A Hierarchical Inverse Lithography Method Considering the Optimization and Manufacturability Limit by Gradient Descent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lithography Imaging Model
3. Methodology
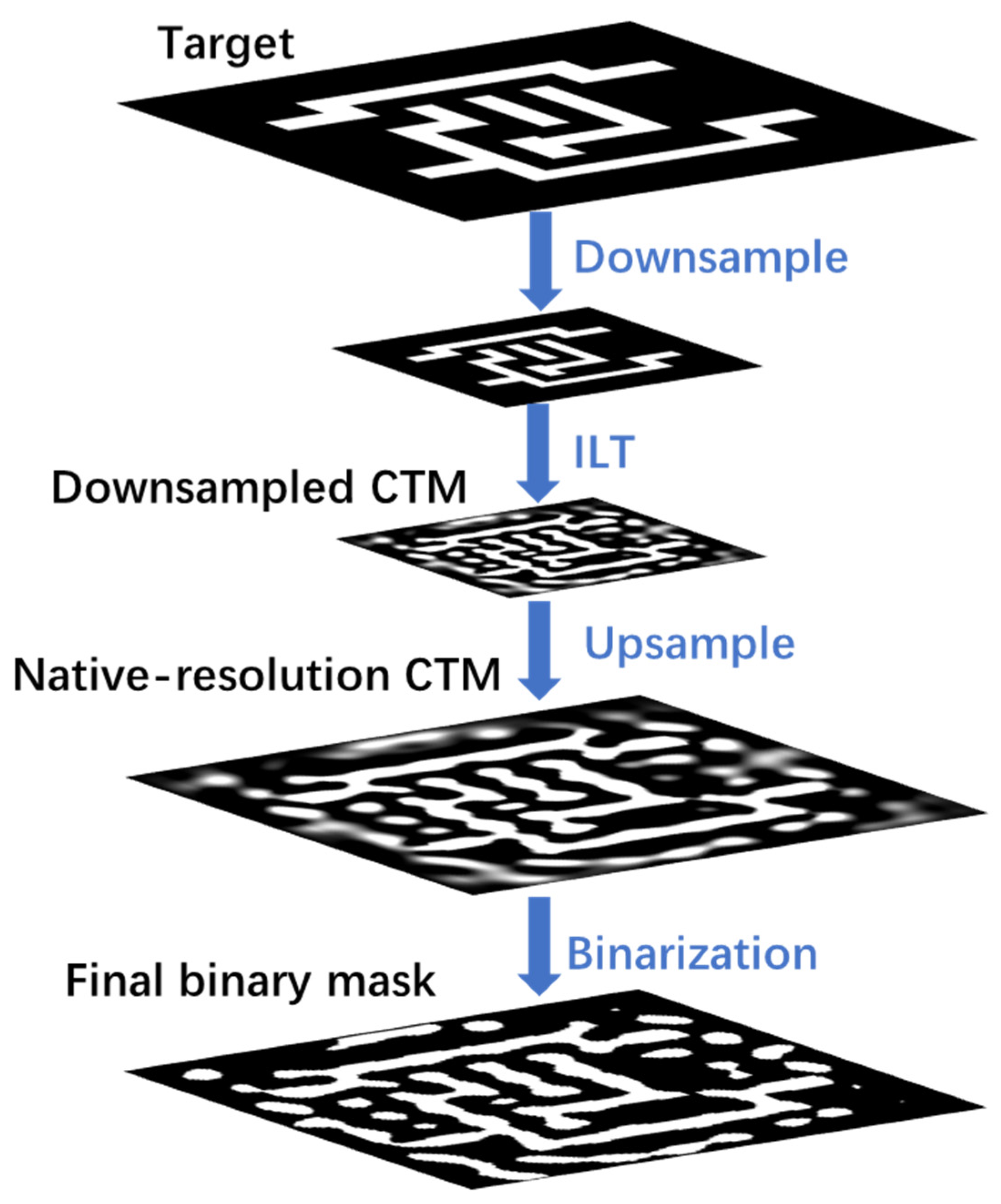
3.1. Inverse Lithography
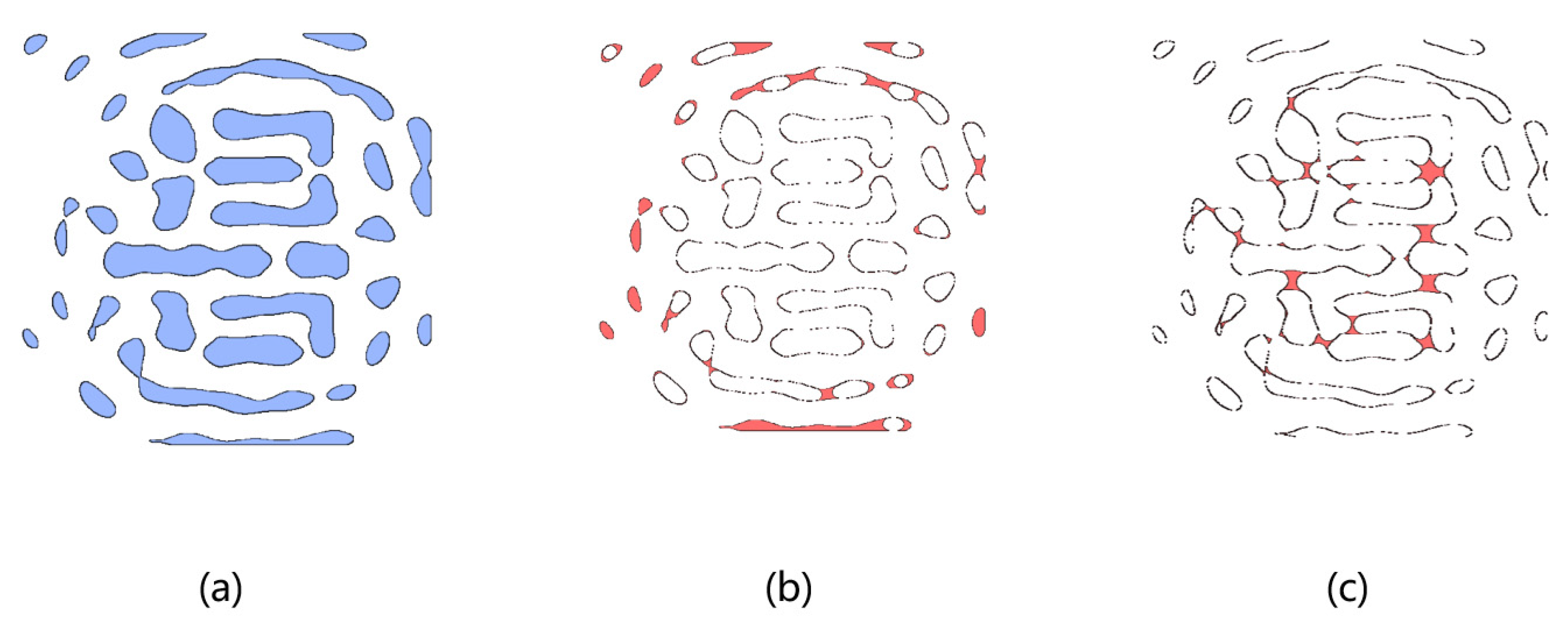
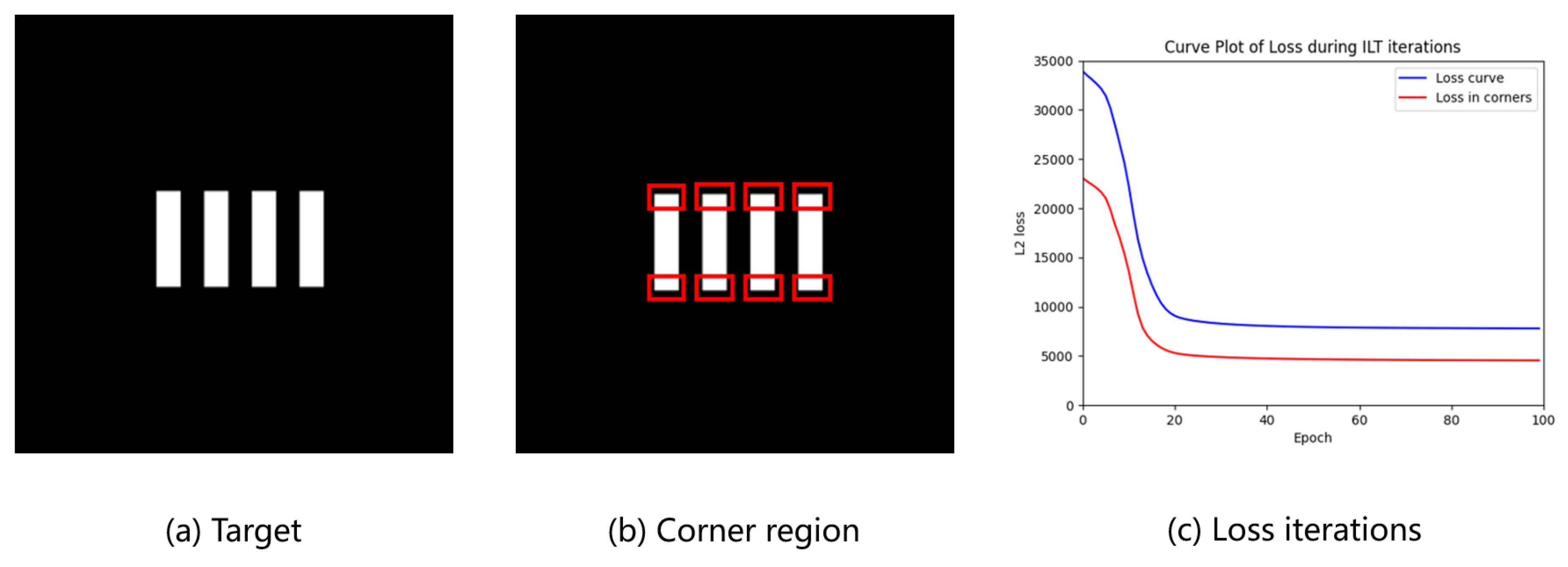
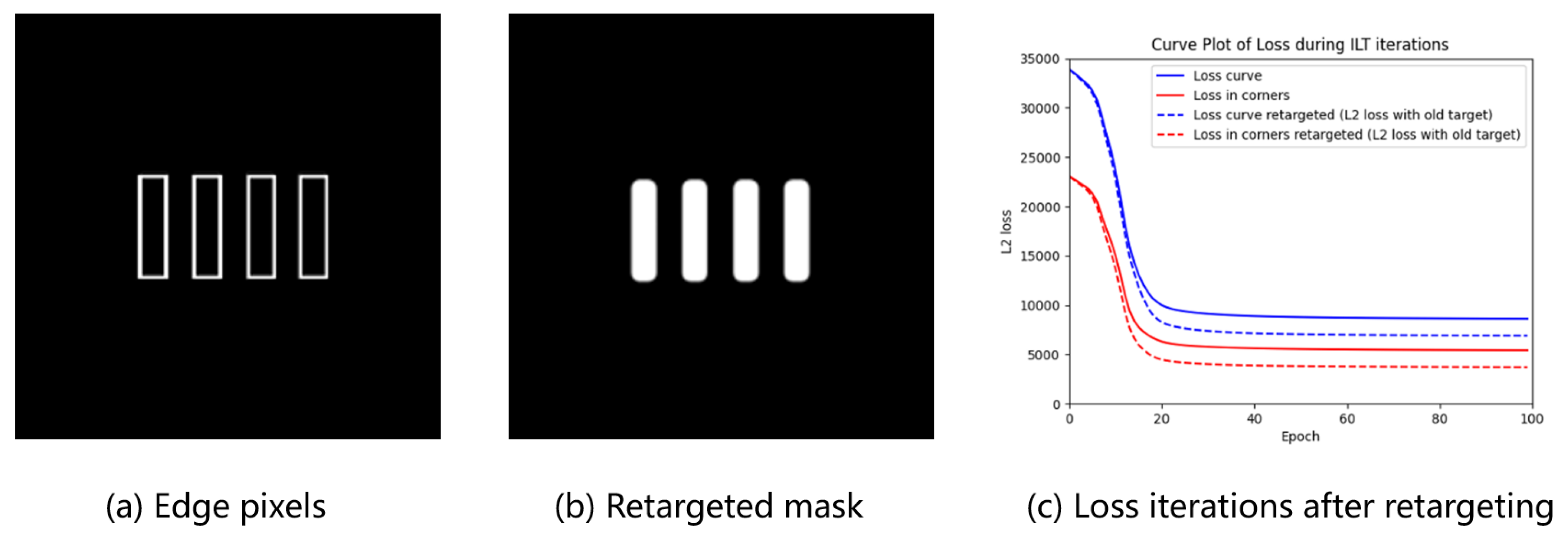
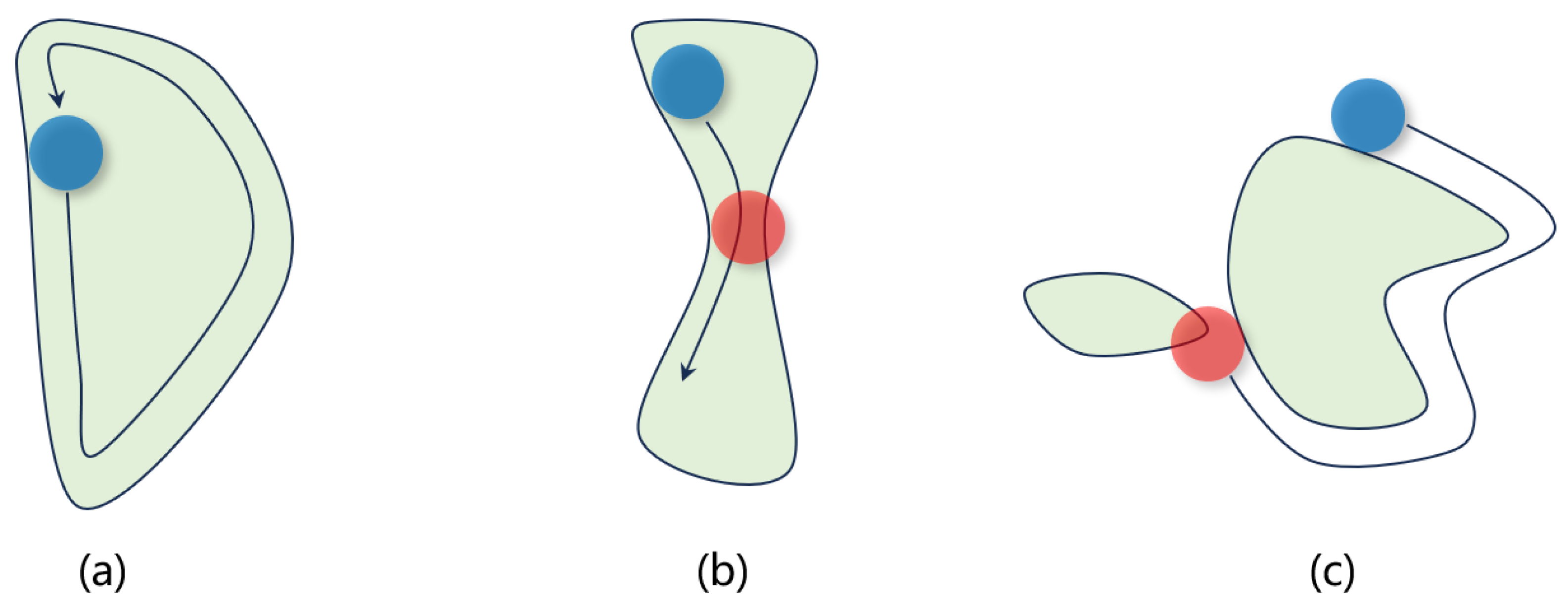
3.2. Corner Rounding
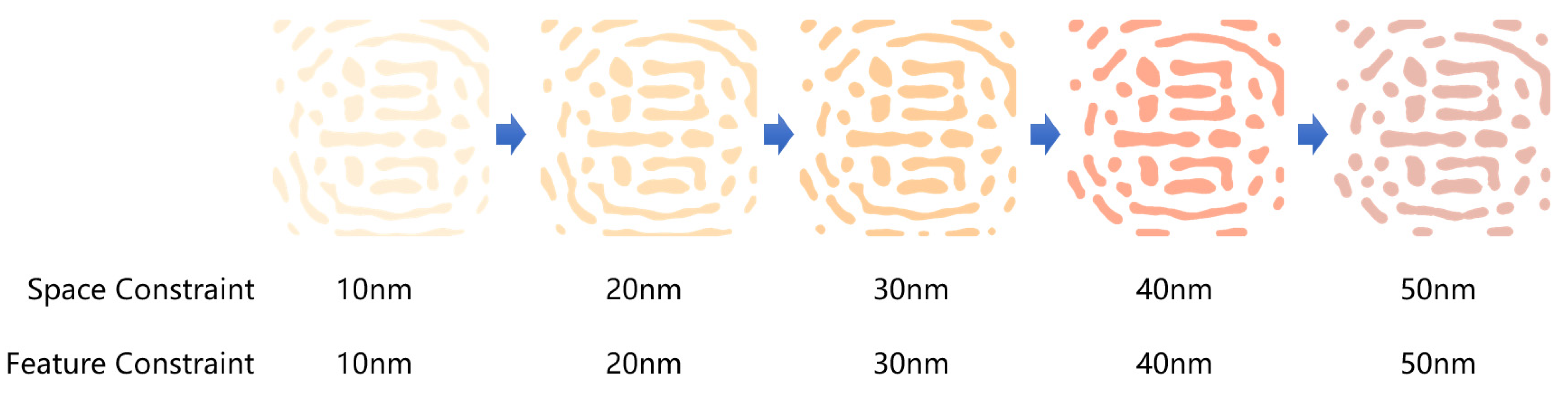
3.3. MRC and Violation Penalty
- Minimum feature size: The smallest allowable dimension of a pattern element;
- Minimum spacing: The smallest permitted distance between adjacent features;
- Minimum feature area: The smallest area allowed for a single feature.
| Algorithm 1: Differentiable morphological operation |
|
| Algorithm 2: Differentiable manufacturability penalty |
|
4. Experiments and Results
- MSE: Represents the L2 loss as defined in Equation (3);
- PVB (Process Variation Bandwidth): Characterizes manufacturing process robustness by calculating the maximum contour separation area between the outermost contour and the innermost contour under various process conditions;
- EPE: Measures the critical dimension at predefined edge test positions. If it exceeds a specified threshold, it is counted as an error;
- For manufacturability, two metrics are employed: FVP (Feature Violation Penalty) and SVP (Space Violation Penalty), corresponding to the space constraint penalty and feature constraint penalty described in Algorithm 2.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molesky, S.; Lin, Z.; Piggott, A.Y.; Jin, W.; Vucković, J.; Rodriguez, A.W. Inverse Design in Nanophotonics. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, W.; Chrostowski, L. Silicon Photonics Circuit Design: Methods, Tools and Challenges. Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1700237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Lei, H.; Wang, P. A Deep Learning Approach for Inverse Design of Gradient Mechanical Metamaterials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 240, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granchi, N.; Intonti, F.; Florescu, M.; García, P.D.; Gurioli, M.; Arregui, G. Q-Factor Optimization of Modes in Ordered and Disordered Photonic Systems Using Non-Hermitian Perturbation Theory. ACS Photonics 2023, 10, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Mao, X.; Ding, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Inverse-Designed Polarization-Insensitive Metasurface Holography Fabricated by Nanoimprint Lithography. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, C.A. Thirty Years of Lithography Simulation. In Proceedings of the Optical Microlithography XVIII, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 February–4 March 2005; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5754, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.C. Burn Jeng Lin A Study of Projected Optical Images for Typical IC Mask Patterns Illuminated by Partially Coherent Light. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1983, 30, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, O.W.; Henderson, R.C. Integrating Proximity Effect Corrections with Photomask Data Preparation. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1995 Symposium on Microlithography, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 19–24 February 1995; Brunner, T.A., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1995; pp. 184–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Arce, G.R. Computational Lithography; Wiley series in pure and applied optics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-470-59697-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stirniman, J.P.; Rieger, M.L. Fast Proximity Correction with Zone Sampling. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1994 Symposium on Microlithography, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 February–4 March 1994; Brunner, T.A., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1994; pp. 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.B.; Zakhor, A.; Miloslavsky, E.A. Mathematical and CAD Framework for Proximity Correction. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1996 International Symposium on Microlithography, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 10–15 March 1996; Fuller, G.E., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1996; pp. 208–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, L. Mask Optimization Approaches in Optical Lithography Based on a Vector Imaging Model. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2012, 29, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L. Fast Lithography Aerial Image Calculation Method Based on Machine Learning. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaret, A.; Tritchkov, A.; Entradas, J.; Yesilada, E. Inverse Lithography Technique for Advanced CMOS Nodes. In Proceedings of the SPIE Advanced Lithography, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–28 February 2013; Conley, W., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; p. 86830E. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L. Inverse Lithography Technology: 30 Years from Concept to Practical, Full-Chip Reality. J. Micro/Nanopatterning Mater. Metrol. 2021, 20, 030901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granik, Y. Fast Pixel-Based Mask Optimization for Inverse Lithography. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2006, 5, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-C.; Yu, P. Impacts of Cost Functions on Inverse Lithography Patterning. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Zhang, J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z. An Analytic Gradient-Based Inverse Lithography Approach for Partially-Coherent Double-Exposure Lithography. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2010, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Lam, E.Y. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Robust Inverse Photomask Synthesis in Optical Lithography. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 4173–4176. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Arce, G.R. Pixel-Based OPC Optimization Based on Conjugate Gradients. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scranton, G.; Bhargava, S.; Ganapati, V.; Yablonovitch, E. Single Spherical Mirror Optic for Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography Enabled by Inverse Lithography Technology. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 25027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Yang, C. Pixelated Source Optimization for Optical Lithography via Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2016, 15, 013506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Sheng, N.; Li, E.; Sun, Y. Multi-Objective Defocus Robust Source and Mask Optimization Using Sensitive Penalty. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wu, J.-S.; Yu, P. Inverse Reticle Optimization with Quantum Annealing and Hybrid Solvers. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 33069–33078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S. Bandwidth-Aware Fast Inverse Lithography Technology Using Nesterov Accelerated Gradient. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 42639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonawala, A.; Milanfar, P. Mask Design for Optical Microlithography—An Inverse Imaging Problem. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, H.; Jin, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Frequency-Decoupled Dual-Stage Inverse Lithography Optimization via Hierarchical Sampling and Morphological Enhancement. Micromachines 2025, 16, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Li, Z.; Nassif, S.R. ICCAD-2013 CAD Contest in Mask Optimization and Benchmark Suite. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Poonawala, A.; Milanfar, P. A Pixel-Based Regularization Approach to Inverse Lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 2837–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Lam, E.Y. Pixelated Source Mask Optimization for Process Robustness in Optical Lithography. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X. Resolution Enhancement Optimization Methods in Optical Lithography with Improved Manufacturability. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2011, 10, 023009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chu, C. Line Search-Based Inverse Lithography Technique for Mask Design. VLSI Des. 2012, 2012, 589128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-R.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Pan, D.Z. MOSAIC. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, B.; Young, E.F.Y. Neural-ILT. In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 July 2022; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 967–972. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Efficient Optical Proximity Correction Based on Virtual Edge and Mask Pixelation with Two-Phase Sampling. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 17440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, D.; Zeng, F.; Du, Y.; Xie, L.; Shen, Y.; Chen, H. Inverse Lithography with Adaptive Mask Complexity. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of Science and Technology for Integrated Circuits (CSTIC), Shanghai, China, 17–18 March 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Shi, Z.; Yan, X.; Geng, Z. SVM Based Layout Retargeting for Fast and Regularized Inverse Lithography. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. C 2014, 15, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ren, H. GPU-Accelerated Inverse Lithography Towards High Quality Curvy Mask Generation. In Proceedings of the ISPD’25: International Symposium on Physical Design, Austin, TX, USA, 16–19 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks, C.L.L.; van Vliet, L.J. Basic Morphological Operations, Band-Limited Images and Sampling. In Scale Space Methods in Computer Vision, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, Isle of Skye, UK, 10–12 June 2003; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Griffin, L.D., Lillholm, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, W.; Yamasaki, K.; Narukawa, S.; Hayashi, N. Mask Rule Check for Inspection of Leading-Edge Photomask. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photomask Technology, Monterey, CA, USA, 3–7 October 2005; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5992, p. 59924E. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Endo, M.; Inoue, T.; Hagiwara, R.; Yasaka, A. Mask Rule Check Using Priority Information of Mask Patterns. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photomask Technology, Monterey, CA, USA, 17–21 September 2007; Naber, R.J., Kawahira, H., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; p. 67304F. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, R.; Woods, R. Digital Image Processing, 4th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-13-335672-4. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, M.L.; Delp, E.J. Morphological Operations. In The Colour Image Processing Handbook; Sangwine, S.J., Horne, R.E.N., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 210–227. ISBN 978-1-4615-5779-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Yu, B. A GPU-Enabled Level Set Method for Mask Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.-R.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Pan, D.Z. MOSAIC: Mask Optimizing Solution with Process Window Aware Inverse Correction. In Proceedings of the 2014 51st ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Yang, F.; Yu, B.; Shang, L.; Zeng, X. Efficient ILT via Multi-Level Lithography Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2023 60th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
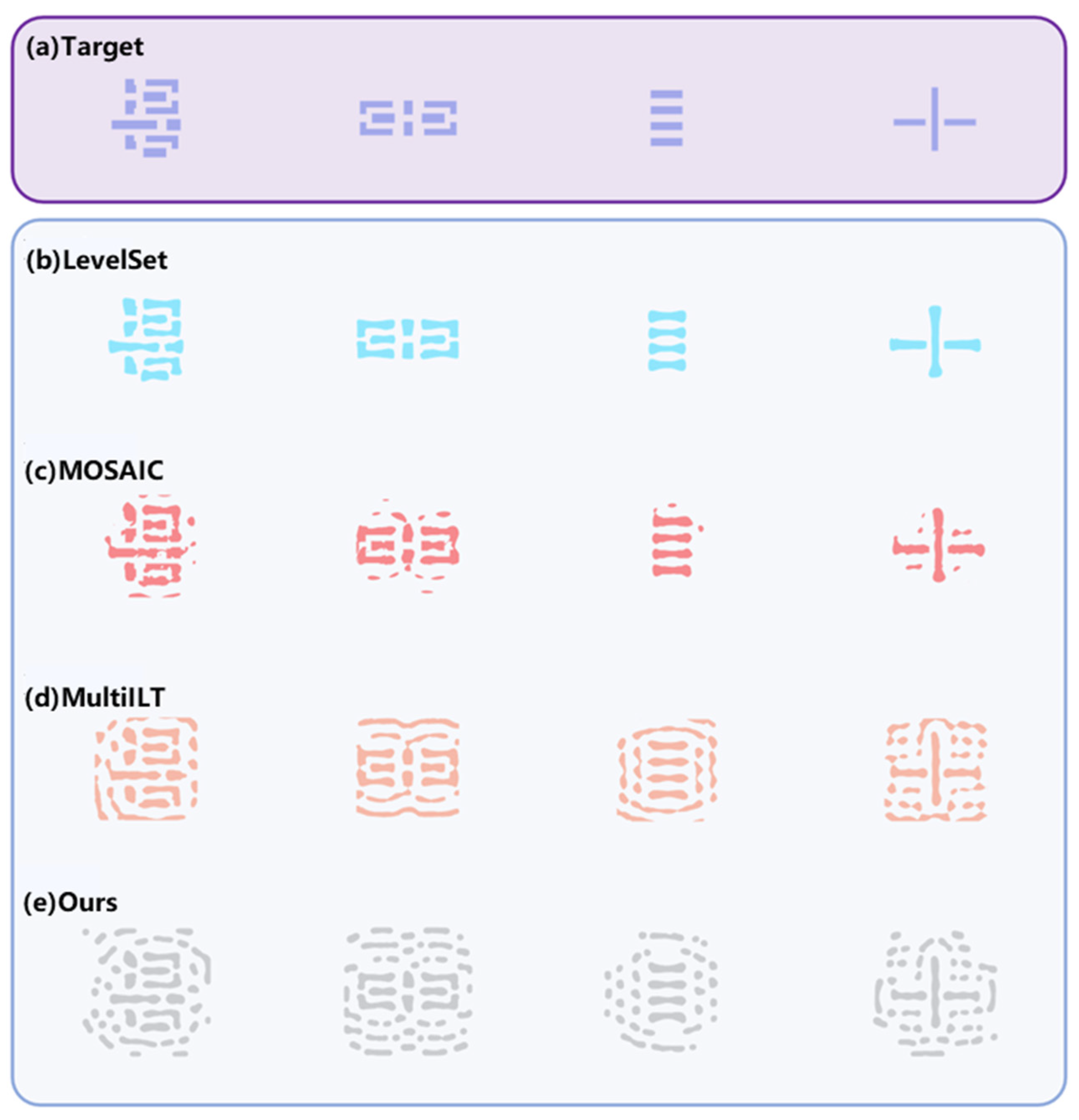
| Case | LevelSet | MOSAIC | MultiILT | Ours | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | PV | EPE | MSE | PV | EPE | MSE | PV | EPE | FVP | SVP | MSE | PV | EPE | FVP | SVP | |
| 1 | 45,520 | 57,468 | 6 | 48,896 | 55,028 | 8 | 39,533 | 44,887 | 3 | 2282 | 23 | 39,984 | 44,380 | 3 | 440 | 20 |
| 2 | 33,571 | 49,680 | 1 | 37,327 | 46,019 | 4 | 32,516 | 37,374 | 0 | 1102 | 50 | 29,962 | 36,806 | 0 | 110 | 31 |
| 3 | 78,695 | 90,748 | 39 | 81,327 | 86,685 | 47 | 65,315 | 75,011 | 23 | 4648 | 65 | 62,374 | 72,197 | 15 | 120 | 20 |
| 4 | 18,040 | 27,710 | 2 | 16,409 | 26,358 | 2 | 9099 | 21,484 | 0 | 3899 | 905 | 8648 | 22,746 | 0 | 99 | 25 |
| 5 | 38,226 | 59,035 | 2 | 37,810 | 57,472 | 0 | 30,015 | 48,696 | 0 | 2321 | 716 | 28,908 | 47,368 | 0 | 284 | 14 |
| 6 | 35,962 | 54,163 | 0 | 36,706 | 52,566 | 0 | 33,400 | 42,788 | 0 | 5917 | 351 | 29,844 | 42,230 | 0 | 71 | 26 |
| 7 | 30,542 | 48,173 | 2 | 29,520 | 47,598 | 2 | 17,419 | 36,241 | 0 | 3418 | 573 | 14,098 | 36,414 | 0 | 56 | 19 |
| 8 | 14,252 | 25,043 | 1 | 14,291 | 24,268 | 1 | 11,552 | 18,987 | 0 | 4922 | 1083 | 10,292 | 19,631 | 0 | 70 | 28 |
| 9 | 43,390 | 68,229 | 1 | 47,367 | 64,932 | 2 | 37,219 | 54,792 | 0 | 2777 | 707 | 34,435 | 54,336 | 0 | 69 | 16 |
| 10 | 8919 | 20,878 | 0 | 8950 | 19,871 | 0 | 7180 | 14,979 | 0 | 5270 | 382 | 7193 | 15,796 | 0 | 33 | 19 |
| Avg | 34,712 | 50,113 | 5.4 | 35,860 | 35,860 | 6.6 | 28,325 | 39,524 | 2.6 | 3656 | 486 | 26,574 | 39,190 | 1.8 | 135 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Gong, J.; Jin, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. A Hierarchical Inverse Lithography Method Considering the Optimization and Manufacturability Limit by Gradient Descent. Micromachines 2025, 16, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070798
Sun H, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Gong J, Jin C, Zhou J, Liu J. A Hierarchical Inverse Lithography Method Considering the Optimization and Manufacturability Limit by Gradient Descent. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070798
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haifeng, Qingyan Zhang, Jie Zhou, Jianwen Gong, Chuan Jin, Ji Zhou, and Junbo Liu. 2025. "A Hierarchical Inverse Lithography Method Considering the Optimization and Manufacturability Limit by Gradient Descent" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070798
APA StyleSun, H., Zhang, Q., Zhou, J., Gong, J., Jin, C., Zhou, J., & Liu, J. (2025). A Hierarchical Inverse Lithography Method Considering the Optimization and Manufacturability Limit by Gradient Descent. Micromachines, 16(7), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070798






