Calcium Homeostasis and Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Extraction
| Exposure or Outcome | Reference | Participants | Web Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels | PMID: 32059762 [33] | 443,734 individuals | * ebi-a-GCST010144 |
| Calcium | PMID: 34662886 [32] a | 315,153 individuals | * ukb-d-30680_irnt |
| Fibroblast growth factor 23 | PMID: 33067605 [34] | 21,758 individuals | * ebi-a-GCST90012022 |
| Parathyroid hormone | PMID: 29875488 [35] | 3301 individuals | * prot-a-2431 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | PMID: 30617256 [36] | 71,880 cases and 383,378 controls | PGC |
| Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | PMID: 29325848 [37] | 38,691 cases and 38,691 controls | PGC |
| Anorexia nervosa | PMID: 28494655 [38] | 3495 cases and 10,982 controls | PGC |
| Autism spectrum disorder | PMID: 30804558 [39] | 18,381 cases and 27,969 controls | PGC |
| Bipolar disorder | PMID: 31043756 [40] | 20,352 cases and 31,358 controls | PGC |
| Major depressive disorder | PMID: 30718901 [41] | 170,756 cases and 329,443 controls | PGC |
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder | PMID: 28761083 [42] | 2688 cases and 7037 controls | PGC |
| Schizophrenia | PMID: 35396580 [43] | 52,017 cases and 75,889 controls | PGC |
| Tourette syndrome | PMID: 30818990 [44] | 4819 cases and 9488 controls | PGC |
2.3. Selection of the Instrumental Variables (IVs)
2.4. Two-Sample Univariable MR Analysis
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. MVMR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Instruments Selected in MR
3.2. Causal Effect of Genetically Predicted Calcium Homeostasis on Psychiatric Disorders
3.3. Causal Effect of Genetically Predicted Psychiatric Disorders on Calcium Homeostasis
3.4. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Ding, C.; Xu, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D.; Pang, W.; Tu, W.; Chen, Y. Effects of vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy on offspring health at birth: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Marco, L. Calcium, Vitamin D, and Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wu, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G.; Li, F. Disorders of Calcium and Phosphorus Metabolism and the Proteomics/Metabolomics-Based Research. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 576110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, J.C. The role of vitamin D in the endocrinology controlling calcium homeostasis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 453, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prie, D.; Friedlander, G. Reciprocal control of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and FGF23 formation involving the FGF23/Klotho system. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disease, G.B.D.; Injury, I.; Prevalence, C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, D.; Thornicroft, G.; Atun, R. Estimating the true global burden of mental illness. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assary, E.; Vincent, J.P.; Keers, R.; Pluess, M. Gene-environment interaction and psychiatric disorders: Review and future directions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 77, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, L.R.; Burne, T.H.; Eyles, D.W.; McGrath, J.J. Vitamin D and the brain. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, A.; Lumsden, A.; Hypponen, E. Relationship between Serum 25(OH)D and Depression: Causal Evidence from a Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2020, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Bojesen, S.E.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Reduced 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucksdorff, M.; Brown, A.S.; Chudal, R.; Surcel, H.M.; Hinkka-Yli-Salomaki, S.; Cheslack-Postava, K.; Gyllenberg, D.; Sourander, A. Maternal Vitamin D Levels and the Risk of Offspring Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 60, 142–151.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Shan, L.; Du, L.; Feng, J.; Xu, Z.; Staal, W.G.; Jia, F. Serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 25, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valipour, G.; Saneei, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Serum vitamin D levels in relation to schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3863–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernell, E.; Bejerot, S.; Westerlund, J.; Miniscalco, C.; Simila, H.; Eyles, D.; Gillberg, C.; Humble, M.B. Autism spectrum disorder and low vitamin D at birth: A sibling control study. Mol. Autism 2015, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, N.M.; Khademalhoseini, S.; Vakili, Z.; Assarian, F. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on depression in elderly patients: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorde, R.; Sneve, M.; Figenschau, Y.; Svartberg, J.; Waterloo, K. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on symptoms of depression in overweight and obese subjects: Randomized double blind trial. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedelin, M.; Lof, M.; Olsson, M.; Lewander, T.; Nilsson, B.; Hultman, C.M.; Weiderpass, E. Dietary intake of fish, omega-3, omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin D and the prevalence of psychotic-like symptoms in a cohort of 33,000 women from the general population. BMC Psychiatry 2010, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Samaan, Z.; Falavigna, M.; Zhang, S.; Adachi, J.D.; Cheng, J.; Papaioannou, A.; Thabane, L. Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in depression in adults: A systematic review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.; Elserogy, Y.M.; Al-Atram, A.A.; Cannell, J.J.; Bjorklund, G.; Abdel-Reheim, M.K.; Othman, H.A.; El-Houfey, A.A.; Abd El-Aziz, N.H.; et al. Vitamin D status in autism spectrum disorders and the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in autistic children. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, N.; Jazayeri, S.; Tehrani-Doost, M.; Djalali, M.; Hosseini, M.; Effatpanah, M.; Davari-Ashtiani, R.; Karami, E. Effect of vitamin D supplementation as adjunctive therapy to methylphenidate on ADHD symptoms: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.; Saari, K.; Hakko, H.; Jokelainen, J.; Jones, P.; Jarvelin, M.R.; Chant, D.; Isohanni, M. Vitamin D supplementation during the first year of life and risk of schizophrenia: A Finnish birth cohort study. Schizophr. Res. 2004, 67, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, J.; Galer, P.; Ma, D.; Chen, C.; Xiong, T. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 670–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C. The effect of vitamin D supplementation in treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Xiong, R.; Xu, Z.; Luo, X.; Li, G.; Tan, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid FGF23 levels correlate with a measure of impulsivity. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 264, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Platt, G.; Gonzalez-Reimers, E.; Rodriguez-Gaspar, M.; Martin-Gonzalez, C.; Perez-Hernandez, O.; Romero-Acevedo, L.; Espelosin-Ortega, E.; Vega-Prieto, M.J.; Santolaria-Fernandez, F. Alpha Klotho and Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Among Alcoholics. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2017, 52, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, E.; Fransson, E.; White, R.A.; Papadopoulos, F.C.; Edvinsson, A.; Kamali-Moghaddam, M.; Cunningham, J.L.; Sundstrom-Poromaa, I.; Skalkidou, A. Inflammatory markers in women with postpartum depressive symptoms. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Paz Oliveira, G.; Elias, R.M.; Peres Fernandes, G.B.; Moyses, R.; Tufik, S.; Bichuetti, D.B.; Coelho, F.M.S. Decreased concentration of klotho and increased concentration of FGF23 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with narcolepsy. Sleep Med. 2021, 78, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Davey Smith, G.; Windmeijer, F.; Bowden, J. An examination of multivariable Mendelian randomization in the single-sample and two-sample summary data settings. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A. Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backman, J.D.; Li, A.H.; Marcketta, A.; Sun, D.; Mbatchou, J.; Kessler, M.D.; Benner, C.; Liu, D.; Locke, A.E.; Balasubramanian, S.; et al. Exome sequencing and analysis of 454,787 UK Biobank participants. Nature 2021, 599, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousaki, D.; Mitchell, R.; Dudding, T.; Haworth, S.; Harroud, A.; Forgetta, V.; Shah, R.L.; Luan, J.; Langenberg, C.; Timpson, N.J.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study for Vitamin D Levels Reveals 69 Independent Loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkersen, L.; Gustafsson, S.; Wang, Q.; Hansen, D.H.; Hedman, A.K.; Schork, A.; Page, K.; Zhernakova, D.V.; Wu, Y.; Peters, J.; et al. Genomic and drug target evaluation of 90 cardiovascular proteins in 30,931 individuals. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.B.; Maranville, J.C.; Peters, J.E.; Stacey, D.; Staley, J.R.; Blackshaw, J.; Burgess, S.; Jiang, T.; Paige, E.; Surendran, P.; et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature 2018, 558, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hagg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new loci and functional pathways influencing Alzheimer’s disease risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Walters, R.K.; Demontis, D.; Mattheisen, M.; Lee, S.H.; Robinson, E.; Brikell, I.; Ghirardi, L.; Larsson, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; et al. A Genetic Investigation of Sex Bias in the Prevalence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, L.; Yilmaz, Z.; Gaspar, H.; Walters, R.; Goldstein, J.; Anttila, V.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Ripke, S.; Eating Disorders Working Group of the Psychiatric; Genomics, C.; et al. Significant Locus and Metabolic Genetic Correlations Revealed in Genome-Wide Association Study of Anorexia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Ripke, S.; Als, T.D.; Mattheisen, M.; Walters, R.K.; Won, H.; Pallesen, J.; Agerbo, E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Anney, R.; et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.A.; Breen, G.; Forstner, A.J.; McQuillin, A.; Ripke, S.; Trubetskoy, V.; Mattheisen, M.; Wang, Y.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Foundation Genetics Collaborative (IOCDF-GC) and OCD Collaborative Genetics Association Studies (OCGAS). Revealing the complex genetic architecture of obsessive-compulsive disorder using meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoy, V.; Pardinas, A.F.; Qi, T.; Panagiotaropoulou, G.; Awasthi, S.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Bryois, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Dennison, C.A.; Hall, L.S.; et al. Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature 2022, 604, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Sul, J.H.; Tsetsos, F.; Nawaz, M.S.; Huang, A.Y.; Zelaya, I.; Illmann, C.; Osiecki, L.; Darrow, S.M.; Hirschtritt, M.E.; et al. Interrogating the Genetic Determinants of Tourette’s Syndrome and Other Tic Disorders Through Genome-Wide Association Studies. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomes Project, C.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Gibbs, R.A.; Hurles, M.E.; McVean, G.A. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010, 467, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G.; Collaboration, C.C.G. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Dudbridge, F.; Thompson, S.G. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: Comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat. Med. 2016, 35, 1880–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Pan, L.; Zhang, M.; Wan, X.; Xu, H.; Hua, R.; Zhu, M.; Gao, P. Systemic inflammatory regulators and risk of acute-on-chronic liver failure: A bidirectional mendelian-randomization study. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1125233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Dou, M.; Cao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Y. Peripheral level of CD33 and Alzheimer’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, A.J.; Burgess, S. Pleiotropy robust methods for multivariable Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.G.; Chu, Z.X.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Ge, J.F.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, P. High levels of vitamin D in relation to reduced risk of schizophrenia with elevated C-reactive protein. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Hypponen, E. Vitamin D deficiency and C-reactive protein: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Pedersen, C.B.; Anderson, C.; Ko, P.; Burne, T.H.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; Mortensen, P.B. Neonatal vitamin D status and risk of schizophrenia: A population-based case-control study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coentre, R.; Canelas da Silva, I. Symptomatic Correlates of Vitamin D Deficiency in First-Episode Psychosis. Psychiatry J. 2019, 2019, 7839287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, A.; Suppiah, V.; Hypponen, E. Schizophrenia and co-morbidity risk: Evidence from a data driven phenomewide association study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 162, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, M.D.E.; Jimenez-Sanchez, L.; Shen, X.; Edmondson-Stait, A.J.; Green, C.; Adams, M.J.; Rifai, O.M.; McIntosh, A.M.; Lyall, D.M.; Whalley, H.C.; et al. Associations between major psychiatric disorder polygenic risk scores and blood-based markers in UK biobank. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 97, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, M.G.; Marzulli, L.; Margari, F.; De Giacomo, A.; Gabellone, A.; Giannico, O.V.; Margari, L. Vitamin D Deficiency in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 9292560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakos, S.; Dhawan, P.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Gomez, J.M.; Bouillon, R. Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation? Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; McGrath, J.J. Vitamin D, effects on brain development, adult brain function and the links between low levels of vitamin D and neuropsychiatric disease. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2013, 34, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Eyles, D.W.; Magnusson, C.; Newschaffer, C.J.; McGrath, J.J.; Kvaskoff, D.; Ko, P.; Dalman, C.; Karlsson, H.; Gardner, R.M. Developmental vitamin D and autism spectrum disorders: Findings from the Stockholm Youth Cohort. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazahery, H.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Conlon, C.; Beck, K.L.; Kruger, M.C.; von Hurst, P.R. Vitamin D and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsi, E.; Kotsi, E.; Perrea, D.N. Vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A meta-analysis. Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2019, 11, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunsoy, N.; Yuksel, R.N.; Cingi Yirun, M.; Kilicarslan, A.; Aydemir, C. Exploring the relationship between vitamin D and mania: Correlations between serum vitamin D levels and disease activity. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2018, 72, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, G.; Enrico, P.; Ciappolino, V.; Delvecchio, G.; Brambilla, P. The role of vitamin D in bipolar disorder: Epidemiology and influence on disease activity. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 278, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landel, V.; Annweiler, C.; Millet, P.; Morello, M.; Feron, F. Vitamin D, Cognition and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Therapeutic Benefit is in the D-Tails. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 53, 419–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerhus, M.; Berg, A.O.; Dahl, S.R.; Holvik, K.; Gardsjord, E.S.; Weibell, M.A.; Bjella, T.D.; Andreassen, O.A.; Melle, I. Vitamin D status in psychotic disorder patients and healthy controls--The influence of ethnic background. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Li, X.; Timofeeva, M.N.; He, Y.; Spiliopoulou, A.; Wei, W.Q.; Gifford, A.; Wu, H.; Varley, T.; Joshi, P.; et al. Phenome-wide Mendelian-randomization study of genetically determined vitamin D on multiple health outcomes using the UK Biobank study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

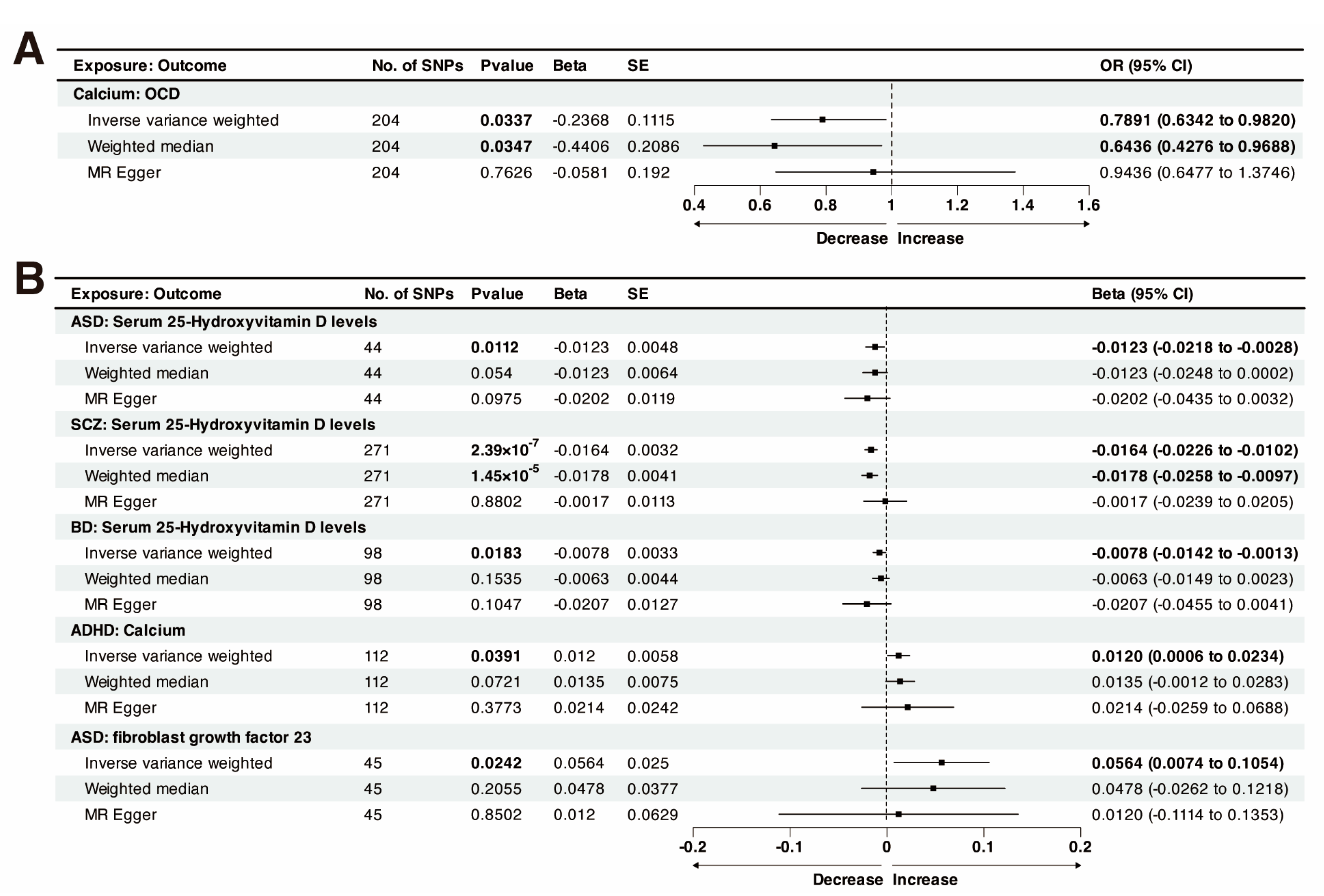
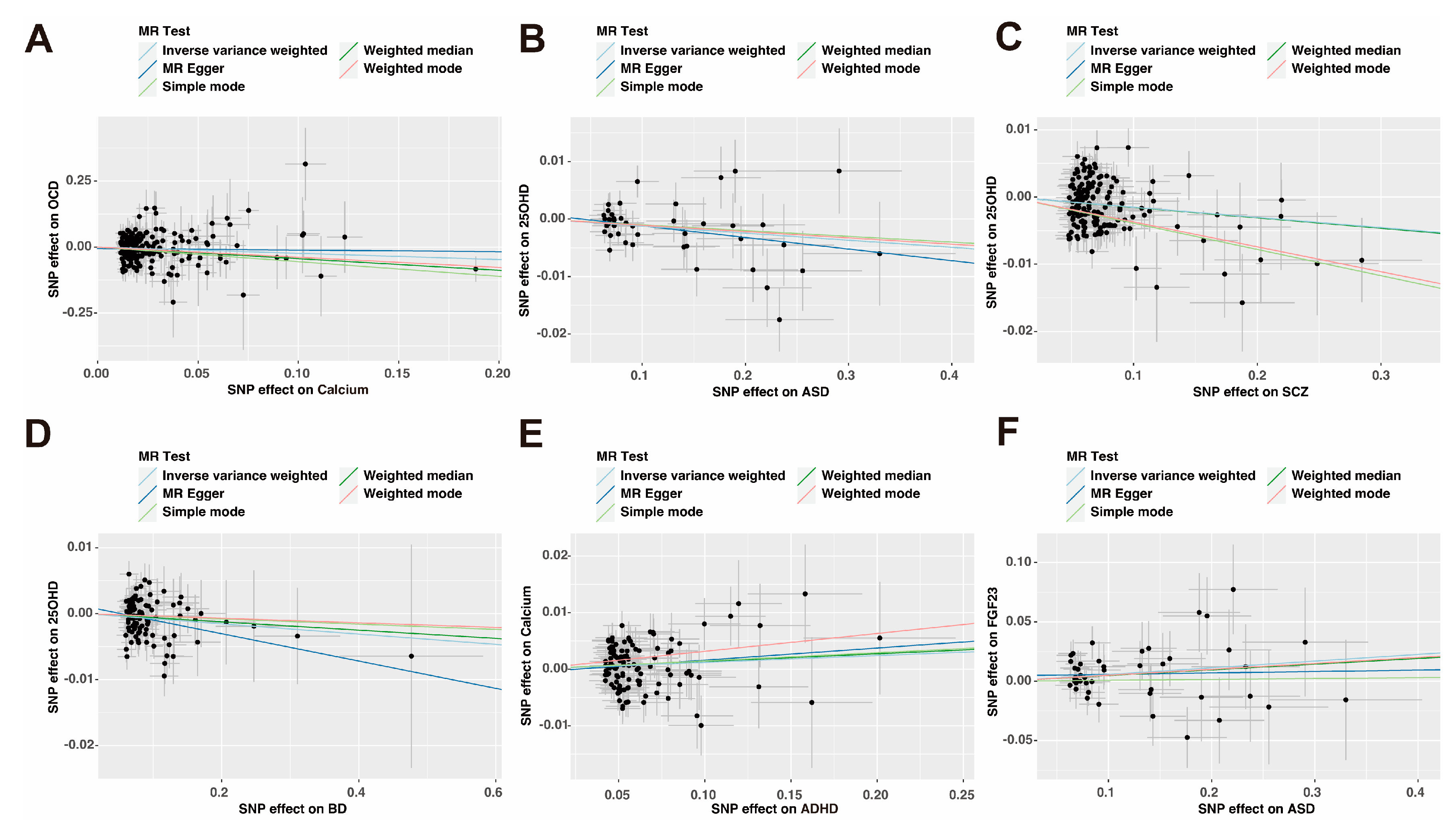
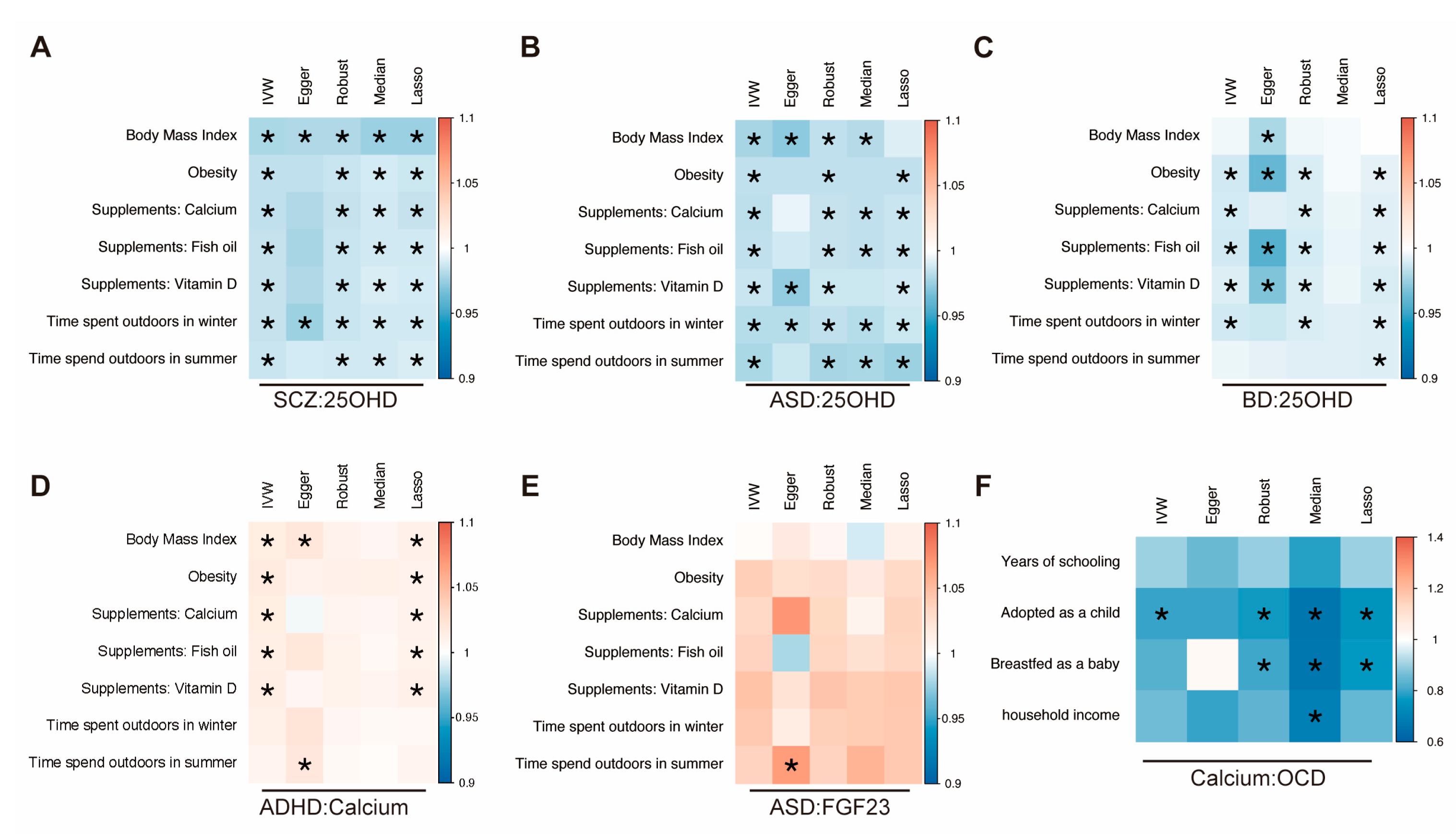
| Exposure: Outcome | F-Statistic | MR-Egger_ Intercept | Egger Intercept _Pval a | IVW_ Cochrane_Q | Cochrane _Q_Pval b | Steiger Test | Steiger Test _Pval c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium: OCD | 76.1028 | −0.0058 | 0.2540 | 206.4289 | 0.4198 | TRUE | 1.83 × 10−11 |
| SCZ: 25OHD | 255.2465 | −0.0009 | 0.1764 | 497.7460 | 1.02 × 10−15 | TRUE | <0.001 |
| ASD: 25OHD | 124.8705 | 0.0008 | 0.4721 | 52.9345 | 0.1425 | TRUE | 1.09 × 10−191 |
| BD: 25OHD | 168.0641 | 0.0011 | 0.2916 | 128.5298 | 0.0177 | TRUE | 5.96 × 10−10 |
| ADHD: Calcium | 108.0976 | −0.0005 | 0.6884 | 163.5865 | 0.0009 | TRUE | <0.001 |
| ASD: FGF23 | 125.5161 | 0.0046 | 0.4457 | 41.1640 | 0.5939 | TRUE | 8.73 × 10−39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, M.; Yan, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Calcium Homeostasis and Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184051
Jiang M, Yan W, Li X, Zhao L, Lu T, Zhang D, Li J, Wang L. Calcium Homeostasis and Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184051
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Miaomiao, Weiheng Yan, Xianjing Li, Liyang Zhao, Tianlan Lu, Dai Zhang, Jun Li, and Lifang Wang. 2023. "Calcium Homeostasis and Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184051
APA StyleJiang, M., Yan, W., Li, X., Zhao, L., Lu, T., Zhang, D., Li, J., & Wang, L. (2023). Calcium Homeostasis and Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients, 15(18), 4051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184051






