Abstract
Microbial fermentation provides a valorization strategy, through biotransformation, to convert plant-derived raw materials into health-promoting agents. In this study, we have investigated the antioxidative activity of Abelmoschus manihot fermented with various Bacillaceae strains from specific environments and demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effects of Bacillus licheniformis CP6 fermented A. manihot extract (FAME) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated Raw264.7 macrophages. Of 1500 bacteria isolated from various specific environments, 47 extracellular protease- and amylase-producing strains with qualified presumption safety status, belonging to the family Bacillaceae, were selected for A. manihot fermentation. Among them, strain CP6, a halophilic bacterium isolated from Tongyeong seawater in Korea and identified as B. licheniformis, showed the highest antioxidant activity. In particular, FAME exerted anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 macrophages. Consequently, FAME had a potent inhibitory effect on nitric oxide (NO) production in LPS-stimulated macrophages, without cytotoxicity. Moreover, FAME downregulated LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediator and enzyme levels in LPS-induced Raw264.7 cells, including IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, and COX-2, compared to levels when cells were incubated in A. manihot extract (IAME). Further detailed characterization indicated that FAME suppresses inflammation by blocking NF-κB via IKK phosphorylation inhibition and IκB-α degradation and by downregulating NO production, and inflammatory mediators also decreased NF-κB translocation. Furthermore, FAME inhibited LPS-stimulated activation of MAPKs, including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38, compared to that with either IAME. Therefore, we suggest that FAME could be used for inflammation-related disorders.
1. Introduction
In biological systems, inflammation is the main physiological defense mechanism that can protect against injuries caused by harmful stimuli, such as pathogens and poisons. During this process, macrophages are key mediators of the inflammatory response that function by mobilizing the host defense against exogenous pathogens [1]. This mobilization occurs when macrophages are exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on the outer membranes of bacterial toxins [2]. Upon binding to macrophage pathogen-associated molecular pattern receptors, LPS activates various intracellular signaling pathways involved in the inflammatory burst, which includes the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines, such as interleukins, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) [3,4]. Numerous inflammatory disorders, including atherosclerosis, chronic hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory brain diseases, have been linked to the pathophysiology of excessive inflammatory mediator production induced by activated macrophages [5]. Thus, the inhibition of these inflammatory mediators is a key target for the treatment of diseases associated with inflammation.
In particular, nuclear factor (NF)-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) have a critical function in inflammation. Among transcription factors of the NF-κB family, the heterodimer NF-κB p50/p65 is bound to the inhibitor of κB (IκBα) and remains in its inactive form in the cytoplasm of unstimulated cells. However, in response to LPS stimulation, NF-κB is released and translocated into the nucleus, owing to the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα [6,7]. The free NF-κB then translocates into the nucleus, where it binds at κB-binding sites in the promoter regions of target genes, inducing the transcription of genes encoding pro-inflammatory mediators such as COX-2, iNOS, TNF-α, IL-1β, and others [8]. Moreover, LPS induces the phosphorylation of proteins of the MAPK family, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38, leading to the activation of NF-κB in macrophages [9]. Therefore, the inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK pathways might contribute to anti-inflammatory effects.
Synthetic steroids are generally used as a primary treatment for chronic inflammation. However, they are thought to weaken the immune system by interfering with the cytokine network [10]. As a result, for the prevention of inflammatory diseases, effective natural therapeutic approaches that can target intraplaque macrophages and their secreted products have been suggested. Some plants that have long been used worldwide in traditional medicine have been evaluated as potential platforms for developing new drugs to treat various diseases. Among them, Abelmoschus manihot, belonging to the Malvaceae family and commonly called Jinhuakui (in Chinese) and Geumhwagyu (in Korean), is an annual or perennial herbaceous flowering plant and an edible form of hibiscus [11]. Especially, the flowers and calyces of A. manihot are rich in bioactive substances, which have a variety of biological activities, including anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation, and other functions [12].
The fermentation process has been reported to enhance the biological properties of raw materials, including the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity properties, through the production of new bioactive compounds [13]. In particular, extremophiles, microorganisms that thrive under extreme environmental conditions are of biotechnological interest, as they produce extremozymes [14]. However, the effect of fermented A. manihot on macrophage-mediated inflammation and its underlying mechanism remains unknown.
Thus, in this study, we selected Bacillus licheniformis CP6, isolated from Tongyeong seawater in the Republic of Korea, which seems to have a qualified presumption of safety (QPS) status, specifically pertaining to microorganisms that do not raise safety concerns [15]. Hence, A. manihot was fermented with B. licheniformis CP6, and total phenolic and total flavonoid contents were investigated. Moreover, we evaluated the pharmacologic effects of B. licheniformis CP6-fermented A. manihot extract (FAME) on the production of inflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide (NO) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, in LPS-stimulated mouse macrophages and identified the mechanism underlying such effects based on the regulation of transcription, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling pathways.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Bacterial strains isolated from diverse extreme environments stored at the food biotechnology laboratory, Department of Bioscience, Silla University, were used. Strains with a QPS status for the fermentation of Abelmoschus manihot were selected among Bacillaceae species with extracellular protease and amylase activity. Strains were cultured on Nutrient agar (Difco, Sparks, MD, USA) supplemented with a 3% (w/v) NaCl concentration at the optimal temperature for the strains.
2.2. Microbial Fermentation of Abelmoschus manihot
Abelmoschus manihot was purchased from Buan Dongjin Farm (Republic of Korea). After removing the pistil and stamen, separate flower petals and sepals were used in the experiment. The A. manihot petal and sepal were air-dried at 60 °C for 48 h and consequently crushed using a hood mixer (SMX-4000 DY, Cheonan, Republic of Korea). The fermentation medium was prepared using petal and sepal powder (1:1) for the experiment. Selected strains were cultured overnight on Nutrient agar supplemented with 3% (w/v) NaCl. Subsequently, colonies were grown in the same liquid medium for 12 h. Then, 1% of pre-seeding cultures were inoculated into the same liquid medium and grown for 9 h until the late exponential phase. Main culture fermentation was carried out using an A. manihot fermentation medium. The A. manihot fermentation medium was composed of 0.1% yeast extract (w/v), 3% NaCl (w/v), and 1% dried powder of A. manihot flower (w/v). Seed cultures were inoculated onto the main culture at a final OD600 nm of 0.1 (~5.642 log colony-forming units (CFU)/mL) and incubated for 5 days. During incubation, aliquots were collected, and the growth of the strains was determined based on CFU/mL on Nutrient agar supplemented with 3% NaCl (w/v). We named the fermented product cultured by inoculating B. licheniformis CP6 into the above-mentioned main fermentation medium as FAME and the incubated product under the same conditions without inoculation as IAME. The experiment was repeated three times.
2.3. Antioxidant Activity Measurement
The antioxidant activity was determined by estimating the reducing power and radical scavenging ability by performing a 2,2′-azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical scavenging activity assay. The radical cation scavenging capacity of the extract was examined against ABTS, generated based on the method in [16]. ABTS radical cation (ABTS+) was produced via the reaction of ABTS stock solution (7 mM) with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate (1:1) and by allowing the mixture solution to stand in a dark at room temperature for 12–16 h before use. Fresh ABTS+ solution was prepared each day. The ABTS+ solution was diluted with distilled water to an absorbance of 0.70 ± 0.02 at 734 nm. The ABTS+ reaction mixture contained 180 μL of ABTS+ and 20 μL of the antioxidant testing sample with an absorbance at 734 nm, recorded as Asample. The reaction was monitored for 2 min. The radical scavenging activity of each solution was then calculated as a percent according to the following equation:
where ABlank is the absorbance of the solvent. The experiment was repeated three times at each concentration. Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control.
Radical scavenging activity (%) = 1 − [(Asample − ABlank)/(Acontrol − ABlank)] × 100
2.4. Preparation of A. manihot Fermentation Extract
FAME (with inoculation) and IAME (without inoculation) were prepared via whole culture medium extraction. Twenty times (w/v) 70% ethanol was added to a 1 L culture medium (41 g of solid content) in an Erlenmeyer flask and extracted for 12 h at room temperature. Extraction was performed in triplicates. After extraction, the extract was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was filtered using Whatman filter paper No. 4 and evaporated at 40 °C. After completely removing the solvent with a lyophilizer, the extract was stored at −80 °C for further experiments. The yield of the final extract is IAME (obtaining 3.85 g based on 1L = yield rate 9.39%) and FAME (obtaining 5.58 g based on 1 L = yield rate 13.61%).
2.5. Measurement of Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents
Total phenolic content (TPC) was determined via a colorimetric assay described by Folin-Denis [17]. Each sample (1 mg/mL) and different concentrations of tannic acid were prepared in a 96-well plate. An aliquot of 40 μL of FAME or standard was mixed with 20% Na2CO3 (60 μL, w/v), 1 M of Folin–Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent, and incubated at 37 °C in the dark for 30 min to facilitate the reaction. The absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 700 nm using a microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA). The obtained data were expressed as standard equivalents (tannic acid equivalent (TAE) mg/1 g dry mass).
Total flavonoid content was measured according to a method described previously [18]. A volume of 25 μL of FAME (1 mg/mL) and quercetin (standard) with different concentrations were mixed with 125 μL D.W in a 96-well plate. Next, 5% NaNO3 was added, and the mixture was kept in a shaker for 5 min. Then, 10% AlCl3 was added to the mixture and was kept shaking for 6 min. The reaction was stopped by adding 0.1 M NaOH and D.W. After mixing, the flavonoid content was detected at 517 nm using a microplate reader. The calculated data were expressed as standard equivalents (quercetin equivalent (QE) mg/1 g dry mass).
2.6. Cell Culture
The Raw264.7 cell, a mouse macrophage line, was obtained from the Korea Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Republic of Korea). The cells were cultured at 37 °C in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (GibcoBRL, Grand Island, NY, USA), supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 10% fetal bovine serum (GibcoBRL, Grand Island, NY, USA) in a 5% CO2 incubator. Raw264.7 cells were maintained via weekly passage and cells were utilized for experimentation at 60–80% confluence.
2.7. Cell Viability
Cell viability was determined by performing an MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay, as described previously [19]. Briefly, cells were seeded into flat-bottomed 96-well microplates at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well and incubated for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were incubated in a culture medium containing various concentrations of FAME and A. manihot extract (IAME) for 20 h. After treatment, the medium was discarded, and a fresh medium containing 5 mg/mL MTT was added per well and incubated for 4 h. Formazan salts were dissolved in DMSO (100 µL) and the absorbance was measured at 550 nm using a microplate reader.
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis of NO Production
NO levels were measured by performing flow cytometry using the Nitric Oxide kit (Luminex Co., Austin, TX, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of 1 × 106 cells/well. After 24 h, the cells were pretreated in a culture medium containing 100 μg/mL of FAME and IAME for 2 h, and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for an additional 20 h. After treatment, cells were further incubated with an NO working solution at 37 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, cells were mixed and analyzed for NO production using the Guava Muse Cell Analyzer and Muse analysis software (Luminex co., Austin, TX, USA).
2.9. IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α Production
Raw264.7 cells were pre-incubated overnight in 6-well plates at a density of 1 × 106 cells/well. After 24 h, the cells were pretreated in a culture medium containing 100 μg/mL of FAME and IAME for 2 h, and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for an additional 20 h. IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α contents in the culture medium were measured using an enzyme immunoassay system (R&D System Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were calculated according to the standard curve using each of the recombinant cytokines in the ELISA kits (R&D system Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA).
2.10. Western Blotting
The cells were suspended in a lysis buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 250 mM NaCl, 1% v/v NP-40, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)) and a protein inhibitor cocktail (10 μg/mL aprotinin, 1 μg/mL leupeptin). The cells were centrifuged for 15 min at 20,000× g and 4 °C, and the supernatants were collected. The concentration of protein in the lysate was quantified using a Bio-Rad protein kit, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The lysate was loaded onto 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels for separation by electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in 5% non-fat milk for 1 h and incubated overnight with primary antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, MA, USA) at 4 °C. After washing, the membranes were then incubated for 1 h with a goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit IgG horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody at room temperature. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent and scanned by a luminescent image analyzer LAS-1000-plus (FUJIFILM, Tokyo, Japan). The band intensities were quantified using Multi Gauge V3.1, an image analysis program, (FUJIFILM Corporation, Valhalla, NY, USA), and normalized by the intensity of the corresponding β-actin band.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate. The results were expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis, including analysis of variance, was performed using SAS 9.1 software. The values were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by post hoc Duncan’s multiple range test, and p-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Screening Bacterial Strains for A. manihot Fermentation
In this study, we isolated 1500 bacterial strains (Tables S1 and S2) from various specific environments (Figure 1a,b). Of them, we selected suitable strains for the fermentation of A. manihot based on their QPS status, extracellular proteases, and amylase activity among Bacillaceae species. To select suitable strains for A. manihot fermentation, we grew 47 strains in A. manihot medium, which yielded only six strains (CP-6, CP-7, CP-35, CP-37, CP-39, and CP-42) with an average concentration of ~7.95 log CFU/mL (Figure 2). Additionally, we examined their antioxidant activity by measuring the ABTS radical scavenging activity of the fermented A. manihot at 0, 1, 3, and 5 days of fermentation. The results showed that four strains promoted the antioxidant activity of A. manihot. However, the B. licheniformis CP6 strain exhibited relatively better performance, in terms of ABTS activity (50.0%), compared to that of the control and was maintained for 2 days (Table 1). To determine the optimal fermentation time for CP6, we investigated the growth pattern of CP6 in A. manihot medium for 60 h and determined the ABTS radical scavenging activity (Figure 3). The B. licheniformis CP6 isolate was deposited into the Korean Collection for Type Cultures (KCTC), with culture collection number KCTC18811P.
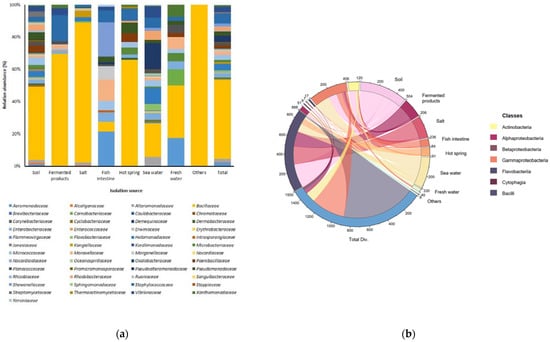
Figure 1.
Relative abundances and bacterial diversity in specific environments. (a) Bacterial diversity at the family level; isolation sources were plotted on the horizontal axis, and the relative percentage of the family is visualized on the vertical axis, with each taxon shown as a specific color in the stacked columns. (b) A 3D chord diagram illustrating bacterial diversity at the class level; each arc shows overlapping diversity in specific environments. Total Div.: presenting the total diversity in specific environments (soil, fermented products, salt, fish intestine, hot spring, seawater, freshwater, and including other sources).
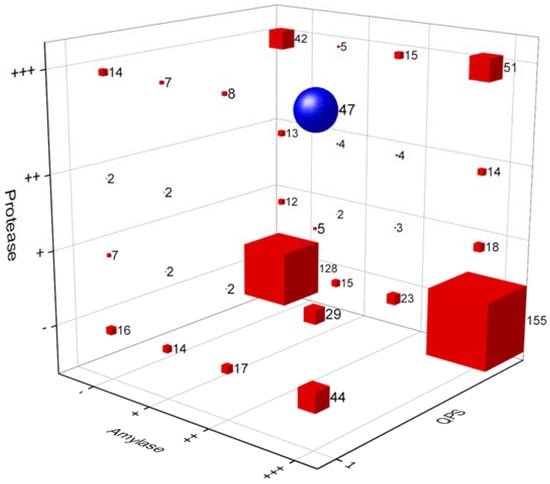
Figure 2.
A 3D bubble plot of the primary selection of strains for the fermentation of Abelmoschus manihot, with a qualified presumption of safety (QPS) status among Bacillaceae species with extracellular protease and amylase activity. Blue circle: a group of 47 strains selected for primary fermentation. Values on the X-axis indicate amylase activity, the Y-axis is protease activity, and the Z-axis is the QPS status of the strains. Hydrolase (protease and amylase) enzyme activities were determined based on the agar diffusion method. The activity of the enzymes was measured based on the radius of the halo zone around colonies (+++: >7 mm, ++: 4–6 mm, +: 1–3 mm, -: no activity). Strains with a QPS status are labeled as 1 and other strains are labeled as 0.

Table 1.
Antioxidant activity of six strains that showed growth of 1% Abelmoschus manihot medium.
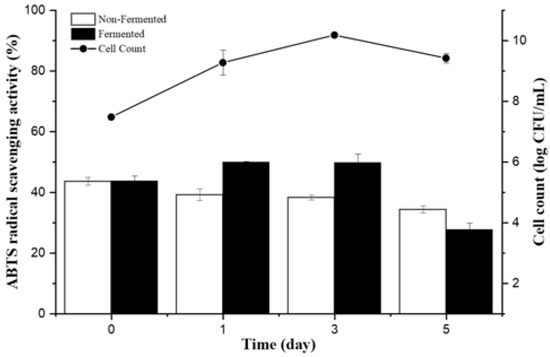
Figure 3.
Change in bacterial viability and antioxidant activity of Abelmoschus manihot fermented with Bacillus licheniformis CP6 during fermentation.
3.2. Effects of FAME on Cytotoxicity and Morphological Changes in Raw264.7 Cells
Total phenolic contents of FAME and IAME were 29.52 mg and 20.8 mg TAE per 1 g of dry mass, respectively. The flavonoid contents of FAME and IAME were 33.12 mg and 18.32 mg QE per 1 g dry mass, respectively (data not shown). Interestingly, phenolic and flavonoid contents were significantly more abundant in FAME than in IAME. In particular, the flavonoid content in FAME was 2-fold higher than that in IAME.
The cytotoxic effect of FAME and IAME on the viability of Raw264.7 cells was investigated by performing an MTT assay. As shown in Figure 4a, exposing the Raw264.7 cells to 100 or 500 μg/mL of FAME for 20 h did not affect the viability of cells. However, the viability of cells exposed to 500 μg/mL of IAME for 20 h was reduced to 93% of that of the controls. The results showed that FAME and IAME had no cytotoxic effects at any of the concentrations examined.
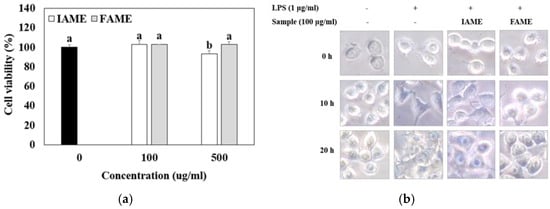
Figure 4.
Effects of IAME and FAME on (a) cytotoxicity and (b) morphological changes in Raw264.7 cells. (a) Raw264.7 cells were incubated with IAME and FAME for 20 h. The cell viability of Raw264.7 cells was assessed by performing an MTT assay. (b) Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME for 2 h and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 10 or 20 h on cover slides. Morphological changes in Raw264.7 were visualized via optical microscopy (×400). IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
Meanwhile, LPS is known to cause the morphological transformation of macrophage Raw264.7 cells [20]. Thus, whether FAME and IAME affect LPS-induced morphological changes in Raw264.7 cells was investigated. As shown in Figure 4b, the untreated normal Raw264.7 cells were round, with smooth cell edges, and without pseudopodia, but those stimulated with LPS for 20 h showed characteristics of macrophage activation, such as an increase in cell size and spindle-shaped pseudopodia. FAME treatment reversed this process, and thus, the original round shape of cells was restored. Thus, fermentation was observed to increase the anti-inflammatory properties of IAME.
3.3. Effects of FAME on the Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 Cells
During immune responses, NO is a crucial physiological messenger [21]. To examine the inhibitory effect of FAME on LPS-induced NO production, Raw264.7 cells were treated with LPS in the presence or absence of the extract for 20 h. As shown in Figure 5, the number of NO (+) cells was elevated by LPS treatment. However, when pretreated with FAME and IAME, LPS-induced NO (+) cell production was inhibited. Moreover, FAME decreased NO production more than IAME. These findings demonstrated that fermentation can increase the anti-inflammatory properties of IAME.
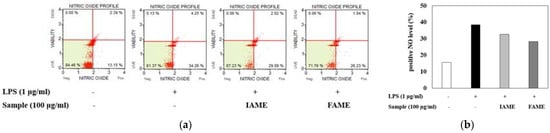
Figure 5.
Effects of IAME and FAME on nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated Raw264.7 cells. (a) Quantitative measurements of NO production were performed via cytometry, using the Muse Nitric Oxide kit. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME (100 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 20 h. (b) The graph shows the NO percent positivity. IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; FAME, A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
3.4. Effects of FAME on the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 Cells
Because LPS can induce pro-inflammatory cytokine production, we evaluated the effects of FAME and IAME on the levels of cytokine (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) production in LPS-stimulated macrophages using ELISA kits. The results revealed that IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were increased in the culture media of LPS-stimulated cells; however, these increases were inhibited by treatment with FAME and IAME (Figure 6). In particular, compared to those with IAME treatment, FAME effectively inhibited the levels of cytokines. These results suggested that IAME modified by fermentation has elevated inhibitory activity with respect to pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
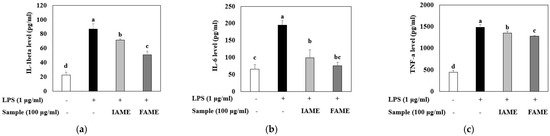
Figure 6.
Effects of IAME and FAME on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α release in Raw264.7 cells. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME (100 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 20 h. After incubation, the levels of (a) IL-1β, (b) IL-6, and (c) TNF-α present in the supernatants were measured using ELISA kits. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). a–d Values with different letters are different at p < 0.05, as analyzed by Duncan’s multiple range test. IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
3.5. Effects of FAME on iNOS and COX-2 Expression in LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 Cells
Next, we investigated whether the inhibitory effects of FAME on NO production are related to the modulation of the expression of iNOS and COX-2, which mediate their synthesis. iNOS and COX-2 genes are usually strongly activated in response to immune stimulators, such as LPS. Further, iNOS and COX-2 mediate inflammatory reactions and catalyze NO synthesis [22]. As shown in Figure 7, IAME and FAME effectively attenuated protein expressions of iNOS and COX-2, as compared to the LPS-stimulated cells. Moreover, the inhibitory effects of FAME against iNOS and COX-2 protein expression were higher than that of IAME. These results indicated that FAME represses both iNOS and COX-2 protein expression, inhibiting NO production.
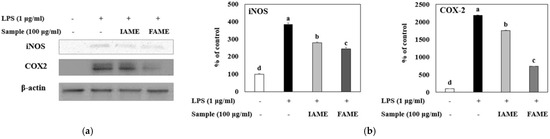
Figure 7.
Effects of IAME and FAME on iNOS and COX-2 protein expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated Raw264.7 cells. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME (100 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 20 h. Equal amounts of cell lysates (30 μg) were subjected to electrophoresis and analyzed for iNOS and COX-2 expression by performing Western blotting. Actin was used as an internal control. (a) iNOS and COX-2 protein expression. (b) Expression levels of iNOS and COX-2. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). a–d Values with different letters are different at p < 0.05, as analyzed by Duncan’s multiple range test. IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
3.6. Effects of FAME on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 Cells
Inflammatory stimuli, such as LPS, activate NF-κB, mediating the transcriptional induction of pro-inflammatory gene expression [23]. We investigated whether FAME and IAME would exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating NF-κB signaling in LPS-stimulated macrophages. As shown in Figure 8a and b, LPS stimulation resulted in a notable increase in p65 and IκBa phosphorylation. Further, the LPS-induced nuclear translocation of p65 was inhibited modestly by IAME, but the inhibitory effect of FAME was increased. In addition, FAME blocked the phosphorylation of IκBa in the cytosol more than IAME. These results showed that FAME strongly prevents IκBa degradation and NF-κB activation to a greater degree than IAME. Moreover, FAME effectively inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells.
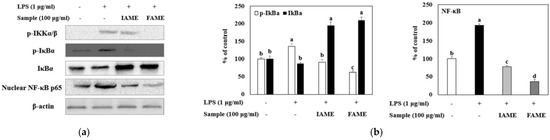
Figure 8.
Effects of IAME and FAME on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated NF-κB signaling pathway. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME (100 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 20 h. Equal amounts of cell lysates (30 μg) were subjected to electrophoresis and analyzed for p-IKKα/β, p-IκBα, IκBα, and NF-κB p65 expression by performing Western blotting. Actin was used as an internal control. (a) p-IKKα/β, p-IκBα, IκBα, and NF-κB p65 protein expression. (b) Expression levels of p-IκBα, IκBα, and NF-κB p65. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). a–d Values with different letters are different at p < 0.05, as analyzed by Duncan’s multiple range test. IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
3.7. Effects of FAME on the MAPK Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 Cells
MAPK molecules are widely recognized as key signaling mediators that regulate cellular processes, including the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines during the inflammatory response [24]. To evaluate whether FAME and IAME could affect MAPK signaling, we analyzed their effects on the phosphorylation of MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38) in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells by performing Western blotting. Figure 9 shows the LPS-induced phosphorylation of MAPKs. After FAME and IAME treatment, the protein expression levels of p-ERK, p-JNK, and p-p38 were decreased in LPS-induced Raw264.7 cells. Interestingly, compared to those with IAME treatment, FAME significantly suppressed the phosphorylation of all MAPKs upon LPS stimulation. These findings indicated that the fermentation of IAME by B. licheniformis CP6 augments its repressive effect on MAPK activation in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells.
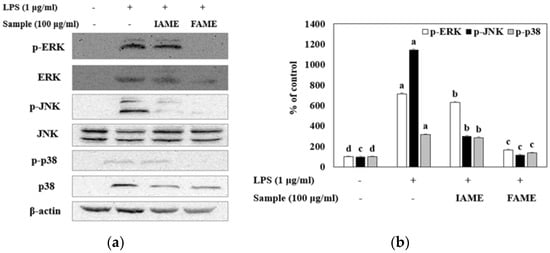
Figure 9.
Effect of IAME and FAME on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated MAPK signaling pathway. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with IAME and FAME (100 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 20 h. Equal amounts of cell lysates (30 μg) were subjected to electrophoresis and analyzed for p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38, and p38, expression by performing Western blotting. Actin was used as an internal control. (a) p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38, and p38 protein expression. (b) Expression levels of p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, and p-p38. (c) Expression levels of ERK, JNK, and p38. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). a–d Values with different letters are different at p < 0.05, as analyzed by Duncan’s multiple range test. IAME, Abelmoschus manihot extract; A. manihot extract fermented by Bacillus licheniformis CP6.
4. Discussion
Fermentation is the process wherein microorganisms produce substances that are useful to humans [25]. Recent research has focused on applying these fermentation techniques to natural products to obtain more useful and improved physiological activity. During fermentation, the microorganisms associated with fermentation break down plant cell walls, allowing biologically active compounds to be released during the next extraction stage. Among these organisms, extremophilic microbes, which can survive in extreme conditions, are not only of ecological importance but are also gaining significance in biotechnological research and industrial applications [26]. Thus, in the current study, we isolated B. licheniformis CP6, a halophilic bacterium, from Tongyeong seawater. Further, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of A. manihot fermented by B. licheniformis CP6 and determined its effects on NO production, inflammatory cytokine expression, the iNOS-mediated COX-2-induced pathway, the NF-κB pathway, and the MAPK pathway in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells exposed to the fermented product.
In response to LPS, macrophages play an active role in inflammatory responses by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-, IL-1, and IL-6, as well as inflammatory factors, such as NO, which recruit additional immune cells to infection or tissue injury sites [5]. Thus, inhibitors of these inflammatory molecules have been considered anti-inflammatory drug candidates. NO has been recognized as a crucial mediator and regulator of inflammatory responses, and it is generated by iNOS in activated inflammatory cells [27]. iNOS, the major protein involved in NO production, is closely linked to inflammatory disorders such as neurodegeneration, atherosclerosis, and septic shock [28]. COX-2 is regarded as a central mediator of inflammation, and its modulation was suggested as a potential therapeutic target. Furthermore, NO and iNOS have a direct effect on the enzymatic activity of COX-2 [29]. In this study, our data showed that FAME inhibited LPS-stimulated NO production more effectively than IAME. FAME strongly suppressed the protein expressions of iNOS and COX-2. A previous study reported that flavonoids inhibit NO production in Raw264.7 cells and that their inhibitory activity might be due to a reduction in iNOS expression [30]. Interestingly, in this study, phenolic and flavonoid contents were significantly more abundant in FAME than in IAME. Taken together, our findings demonstrated that fermentation increases the anti-inflammatory properties of IAME. Moreover, these findings demonstrated that the inhibition of NO generation mediated by FAME might be due to the suppression of iNOS and COX-2 upregulation during macrophage activation induced by LPS.
However, pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, are important mediators involved in a range of acute and chronic responses to inflammatory diseases [31]. IL-1β is a key pro-inflammatory cytokine, primarily released by macrophages, and it is thought to play a major role in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis [32]. IL-6 also acts as a powerful stimulator of the acute-phase response during the early phases of inflammation [33]. In addition, TNF-α is an inflammatory cytokine synthesized by macrophages that can stimulate the production or expression of IL-1β, IL-6, collagenase, and adhesion molecules [34]. Our data revealed that FAME has better inhibitory effects on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators than IAME, suggesting that the fermentation of IAME using B. licheniformis CP6 is effective for inflammation control. Ramiro et al. reported that isoquercitrin, a flavonoid, has potent anti-inflammatory activity and functions by reducing TNF-α levels [35]. Thus, we assume that FAME, which contains an increased amount of flavonoids, owing to fermentation, could be an effective inhibitor of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are paramount in generating an inflammatory response in activated macrophages.
NF-κB pathways are major signaling pathways that regulate the transcription of inflammatory mediators in macrophages. NF-κB is a key factor involved in the control of cell survival genes and induces the expression of inflammatory enzymes and cytokines, such as iNOS, COX-2, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α [6,36]. In general, NF-κB and IκB bind together, forming a complex in the cytoplasm. After the LPS-induced phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα in the cytosol, NF-κB p65 subunits are free to translocate to the nucleus [37]. Following nuclear translocation, these subunits bind to the promoters of target genes, such as iNOS and COX-2, ultimately resulting in the release of many cytokines and chemokines [38]. In the present study, we revealed that the LPS-induced nuclear translocation of p65 was modestly inhibited by IAME but that FAME increased the inhibitory effect on the nuclear translocation of p65 through the elevated phosphorylation of IκBα, followed by its degradation. FAME dramatically attenuated the LPS-mediated upregulation of IKKα/β, IκB, and p65 phosphorylation, IκBα degradation, and the translocation of p65 from the cytoplasm and to the nucleus. According to one report, isoquercitrin is a major compound of A. manihot, and it was found to potently inhibit NF-κB activation in human basophil cells [39]. These results indicate that FAME strongly prevents NF-κB activation, more so than IAME.
MAPK signaling pathways are also important factors in a variety of biological processes, including inflammation [40]. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK 1/2), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 are intracellular serine/threonine protein kinases known as MAPKs [41]. LPS treatment results in the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK-1/2, and p38, leading to NF-κB activation in macrophages. In addition, MAPKs modulate the synthesis of cytokines and the expression of pro-inflammatory enzymes, such as iNOS, COX-2, IL-1β, and TNF-α [42,43]. Therefore, targeting MAPK pathways could be an effective anti-inflammatory therapeutic strategy. In this study, compared to those with IAME treatment, FAME significantly inhibited the LPS-stimulated phosphorylation of MAPKs. These findings suggested that fermentation by B. licheniformis CP6 enhances the suppressive effect of IAME on MAPK activities after LPS stimulation.
Fermentation of plant-based products commonly increases the bioactive phenolic compounds and enhances their antioxidant activity [44]. In this study, fermentation was observed to increase the anti-inflammatory properties of IAME. Moreover, our results showed that FAME (fermented IAME) had a significant effect on flavonoid and polyphenol contents. Numerous biological actions of flavonoids have been demonstrated, including antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and hepatoprotective properties [45]. The fermentation of A. manihot is thought to cause various compositional and functional changes, as fermentation generates a large range of bioactive compounds through the metabolic activity of diverse microbes. Thus, we assume that FAME, containing an increased amount of flavonoids owing to fermentation by B. licheniformis CP6, could be an effective suppressor of inflammation. We assume that through biodegradation/bioconversion of Abelmoshcus manihot flowers by CP6, flowers were specifically decomposed, resulting increase in phenolic compounds [46]. On the other side, the phenolic compounds may be produced through the metabolic processes of Bacillus licheniformis CP6 [47,48].
Taken together, our findings demonstrated fermentation can increase the anti-inflammatory properties of IAME. FAME had potent anti-inflammatory activity, inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and the enzymes that govern their synthesis, namely iNOS and COX2. Furthermore, FAME strongly inhibited the LPS-induced activation of NF-κB translocation, IκBα degradation, and the MAPK pathway. These results suggest that FAME could be developed as a new anti-inflammatory therapeutic herbal medicine, without cytotoxicity, for the treatment of inflammation-related disorders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15020309/s1, Table S1: List of bacterial strains isolated from specific environments; Table S2: Characteristics of the strains with excellent extracellular enzyme activities of CP series.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.P., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; methodology, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; software, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., M.K.K. and S.-B.K.; validation, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., M.K.K. and S.-B.K.; formal analysis, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; investigation, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; resources, M.H.P., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; data curation, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., M.K.K., S.-B.K., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.P., D.G., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; visualization, M.H.P., Y.J.Y., D.G., M.K.K., S.-B.K., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; supervision, M.H.P., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; project administration, Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L.; funding acquisition, M.H.P., Y.-J.L. and S.-J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), grant numbers NRF-2020R1C1C1006299, NRF-2021R1F1A1064036, NRF-2019R1F1A1060737, and NRF-2020R1F1A1076624.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dong-Woo Lee from Yonsei University for critical reading and helpful comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, D.Y.; Xue, M.Y.; Geng, Z.R.; Chen, P.Y. The suppressive effects of Bursopentine (BP5) on oxidative stress and NF-κB activation in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine peritoneal macrophages. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, J.; Biswas, S.; Datta, A.G. Mode of action of endotoxin: Role of free radicals and antioxidants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O. Regulators of macrophage activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somensi, N.; Rabelo, T.K.; Guimarães, A.G.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Gelain, D.P. Carvacrol suppresses LPS-induced pro-inflammatory activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages through ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscá, L.; Zeini, M.; Través, P.G.; Hortelano, S. Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: A role for NO in macrophage function and fate. Toxicology 2005, 208, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF- κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappas, M.; Permezel, M.; Georgiou, H.M.; Rice, G.E. Nuclear factor kappa B regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in human gestational tissues in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. NF-kappa B: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and the evolution of Alzheimer’s: A revolutionary neurogenetic axis for therapeutic intervention? Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, W.S.; Carlson, B.J.; Formichella, C.R.; Sappington, R.M.; Ahlem, C.; Calkins, D.J. Oral delivery of a synthetic sterol reduces axonopathy and inflammation in a rodent model of glaucoma. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Yoon, K.D.; Shin, S.S. Effect of Aurea Helianthus stem extract on anti-melanogenesis. Biosci. Biothechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, C.G.; Varghese, R.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.O.; Sung, G.H. In-vitro antioxidative, antiinflammatory properties of Aurea helianthus leaf extract a Korean traditional medicinal plant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, M.; Ogasawara, Y.; Endou, K.; Akano, H.; Nakajima, T.; Aoyama, T.; Nakamura, K. Fermentation-induced changes in the concentrations of organic acids, amino acids, sugars, and minerals and superoxide dismutase-like activity in tomato vinegar. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Adebisi, W.A.; Ahmad, F.; Setupathy, S.; Danso, B.; Sun, J. Recent Development of extremophilic bacteria and their application in biorefinery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA BIOHAZ Panel. Uptated list of QPS-recommended biological agents for safety risk assessments carried out by EFSA. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7408. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Tiwari, R.; Sharma, N. Assessment of phenol and flavonoid content in the plant materials. J. New Biol. Rep. 2013, 2, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hakiman, M.; Syed, M.A.; Syahidal, A.; Maziah, M. Total antioxidant, polyphenol, phenolic acid, and flavonoid content in Ficus deltoidea varieties. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 4776–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.A.; Tumber, A.; Meikle, M.C. Multiple extracellular signals promote osteoblast survival and apoptosis. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 3849–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.K.; Vallyathan, V.; Lewis, D.M. Evidence for lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophage cell line into dendritic like cells. J. Biosci. 2003, 28, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Geng, S.; Zhong, C. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.K.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.G. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondeson, J. The mechanisms of action of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A review with emphasis on macrophage signal transduction and the induction of proinflammatory cytokines. Gen. Pharmacol. 1997, 29, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taveira, I.C.; Nogueira, K.M.V.; Oliveira, D.L.G.; Silva, R.D.N. Fermentation: Humanity’s oldest biotechnological tool. Front. Young Minds 2021, 9, 568656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Ranosyan, H. Extremophiles: Applications and roles in environmental sustainability. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, E.; Haboubi, H.N.; Forrester, G.; Eltahir, Z.; Spencer-Harty, S.; Davies, C.; Griffiths, A.P.; Baxter, J.N.; Jenkins, G.J.S. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and nitric oxide (NO) are important mediators of reflux-induced cell signalling in esophageal cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 33, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsanis, C.; Androulidaki, A.; Venihaki, M.; Margioris, A.N. Signalling networks regulating cyclooxygenase-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Cheon, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.P. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure–activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.H. Naturally occurring NF-κB inhibitors. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasifard, M.; Khorramdelazad, H. The bio-mission of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of COVID-19: A brief look at potential therapeutic tactics. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K.L.; Lamon-Fava, S.; Matthan, N.R.; Wu, D.; Lichtenstein, A.H. Docosahexaenoic acid differentially affects TNFα and IL-6 expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 97, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro, E.; Franch, A.; Castellote, C.; Pérez-Cano, F.; Permanyer, J.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Castell, M. Flavonoids from Theobroma cacao down-regulate inflammatory mediators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8506–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, A. Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepali, S.; Ki, H.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, Y.M. Wheatgrass-derived polysaccharide has antiinflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects on LPS-induced hepatic injury in mice. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cui, Y.; Kang, N.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; et al. Isoacteoside, a dihydroxyphenylethyl glycoside, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects through blocking toll-like receptor 4 dimerization. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2880–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, G.R.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.M. Isoquercitrin suppresses the expression of histamine and pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of MAP Kinases and NF-κB in human KU812 cells. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reibman, J.; Talbot, A.T.; Hsu, Y.; Ou, G.; Jover, J.; Nilsen, D.; Pillinger, M.H. Regulation of expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human bronchial epithelial cells: Roles of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Kim, M.M.; Mendis, E.; Kim, S.K. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by carboxybutyrylated glucosamine takes place via down-regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Immunology 2008, 123, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signaling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.C.; Yoon, Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Oh, S. Effect of Lactobacillus fermentation on the anti-inflammatory potential of turmeric. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Gabriela Medina-Meza, I. Impact of fermentation on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of whole cereal grains: A mini review. Molecules 2020, 25, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Sun-waterhouse, D.; Zhong, H.; Cui, C. A value-added approach to improve the nutritional quality of soybean meal byproduct: Enhancing its antioxidant activity through fermentation by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SWJS22. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, J.A.; Zabed, H.M.; Nizami, A.-S.; Mehedi Hassan, M.; Roknul Azam, S.M.; Kumar Awasthi, M.; Janet, Q.; Chen, G.; Dzidzorgbe Kwaku Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.; Ma, H. Bioconversion of agro-food industrial wastes into value-added peptides by a Bacillus sp. mutant through solid-state fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).