Longitudinal Association between Physical Activity, Blood Lipids, and Risk of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2009 and 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
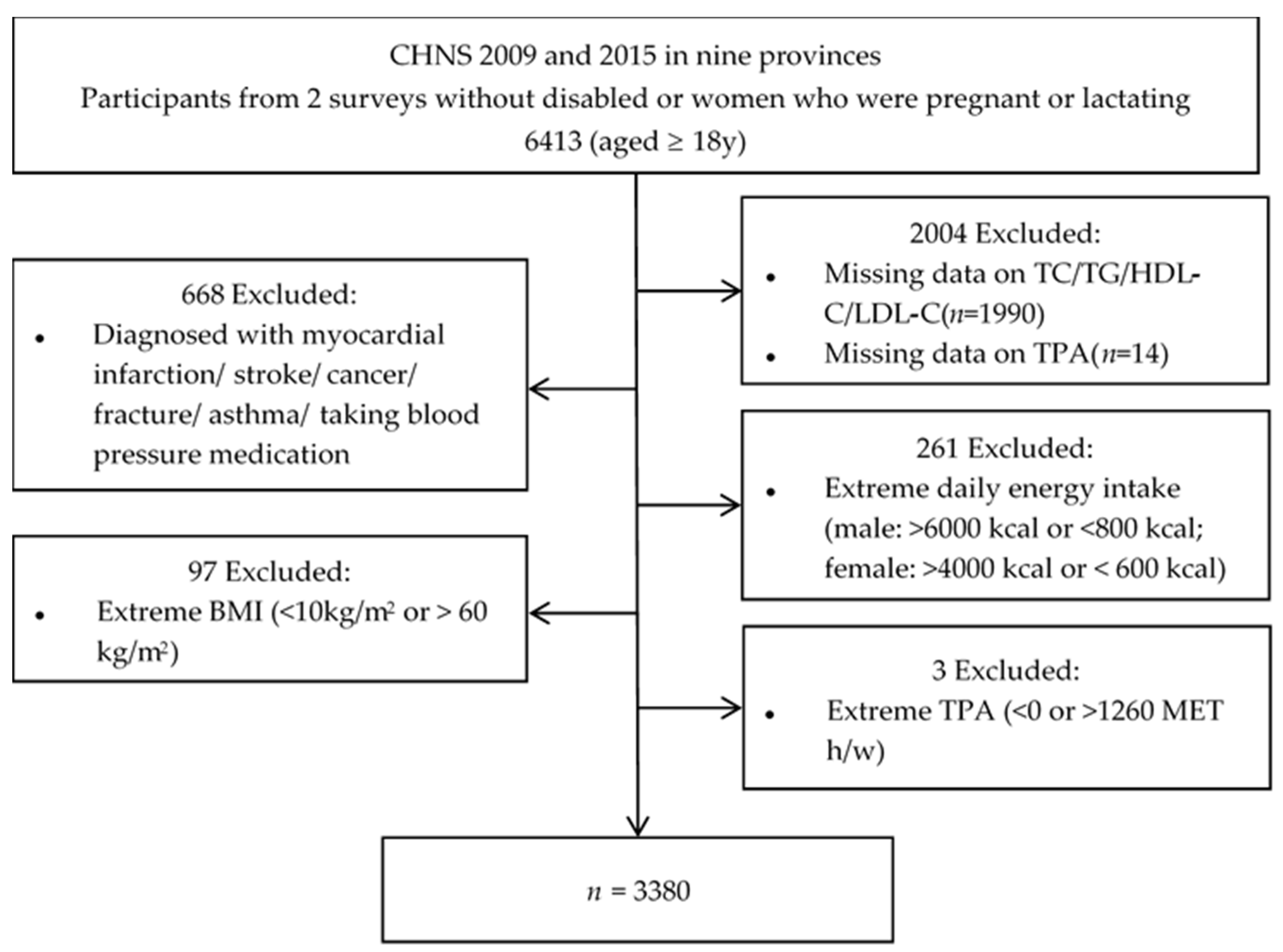
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Physical Activity and Sedentary Assessment
2.3. Anthropometrics and Blood Biomarker Measurements
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
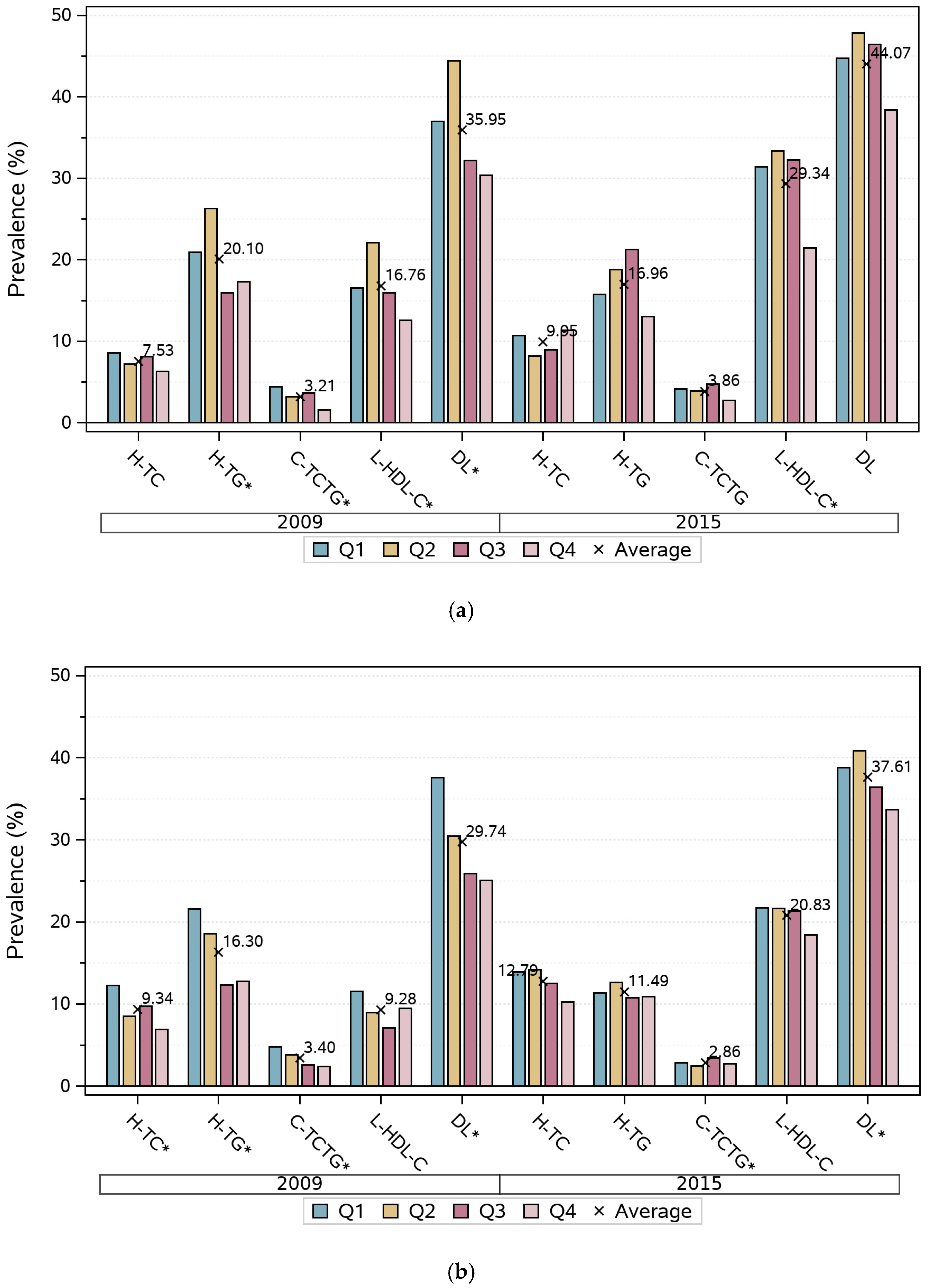
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Participants in Each Survey Round
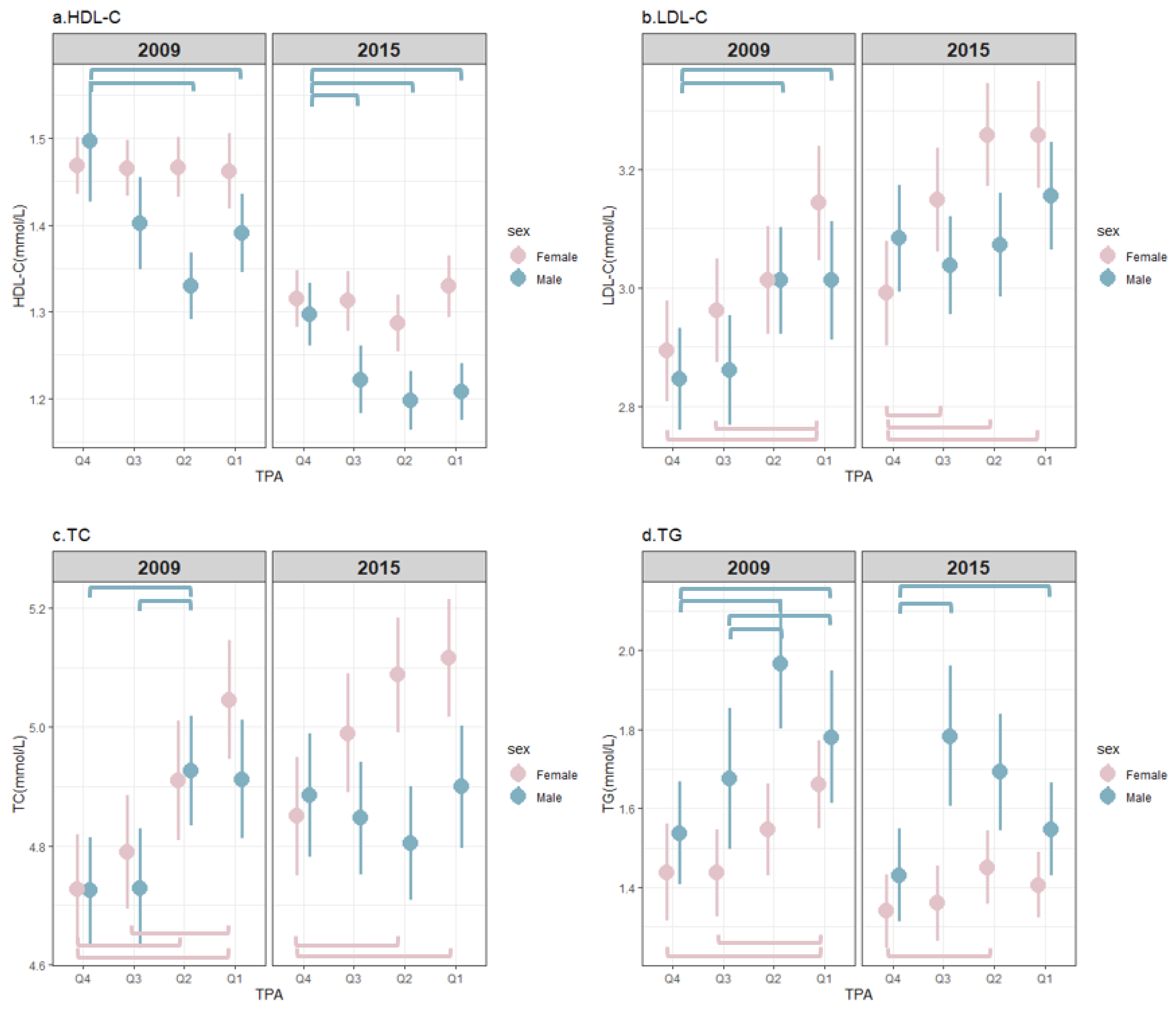
3.2. The Distribution of Blood Lipids with Different TPA Levels
3.3. Regression Coefficients for Serum Lipid Variables by Quartiles of TPA
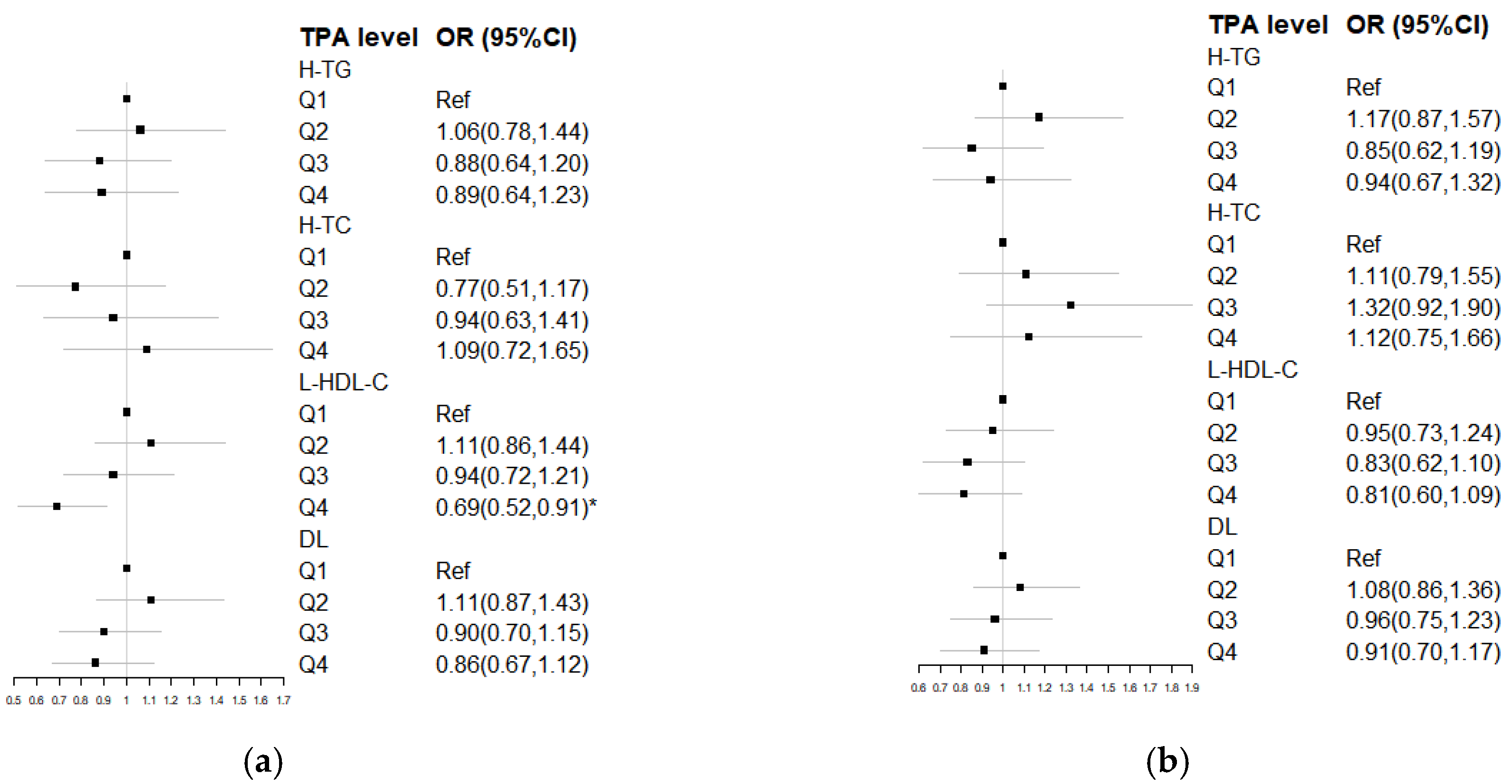
3.4. Odds Ratio for DL by Quartiles of TPA
3.5. Regression Coefficients for Serum Lipids on Four Types of Physical Activity
3.6. Regression Coefficients for Serum Lipids on TPA at Baseline Interacted with Change within 6 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristics | 2009 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline age (years old) | 50.52 (41.57, 58.87) | 50.52 (41.57, 58.87) |
| Married (%) | 3057 (90.44) | 3055 (90.38) |
| Education (%) # | 730 (21.60) | 872 (25.80) |
| Annual per capita household income (thousand yuan) # | 9.16 (4.89, 15.73) | 14.42 (6.15, 27.13) |
| Urbanization index # | 14.00 (9.83, 23.33) | 14.00 (7.50, 22.17) |
| Current smoker (%) # | 944 (27.93) | 809 (23.93) |
| Alcohol drinker (%) # | 1147 (33.93) | 947 (28.02) |
| Energy intake (1000 kcal/day) # | 2.16 (1.78, 2.63) | 1.93 (1.52, 2.42) |
| Energy from dietary fat (%) # | 31.15 (24.12, 38.22) | 34.71 (27.18, 43.64) |
| Dietary cholesterol (mg/d) # | 221.02 (119.13, 367.34) | 207.26 (99.27, 350.34) |
| BMI (kg/m2) # | 23.19 (21.06, 25.56) | 23.82 (21.63, 26.30) |
| Waist circumference (cm) # | 82.00 (75.50, 89.50) | 85.00 (78.00, 92.00) |
| Sedentary activity time (h) # | 14.00 (9.83, 23.33) | 14.00 (7.50, 22.17) |
| Participation in LTPA (%) | 255 (7.54) | 237 (7.01) |
| TPA (MET·h/w) # | 178.74 (80.81, 330.90) | 100.49 (39.67, 216.50) |
| Q4 | 466.84 (384.87, 617.61) | 337.06 (264.38, 462.5) |
| Q3 | 245.12 (210.00, 287.00) | 153.6 (127.04, 183.28) |
| Q2 | 126.52 (104.20, 149.48) | 62.86 (51.28, 80.34) |
| Q1 | 40.78 (16.10, 59.13) | 17.21 (0, 28.88) |
| Occupational PA (MET·h/week) # | 120.00 (0.00, 280.00) | 55 (0, 175) |
| Travel PA (MET·h/week) # | 1.25 (0.00, 6.67) | 0.00 (0, 3.75) |
| Domestic PA (MET·h/week) # | 32.36 (5.37, 58.71) | 23.8 (5.37, 43.75) |
| LTPA (MET·h/week) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) |
| TC (mmol/L) # | 4.77 (4.15, 5.42) | 4.89 (4.25, 5.53) |
| TG (mmol/L) # | 1.23 (0.83, 1.88) | 1.17 (0.81, 1.77) |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) # | 1.39 (1.17, 1.64) | 1.24 (1.04, 1.47) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) # | 2.91 (2.35, 3.50) | 3.06 (2.51, 3.68) |
| DL (%) # | 1100 (32.54) | 1370 (40.53) |
| Hypercholesterolemia (%) # | 288 (8.52) | 388.00 (11.50) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia (%) # | 608 (17.99) | 472.00 (13.99) |
| Low HDL-C (%) # | 427 (12.64) | 832.00 (24.67) |
| Combined hyperlipidemia | 112 (3.31) | 112 (3.32) |
References
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, H.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; Ran, S.; et al. Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases in China, 1990-2016: Findings From the 2016 Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Cardiol 2019, 4, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Ding, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Tan, L.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Availability of Lipid-Lowering Medications Among Primary Health Care Settings in China. JAMA Netw Open 2021, 4, e2127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on Chinese Nutrition and Chronic Diseases (2020); National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.K.; Man, Q.Q.; Li, H.; Pang, S.J.; Jia, S.S.; Li, Y.Q.; He, L.; Zhao, W.H.; Zhang, J. Trends in Lipids Level and Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults, 2002-2015. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2019, 32, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Lacher, D.A.; Shero, S.T.; Mussolino, M.E. Trends in Lipids and Lipoproteins in US Adults, 1988–2010. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 308, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Loerbroks, A.; Angerer, P. Physical activity and risk of cardiovascular disease: What does the new epidemiological evidence show? Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2013, 28, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Physical activity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/physical-activity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Physical Activity 2018–2030: More Active People for a Healthier World; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman, Y.; Jellinger, P.S.; Guerin, C.K.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Brinton, E.A.; Budoff, M.J.; Davidson, M.H.; Einhorn, D.; Fazio, S.; Fonseca, V.A.; et al. Consensus Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the Management of Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Algorithm—2020 Executive Summary. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 1196–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhang, B. Longitudinal association between physical activity and blood pressure, risk of hypertension among Chinese adults: China Health and Nutrition Survey 1991–2015. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.H.; Xie, Q.; Li, X.L.; Chen, J.G.; Pan, X.L.; Ye, B.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, W.W.; et al. Association between Health-Related Physical Fitness and Risk of Dyslipidemia in University Staff: A Cross-Sectional Study and a ROC Curve Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, P. Research progress of the effect of exercise training on lipid metabolism. Chin. Prev. Med. 2019, 20, 881–886. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S.; Beedie, C.; Jimenez, A. Differential effects of aerobic exercise, resistance training and combined exercise modalities on cholesterol and the lipid profile: Review, synthesis and recommendations. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, G.; Stensel, D.; Hamer, M.; Stamatakis, E. The association between leisure-time physical activity, low HDL-cholesterol and mortality in a pooled analysis of nine population-based cohorts. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Q. Separate and combined associations of physical activity and obesity with lipid-related indices in non-diabetic and diabetic patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, N.P.; Martin, S.E.; Crouse, S.F. Acute exercise and training alter blood lipid and lipoprotein profiles differently in overweight and obese men and women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012, 20, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Liu, X.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, H.M.; Yin, S.F.; Guo, C.Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.L.; Feng, F.M.; Yuan, J.X. High Physical Activity is Associated with an Improved Lipid Profile and Resting Heart Rate among Healthy Middle-aged Chinese People. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2015, 28, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Vera, T.; Sañudo, B.; Pozo-Cruz, B.d.; Pozo-Cruz, J.d.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J. Influence of the level of physical activity on physical fitness, lipid profile and health outcomes in overweigh/obese adults with similar nutritional status. Sci. Sport. 2017, 32, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989-2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 1), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.; Howard, A.G.; Wang, H.J.; Su, C.; Zhang, B. The physical activity transition among adults in China: 1991-2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 1), 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Herrmann, S.D.; Meckes, N.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Greer, J.L.; Vezina, J.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Leon, A.S. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.J. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A Second Update of Codes and MET Values. Yearb. Sport. Med. 2012, 2012, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.; et al. Compendium of Physical Activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Off. J. Am. Coll. Sport. Med. 2000, 32, S498–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Smith, J.C.; Popkin, B.M. Understanding community context and adult health changes in China: Development of an urbanicity scale. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yin, R.X.; Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, L.; China National Survey of Chronic Kidney Disease Working, G. The prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Shin, N.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Association between Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and Possible Risk of Dyslipidemia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, P.A.; Otero, J.; Perez, M.; Arcos, E.; Garcia, H.; Narvaez, C.; Molina, D.I.; Sanchez, G.; Duran, M.; Cure, C.; et al. The spectrum of the dyslipidemia in Colombia: The PURE study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 284, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.I.; Elmi, F.; Stojanovska, L.; Ibrahim, N.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Al Dhaheri, A.S. Associations of Dyslipidemia with Dietary Intakes, Body Weight Status and Sociodemographic Factors among Adults in the United Arab Emirates. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, Z.; Noroozi Karimabad, M.; Khalili, P.; Sadeghi, T.; Sayadi, A.; Mohammadakbari Rostamabadi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Esmaeili-Nadimi, A. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and its association with opium consumption in the Rafsanjan cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, S.; Gan, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, D.; Addo-Yobo, E.; Trofimovitch, D.; Yue, W.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Prevalence and risk factors for dyslipidemia among adults in rural and urban China: Findings from the China National Stroke Screening and prevention project (CNSSPP). BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Deng, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets in Chinese adults: A nationally representative survey of 163,641 adults. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 260, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Luz, P.L.; Favarato, D.; Faria-Neto, J.R., Jr.; Lemos, P.; Chagas, A.C. High ratio of triglycerides to HDL-cholesterol predicts extensive coronary disease. Clinics 2008, 63, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, L.; Lecoultre, V.; Theytaz, F.; Campos, V.; Hodson, L.; Schneiter, P.; Mittendorfer, B.; Patterson, B.W.; Fielding, B.A.; Gerber, P.A.; et al. Exercise prevents fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in healthy young subjects. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest, C.P.; Artero, E.G.; Sui, X.; Lee, D.C.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N. Cross-sectional association between maximal estimated cardiorespiratory fitness, cardiometabolic risk factors, and metabolic syndrome in the aerobics center longitudinal study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberga, A.S.; Prud’homme, D.; Kenny, G.P.; Goldfield, G.S.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Gougeon, R.; Phillips, P.; Malcolm, J.; Wells, G.; Doucette, S.; et al. Effects of aerobic and resistance training on abdominal fat, apolipoproteins and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in adolescents with obesity: The HEARTY randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesaniemi, Y.A.; Danforth, E., Jr.; Jensen, M.D.; Kopelman, P.G.; Lefebvre, P.; Reeder, B.A. Dose-response issues concerning physical activity and health an evidence-based symposium. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, S351–S358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; Arena, R.; Swift, D.L.; Johannsen, N.M.; Sui, X.; Lee, D.C.; Earnest, C.P.; Church, T.S.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Milani, R.V.; et al. Exercise and the cardiovascular system: Clinical science and cardiovascular outcomes. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, I.; Vesterbekkmo, E.K.; Retterstol, K.; Anderssen, S.A.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Helge, J.W.; Lydersen, S.; Wisloff, U.; Stensvold, D. The Long-term Effect of Different Exercise Intensities on High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Older Men and Women Using the Per Protocol Approach: The Generation 100 Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 5, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Menopause-Associated Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Foods Beneficial for Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esan, O.; Wierzbicki, A.S. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Wolters Kluwer Health 2021, 36, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelantonio, E.D.; Sarwar, N.; Perry, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Ray, K.K.; Thompson, A.; Wood, A.M.; Lewington, S.; Sattar, N.; Packard, C.J.; et al. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA 2009, 302, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, W.; Su, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, B. Trends in Leisure-Time Physical Activity Among Chinese Adults—China, 2000–2015. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Hong, F.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Guan, H.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, D.; Nie, F.; et al. The relationship between occupational physical activity and dyslipidaemia in farmers with varying working modes in southwest China: The China multi-ethnic cohort study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byberg, L.; Zethelius, B.; McKeigue, P.M.; Lithell, H.O. Changes in physical activity are associated with changes in metabolic cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 2134–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskinen, T.; Stenholm, S.; Heinonen, O.J.; Pulakka, A.; Aalto, V.; Kivimaki, M.; Vahtera, J. Change in physical activity and accumulation of cardiometabolic risk factors. Prev. Med. 2018, 112, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Fu, C. Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tse, L.A.; Liu, Z.; Rangarajan, S.; Hu, B.; Yin, L.; Leong, D.P.; Li, W.; China, P.s.i. Predictive Values of Anthropometric Measurements for Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Diseases Among 44 048 Chinese. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Han, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X. Association of dietary cholesterol and dyslipidemia in Chinese health examinees. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2022, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | 2009 | 2015 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n = 1527) | Female (n = 1853) | Male (n = 1527) | Female (n = 1853) | |
| Baseline age (years old) | 51.09 (41.72, 59.50) | 49.62 (41.48, 58.40) | 51.09 (41.72, 59.50) | 49.62 (41.48, 58.40) |
| Married (%) | 1378 (90.24) | 1679 (90.61) | 1401 (91.75) | 1654 (89.26) * |
| Education (%) # | 406 (26.59) | 324 (17.49) * | 478 (31.30) | 394 (21.26) * |
| Annual per capita household income (thousand yuan) # | 9.37 (5.15, 15.87) | 8.88 (4.72, 15.51) | 14.88 (6.65, 27.49) | 14.06 (5.74, 26.79) |
| Urbanization index # | 60.32 (50.61, 82.41) | 60.11 (50.63, 82.96) | 68.82 (55.10, 83.59) | 68.57 (55.21, 84.07) |
| Current smoker (%) # | 865 (56.65) | 79 (4.26) * | 755 (49.44) | 54 (2.91) * |
| Alcohol drinker (%) # | 975 (63.85) | 172 (9.28) * | 847 (55.47) | 100 (5.40) * |
| Energy intake (1000 kcal/day) # | 2.39 (2.00, 2.85) | 2.00 (1.65, 2.38) * | 2.11 (1.69, 2.65) | 1.78 (1.43, 2.22) * |
| Energy from dietary fat (%) # | 31.16 (24.27, 38.11) | 31.14 (23.98, 38.29) | 34.54 (27.18, 43.62) | 34.88 (27.15, 43.66) |
| Dietary cholesterol (mg/d) # | 243.36 (137.35, 393.81) | 205.92 (104.35, 344.89) * | 225.12 (111.64, 376.46) | 194.17 (86.20, 327.20) * |
| BMI (kg/m2) # | 23.11 (20.87, 25.42) | 23.23 (21.20, 25.65) | 23.72 (21.36, 26.18) | 23.92 (21.80, 26.43) * |
| Waist circumference (cm) # | 84.00 (77.00, 90.10) | 81.00 (74.50, 88.00) * | 86.00 (79.65, 94.00) | 83.00 (76.50, 90.00) * |
| Sedentary activity time (h) # | 16.00 (10.50, 26.00) | 14.00 (9.00, 21.00) * | 14.00 (9.33, 24.77) | 14.00 (7.00, 21.00) * |
| Participation in LTPA (%) | 134 (8.78) | 121 (6.53) * | 84 (5.50) | 153 (8.26) * |
| TPA (MET·h/w) # | 179.20 (80.00, 331.18) | 178.51 (81.49, 330.63) | 107.67 (29.05, 226.50) | 96.68 (45.31, 209.00) |
| Q4 | 454.50 (378.00, 625.50) | 476.59 (390.58, 613.37) | 338.77 (265.00, 452.90) | 334.62 (264.24, 475.23) |
| Q3 | 244.51 (209.82, 282.62) | 247.38 (211.28, 290.30) | 156.98 (126.40, 183.75) | 152.11 (127.29, 182.93) |
| Q2 | 127.75 (104.26, 152.60) | 125.68 (104.13, 148.18) | 68.97 (52.78, 83.33) | 60.83 (49.99, 77.93) |
| Q1 | 23.86 (2.63, 48.10) | 50.05 (31.56, 64.46) | 8.05 (0.00, 24.00) | 23.80 (11.96, 32.01) |
| Occupational PA (MET·h/week) # | 152.27 (36.00, 300.00) | 96.00 (0.00, 266.00) * | 80.00 (0.00, 202.00) | 32.00 (0.00, 150.00) * |
| Travel PA (MET·h/week) # | 2.50 (0.00, 6.67) | 0.00 (0.00, 6.25) * | 0.00 (0.00, 5.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.50) * |
| Domestic PA (MET·h/week) # | 5.37 (0.00, 24.12) | 51.39 (33.02, 75.83) * | 7.93 (0.00, 22.52) | 36.75 (21.88, 55.88) * |
| LTPA (MET·h/week) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) * | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) * |
| TC (mmol/L) # | 4.75 (4.14, 5.39) | 4.78 (4.16, 5.43) | 4.82 (4.17, 5.43) | 4.93 (4.32, 5.63) * |
| TG (mmol/L) # | 1.25 (0.84, 2.02) | 1.20 (0.82, 1.77) * | 1.20 (0.82, 1.91) | 1.15 (0.81, 1.70) * |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) # | 1.33 (1.11, 1.59) | 1.44 (1.22, 1.67) * | 1.19 (1.00, 1.43) | 1.29 (1.07, 1.51) * |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) # | 2.88 (2.31, 3.44) | 2.93 (2.38, 3.56) * | 3.04 (2.47, 3.62) | 3.08 (2.54, 3.72) * |
| DL (%) # | 549 (35.95) | 551 (28.74) * | 673 (44.07) | 697 (37.61) * |
| Hypercholesterolemia (%) # | 115 (7.53) | 173 (9.34) | 152.00 (9.95) | 237.00 (12.79) * |
| Hypertriglyceridemia (%) # | 307 (20.10) | 302 (16.30) * | 259.00 (16.96) | 213.00 (11.49) * |
| Low HDL-C (%) # | 256 (16.76) | 172 (9.28) * | 448.00 (29.34) | 386.00 (20.83) * |
| Combined hyperlipidemia | 49 (3.21) | 63 (3.40) | 59 (3.86) | 53 (2.86) |
| Gender | Variables | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | HDL-C (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | −0.020 (−0.064, 0.023) | 0.033 (−0.010, 0.077) | 0.080 (0.036, 0.125) * |
| Model 2 | Ref | −0.021 (−0.064, 0.023) | 0.022 (−0.021, 0.065) | 0.060 (0.016, 0.105) * | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | −0.023 (−0.066, 0.021) | 0.017 (−0.027, 0.060) | 0.050 (0.005, 0.096) * | ||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | −0.015 (−0.098, 0.068) | −0.055 (−0.138, 0.028) | −0.027 (−0.113, 0.059) | |
| Model 2 | Ref | −0.014 (−0.097, 0.070) | −0.039 (−0.123, 0.045) | −0.005 (−0.092, 0.083) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | −0.012 (−0.095, 0.071) | −0.035 (−0.118, 0.049) | 0.003 (−0.085, 0.092) | ||
| TC (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | 0.012 (−0.076, 0.099) | −0.040 (−0.128, 0.048) | 0.004 (−0.087, 0.095) | |
| Model 2 | Ref | 0.004 (−0.085, 0.092) | −0.036 (−0.125, 0.053) | 0.016 (−0.077, 0.109) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | 0.006 (−0.082, 0.095) | −0.029 (−0.118, 0.060) | 0.028 (−0.066, 0.122) | ||
| TG (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | 0.051 (−0.097, 0.198) | −0.054 (−0.200, 0.092) | −0.196 (−0.344, −0.049) * | |
| Model 2 | Ref | 0.029 (−0.116, 0.174) | −0.040 (−0.184, 0.104) | −0.145 (−0.292, 0.002) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | 0.038 (−0.107, 0.183) | −0.016 (−0.161, 0.129) | −0.103 (−0.252, 0.047) | ||
| Female | HDL-C (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | −0.013 (−0.040, 0.014) | −0.004 (−0.032, 0.024) | 0.014 (−0.015, 0.044) |
| Model 2 | Ref | −0.014 (−0.041, 0.013) | 0.001 (−0.028, 0.030) | 0.018 (−0.012, 0.048) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | −0.014 (−0.041, 0.013) | 0.002 (−0.027, 0.031) | 0.020 (−0.010, 0.050) | ||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | 0.012 (−0.054, 0.077) | 0.010 (−0.059, 0.079) | −0.065 (−0.138, 0.007) | |
| Model 2 | Ref | 0.027 (−0.039, 0.094) | 0.024 (−0.046, 0.094) | −0.045 (−0.119, 0.029) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | 0.028 (−0.038, 0.095) | 0.028 (−0.043, 0.098) | −0.038 (−0.113, 0.037) | ||
| TC (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | 0.016 (−0.055, 0.087) | 0.013 (−0.062, 0.088) | −0.042 (−0.121, 0.037) | |
| Model 2 | Ref | 0.038 (−0.035, 0.110) | 0.035 (−0.041, 0.112) | −0.010 (−0.091, 0.071) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | 0.039 (−0.033, 0.111) | 0.041 (−0.036, 0.118) | 0.000 (−0.081, 0.082) | ||
| TG (mmol/L) | Model 1 | Ref | 0.013 (−0.072, 0.099) | −0.023 (−0.114, 0.067) | −0.049 (−0.142, 0.045) | |
| Model 2 | Ref | 0.030 (−0.055, 0.115) | −0.018 (−0.107, 0.072) | −0.035 (−0.128, 0.059) | ||
| Model 3 | Ref | 0.031 (−0.054, 0.116) | −0.016 (−0.106, 0.074) | −0.031 (−0.127, 0.064) | ||
| Variables | Occupational PA | Travel PA | Domestic PA | LTPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.004 (0.002, 0.007) * | −0.057 (−0.115, 0.001) | −0.008 (−0.023, 0.006) | 0.007 (−0.017, 0.031) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.003 (−0.002, 0.008) | 0.022 (−0.089, 0.133) | 0.012 (−0.016, 0.040) | 0.007 (−0.040, 0.054) |
| TC (mmol/L) | 0.005 (−0.000, 0.010) | 0.044 (−0.073, 0.162) | −0.015 (−0.045, 0.015) | −0.009 (−0.059, 0.040) |
| TG (mmol/L) | −0.006 (−0.014, 0.003) | 0.213 (0.020, 0.407) * | −0.029 (−0.078, 0.019) | −0.081 (−0.162, −0.001) * |
| Female | ||||
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.002 (0.000, 0.004) * | −0.010 (−0.047, 0.027) | −0.004 (−0.009, 0.002) | 0.004 (−0.013, 0.021) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | −0.003 (−0.007, 0.002) | −0.002 (−0.093, 0.089) | −0.009 (−0.022, 0.004) | −0.020 (−0.062, 0.023) |
| TC (mmol/L) | −0.001 (−0.005, 0.004) | −0.034 (−0.133, 0.066) | −0.002 (−0.016, 0.013) | −0.023 (−0.069, 0.023) |
| TG (mmol/L) | −0.004 (−0.009, 0.002) | −0.066 (−0.183, 0.051) | 0.008 (−0.009, 0.024) | −0.019 (−0.073, 0.035) |
| TPA Levels and Change | HDL-C (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| Vigorous and increased | 0.197 (0.101, 0.293) * | −0.090 (−0.294, 0.114) | 0.005 (−0.220, 0.230) | −0.216 (−0.536, 0.104) |
| Vigorous and stable | 0.148 (0.059, 0.238) * | −0.147 (−0.335, 0.040) | −0.170 (−0.378, 0.038) | −0.526 (−0.825, −0.226) * |
| Vigorous and decreased | 0.116 (0.054, 0.178) * | −0.137 (−0.268, −0.005) * | −0.149 (−0.294, −0.003) * | −0.401 (−0.603, −0.199) * |
| Moderate and increased | 0.114 (0.043, 0.185) * | −0.113 (−0.263, 0.038) | −0.078 (−0.244, 0.089) | −0.264 (−0.502, −0.026) * |
| Moderate and stable | 0.033 (−0.036, 0.101) | −0.066 (−0.210, 0.077) | −0.088 (−0.247, 0.071) | −0.136 (−0.366, 0.094) |
| Moderate and decreased | 0.029 (−0.044, 0.102) | −0.172 (−0.325, −0.018) * | −0.229 (−0.399, −0.059) * | −0.233 (−0.480, 0.014) |
| Low and increased | 0.075 (0.014, 0.137) * | −0.095 (−0.224, 0.033) | −0.074 (−0.217, 0.069) | −0.133 (−0.341, 0.075) |
| Female | ||||
| Vigorous and increased | 0.094 (0.014, 0.175) * | −0.009 (−0.213, 0.195) | 0.031 (−0.192, 0.254) | −0.194 (−0.424, 0.036) |
| Vigorous and stable | 0.023 (−0.052, 0.097) | 0.048 (−0.141, 0.238) | 0.064 (−0.142, 0.271) | −0.041 (−0.255, 0.173) |
| Vigorous and decreased | 0.019 (−0.027, 0.064) | −0.041 (−0.158, 0.077) | −0.040 (−0.168, 0.088) | −0.088 (−0.218, 0.042) |
| Moderate and increased | 0.032 (−0.023, 0.086) | −0.065 (−0.202, 0.072) | −0.047 (−0.197, 0.102) | 0.003 (−0.153, 0.158) |
| Moderate and stable | 0.032 (−0.019, 0.082) | 0.086 (−0.042, 0.213) | 0.130 (−0.009, 0.269) | −0.016 (−0.161, 0.130) |
| Moderate and decreased | 0.030 (−0.027, 0.087) | −0.008 (−0.152, 0.137) | 0.007 (−0.150, 0.165) | −0.069 (−0.233, 0.095) |
| Low and increased | 0.0260 (−0.021, 0.073) | −0.025 (−0.142, 0.093) | 0.000 (−0.128, 0.129) | 0.002 (−0.132, 0.136) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Q.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Luo, S.; Tan, T.; Song, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Longitudinal Association between Physical Activity, Blood Lipids, and Risk of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2009 and 2015. Nutrients 2023, 15, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020341
Zou Q, Su C, Du W, Wang H, Zhang B, Luo S, Tan T, Song X, Zhong X, Zhang H, et al. Longitudinal Association between Physical Activity, Blood Lipids, and Risk of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2009 and 2015. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020341
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Qinpei, Chang Su, Wenwen Du, Huijun Wang, Bing Zhang, Shuquan Luo, Tao Tan, Xiaoyun Song, Xiaoni Zhong, Huadong Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Longitudinal Association between Physical Activity, Blood Lipids, and Risk of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2009 and 2015" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020341
APA StyleZou, Q., Su, C., Du, W., Wang, H., Zhang, B., Luo, S., Tan, T., Song, X., Zhong, X., Zhang, H., & Chen, Y. (2023). Longitudinal Association between Physical Activity, Blood Lipids, and Risk of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2009 and 2015. Nutrients, 15(2), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020341






