The Development and Validation of a Disordered Eating Screening Tool for Current and Former Athletes: The Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Screening Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
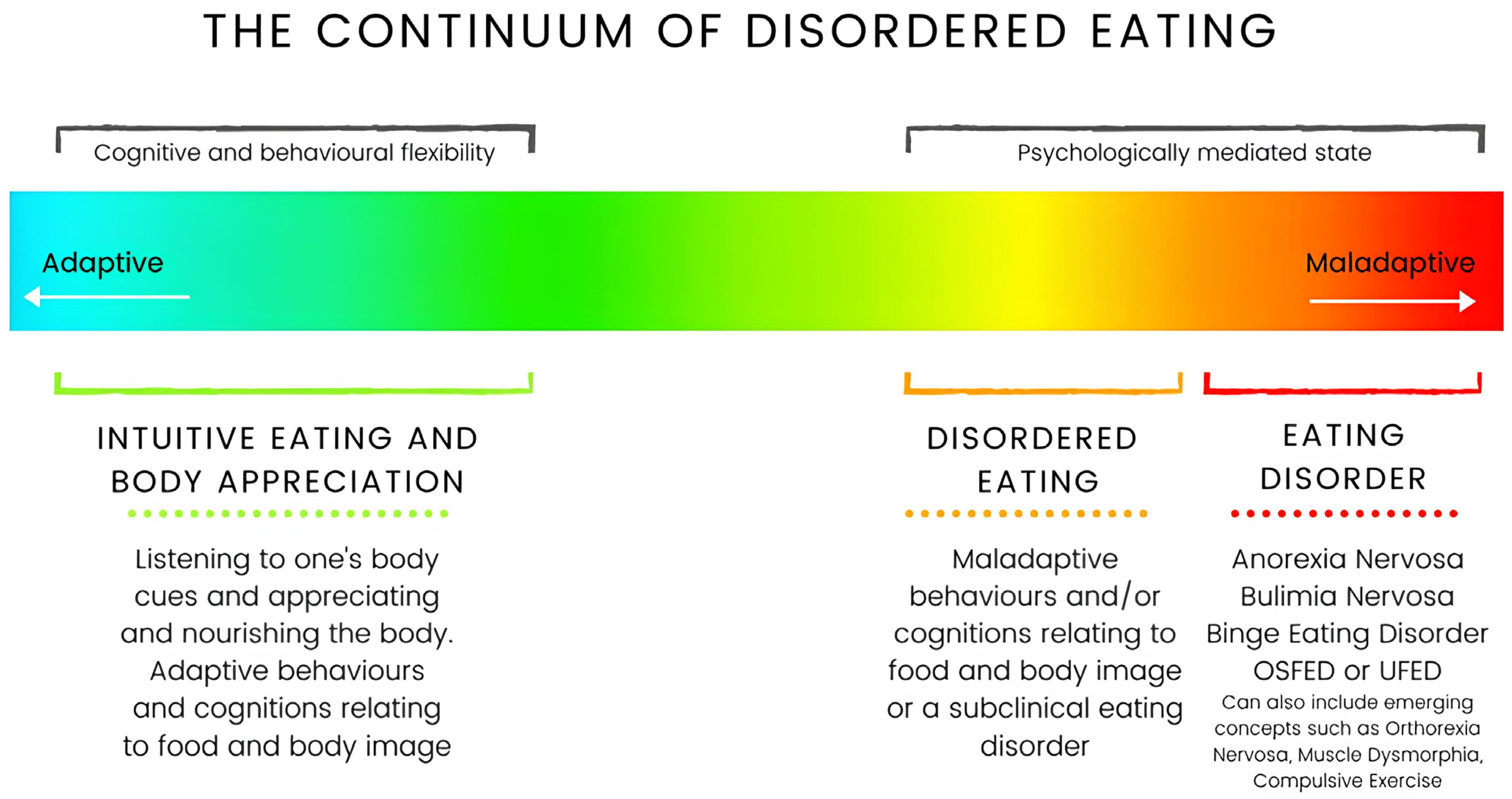
2.1. Methodology and Defining Disordered Eating
2.2. Scale Development
2.3. Participant Recruitment
2.4. Participant Demographics
2.5. Item Pool Generation
2.6. Classic Test Theory Initial Item Evaluation
2.7. Factor Analysis
2.8. Rasch Analysis
2.9. Classic Test Theory Final Scale Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Iterative Item Response Pool Process
3.2. Classic Test Theory Initial Item Evaluation
3.3. Factor Analysis
3.4. Rasch Analysis
3.5. Classic Test Theory Final Item Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Statistical Analysis | Participant Number (n) |
| Construct Validation (Discriminative or Known Groups) | ≥100 |
| Construct Validation (Hypothesis Testing) | ≥100 |
| Content Validation (Qualitative) | ≥7 |
| Content Validation (Quantitative) | ≥50 |
| Criterion Validation | ≥50 per group |
| Cross-Cultural Validation (Regression Analysis) | ≥200 |
| Cross-Cultural Validation (Rasch Analysis) | ≥200 |
| Cross-Cultural Validation (Multi-Group Confirmatory Factor Analysis) | ≥100 per group Or 7× the number of items |
| Factor Analysis | ≥100 Or 7× the number of items |
| Factor Analysis (Rasch Analysis) | ≥200 |
| Internal Consistency | ≥100 |
| Measurement Error | ≥100 |
| Test-Retest Reliability | ≥100 |
References
- Pope, Z.; Gao, Y.; Bolter, N.; Pritchard, M. Validity and reliability of eating disorder assessments used with athletes: A review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 4, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Torstveit, M.K. Prevalence of eating disorders in elite athletes is higher than in the general population. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2004, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapa, D.A.N.; Johnson, S.N.; Richson, B.N.; Bjorlie, K.; Won, Y.Q.; Nelson, S.V.; Ayres, J.; Jun, D.; Forbush, K.T.; Christensen, K.A.; et al. Eating-disorder psychopathology in female athletes and non-athletes: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 55, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, G.L.; Hall, L.E.; Lassemillante, A.-C.M.; Ackerman, K.E.; Belski, R. Retired Athletes and the Intersection of Food and Body: A Systematic Literature Review Exploring Compensatory Behaviours and Body Change. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrer, Y.; Halioua, R.; Mötteli, S.; Iff, S.; Seifritz, E.; Jäger, M.; Claussen, M.C. Disordered eating and eating disorders in male elite athletes: A scoping review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, G. Furthering the Conceptualisation of Disordered Eating in Current and Former Athletes for the Development, Validation and Evaluation of the Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Scale; Swinburne University of Technology: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, S.F.; Kovan, J.; Werner, E.; Mancine, R.; Gusfa, D.; Kleiman, H. Initial validation of a screening tool for disordered eating in adolescent athletes. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmsted, M.P.; Bohr, Y.; Garfinkel, P.E. The eating attitudes test: Psychometric features and clinical correlates. Psychol. Med. 1982, 12, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairburn, C.G.; Beglin, S.J. Assessment of eating disorders: Interview or self-report questionnaire? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1994, 16, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmstead, M.P.; Polivy, J. Development and Validation of a Multidimensional Eating Disorder Inventory for Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1983, 2, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, D.L.; Black, D.R.; Leverenz, L.J.; Coster, D.C. Evaluation of a screening test for female college athletes with eating disorders and disordered eating. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 431. [Google Scholar]
- McNulty, K.Y.; Adams, C.H.; Anderson, J.M.; Affenito, S.G. Development and validation of a screening tool to identify eating disorders in female athletes. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, M.; Holme, I.; Pensgaard, A.M.; Torstveit, M.K.; Sundgot-Borgen, J. The Development of the Brief Eating Disorder in Athletes Questionnaire. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazzard, V.M.; Schaefer, L.M.; Mankowski, A.; Carson, T.L.; Lipson, S.M.; Fendrick, C.; Crosby, R.D.; Sonneville, K.R. Development and validation of the Eating Disorders Screen for Athletes (EDSA): A brief screening tool for male and female athletes. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 50, 101745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F. Scale Development: Theory and Applications, 3rd ed.; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J. Scale Development, Rasch Analysis and Item Response Theory; Melbourne Australian Consortium for Social & Political Research Inc.: Alphington, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.L. The Value of Item Response Theory in Clinical Assessment: A Review. Assessment 2011, 18, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.J.; Yen, W.M. Introduction to Measurement Theory; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, J.W.; Plano Clark, V. Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research, 3rd ed.; International Student ed.; SAGE Publications Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison, D.; Hay, P.; Slewa-Younan, S.; Mond, J. The changing demographic profile of eating disorder behaviors in the community. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchison, D.; Mond, J. Epidemiology of eating disorders, eating disordered behaviour, and body image disturbance in males: A narrative review. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, N.L.; Schaefer, L.M.; Hazzard, V.M.; Rodgers, R.F. Where identities converge: The importance of intersectionality in eating disorders research. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.; Woodman, T. Disordered eating in male athletes: A meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 34, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, Z.; Fairburn, C. The eating disorder examination: A semi-structured interview for the assessment of the specific psychopathology of eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1987, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, D.M.; Garfinkel, P.E. The Eating Attitudes Test: An index of the symptoms of anorexia nervosa. Psychol. Med. 1979, 9, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokkink, L.B.; Prinsen, C.A.; Patrick, D.L.; Alonso, J.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C.; Terwee, C.B. COSMIN Study Design Checklist for Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement Instruments; COSMIN: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, P. The Handbook of Psychological Testing; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Prinsen, C.A.; Mokkink, L.B.; Bouter, L.M.; Alonso, J.; Patrick, D.L.; De Vet, H.C.; Terwee, C.B. COSMIN guideline for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual. Life Res. 2018, 27, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, R.K.; Wolf, M.B. Instrument Development in the Affective Domain: Measuring Attitudes and Values in Corporate and School Settings; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric theory—25 years ago and now. Educ. Res. 1975, 4, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Polit, D.F.; Beck, C.T. The content validity index: Are you sure you know what’s being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res. Nurs. Health 2006, 29, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, M.R. Determination and Quantification Of Content Validity. Nurs. Res. 1986, 35, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2017.
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S.; Ullman, J.B. Using Multivariate Statistics; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, H.F. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika 1974, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, R.B. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.E.; Tinsley, D.J. Uses of factor analysis in counseling psychology research. J. Couns. Psychol. 1987, 34, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.L. A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis. Psychometrika 1965, 30, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrich, D.; Lyne, A.; Sheridan, B.; Luo, G. RUMM2020; RUMM Laboratory Pty Ltd.: Perth, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J.F.; Tennant, A. An introduction to the Rasch measurement model: An example using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, P.W.; Wainer, H. Differential Item Functioning; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993; p. 453. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.V. Detecting and evaluating the impact of multidimensionality using item fit statistics and principal component analysis of residuals. J. Appl. Meas. 2002, 3, 205–231. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, Z.; Cooper, P.J.; Fairburn, C.G. The validity of the eating disorder examination and its subscales. Br. J. Psychiatry 1989, 154, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawks, S.; Merrill, R.M.; Madanat, H.N. The intuitive eating scale: Development and preliminary validation. Am. J. Health Educ. 2004, 35, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, L.; Tylka, T.L.; Wood-Barcalow, N. The Body Appreciation Scale: Development and psychometric evaluation. Body Image 2005, 2, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.; Peat, J. Medical Statistics: A Guide to SPSS, Data Analysis and Critical Appraisal; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, L.; Murray, S.B.; Walen, A.; Wooldridge, T. Including the excluded: Males and gender minorities in eating disorder prevention. Eat. Disord. 2016, 24, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavisakalyan, A. Gender in language and gender in employment. Oxf. Dev. Stud. 2015, 43, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, K. The “Science” of Fair Play in Sport: Gender and the Politics of Testing. Signs J. Women Cult. Soc. 2014, 39, 787–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Participant Group and Purpose | Recruitment Method | Number of Participants (n) | Relevant Statistical Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Expert Validation—Selected global experts in the field of sports nutrition and/or eating disorders | Purposive sampling via email invitation | 11 | Content Validation Qualitative Feedback |
| 2. Pilot Study of Current and Former Athletes | Purposive sampling via social media | 51 | Content Validation Qualitative Feedback |
| 3. Development Sample of Current and Former Athletes | Convenience sampling via social media (including the use of paid advertising) and colleague email recruitment | 851 | Initial Item Evaluation Exploratory Factor Analysis Confirmatory Factor Analysis Rasch Analysis Cross-Cultural Validity Construct Validity Internal Consistency Reliability |
| 4. Test-Retest Sample of Current and Former Athletes | Purposive sampling for follow up from development sample | 125 | Test-Retest Reliability |
| Education | Tertiary Qualification | 64.9% (n = 552) | ||
| Employment | Full-time employment | 33.3% (n = 283) | ||
| Nationality | Australia | 35.4% (n = 301) | Greece | 4.5% (n = 38) |
| USA | 15.0% (n = 128) | Ireland | 4.5% (n = 38) | |
| Singapore | 8.8% (n = 75) | New Zealand | 3.5% (n = 30) | |
| South Africa | 6.8% (n = 58) | Hungary | 2.0% (n = 17) | |
| UK | 6.2% (n = 53) | Russia | 1.2% (n = 10) | |
| Canada | 5.3% (n = 45) | Other | 6.8% (n = 58) * | |
| Sporting Categories | Ball Sports | 31.6% (n = 169) | Weight Class | 7.1% (n = 60) |
| Endurance | 28.1% (n = 239) | Technical | 4.5% (n = 38) | |
| Power | 11.5% (n = 98) | Antigravitational | 1.3% (n = 11) | |
| Aesthetic | 7.8% (n = 66) | Other | 8.2% (n = 70) | |
| Highest Competition Level | Club | 22.2% (n = 189) | National | 35.7% (n = 304) |
| State | 16.9% (n = 144) | International | 25.1% (n = 214) | |
| Previous Eating Disorder (23.6%, n = 201) | Anorexia Nervosa | 8.1% (n = 69) | Binge Eating Disorder | 3.1% (n = 26) |
| Bulimia Nervosa | 4.2% (n = 36) | OSFED | 2.1% (n = 18) | |
| Orthorexia Nervosa | 2.5% (n = 21) | UFED | 1.6% (n = 14) | |
| Other | 2.0% (n = 17) | |||
| Current Eating Disorder | No | 90.1% (n = 773) | Yes | 9.2% (n = 78) ** |
| Factor 1 (n = 5 Items) | Factor 2 (n = 3 Items) | Factor 3 (n = 4 Items) ** | Factor 4 (n = 5 Items) | Whole Scale (n = 17 Items) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item Fit Residual (mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) | 1.03 ± 0.43 | 0.52 ± 1.64 | 0.65 ± 1.40 | 0.27 ± 1.80 | 3.38 ± 0.43 |
| Person Fit Residual (mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) | 1.05 ± 0.32 | −0.47 ± 1.06 | −0.53 ± 1.38 | −0.38 ± 1.10 | 1.58 ± 0.34 |
| Item Chi Square Statistic | 57.8 | 30.7 | 41.7 | 50.2 | 495.2 |
| Degrees of Freedom | 45.0 | 27.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 153.0 |
| Chi Square Probability * | 0.095, p > 0.010 | 0.284, p > 0.017 | 0.610, p > 0.012 | 0.280, p > 0.010 | 0.000, p < 0.003 |
| Person Separation Index | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 0.90 |
| Coefficient Alpha | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
| ADE Screening Tool | Subscale 1 Food Control | Subscale 2 Binge | Subscale 3 Body Control | Subscale 4 Body Discontent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate Disordered Eating Indication | Cut-Off | 25.0 | ||||
| Sensitivity | 99.3% | |||||
| Specificity | 27.3% | |||||
| High Disordered Eating Indication | Cut-Off | 33.0 | 10.5 | 6.5 | 11.5 | 14.5 |
| Sensitivity | 96.8% | 85.6% | 61.2% | 65.5% | 87.8% | |
| Specificity | 49.7% | 78.3% | 64.2% | 79.9% | 75.9% | |
| Very High Disordered Eating Indication | Cut-Off | 45.0 | ||||
| Sensitivity | 79.9% | |||||
| Specificity | 84.7% | |||||
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | 1 | |||
| Factor 2 | 0.444 | 1 | ||
| Factor 3 | 0.319 | 0.206 | 1 | |
| Factor 4 | 0.418 | 0.196 | 0.345 | 1 |
| Item | Pattern Coefficients | Structure Coefficients | Communalities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | ||
| I feel bad when an athlete has a better-looking body than mine | 0.841 | 0.853 | 0.728 | ||||||
| I am dissatisfied with my body size or shape | 0.853 | 0.837 | 0.707 | ||||||
| I compare my body to other athletes or my former self | 0.778 | 0.826 | 0.711 | ||||||
| My performance or mood is influenced by how I feel about my body | 0.692 | 0.792 | 0.651 | ||||||
| I fear fat gain or muscle loss | 0.647 | 0.763 | 0.642 | ||||||
| Once I start eating, I find it hard to stop | 0.863 | 0.874 | 0.774 | ||||||
| There are certain foods I can not control myself around | 0.867 | 0.859 | 0.748 | ||||||
| I overeat when I am allowed to eat freely, i.e., off-season or a buffet | 0.853 | 0.834 | 0.721 | ||||||
| I am motivated to train harder to influence my body shape or weight | 0.849 | 0.863 | 0.748 | ||||||
| I will perform extra exercise to influence my body shape | 0.826 | 0.855 | 0.746 | ||||||
| I look to control my food when I want more out of my body | 0.524 | 0.650 | 0.550 | ||||||
| To change my body, I cut back on foods or ingredients | 0.383 | 0.587 | 0.569 | ||||||
| I carefully plan and think about what I eat | 0.830 | 0.785 | 0.658 | ||||||
| I avoid social situations if there will be foods I do not feel comfortable eating | 0.621 | 0.705 | 0.561 | ||||||
| I find spontaneous eating decisions challenging | 0.584 | 0.681 | 0.583 | ||||||
| If I have not exercised that day I will limit my food | 0.527 | 0.680 | 0.568 | ||||||
| I think about the calories/kilojoules I am burning when I train or exercise | 0.364 | 0.580 | 0.503 | ||||||
| ADE Screening Tool | Subscale 1 Food Control | Subscale 2 Binge | Subscale 3 Body Control | Subscale 4 Body Discontent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Males | 0.875 | 0.652 | 0.766 | 0.791 | 0.858 |
| Former Males | 0.873 | 0.640 | 0.815 | 0.693 | 0.836 |
| Current Females | 0.918 | 0.810 | 0.840 | 0.832 | 0.902 |
| Former Females | 0.931 | 0.846 | 0.849 | 0.829 | 0.896 |
| ADE Screening Tool | Subscale 1 Food Control | Subscale 2 Binge | Subscale 3 Body Control | Subscale 4 Body Discontent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Males | 0.289 | 0.272 | 0.522 | 0.487 | 0.546 |
| Former Males | 0.287 | 0.262 | 0.595 | 0.361 | 0.504 |
| Current Females | 0.402 | 0.460 | 0.637 | 0.554 | 0.649 |
| Former Females | 0.523 | 0.523 | 0.651 | 0.548 | 0.632 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buckley, G.L.; Lassemillante, A.-C.M.; Cooke, M.B.; Belski, R. The Development and Validation of a Disordered Eating Screening Tool for Current and Former Athletes: The Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Screening Tool. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162758
Buckley GL, Lassemillante A-CM, Cooke MB, Belski R. The Development and Validation of a Disordered Eating Screening Tool for Current and Former Athletes: The Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Screening Tool. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162758
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuckley, Georgina L., Annie-Claude M. Lassemillante, Matthew B. Cooke, and Regina Belski. 2024. "The Development and Validation of a Disordered Eating Screening Tool for Current and Former Athletes: The Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Screening Tool" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162758
APA StyleBuckley, G. L., Lassemillante, A.-C. M., Cooke, M. B., & Belski, R. (2024). The Development and Validation of a Disordered Eating Screening Tool for Current and Former Athletes: The Athletic Disordered Eating (ADE) Screening Tool. Nutrients, 16(16), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162758




