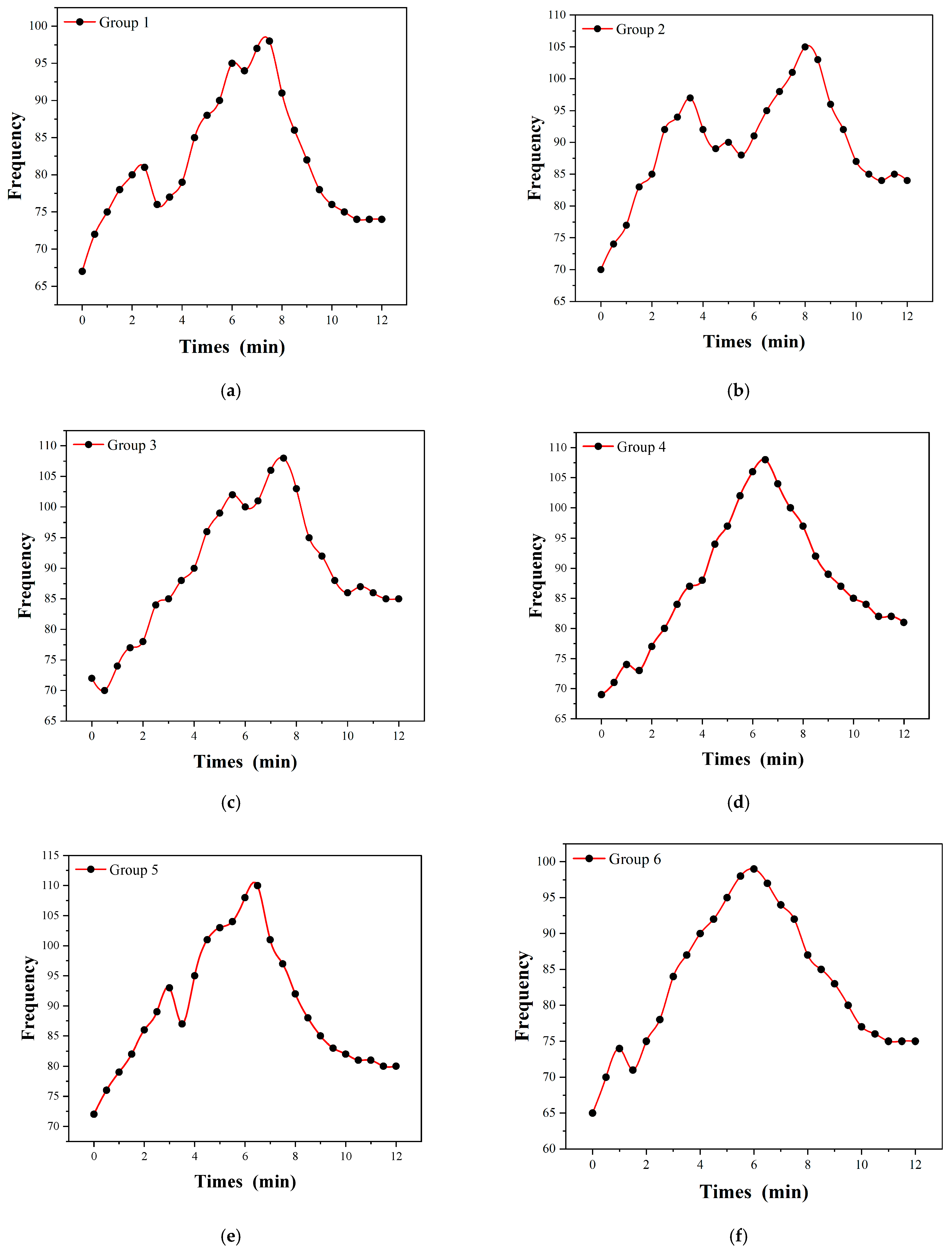
5.2. Experimental Results of Radial Artery Pulsation Frequency Test
5.3. Experimental Data Analysis of Radial Artery Pulse Frequency Test
6. Simulation Experiment
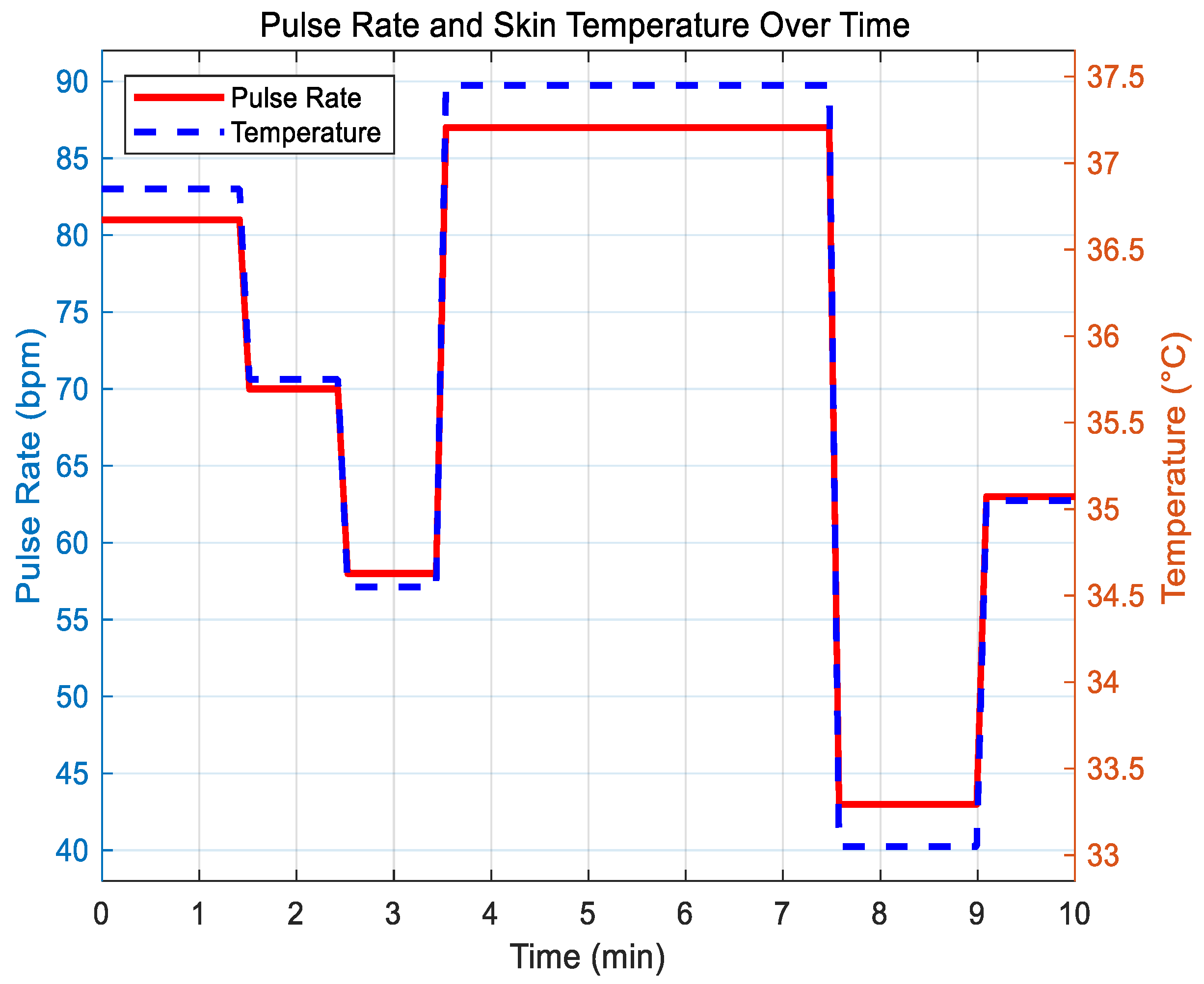
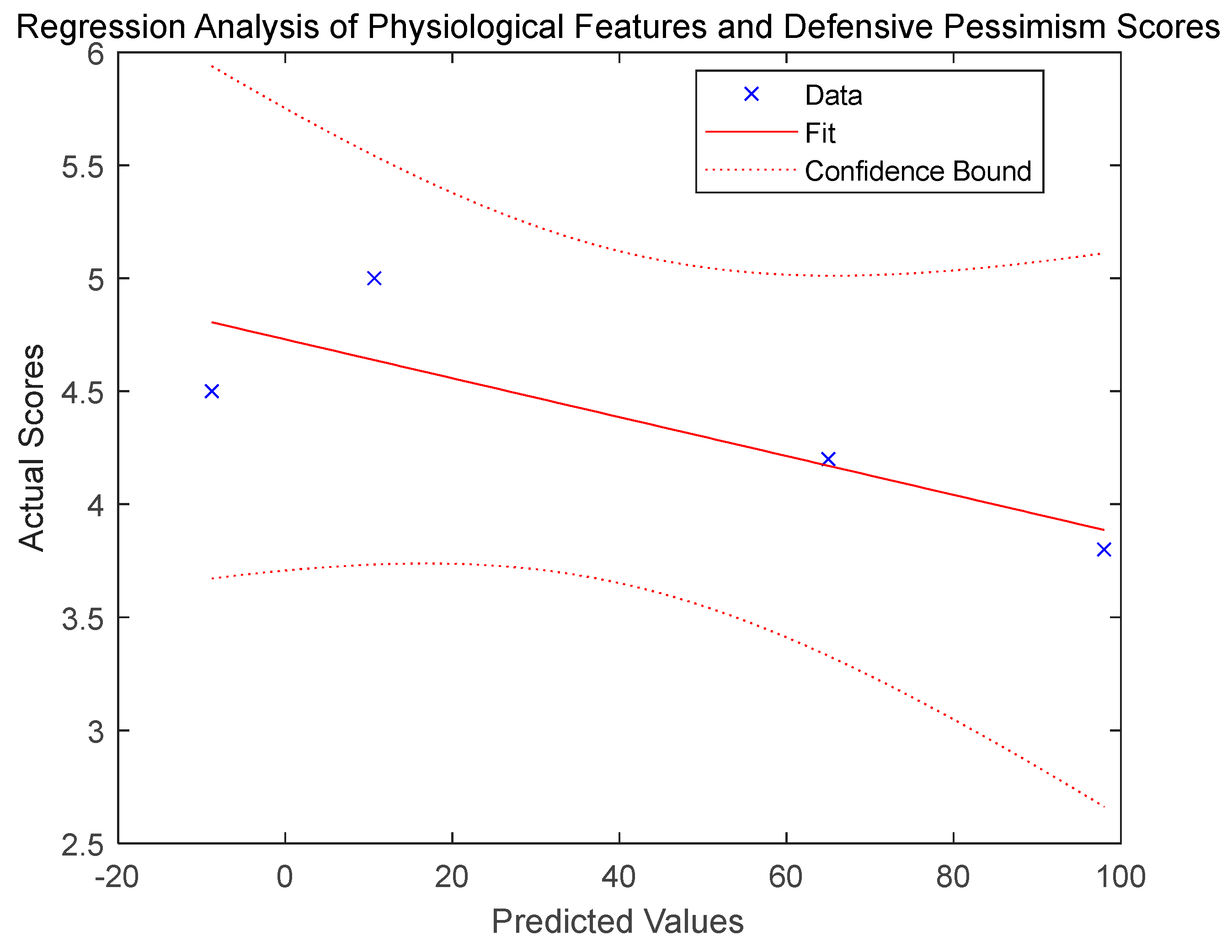
6.1. Correlation Simulation and Correlation Analysis of Physiological Indexes
6.2. Correlation Simulation and Filtering Optimization Analysis of Radial Artery Pulse Frequency and Skin Temperature
6.3. Research on Data Feature Extraction and Personality Recognition Modeling of Physiological Sensor
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norem, J.K.; Cantor, N. Defensive pessimism: Using anxiety to motivate adaptive outcomes. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, M.; Shi, H. Augustus Zheng Review of defensive pessimism. Prog. Psychol. 2020, 10, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, M.; Fang, J.; Li, M. The influence of upward social comparison on self-attrition: The mediating effect of relative deprivation and the moderating effect of defensive pessimism. In Proceedings of the 25th Chinese Psychological Society Abstract Collection-Oral Report in Groups, Department of Applied Psychology, School of Human Resources, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu, China, 13 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus, Y.L.; Wang, J.S.; Chiang, W.C.; Hung, C.H. Automatic ECG-based emo-tion recognition in music listening. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 11, 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Bowlds, R.L.; Gu, Y.; Yu, X. Pulse wave sensor for non-intrusive driver’s drowsiness detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 2312–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, K.; Qiu, Y.; Li, S. Development and research of cushion-type multi-physiological parameter detection system. China J. Med. Devices 2016, 40, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Fang, J.; Liu, S.; Wan, H.; Zhang, J. Emotion recognition method of ECG signal based on comparative learning. Appl. Res. Comput. 2024, 41, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. Research on Human Motion Recognition Method Based on Wearable Motion Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Preparation and Performance Study of High Temperature Flexible Thin Film Strain/Temperature Sensor. Master’s Thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, M. Research on the Surface Temperature Sensor of Thin-Film Thermocouple Based on New Wire Connection Technology. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Development and Performance Study of Transient Thermopile Thin Film Heat Flow Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, C.; Gontean, A. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Solutions: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. Research on the Design of Miniaturized Rainfall Sensor Based on Piezoelectric Effect. Master’s Thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Peng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Research and discussion on damage detection of civil engineering structures based on piezoelectric sensors. Urban Constr. Theory Res. (Electron. Ed.) 2024, 36, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N. Research on Contact Pattern and Texture Information Recognition Based on Piezoelectric Tactile Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Jianzhu University, Hefei, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Shi, M.; Dong, J. High-precision NiCr/NiSi thin-film thermocouple high-temperature testing system. Instrum. Technol. sensor. 2024, 2, 1–5+10. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y. Research on NiCr/NiSi Thin Film Thermocouple Temperature Measuring Tool for Transient Cutting. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.; Han, Y. Preparation and performance analysis of infrared thermal insulation and protective film on polyimide flexible substrate. J. Jilin Univ. 2024, 62, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, P.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhu, X. Study on dielectric properties of anodic alumina films formed at different temperatures. Electron. Compon. Mater. 2024, 43, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Research on Transient Multi-Point Temperature Measuring Tool with Thin Film Thermocouple for Titanium Alloy Turning. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q. Design and Research of Resistance Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Device for Continuous Coating. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Ligong University, Shenyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Song, H. Mn-Co-Ni-O thin films synthesized by magnetron sputtering and electron beam evaporation. J. Chang. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 47, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Ji, L. Study on the structure and corrosion resistance of Zn-Ni alloy thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Mater. Prot. 2024, 57, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Study on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Ti/Ti-Nb Alloy Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Research on Nano-ZnO Piezoelectric Film Flexible Pressure Sensor Array. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A. Study on ZnO: Li Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y.; An, N.; Zhou, Y. A high performance P (VDF-TrFE) nanogenerator with self-connected and vertically integrated fibers by pat-terned EHD pulling. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11536–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Guo, H.; Guo, Y. Effect of grain boundary engineering on electrical conductivity and thermal stability of microalloyed pure Cu. Spec. Cast. Non-Ferr. Alloys 2025, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lao, S.; Zhong, G. Research on a K-type thermocouple temperature control system. Pop. Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Research on Precise Temperature Monitoring and Thermal Management Optimization of Automobile Engines Based on High-Precision Thin-Film Thermocouple Technology. Micromachines 2025, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cougnon, F.G.; Depla, D. The Seebeck Coefficient of Sputter Deposited Metallic Thin Films: The Role of Process Conditions. Coatings 2019, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Lv, C. Precise measurement of thermoelectric potential of E-type thermocouple based on MCU. Sens. World 2010, 16, 19–21+18+18+4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Duan, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, L. On-Skin Flexible Pressure Sensor with High Sensitivity for Portable Pulse Monitoring. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M. Ultra-Sensitive Flexible Pressure Sensor Based on Microstructured Electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. J Psychosom Res. 2002, 53, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-H.; Aksan, N.; Anderson, S.W.; Grafft, A.; Chapleau, M.W. Habituation of parasympathetic-mediated heart rate responses to recurring acoustic startle. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Rab, S.L.; Admon, R. Dynamics in physiological acute stress response trajectories: Uncovering latent variability. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Webb, H.E.; Zourdos, M.C.; Acevedo, E.O. Cardiovascular reactivity, stress, and physical activity. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porges, S.W. The polyvagal perspective. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kreibig, S.D. Autonomic nervous system activity in emotion: A review. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 84, 394–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda, E.; Peluffo-Ordóñez, D.H.; Rosero-Montalvo, P.; Becerra, M.A.; Umaquinga-Criollo, A.C.; Ramírez, L. Heart Rate Detection using a Piezoelectric Ceramic Sensor: Preliminary results. Revis. Bionatura. 2022, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, D.; Mulgrew, J.; Hautus, M.J. Exploring the autonomic correlates of personality. Auton. Neurosci. 2015, 192, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, J.; Ducharme, M.B.; Pasto, L.; Thompson, M. Response to thermal stress and personality. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 80, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Seebeck Coefficient (μV/°C) | Average (μV/°C) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41.2 | 41.27 | 0.473872932 |
| 41.5 | |||
| 2 | 40.3 | ||
| 40.7 | |||
| 3 | 41.7 | ||
| 41.9 | |||
| 4 | 41.5 | ||
| 41.4 | |||
| 5 | 41.1 | ||
| 41.4 |
| Group | Seebeck Coefficient (μV/°C) | Average (μV/°C) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.1 | 38.98 | 0.540370243 |
| 2 | 38.1 | ||
| 3 | 39.5 | ||
| 4 | 39.3 | ||
| 5 | 38.9 |
| Group | Seebeck Coefficient (μV/°C) | Average (μV/°C) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 57.7 | 57.23 | 0.561842208 |
| 57.2 | |||
| 2 | 56.4 | ||
| 58.3 | |||
| 3 | 56.4 | ||
| 57.3 | |||
| 4 | 57.4 | ||
| 57.1 | |||
| 5 | 57.4 | ||
| 57.1 |
| Test Scenario | Key Parameter | Sensor Output Stability (CV%) | Fidelity of Characteristic Waveform | Motion Jamming Signal-to-Noise Ratio (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resting state (5 min) | Heart rate: 68 ± 3 BPM | 1.2% | P1–P5 Full feature detection | N/A (No movement) |
| Wrist 90° flexion and extension | Flexion and extension frequency: 0.5 Hz | 8.7% (Action period) | P1/P4 Amplitude retention > 95% | 24.5 |
| Moving state (4 km/h) | Acceleration interference: 0.3–2 g | 4.3% | P3 Characteristic ambiguity < 10% | 19.8 |
| Language communication | Interference of vocal cord vibration conduction | 3.1% | No additional impurity peak | 28.1 |
| Deep breathing (0.1 Hz) | Chest pressure fluctuation amplitude: ±2 kPa | 6.5% | Baseline drift <5% | 17.2 |
| Test Condition | Cycles | Sensitivity Attenuation (S1/S0) | Baseline Drift (ΔI/I0) | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 kPa, 1 Hz (Resting simulation) | 20,000 | −2.1% | +0.8% | 15 ms→16 ms |
| 40 kPa, 1.8 Hz (Motion simulation) | 20,000 | −5.3% | +3.2% | 15 ms→18 ms |
| Impact load (100 kPa, 0.5 s) | 5000 | −1.7% | +1.1% | No change |
| Time Interval | Heart Rate Error (BPM) | Waveform Coefficient K Drift | Signal Attenuation (ΔA/A0) | Environmental Disturbance Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4 h | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.002 | −0.5% | Room temperature meditation |
| 4–8 h | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 0.005 | −1.2% | Eating (increased hand activity) |
| 8–12 h | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 0.008 | −2.1% | Walk for 30 min |
| 12–24 h | 2.1 ± 1.0 | 0.012 | −3.8% | Sleep posture change |
| Interference Source | Abnormal Sensor Output | Recovery Time | Clinical Parameter Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweat soaking (NaCl 0.9%) | Instantaneous noise + 15% (Lasts for 10 s) | <30 s | Heart rate + 0.8 BPM |
| Sudden temperature change (25→40 °C) | Baseline migration + 7.3% | 120 s | K value + 0.006 |
| Electromagnetic interference (GSM 1.8 GHz) | No abnormality was detected. | N/A | No influence |
| Lateral shear force (30°) | P3 amplitude reduction 12% | Recovers immediately | DAI influence + 3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Deng, B.; Liang, W. Leveraging Wearable Sensors for the Identification and Prediction of Defensive Pessimism Personality Traits. Micromachines 2025, 16, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080906
Zhou Y, Li D, Deng B, Liang W. Leveraging Wearable Sensors for the Identification and Prediction of Defensive Pessimism Personality Traits. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080906
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, You, Dongfen Li, Bowen Deng, and Weiqian Liang. 2025. "Leveraging Wearable Sensors for the Identification and Prediction of Defensive Pessimism Personality Traits" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080906
APA StyleZhou, Y., Li, D., Deng, B., & Liang, W. (2025). Leveraging Wearable Sensors for the Identification and Prediction of Defensive Pessimism Personality Traits. Micromachines, 16(8), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080906





