Z-Shaped Electrothermal Microgripper Based on Novel Asymmetric Actuator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
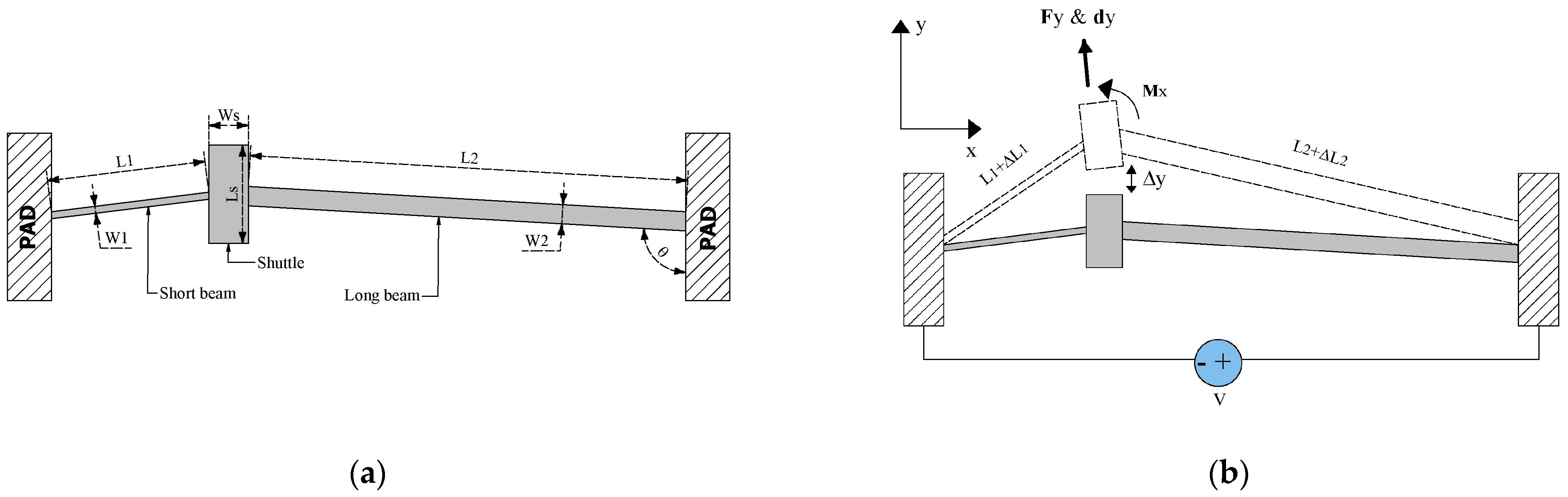
2.1. Design Concept and Simulation
2.2. Modelling of the Asymmetric Actuator
2.2.1. Displacement of the V-Shaped Actuator
2.2.2. Displacement of the Asymmetric Actuator
2.2.3. Force of V-Shaped Actuator
2.2.4. Force of Asymmetric Actuator
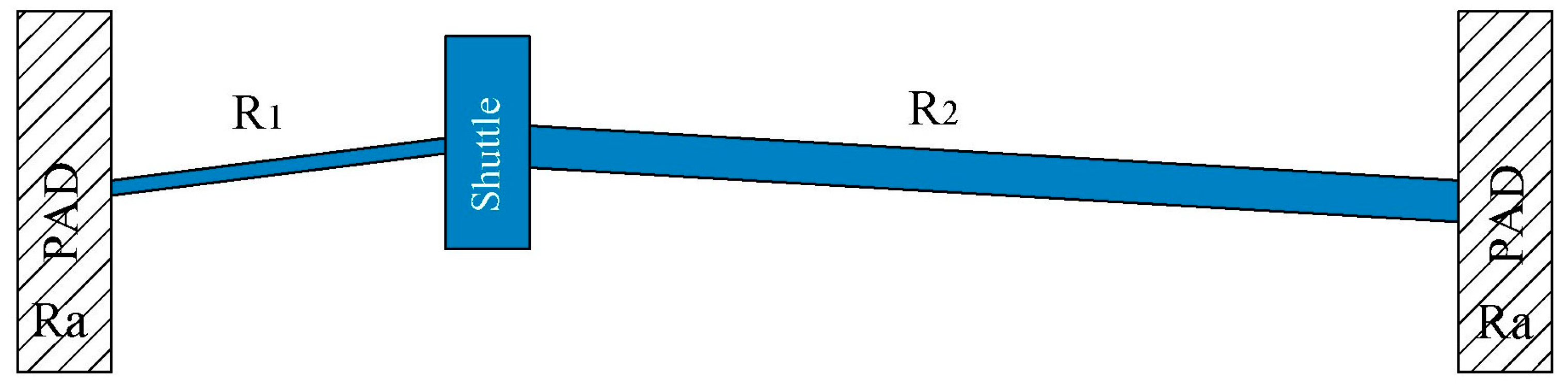
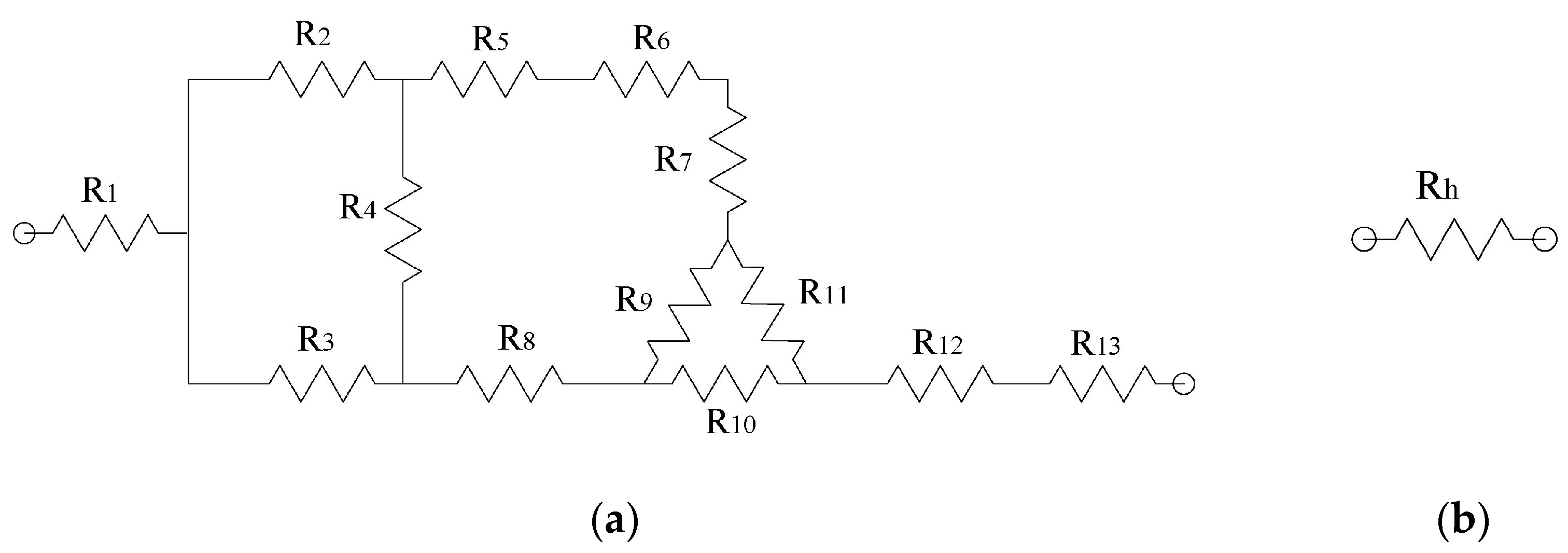
2.2.5. Electric Modelling of the Asymmetrical Microactuator
2.3. Electrical Modeling of Microgripper
3. Results
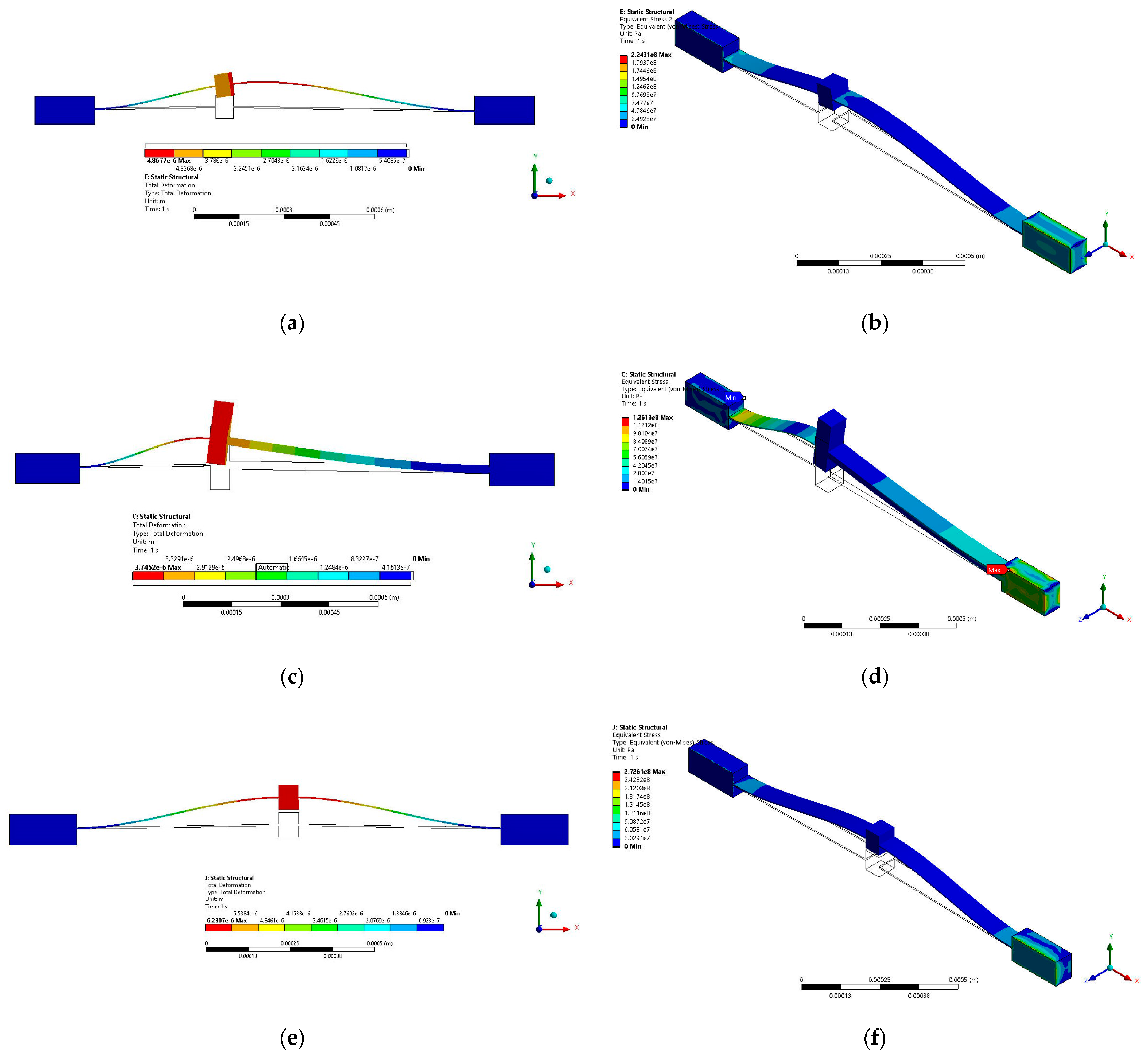
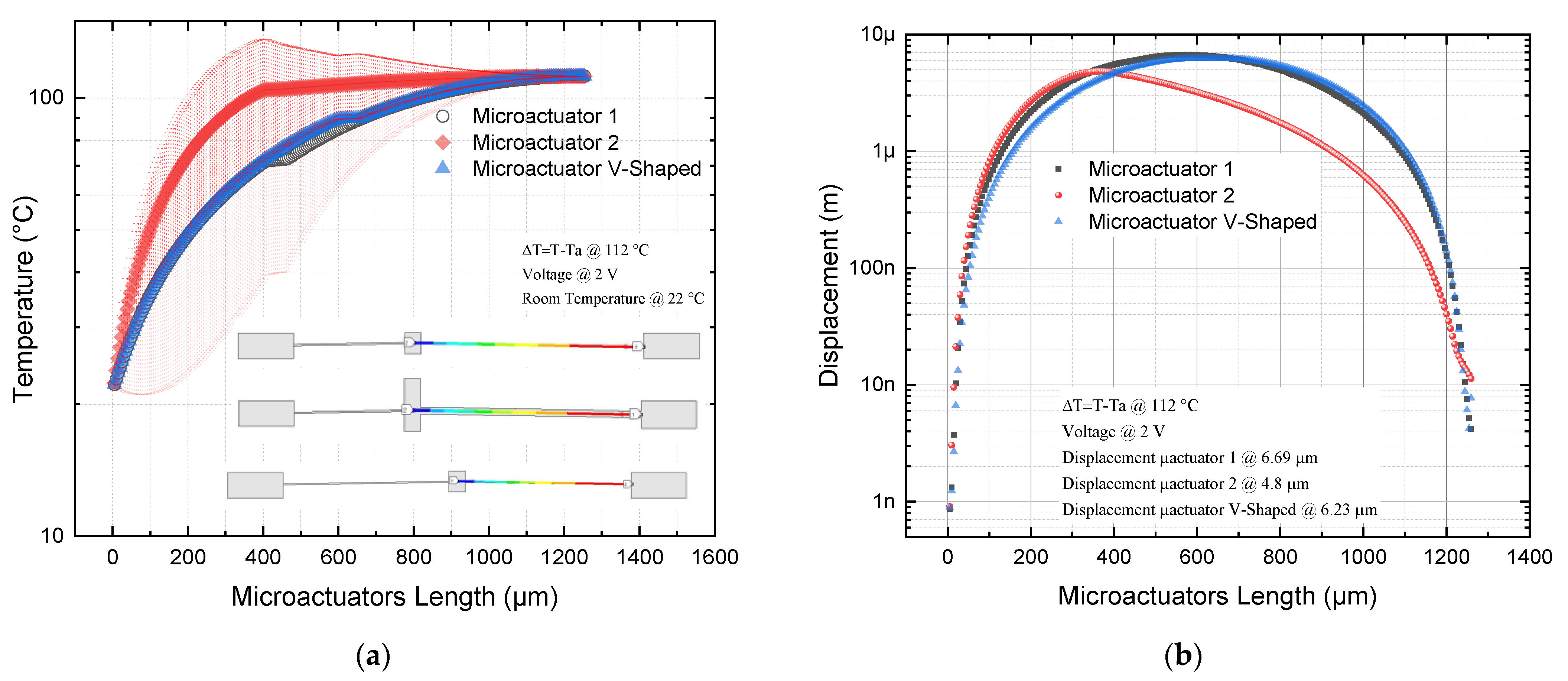
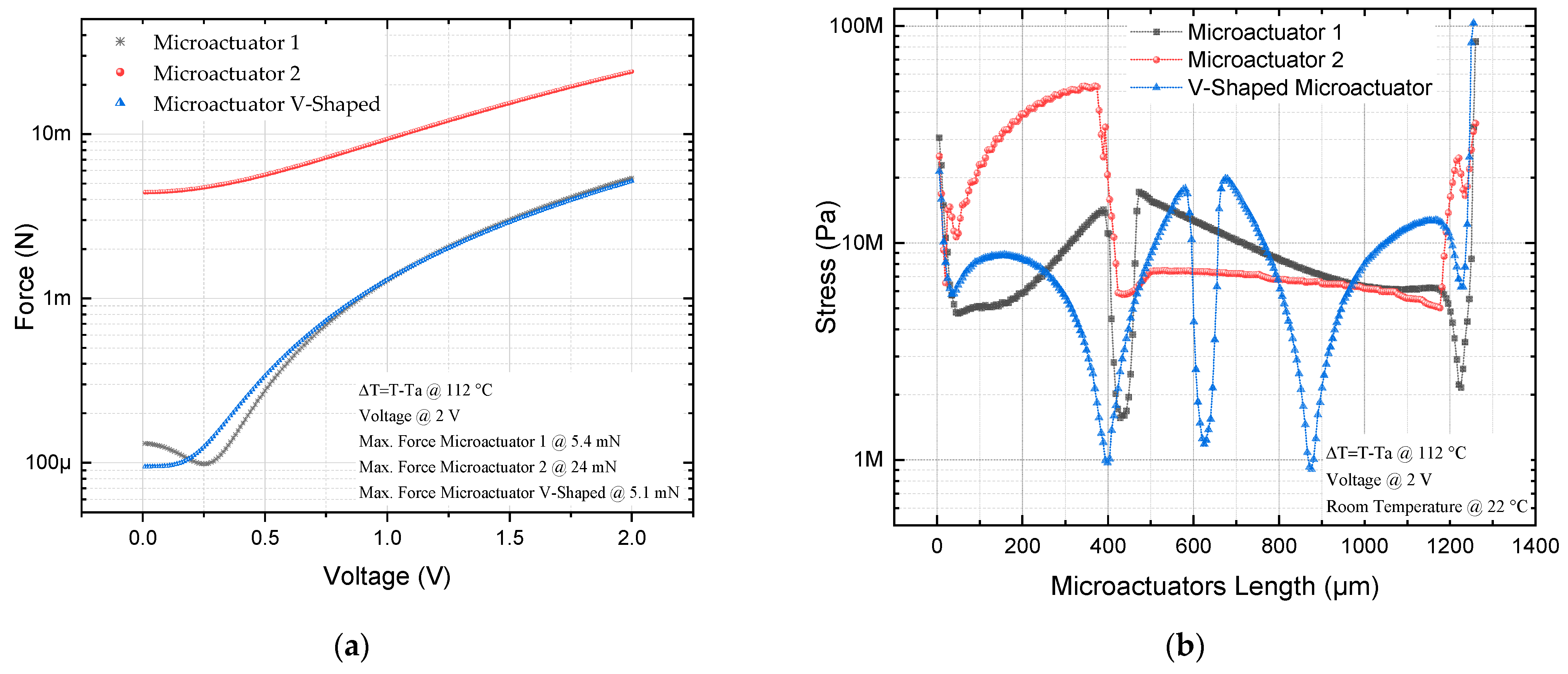
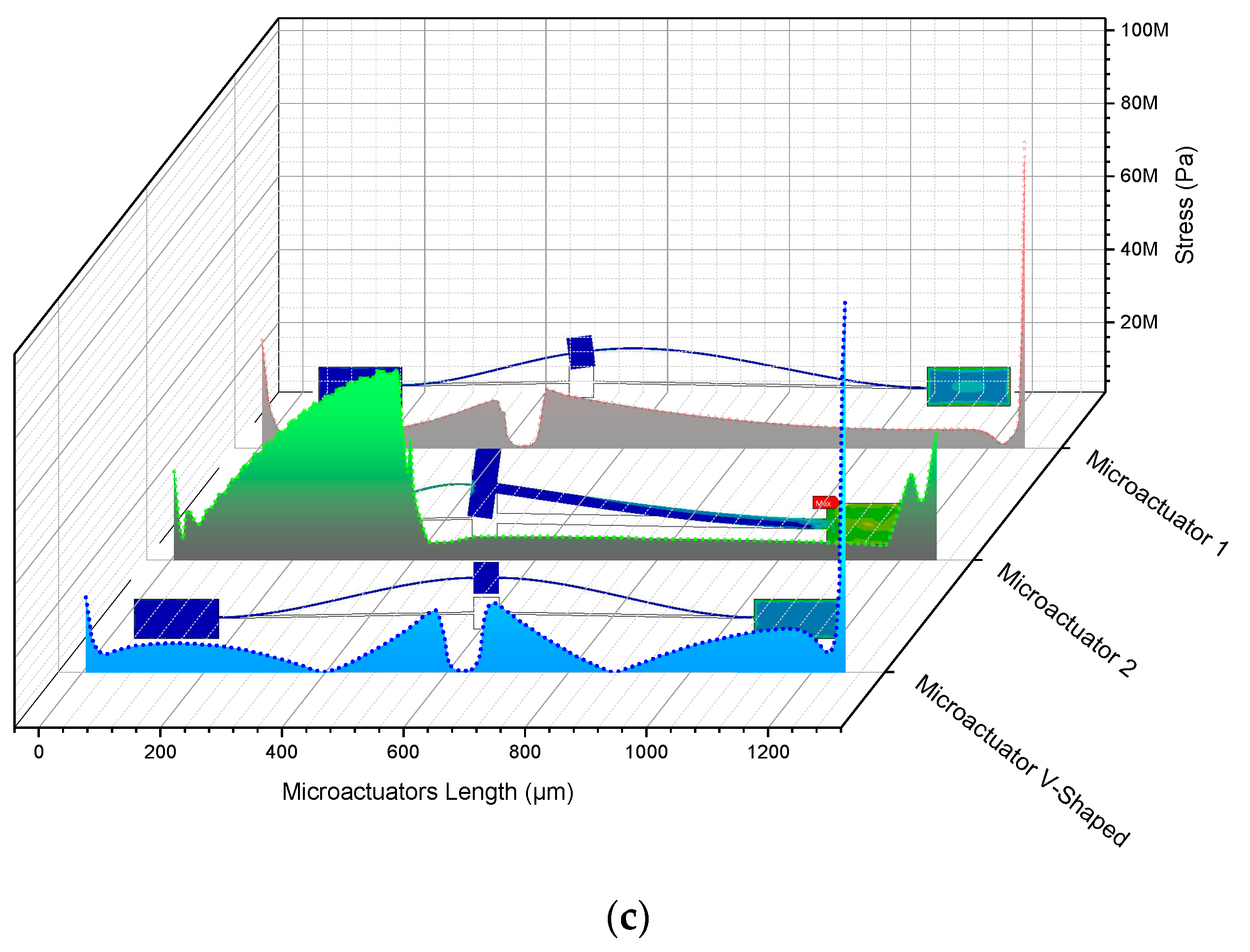
3.1. Multiphysics FEM Model of Asymmetric Microactuator
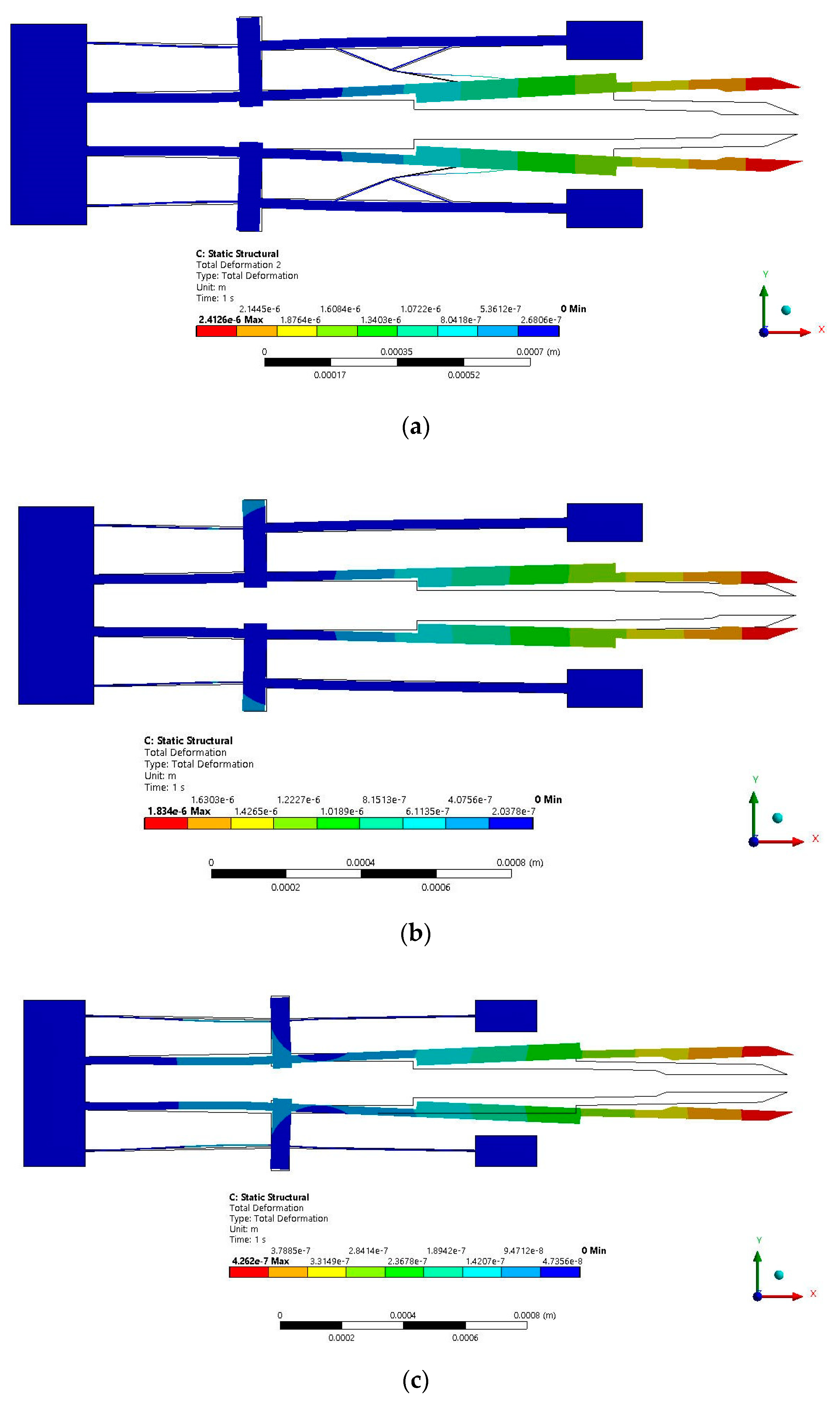
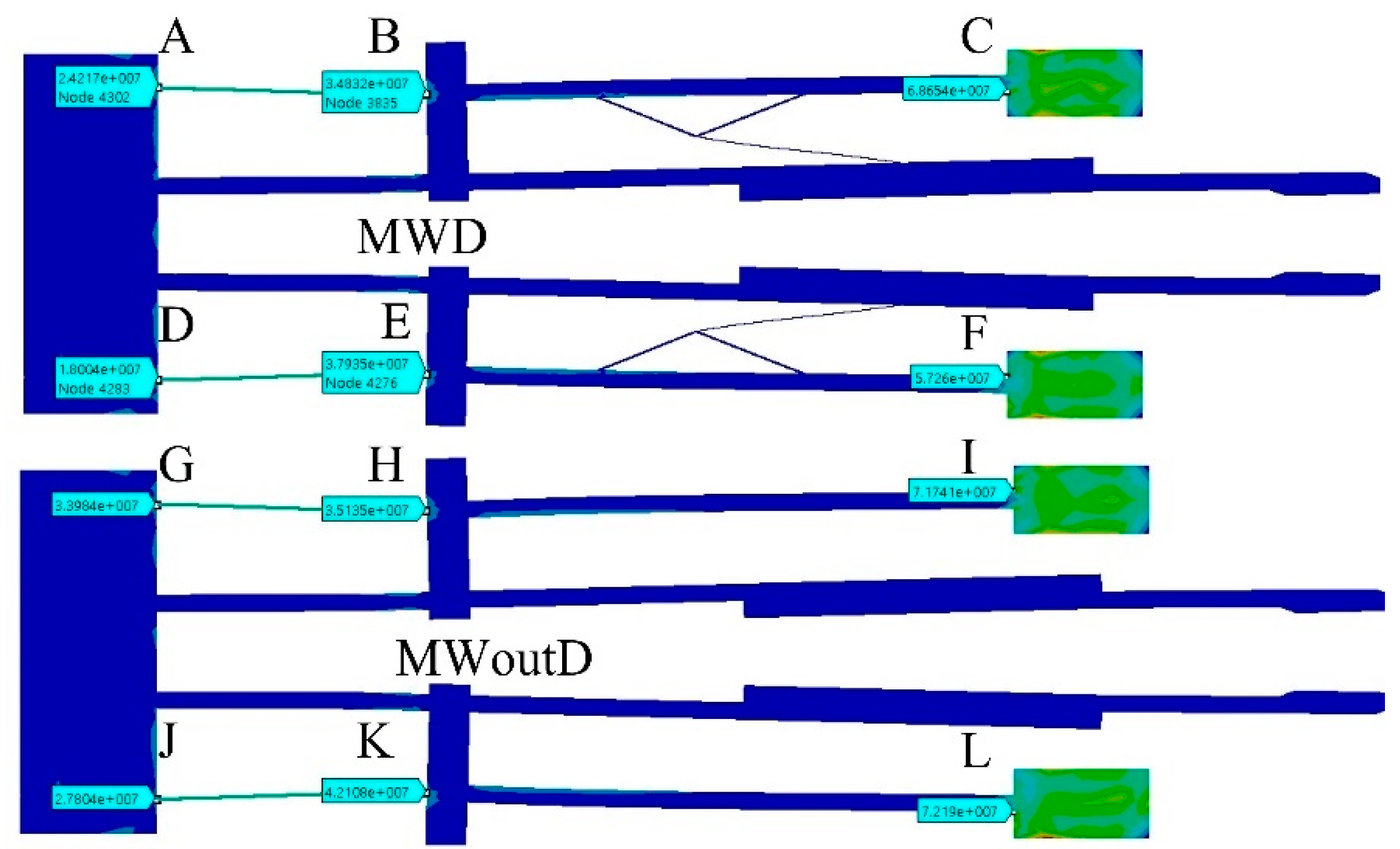
3.2. Multiphysics FEM Model of Microgripper
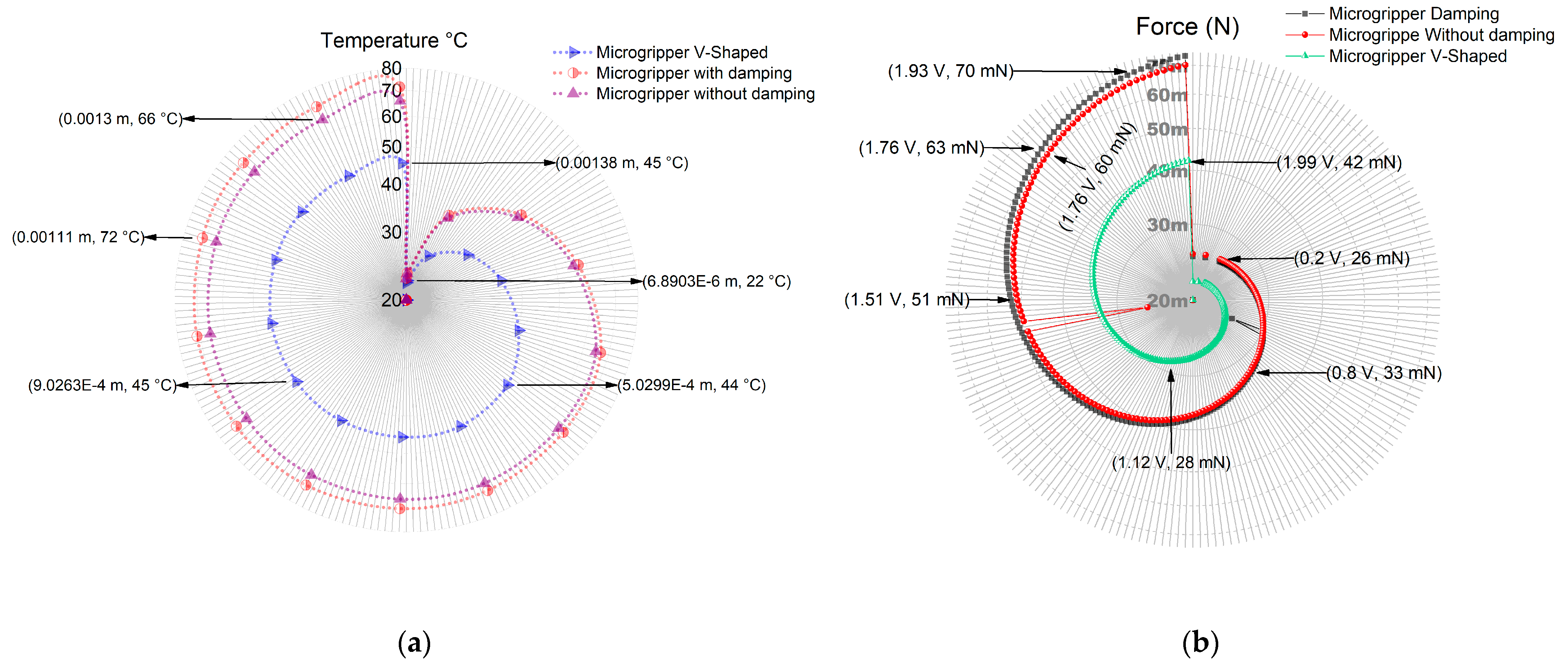
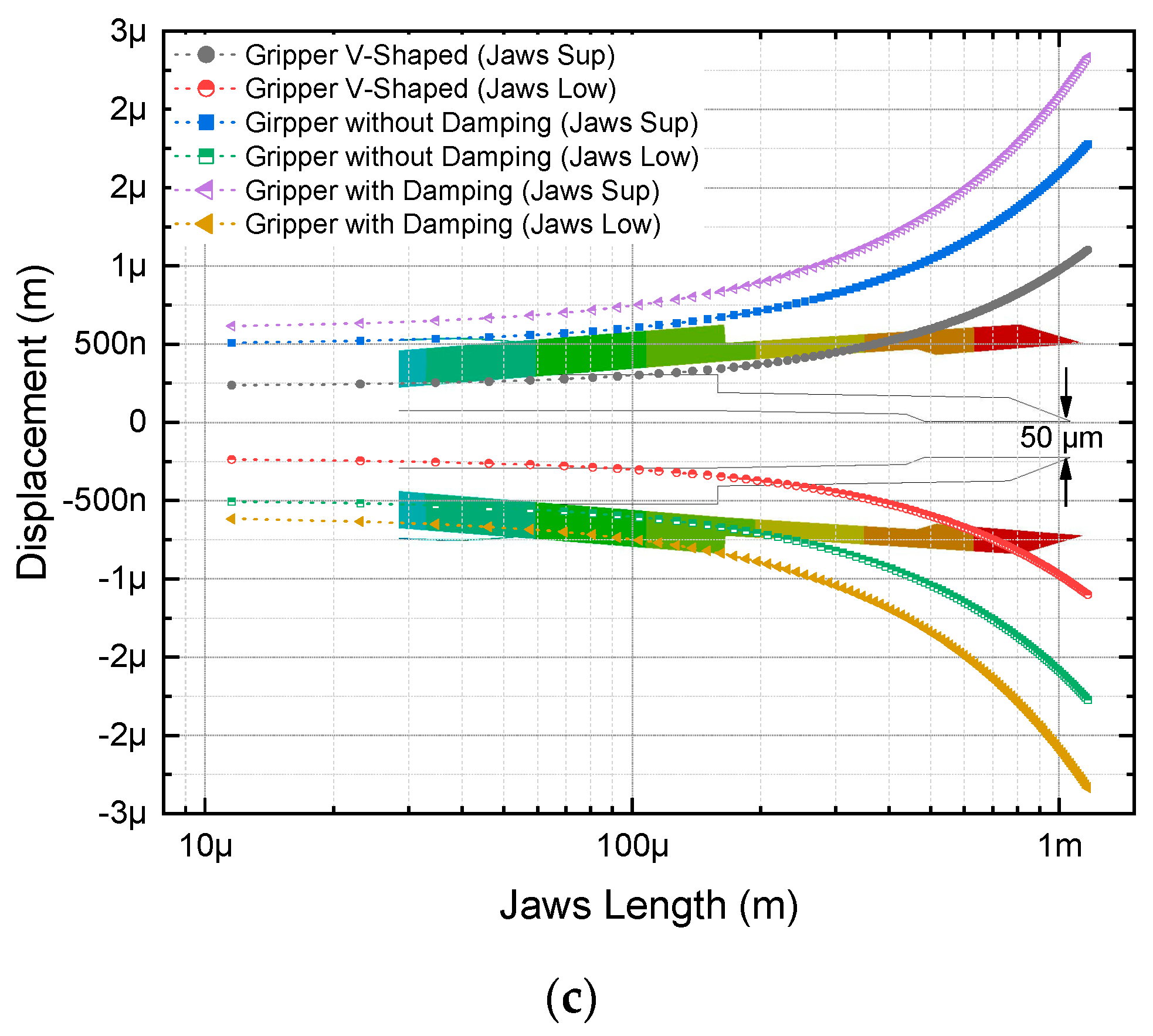
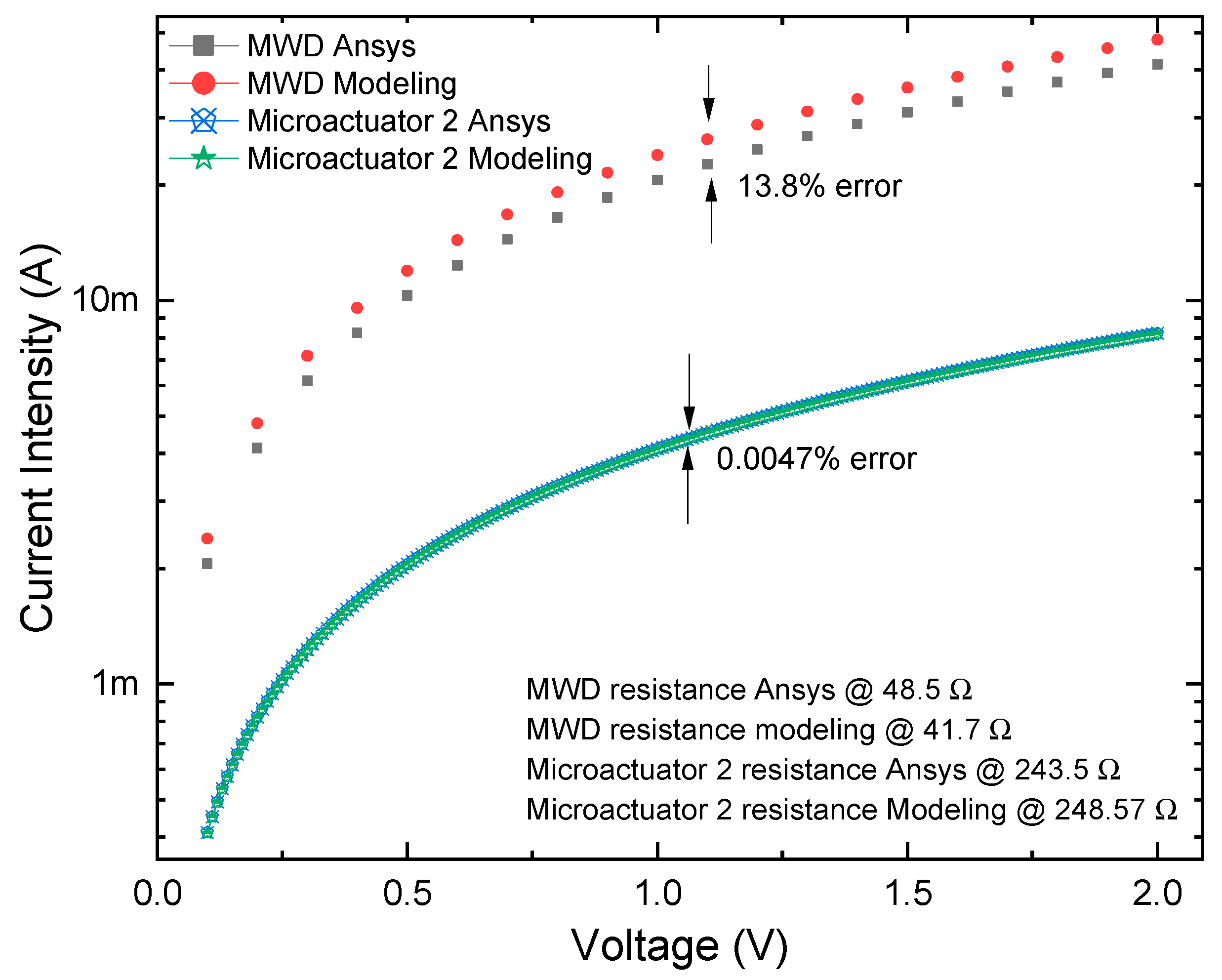
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pistorio, F.; Saleem, M.M.; Somà, A. A dual-mass resonant MEMS gyroscope design with electrostatic tuning for frequency mismatch compensation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasras, M.; Elfadel, I.A.; Ngo, H.D. Editorial for the special issue on MEMS accelerometers. Micromachines 2019, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. Vibration modes and parameter analysis of V-shaped electrothermal microactuators. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 1080652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-C.; Li, Y.; Ding, B.-X.; Xu, H.-Y. An investigation on kinematics and dynamics performance of a novel 3-PRC-compliant parallel micromanipulator. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 168781401878980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, X. The designing of magnetic-driven micromirror for portable ftirs. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 1460582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaali, H.; Najar, F.; Choura, S. Dynamic Study of a capacitive MEMS switch with double clamped-clamped Microbeams. Shock Vib. 2014, 2014, 807489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Nabi, M.; Rahman, N. Finite element compatible matrix interpolation for parametric model order reduction of electrothermal microgripper. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2021, 8, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, H.; Ghayesh, M.H.; Hussain, S. Large-amplitude dynamical behaviour of microcantilevers. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 106, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Khan, S.; Lehana, P. Analytic model of Microcantilevers as low frequency generator. Modell. Simul. Eng. 2014, 2014, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Díez, V.; Hernando-García, J.; Toledo, J.; Ababneh, A.; Seidel, H.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Piezoelectric MEMS linear motor for nanopositioning applications. Actuators 2021, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramdas, R.; Pratap, R. Scaling and performance analysis of MEMS Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters. J Microelectromech Syst 2017, 26, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, H.; Stifter, M.; Hortschitz, W.; Keplinger, F. Planar magnetostrictive micromechanical actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 4700104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Miao, J.; Lye, S.W.; Hu, X. Sandwich-structured two-dimensional MEMS electret power generator for low-level ambient vibrational energy harvesting. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2015, 228, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Suzuki, Y. A design method of in-plane MEMS Electret Energy Harvester with comb drives. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 557, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Ling, Z.; Yu, W.; Shi, J. A review of MEMS scale Piezoelectric Energy Harvester. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bußmann, A.; Leistner, H.; Zhou, D.; Wackerle, M.; Congar, Y.; Richter, M.; Hubbuch, J. Piezoelectric silicon micropump for drug delivery applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacci, J.; Tagliapietra, G. Getting Ready for Beyond-5G, Super-IoT and 6G at Hardware Passive Components Level—A Multi-State RF-MEMS Monolithic Step Attenuator Analyzed up to 60 GHz. Springer Link 2022, 28, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Yadav, R.; Nehra, V.; Rangara, K.J. RF MEMS Switches: Fabrication, Key Features, Application & Design Tools. Int. J. Electron. Eng. 2011, 3, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Comtois, J.H.; Bright, V.M. Applications for surface-micromachined polysilicon thermal actuators and arrays. Sens. Actuators 1997, 58, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varona, J.; Tecpoyotl-Torres, M.; Velazquez, R. Micro sensor-actuador térmico sin baterias para aplicaciones en microelectrónica de ultra-bajo consumo de potencia. Rev. Mex. De Fis. 2013, 59, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Begbie, M.; Brown, G.; Uttamchandani, D. Design, simulation and characterization of a MEMS Optical Scanner. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, Z.; Johar, M.A. Comparative performance study of smart structure for thermal microactuators. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1931, 020041. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chun, Q.; You, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Dynamic modelling and experimental study of asymmetric optothermal microactuator. Opt. Commun. 2017, 383, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, A.; Rengaswamy, R.; Sukumar, P.K.; Sekar, R. Modelling of chevron electrothermal actuator and its performance analysis. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Pham, P.H. Impact of design parameters on working stability of the electrothermal V-shaped actuator. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 26, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.F.; Zhou, Z.F.; Meng, M.Z.; Li, M.J.; Huang, Q.A. An efficient electro-thermo-mechanical model for the analysis of V-shaped thermal actuator connected with driven structures. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2020, 34, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecpoyotl Torres, M.; Cabello-Ruiz, R.; Vera-Dimas, J.G. Diseño y Simulación de un Microactuador Electrotérmico Optimizado con Brazos en Forma Z. Acta Univ. 2015, 25, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. A comparison model of V- and Z-shaped electrothermal microactuators. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Beijing, China, 2–5 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Closed-form modelling and design analysis of V- and Z-shaped electrothermal microactuators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 27, 015023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enikov, E.T.; Kedar, S.S.; Lazarov, K.V. Analytical model for analysis and design of V-shaped thermal microactuators. J Microelectromech Syst 2005, 14, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhu, Y. An electrothermal microactuator with Z-shaped beams. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 085014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, G. Modeling V-shape thermal in-plane microactuator using chained beam-constraint-model. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–31 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alamin Dow, A.B.; Jazizadeh, B.; Kherani, N.P.; Rangelow, I. Development and modeling of an electrothermally MEMS microactuator with an integrated microgripper. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Kivi, A.; Azizi, S. On the dynamics of a micro-gripper subjected to electrostatic and piezoelectric excitations. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2015, 77, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivhare, P.; Uma, G.; Umapathy, M. Design enhancement of a chevron electrothermally actuated microgripper for improved gripping performance. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 22, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Q. Design of a microelectromechanical systems microgripper with integrated electrothermal actuator and Force Sensor. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 172988141666337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, X. Design, modeling, and characterization of a MEMS electrothermal microgripper. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchi, M.; Grech, I.; Mallia, B.; Mollicone, P.; Portelli, B.; Sammut, N. Essential design and fabrication considerations for the reliable performance of an electrothermal MEMS microgripper. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 28, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.U.; Saleem, M.M.; Khan, U.S.; Hamza, A. Design, closed-form modeling and analysis of su-8 based electrothermal microgripper for biomedical applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 25, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhina, A.; Voicu, R.-C.; Muller, R.; Al-Zandi, M.H.; Wang, C. Design and characterization of a polymer electrothermal microgripper with a polynomial flexure for efficient operation and studies of moisture effect on negative deflection. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 27, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Corigliano, A.; Espinosa, H. A thermal actuator for nanoscale in situ microscopy testing: Design and characterization. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, L.; Wang, X.; Adnan, S. Design of a test structure based on chevron-shaped thermal actuator for in-situ measurement of the fracture strength of MEMS thin films. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2019, 2, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novely, B. Análisis Matricial de estructuras por el método de la rigidez. In Problemas Resueltos e Introducción a los Elementos Finitos; Editor Independiente: Pamplona, Colombia, 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Ref. | Microactuator Type | Structural Material | Number of Pair of Beams | Inclination Angle | Dimensions (µm) | Software for Simulation | Displacement (µm) | Force (µN) | Stiffness (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | V-shaped | Poly-Si | 1 | NA | 600 × 100 × 20 | Ansys™ | NA | NA | NA |
| [12] | Planar magnetostrictive | Ni | 6 | 4° | 4 × 2 × 0.4 | Comsol™ | 10.2 | NA | 5.56 |
| [24] | Chevron thermal | Al | 4 | 10° | 510 × 335 × 10 | Comsol™ | 10.94 | NA | NA |
| [25] | V-shaped | Si | 10 | 2° | ≈1500 × 300 × 30 | Ansys™ | 70 | NA | NA |
| [26] | V-shaped | Poly-Si | 10 | 10° | ≈600 × 400 × 10 | Comsol™ | 0.6 | NA | NA |
| [28] | Z-shaped | Si | 2 | NA | 412 × 60 × 10 | Ansys™ | 0.2107 | NA | NA |
| [30] | V-shaped | Ni | 1 | 0.5° | ≈1.5 × 12 × 21 | Ansys™ | ≈50 | 1000 | NA |
| [31] | Z-shaped | Si | 2 | 10° | ≈176 × 88 × 10 | Ansys™ | 0.750 | 30–40 | NA |
| [32] | V-shaped | Poly-Si | 3 | NA | ≈600 × 4 × 6.95 | Abaqus™ | ≈5 | ≈400 | NA |
| Ref. | Microgripper Type | Microactuator Type | Structural Material | Simulated or Fabricated | Dimensions (µm) | Displacement of Tips (µm) | Initial Gap (µm) | Stress Max (kPa) | Force on Tips (µN) | Stiffness (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | Electrothermal | U-beam | Si | Fabricated | ≈375 × 200 × 60 | ≈11 at 9 V | ≈15 | NA | NA | NA |
| [34] | Electrostatic and piezoelectric | Two fully clamped symmetrically microbeams | Si and PZT | Simulated | ≈600 × 600 × NA | 2 at 18 V | ≈2 | ≈0.156 | NA | NA |
| [35] | Electrothermal | Chevron | Poly-Si | Simulated | ≈1000 × 900 × 10 | 19.2 at 1 V | 100 | 470 | 0–17,000 | NA |
| [36] | Electrothermal | Z-shaped | Poly-Si | Simulated | ≈2680 × 2750 × 50 | 80 at 6 V | 100 | Na | 6575 | 263 × 10−6 |
| [37] | Electrothermal | U-shaped | Poly-Si | Fabricated | ≈280 × 100 × NA | 9.1 at 14 V | 20 | 104 | 36 to 14 V | 4.05 |
| [38] | Electrothermal | U-shaped | Poly-Si | Fabricated | ≈1000 × 210 × 2 | 19.6 at 5 V | 5 | ND | 0.011 | NA |
| [39] | Electrothermal | V-shaped | SU-8 | Simulated | ≈1650 × 800 × 9.85 | 11 at 80 mV | ND | 22 | 231 | NA |
| [40] | Electrothermal | Z-shaped | SU-8 | Fabricated | ≈1300 × 500 × 20 | 80 at 0.4 V | 203.8 | NA | 26.3 | NA |
| Parameters | Silicon Values |
|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 2329 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient, α (C−1) | 2.568 × 10−6 |
| Young’s modulus, E (GPa) | 130.1 |
| Poisson’s ratio, ν | 0.33 |
| Isotropic thermal conductivity, κ (W/m °C) | 148 |
| Isotropic resistivity, (Ω × m) | 0.00015 |
| Average heat transfer coefficient, h (W/m2K) | 25 |
| Ultimate strength, (MPa) | 250 |
| Convection coefficient (W/m2 °C) | 25 |
| Element Description | Dimensions (µm) | Element Description | Dimensions (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of the short and thin beam of the microactuator (L1) | 400 | Gripper length from shaft to damping elements 1 (Lg1) | 631 |
| Length of long and thick beam length of the microactuator (L2 = 2 × L1) | 800 | Gripper length from damping elements to jaw 2 (Lg2) | 770 |
| Width of the short and thin beam of the microactuator (w1) | 5 | Width of the base beam of gripper 1 (wg1) | 25 |
| Width of long and thick beam length of the microactuator (w2) | 25 | Width of the Z section of gripper 2 (wg2) | 50 |
| Length of shuttle (Ls) | 192.5 | Width of the base of jaw 3 (wg3) | 25 |
| Width of shuttle (Ws) | 60 | Thickness of the structure (t) | 70 |
| Length of damping beam 1 (L3) | 154.5 | Gap (initial aperture between jaws) | 50 |
| Length of damping beam 2 (L4) | 301 | Pre-bending angle of the microactuator beams (θ) | 91° |
| Length of damping beam 3 (L5) | 170.5 | Pre-bending angle of the damping beam 2 (θ2) | 22° |
| Width of upper gap between gripper arms (w3) | 78.5 | Pre-bending angle of the damping beam 3 (θ3) | 31° |
| Width of damping beams (w4) | 9.5 | Pre-bending angle between the beam base of the gripper and the pad (θ4) | 80° |
| Resistance | Length (µm) | Width (µm) | Resistance | Length (µm) | Width (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 200 | 263.72 | R8 | 192 | 25 |
| R2 | 400 | 25 | R9 | 154.6 | 3.5 |
| R3 | 400 | 5 | R10 | 293.56 | 25 |
| R4 | 232.5 | 60 | R11 | 170.44 | 3.57 |
| R5 | 400 | 25 | R12 | 300 | 25 |
| R6 | 240.92 | 50 | R13 | 200 | 100 |
| R7 | 300.7 | 1.75 |
| Device | Solver Target | Element Type/Mesh/Number of DOF | Face Sizing with Element Size | Inflation | Convergence | Total Mass (kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Ratio | Max. Layers | Growth Rate | No. of Total Nodes | No. of Total Elements | |||||
| Microactuator 1 | Mechanical APDL | SOLID 187/refinement controlled program | Default | 0.272 | 5 | 1.2 | 3941 | 1749 | 0.7776 × 10−8 |
| Microactuator 2 | 3003 | 1324 | 1.176 × 10−8 | ||||||
| V-shaped microactuator | 26,237 | 12507 | 7.77 × 10−9 | ||||||
| Device | Displacement @ 2 V (µm) | Force at 2 V (mN) | Stiffness (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microactuator 1 | 6.69 | 5.4 | 807.17 |
| Microactuator 2 | 4.8 | 24 | 5000 |
| V-shaped actuator | 6.23 | 5.1 | 818.620 |
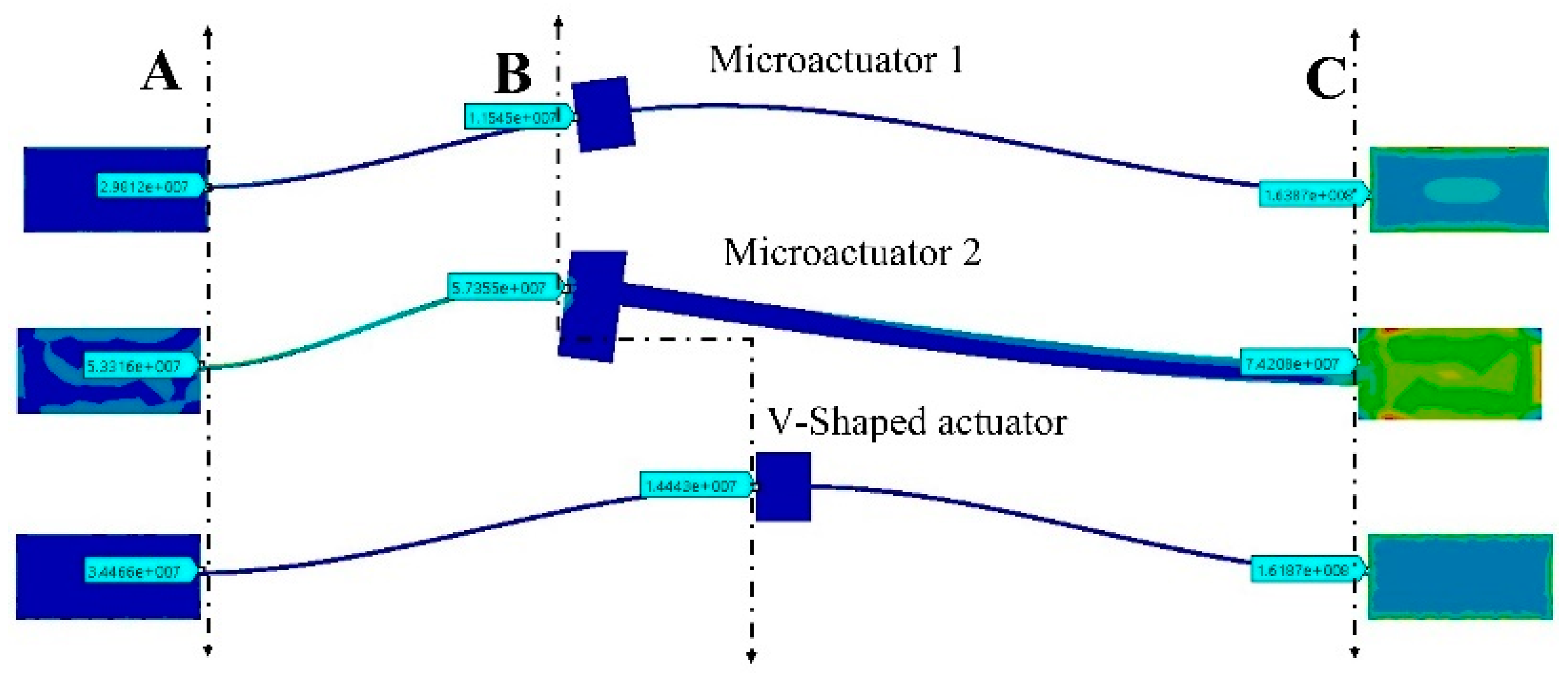
| Device | Maximum Von Misses Stress (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Point A | Point B | Point C | |
| Microactuator 1 | 29.8 | 11.5 | 163.8 |
| Microactuator 2 | 53.3 | 57.3 | 74.2 |
| V-shaped actuator | 34.4 | 14.4 | 161.8 |
| Device | Solver Target | Physics Type and Analysis Type | Element Type/Mesh/Number of DOF | Inflation | Convergence | Total Mass (kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Ratio | Max. Layers | Growth Rate | No. of Total Nodes | No. of Total Elements | |||||
| *MWD | Mechanical APDL | Electric -> steady-state Thermal-electric conduction (1) | Solid187/refinement/39356 | 0.272 | 5 | 1.2 | 20,223 | 10877 | 0.551 × 10−7 |
| *MWoutD | Solid187/refinement/36432 | 12,834 | 5685 | 0.545 × 10−7 | |||||
| *MWVS | Structural -> static structural (2) | Solid187/refinement/38304 | 13,478 | 5930 | 0.534 × 10−7 | ||||
| Actuator | Displacement (µm) at 2 V | Force (mN) at 2 V | ∆T at 2 V | Natural Frequency (kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWoutD | 1.830 | 70.151 | 111.53 | 14.899 |
| MWD | 2.426 | 73.61 | 111.52 | 37.994 |
| MWVS | 0.426 | 42.11 | 111.09 | 11.361 |
| Von Misses Stress (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWD | |||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 24.2 | 34.8 | 68.65 | 18.0 | 37.93 | 57.26 |
| MWoutD | |||||
| G | H | I | J | K | L |
| 33.98 | 35.13 | 71.74 | 27.8 | 42.1 | 72.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tecpoyotl-Torres, M.; Vargas-Chable, P.; Escobedo-Alatorre, J.; Cisneros-Villalobos, L.; Sarabia-Vergara, J. Z-Shaped Electrothermal Microgripper Based on Novel Asymmetric Actuator. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091460
Tecpoyotl-Torres M, Vargas-Chable P, Escobedo-Alatorre J, Cisneros-Villalobos L, Sarabia-Vergara J. Z-Shaped Electrothermal Microgripper Based on Novel Asymmetric Actuator. Micromachines. 2022; 13(9):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091460
Chicago/Turabian StyleTecpoyotl-Torres, Margarita, Pedro Vargas-Chable, Jesus Escobedo-Alatorre, Luis Cisneros-Villalobos, and Josahandy Sarabia-Vergara. 2022. "Z-Shaped Electrothermal Microgripper Based on Novel Asymmetric Actuator" Micromachines 13, no. 9: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091460
APA StyleTecpoyotl-Torres, M., Vargas-Chable, P., Escobedo-Alatorre, J., Cisneros-Villalobos, L., & Sarabia-Vergara, J. (2022). Z-Shaped Electrothermal Microgripper Based on Novel Asymmetric Actuator. Micromachines, 13(9), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091460








