Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Ethics Committee
2.4. Screening Process
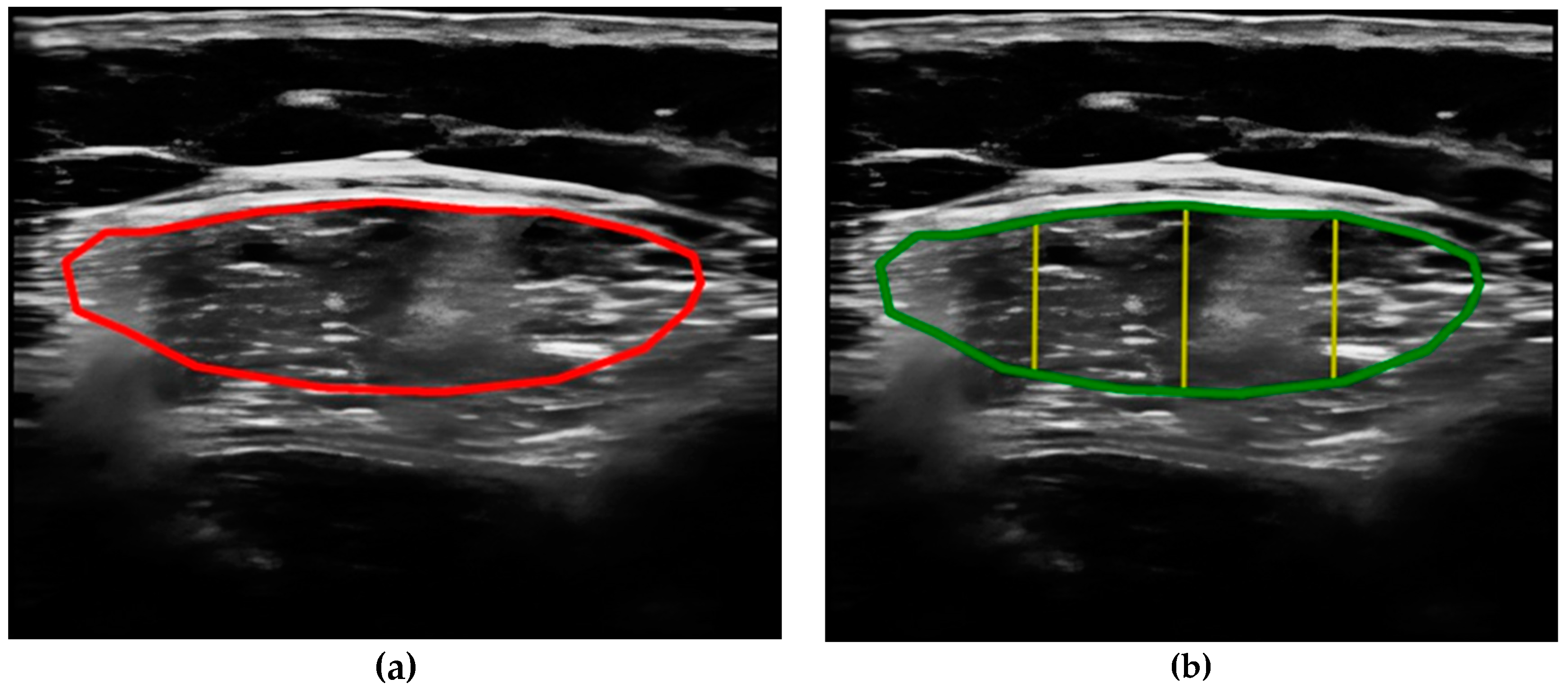
- Compare the measurements of the unilateral (right) RF of the patients performed by the expert evaluator (rater 1) using the standard tools included in the ultrasound image device (i.e., method A), see Figure 2, with those obtained by applying the PIIXMEDTM Ultrasound Imaging System (Dawako Medtech S.L., Valencia, Spain) (rater 2) (i.e., method B) [15,16,17,18,19] on the same acquired raw images, see Figure 3 and Figure 4.
- Calculate and evaluate the inter-rater reliability of quantitative muscle architecture parameters (MAP) of the unilateral (right) RF measurements performed by the expert evaluator (rater 1) (i.e., method A) against the measurements using the automated PIIXMEDTM Ultrasound Imaging System (rater 2) (Dawako Medtech S.L., Valencia, Spain) (i.e., method B) on the same acquired raw images.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Summary and Descriptive Analysis
3.3. Coefficient of Variation (CV)
3.4. Pearson and Spearman Correlation Coefficients
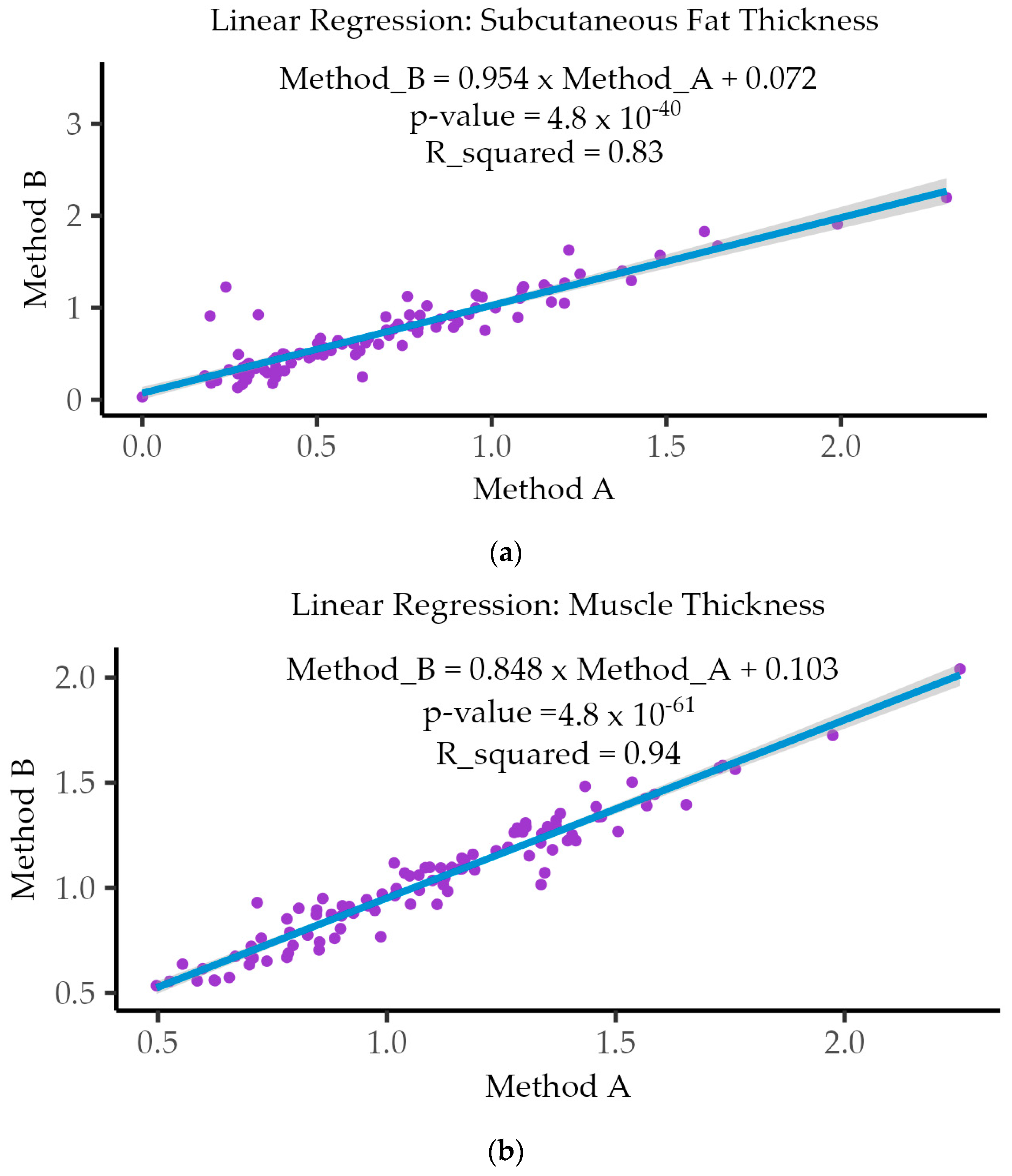
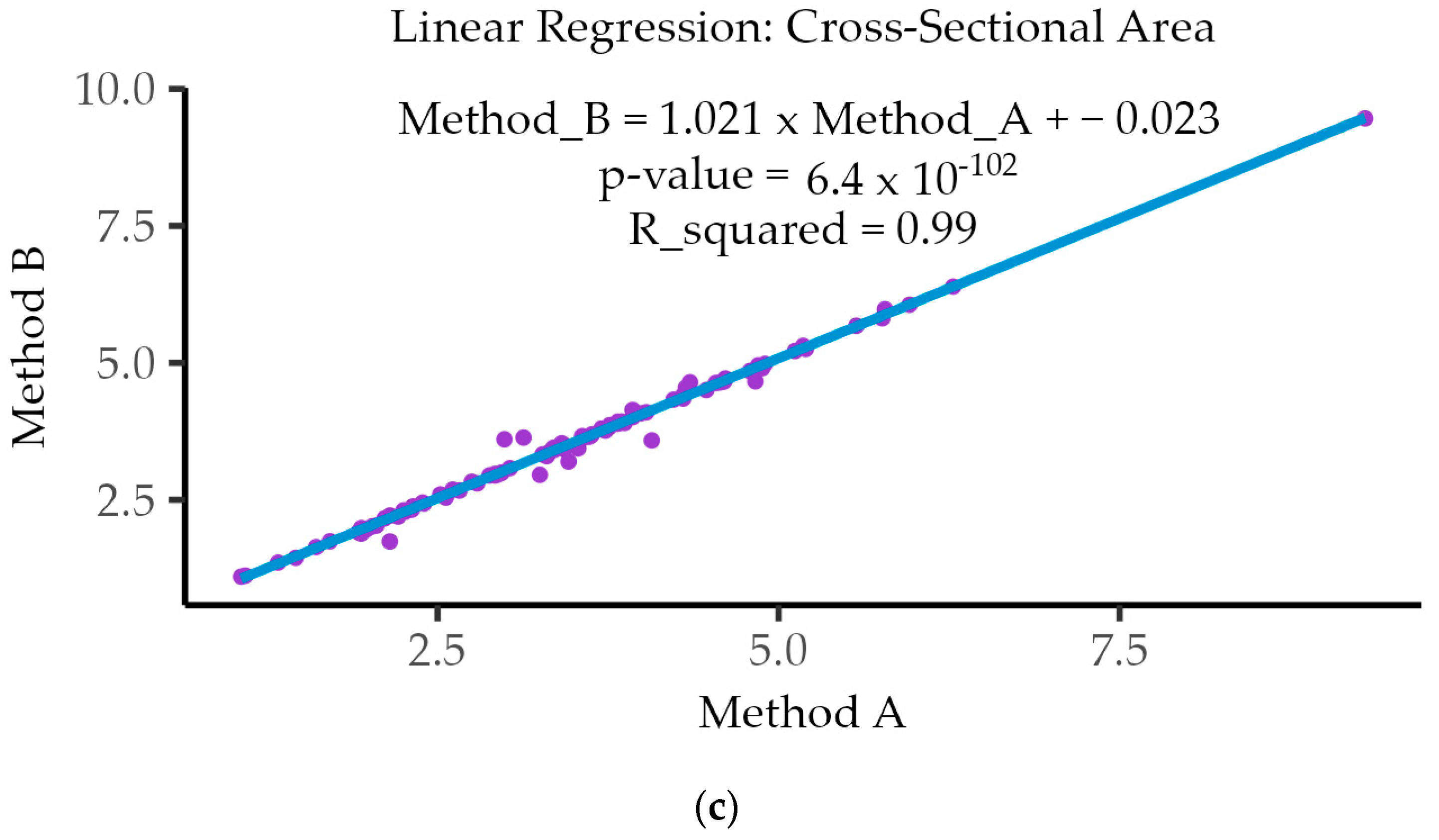
3.5. Linear Regression Analysis
3.6. Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC)
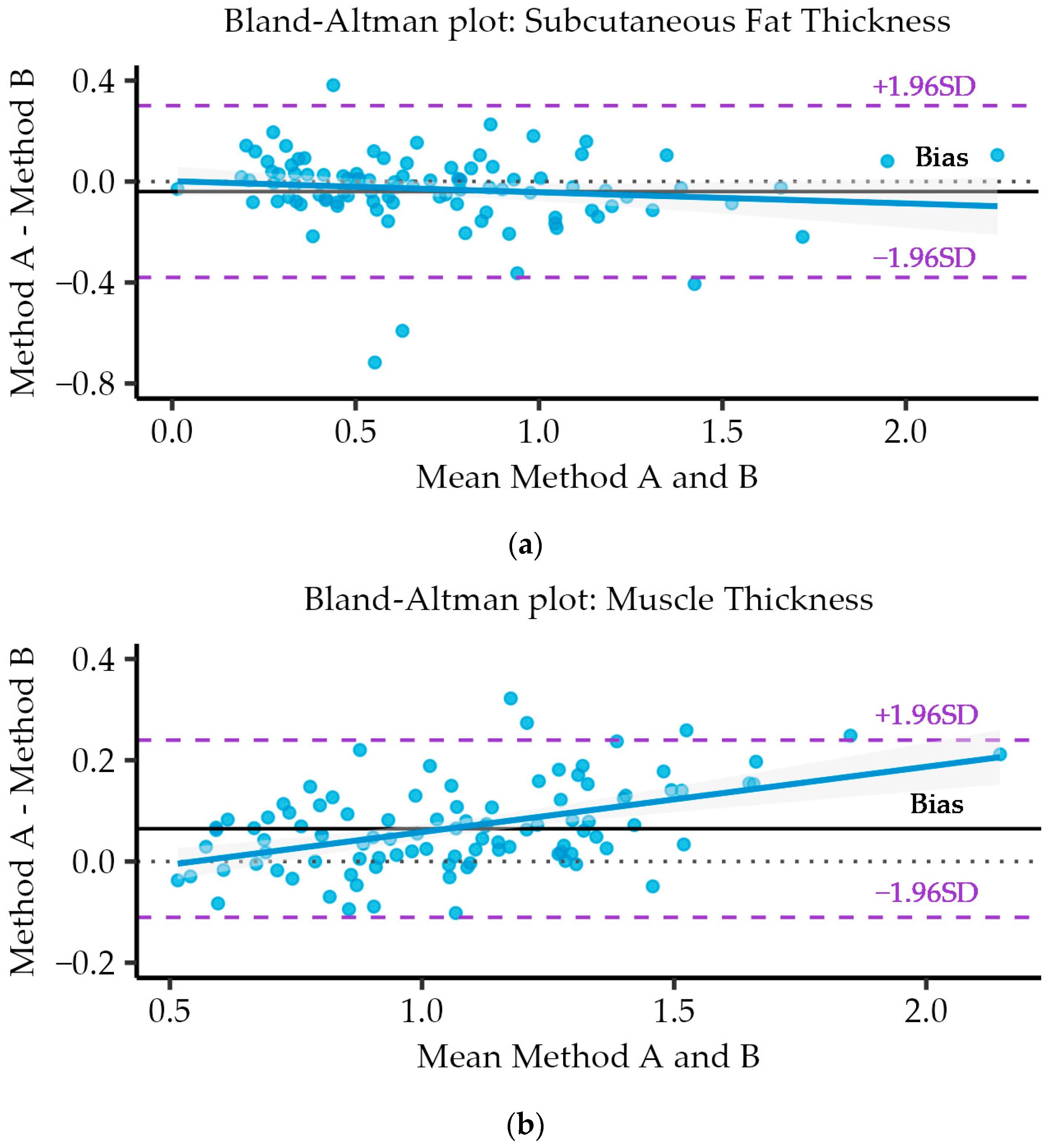
3.7. Bland–Altman Analysis and Plots
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Bachiller, B.R.; de Luis Roman, D. Management of disease-related malnutrition: A real-world experience with a novel concentrated high-protein energy-dense oral nutritional supplement. Postgrad. Med. 2024, 136, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Hernández, J. Prevalencia y costes de la malnutrición en pacientes hospitalizados: Estudio PREDyCES®. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Merker, M. Association of baseline inflammation with effectiveness of nutritional support among patients with disease-related malnutrition: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e200663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaegi-Braun, N. Validation of modified GLIM criteria to predict adverse clinical outcome and response to nutritional treatment: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Sanz, M.; Brosa, M.; Planas, M.; García-de-Lorenzo, M.; Celaya-Pérez, S.; Alvarez, J. PREDyCES study: The cost of hospital malnutrition in Spain. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingrich, A. Prevalence and overlap of sarcopenia, frailty, cachexia and malnutrition in older medical inpatients. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B. Consensus-defined sarcopenia predicts adverse outcomes after elective abdominal surgery: Meta-analysis. BJS Open 2023, 7, 065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Almeida, J.M. Nutritional ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, technical considerations and standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2023, 70, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: Towards standardized measurements. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; Bastijns, S.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, D.; Piotrowicz, K.; De Cock, A.M.; Full SARCUS Working Group. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: 2020 SARCUS update: Reply to the letter to the editor: SARCUS working group on behalf of the Sarcopenia Special Interest Group of the European Geriatric Medicine Society. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standard, D. Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine. Strateg. Doc. Available online: https://www.dicomstandard.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Cath, S.; Wachter, B.; Mittelstadt, M.; Floridi, L. Artificial intelligence and the ‘good society’: The US, EU, and UK approach. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2018, 24, 505–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1973, 6, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, M.M. Texture analysis using gray level run lengths. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1975, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, A.I.; Loew, M.H. Estimating fractal dimension with fractal interpolation function models. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Fractal dimension and retinal pathology: A meta-analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, F.; Alonso, F.J. A comparison among different Hill-type contraction dynamics formulations for muscle force estimation. Mech. Sci. 2016, 7, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, K.V.; Steeds, R.P.; Slater, L.T.; Rogers, J.K.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Kotecha, D. A Practical Guide to Assess the Reproducibility of Echocardiographic Measurements. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.F.; Lynn, F.; Meade, B.D. Use of coefficient of variation in assessing variability of quantitative assays. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2002, 9, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass Correlations: Uses in Assessing Rater Reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, G.; Stokes, M. Reliability of assessment tools in rehabilitation: An illustration of appropriate statistical analyses. Clin. Rehabil. 1998, 12, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljequist, D.; Elfving, B.; Skavberg Roaldsen, K. Intraclass correlation—A discussion and demonstration of basic features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J. Nutritional Ultrasonography, a method to evaluate Muscle Mass and Quality in Morphofunctional Assessment of Disease Related Malnutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahathevan, S. Association of ultrasound-derived metrics of the quadriceps muscle with protein energy wasting in hemodialysis patients: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luis Roman, D.A.; Lopez Gomez, J.J. Morphofunctional Nutritional Assessment in Clinical Practice: A New Approach to Assessing Nutritional Status. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
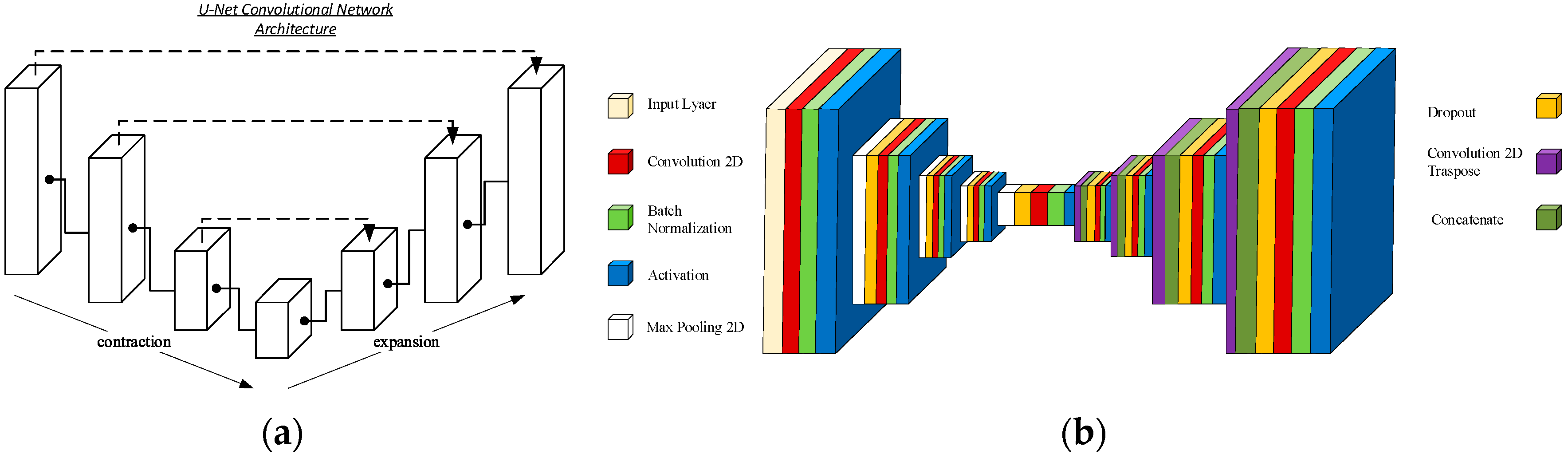
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.M. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCague, C. Introduction to radiomics for a clinical audience. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, R.G.; Burton, K.R.; Yu, J.P.; Scalzetti, E.M.; Yankeelov, T.E.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Mendiratta-Lala, M.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Ganeshan, D.; Lenchik, L.; et al. Methods, and challenges in quantitative imaging biomarker development. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Ullah, N.; Khan, J.A.; Assam, M.; Guzzo, A.; Aljuaid, H. Deep Breast Cancer Net: A Novel Deep Learning Model for Breast Cancer Detection Using Ultrasound Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, R.; Ayyoubzadeh, S.M.; Sohrabei, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Atashi, A. Prediction of Breast Cancer using Machine Learning Approaches. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2022, 12, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anari, S.; Tataei Sarshar, N.; Mahjoori, N.; Dorosti, S.; Rezaie, A. Review of deep learning approaches for thyroid cancer diagnosis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 20, 5052435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Deep learning-based radiomics allows for a more accurate assessment of sarcopenia as a prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2024, 25, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, C.B.; Ovalle, H.F.; Moreno, M.F.; Aller de la Fuente, R.; de Luis Román, D. Undernutrition measured by the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) test and related risk factors in older adults under hospital emergency care. Nutrition 2019, 66, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmas, F.; Mucarzel, F.; Ricart, M.; Lluch, A.; Burgos, R. Body composition assessment with ultrasound muscle measurement: Optimization through the use of semi-automated tools in colorectal cancer. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1372816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, M.; Trappe, S.; Trappe, T.A. Human skeletal muscle size with ultrasound imaging: A comprehensive review. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen, J.P.; Hoffren, M.; Hulmi, J.J.; Pietikäinen, M.; Mero, A.A.; Avela, J.; Häkkinen, K. Panoramic ultrasonography is a valid method to measure changes in skeletal muscle cross-sectional area. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56.9 ± 16 |
| Weight (kg) | 55.6 ± 14.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.9 ± 4.3 |
| Sex (male/female) | 40/60 |
| Subcutaneous Fat Thickness (SFT) | Muscle Thickness (MT) | Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method A | Method B | Method A | Method B | Method A | Method B | |
| N | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Mean | 0.70 | 0.74 | 1.10 | 1.04 | 3.47 | 3.52 |
| SD | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 1.27 | 1.30 |
| Min | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 1.06 | 1.10 |
| Max | 2.30 | 2.20 | 2.25 | 2.04 | 9.30 | 9.46 |
| Skewness | 1.21 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.97 |
| Kurtosis | 1.94 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 3.08 | 2.96 |
| SE | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Coefficient of Variation (%) Method A and Method B | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Subcutaneous Fat Thickness (SFT) | Muscle Thickness (MT) | Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) |
| A | 58.39 | 30.50 | 36.50 |
| B | 57.68 | 28.36 | 36.91 |
| Correlation between Method A and Method B | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | Correlation | p_value |
| Subcutaneous Fat Thickness (SFT) | 0.864 ⁺ | 5.2 × 10−32 |
| Muscle Thickness (MT) | 0.969 * | 4.82 × 10−61 |
| Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) | 0.991 ⁺ | 1.92 × 10−86 |
| Subcutaneous Fat Thickness (SFT) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Bland Altman Test | ||||||
| Raters | ICC Coeff. | CI 95% | Mean Diff. | SE Diff. | CI 95% Diff. | SD Diff. | Lim. 95% Agreement |
| Single fixed raters | 0.912 | [0.872, 0.940] | −0.04 | 0.017 | [−0.07, −0.005] | 0.174 | [−0.38, 0.30] |
| Average fixed raters | 0.954 | [0.931, 0.969] | |||||
| (a) | |||||||
| Muscle Thickness | |||||||
| ICC | Bland Altman Test | ||||||
| Raters | ICC Coeff. | CI 95% | Mean Diff. | SE Diff. | CI 95% Diff. | SD Diff. | Lim. 95% Agreement |
| Single fixed raters | 0.960 | [0.941, 0.973] | 0.065 | 0.009 | [0.047, 0.082] | 0.089 | [−0.11, 0.24] |
| Average fixed raters | 0.980 | [0.970, 0.986] | |||||
| (b) | |||||||
| Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) | |||||||
| ICC | Bland Altman Test | ||||||
| Raters | ICC Coeff. | CI 95% | Mean Diff. | SE Diff. | CI 95% Diff. | SD Diff. | Lim. 95% Agreement |
| Single fixed raters | 0.995 | [0.993, 0.997] | −0.051 | 0.013 | [−0.076, −0.026] | 0.127 | [−0.3, 0.20] |
| Average fixed raters | 0.998 | [0.996, 0.998] | |||||
| (c) | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Herreros, S.; López Gómez, J.J.; Cebria, A.; Izaola, O.; Salvador Coloma, P.; Nozal, S.; Cano, J.; Primo, D.; Godoy, E.J.; de Luis, D. Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM). Nutrients 2024, 16, 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121806
García-Herreros S, López Gómez JJ, Cebria A, Izaola O, Salvador Coloma P, Nozal S, Cano J, Primo D, Godoy EJ, de Luis D. Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM). Nutrients. 2024; 16(12):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121806
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Herreros, Sergio, Juan Jose López Gómez, Angela Cebria, Olatz Izaola, Pablo Salvador Coloma, Sara Nozal, Jesús Cano, David Primo, Eduardo Jorge Godoy, and Daniel de Luis. 2024. "Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM)" Nutrients 16, no. 12: 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121806
APA StyleGarcía-Herreros, S., López Gómez, J. J., Cebria, A., Izaola, O., Salvador Coloma, P., Nozal, S., Cano, J., Primo, D., Godoy, E. J., & de Luis, D. (2024). Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM). Nutrients, 16(12), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121806









