The Effect of a Nutritional Intervention with the Use of Biofortified Beef Meat on Selected Biochemical Parameters in Blood from Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Producing Biofortified Meat
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Data Collection and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
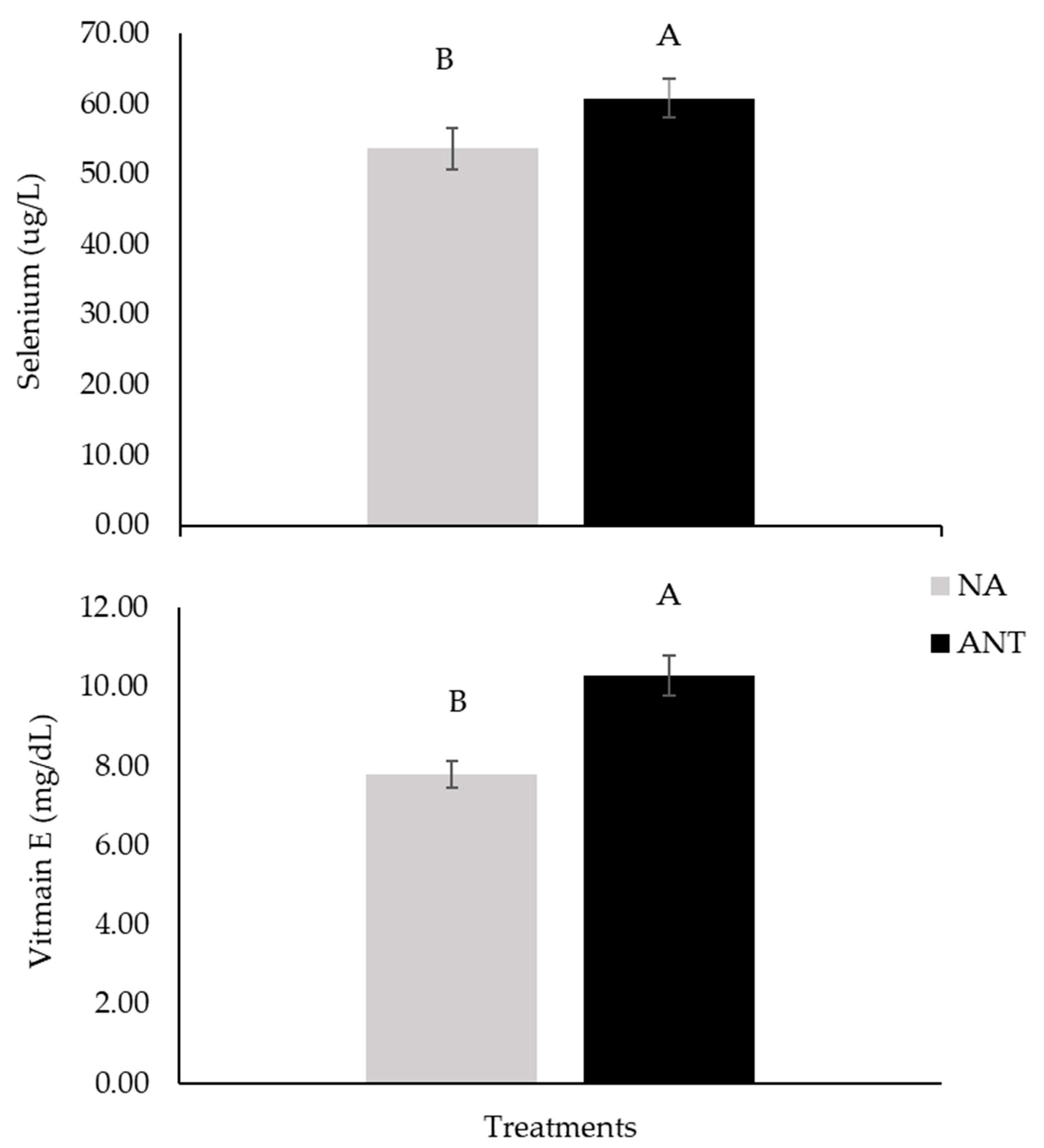
3.1. Blood Serum Selenium and Vitamin E
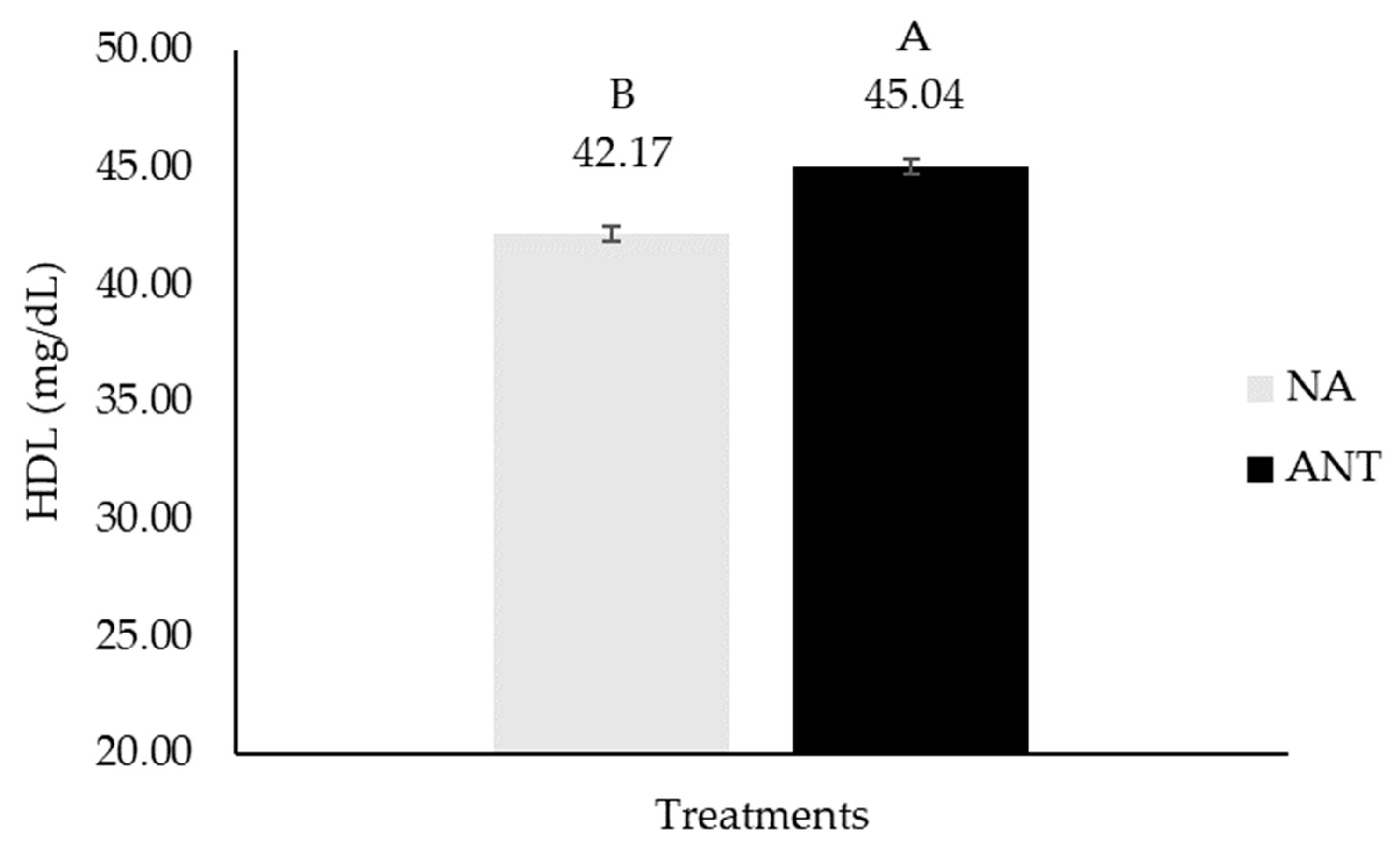
3.2. Blood Serum Biochemical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rybka, J.; Kupczyk, D.; Kędziora-Kornatowska, K.; Pawluk, H.; Czuczejko, J.; Szewczyk-Golec, K.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Antonioli, M.; Carvalho, L.A.; Kędziora, J. Age-related changes in an antioxidant defense system in elderly patients with essential hypertension compared with healthy controls. Redox Rep. 2011, 16, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gano, L.B.; Donato, A.J.; Pierce, G.L.; Pasha, H.M.; Magerko, K.A.; Roeca, C.; Seals, D.R. Increased proinflammatory and oxidant gene expression in circulating mononuclear cells in older adults: Amelioration by habitual exercise. Physiol. Genom. 2011, 43, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.H.; Riaz, J.; Mahmood, A.; Tariq, M.; Sahar, N.; Ali, R.S.; Ahmad, N.; Irshad, S.; Ahmad, M.H.; Arshad, H.; et al. Risk Factors of Postoperative Acute Heart Failure in Elderly Patients After Hip Fracture Surgery. Cureus 2024, 16, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viderman, D.; Tapinova, K.; Aubakirova, M. The Prevalence of Pain in Chronic Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews. J. Clin. Med. Rev. 2023, 12, 7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Du, C.; Song, P.; Chen, T.; Rui, S.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deng, W. Molecular Mechanisms of Dietary Bioactive Compounds in Redox Balance and Metabolic Disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, F.; Rossi, M.; Kaur, S.; Garcia-Villar, E.; Molasky, N.; Belli, S.; Sitek, J.D.; Gionfra, F.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Incerpi, S. Antioxidant properties of embelin in cell culture. Electrochemistry and theoretical mechanism of scavenging. potential scavenging of superoxide radical through the membrane cell. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, A.; Cunnane, S.C.; Minihane, A.M. Can nutrition support healthy cognitive ageing and reduce dementia risk? BMJ 2020, 369, m2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.S.; Rodriguez, F.D.; Trettel, M.; Abal, R.T.; Lima, C.G.; Yoshikawa, C.Y.C.C.; Zanetti, M.A. Performance, carcass characteristics and meat quality of Nellore cattle supplemented with supranutritional doses of sodium selenite or selenium-enriched yeast. Animal 2019, 14, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Benedí, J.; Garcimartin, A.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Jimenez-Colmenero, F. A comprehensive approach to formulation of seaweed-enriched meat products: From technological development to assessment of healthy properties. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, L.B.; Saran Netto, A.; da Silva, J.S.; Cônsolo, N.R.B.; Pugine, S.M.P.; de Melo, M.P.; Santana, R.S.d.S.; Zanetti, M.A. Changes on meat fatty acid profile, cholesterol and hepatic metabolism associated with antioxidants and canola oil supplementation for Nellore cattle. Livest. Sci. 2022, 257, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.A.; Medeiros, F.; Trindade, M.; Cohen, C.; Oigman, W.; Neves, M.F. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation improves endothelial function and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients with hypertriglyceridemia and high cardiovascular risk. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 11, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, D.M.; Hampton, M.; Kurtzer, K.; Parelman, M.; Al-Tamimi, E.; Drouillard, J.S. Feeding enriched omega-3 fatty acid beef to rats increases omega-3 fatty acid content of heart and liver membranes and decreases serum vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and cholesterol levels. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallen Lopes Nogueira, B.; Ducatti, M.; Horiquini-Barbosa, E. O consumo de selênio e sua relação com a manutenção da função cognitiva: Uma revisão sistemática sobre humanos e animais. Rev. Neurociências 2020, 28, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhan, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J. Development and application of a HPLC-ICP-MS method to determine selenium speciation in muscle of pigs treated with different selenium supplements. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Niki, E.; Noguchi, N. Comparative study on the action of tocopherols and tocotrienols as antioxidant: Chemical and physical effects. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 123, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, N.; Tan, E.; Loh, L.J.; Soh, B.S.; Yap, W.N. Tocotrienol is a cardioprotective agent against ageing-associated cardiovascular disease and its associated morbidities. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, M.E.; Villano, I.; Monda, M.; Messina, A.; Cibelli, G.; Valenzano, A.; Pisanelli, D.; Panaro, M.A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ambrosi, A.; et al. Role of Vitamin E and the Orexin System in Neuroprotection. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrimer, K.; Ferriolli, E.; Takeuchi, P.L.; Salles, M.S.V.; Saran Netto, A.; Zanetti, M.A.; Roma Junior, L.C.; Braga, C.B.M.; Domenici, F.A.; Valim, Y.M.L.; et al. Effects of the Consumption of Milk Biofortified with Selenium, Vitamin E, and Different Fatty Acid Profile on Immune Response in the Elderly. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznariç, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.B.; Saran Netto, A.; Cônsolo, N.R.B.; Garrine, C.M.L.P.; Yoshikawa, C.Y.C.; da Cunha, J.A.; da Silva, J.S.; Silva, S.L.; Zanetti, M.A. Effects of canola oil and antioxidants on performance, serum parameters, carcass traits, and rumen fermentation patterns of Nellore cattle. Animal 2021, 15, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, O.E.; Palmer, L.S.; Cary, E.L. Modification of the official Fluorimetric method for selenium in plants. J. AOAC 1975, 58, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetter, P.A.; Ullrey, D.E. Improved Fluorometric Method for Determining Selenium. J. AOAC Int. 1978, 61, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Scheller, K.K.; Arp, S.C.; Schaefer, D.M.; Williams, S.N. Titration of Fresh Meat Color Stability and Malondialdehyde Development with Holstein Steers Fed Vitamin E-Supplemented Diets. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Rasane, P.; Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, V.; Mahato, D.K.; Dey, A.; Dhawan, K.; Kumar, S. Nutritional Interventions for Elderly and Considerations for the Development of Geriatric Foods. Curr. Aging Sci. 2019, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Abraini, F.; Beal, T.; Dominguez-Salas, P.; Gregorini, P.; Manzano, P.; Rowntree, J.; van Vliet, S. Animal board invited review: Animal source foods in healthy, sustainable, and ethical diets—An argument against drastic limitation of livestock in the food system. Animal 2022, 16, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelska-Nowicka, E.; Atanasov, A.G.; Horbańczuk, J.; Wierzbicka, A. Bioactive compounds in functional meat products. Molecules 2018, 23, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, M.S.V.; Netto, A.S.; Zanetti, M.A.; Samóra, T.S.A.; Junior, L.C.R.; Lima, C.G.; Salles, F.A. Milk biofortification through dietary supplementation of combined selenium, vitamin E and sunflower oil. Livest. Sci. 2022, 258, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran Netto, A.; Silva, T.H.; Martins, M.M.; Vidal, A.M.C.; Salles, M.S.V.; Roma Júnior, L.C.; Zanetti, M.A. Inclusion of Sunflower Oil, Organic Selenium, and Vitamin E on Milk Production and Composition, and Blood Parameters of Lactating Cows. Animals 2022, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansou, D.M.; Wang, H.; Nugroho, R.D.; He, W.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Effects of duration and supplementation dose with astaxanthin on egg fortification. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnampalam, E.N.; Kearns, M.; Kiani, A.; Santhiravel, S.; Vahmani, P.; Prache, S.; Monahan, F.J.; Mapiye, C. Enrichment of ruminant meats with health enhancing fatty acids and antioxidants: Feed-based effects on nutritional value and human health aspects—Invited review. Front. Anim. Sci. 2024, 5, 1329346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, N.; Drobyshev, E.; Bjørklund, G.; Dubrovskii, Y.; Lysiuk, R.; Rayman, M.P. Selenium, selenoprotein P, and Alzheimer’s disease: Is there a link? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Lu, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Parent material modulates land use e ff ects on soil selenium bioavailability in a selenium-enriched region of southwest China. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Błazejak, S. Current knowledge on the importance of selenium in food for living organisms: A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cônsolo, N.R.B.; Gardinal, R.; Gandra, J.R.; de Freitas Junior, J.E.; Rennó, F.P.; De, M.H.; Pflanzer Junior, S.B.; Pereira, A.S.C. High levels of whole raw soybean in diets for Nellore bulls in feedlot: Effect on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 99, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Lin, Z.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yin, X.; Li, M. Biofortification and phytoremediation of selenium in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, H.; Jamshidi, S.; Askari, G. Dietary intake of antioxidants in the elderly people under nursing care: A case-control study. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mubarak, A.A.; van der Meer, P.; Bomer, N. Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Heart Failure: Current Knowledge and Future Perspective. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, L.; Song, A.; Zhang, C. Selenium Status and Its Antioxidant Role in Metabolic Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7009863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M. Selenium Intake And Status In Health & Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laclaustra, M.; Stranges, S.; Navas-Acien, A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Guallar, E. Serum selenium and serum lipids in US adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003–2004. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Gao, S.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Cheng, Y.; Hake, A.M.; Xin, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Ma, F.; Bian, J.; et al. Selenium Level and Dyslipidemia in Rural Elderly Chinese. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Luo, T.; Zhao, Z.; Rong, H.; Zhao, G.; Lei, L. Food Chemistry of Selenium and Controversial Roles of Selenium in Affecting Blood Cholesterol Concentrations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4935–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.C.; Neill, H.A.O. The animal fat paradox and meat quality. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, J.; Maggiolino, A.; Bravo, S.; Muñoz, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cancino, D.; Díaz, R.; Saenz, C.; Sepúlveda, N.; De Palo, P. Effect of canola oil on meat quality and fatty acid profile of Araucano creole lambs during fattening period. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 248, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Hopkins, D.L. The effect of palm oil or canola oil on feedlot performance, plasma and tissue fatty acid pro fi le and meat quality in goats. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaś, K.; Piwowar, A.; Harasym, J. The potential of rapeseed (canola) oil nutritional benefits wide spreading via oleogelation. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefi, M.; Pishdad, G.R.; Faghih, S. The effects of canola and olive oils on insulin resistance, inflammation and oxidative stress in women with type 2 diabetes: A randomized and controlled trial. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2018, 17, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Risé, P.; Milani, G.P.; Sala, A. Bioactive Compounds in Edible Oils and Their Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 659551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Meat 1 | Biofortified Meat 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | C | A | O | AO |
| Se and Vit E, mg/100 g of meat | ||||
| Selenium | 0.0046 b ± 0.004 | 0.0422 a ± 0.015 | 0.0057 b ± 0.002 | 0.0367 a ± 0.031 |
| Vitamin E | 0.380 b ± 0.14 | 0.765 a ± 0.27 | 0.398 b ± 0.16 | 0.778 a ± 0.36 |
| Fatty acids, g/100 g of meat | ||||
| C18:2c9 t11 (CLA) | 0.78 b ± 0.05 | 0.85 b ± 0.05 | 1.27 a ± 0.05 | 1.08 a ± 0.05 |
| 18:0 (stearic) | 16.28 ± 0.29 | 14.92 ± 0.29 | 15.09 ± 0.29 | 15.61 ± 0.29 |
| C18:1 c9 (oleic) | 36.41 ± 0.35 | 37.69 ± 0.35 | 37.54 ± 0.35 | 37.82 ± 0.35 |
| Saturated | 47.04 a ± 0.49 | 45.55 a ± 0.49 | 42.87 b ± 0.49 | 43.58 b ± 0.49 |
| Mono | 50.24 b ± 0.48 | 51.46 b ± 0.48 | 53.99 a ± 0.48 | 53.53 a ± 0.48 |
| Poly | 2.72 ± 0.12 | 2.99 ± 0.12 | 3.14 ± 0.12 | 2.89 ± 0.12 |
| H/h | 0.55 a ± 0.01 | 0.53 a ± 0.01 | 0.46 b ± 0.01 | 0.47 b ± 0.01 |
| n-6/n-3 | 12.51 a ± 0.52 | 9.22 a ± 0.52 | 8.27 b ± 0.52 | 8.09 b ± 0.52 |
| Treatments 1 | Time | p-Value 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | C | A | O | AO | Basal | 90 Days | OIL | ANT | O*A | Time |
| Selenium, µg/L | 52.69 B ± 4.63 | 60.65 A ± 4.36 | 54.61 B ± 4.36 | 61.05 A ± 3.70 | 38.02 b ± 1.22 | 57.25 a ± 2.14 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 0.42 | *** |
| Vitamin E, mg/dL | 7.53 B ± 0.71 | 10.37 A ± 0.76 | 8.05 B ± 0.71 | 10.19 A ± 0.69 | 10.44 b ± 0.42 | 9.04 a ± 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.54 | ** |
| Treatments 1 | Time | p-Value 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | C | A | O | AO | Basal | 90 Days | O | A | O*A | Time |
| Cholesterol, mg/dL | 175.95 ± 7.18 | 167.41 ± 7.58 | 182.37 ± 7.31 | 172.27 ± 6.90 | 189.43 ± 4.39 | 174.50 ± 3.62 | 0.76 | 0.49 | 0.92 | ** |
| HDL, mg/dL | 35.61 ± 1.81 | 44.40 ± 1.95 | 42.79 ± 1.82 | 42.33 ± 1.78 | 44.79 ± 0.83 | 41.28 ± 0.92 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.18 | ** |
| LDL + VLDL, mg/dL | 136.75 ± 5.46 | 137.41 ± 5.27 | 140.78 ± 5.38 | 133.37 ± 5.34 | 144.64 ± 4.72 | 133.30 ± 3.53 | 0.93 | 0.33 | 0.83 | * |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 130.10 ± 8.94 | 139.13 ± 8.52 | 135.82 ± 8.81 | 133.41 ± 8.64 | 126.16 ± 6.05 | 136.90 ± 6.59 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.44 | * |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 89.04 ± 4.02 | 89.68 ± 3.92 | 93.21 ± 3.96 | 85.51 ± 3.98 | 89.47 ± 2.85 | 85.18 ± 3.31 | 0.91 | 0.17 | 0.67 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correa, L.B.; Silva, J.S.d.; Zanetti, M.A.; Cônsolo, N.R.B.; Pfrimer, K.; Netto, A.S. The Effect of a Nutritional Intervention with the Use of Biofortified Beef Meat on Selected Biochemical Parameters in Blood from Older Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142281
Correa LB, Silva JSd, Zanetti MA, Cônsolo NRB, Pfrimer K, Netto AS. The Effect of a Nutritional Intervention with the Use of Biofortified Beef Meat on Selected Biochemical Parameters in Blood from Older Adults. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142281
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrea, Lisia Bertonha, Janaina Silveira da Silva, Marcus Antonio Zanetti, Nara Regina Brandão Cônsolo, Karina Pfrimer, and Arlindo Saran Netto. 2024. "The Effect of a Nutritional Intervention with the Use of Biofortified Beef Meat on Selected Biochemical Parameters in Blood from Older Adults" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142281
APA StyleCorrea, L. B., Silva, J. S. d., Zanetti, M. A., Cônsolo, N. R. B., Pfrimer, K., & Netto, A. S. (2024). The Effect of a Nutritional Intervention with the Use of Biofortified Beef Meat on Selected Biochemical Parameters in Blood from Older Adults. Nutrients, 16(14), 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142281






