Investigating the Influence of Heavy Metals and Environmental Factors on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Based on Nutrient Intake: Machine Learning Analysis of Data from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Abstract
1. Introduction
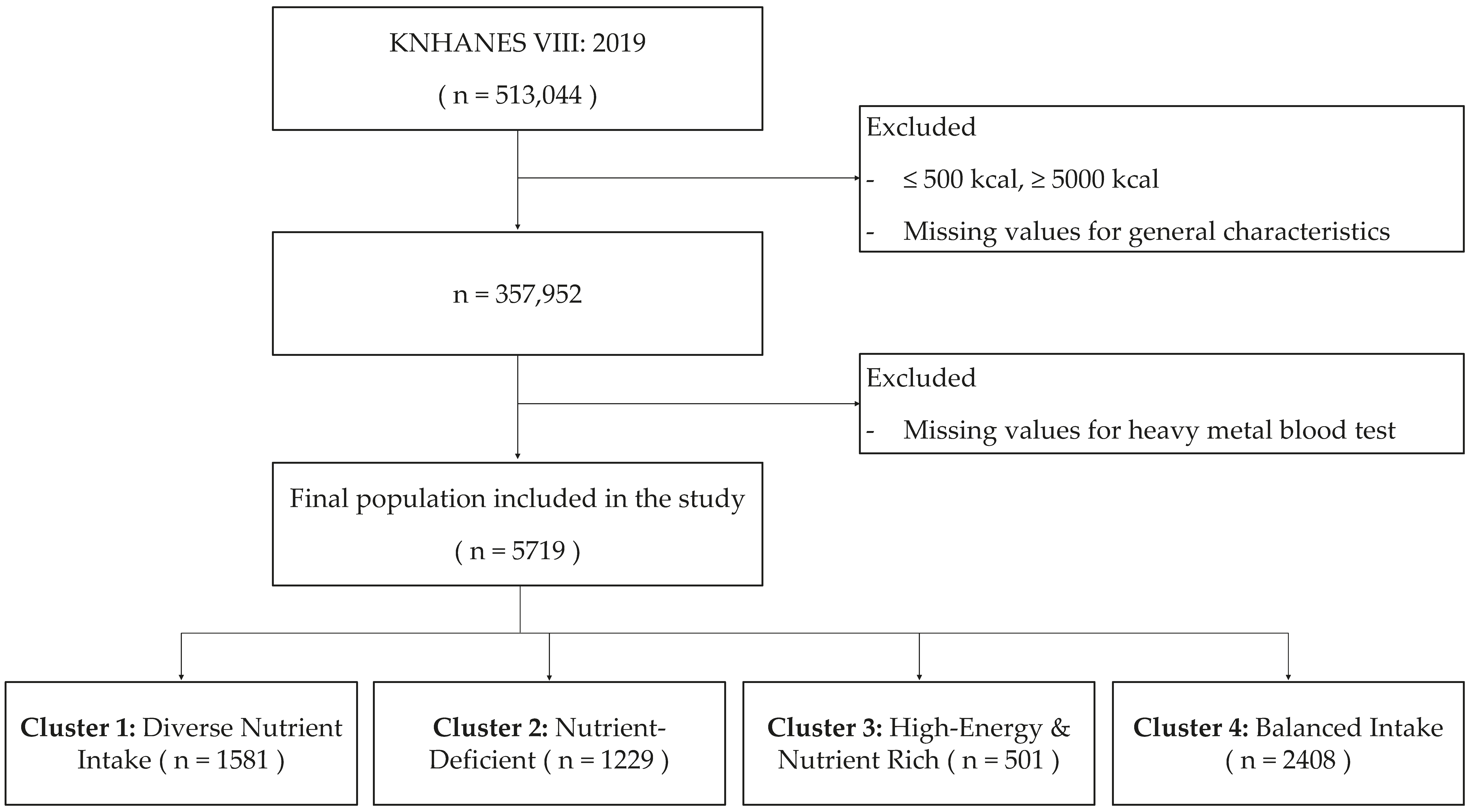
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Machine Learning Approach
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Participants and Their Nutrient Intake Phenotypes
3.2. Characteristics of Heavy Metals and Five Metabolic Syndrome Factors According to Nutrient Intake Level
3.3. Nutrient Intake of Participants across Four Distinct Clusters
3.4. Cluster Characteristics across Nutrient Intake Levels
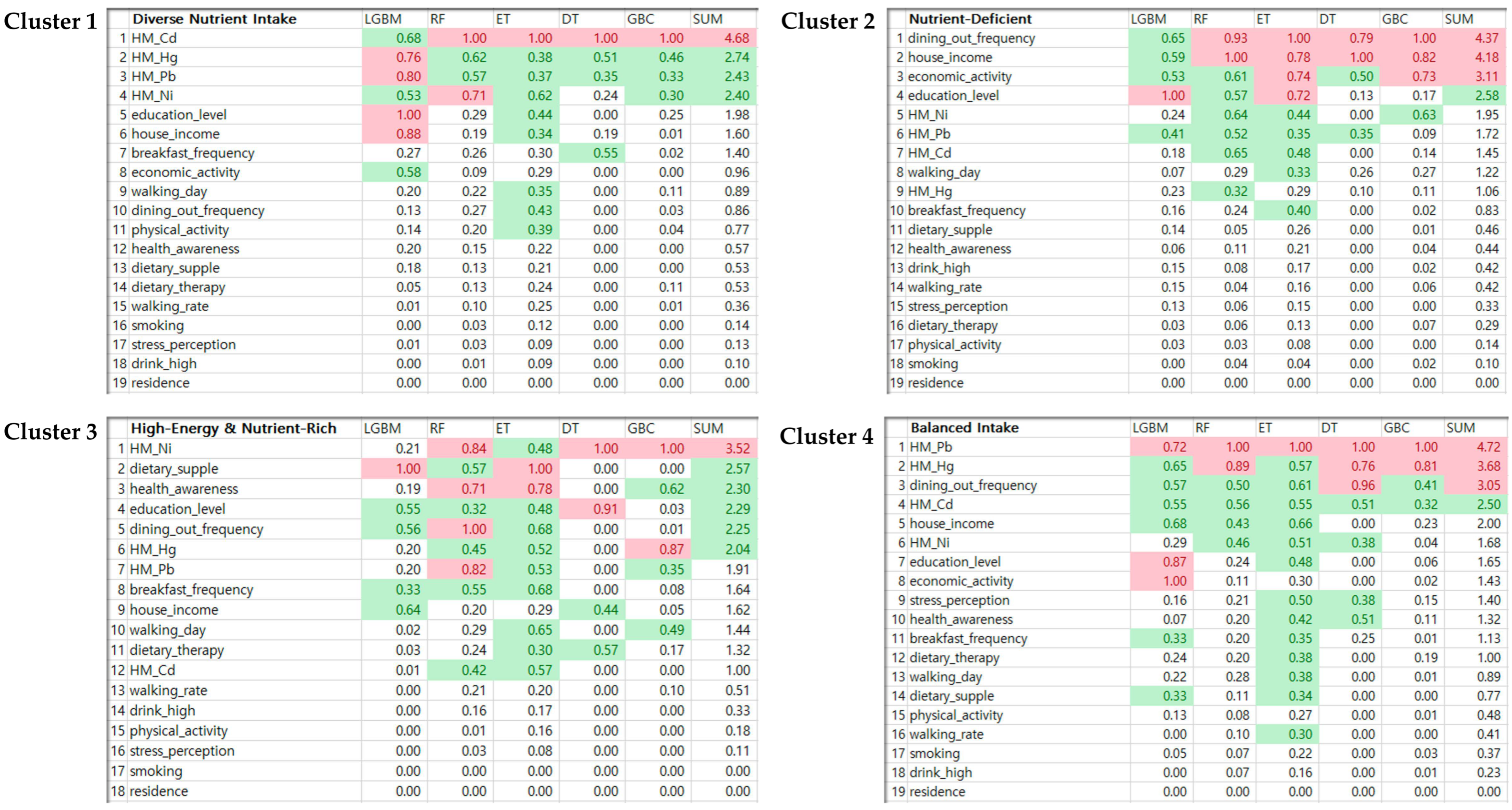
3.5. The Relationship between Various Nutrient Intake Phenotypes and Associated Risk Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Level Cluster Analysis
4.2. Analysis of Risk Factors Related to Metabolic Syndrome Using Machine Learning
4.3. Nutrient and Lifestyle Clustering
4.4. Underlying Themes in Clusters
4.5. Implications for Metabolic Syndrome
4.6. Limitations
4.7. Recommendations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| IS | Importance scores |
| ISMM | Importance Score Mathematical Model |
| KNHANES | Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| SD | Standard deviations |
References
- Li, W.; Chen, D.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Z.; Kwan, M.P.; Tse, L.A. Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e44073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Senapati, S.; Bhattacharya, N.; Bhattacharya, A.; Maurya, S.K.; Husain, H.; Bhatti, J.S.; Pandey, A.K. Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 5840–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovolini, A.; Garcia, J.; Andrade, M.A.; Duarte, J.A. Metabolic Syndrome Pathophysiology and Predisposing Factors. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Shruthi, N.R.; Banerjee, A.; Jothimani, G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. Endothelial dysfunction, platelet hyperactivity, hypertension, and the metabolic syndrome: Molecular insights and combating strategies. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1221438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, S.O.; Islam, M.A.; Musa, K.I.; Shafique, K. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome among Apparently Healthy Adult Population in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2023, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, Z.; Deng, T.; Lou, Q.; Wu, H.; Tang, W.; Xu, F. Association of socioeconomic status with metabolic syndrome and its components among adult population: A community-based cross-sectional study in Nanjing Municipality of China. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e074059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.C.; Ferrer, B.; Tinkov, A.A.; Caito, S.; Deza-Ponzio, R.; Skalny, A.V.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Association between Heavy Metals, Metalloids and Metabolic Syndrome: New Insights and Approaches. Toxics 2023, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gui, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, L.L.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Yuan, T.; et al. Predicting metabolic syndrome by obesity- and lipid-related indices in mid-aged and elderly Chinese: A population-based cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1201132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, D.W.; Lim, J.A.; Choi, B.S.; Shin, H.J.; Yun, S.W.; Yoon, H.J.; et al. Reference levels of blood mercury and association with metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2014, 87, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.A.; Kim, B.; Kim, E.; Kwon, K. Interaction between blood cadmium and lead concentration and physical activity on hypertension from the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey in 2008–2013. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Adair, L.S.; Ng, S.W. Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, Y.P.; Marais, D.; Newlands, D. Where is Nepal in the nutrition transition? Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 26, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biesbroek, S.; Kok, F.J.; Tufford, A.R.; Bloem, M.W.; Darmon, N.; Drewnowski, A.; Fan, S.; Fanzo, J.; Gordon, L.J.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Toward healthy and sustainable diets for the 21st century: Importance of sociocultural and economic considerations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219272120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, J.D.; Namee, B.M.; D’Arcy, A. Fundamentals of Machine Learning for Predictive Data Analytics: Algorithms, Worked Examples, and Case Studies; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Shim, S.; Oh, S. Machine learning-based predictive model for prevention of metabolic syndrome. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Heo, J.H.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, Y. Development of a Metabolic Syndrome Classification and Prediction Model for Koreans Using Deep Learning Technology: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) (2013–2018). Clin. Nutr. Res. 2023, 12, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Mun, S.; Lee, S.; Jeong, K.; Baek, Y. Prediction of metabolic and pre-metabolic syndromes using machine learning models with anthropometric, lifestyle, and biochemical factors from a middle-aged population in Korea. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.; Khang, Y.H.; Oh, K. Data resource profile: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Park, O.; Jeong, E.K. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: Accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol. Health 2021, 43, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S. Additive effect of heavy metals on metabolic syndrome in the Korean population: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2009–2010. Endocrine 2014, 46, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.K.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, Y.; Shin, M.J. Contribution of dietary patterns to blood heavy metal concentrations in Korean adults: Findings from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iglewicz, B.; Hoaglin, D.C. How to Detect and Handle Outliers; A.S.Q.C. Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1993; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Ahern, S.; Earnest, A. Evaluations of statistical methods for outlier detection when benchmarking in clinical registries: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e069130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damigos, G.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Zerva, N.; Pavlopoulos, A.; Chatzikyrkou, K.; Koumenti, A.; Moustakas, K.; Pantos, C.; Mourouzis, I.; Lourbopoulos, A. Machine learning based analysis of stroke lesions on mouse tissue sections. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2022, 42, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangni, E.K.; Huybrechts, B.; Masquelier, J.; Van Hoeck, E. Organisation of Multi-Mycotoxin Proficiency Tests: Evaluation of the Performances of the Laboratories Using the Triple A Rating Approach. Toxins 2021, 13, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabrah, A. An Improved CCF Detector to Handle the Problem of Class Imbalance with Outlier Normalization Using IQR Method. Sensors 2023, 23, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlits, J.; McAfee, S.; Taylor, J.A.; Shum, E.; Yang, Q.; Nunez, E.; Kameron, K.; Fenech, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Torri, A.; et al. Statistical Approaches for Establishing Appropriate Immunogenicity Assay Cut Points: Impact of Sample Distribution, Sample Size, and Outlier Removal. AAPS J. 2023, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuwon, B.I.; Roper, K.; Richardson, A.; Lidbury, B.A. Routine blood test markers for predicting liver disease post HBV infection: Precision pathology and pattern recognition. Diagnosis 2023, 10, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, A.; Saranti, A.; Angerschmid, A.; Finzel, B.; Schmid, U.; Mueller, H. Toward human-level concept learning: Pattern benchmarking for AI algorithms. Patterns 2023, 4, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmaijer, E.S.; Nord, C.L.; Astle, D.E. Statistical power for cluster analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Hawkins, E.; Bathelt, J.; Astle, D.E. Mapping differential responses to cognitive training using machine learning. Dev. Sci. 2020, 23, e12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, H.L.; Wei, M.H.; Song, W.J.; Di, D.S.; Zhang, R.Y.; Wei, S.; Liu, J.A.; Wang, Q. Multiple vitamin co-exposure and mortality risk: A prospective study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, V.M.B.; de Santana, M.L.P.; Fukutani, K.F.; Queiroz, A.T.L.; Arriaga, M.B.; Conceição-Machado, M.E.P.; Silva, R.C.R.; Andrade, B.B. Multidimensional Analysis of Food Consumption Reveals a Unique Dietary Profile Associated with Overweight and Obesity in Adolescents. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S. Building and analyzing machine learning-based warfarin dose prediction models using scikit-learn. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 30, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.K. Identification of Risk Groups for and Factors Affecting Metabolic Syndrome in South Korean Single-Person Households Using Latent Class Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques: Secondary Analysis Study. JMIR Form Res. 2023, 7, e42756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, L.K.; Ard, J.D.; Bailey, R.L.; Bates, M.; Bazzano, L.A.; Boushey, C.J.; Brown, C.; Butera, G.; Callahan, E.H.; de Jesus, J.; et al. Evaluation of Dietary Patterns and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2122277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Li, Y.; Afshin, A.; Springmann, M.; Mozaffarian, D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hu, F.B.; Murray, C.J.L.; Willett, W.C. Global Improvement in Dietary Quality Could Lead to Substantial Reduction in Premature Death. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, R.J.; Horgan, G.; Robinson, E.; Hopkins, M.; Dakin, C.; Finlayson, G. Diet composition and energy intake in humans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.D.; Ragalie-Carr, J.; Torres-Gonzalez, M. Perspective: Seeing the Forest Through the Trees: The Importance of Food Matrix in Diet Quality and Human Health. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehouel, F.; Fowler, S.W. Review of the toxic trace elements arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury in seafood species from Algeria and contiguous waters in the Southwestern Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 3288–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Association of eating habits with health perception and diseases among Chinese physicians: A cross-sectional study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1226672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Jolly, Y.N.; Enyoh, C.E.; Khandaker, M.U.; Hossain, M.B.; Akther, S.; Alsubaie, A.; Almalki, A.S.A.; Bradley, D.A. Levels and health risk assessment of heavy metals in dried fish consumed in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobihah, N.N.; Ahmad Zaharin, A.; Khairul Nizam, M.; Ley Juen, L.; Kyoung-Woong, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in maricultured fish, Lates calcarifer (Barramudi), Lutjanus campechanus (red snapper) and Lutjanus griseus (grey snapper). Chemosphere 2018, 197, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.; Aslam, A.; Sheraz, M.; Ali, B.; Ulhassan, Z.; Najeeb, U.; Zhou, W.; Gill, R.A. Lead Toxicity in Cereals: Mechanistic Insight Into Toxicity, Mode of Action, and Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 587785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noger-Huet, É.; Vagner, M.; Le Grand, F.; Graziano, N.; Bideau, A.; Brault-Favrou, M.; Churlaud, C.; Bustamante, P.; Lacoue-Labarthe, T. Risk and benefit assessment of seafood consumption harvested from the Pertuis Charentais region of France. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; Shen, P.; Lin, H.; Shui, L.; Tang, M.; Jin, M.; Chen, K.; Wang, J. Associations of Diet Quality and Heavy Metals with Obesity in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Nutrients 2022, 14, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.; Webb, P.; Cudhea, F.; Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Reedy, J.; Erndt-Marino, J.; Coates, J.; Mozaffarian, D. Global dietary quality in 185 countries from 1990 to 2018 show wide differences by nation, age, education, and urbanicity. Nat. Food. 2022, 3, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachat, C.; Nago, E.; Verstraeten, R.; Roberfroid, D.; Van Camp, J.; Kolsteren, P. Eating out of home and its association with dietary intake: A systematic review of the evidence. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Rimm, E.B. Fish intake, contaminants, and human health: Evaluating the risks and the benefits. JAMA 2006, 296, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algur, Y.; Rummo, P.E.; McAlexander, T.P.; De Silva, S.S.A.; Lovasi, G.S.; Judd, S.E.; Ryan, V.; Malla, G.; Koyama, A.K.; Lee, D.C.; et al. Assessing the association between food environment and dietary inflammation by community type: A cross-sectional REGARDS study. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2023, 22, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, L.; Sundström, J.; Elmståhl, S.; Dekkers, K.F.; Smith, J.G.; Engström, G.; Fall, T.; Ärnlöv, J. The metabolomic profile associated with clustering of cardiovascular risk factors-A multi-sample evaluation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Qiu, L.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Hu, F.; Zhang, Z. Early prediction of body composition parameters on metabolically unhealthy in the Chinese population via advanced machine learning. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1228300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Jorquera, H.; Cid-Jofré, V.; Landaeta-Díaz, L.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Martorell, M.; Zbinden-Foncea, H.; Ferrari, G.; Jorquera-Aguilera, C.; Cristi-Montero, C. Plant-Based Nutrition: Exploring Health Benefits for Atherosclerosis, Chronic Diseases, and Metabolic Syndrome—A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Nutrient Intake Phenotypes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Cluster 1 (1) | Cluster 2 (2) | Cluster 3 (3) | Cluster 4 (4) | ||||||
| (n = 5719) | (n = 1581) | (n = 1229) | (n = 501) | (n = 2408) | ||||||
| n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | |
| Age (yrs.) (5) | 45.70 ± 16.42 | <0.0001 | 49.40 ± 16.75 | <0.0001 | 44.77 ± 17.19 | <0.0001 | 41.75 ± 14.49 | <0.0001 | 44.56 ± 15.76 | <0.0001 |
| Sex | <0.0001 | 0.0528 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Male | 2254 (39.41%) | 752 (47.56%) | 133 (10.82%) | 443 (88.42%) | 926 (38.46%) | |||||
| Female | 3465 (60.59%) | 829 (52.44%) | 1096 (89.18%) | 58 (11.58%) | 1482 (61.54%) | |||||
| Pb (µg/dL) (5) | 1.56 ± 0.68 | <0.0001 | 1.44 ± 0.85 | <0.0001 | 1.46 ± 0.52 | <0.0001 | 1.82 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 | 1.65 ± 0.67 | <0.0001 |
| Hg (µg/L) (5) | 3.27 ± 2.23 | <0.0001 | 3.16 ± 2.69 | <0.0001 | 2.71 ± 1.92 | <0.0001 | 3.77 ± 1.55 | <0.0001 | 3.53 ± 2.09 | <0.0001 |
| Cd (µg/L) (5) | 0.87 ± 0.56 | <0.0001 | 0.99 ± 0.68 | <0.0001 | 0.84 ± 0.45 | <0.0001 | 0.57 ± 0.51 | <0.0001 | 0.86 ± 0.51 | <0.0001 |
| Ni (µg/L) (5) | 0.33 ± 0.07 | <0.0001 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | <0.0001 | 0.33 ± 0.06 | <0.0001 | 0.30 ± 0.06 | <0.0001 | 0.35 ± 0.07 | <0.0001 |
| Obese | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1194 (20.88%) | 573 (36.24%) | 40 (3.25%) | 298 (59.48%) | 283 (11.75%) | |||||
| No | 4525 (79.12%) | 1008 (63.76%) | 1189 (96.75%) | 203 (40.52%) | 2125 (88.25%) | |||||
| Diabetes | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 646 (11.30%) | 276 (17.46%) | 105 (8.54%) | 158 (31.54%) | 107 (4.44%) | |||||
| No | 5073 (88.70%) | 1305 (82.54%) | 1124 (91.46%) | 343 (68.46%) | 2301 (95.56%) | |||||
| High blood cholesterol | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0006 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1715 (29.99%) | 473 (29.92%) | 293 (23.84%) | 212 (42.32%) | 737 (30.61%) | |||||
| No | 4004 (70.01%) | 1108 (70.08%) | 936 (76.16%) | 289 (57.68%) | 1671 (69.39%) | |||||
| High blood pressure | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0006 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1369 (23.94%) | 293 (18.53%) | 80 (6.51%) | 212 (42.32%) | 784 (32.56%) | |||||
| No | 4350 (76.06%) | 1288 (81.47%) | 1149 (93.49%) | 289 (57.68%) | 1624 (67.44%) | |||||
| High Fasting blood glucose | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 2485 (43.45%) | 1007 (63.69%) | 388 (31.57%) | 331 (66.07%) | 759 (31.52%) | |||||
| No | 3234 (56.55%) | 574 (36.31%) | 841 (68.43%) | 170 (33.93%) | 1649 (68.48%) | |||||
| High blood TG (6) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.8934 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1672 (29.24%) | 413 (26.12%) | 108 (8.79%) | 249 (49.70%) | 902 (37.46%) | |||||
| No | 4047 (70.76%) | 1168 (73.88%) | 1121 (91.21%) | 252 (50.30%) | 1506 (62.54%) | |||||
| Central obesity | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1060 (18.53%) | 321 (20.30%) | 310 (25.22%) | 61 (12.18%) | 368 (15.28%) | |||||
| No | 4659 (81.47%) | 1260 (79.70%) | 919 (74.78%) | 440 (87.82%) | 2040 (84.72%) | |||||
| Low HDL (7) cholesterol | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 989 (17.29%) | 265 (16.76%) | 87 (7.08%) | 61 (12.18%) | 576 (23.92%) | |||||
| No | 4730 (82.71%) | 1316 (83.24%) | 1142 (92.92%) | 440 (87.82%) | 1832 (76.08%) | |||||
| Number of MetS (8) risk factors | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| 0 | 1896 (33.15%) | 233 (14.74%) | 531 (43.21%) | 140 (27.94%) | 992 (41.20%) | |||||
| 1 | 1375 (24.04%) | 561 (35.48%) | 437 (35.56%) | 88 (17.56%) | 289 (12.00%) | |||||
| 2 | 1261 (22.05%) | 623 (39.41%) | 247 (20.10%) | 54 (10.78%) | 337 (14.00%) | |||||
| 3 | 1098 (19.20%) | 164 (10.37%) | 14 (1.14%) | 158 (31.54%) | 762 (31.64%) | |||||
| 4 | 61 (1.07%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 61 (12.18%) | 0 (0.00%) | |||||
| 5 | 28 (0.49%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 28 (1.16%) | |||||
| Heavy drinking | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 627 (10.96%) | 116 (7.34%) | 95 (7.73%) | 84 (16.77%) | 332 (13.79%) | |||||
| No | 5092 (89.04%) | 1465 (92.66%) | 1134 (92.27%) | 417 (83.23%) | 2076 (86.21%) | |||||
| Current smoking | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 653 (11.42%) | 247 (15.62%) | 14 (1.14%) | 0 (0.00%) | 392 (16.28%) | |||||
| No | 5066 (88.58%) | 1334 (84.38%) | 1215 (98.86%) | 501 (100.00%) | 2016 (83.72%) | |||||
| Eating out | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| ≥1 time/d | 1526 (26.68%) | 495 (31.31%) | 374 (30.43%) | 389 (77.64%) | 268 (11.13%) | |||||
| ≥1 time/w | 3113 (54.43%) | 690 (43.64%) | 670 (54.52%) | 54 (10.78%) | 1699 (70.56%) | |||||
| <1 time/w | 1080 (18.88%) | 396 (25.05%) | 185 (15.05%) | 58 (11.58%) | 441 (18.31%) | |||||
| Eating breakfast | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| 5–7 times/w | 3526 (61.65%) | 1093 (69.13%) | 605 (49.23%) | 270 (53.89%) | 1558 (64.70%) | |||||
| 3–4 times/w | 416 (7.27%) | 193 (12.21%) | 56 (4.56%) | 30 (5.99%) | 137 (5.69%) | |||||
| 1–2 times/w | 789 (13.80%) | 39 (2.47%) | 355 (28.89%) | 67 (13.37%) | 328 (13.62%) | |||||
| 0 times/w | 988 (17.28%) | 256 (16.19%) | 213 (17.33%) | 134 (26.75%) | 385 (15.99%) | |||||
| Diet therapy | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1550 (27.10%) | 559 (35.56%) | 119 (9.68%) | 188 (37.52%) | 684 (28.41%) | |||||
| No | 4169 (72.90%) | 1022 (64.64%) | 1110 (90.32%) | 313 (62.48%) | 1724 (71.59%) | |||||
| Eating dietary supplements in a year | <0.0001 | 0.5974 | <0.0001 | 0.6876 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 3331 (58.24%) | 801 (50.66%) | 483 (39.30%) | 246 (49.10%) | 1801 (74.79%) | |||||
| No | 2388 (41.76%) | 780 (49.34%) | 746 (60.70%) | 255 (50.90%) | 607 (25.21%) | |||||
| Self-reported health status | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0049 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Good | 2100 (36.72%) | 1035 (65.46%) | 239 (19.45%) | 282 (56.29%) | 544 (22.59%) | |||||
| Average or poor | 3619 (63.28%) | 546 (34.54%) | 990 (80.55%) | 219 (43.71%) | 1864 (77.41%) | |||||
| Education level | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0814 | <0.0001 | |||||
| High school or lower | 3225 (56.39%) | 1166 (73.75%) | 696 (56.63%) | 270 (53.89%) | 1093 (45.39%) | |||||
| College or higher | 2494 (43.61%) | 415 (26.25%) | 533 (43.37%) | 231 (46.11%) | 1315 (54.61%) | |||||
| Household income level | <0.0001 | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Low or mid-low | 1636 (28.61%) | 557 (35.23%) | 494 (40.20%) | 67 (13.37%) | 518 (21.51%) | |||||
| Mid-high | 2349 (41.07%) | 457 (28.91%) | 482 (39.22%) | 373 (74.45%) | 1037 (43.06%) | |||||
| High | 1734 (30.32%) | 567 (35.86%) | 253 (20.59%) | 61 (12.18%) | 853 (35.42%) | |||||
| Economic activity | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 3728 (65.19%) | 1121 (70.90%) | 710 (57.77%) | 417 (83.23%) | 1480 (61.46%) | |||||
| No | 1991 (34.81%) | 460 (29.10%) | 519 (42.23%) | 84 (16.77%) | 928 (38.54%) | |||||
| Stress awareness | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Low | 4430 (77.46%) | 1399 (88.49%) | 865 (70.38%) | 434 (86.63%) | 1732 (71.93%) | |||||
| High | 1289 (22.54%) | 182 (11.51%) | 364 (29.62%) | 67 (13.37%) | 676 (28.07%) | |||||
| Walking | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0035 | |||||
| <5 days | 2085 (36.46%) | 325 (20.56%) | 768 (62.49%) | 61 (12.18%) | 931 (38.66%) | |||||
| ≥5 days | 3634 (63.54%) | 1256 (79.44%) | 461 (37.51%) | 440 (87.82%) | 1477 (61.34%) | |||||
| Moderate intensity physical activity | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Yes | 1628 (28.47%) | 497 (31.44%) | 131 (10.66%) | 67 (13.37%) | 933 (38.75%) | |||||
| No | 4091 (71.53%) | 1084 (68.56%) | 1098 (89.34%) | 434 (86.63%) | 1475 (61.25%) | |||||
| Physical activity | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| <5 days, 30 min | 2337 (40.86%) | 445 (28.15%) | 830 (67.53%) | 61 (12.18%) | 1001 (41.57%) | |||||
| ≥5 days, 30 min | 3382 (59.14%) | 1136 (71.85%) | 399 (32.47%) | 440 (87.82%) | 1407 (58.43%) | |||||
| Variables | Nutrient Intake Phenotypes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Cluster 1 (1) | Cluster 2 (2) | Cluster 3 (3) | Cluster 4 (4) | ||||||
| (n = 5719) | (n = 1581) | (n = 1229) | (n = 501) | (n = 2408) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | |
| Energy | 1942.76 ± 635.85 | <0.0001 | 2281.31 ± 362.45 | <0.0001 | 1235.07 ± 330.48 | <0.0001 | 3165.82 ± 421.43 | <0.0001 | 1827.21 ± 354.82 | <0.0001 |
| Water | 1024.28 ± 425.29 | <0.0001 | 1318.92 ± 352.61 | <0.0001 | 633.97 ± 287.14 | <0.0001 | 1523.31 ± 258.77 | <0.0001 | 926.22 ± 309.54 | <0.0001 |
| Carbohydrate | 293.73 ± 98.81 | <0.0001 | 342.17 ± 87.59 | <0.0001 | 207.24 ± 65.99 | <0.0001 | 389.02 ± 100.92 | <0.0001 | 286.24 ± 80.70 | <0.0001 |
| Protein | 73.14 ± 29.63 | <0.0001 | 85.89 ± 13.58 | <0.0001 | 43.36 ± 14.51 | <0.0001 | 139.21 ± 29.91 | <0.0001 | 66.21 ± 12.46 | <0.0001 |
| Fat | 47.97 ± 25.71 | <0.0001 | 63.33 ± 17.52 | <0.0001 | 23.94 ± 10.94 | <0.0001 | 94.22 ± 24.50 | <0.0001 | 40.53 ± 15.26 | <0.0001 |
| SFA | 15.19 ± 8.73 | <0.0001 | 20.90 ± 7.97 | <0.0001 | 7.73 ± 5.42 | <0.0001 | 25.00 ± 9.84 | <0.0001 | 13.21 ± 5.51 | <0.0001 |
| MUFA | 15.23 ± 9.00 | <0.0001 | 19.35 ± 5.93 | <0.0001 | 7.87 ± 4.23 | <0.0001 | 34.01 ± 8.12 | <0.0001 | 12.38 ± 5.13 | <0.0001 |
| PUFA | 12.82 ± 8.61 | <0.0001 | 16.34 ± 5.83 | <0.0001 | 6.00 ± 2.60 | <0.0001 | 28.00 ± 14.41 | <0.0001 | 10.82 ± 4.82 | <0.0001 |
| N3 | 2.00 ± 1.56 | <0.0001 | 2.45 ± 1.86 | <0.0001 | 1.07 ± 0.64 | <0.0001 | 3.76 ± 2.03 | <0.0001 | 1.81 ± 1.08 | <0.0001 |
| N6 | 10.78 ± 7.67 | <0.0001 | 13.82 ± 5.31 | <0.0001 | 4.88 ± 2.31 | <0.0001 | 24.30 ± 12.88 | <0.0001 | 8.99 ± 4.34 | <0.0001 |
| Cholesterol | 257.30 ± 197.97 | <0.0001 | 357.41 ± 236.22 | <0.0001 | 120.44 ± 87.06 | <0.0001 | 356.83 ± 121.84 | <0.0001 | 240.72 ± 176.18 | <0.0001 |
| Fiber | 26.13 ± 10.87 | <0.0001 | 33.71 ± 9.20 | <0.0001 | 15.33 ± 4.73 | <0.0001 | 43.26 ± 9.20 | <0.0001 | 23.10 ± 5.33 | <0.0001 |
| Sugar | 63.20 ± 36.52 | <0.0001 | 85.82 ± 40.13 | <0.0001 | 40.01 ± 24.30 | <0.0001 | 84.06 ± 37.56 | <0.0001 | 55.85 ± 27.60 | <0.0001 |
| Calcium | 558.13 ± 267.47 | <0.0001 | 833.62 ± 241.88 | <0.0001 | 297.38 ± 151.46 | <0.0001 | 681.87 ± 153.30 | <0.0001 | 484.59 ± 147.62 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphate | 1121.26 ± 399.43 | <0.0001 | 1426.54 ± 194.93 | <0.0001 | 652.43 ± 167.82 | <0.0001 | 1843.68 ± 371.05 | <0.0001 | 1009.82 ± 128.86 | <0.0001 |
| Iron | 11.85 ± 4.29 | <0.0001 | 14.29 ± 3.47 | <0.0001 | 6.88 ± 2.69 | <0.0001 | 17.27 ± 2.84 | <0.0001 | 11.66 ± 2.79 | <0.0001 |
| Sodium | 3014.86 ± 1237.48 | <0.0001 | 3696.46 ± 1144.95 | <0.0001 | 2091.83 ± 1133.90 | <0.0001 | 4232.85 ± 923.76 | <0.0001 | 2785.04 ± 917.79 | <0.0001 |
| Potassium | 2992.26 ± 1120.88 | <0.0001 | 3826.90 ± 913.52 | <0.0001 | 1778.61 ± 481.10 | <0.0001 | 4501.70 ± 1241.59 | <0.0001 | 2749.64 ± 505.69 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin A | 389.98 ± 214.61 | <0.0001 | 508.49 ± 193.15 | <0.0001 | 205.77 ± 119.16 | <0.0001 | 633.34 ± 230.26 | <0.0001 | 355.54 ± 163.11 | <0.0001 |
| Carotene | 3135.18 ± 1994.79 | <0.0001 | 3594.08 ± 1749.21 | <0.0001 | 1704.95 ± 1180.96 | <0.0001 | 5729.98 ± 2428.39 | <0.0001 | 3023.99 ± 1706.27 | <0.0001 |
| Retinol | 127.94 ± 139.69 | <0.0001 | 208.98 ± 206.79 | <0.0001 | 63.69 ± 51.62 | <0.0001 | 155.85 ± 98.71 | <0.0001 | 101.70 ± 87.37 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin B1 | 1.35 ± 0.70 | <0.0001 | 1.58 ± 0.47 | <0.0001 | 0.77 ± 0.34 | <0.0001 | 2.45 ± 1.22 | <0.0001 | 1.28 ± 0.42 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.59 ± 0.68 | <0.0001 | 2.17 ± 0.42 | <0.0001 | 0.82 ± 0.25 | <0.0001 | 2.72 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 | 1.36 ± 0.31 | <0.0001 |
| Niacin | 14.59 ± 7.01 | <0.0001 | 16.59 ± 5.33 | <0.0001 | 8.61 ± 3.84 | <0.0001 | 29.21 ± 6.70 | <0.0001 | 13.28 ± 3.78 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin C | 74.75 ± 69.55 | <0.0001 | 113.04 ± 78.15 | <0.0001 | 37.36 ± 22.52 | <0.0001 | 110.96 ± 71.90 | <0.0001 | 61.16 ± 63.35 | <0.0001 |
| Variables | Nutrient Intake Phenotypes | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Cluster 1 (1) | Cluster 2 (2) | Cluster 3 (3) | Cluster 4 (4) | ||||||||||||||||
| (n = 5719) | (n = 1581) | (n = 1229) | (n = 501) | (n = 2408) | ||||||||||||||||
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |||||||||||
| Pb (µg/dL) | 3.388 | 3.140 | 3.657 | <0.0001 | 2.053 | 1.826 | 2.307 | <0.0001 | 3.171 | 2.565 | 3.919 | <0.0001 | 47.081 | 23.867 | 92.874 | <0.0001 | 6.047 | 5.294 | 6.907 | <0.0001 |
| Hg (µg/L) | 1.23 | 1.203 | 1.257 | <0.0001 | 1.144 | 1.104 | 1.185 | <0.0001 | 0.867 | 0.819 | 0.918 | <0.0001 | 1.755 | 1.567 | 1.964 | <0.0001 | 1.464 | 1.407 | 1.523 | <0.0001 |
| Cd (µg/L) | 1.03 | 0.948 | 1.119 | 0.4875 | 2.149 | 1.867 | 2.474 | <0.0001 | 1.388 | 1.099 | 1.752 | 0.0059 | 1.705 | 1.249 | 2.327 | 0.0008 | 0.56 | 0.483 | 0.650 | <0.0001 |
| Ni (µg/L) | 0.087 | 0.046 | 0.165 | <0.0001 | 0.734 | 0.263 | 2.048 | 0.5546 | - | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 | 0.034 | 0.012 | 0.100 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Heavy drinking | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.2614 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| Yes | 2.680 | 2.306 | 3.116 | 2.307 | 1.618 | 3.288 | 2.771 | 1.878 | 4.087 | 0.786 | 0.516 | 1.196 | 3.673 | 2.934 | 4.597 | |||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Current smoking | <0.0001 | 0.0939 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 2.367 | 2.043 | 2.742 | 1.238 | 0.964 | 1.590 | - | - | 2.712 | 2.213 | 3.325 | |||||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Eating out | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3581 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| ≥1 time/d | 0.349 | 0.303 | 0.402 | 0.377 | 0.292 | 0.486 | 0.068 | 0.046 | 0.101 | 2.085 | 1.263 | 3.443 | 0.12 | 0.089 | 0.162 | |||||
| ≥1 time/w | 0.393 | 0.346 | 0.445 | 0.175 | 0.137 | 0.224 | 1.312 | 0.968 | 1.777 | 1.859 | 0.953 | 3.626 | 0.213 | 0.172 | 0.262 | |||||
| <1 time/w | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Eating breakfast | 0.0354 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.9332 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| 5–7 times/w | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 3–4 times/w | 1.151 | 0.960 | 1.380 | 2.73 | 2.034 | 3.664 | 19.105 | 9.568 | 38.15 | 0.255 | 0.128 | 0.508 | 0.532 | 0.385 | 0.737 | |||||
| 1–2 times/w | 0.329 | 0.284 | 0.380 | 0.586 | 0.325 | 1.058 | 0.39 | 0.303 | 0.502 | - | 0.446 | 0.356 | 0.558 | |||||||
| 0 times/w | 0.625 | 0.550 | 0.710 | 19.905 | 14.52 | 27.288 | 0.079 | 0.053 | 0.117 | 0.461 | 0.317 | 0.671 | 0.37 | 0.298 | 0.459 | |||||
| Diet therapy | 0.0472 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.7242 | 0.0097 | |||||||||||||||
| Yes | 1.112 | 1.001 | 1.234 | 0.415 | 0.342 | 0.503 | 3.589 | 2.515 | 5.123 | 1.06 | 0.767 | 1.465 | 1.238 | 1.053 | 1.456 | |||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Eating dietary supplements in a year | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0247 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| Yes | 1.486 | 1.351 | 1.634 | 0.266 | 0.219 | 0.323 | 0.782 | 0.632 | 0.969 | 3.684 | 2.647 | 5.127 | 3.921 | 3.254 | 4.724 | |||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Self-reported health status | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Good | 1 | 0.7804 | 1 | <0.0001 | 1 | 0.3500 | 1 | 1 | 0.0008 | |||||||||||
| Average or poor | 1.014 | 0.921 | 1.117 | 0.502 | 0.414 | 0.609 | 0.883 | 0.679 | 1.147 | - | 1.354 | 1.135 | 1.616 | |||||||
| Education level | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0038 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| High school or lower | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| College or higher | 0.528 | 0.48 | 0.581 | 0.294 | 0.237 | 0.364 | 0.118 | 0.092 | 0.151 | 1.596 | 1.164 | 2.190 | 0.619 | 0.534 | 0.717 | |||||
| Household income level | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||
| Low or mid-low | 1 | <0.0001 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Mid-high | 0.447 | 0.399 | 0.502 | 0.469 | 0.371 | 0.592 | 0.048 | 0.035 | 0.065 | - | 0.380 | 0.312 | 0.464 | |||||||
| High | 0.992 | 0.879 | 1.119 | 0.172 | 0.137 | 0.218 | 0.094 | 0.068 | 0.131 | - | 1.776 | 1.454 | 2.170 | |||||||
| Economic activity | 0.1310 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.2614 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| Yes | 1.078 | 0.978 | 1.189 | 3.312 | 2.681 | 4.092 | 2.863 | 2.305 | 3.556 | 0.786 | 0.516 | 1.196 | 0.712 | 0.612 | 0.828 | |||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Stress awareness | 0.0274 | 0.6566 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||
| Low | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| High | 1.133 | 1.014 | 1.266 | 1.066 | 0.803 | 1.416 | 0.520 | 0.411 | 0.657 | - | 2.847 | 2.409 | 3.365 | |||||||
| Walking | 0.0225 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||
| <5 days | 0.894 | 0.811 | 0.984 | 0.222 | 0.175 | 0.282 | 1.777 | 1.427 | 2.212 | - | 1.531 | 1.317 | 1.780 | |||||||
| ≥5 days | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Moderate intensity physical activity | 0.0092 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 0.872 | 0.786 | 0.967 | 2.144 | 1.756 | 2.619 | 0.295 | 0.201 | 0.433 | - | 0.736 | 0.633 | 0.856 | |||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical activity | 0.0214 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||
| <5 days, 30 min | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| ≥5 days, 30 min | 1.118 | 1.017 | 1.229 | 3.813 | 3.083 | 4.716 | 0.433 | 0.343 | 0.545 | - | 0.681 | 0.587 | 0.790 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Choi, Y.-J. Investigating the Influence of Heavy Metals and Environmental Factors on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Based on Nutrient Intake: Machine Learning Analysis of Data from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Nutrients 2024, 16, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050724
Jeong S, Choi Y-J. Investigating the Influence of Heavy Metals and Environmental Factors on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Based on Nutrient Intake: Machine Learning Analysis of Data from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050724
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Seungpil, and Yean-Jung Choi. 2024. "Investigating the Influence of Heavy Metals and Environmental Factors on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Based on Nutrient Intake: Machine Learning Analysis of Data from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050724
APA StyleJeong, S., & Choi, Y.-J. (2024). Investigating the Influence of Heavy Metals and Environmental Factors on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Based on Nutrient Intake: Machine Learning Analysis of Data from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Nutrients, 16(5), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050724





