Relationship between Eating Alone and Handgrip Strength in Korean Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Eating Alone and Dietary Assessment
2.3. Handgrip Strength, Relative Handgrip Strength, and Dynapenia
2.4. Other Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics According to the Frequency of Eating Alone
3.2. Grip Strength According to the Frequency of Eating Alone by Sex
3.3. Dietary Intake According to the Frequency of Eating Alone in Men
3.4. Dietary Intake According to the Frequency of Eating Alone among Women
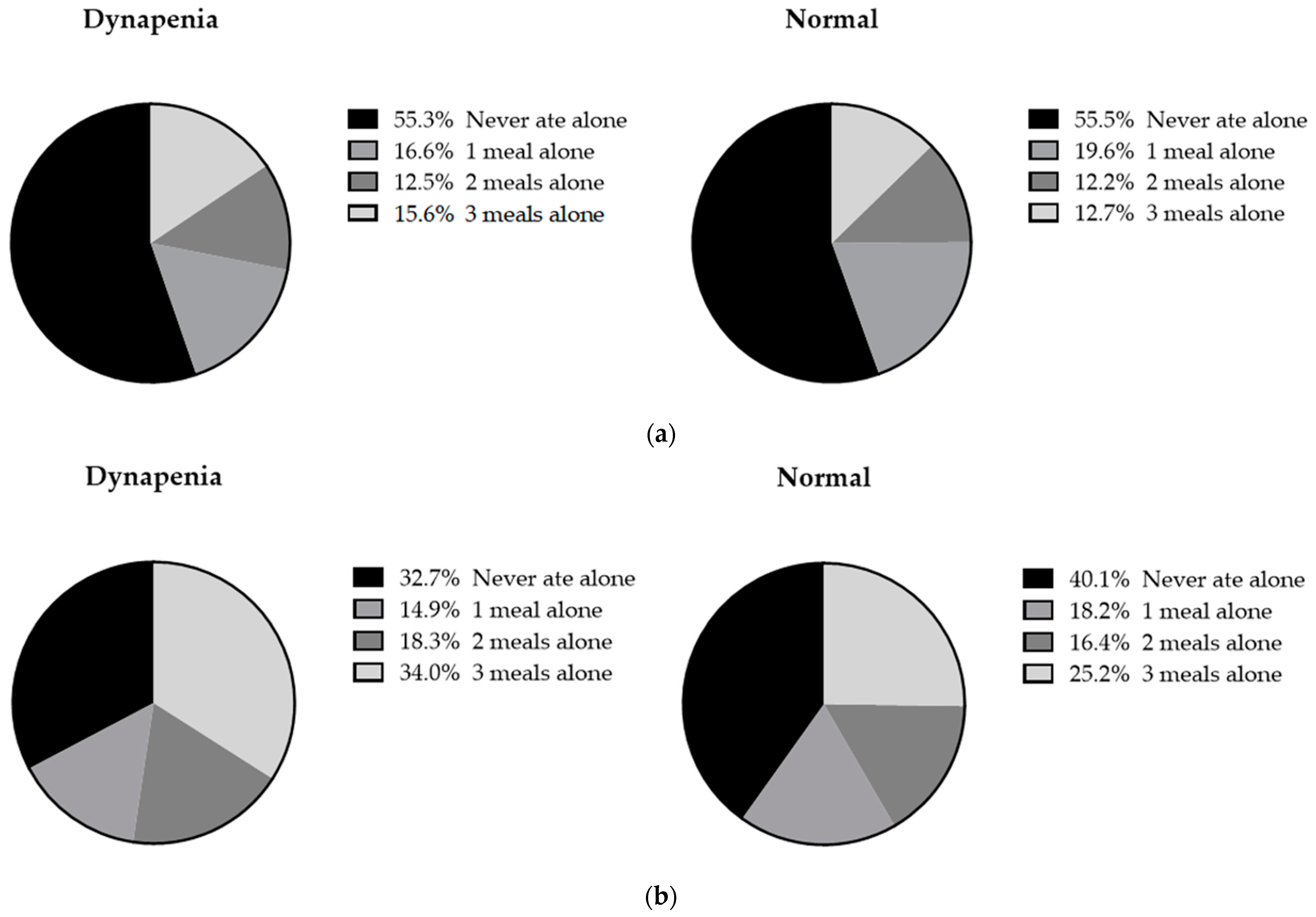
3.5. The Proportion of Eating Alone among Participants with Dynapenia
3.6. Multivariable Analysis of the Association between Eating Alone and Dynapenia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistic Korea. Aging Statics. 2023. Available online: https://kostat.go.kr (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism 2023, 144, 155533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Morley, J.E. Sarcopenia Is Recognized as an Independent Condition by an International Classification of Disease, tenth revision, clinical modification (ICD-10-CM) Code. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, T.M.; Clark, B.C. Dynapenia and aging: An update. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, H.; Cao, L.; Yuan, S.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia: Findings from a Chinese community-dwelling old adults cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Lee, W.J.; Peng, L.N.; Liu, L.K.; Arai, H.; Akishita, M. Recent advances in sarcopenia research in Asia: 2016 update from the Asian working group for sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 767.e1–767.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.D.; Duchowny, K.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. Low normalized grip strength is a biomarker for cardiometabolic disease and physical disabilities among U.S. and Chinese adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Grip strength: An indispensable biomarker for older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.Y.; Huang, K.S.; Chen, K.M.; Chou, C.P.; Tu, Y.K. Exercise, nutrition, and combined exercise and nutrition in older adults with sarcopenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Maturitas 2021, 145, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Santos, A.R.; Afonso, C.; Borges, N.; Santos, A.; Padrão, P.; Moreira, P.; Amaral, T.F. Factors associated with sarcopenia and undernutrition in older adults. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 76, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnwall, A.; Mattsson Sydner, Y.; Koochek, A.; Neuman, N. Eating alone or together among community-living older people-A scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, R.; Kawai, H.; Suzuki, H.; Kim, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Hirano, H.; Ihara, K.; Obuchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y. Association of eating alone with depression among older adults living alone: Role of poor social networks. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.M.; Han, J.; Roh, Y.K.; Song, H.J. Eating alone and cognitive decline in Korean older adults: A 3-year prospective study. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2021, 25, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.J. Association between eating alone and cardiovascular diseases in elderly women: A cross-sectional study of KNHANES 2016 data. Menopause 2021, 29, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Shin, H.E.; Kim, M.; Won, C.W.; Song, Y.M. Longitudinal association between eating alone and deterioration in frailty status: The Korean frailty and aging cohort study. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Tomiyama, N.; Ochi, A.; Hayashi, H. Eating alone and weight change in community-dwelling older adults during the coronavirus pandemic: A longitudinal study. Nutrition 2022, 102, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, H.; Michaud, M.; Neuman, N. What Is Commensality? A Critical Discussion of an Expanding Research Field. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, Y.; Kondo, N.; Takagi, D.; Saito, M.; Hikichi, H.; Ojima, T.; Kondo, K. Combined effects of eating alone and living alone on unhealthy dietary behaviors, obesity and underweight in older Japanese adults: Results of the JAGES. Appetite 2015, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, W.; Ju, Y.J.; Shin, J.; Jang, S.I.; Park, E.C. Association between eating behaviour and diet quality: Eating alone vs. eating with others. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Maeda, K.; Satake, S.; Matsui, Y.; Arai, H. Osteosarcopenia, the co-existence of osteoporosis and sarcopenia, is associated with social frailty in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, S.; Lee, J.E.; Oh, K.; Shim, J.; Kweon, S.; Paik, H.Y.; Joung, H. Reproducibility and validity of an FFQ developed for the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Min, J.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Yang, H.I.; Park, J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Park, I.; et al. Development of the Korean Global Physical Activity Questionnaire: Reliability and validity study. Glob. Health Promot. 2020, 27, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Merchant, R.A.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Aprahamian, I.; Arai, H.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Bernabei, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 824–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Rajaguru, V.; Kim, B.; Jang, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, T.H. Association of behavior pattern with overweight and obesity in South Korean adults-A multi correspondence analysis (KNHANES-2018-2020). PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0002384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahyoun, N.R.; Jacques, P.F.; Dallal, G.E.; Russell, R.M. Nutrition screening initiative checklist may be a better awareness/educational tool than a screening one. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1997, 97, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthutvoravut, U.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, K.; Akishita, M.; Iijima, K. Living with family yet eating alone is associated with frailty in community-dwelling older adults: The Kashiwa study. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, Y.; Motokawa, K.; Shirobe, M.; Edahiro, A.; Ohara, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Kim, H.; et al. Relationship between eating alone and poor appetite using the simplified nutritional appetite questionnaire. Nutrients 2022, 14, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinugawa, A.; Kusama, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kiuchi, S.; Nakazawa, N.; Kondo, K.; Osaka, K.; Aida, J. Association of poor dental status with eating alone: A cross-sectional Japan gerontological evaluation study among independent older adults. Appetite 2022, 168, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, Y.; Motokawa, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Shirobe, M.; Inagaki, H.; Motohashi, Y.; Edahiro, A.; Hirano, H.; Kitamura, A.; Awata, S.; et al. Association of eating alone with oral frailty among community-dwelling older adults in Japan. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 87, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, I.; Kitamura, A.; Seino, S.; Nishi, M.; Tomine, Y.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Narita, M.; Shinkai, S. Relationship between eating alone and dietary variety among urban older Japanese adults. [Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi] Jpn. J. Public Health 2018, 65, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Hong, K.H.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, S. How does the frequency of eating-alone among older people in Korea affect their health and dietary behavior? Nutrients 2023, 15, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C.; Youssef, J. Aging and the (Chemical) Senses: Implications for Food Behaviour Amongst Elderly Consumers. Foods 2021, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, T.; Owen, A.J.; McCaffrey, T.A. Past, present and future influences of diet among older adults—A scoping review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Pan, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. Effects of fish oil-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on body composition, muscle strength and physical performance in older people: A secondary analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, P.T.; Zeng, B.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Liao, Y.C.; Stubbs, B.; Kuo, J.S.; Sun, C.K.; Cheng, Y.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in sarcopenia management: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 90, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy, A.; Nieves, J.W. Nutrition and Sarcopenia-What Do We Know? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Chen, M.; Gray, S.R.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Factors associated with sarcopenia: A cross-sectional analysis using UK Biobank. Maturitas 2020, 133, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, A.A.; Jennings, A.; Kelaiditi, E.; Skinner, J.; Steves, C.J. Cross-Sectional Associations Between Dietary Antioxidant Vitamins C, E and Carotenoid Intakes and Sarcopenic Indices in Women Aged 18-79 Years. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstgeest, L.E.M.; Schaap, L.A.; Heymans, M.W.; Hengeveld, L.M.; Naumann, E.; Houston, D.K.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Simonsick, E.M.; Newman, A.B.; Farsijani, S.; et al. Sex-and race-specific associations of protein intake with change in muscle mass and physical function in older adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiol, A.N.; von Hurst, P.R.; Conlon, C.A.; Beck, K.L. Associations of protein intake, sources and distribution on muscle strength in community-dwelling older adults living in Auckland, New Zealand. J. Nutr. Sci. 2023, 12, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Haseda, M.; Kondo, K.; Kondo, N. Eating alone and depression in older men and women by cohabitation status: The JAGES longitudinal survey. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Wada, T.; Okumiya, K.; Ishimoto, Y.; Fukutomi, E.; Kasahara, Y.; Chen, W.; Sakamoto, R.; Fujisawa, M.; Otsuka, K.; et al. Eating alone among community-dwelling Japanese elderly: Association with depression and food diversity. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tsuji, T.; Ide, K.; Nakagomi, A.; Ling, L.; Kondo, K. Does eating with others promote happiness among older adults living alone? A 3-year longitudinal study of the Japan gerontological evaluation study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 38, e6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.M.; Park, Y.S. Handgrip strength, dynapenia, and mental health in older Koreans. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damluji, A.A.; Alfaraidhy, M.; AlHajri, N.; Rohant, N.N.; Kumar, M.; Al Malouf, C.; Bahrainy, S.; Ji Kwak, M.; Batchelor, W.B.; Forman, D.E.; et al. Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases. Circulation 2023, 147, 1534–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Never Ate Alone | 1 Meal Alone | 2 Meals Alone | 3 Meals Alone | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 3455) | (n = 1261) | (n = 974) | (n = 1588) | ||
| Age | <0.001 | ||||
| 65–74 | 59.9% (1.1%) | 70.1% (1.5%) | 64.7% (1.8%) | 50.8% (1.5%) | |
| ≥75 | 40.1% (1.1%) | 29.9% (1.5%) | 35.3% (1.8%) | 49.2% (1.5%) | |
| Male | 56.5% (0.7%) | 49.5% (1.6%) | 38.9% (1.8%) | 29.7% (1.4%) | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.211 | ||||
| <18.5 | 2.9% (0.3%) | 2.9% (0.6%) | 2.1% (0.4%) | 3.3% (0.6%) | |
| 18.5–24.9 | 63.0% (0.9%) | 62.9% (1.6%) | 59.7% (1.9%) | 59.8% (1.5%) | |
| ≥25 | 34.1% (0.9%) | 34.2% (1.5%) | 38.2% (1.9%) | 36.9% (1.5%) | |
| Education attainment | <0.001 | ||||
| Less than elementary school | 51.6% (1.2%) | 50.2% (1.8%) | 58.2% (2.0%) | 69.2% (1.5%) | |
| Middle school | 14.1% (0.7%) | 17.4% (1.3%) | 15.7% (1.4%) | 13.1% (1.1%) | |
| High school | 20.8% (0.9%) | 19.8% (1.3%) | 17.2% (1.6%) | 11.6% (1.0%) | |
| College and higher | 13.5% (0.9%) | 12.5% (1.2%) | 8.9% (1.1%) | 6.1% (0.8%) | |
| Household income | <0.001 | ||||
| Low | 42.0% (1.3%) | 33.3% (1.7%) | 40.9% (2.0%) | 63.1% (1.5%) | |
| Lower middle | 28.6% (1.1%) | 31.3% (1.5%) | 27.9% (1.7%) | 20.9% (1.2%) | |
| Upper middle | 17.0% (1.0%) | 20.8% (1.5%) | 18.4% (1.5%) | 10.1% (1.0%) | |
| High | 12.4% (0.9%) | 14.6% (1.4%) | 12.8% (1.4%) | 5.9% (0.8%) | |
| Marital status (married) | 99.9% (0.1%) | 99.9% (0.1%) | 99.0% (0.3%) | 98.5% (0.3%) | <0.001 |
| Smoking | <0.001 | ||||
| Never smoker | 55.5% (0.9%) | 59.7% (1.6%) | 66.2% (1.9%) | 70.5% (1.4%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 36.0% (0.8%) | 32.2% (1.5%) | 23.2% (1.6%) | 21.0% (1.2%) | |
| Current smoker | 8.5% (0.5%) | 8.1% (0.9%) | 10.6% (1.2%) | 8.5% (0.9%) | |
| Alcohol drinking | 41.2% (1.0%) | 39.2% (1.6%) | 35.4% (1.9%) | 28.8% (1.4%) | <0.001 |
| Physical exercise | |||||
| Resistance exercise | 22.3% (0.9%) | 23.1% (1.5%) | 20.9% (1.6%) | 12.9% (1.0%) | <0.001 |
| Aerobic exercise | 35.5% (1.1%) | 36.6% (1.7%) | 37.0% (1.9%) | 27.4% (1.3%) | <0.001 |
| Multimorbidity | <0.001 | ||||
| ≥3 | 19.5% (0.8%) | 19.5% (1.3%) | 23.3% (1.7%) | 24.6% (1.3%) | |
| 1–2 | 56.8% (1.0%) | 57.2% (1.6%) | 53.3% (1.9%) | 57.7% (1.4%) | |
| 0 | 23.7% (0.8%) | 23.3% (1.4%) | 23.4% (1.6%) | 17.6% (1.1%) | |
| Handgrip strength | 27.80 (0.18) | 27.14 (0.30) | 25.15 (0.34) | 23.53 (0.26) | <0.001 |
| Relative handgrip strength | 1.18 (0.01) | 1.15 (0.01) | 1.06 (0.01) | 0.99 (0.01) | <0.001 |
| Dynapenia | 23.5% (0.9%) | 22.6% (1.4%) | 28.7% (1.8%) | 33.8% (1.5%) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Never Ate Alone | 1 Meal Alone | 2 Meals Alone | 3 Meals Alone | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 3455) | (n = 1261) | (n = 974) | (n = 1588) | ||
| Men (n = 3273) | (n = 1902) | (n = 586) | (n = 357) | (n = 428) | |
| Handgrip strength | 33.23 (0.20) | 33.89 (0.32) | 33.69 (0.45) | 32.92 (0.41) | 0.185 |
| Relative handgrip strength | 1.42 (0.01) | 1.45 (0.01) | 1.44 (0.02) | 1.41 (0.02) | 0.187 |
| Dynapenia | 20.9% (1.1%) | 18.3% (1.8%) | 21.4% (2.7%) | 24.6% (2.5%) | 0.230 |
| Women (n = 4005) | (n = 1553) | (n = 675) | (n = 617) | (n = 1160) | |
| Handgrip strength | 20.75 (0.15) | 20.54 (0.21) | 19.71 (0.22) | 19.57 (0.18) | <0.001 |
| Relative handgrip strength | 0.87 (0.01) | 0.86 (0.01) | 0.81 (0.01) | 0.81 (0.01) | <0.001 |
| Dynapenia | 26.8% (1.4%) | 26.8% (2.0%) | 33.3% (2.2%) | 37.7% (1.8%) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Never Ate Alone | 1 Meal Alone | 2 Meals Alone | 3 Meals Alone | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 1902) | (n = 586) | (n = 357) | (n = 428) | ||
| Total energy (kcal/day) | 1923.40 (20.27) | 2019.57 (32.64) | 1984.26 (48.18) | 1866.34 (36.58) | 0.009 |
| Protein (g/day) | 64.80 (0.87) | 68.08 (1.26) | 68.84 (2.05) | 61.50 (1.72) | 0.005 |
| Carbohydrate (g/day) | 322.26 (3.25) | 334.96 (5.62) | 330.07 (8.19) | 312.69 (6.26) | 0.046 |
| Fat (g/day) | 31.69 (0.72) | 32.30 (0.96) | 33.49 (1.50) | 29.67 (1.28) | 0.237 |
| n-3 PUFA (g/day) | 1.86 (0.07) | 1.71 (0.07) | 1.70 (0.11) | 1.71 (0.12) | 0.431 |
| n-6 PUFA (g/day) | 7.51 (0.19) | 7.46 (0.24) | 7.18 (0.33) | 6.90 (0.30) | 0.335 |
| Calcium (mg/day) | 513.81 (9.94) | 499.64 (13.38) | 516.81 (26.33) | 472.96 (18.37) | 0.226 |
| Iron (mg/day) | 14.60 (0.22) | 15.27 (0.46) | 14.61 (0.58) | 13.20 (0.43) | 0.008 |
| Sodium (mg/day) | 3528.61 (57.95) | 3565.72 (91.63) | 3527.35 (129.29) | 3355.96 (112.79) | 0.498 |
| Potassium (mg/day) | 3011.86 (41.53) | 3040.96 (64.10) | 2987 (94.83) | 2726.54 (80.45) | 0.008 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 74.43 (2.11) | 78.87 (4.66) | 79.35 (6.79) | 59.90 (4.26) | 0.005 |
| Carotene (µg/day) | 3296.52 (116.97) | 3451.12 (221.69) | 3235.54 (224.90) | 2959.15 (214.49) | 0.409 |
| Retinol (µg/day) | 110.32 (17.06) | 88.38 (8.22) | 105.87 (12.89) | 78.76 (12.10) | 0.295 |
| Thiamine (mg/day) | 1.53 (0.02) | 1.59 (0.04) | 1.58 (0.05) | 1.45 (0.04) | 0.061 |
| Riboflavin (mg/day) | 1.33 (0.02) | 1.35 (0.03) | 1.37 (0.05) | 1.20 (0.04) | 0.021 |
| Niacin (mg/day) | 13.21 (0.20) | 13.81 (0.31) | 13.76 (0.53) | 12.01 (0.37) | 0.002 |
| Dietary fiber (g/day) | 28.14 (0.42) | 29.24 (0.83) | 27.27 (0.98) | 25.23 (0.81) | 0.003 |
| Variable | Never Ate Alone | 1 Meal Alone | 2 Meals Alone | 3 Meals Alone | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 1553) | (n = 675) | (n = 617) | (n = 1160) | ||
| Total energy (kcal/day) | 1529.06 (16.98) | 1530.58 (33.12) | 1430.10 (28.99) | 1406.74 (21.35) | <0.001 |
| Protein (g/day) | 49.97 (0.74) | 48.73 (1.11) | 46.63 (1.02) | 45.38 (0.88) | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate (g/day) | 275.92 (3.09) | 273.58 (6.19) | 255.62 (5.67) | 255.06 (3.79) | <0.001 |
| Fat (g/day) | 23.63 (0.53) | 25.45 (1.08) | 23.21 (0.81) | 21.00 (0.67) | 0.001 |
| n-3 PUFA (g/day) | 1.45 (0.05) | 1.49 (0.11) | 1.24 (0.08) | 1.18 (0.71) | 0.001 |
| n-6 PUFA (g/day) | 5.73 (0.14) | 5.89 (0.24) | 5.54 (0.23) | 4.91 (0.18) | 0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/day) | 411 (8.44) | 408.44 (11.85) | 391.20 (12.20) | 377.67 (9.99) | 0.049 |
| Iron (mg/day) | 12.07 (0.40) | 12.07 (0.52) | 10.40 (0.33) | 10.68 (0.27) | 0.001 |
| Sodium (mg/day) | 2681.33 (52.14) | 2519.27 (80.32) | 2380.37 (74.79) | 2350.08 (58.40) | <0.001 |
| Potassium (mg/day) | 2557.63 (41.24) | 2455.69 (64.18) | 2327.35 (63.58) | 2251.82 (46.76) | <0.001 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 76.39 (3.29) | 69.50 (3.63) | 69.56 (4.53) | 57.9 (2.28) | <0.001 |
| Carotene (µg/day) | 2915.32 (120.72) | 2876.21 (149.12) | 2472.45 (145.50) | 2441.62 (126.11) | 0.011 |
| Retinol (µg/day) | 61.27 (2.69) | 85.27 (19.16) | 74.18 (6.42) | 61.11 (3.44) | 0.162 |
| Thiamine (mg/day) | 1.23 (0.02) | 1.19 (0.03) | 1.12 (0.03) | 1.12 (0.02) | 0.001 |
| Riboflavin (mg/day) | 1.05 (0.20) | 1.07 (0.31) | 1.00 (0.31) | 0.94 (0.23) | <0.001 |
| Niacin (mg/day) | 10.18 (0.17) | 10.03 (0.25) | 9.37 (0.25) | 9.01 (0.19) | <0.001 |
| Dietary fiber (g/day) | 24.30 (0.43) | 24.39 (0.78) | 22.03 (0.67) | 21.55 (0.50) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Crude | Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |
| Men | ||||||
| Never ate alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 meal alone | 0.85 | (0.65–1.11) | 1.10 | (0.83–1.47) | 1.03 | (0.74–1.42) |
| 2 meals alone | 1.03 | (0.74–1.43) | 1.42 | (1.01–1.99) | 1.27 | (0.84–1.93) |
| 3 meals alone | 1.23 | (0.93–1.64) | 1.26 | (0.93–1.70) | 1.12 | (0.79–1.59) |
| Never ate alone or 1 meal alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 2 or 3 meals alone | 1.18 | (0.94–1.48) | 1.29 | (1.02–1.65) | 1.18 | (0.89–1.56) |
| Women | ||||||
| Never ate alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 meal alone | 1.00 | (0.78–1.28) | 1.08 | (0.84–1.39) | 1.03 | (0.78–1.36) |
| 2 meals alone | 1.37 | (1.08–1.73) | 1.31 | (1.03–1.67) | 1.35 | (1.03–1.77) |
| 3 meals alone | 1.66 | (1.35–2.03) | 1.37 | (1.11–1.70) | 1.20 | (0.95–1.52) |
| Never ate alone or 1 meal alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 2 or 3 meals alone | 1.54 | (1.32–1.80) | 1.32 | (1.12–1.55) | 1.25 | (1.04–1.50) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, M.Y.; Song, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Seo, Y.-G.; An, H.-J.; Paek, Y.-J.; Noh, H.-M. Relationship between Eating Alone and Handgrip Strength in Korean Older Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050654
Yoo MY, Song HJ, Park KH, Seo Y-G, An H-J, Paek Y-J, Noh H-M. Relationship between Eating Alone and Handgrip Strength in Korean Older Adults. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050654
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Min Young, Hong Ji Song, Kyung Hee Park, Young-Gyun Seo, Hye-Ji An, Yu-Jin Paek, and Hye-Mi Noh. 2024. "Relationship between Eating Alone and Handgrip Strength in Korean Older Adults" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050654
APA StyleYoo, M. Y., Song, H. J., Park, K. H., Seo, Y.-G., An, H.-J., Paek, Y.-J., & Noh, H.-M. (2024). Relationship between Eating Alone and Handgrip Strength in Korean Older Adults. Nutrients, 16(5), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050654






