Oral Treatment with the Extract of Euterpe oleracea Mart. Improves Motor Dysfunction and Reduces Brain Injury in Rats Subjected to Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clarified Lyophilized Açaí (Euterpe oleracea) Extract
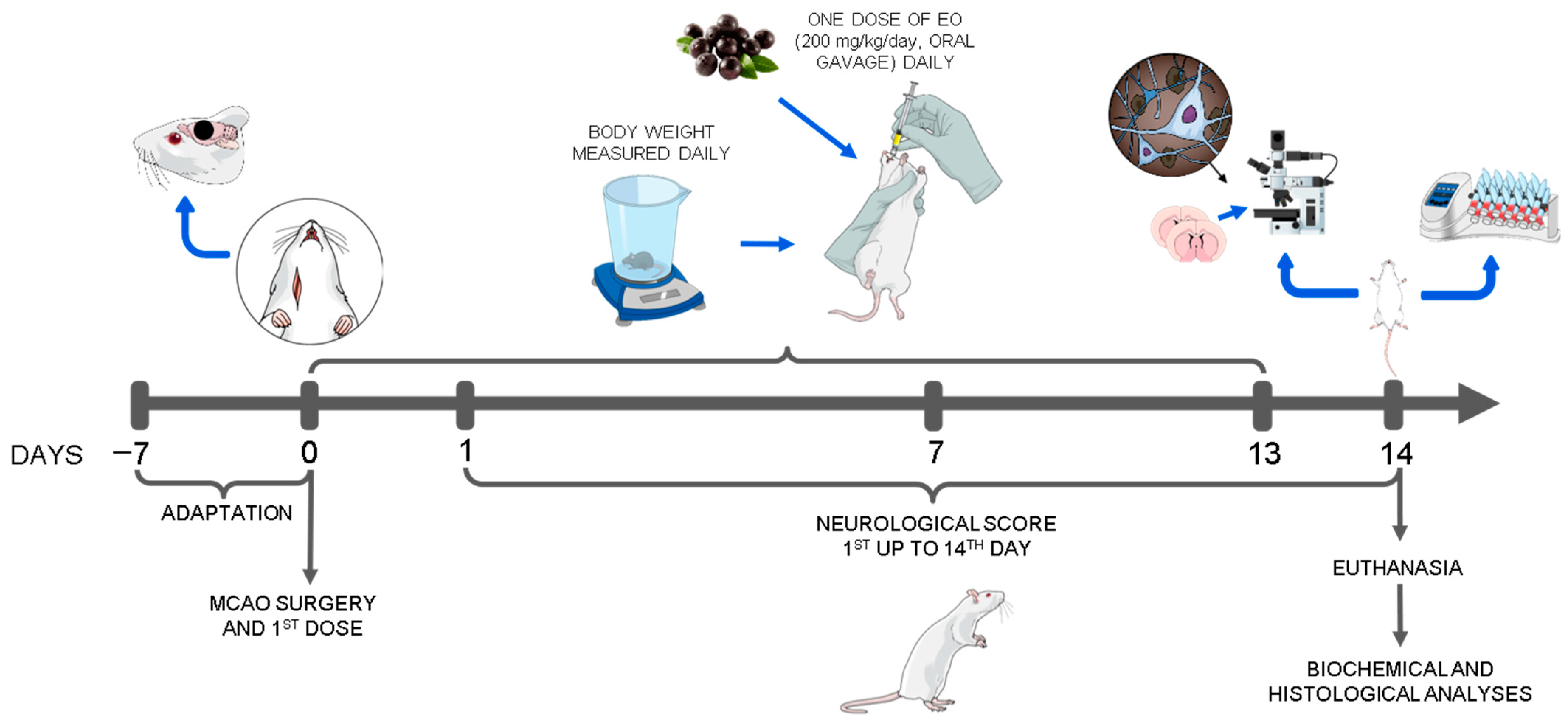
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Surgery
2.4. Neurological Score and Behavioral Test
2.5. Histological Analyses
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
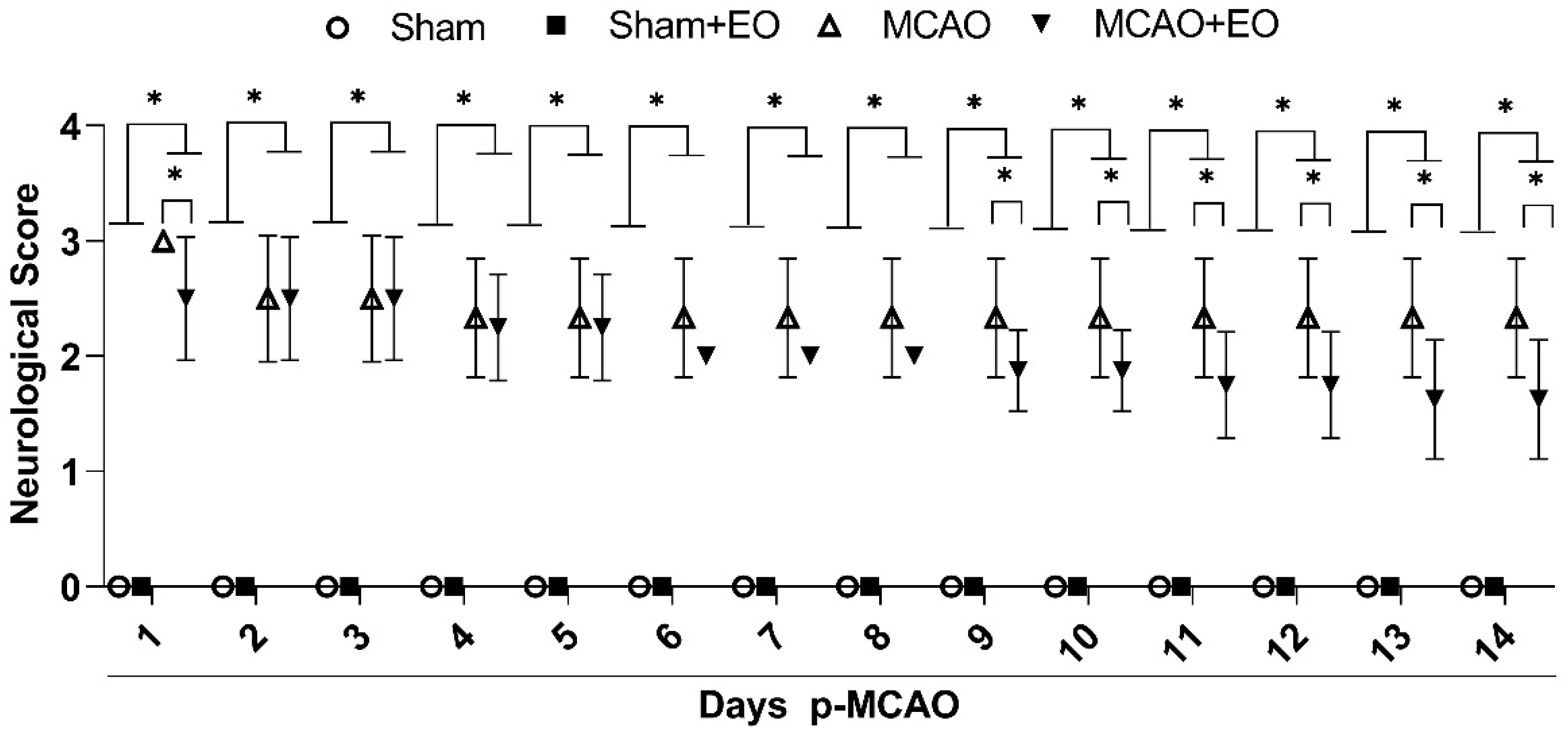
3.1. Açaí Extract Improves the Behavioral Outcome of Animals Submitted to Ischemic Stroke
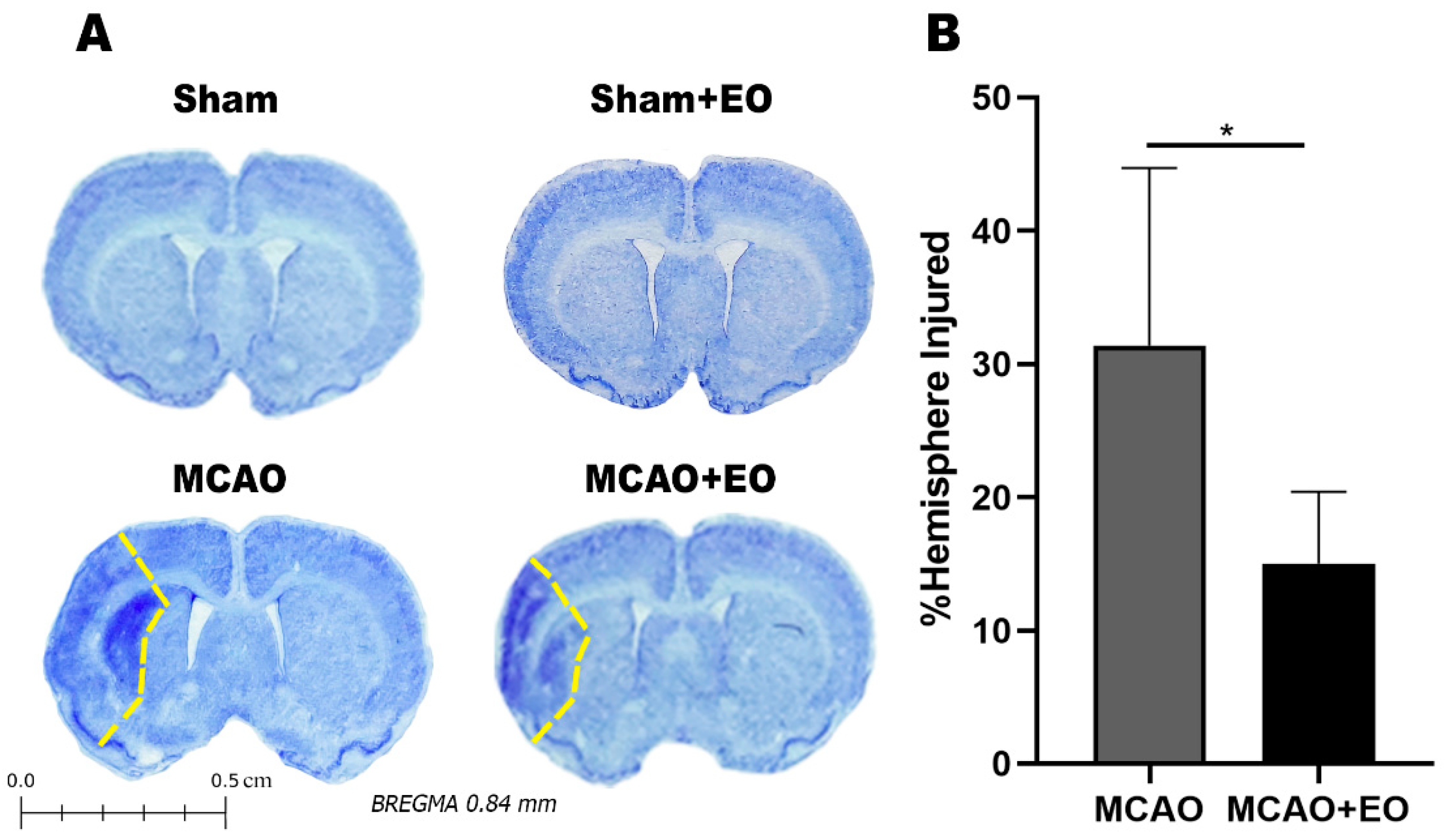
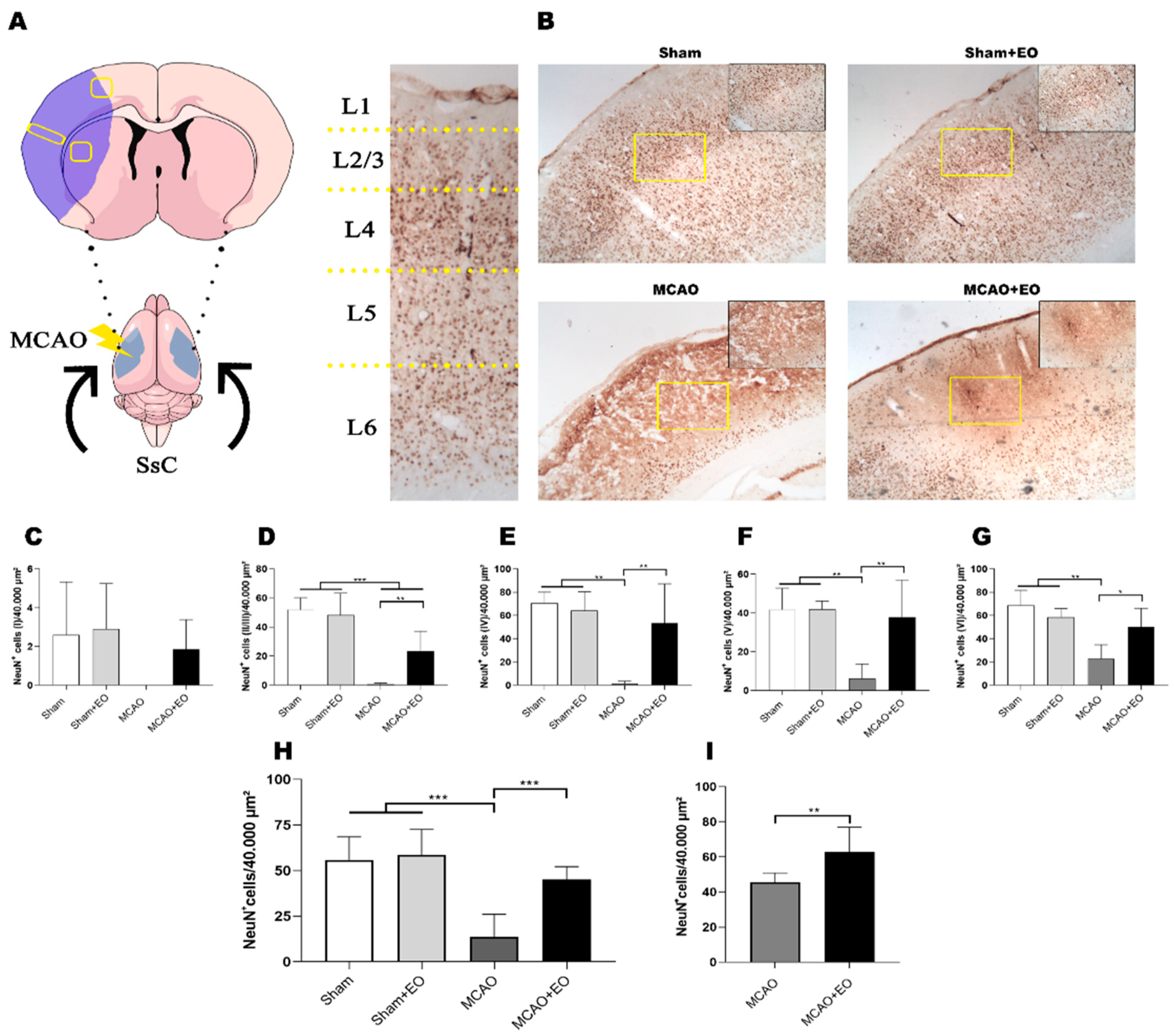
3.2. Açaí Extract Reduces the Size of the Area of Infarction and Increases the Number of Surviving Neurons after Ischemic Stroke
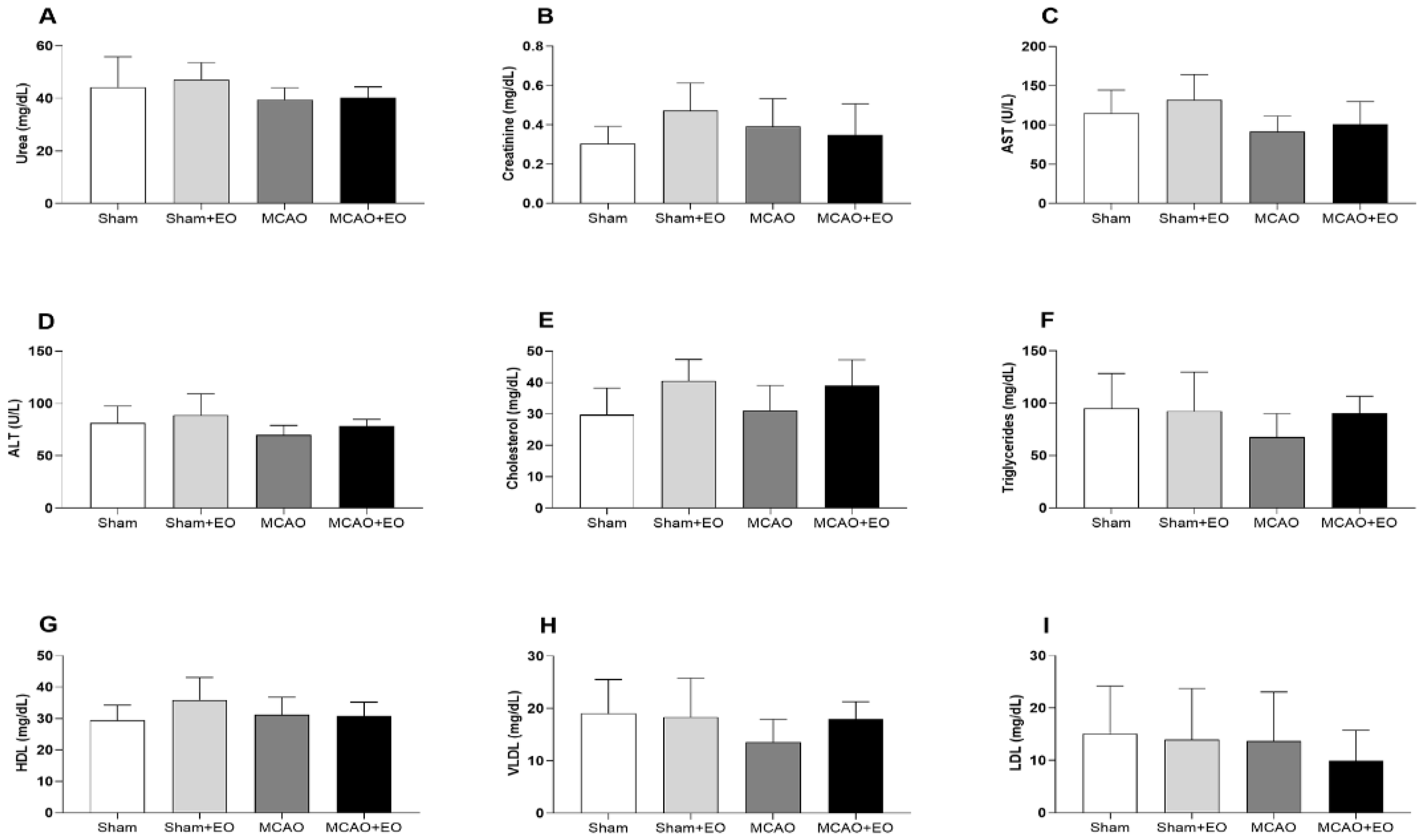
3.3. Açaí Extract Did Not Cause Biochemical Alterations after Ischemic Stroke
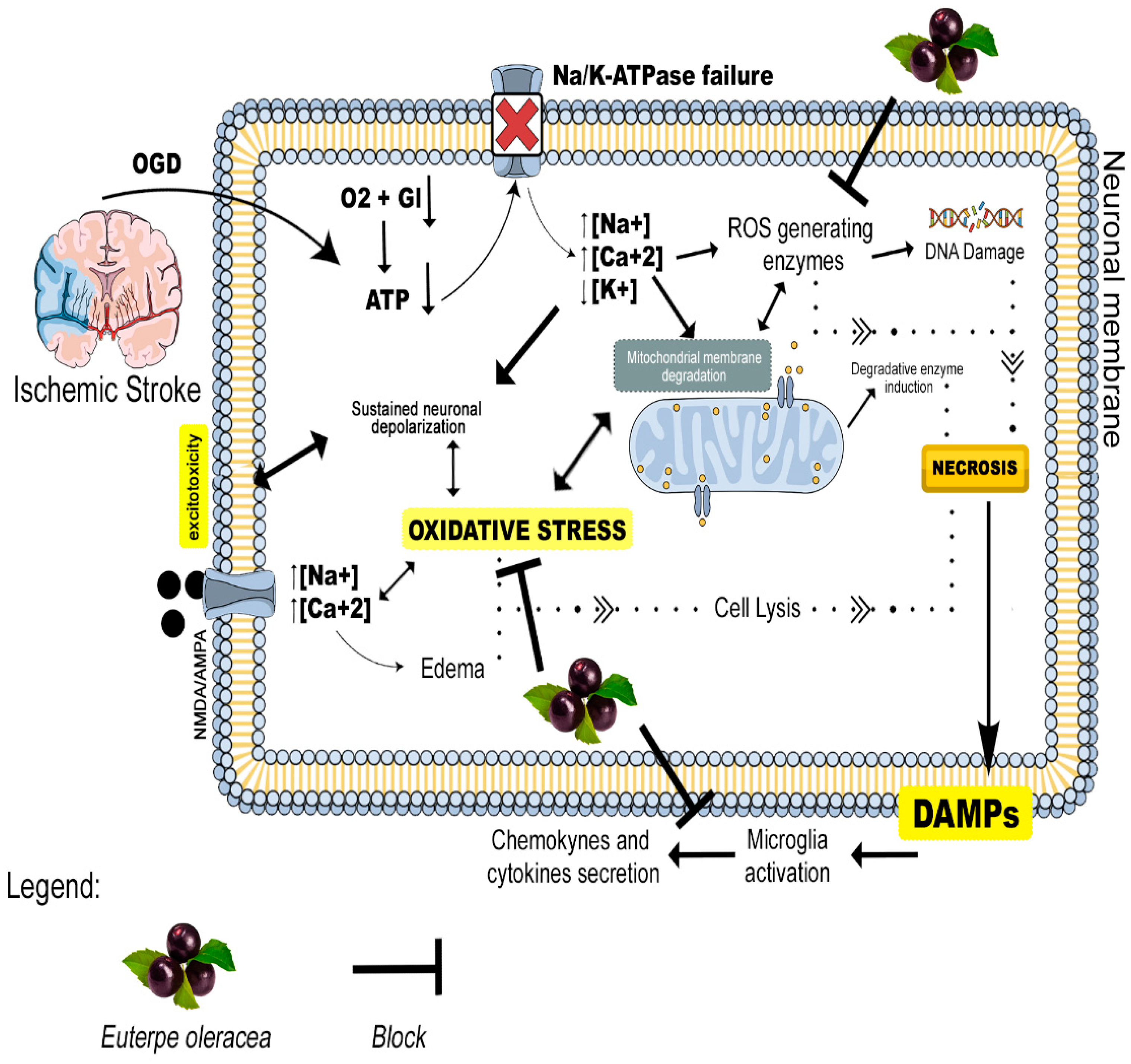
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Carrion, J.; Martin-Rodriguez, J.F.; Damas-Lopez, J.; Barroso y Martin, J.M.; Dominguez-Morales, M.R. Delta–alpha ratio correlates with level of recovery after neurorehabilitation in patients with acquired brain injury. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povlsen, G.K.; Longden, T.A.; Bonev, A.D.; Hill-Eubanks, D.C.; Nelson, M.T. Uncoupling of neurovascular communication after transient global cerebral ischemia is caused by impaired parenchymal smooth muscle Kir channel function. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Winlow, W.; Farzaneh, M.; Farbood, Y.; Moghaddam, H.F. Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic stroke. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1167–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Neurovascular Unit: A critical role in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Datta, S. Medicinal Plants against Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.H. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Challenges and prospective. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 216, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.d.S.P.; Lemos, M.A.; dos Santos, E.O.; dos Santos, V.F. Coeficiente de caminhamento entre caracteres agronômicos e a produção de frutos em açaizeiro (Euterpe oleracea Mart.). Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2000, 22, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.P.; Cunha, V.M.B.; Sousa, S.H.B.; Menezes, E.G.O.; Bezerra, P.d.N.; de Farias Neto, J.T.; Filho, G.N.R.; Araújo, M.E.; de Carvalho, R.N., Jr. Supercritical CO2 extraction of lyophilized Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) pulp oil from three municipalities in the state of Pará, Brazil. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 31, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udani, J.K.; Singh, B.B.; Singh, V.J.; Barrett, M.L. Effects of Açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) berry preparation on metabolic parameters in a healthy overweight population: A pilot study. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minighin, E.C.; Anastácio, L.R.; Melo, J.O.F.; Labanca, R.A. Açai (Euterpe oleracea) e suas contribuições para alcance da ingestão diária aceitável de ácidos graxos essenciais. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, L.N.; Silva, M.G.; Uehara, S.K.; Luiz, R.R.; Nogueira Neto, J.F.; Rosa, G.; Moraes de Oliveira, G.M. Effects of a hypoenergetic diet associated with açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) pulp consumption on antioxidant status, oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in overweight, dyslipidemic individuals. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida Magalhães, T.S.S.; de Oliveira Macedo, P.C.; Converti, A.; Neves de Lima, Á.A. The Use of Euterpe oleracea Mart. As a New Perspective for Disease Treatment and Prevention. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrifano, G.P.F.; Lichtenstein, M.P.; Souza-Monteiro, J.R.; Farina, M.; Rogez, H.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Suñol, C.; Crespo-López, M.E. Clarified Açaí (Euterpe oleracea) Juice as an Anticonvulsant Agent: In Vitro Mechanistic Study of GABAergic Targets. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Thakali, K.M.; Xie, C.; Kondo, M.; Tong, Y.; Ou, B.; Jensen, G.; Medina, M.B.; Schauss, A.G.; Wu, X. Bioactivities of açaí (Euterpe precatoria Mart.) fruit pulp, superior antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to Euterpe oleracea Mart. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, S.M.; Fisher, D.R.; Larson, J.; Bielinski, D.F.; Rimando, A.M.; Carey, A.N.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Anthocyanin-rich Açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Fruit Pulp Fractions Attenuate Inflammatory Stress Signaling in Mouse Brain BV-2 Microglial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Magalhães, T.S.S.; de Oliveira Macedo, P.C.; Kawashima Pacheco, S.Y.; da Silva, S.S.; Barbosa, E.G.; Pereira, R.R.; Costa, R.M.R.; Silva Junior, J.O.C.; da Silva Ferreira, M.A.; de Almeida, J.C.; et al. Development and Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Modulatory Activity of Inclusion Complex of Euterpe oleracea Mart Oil and β-Cyclodextrin or HP-β-Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Palencia, L.A.; Mertens-Talcott, S.; Talcott, S.T. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Properties, and Thermal Stability of a Phytochemical Enriched Oil from Açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4631–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favacho, H.A.S.; Oliveira, B.R.; Santos, K.C.; Medeiros, B.J.L.; Sousa, P.J.C.; Perazzo, F.F.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Euterpe oleracea Mart., Arecaceae, oil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 21, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Monteiro, J.R.; Hamoy, M.; Santana-Coelho, D.; Arrifano, G.P.F.F.; Paraense, R.S.O.O.; Costa-Malaquias, A.; Mendonça, J.R.; da Silva, R.F.; Monteiro, W.S.C.C.; Rogez, H.; et al. Anticonvulsant properties of Euterpe oleracea in mice. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.; Cruz, A.P.G.; Cabral, L.M.C.; de Freitas, S.C.; Taxi, C.M.A.D.; Donangelo, C.M.; de Andrade Mattietto, R.; Friedrich, M.; da Matta, V.M.; Marx, F. Chemical characterization and evaluation of antioxidant properties of Açaí fruits (Euterpe oleraceae Mart.) during ripening. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, G.A.; Narváez-Cuenca, C.-E.; Vincken, J.-P.; Gruppen, H. Polyphenolic composition and antioxidant activity of açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) from Colombia. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-Peixoto, J.; Moura, M.R.L.; Cunha, F.A.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Monteiro, W.D.; de Carvalho, L.M.J.; Farinatti, P.d.T.V. Consumption of açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) functional beverage reduces muscle stress and improves effort tolerance in elite athletes: A randomized controlled intervention study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.C.; Martins, A.B.; Rocha, M.C.F.; Cavalcante Júnior, S.M.; Feitosa, C.M. Espécies medicinais do Brasil com potencial anti-inflamatório ou antioxidante: Uma revisão. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e10310716196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.L.S.; Rozet, E.; Larondelle, Y.; Hubert, P.; Rogez, H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Development and validation of an UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS method for non-anthocyanin flavonoids quantification in Euterpe oleracea juice. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9235–9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.L.S.; Rozet, E.; Chataigné, G.; Oliveira, A.C.; Rabelo, C.A.S.; Hubert, P.; Rogez, H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. A rapid validated UHPLC–PDA method for anthocyanins quantification from Euterpe oleracea fruits. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 907, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandra-Perini, J.; Perini, J.A.; Rodrigues-Baptista, K.C.; de Moura, R.S.; Junior, A.P.; dos Santos, T.A.; Souza, P.J.C.; Nasciutti, L.E.; Machado, D.E. Euterpe oleracea extract inhibits tumorigenesis effect of the chemical carcinogen DMBA in breast experimental cancer. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bem, G.F.; Costa, C.A.; Santos, I.B.; Cristino Cordeiro, V.d.S.; de Carvalho, L.C.R.M.; de Souza, M.A.V.; Soares, R.d.A.; Sousa, P.J.d.C.; Ognibene, D.T.; Resende, A.C.; et al. Antidiabetic effect of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (açaí) extract and exercise training on high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: A positive interaction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.O.; Mattos, B.G.; Jóia de Mello, V.; Martins-Filho, A.J.; da Costa, E.T.; Yamada, E.S.; Hamoy, M.; Lopes, D.C.F. Increased Relative Delta Bandpower and Delta Indices Revealed by Continuous qEEG Monitoring in a Rat Model of Ischemia-Reperfusion. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 645138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, P.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Guo, H.; Guo, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, W.; Sun, Y.; et al. The novel estrogenic receptor GPR30 alleviates ischemic injury by inhibiting TLR4-mediated microglial inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Kriz, J.; Seidah, N.G. Mouse Model of Intraluminal MCAO: Cerebral Infarct Evaluation by Cresyl Violet Staining. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 69, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Osaki, H.; Ueta, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Muragaki, Y.; Kawamata, T.; Miyata, M. Layer-specific sensory processing impairment in the primary somatosensory cortex after motor cortex infarction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, E.-J. Protective effect of anthocyanins in middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion model of cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunil, A.G.; Kesavanarayanan, K.S.; Kalaivani, P.; Sathiya, S.; Ranju, V.; Priya, R.J.; Pramila, B.; Paul, F.D.S.; Venkhatesh, J.; Babu, C.S. Total oligomeric flavonoids of Cyperus rotundus ameliorates neurological deficits, excitotoxicity and behavioral alterations induced by cerebral ischemic–reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 84, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.-X.; Chen, J.-H.; Li, J.-W.; Cheng, F.-R.; Yuan, K. Protection of Anthocyanin from Myrica rubra against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Modulation of the TLR4/NF-$κ$B and NLRP3 Pathways. Molecules 2018, 23, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y. Grape seed proanthocyanidins attenuate apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Cristino Cordeiro, V.; de Bem, G.F.; da Costa, C.A.; Santos, I.B.; de Carvalho, L.C.R.M.; Ognibene, D.T.; da Rocha, A.P.M.; de Carvalho, J.J.; de Moura, R.S.; Resende, A.C. Euterpe oleracea Mart. seed extract protects against renal injury in diabetic and spontaneously hypertensive rats: Role of inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, L.d.F.; Silva, D.N.; Boasquivis, P.F.; Paiva, F.A.; Guerra, J.F.d.C.; Martins, T.A.F.; de Jesus Torres, Á.G.; de Paula, I.T.B.R.; Caneschi, W.L.; Jacolot, P.; et al. Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Modulates Oxidative Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans by Direct and Indirect Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira de Souza, M.; Barbosa, P.; Pala, D.; Ferreira Amaral, J.; Pinheiro Volp, A.C.; Nascimento de Freitas, R. A prospective study in women: Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Martius) dietary intake affects serum p-selectin, leptin, and visfatin levels. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 38, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.O.; Pala, D.; Silva, C.T.; de Souza, M.O.; do Amaral, J.F.; Vieira, R.A.L.; Folly, G.A.d.F.; Volp, A.C.P.; de Freitas, R.N. Açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) pulp dietary intake improves cellular antioxidant enzymes and biomarkers of serum in healthy women. Nutrition 2016, 32, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabrun, S.; Hillier, S. Evidence for the retraining of sensation after stroke: A systematic review. Clin. Rehabil. 2009, 23, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. Modulation of Proprioceptive Integration in the Motor Cortex Shapes Human Motor Learning. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9000–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friel, K.M.; Barbay, S.; Frost, S.B.; Plautz, E.J.; Hutchinson, D.M.; Stowe, A.M.; Dancause, N.; Zoubina, E.V.; Quaney, B.M.; Nudo, R.J. Dissociation of Sensorimotor Deficits After Rostral Versus Caudal Lesions in the Primary Motor Cortex Hand Representation. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudo, R.J.; Friel, K.M.; Delia, S.W. Role of sensory deficits in motor impairments after injury to primary motor cortex. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernaskie, J.; Chernenko, G.; Corbett, D. Efficacy of Rehabilitative Experience Declines with Time after Focal Ischemic Brain Injury. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreanu, L.; Mao, T.; Sternson, S.M.; Svoboda, K. The subcellular organization of neocortical excitatory connections. Nature 2009, 457, 1142–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamisawa, G.; Kwon, S.E.; Chevée, M.; Brown, S.P.; O’Connor, D.H. A Non-canonical Feedback Circuit for Rapid Interactions between Somatosensory Cortices. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2718–2731.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Sherman, S.M. A Sensorimotor Pathway via Higher-Order Thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Alloway, K.D. Rat whisker motor cortex is subdivided into sensory-input and motor-output areas. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Kusefoglu, D.; Hooks, B.M.; Huber, D.; Petreanu, L.; Svoboda, K. Long-Range Neuronal Circuits Underlying the Interaction between Sensory and Motor Cortex. Neuron 2011, 72, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, K.A.; Adkins, D.L.; Donlan, N.A.; Asay, A.L.; Thomas, N.; Kleim, J.A.; Jones, T.A. The Organization of the Forelimb Representation of the C57BL/6 Mouse Motor Cortex as Defined by Intracortical Microstimulation and Cytoarchitecture. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.C.; Batista, A.; da Costa, D.C.F.; Moura-Nunes, N.; Koury, J.C.; da Costa, C.A.; Resende, Â.C.; Daleprane, J.B. Açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) seed flour prevents obesity-induced hepatic steatosis regulating lipid metabolism by increasing cholesterol excretion in high-fat diet-fed mice. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feio, C.A.; Izar, M.C.; Ihara, S.S.; Kasmas, S.H.; Martins, C.M.; Feio, M.N.; Maués, L.A.; Borges, N.C.; Moreno, R.A.; Póvoa, R.M.; et al. Euterpe oleracea (Açai) Modifies Sterol Metabolism and Attenuates Experimentally-Induced Atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2012, 19, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, D.Y.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Manzanero, S.; Chunduri, P.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathogenesis of acute stroke and the role of inflammasomes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 941–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brait, V.H.; Arumugam, T.V.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G. Importance of T Lymphocytes in Brain Injury, Immunodeficiency, and Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teixeira, L.L.; Alencar, H.M.N.d.S.; Ferreira, L.O.; Rodrigues, J.C.M.; de Souza, R.D.; Celestino Pinto, L.; Muto, N.A.; Rogez, H.; Martins-Filho, A.J.; Joia de Mello, V.; et al. Oral Treatment with the Extract of Euterpe oleracea Mart. Improves Motor Dysfunction and Reduces Brain Injury in Rats Subjected to Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051207
Teixeira LL, Alencar HMNdS, Ferreira LO, Rodrigues JCM, de Souza RD, Celestino Pinto L, Muto NA, Rogez H, Martins-Filho AJ, Joia de Mello V, et al. Oral Treatment with the Extract of Euterpe oleracea Mart. Improves Motor Dysfunction and Reduces Brain Injury in Rats Subjected to Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeixeira, Leonan Lima, Helma Maria Negrão da Silva Alencar, Luan Oliveira Ferreira, João Cleiton Martins Rodrigues, Rafael Dias de Souza, Laine Celestino Pinto, Nilton Akio Muto, Hervé Rogez, Arnaldo Jorge Martins-Filho, Vanessa Joia de Mello, and et al. 2023. "Oral Treatment with the Extract of Euterpe oleracea Mart. Improves Motor Dysfunction and Reduces Brain Injury in Rats Subjected to Ischemic Stroke" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051207
APA StyleTeixeira, L. L., Alencar, H. M. N. d. S., Ferreira, L. O., Rodrigues, J. C. M., de Souza, R. D., Celestino Pinto, L., Muto, N. A., Rogez, H., Martins-Filho, A. J., Joia de Mello, V., Hamoy, M., Costa, E. T. d., & Lopes, D. C. F. (2023). Oral Treatment with the Extract of Euterpe oleracea Mart. Improves Motor Dysfunction and Reduces Brain Injury in Rats Subjected to Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients, 15(5), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051207





