Diagnosing Sarcopenia with AI-Aided Ultrasound (DINOSAUR)—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
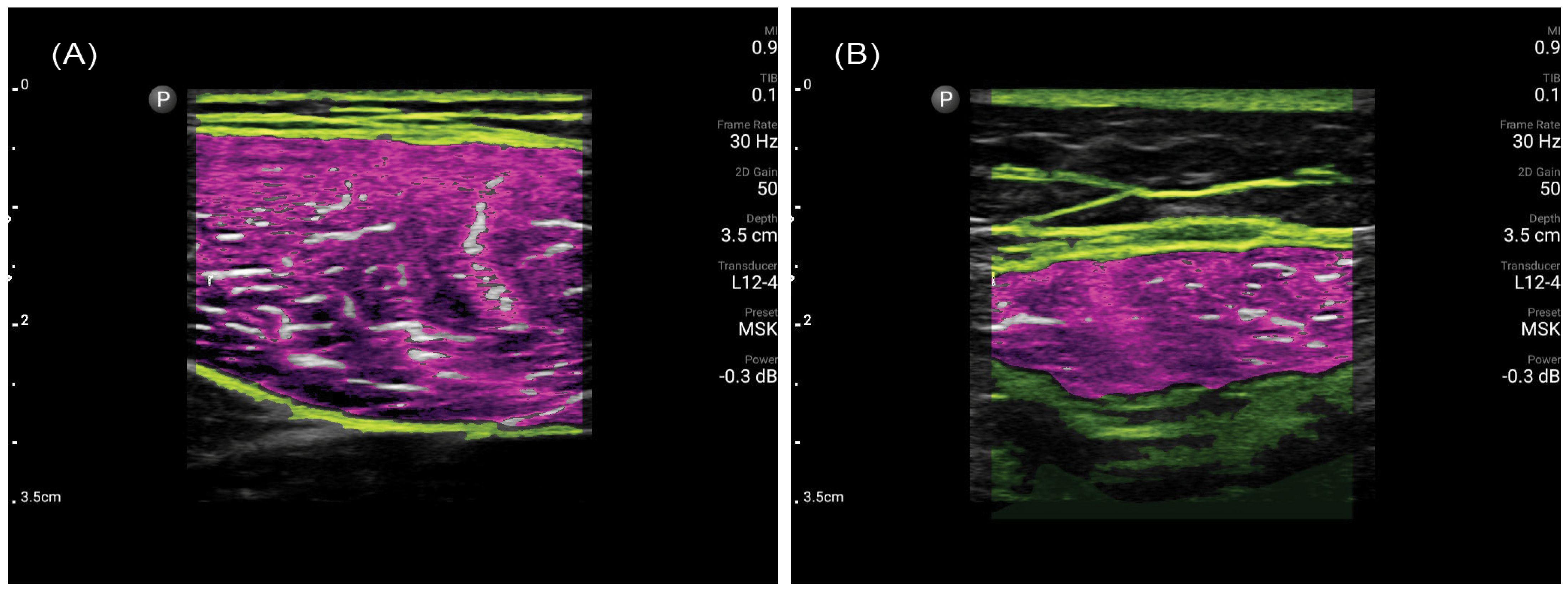
2.2. Muscle Ultrasonography Procedure
2.3. Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
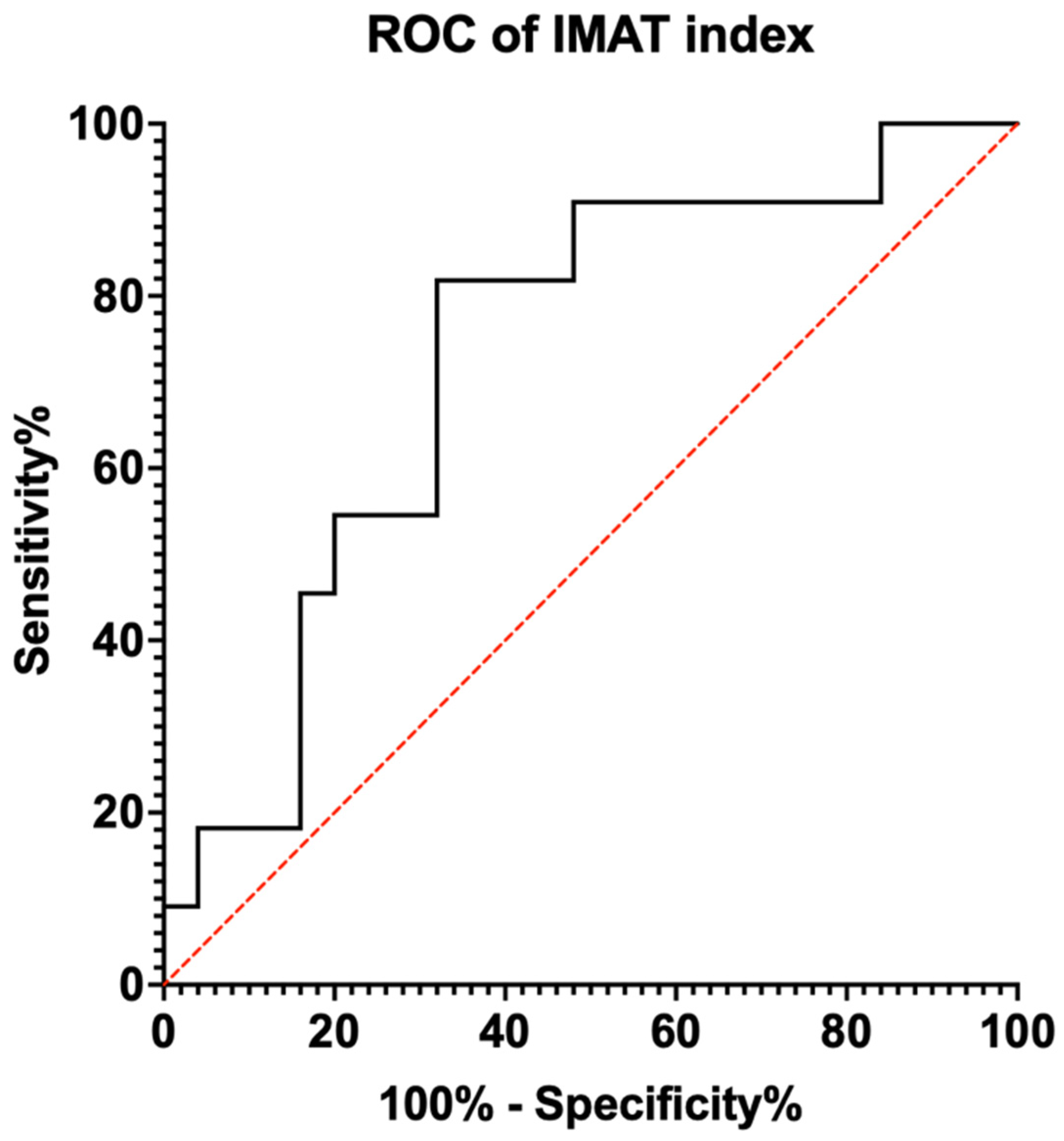
3.2. Diagnostic Capability
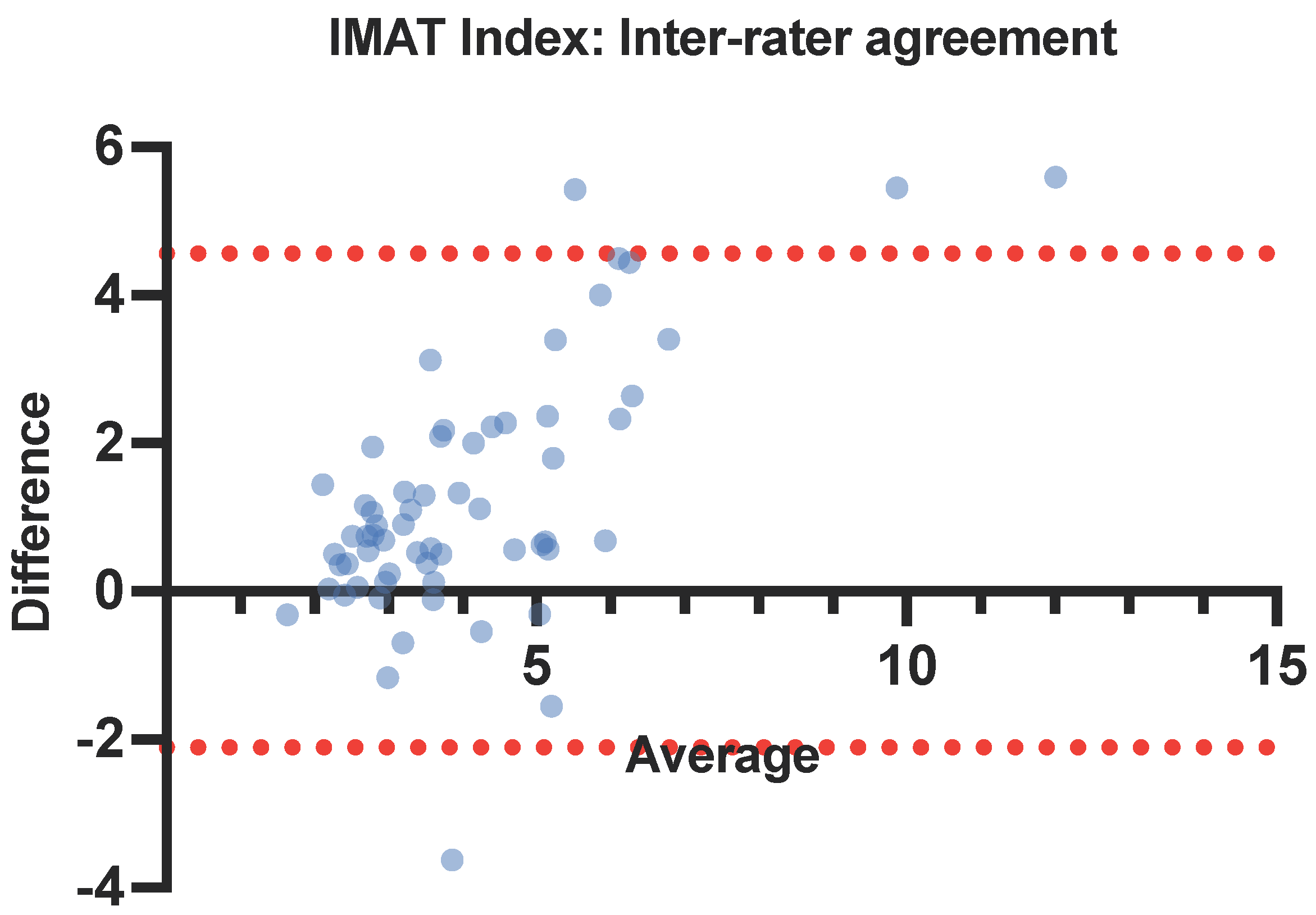
3.3. Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficient—Intra-Rater Variability
4.2. Reliable—Inter-Rater Variability
4.3. Accurate—Ultrasound for Sarcopenia Diagnosis
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Balntzi, V.; Gray, S.R.; Lara, J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.M.; Ingles, M.; Salvador-Pascual, A.; Cominetti, M.R.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Viña, J. Sarcopenia, frailty and their prevention by exercise. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 132, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, J. Initiatives in Place to Tackle Ageing Issues as S’pore Hits ‘Super-Aged’ Status in 2026: Health Minister, in The Straits Times; SPH Media: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, T.G.; Haynes, A.B.; Molina, G.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Esquivel, M.M.; Uribe-Leitz, T.; Fu, R.; Azad, T.; Chao, T.E.; Berry, W.R.; et al. Size and Distribution of the Global Volume of Surgery in 2012. Bull. World Health Organ 2016, 94, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Z.; Dharmawan, A.; Zhang, X.; Chua, D.Y.; Low, J.K. The changing landscape of general surgery in the elderly-trends over a decade in a tertiary centre in Singapore. ANZ J. Surg. 2022, 92, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipek, L.Z.; Baptista, C.G.; Nascimento, R.F.; Taba, J.V.; Suzuki, M.O.; do Nascimento, F.S.; Martines, D.R.; Nii, F.; Iuamoto, L.R.; Carneiro-D’Albuquerque, L.A.; et al. The impact of properly diagnosed sarcopenia on postoperative outcomes after gastrointestinal surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, T.; Yang, W.; Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Hui, Y.; Cui, B.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; et al. Reduced muscle strength is closely linked to computed tomography-defined myosteatosis among inpatients with cirrhosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 100, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Zi, L.; Wang, K.; Kuang, T.; Zhao, K.; Wang, W. High intramuscular adipose tissue content associated with prognosis and postoperative complications of cancers. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeyer, P.; Haines, K.; Molinger, J. 411: Temporalis muscle intramuscular adipose tissue correlates with cardiorespiratory fitness. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.A.; van Dijk, D.P.; Gleadowe, F.; Reeves, T.; Primrose, J.N.; Abu Hilal, M.; Edwards, M.R.; Jack, S.; Rensen, S.S.; Grocott, M.P.; et al. Myosteatosis is associated with poor physical fitness in patients undergoing hepatopancreatobiliary surgery. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Park, S. Myosteatosis: A potential missing link between hypertension and metabolic disorder in the Asian population. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianca, V.; Albano, D.; Messina, C.; Gitto, S.; Ruffo, G.; Guarino, S.; Del Grande, F.; Sconfienza, L.M. Sarcopenia: Imaging assessment and clinical application. Abdom Radiol. 2022, 47, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogele, D.; Otto, S.; Sollmann, N.; Haggenmüller, B.; Wolf, D.; Beer, M.; Schmidt, S.A. Sarcopenia—Definition, Radiological Diagnosis, Clinical Significance. Rofo 2023, 195, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Ahammer, H.; Lohman, T.G.; Meyer, N.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Müller, T.; et al. Relative Body Weight and Standardised Brightness-Mode Ultrasound Measurement of Subcutaneous Fat in Athletes: An International Multicentre Reliability Study, under the Auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwaaijen, E.J.; van Hulst, A.M.; Molinger, J.; Hartman, A.; Pieters, R.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; van den Akker, E.L.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M. The utility of a portable muscle ultrasound in the assessment of muscle alterations in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; San-Millan, I. Winning the war against ICU-acquired weakness: New innovations in nutrition and exercise physiology. Crit. Care 2015, 19 (Suppl. 3), S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; Bastijns, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beaudart, C.; Beckwée, D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Gasowski, J.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: 2020 SARCUS update. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism 2023, 144, 155533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, F.; Mariani, L. Defining and classifying cancer cachexia: A proposal by the SCRINIO Working Group. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2009, 33, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.F.; Lim, Z.Y.; Choe, R.; Seetharaman, S.; Merchant, R. Screening for Frailty and Sarcopenia among Older Persons in Medical Outpatient Clinics and its Associations with Healthcare Burden. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, J.; van Alfen, N. Muscle ultrasound: Present state and future opportunities. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashir, A.; Jerban, S.; Barrère, V.; Wu, Y.; Shah, S.B.; Andre, M.P.; Chang, E.Y. Skeletal Muscle Assessment Using Quantitative Ultrasound: A Narrative Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.J.; Jenkins, N.T.; Zhao, Q.; Mccully, K.K. Measurement of intramuscular fat by muscle echo intensity. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.D.; Eliasziw, M.; Donner, A. Sample size and optimal designs for reliability studies. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, Criteria, and Rules of Thumb for Evaluating Normed and Standardized Assessment Instruments in Psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.J.; Dona, S.T.; Cintineo, H.P.; McFadden, B.A.; Sanders, D.J.; Monaco, R.; Arent, S.M. Intra-and Inter-Rater Reliability of Assessing Body Composition Using B-Mode Ultrasound in Conjunction with Artificial Intelligence Software Original Research. J. Exerc. Nutr. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.P.; Klawitter, L.; Carver, E.; Johnson, Z.; McGrath, R.; Stastny, S.; Christensen, B.; Hackney, K.J. Reliability of a Novel Automated Ultrasound Technology for Body Composition Assessment and Comparisons with Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2023, 16, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, A.M.; Stock, M.S. Consistency of novel ultrasound equations for estimating percent intramuscular fat. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; Lamers, S.; Degerickx, R.; Van Mieghem, E.; Vandewoude, M.; Verhoeven, V.; De Cock, A.M. The relation between mortality, intramuscular adipose tissue and sarcopenia in hospitalized geriatric patients. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Bhat, S.; Xia, W.; Barazanchi, A.W.; Frampton, C.; Hill, A.G.; MacCormick, A.D. Consensus-defined sarcopenia predicts adverse outcomes after elective abdominal surgery: Meta-analysis. BJS Open 2023, 7, zrad065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, M.; Driever, D.; Ryan, É.J.; Elliott, J.A.; Finnegan, J.; McNamara, D.; Murphy, I.; Conlon, K.C.; Neary, P.C.; Kavanagh, D.O.; et al. Obesity, Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis: Impact on Clinical Outcomes in the Operative Management of Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, izad225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negm, A.M.; Lee, J.; Hamidian, R.; Jones, C.A.; Khadaroo, R.G. Management of Sarcopenia: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chi, H.; Kok, S.; Chua, J.M.; Huang, X.X.; Zhang, S.; Mah, S.; Foo, L.X.; Peh, H.Y.; Lee, H.B.; et al. Multimodal prerehabilitation for elderly patients with sarcopenia in colorectal surgery. Ann. Coloproctol. 2023, 40, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengul Aycicek, G.; Ozsurekci, C.; Caliskan, H.; Kizilarslanoglu, M.C.; Tuna Dogrul, R.; Balci, C.; Unsal, P.; Esme, M.; Yavuz, B.B.; Cankurtaran, M.; et al. Ultrasonography versus bioelectrical impedance analysis: Which predicts muscle strength better? Acta Clin. Belg. 2021, 76, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Kimura, M.; Yamada, Y. Thigh muscle thickness on ultrasonography for diagnosing sarcopenia: The Kyoto-Kameoka study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2023, 24, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narici, M.; McPhee, J.; Conte, M.; Franchi, M.V.; Mitchell, K.; Tagliaferri, S.; Monti, E.; Marcolin, G.; Atherton, P.J.; Smith, K.; et al. Age-related alterations in muscle architecture are a signature of sarcopenia: The ultrasound sarcopenia index. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Qi, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, A.; Cai, J.; Lai, B.; Sheng, Y.; Ding, G. The correlation of muscle thickness and pennation angle assessed by ultrasound with sarcopenia in elderly Chinese community dwellers. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, M.; Melling, N.; Krause, L.; Kühn, K.; Graß, J.K.; Izbicki, J.R.; Gerdes, L.; Adam, G.; Yamamura, J.; Molwitz, I. Muscle quality, not quantity, is associated with outcome after colorectal cancer surgery. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 49, 107098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Muscle strength | |
| Handgrip strength | M: <28 kg, F: <18 kg |
| Physical performance | |
| 6-meter walk | <1.0 m/s |
| or 5-time chair stand test | ≥12 s |
| or Short Physical Performance Battery | ≤9 |
| Appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) | |
| Dual-energy X-ray-absorptiometry | M: <7.0 kg/m2, F: <5.4 kg/m2 |
| Bioelectrical impedance analysis | M: <7.0 kg/m2, F: <5.7 kg/m2 |
| Sarcopenia | Low ASM + Low Muscle Strength OR Low Physical Performance |
| Severe sarcopenia | Low ASM + Low Muscle Strength AND Low Physical Performance |
| Patient Characteristics | Total n = 36 |
|---|---|
| Age in years, median (range) | 69.5 (26–81) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 17 (47.2%) |
| BMI (kg/m2), median (range) | 23.1 (16.8–33.2) |
| Height (m), median (range) | 1.61 (1.31–1.74) |
| Weight (kg), median (range) | 55 (39–88) |
| Sarcopenia, n (%) | 11 (30.6%) |
| Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity | 1—Specificity | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.7938 | 1.000 | 0.840 | 0.160 |
| 2.9705 | 0.909 | 0.760 | 0.149 |
| 3.3220 | 0.909 | 0.640 | 0.269 |
| 3.6830 | 0.909 | 0.560 | 0.349 |
| 3.7703 | 0.909 | 0.520 | 0.389 |
| 3.9598 | 0.909 | 0.480 | 0.429 |
| 4.6990 | 0.818 | 0.400 | 0.418 |
| 4.7275 | 0.818 | 0.360 | 0.458 |
| 4.8265 | 0.818 | 0.320 | 0.498 |
| 5.0920 | 0.727 | 0.320 | 0.407 |
| 5.3387 | 0.636 | 0.320 | 0.316 |
| 5.5428 | 0.545 | 0.280 | 0.265 |
| 5.7083 | 0.545 | 0.200 | 0.345 |
| 6.0910 | 0.455 | 0.200 | 0.255 |
| 6.9270 | 0.364 | 0.160 | 0.113 |
| 7.3528 | 0.182 | 0.160 | 0.022 |
| 7.8985 | 0.182 | 0.120 | 0.062 |
| Muscle Parameter | Intra-Rater Reliability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Session 1 | Session 2 | Session 3 | ICC | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| RF IMAT (%) | 15.1 (3.12) | 14.6 (3.36) | 14.6 (3.26) | 0.824 | 0.781–0.888 | <0.001 * |
| RF IMAT index (%/cm2) | 3.48 (1.4) | 3.44 (1.42) | 3.36 (1.31) | 0.938 | 0.905–0.961 | <0.001 * |
| Muscle Parameter | Inter-Rater Reliability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User 1 | User 2 | ICC | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| RF IMAT (%) | 14.3 (3.22) | 15.1 (3.12) | 0.631 | 0.377–0.77 | <0.001 * |
| RF IMAT index (%/cm2) | 4.7 (2.44) | 3.48 (1.4) | 0.776 | 0.284–0.852 | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yik, V.; Kok, S.S.X.; Chean, E.; Lam, Y.-E.; Chua, W.-T.; Tan, W.J.; Foo, F.J.; Ng, J.L.; Su, S.S.; Chong, C.X.-Z.; et al. Diagnosing Sarcopenia with AI-Aided Ultrasound (DINOSAUR)—A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162768
Yik V, Kok SSX, Chean E, Lam Y-E, Chua W-T, Tan WJ, Foo FJ, Ng JL, Su SS, Chong CX-Z, et al. Diagnosing Sarcopenia with AI-Aided Ultrasound (DINOSAUR)—A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162768
Chicago/Turabian StyleYik, Vanessa, Shawn Shi Xian Kok, Esther Chean, Yi-En Lam, Wei-Tian Chua, Winson Jianhong Tan, Fung Joon Foo, Jia Lin Ng, Sharmini Sivarajah Su, Cheryl Xi-Zi Chong, and et al. 2024. "Diagnosing Sarcopenia with AI-Aided Ultrasound (DINOSAUR)—A Pilot Study" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162768
APA StyleYik, V., Kok, S. S. X., Chean, E., Lam, Y.-E., Chua, W.-T., Tan, W. J., Foo, F. J., Ng, J. L., Su, S. S., Chong, C. X.-Z., Aw, D. K.-L., Khoo, N. A. X., Wischmeyer, P. E., Molinger, J., Wong, S., Ong, L. W.-L., & Koh, F. H.-X. (2024). Diagnosing Sarcopenia with AI-Aided Ultrasound (DINOSAUR)—A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 16(16), 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162768






