The Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Phase Angle in Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
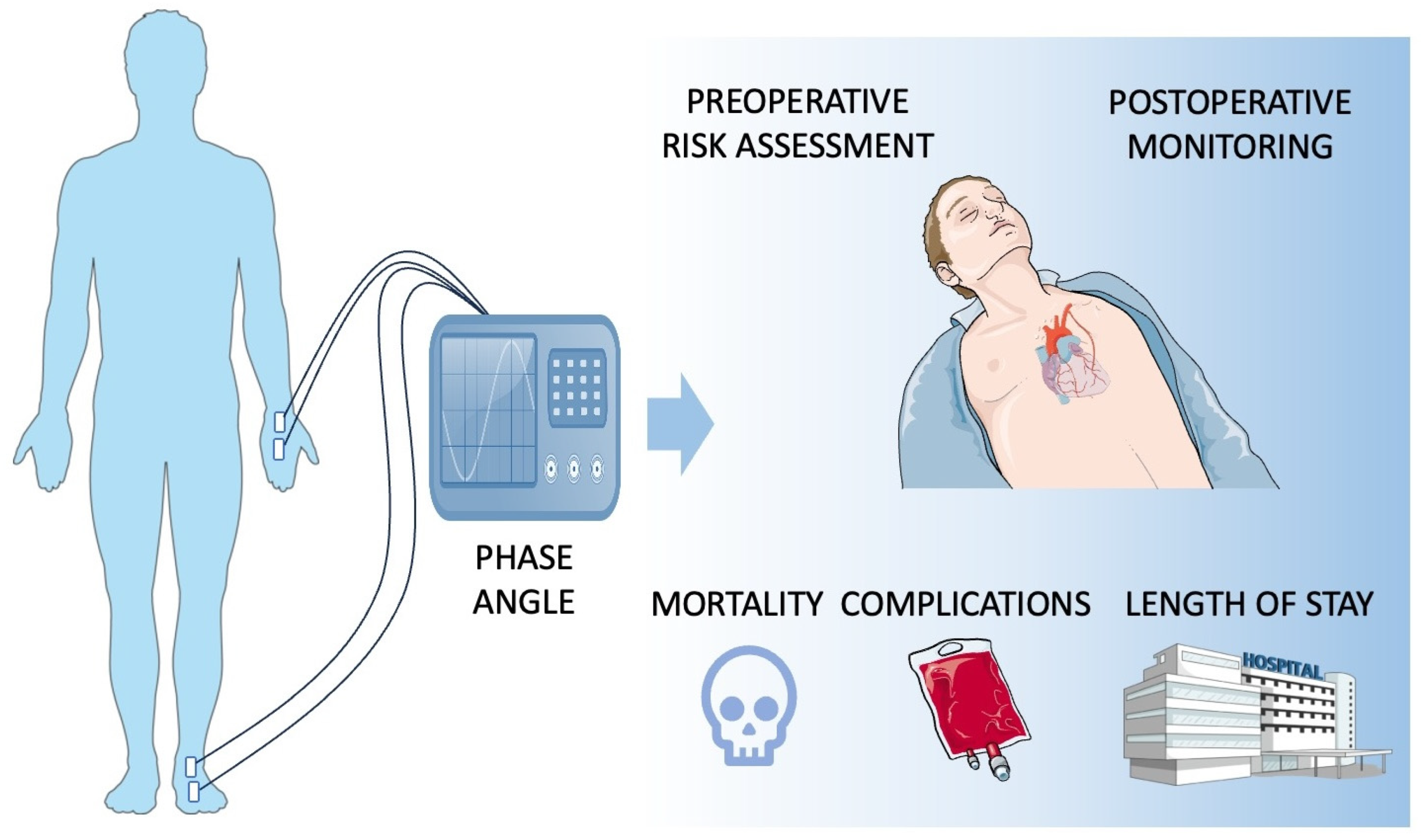
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. PA Impairment Risk Factors
4. PA in Preoperative Risk Assessment
5. PA in Post-Procedural Monitoring
Limitations of the Available Literature
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | aortic cross-clamp |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CABG | coronary artery bypass graft |
| CPB | cardiopulmonary bypass |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESPEN | european society for clinical nutrition and metabolism |
| ECW | extracellular water |
| FFMI | fat-free mass index |
| HGS | handgrip strength |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| LVEF | left ventricle ejection fraction |
| LOS | length of stay |
| MUAC | mid-upper arm circumference |
| PA | phase angle |
| SMML | skeletal muscle mass loss |
References
- Langer, R.D.; Larsen, S.C.; Ward, L.C.; Heitmann, B.L. Phase Angle Measured by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease among Adult Danes. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portugal, M.R.C.; Canella, D.S.; Curioni, C.C.; Bezerra, F.F.; Faerstein, E.; Neves, M.F.; Koury, J.C. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis–Derived Phase Angle Is Related to Risk Scores of a First Cardiovascular Event in Adults. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.N.; Jorge, A.J.L.; de Andrade Martins, W.; Cardoso, G.P.; dos Santos, M.M.S.; Rosa, M.L.G.; Lima, G.A.B.; de Moraes, R.Q.; da Cruz Filho, R.A. Phase Angle Measured by Electrical Bioimpedance and Global Cardiovascular Risk in Older Adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-Ramírez, E.; Castillo-Martínez, L.; Orea-Tejeda, A.; Vázquez-Durán, M.; Rodríguez, A.E.; Keirns-Davis, C. Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle as a Prognostic Marker in Chronic Heart Failure. Nutrition 2012, 28, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicchitano, P.; Ciccone, M.M.; Iacoviello, M.; Guida, P.; De Palo, M.; Potenza, A.; Basile, M.; Sasanelli, P.; Trotta, F.; Sanasi, M.; et al. Respiratory Failure and Bioelectrical Phase Angle Are Independent Predictors for Long-Term Survival in Acute Heart Failure. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2022, 56, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.D.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.; Biolo, A. Prognostic Role of Phase Angle in Hospitalized Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, S.A.; Gonzalez, M.C.; da Silva, A.M.B.; Costa, J.K.D.A.; de Oliveira, C.D.R.; de Sousa, I.M.; Fayh, A.P.T. Is the Standardized Phase Angle a Predictor of Short- and Long-Term Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction? A Cohort Study. Nutrition 2022, 103–104, 111774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlini, L.M.; Alves, F.D.; Ceretta, L.B.; Perry, I.S.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.O. Phase Angle and Mortality: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Kalisz, J.; Chrominski, T.; Szczasny, M.; Blaszczak, P. Nutritional Status Predicts the Length of Stay and Mortality in Patients Undergoing Electrotherapy Procedures. Nutrients 2024, 16, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Kalisz, J.; Hollings, M.; Blaszczak, P. Nutritional Risk Score Predicts the Length of Stay in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. Nutr. Diet. 2025, early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Kalisz, J.; Błaszczak, P. The Impact of Nutritional Risk on the Length of Stay in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Kardiol. Pol. 2025, early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.G.; et al. ESPEN Practical Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4745–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, R.; Rifu, K.; Watanabe, J.; Inaki, N.; Fukunaga, T. Current Status of the Association Between Malnutrition Defined by the GLIM Criteria and Postoperative Outcomes in Gastrointestinal Surgery for Cancer: A Narrative Review. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 149, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization World Health Organization. BMI Classification. Global Database on Body Mass Index. Available online: http://www.who.int/bmi/index.jsp?introPage=intro_3.html (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Definitions and Terminology of Clinical Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Ramussen, H.H.; Hamberg, O.; Stanga, Z.; Camilo, M.; Richardson, R.; Elia, M.; Allison, S.; Meier, R.; Plauth, M. Nutritional Risk Screening (NRS 2002): A New Method Based on an Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.C.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, S.W.; Moon, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.K.; Park, J.H.; Baik, H.W.; Seo, J.M.; Son, M.W.; et al. Prevalence of Malnutrition in Hospitalized Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Kalisz, J.; Szczygiel, K. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Body Composition in Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.C. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Body Composition Assessment: Reflections on Accuracy, Clinical Utility, and Standardisation. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiołek, J.; Teter, M.; Kozak, G.; Powrózek, T.; Mlak, R.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Anthropometrical and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Parameters in Anorexia Nervosa Patients’ Nutritional Status Assessment. Medicina 2019, 55, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka-Massalska, T.; Popiołek, J.; Teter, M.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Dec, M.; Makarewicz, A.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H. Application of Phase Angle for Evaluation of the Nutrition Status of Patients with Anorexia. Psychiatr. Pol. 2017, 51, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Danielzik, S.; Dörhöfer, R.-P.; Later, W.; Wiese, S.; Müller, M.J. Phase Angle From Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Population Reference Values by Age, Sex, and Body Mass Index. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2006, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lammersfeld, C.A.; Vashi, P.G.; King, J.; Dahlk, S.L.; Grutsch, J.F.; Lis, C.G. Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle as a Prognostic Indicator in Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G.; Dahlk, S.L.; Vashi, P.G.; Grutsch, J.F.; Lammersfeld, C.A. Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle as a Prognostic Indicator in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, S.; Sotomayor, G.; Vega, A.; Pérez de José, A.; Verdalles, U.; Jofré, R.; López-Gómez, J.M. The Phase Angle of the Electrical Impedance Is a Predictor of Long-Term Survival in Dialysis Patients. Nefrologia 2011, 31, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.C.; Kubrusly, M.; Mota, R.S.; Silva, C.A.B.; Choukroun, G.; Oliveira, V.N. The Phase Angle and Mass Body Cell as Markers of Nutritional Status in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringaitiene, D.; Gineityte, D.; Vicka, V.; Sabestinaite, A.; Klimasauskas, A.; Gaveliene, E.; Rucinskas, K.; Ivaska, J.; Sipylaite, J. Concordance of the New ESPEN Criteria with Low Phase Angle in Defining Early Stages of Malnutrition in Cardiac Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; van Venrooij, L.M.W.; Wanders, D.C.M.; de Vos, R.; Wisselink, W.; van Leeuwen, P.A.M.; de Mol, B.A.J.M. The Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle as an Indicator of Undernutrition and Adverse Clinical Outcome in Cardiac Surgical Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringaitienė, D.; Gineitytė, D.; Vicka, V.; Žvirblis, T.; Šipylaitė, J.; Irnius, A.; Ivaškevičius, J. Preoperative Risk Factors of Malnutrition for Cardiac Surgery Patients. Acta Medica Litu. 2016, 23, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullie, L.; Obrand, A.; Bendayan, M.; Trnkus, A.; Ouimet, M.-C.; Moss, E.; Chen-Tournoux, A.; Rudski, L.G.; Afilalo, J. Phase Angle as a Biomarker for Frailty and Postoperative Mortality: The BICS Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringaitiene, D.; Gineityte, D.; Vicka, V.; Zvirblis, T.; Norkiene, I.; Sipylaite, J.; Irnius, A.; Ivaskevicius, J. Malnutrition Assessed by Phase Angle Determines Outcomes in Low-Risk Cardiac Surgery Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Kameshima, M.; Adachi, T.; Kito, H.; Tanaka, C.; Sano, T.; Tanaka, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Tamaki, M.; Kitamura, H. Association between Preoperative Phase Angle and All-Cause Mortality after Cardiovascular Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringaitiene, D.; Puodziukaite, L.; Vicka, V.; Gineityte, D.; Serpytis, M.; Sipylaite, J. Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle-Predictor of Blood Transfusion in Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruste, M.; Chabanol, C.; Amaz, C.; Cazenave, L.; Fellahi, J.-L.; Jacquet-Lagrèze, M. Postoperative Phase Angle and Prognosis after Cardiac Surgery: A Historical Cohort Study. Anesthesiology 2024, 141, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousi, G.; Panagidi, M.; Papakostas, P.; Grosomanidis, V.; Stavrou, G.; Kotzampassi, K. Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength as Complements to Body Composition Analysis for Refining Prognostic Accuracy in Cardiac Surgical Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagidi, M.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Moysidis, D.V.; Vlachopoulou, E.; Papadakis, M.; Kouidi, E.; Galanos, A.; Tagarakis, G.; Anastasiadis, K. Prognostic Value of Combined Preoperative Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength in Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.K.; Perry, I.D.S.; Brauner, J.S.; Mancuso, A.C.B.; Souza, G.C.; Vieira, S.R.R. Variations in Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: Prospective Cohort Study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrou, G.; Tzikos, G.; Menni, A.-E.; Chatziantoniou, G.; Vouchara, A.; Fyntanidou, B.; Grosomanidis, V.; Kotzampassi, K. Endothelial Damage and Muscle Wasting in Cardiac Surgery Patients. Cureus 2022, 14, e30534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.V.; Meyer, R.; Johnson, M.; Newell, C.; Johnstone, C.; Magee, A.; Sykes, K.; Wootton, S.A.; Pappachan, J.V. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Measurements of Phase Angle and Height for Age Are Predictive of Outcome in Children Following Surgery for Congenital Heart Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryz, S.; Nixdorf, L.; Puchinger, J.; Lassnigg, A.; Wiedemann, D.; Bernardi, M.H. Preoperative Phase Angle as a Risk Indicator in Cardiac Surgery-A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.K.; Perry, I.D.S.; Brauner, J.S.; Wender, O.C.B.; Souza, G.C.; Vieira, S.R.R. Performance Evaluation of Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: Prospective Cohort Study. Aust. Crit. Care 2018, 31, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisawa, T.; Saitoh, M.; Takahashi, T.; Watanabe, H.; Mochizuki, M.; Kitahara, E.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Nishitani-Yokoyama, M.; Minamino, T.; et al. Association of Phase Angle with Hospital-Acquired Functional Decline in Older Patients Undergoing Cardiovascular Surgery. Nutrition 2021, 91–92, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanson, G.; Doriguzzi, L.; Garbari, P.; Ruggiero, M.J.; Valentinuzzo, I.; Mettulio, T.; Stolfa, E.; Fisicaro, M.; Vecchiet, S.; Mazzaro, E.; et al. The Severity of Early Fluid Overload Assessed by Bioelectrical Vector Impedance as an Independent Risk Factor for Longer Patient Care after Cardiac Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, L.V.; Griksaitis, M.J.; Pappachan, J.V. Preoperative Bioelectrical Impedance Predicts Intensive Care Length of Stay in Children Following Cardiac Surgery. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stąpór, M.; Stąpór, A.; Ostrowska-Kaim, E.; Trębacz, J.; Sobczyński, R.; Kleczyński, P.; Konstanty-Kalandyk, J.; Gackowski, A.; Żmudka, K.; Kapelak, B.; et al. Bioelectrical Phase Angle among Individuals after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Pol. Heart J. (Kardiol. Pol.) 2024, 82, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Tsushima, E.; Yokota, J.; Takahashi, S.; Seki, T.; Kudo, H.; Honjo, H.; Endo, H.; Oda, K.; Sakurada, Y.; et al. Association between Skeletal Muscle Quality Assessed by Phase Angle, Peak Oxygen Uptake and Anaerobic Threshold in Male Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Hirosaki Med. J. 2024, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Size Group | PA Association | Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | |||
| [34] | A total of 204 patients after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass | in-hospital mortality | Retrospective |
| [35] | A total of 179 cardiac surgery patients | in-hospital mortality | Prospective |
| [30] | A total of 277 patients undergoing major cardiac surgery | higher mortality at 1 month and at 12 months. | Prospective |
| [36] | A total of 195 patients undergoing cardiac surgery | higher one-year all-cause mortality | Prospective |
| Length of stay | |||
| [34] | A total of 204 patients after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass | prolonged hospital LOS | Retrospective |
| [30] | A total of 277 patients undergoing major cardiac surgery | prolonged hospital LOS | Prospective |
| [35] | A total of 179 cardiac surgery patients | prolonged hospital LOS | Prospective |
| [28] | A total of 325 cardiac surgical patients | prolonged ICU and hospital LOS | Prospective |
| [37] | A total of 272 cardiac surgery patients | prolonged ICU and hospital LOS | Prospective |
| [36] | A total of 195 patients undergoing cardiac surgery | prolonged ICU LOS | Prospective |
| [38] | A total of 127 well-nourished patients undergoing “on-pump” elective cardiac surgery | prolonged ICU LOS | Prospective |
| [39] | A total of 122 children with congenital heart disease following cardiac surgery | prolonged pediatric ICU LOS | Prospective |
| Complications | |||
| [40] | A total of 168 elective cardiac surgical patients | longer cardiopulmonary bypass times | Prospective |
| [31] | A total of 342 low-operative-risk patients | postoperative morbidity | Prospective |
| [33] | A total of 642 adult patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery | blood transfusion | Retrospective |
| [37] | A total of 272 cardiac surgery patients | decline after procedure restored after 6 months | Prospective |
| [35] | A total of 179 cardiac surgery patients | significant impairment 7 days after the procedure | Prospective |
| [41] | 50 patients undergoing cardiac surgery | mechanical ventilation | Prospective |
| [42] | 114 older patients undergoing elective cardiovascular | predictor of hospital-acquired functional decline risk, undernutrition, and prolonged mechanical ventilation. | Prospective |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popiolek-Kalisz, J.; Kalisz, G.; Zembala, M. The Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Phase Angle in Cardiac Surgery. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111914
Popiolek-Kalisz J, Kalisz G, Zembala M. The Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Phase Angle in Cardiac Surgery. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111914
Chicago/Turabian StylePopiolek-Kalisz, Joanna, Grzegorz Kalisz, and Michal Zembala. 2025. "The Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Phase Angle in Cardiac Surgery" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111914
APA StylePopiolek-Kalisz, J., Kalisz, G., & Zembala, M. (2025). The Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Phase Angle in Cardiac Surgery. Nutrients, 17(11), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111914






