Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Non-Lactobacillus LAB Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
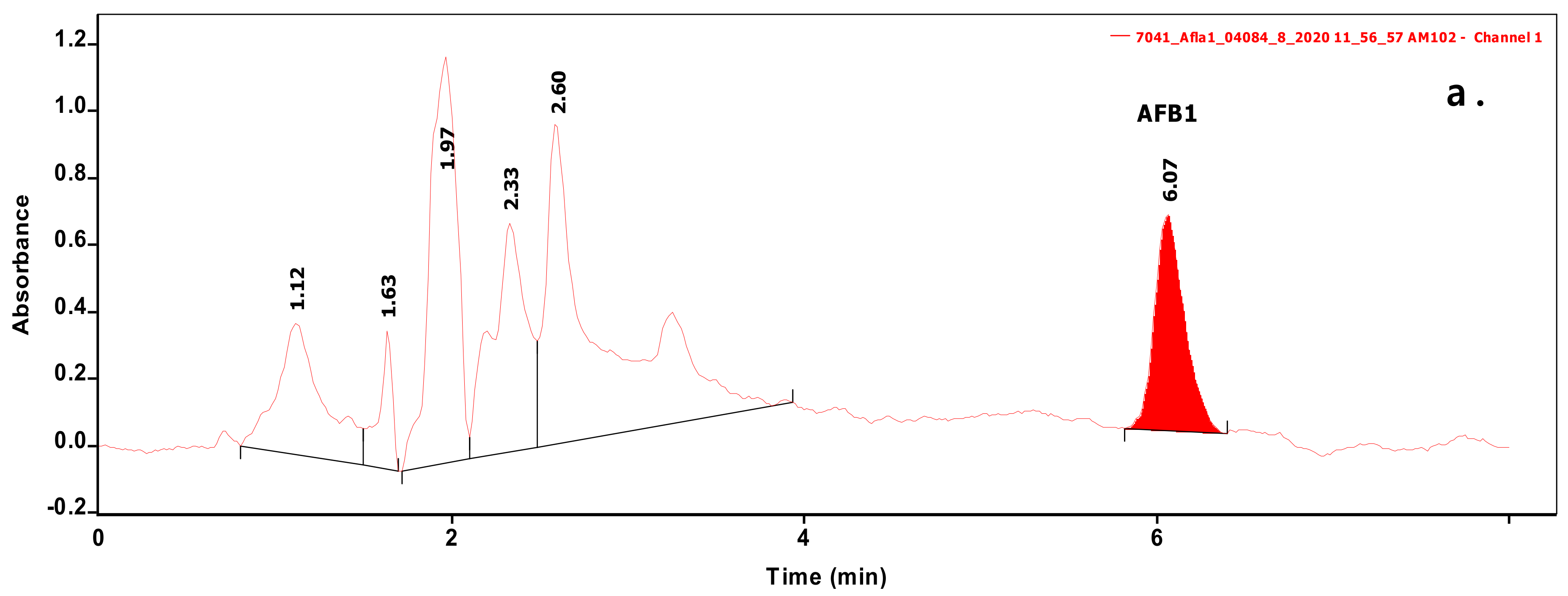
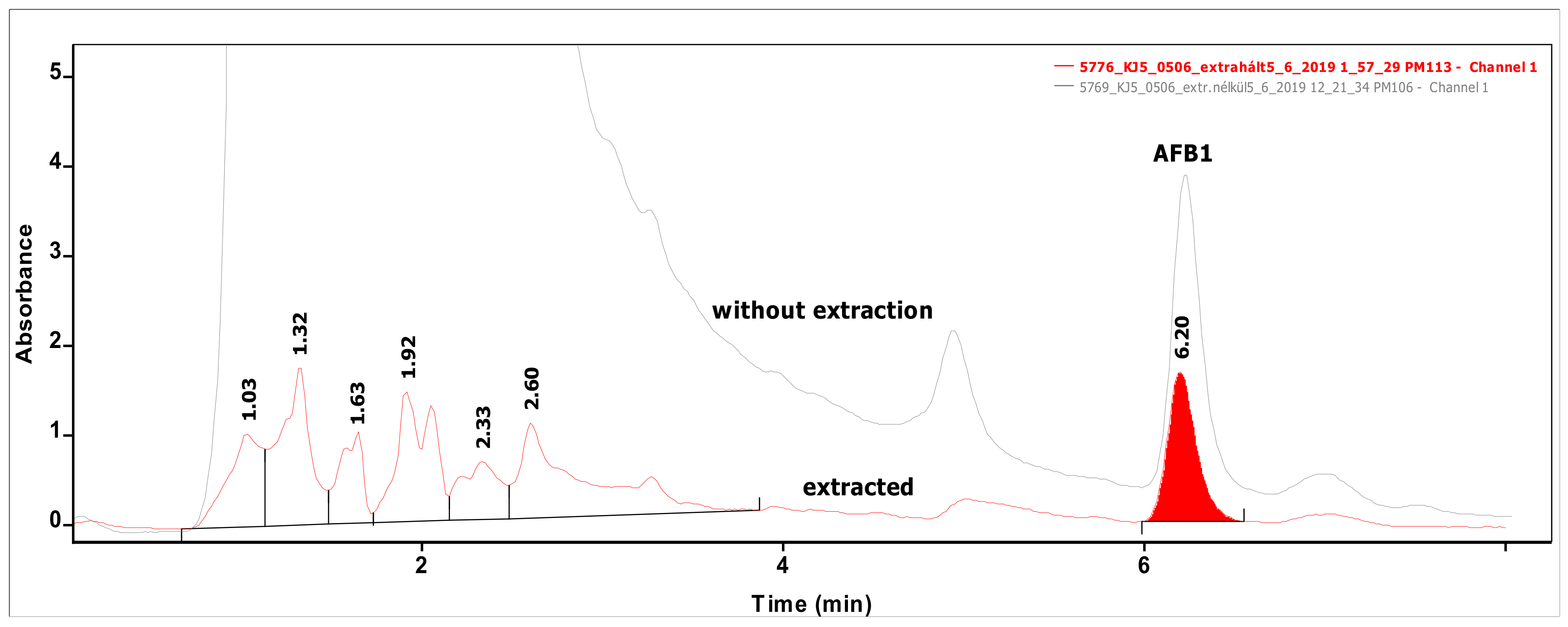
2.1. Instrumental Analysis of Mycotoxins
2.2. Aflatoxin B1 Binding Capacities of LAB Other Then Lactobacilli
2.2.1. Aflatoxin B1 Binding Capacities of Enterococcus Strains
2.2.2. Aflatoxin B1 Binding Capacities of Pediococcus Strains
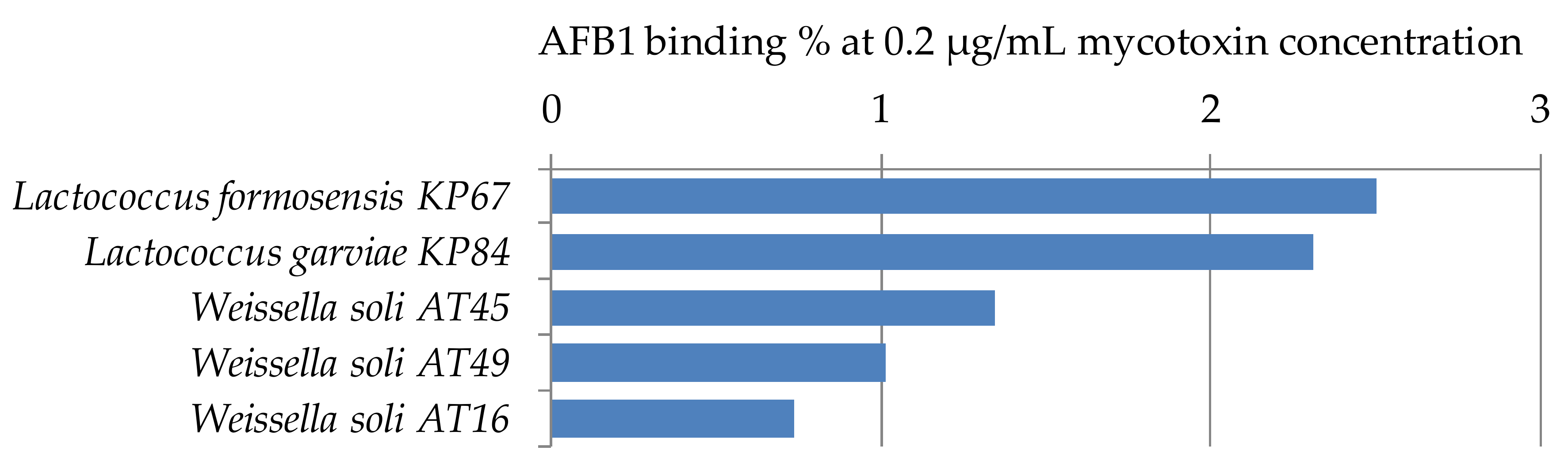
2.2.3. Aflatoxin B1 Binding Capacities of Lactococcus and Weissella Strains
2.2.4. AFB1 Binding Capacities of Lactic Acid Bacteria, Regarding Genus
2.3. Sterigmatocystin Binding Capacities of Pediococcus Strains
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Mycotoxins
4.3. Screening LAB Strains for Mycotoxin Binding Capacities
4.4. Mycotoxin Extraction and HPLC Measurements
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mycotoxins (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Hong, S.-B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.J.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.O.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; et al. Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and other mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Callicott, K.A.; Orbach, M.J.; Cotty, P.J. Molecular Analysis of S-morphology Aflatoxin Producers From the United States Reveals Previously Unknown Diversity and Two New Taxa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgacs, J. Mycotoxicoses—The neglected diseases. Feedstuffs 1962, 34, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, U.L.; Cole, R.J.; Sanders, T.H.; Payne, G.A.; Lee, L.S.; Klich, M.A. Epidemiology of aflatoxin formation by Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987, 25, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detroy, R.W.; Lillehoj, E.B.; Ciegler, A. Aflatoxin and related compounds. In Microbial Toxins, Volume VI: Fungal Toxins; Ciegler, A., Kadis, S., Ajl, S.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 3–178. [Google Scholar]
- Moral, J.; Garcia-Lopez, M.T.; Camiletti, B.X.; Jaime, R.; Michailides, T.J.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Ortega-Beltran, A. Present Status and Perspective on the Future Use of Aflatoxin Biocontrol Products. Agronomy 2020, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Cotty, P.J. Aflatoxin contamination of dried red chilies: Contrasts between the United States and Nigeria, two markets differing in regulation enforcement. Food Control 2017, 80, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.H.; Bosch, F.X.; Bowers, J.C. Aflatoxin, hepatitis and worldwide liver cancer risks. In Mycotoxins and Food Safety; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Aflatoxins. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100F, 225–248. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, C.L. The pathology of mycotoxins. J. Pathol. 1988, 154, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Overall evaluations of carcinogenicity. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1987, 7, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Mokoena, M.P. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins: Classification, Biosynthesis and Applications against Uropathogens: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LPSN. Available online: https://lpsn.dsmz.de/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Gimeno, A.; Martins, M.L. Micotoxinas y Micotoxicosis en Animales y Humanos, 3rd ed.; Special Nutrients: Miami, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumara, S.S.; Gayathri, D.; Hariprasad, P.; Venkateswaran, G.; Swamy, C.T. In vivo AFB1 detoxification by Lactobacillus fermentum LC5/a with chlorophyll and immunopotentiating activity in albino mice. Toxicon 2020, 187, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byakika, S.; Mukisa, I.M.; Wacoo, A.P.; Kort, R.; Byaruhanga, Y.B.; Muyanja, C. Potential application of lactic acid starters in the reduction of aflatoxin contamination in fermented sorghum-millet beverages. Int. J. Food Contam. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.; Kankaanpaa, P.; Salminen, P.; Ahokas, J. Ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind a common food carcinogen, aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.-P.; Nurul-Adilah, Z.; Than, L.T.L.; Mohd-Redzwan, S. The Binding Efficiency and Interaction of Lactobacillus casei Shirota toward Aflatoxin B1. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.J.; Casale, C.H.; Pizzolitto, R.P.; Salvano, M.A.; Oliver, G. Physical Adsorption of Aflatoxin B1 by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A Theoretical Model. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, S.H.; Joutsjoki, V.; Korhonen, H.J. Potential of lactic acid bacteria in aflatoxin risk mitigation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 207, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.S.; Kankaanpää, P.E.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Physicochemical Alterations Enhance the Ability of Dairy Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria to Remove Aflatoxin from Contaminated Media. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskard, C.A.; El-Nezami, H.S.; Kankaanpaa, P.E.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Surface Binding of Aflatoxin B1 by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Garcia, H.S.; Steele, J.L. Screening of Lactobacillus casei strains for their ability to bind aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahtinen, S.J.; Haskard, C.A.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J.; Ahokas, J.T. Binding of aflatoxin B1 to cell wall components of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalié, D.; Deschamps, A.; Richard-Forget, F. Lactic acid bacteria—Potential for control of mold growth and mycotoxins: A review. Food Control 2010, 21, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, K.; El-Nezami, H.; Haskard, C.; Ahokas, J.; Salminen, S. Aflatoxin B1 Binding by Dairy Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2152–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacoo, A.P.; Mukisa, I.M.; Meeme, R.; Byakika, S.; Wendiro, D.; Sybesma, W.; Kort, R. Probiotic Enrichment and Reduction of Aflatoxins in a Traditional African Maize-Based Fermented Food. Nutrients 2019, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Á.; Baka, E.; Bata-Vidács, I.; Luzics, S.; Kosztik, J.; Tóth, E.; Kéki, Z.; Schumann, P.; Táncsics, A.; Nagy, I.; et al. Micrococcoides hystricis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Micrococcaceae, phylum Actinobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztik, J.; Mörtl, M.; Székács, A.; Kukolya, J.; Bata-Vidács, I. Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Lactobacilli. Toxins 2020, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, N.C.; Almeida, R.T.R.; Avíncola, A.; Porto, C.; Galuch, M.B.; Magon, T.F.S.; Pilau, E.J.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Oliveira, C.C. Development of an analytical method for identification of Aspergillus flavus based on chemical markers using HPLC-MS. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, M.L.G.; Martínez, M.P.; Petroselli, G.; Balsells, R.E.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Antifungal and aflatoxin-reducing activity of extracellular compounds produced by soil Bacillus strains with potential application in agriculture. Food Control 2018, 85, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.F.; Yu, J.-H. A Liquid Chromatographic Method for Rapid and Sensitive Analysis of Aflatoxins in Laboratory Fungal Cultures. Toxins 2020, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juri, F.M.G.; Dalcero, A.M.; Magnoli, C.E. In vitro aflatoxin B1 binding capacity by two Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from healthy dog faeces. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinedine, A.; Faid, M.; Benlemlih, M. In vitro reduction of aflatoxin B1 by strains of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Moroccan sourdough bread. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2005, 7, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Nduti, N.N.; Reid, G.; Sumarah, M.; Hekmat, S.; Mwaniki, M.; Njeru, P.N. Weissella cibaria Nn20 isolated from fermented kimere shows ability to sequester AFB1 in vitro and ferment milk with good viscosity and phin comparison to yogurt. Food Sci. Nutr. Technol. 2018, 3, 000137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Singh, S.P.; Kandasamy, S.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Report on aflatoxin-binding activity of galactan exopolysaccharide produced by Weissella confusa KR780676. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapot-Chartier, M.P.; Kulakauskas, S. Cell wall structure and function in lactic acid bacteria. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species | Number of Strains | Average Binding % | STD | Min Binding % | Max Binding % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus lactis | 3 | 2.06 | 1.18 | 1.17 | 3.40 |
| Enterococcus hirae | 7 | 1.49 | 1.39 | 0.72 | 4.62 |
| Enterococcus casseliflavus | 1 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.14 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 4 | 1.10 | 0.23 | 0.89 | 1.35 |
| Enterococcus faecium | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Enterococcus mundtii | 4 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 1.21 |
| Species | Number of Strains | Average Binding % | STD | Min Binding % | Max Binding % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediococcus acidilactici | 8 | 3.43 | 1.95 | 0.80 | 7.60 |
| Pediococcus stilesii | 1 | 3.03 | 3.03 | 3.03 | |
| Pediococcus lolii | 3 | 2.90 | 0.84 | 1.93 | 3.39 |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus | 12 | 2.18 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 4.60 |
| Genus | Number of Strains | Average Binding % | STD | Min Binding % | Max Binding % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | 105 | 3.16 | 1.98 | 0.55 | 11.50 |
| Pediococcus | 24 | 2.72 | 1.42 | 0.80 | 7.60 |
| Lactococcus | 2 | 2.40 | 0.14 | 2.31 | 2.50 |
| Enterococcus | 20 | 1.35 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 4.62 |
| Weissella | 3 | 1.03 | 0.31 | 0.73 | 1.35 |
| Species | Strains |
|---|---|
| Enterococcus | |
| E. casseliflavus | AT20 |
| E. faecalis | OR8, SK31, SK32, SK37 |
| E. faecium | SK40 |
| E. hirae | AT12, OR9, OR36, OR40, OR41, OR75, SK35 |
| E. lactis | AT42r, OR46, SK34 |
| E. mundtii | OR4, OR44, OR45, OR51 |
| Lactococcus | |
| L. formosensis | KP67 |
| L. garviae | KP84 |
| Pediococcus | |
| P. acidilactici | MG1, MG21, MG31, MG82, OR72, OR83, OR95, OR96 |
| P. lolii | MG7, MG44, OR77 |
| P. pentosaceus | AT43A, AT56, AT58, OR52, OR61, OR68, OR78, OR84, OR85, SK28, TS7, TS63 |
| P. stilesii | TS1 |
| Weissella | |
| W. soli | AT16, AT45, AT49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bata-Vidács, I.; Kosztik, J.; Mörtl, M.; Székács, A.; Kukolya, J. Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Non-Lactobacillus LAB Strains. Toxins 2020, 12, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120799
Bata-Vidács I, Kosztik J, Mörtl M, Székács A, Kukolya J. Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Non-Lactobacillus LAB Strains. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120799
Chicago/Turabian StyleBata-Vidács, Ildikó, Judit Kosztik, Mária Mörtl, András Székács, and József Kukolya. 2020. "Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Non-Lactobacillus LAB Strains" Toxins 12, no. 12: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120799
APA StyleBata-Vidács, I., Kosztik, J., Mörtl, M., Székács, A., & Kukolya, J. (2020). Aflatoxin B1 and Sterigmatocystin Binding Potential of Non-Lactobacillus LAB Strains. Toxins, 12(12), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120799








