Aqueous Extract of Freshwater Clam Increases Alcohol Metabolism in Rats in a Preclinical Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Material Preparation
2.3. Animals and Treatment
2.4. Measurement of Serum Ethanol Concentration
2.5. Analysis of Hepatic Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) and Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH) Activities
2.6. Analysis of Hepatic Catalase (CAT) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activities
2.7. Analysis of Hepatic Protein Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of CE Supplement on Serum Ethanol Concentration in Rats
3.2. Effect of CE Supplement on Hepatic ADH and ALDH Activities in Rats
3.3. Effect of CE Supplement on the Activities of Hepatic CAT and SOD in Rats
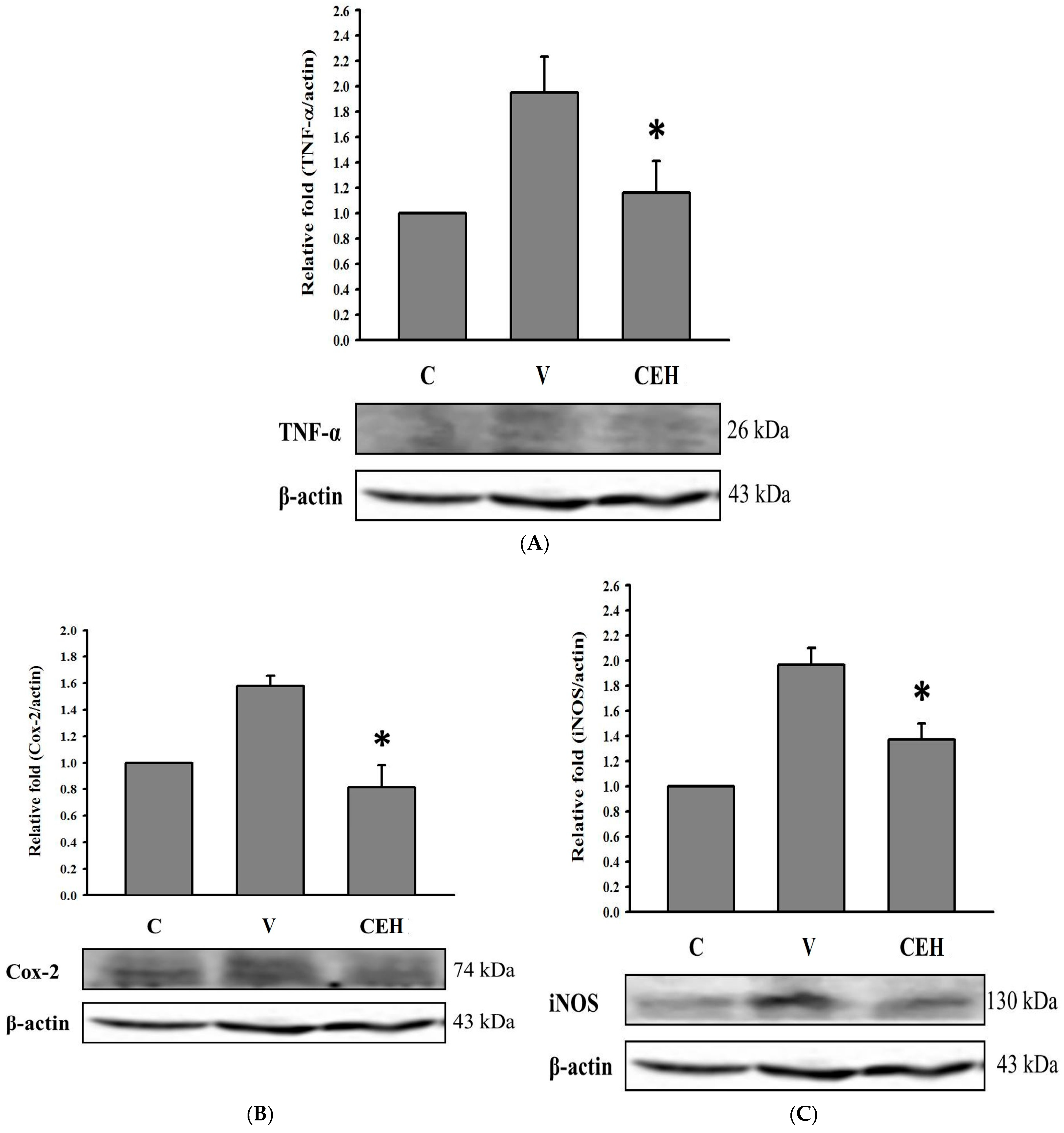
3.4. Effect of CE Supplement on Expression of TNF-α, COX-2, and iNOS Proteins in Liver of Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yokoyama, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Funazu, K.; Yamashita, T.; Kondo, S.; Hosoai, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Nakamura, H. Associations between headache and stress, alcohol drinking, exercise, sleep, and comorbid health conditions in a Japanese population. J. Headache Pain 2009, 10, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, R.; McKinney, A.; Verster, J.C. Alcohol hangover symptoms and their contribution to the overall hangover severity. Alcohol Alcohol. 2012, 47, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, A.K.; Hobbs, M.; Klipp, L.; Bell, S.; Edwards, K.; O’Hara, P.; Drummond, C. Monitoring drinking behaviour and motivation to drink over successive doses of alcohol. Behav. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, R.L.J.; Hammond, L.; Harris, S. Systemic effects of excessive alcohol consumption. Nursing 2023, 53, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, A. Alcohol in the body. BMJ 2005, 330, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaratani, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Douhara, A.; Takaya, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Noguchi, R.; Yoshiji, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Fukui, H. The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 495156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Chao, X.; Ni, H.M.; Ding, W.X. An update on animal models of alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnappa, B.C.; Rubin, E. Modeling alcohol’s effects on organs in animal models. Alcohol Res. Health 2000, 24, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Umulis, D.M.; Gürmen, N.M.; Singh, P.; Fogler, H.S. A physiologically based model for ethanol and acetaldehyde metabolism in human beings. Alcohol 2005, 35, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.F.M.; Barbancho, M. Acetaldehyde detoxification mechanisms in Drosophila melanogaster adults involving aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) and alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) enzymes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 22, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Suh, H.J.; Hong, K.B.; Jung, E.J.; Ahn, Y. Combination of cysteine and glutathione prevents ethanol-induced hangover and liver damage by modulation of Nrf2 signaling in HepG2 cells and mice. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, G.-H.; Hoang, T.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, C.G.; Jo, J.H.; Chung, M.J.; Min, K.; Chae, H.-J. Turmeric extract (Curcuma longa L.) regulates hepatic toxicity in a single ethanol binge rat model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Han, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Wang, Y.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Glutathione and transsulfuration in alcohol-associated tissue injury and carcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1032, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Min, T.; Bai, Y.; He, J.; Cao, H.; Che, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease, focusing on proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilarri, M.I.; Freitas, F.; Costa-Dias, S.; Antunes, C.; Guilhermino, L.; Sousa, R. Associated macrozoobenthos with the invasive Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. J. Sea Res. 2012, 72, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijimatsu, T.; Tatsuguchi, I.; Oda, H.; Mochizuki, S. A freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) extract reduces cholesterol level and hepatic lipids in normal rats and xenobiotics-induced hypercholesterolemic rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3108–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Yen, G.C. Hepatoprotection by freshwater clam extract against CCl4-induced hepatic damage in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Zhong, J.; Wu, N.; Dong, S.; Yang, B.; Liu, D. Antioxidant and anti-tumor activity of a polysaccharide from freshwater clam, Corbicula fluminea. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnain, F.S.; Liao, N.C.; Tsai, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Huang, C.H.; Hsu, J.L.; Wardani, A.K.; Chen, Y.K. Freshwater clam extract attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric damage in vitro and in vivo. Foods 2022, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Lin, B.-C.; Shiao, M.-S.; Pan, B.S. Lipid-lowering and LDL-oxidation inhibitory effects of aqueous extract of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea)—Using tilapia as an animal model. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H148–H154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miszczuk, E.; Bajguz, A.; Kiraga, Ł.; Crowley, K.; Chłopecka, M. Phytosterols and the digestive system: A review study from insights into their potential health benefits and safety. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnain, F.S.; Liao, N.-C.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Hsu, J.-L.; Tsai, P.-J.; Wardani, A.K.; Chen, Y.-K. Protective effect of ethanolic extract of djulis hull on indomethacin-induced gastric injury. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Shih, Y.Y.; Yeh, Y.T.; Huang, C.H.; Liao, C.A.; Hu, C.Y.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Ho, C.T.; Chen, Y.K. Pterostilbene and its derivative 3′-hydroxypterostilbene ameliorated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through synergistic modulation of the gut microbiota and SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4966–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gan, L.Q.; Li, S.K.; Zheng, J.C.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Effects of herbal infusions, tea and carbonated beverages on alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Hsiao, J.-R.; Chen, C.-H. ALDH2 polymorphism and alcohol-related cancers in Asians: A public health perspective. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Y.; Gomelsky, M.; Duan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gomelsky, L.; Zhang, X.; Epstein, P.N.; Ren, J. Overexpression of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) transgene prevents acetaldehyde-induced cell injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Role of ERK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11244–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Chhonker, S.K.; Naik, R.A.; Koiri, R.K. Modulation of antioxidant enzymes, SIRT1 and NF-κB by resveratrol and nicotinamide in alcohol-aflatoxin B1-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermpini, E.E.; Plemenitaš Ilješ, A.; Dolžan, V. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress and the role of antioxidants in alcohol use disorder: A systematic review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.S.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Rocha, S.W.S.; Ribeiro, E.L.; Gomes, F.O.d.S.; e Silva, A.K.S.; Peixoto, C.A. Inhibition of NF-κB activation by diethylcarbamazine prevents alcohol-induced liver injury in C57BL/6 mice. Tissue Cell 2014, 46, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Cheon, Y.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, Y.D.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Jin, S.Y.; et al. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with the progression to cirrhosis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.D.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, T.; Jang, S.A.; Kang, S.C.; Koo, H.J.; Sohn, E.; Bak, J.P.; Namkoong, S.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus protects against alcohol-induced liver damage by modulating inflammatory mediators in mice and HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Jung, E.S.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, D.G.; Ryu, W.S. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abrhaley, A.; Giday, M.; Hailu, A. Challenges and opportunities of translating animal research into human trials in Ethiopia. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf, A. WHO says there’s a critical gap worldwide for SUD treatment. Alcohol. Drug Abus. Wkly. 2024, 36, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, S.; Shiiya, S.; Tokumaru, Y.; Kanda, T. Alanine with the precipitate of tomato juice administered to rats enhances the reduction in blood ethanol levels. J. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 2015, 280781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushida, Y.; Oshima, S.; Aizawa, K.; Suganuma, H.; Nemoto, A.; Ishikiriyama, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Aqueous components of tomato accelerate alcohol metabolism by increasing pyruvate level. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shimazoe, T.; Kobayashi, D.; Kawashiri, T.; Chijimatsu, T.; Umeki, M.; Mochizuki, S. Safety and efficacy of dietary freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) extract in clinical research. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2022, 12, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijimatsu, T.; Yamada, A.; Miyaki, H.; Yoshinaga, T.; Murata, N.; Hata, M.; Abe, K.; Oda, H.; Mochizuki, S. Effect of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) extract on liver function in rats. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol.-Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2008, 55, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Qin, X.; Cao, W.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, Z. Hepatoprotective effect of clam (Corbicula fluminea) protein hydrolysate on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice and partial identification of a hepatoprotective peptide from the hydrolysate. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e61522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, C.J.; Pan, M.H.; Lee, M.F.; Pan, B.S. Hepatoprotective mechanism of freshwater clam extract alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Elucidated in vitro and in vivo models. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 6315–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, R.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, R. Protein-bound polysaccharide from Corbicula fluminea inhibits cell growth in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Natural products for the prevention and treatment of hangover and alcohol use disorder. Molecules 2016, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Jeon, G.; Lee, J.W.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.H. Red ginseng relieves the effects of alcohol consumption and hangover symptoms in healthy men: A randomized crossover study. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Isse, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Baik, H.W.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, M. Effect of Korean pear (Pyruspyrifolia cv. Shingo) juice on hangover severity following alcohol consumption. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.K.; Min, T.S.; Kim, Y.; Yang, S.O.; Kim, H.S.; Hyun, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, H.K. Ameliorating effects of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit on plasma ethanol level in a mouse model assessed with H-NMR based metabolic profiling. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Cui, Z.G.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, D.B. Effects of Asparagus officinalis extracts on liver cell toxicity and ethanol metabolism. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H204–H208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviarasan, S.; Anuradha, C.V. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed polyphenols protect liver from alcohol toxicity: A role on hepatic detoxification system and apoptosis. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Chen, Y.; Ning, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.-K. Proteoglycan isolated from Corbicula fluminea exerts hepato-protective effects against alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J.; Bala, S. Innate immunity and alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30 (Suppl. S1), 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, K.-S.; Choe, W.; Kang, I. Oleic acid reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of iNOS and COX-2 in BV2 murine microglial cells: Possible involvement of reactive oxygen species, p38 MAPK, and IKK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 464, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, P.-Y.; Chiu, I.-C.; Kuan, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-M.; Tseng, K.-C.; Chuang, S.-T.; Tsai, S.-W.; Chen, Y.-K. Aqueous Extract of Freshwater Clam Increases Alcohol Metabolism in Rats in a Preclinical Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111915
Chung P-Y, Chiu I-C, Kuan C-Y, Wu T-M, Tseng K-C, Chuang S-T, Tsai S-W, Chen Y-K. Aqueous Extract of Freshwater Clam Increases Alcohol Metabolism in Rats in a Preclinical Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111915
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Pei-Ying, I-Chen Chiu, Ching-Yi Kuan, Tsung-Meng Wu, Kuo-Chan Tseng, Shu-Ting Chuang, Sen-Wei Tsai, and Yu-Kuo Chen. 2025. "Aqueous Extract of Freshwater Clam Increases Alcohol Metabolism in Rats in a Preclinical Model" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111915
APA StyleChung, P.-Y., Chiu, I.-C., Kuan, C.-Y., Wu, T.-M., Tseng, K.-C., Chuang, S.-T., Tsai, S.-W., & Chen, Y.-K. (2025). Aqueous Extract of Freshwater Clam Increases Alcohol Metabolism in Rats in a Preclinical Model. Nutrients, 17(11), 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111915








