Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Reagent
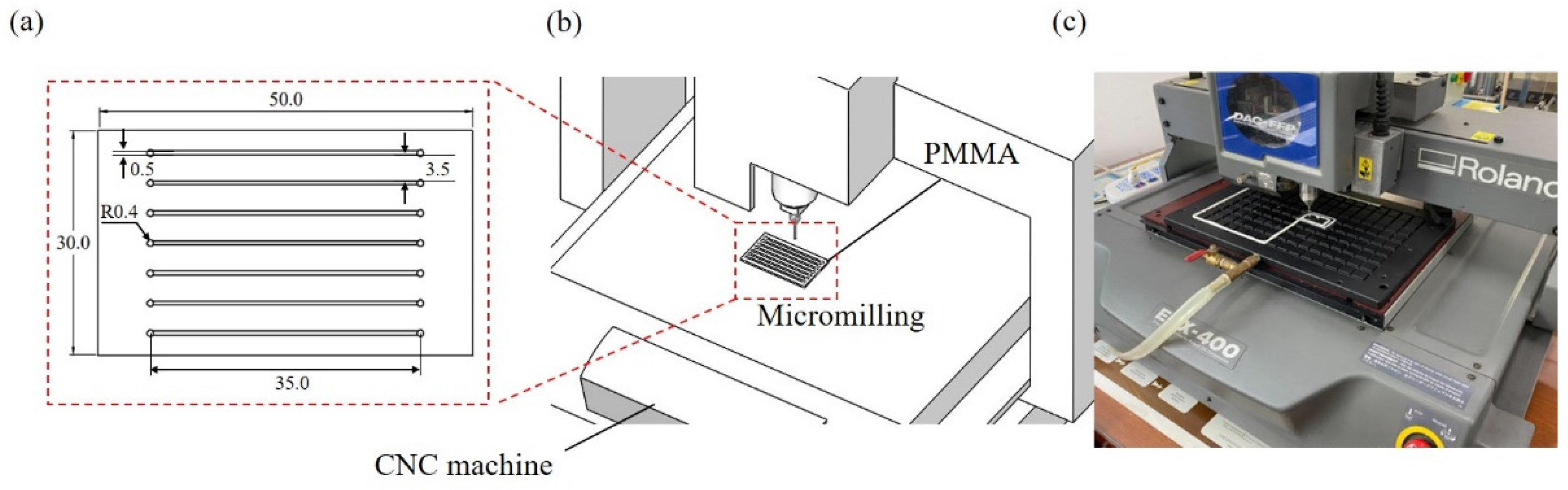
2.2. Microchannel Fabrication
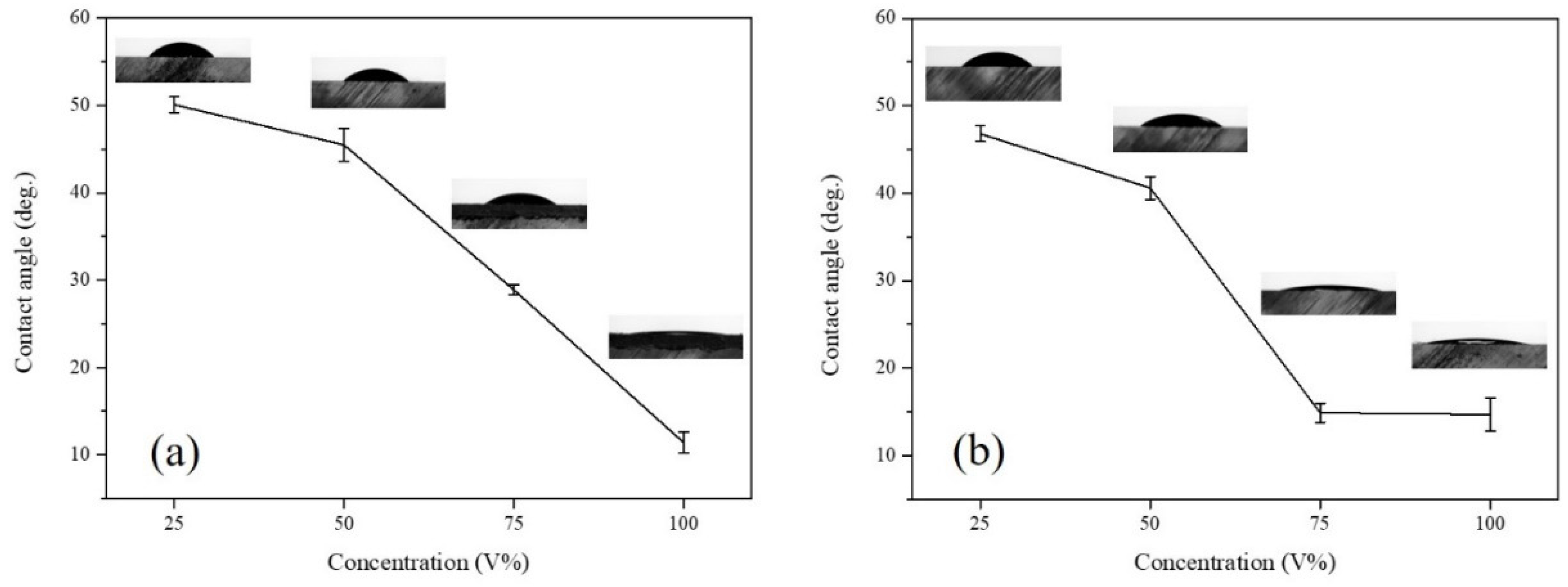
2.3. Contact Angle Measurement
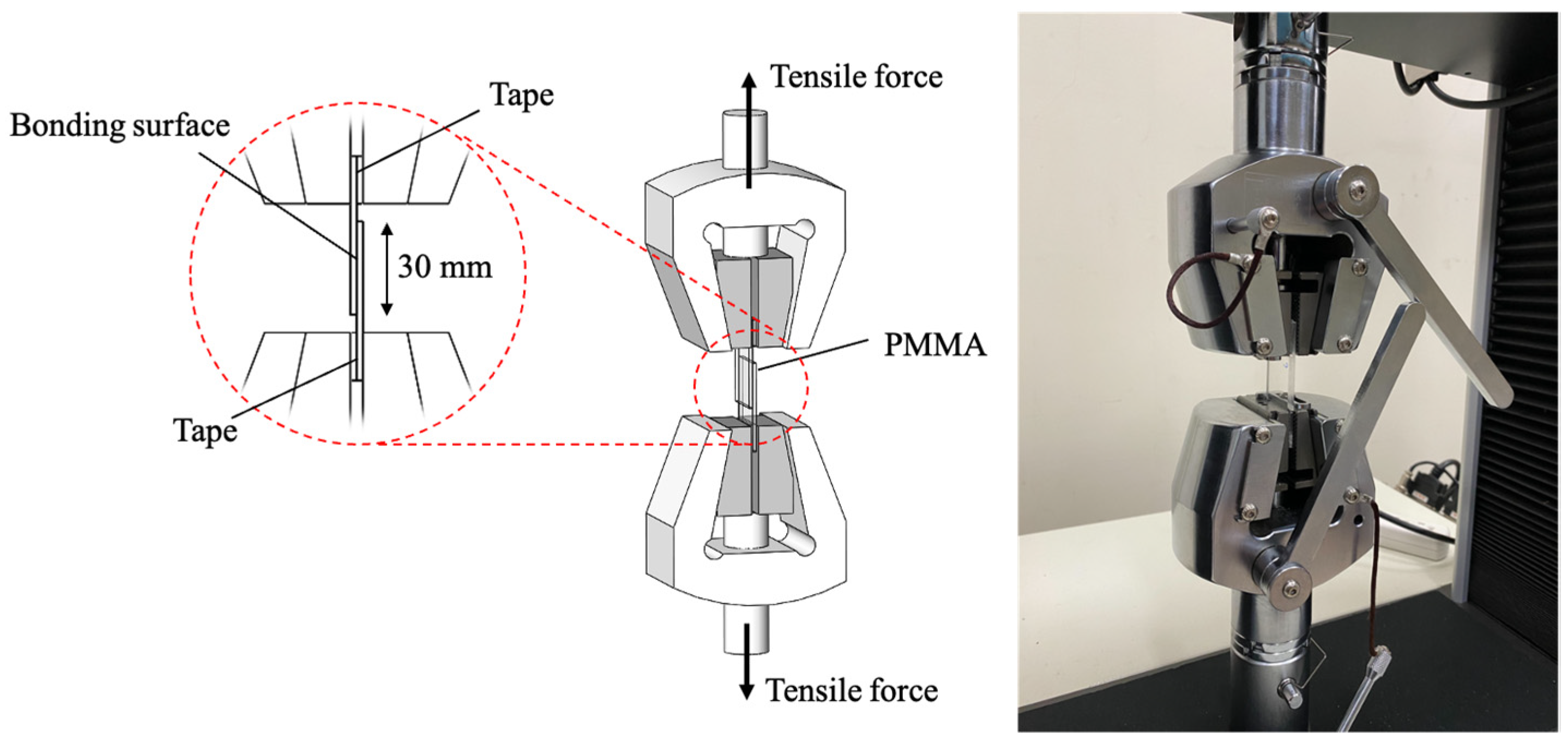
2.4. Bonding Strength Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
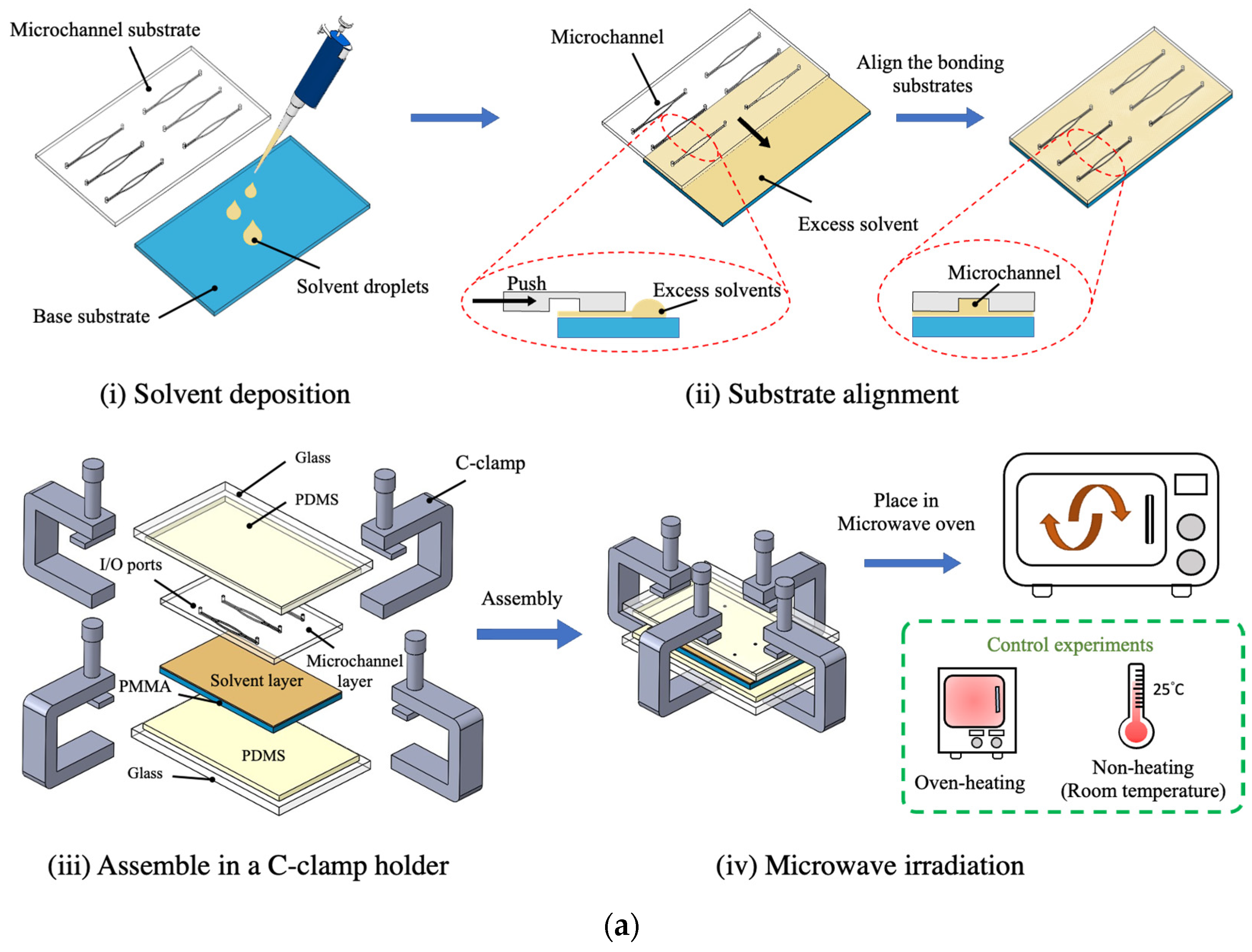
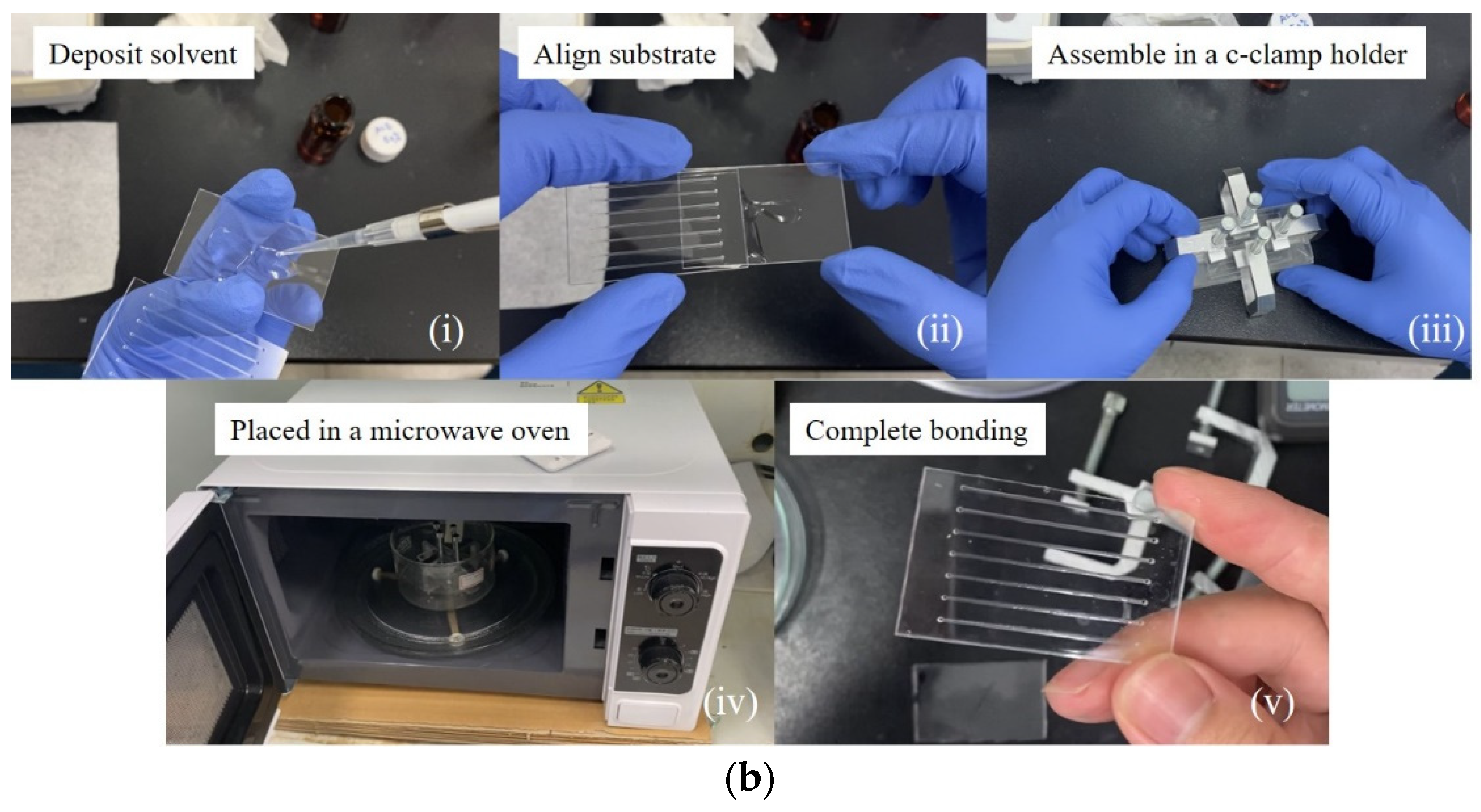
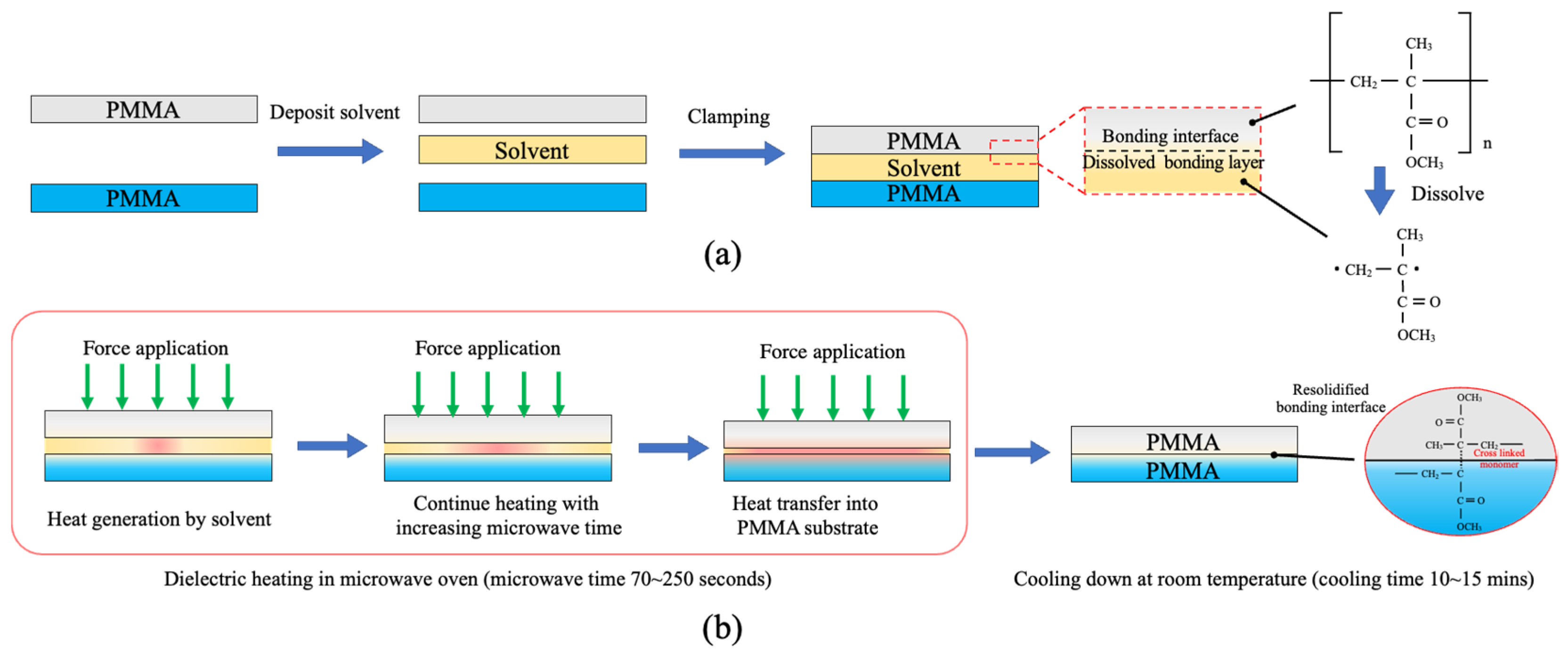
3.1. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding
3.2. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding Mechanism
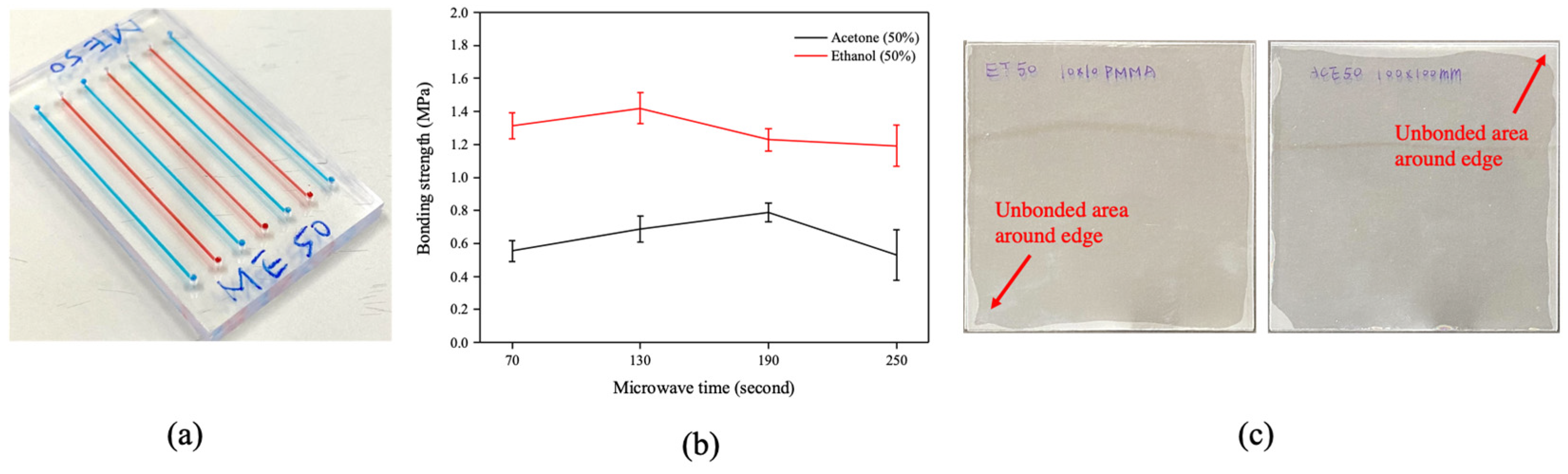
3.3. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding Performance
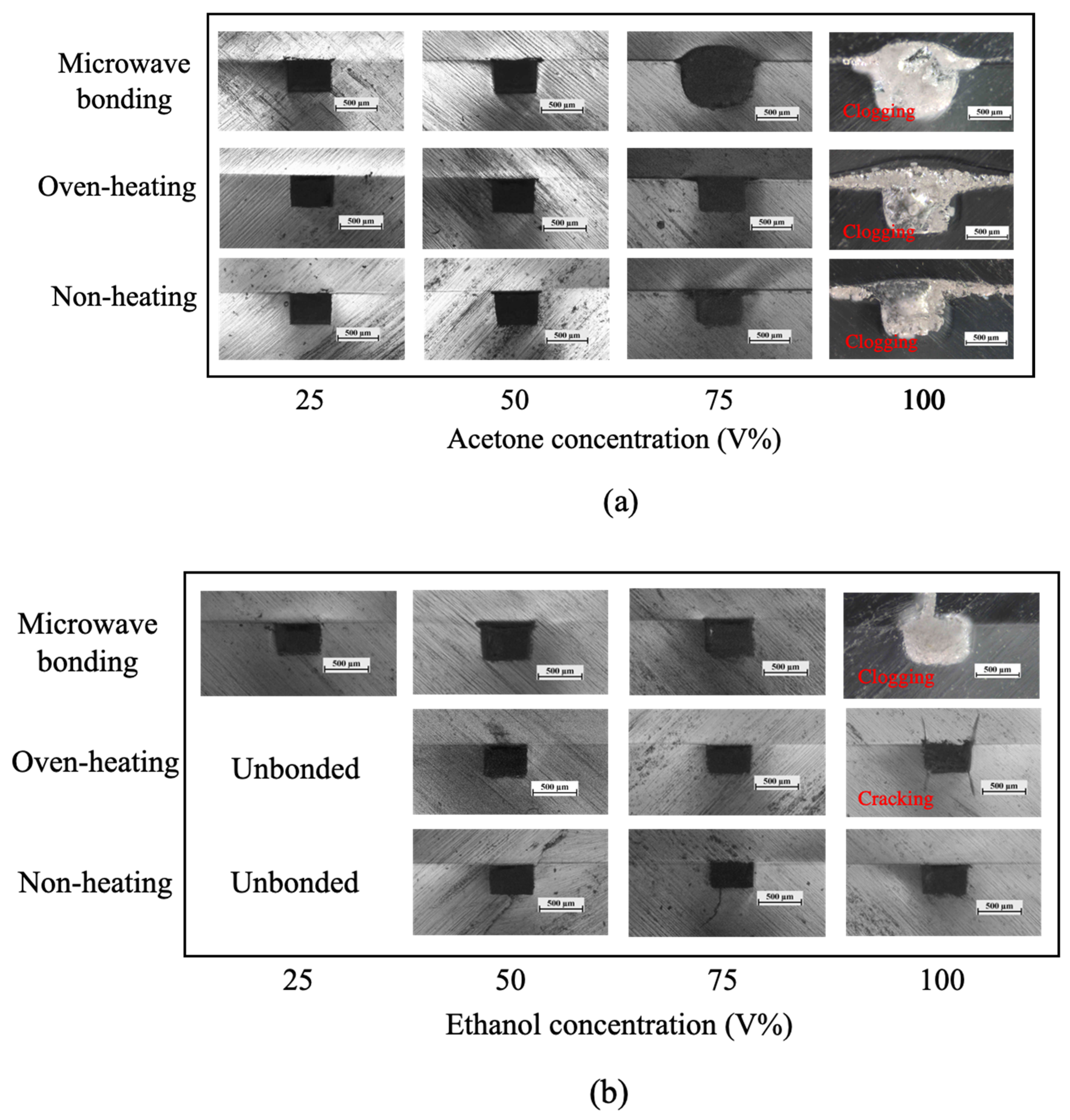
3.3.1. Bonding Coverage Evaluation
3.3.2. Geometry Stability Evaluation
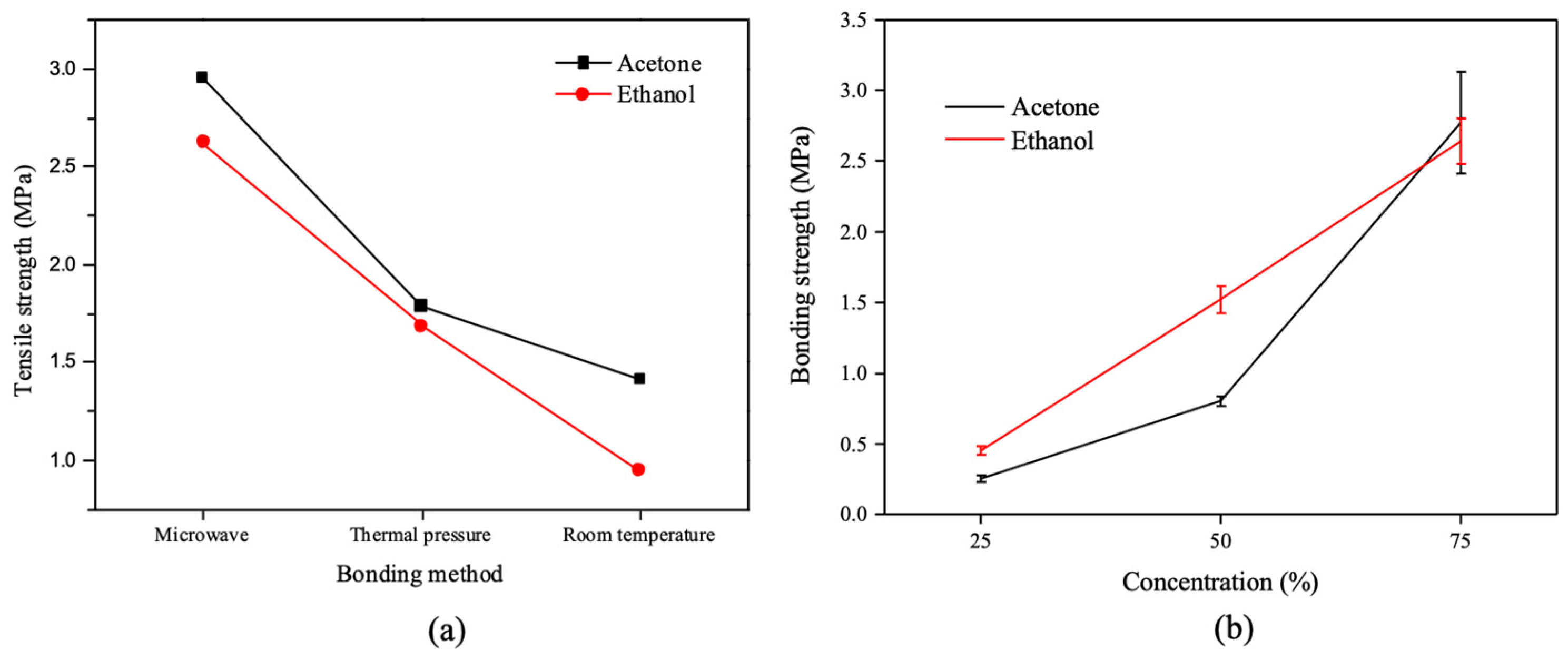
3.3.3. Bonding Strength Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Convery, N.; Gadegaard, N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019, 2, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Pappas, D. Microfluidics for sepsis early diagnosis and prognosis: A review of recent methods. Analyst 2021, 146, 2110–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.L.; Klatser, P.R. A guide to aid the selection of diagnostic tests. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, O.; Martiny, D.; Rochas, O.; van Belkum, A.; Kozlakidis, Z. Considerations for diagnostic COVID-19 tests. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R. Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Low Resource Settings: Present Status and Future Role of Microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Santiago, G.T.-d.; Alvarez, M.M.; Ribas, J.; Jonas, S.J.; Weiss, P.S.; Andrews, A.M.; Aizenberg, J.; Khademhosseini, A. Interplay between materials and microfluidics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chan, C.-W.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.; Mu, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z.; Ren, K. Reliable and reusable whole polypropylene plastic microfluidic devices for a rapid, low-cost antimicrobial susceptibility test. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W. Polymer Microfluidics: Simple, Low-Cost Fabrication Process Bridging Academic Lab Research to Commercialized Production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Deng, Y.; Yi, P.; Lai, X. Micro hot embossing of thermoplastic polymers: A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 24, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, R.; Jin, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Injection molding and characterization of PMMA-based microfluidic devices. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; Chen, T.-Y.; Woon, W.Y.; Lo, C.-J. Rapid polymer microchannel fabrication by hot roller embossing process. Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 18, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; DeVoe, D.L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, Y.; Lovchik, R.D.; Kaigala, G.V.; Delamarche, E. Lab-on-a-chip devices: How to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, K.; Tsao, C.W. Recent Advances in Thermoplastic Microfluidic Bonding. Micromachines 2022, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; Syu, W.-C. Bonding of thermoplastic microfluidics by using dry adhesive tape. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 30289–30296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaegh, S.A.M.; Pourmand, A.; Nabavinia, M.; Avci, H.; Tamayol, A.; Mostafalu, P.; Ghavifekr, H.B.; Aghdam, E.N.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A.; et al. Rapid prototyping of whole-thermoplastic microfluidics with built-in microvalves using laser ablation and thermal fusion bonding. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Park, J.M.; Lim, J. An Interference-Assisted Thermal Bonding Method for the Fabrication of Thermoplastic Microfluidic Devices. Micromachines 2016, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistrup, K.; Poulsen, C.E.; Hansen, M.F.; Wolff, A. Ultrasonic welding for fast bonding of self-aligned structures in lab-on-a-chip systems. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, M.; Chhina, S.; Sameoto, D.; Parameswaran, M. Microwave-induced, thermally assisted solvent bonding for low-cost PMMA microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 015026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Yue, C.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Anand, L. Thermal bonding of microfluidic devices: Factors that affect interfacial strength of similar and dissimilar cyclic olefin copolymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Tian, Y. Study of PMMA thermal bonding. Microsyst. Technol. 2006, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. A spring-driven press device for hot embossing and thermal bonding of PMMA microfluidic chips. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. A low temperature ultrasonic bonding method for PMMA microfluidic chips. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, F.; Liang, C.; Liu, C. Energy director structure and self-balancing jig for the ultrasonic bonding of microfluidic chips. Micro Nano Lett. 2017, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chandrasekar, S.; Wang, C.H. A laser microwelding method for assembly of polymer based microfluidic devices. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 66, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, A.; Di Niso, F.; Gaudiuso, C.; De Rosa, A.; Vazquez, R.M.; Ancona, A.; Lugara, P.M.; Osellame, R. Welding of PMMA by a femtosecond fiber laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 4114–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.J.; McDonagh, C.; McLaughlin, J.A.D.; Mohr, S.; Goddard, N.J.; Fielden, P.R. Microwave bonding of poly(methylmethacrylate) microfluidic devices using a conductive polymer. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2011, 72, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toossi, A.; Moghadas, H.; Daneshmand, M.; Sameoto, D. Bonding PMMA microfluidics using commercial microwave ovens. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 085008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.P.; Wiria, F.E.; Tay, N.B. Low distortion solvent bonding of microfluidic chips. Procedia Eng. 2016, 141, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laher, M.; Hild, S. A detailed micrometer scale investigation of the solvent bonding process for microfluidic chip fabrication. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5371–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamshad, A.; Nikfarjam, A.; Khaleghi, H. A new simple and fast thermally-solvent assisted method to bond PMMA–PMMA in micro-fluidics devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 065017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghih, M.M.; Sharp, M.K. Solvent-based bonding of PMMA-PMMA for microfluidic applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3547–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, L.H.; Chen, P.C. Novel solvent bonding method for creation of a three-dimensional, non-planar, hybrid PLA/PMMA microfluidic chip. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 280, 350–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, A.M.D.; Moore, T.A.; Young, E.W.K. Solvent Bonding for Fabrication of PMMA and COP Microfluidic Devices. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 119, 55175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Duong, L.H. Novel solvent bonding method for thermoplastic microfluidic chips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Thai, D.A.; Chae, W.R.; Lee, N.Y. Rapid Fabrication of Poly(methyl methacrylate) Devices for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications Using Acetic Acid and UV Treatment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17396–17404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Pham, Q.N.; Lee, N.Y. Clog-free and reliable solvent bonding of poly(methyl methacrylate) microdevice mediated by eco-friendly acetic acid at room temperature and its application for polymerase chain reaction and human cell culture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Koerner, T.; Horton, J.H.; Oleschuk, R.D. Fabrication and characterization of poly(methylmethacrylate) microfluidic devices bonded using surface modifications and solvents. Lab A Chip 2006, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.B.; Zhang, L.Y.; Chen, G. Solvent bonding of poly(methyl methacrylate) microfluidic chip using phase-changing agar hydrogel as a sacrificial layer. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3319–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.H.; Peeni, B.A.; Yang, W.; Becerril, H.A.; Woolley, A.T. Rapid prototyping of poly(methyl methacrylate) microfluidic systems using solvent imprinting and bonding. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1162, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Geist, J.; Locascio, L.E.; Gaitan, M.; Rao, M.V.; Vreeland, W.N. Capillarity induced solvent-actuated bonding of polymeric microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3348–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.W.; Li, T.; Han, X.W. Miscible Organic Solvents Soak Bonding Method Use in a PMMA Multilayer Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.M.D.; Sadri, A.; Young, E.W.K. Liquid phase solvent bonding of plastic microfluidic devices assisted by retention grooves. Lab A Chip 2015, 15, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallow, T.I.; Morales, A.M.; Simmons, B.A.; Hunter, M.C.; Krafcik, K.L.; Domeier, L.A.; Sickafoose, S.M.; Patel, K.D.; Gardea, A. Low-distortion, high-strength bonding of thermoplastic microfluidic devices employing case-II diffusion-mediated permeant activation. Lab A Chip 2007, 7, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, E.; Halstead, B.J. Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave dielectric heating. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 213–224. [Google Scholar]

| Thermoplastic/Solvent | Hildebrand Solubility Parameter, δ [(J/cm3)1/2] | Dielectric Constant, εs |
|---|---|---|
| Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) | 20.1 | 4.9 |
| Acetone | 20.4 | 20.7 |
| Ethanol | 26.0 | 24.5 |
| Water | 47.7 | 80.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsao, C.-W.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chien, P.-Y. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071131
Tsao C-W, Chang C-Y, Chien P-Y. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071131
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsao, Chia-Wen, Chang-Yen Chang, and Po-Yen Chien. 2022. "Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device" Micromachines 13, no. 7: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071131
APA StyleTsao, C.-W., Chang, C.-Y., & Chien, P.-Y. (2022). Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device. Micromachines, 13(7), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071131






