Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
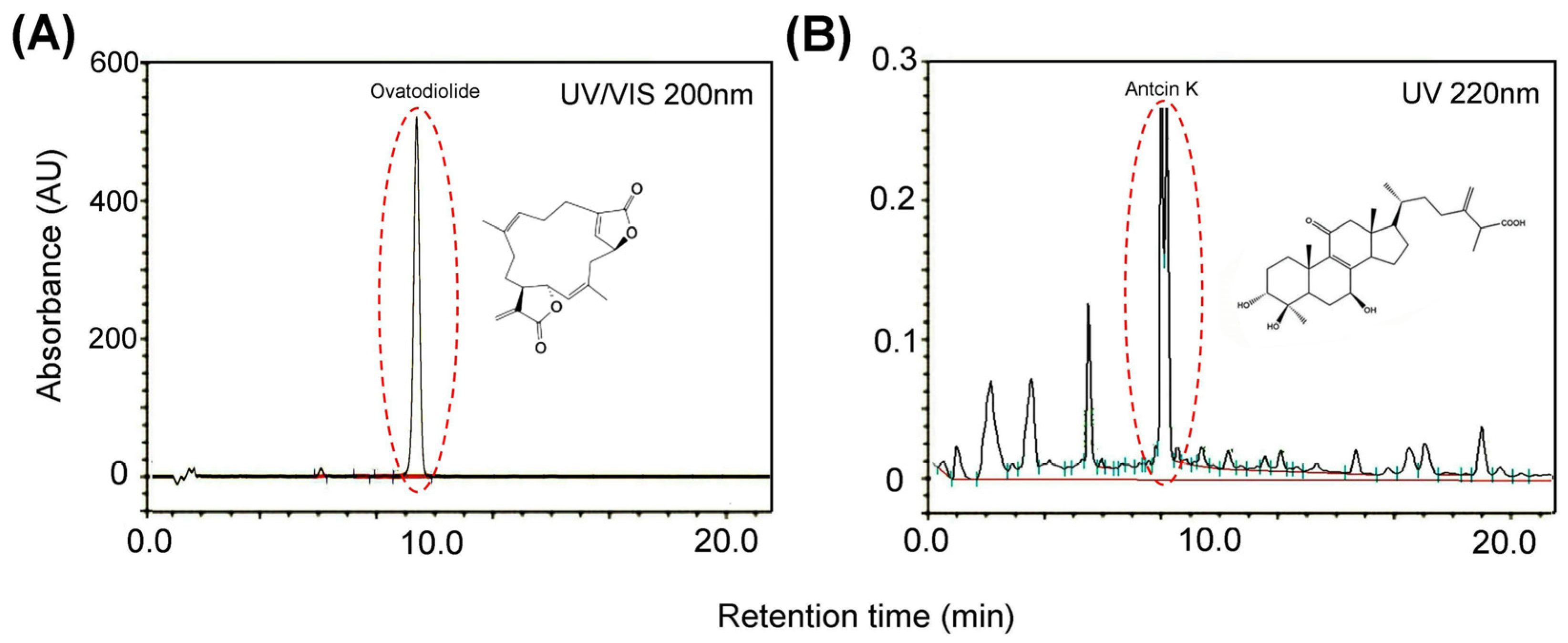
2.1. OAK Supplements Preparation and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.2. DPPH Assay
2.3. Experimental Animal Preparation
2.4. Echocardiography
2.5. Isolation of Primary Murine Macrophage and Cell Culture
2.6. Hematological and Biochemical Analyses
2.7. Oil Red O Staining
2.8. Evaluation of ROS and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.9. Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemical Staining
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DPPH-Scavenging Activity of OAK Supplements
3.2. Effects of OAK Supplements on Mouse Body Weight and Blood Pressure
3.3. Effects of OAK Supplements on Hemocytosis and Serum Lipid Accumulation
3.4. Effects of OAK Supplements on Abnormal Blood Lipid Levels and Liver Damage
3.5. Effects of OAK Supplements on Arterial Accumulation of Lipids and Abnormal Expression of VCAM-1, CD36, and ABCA1 Receptors
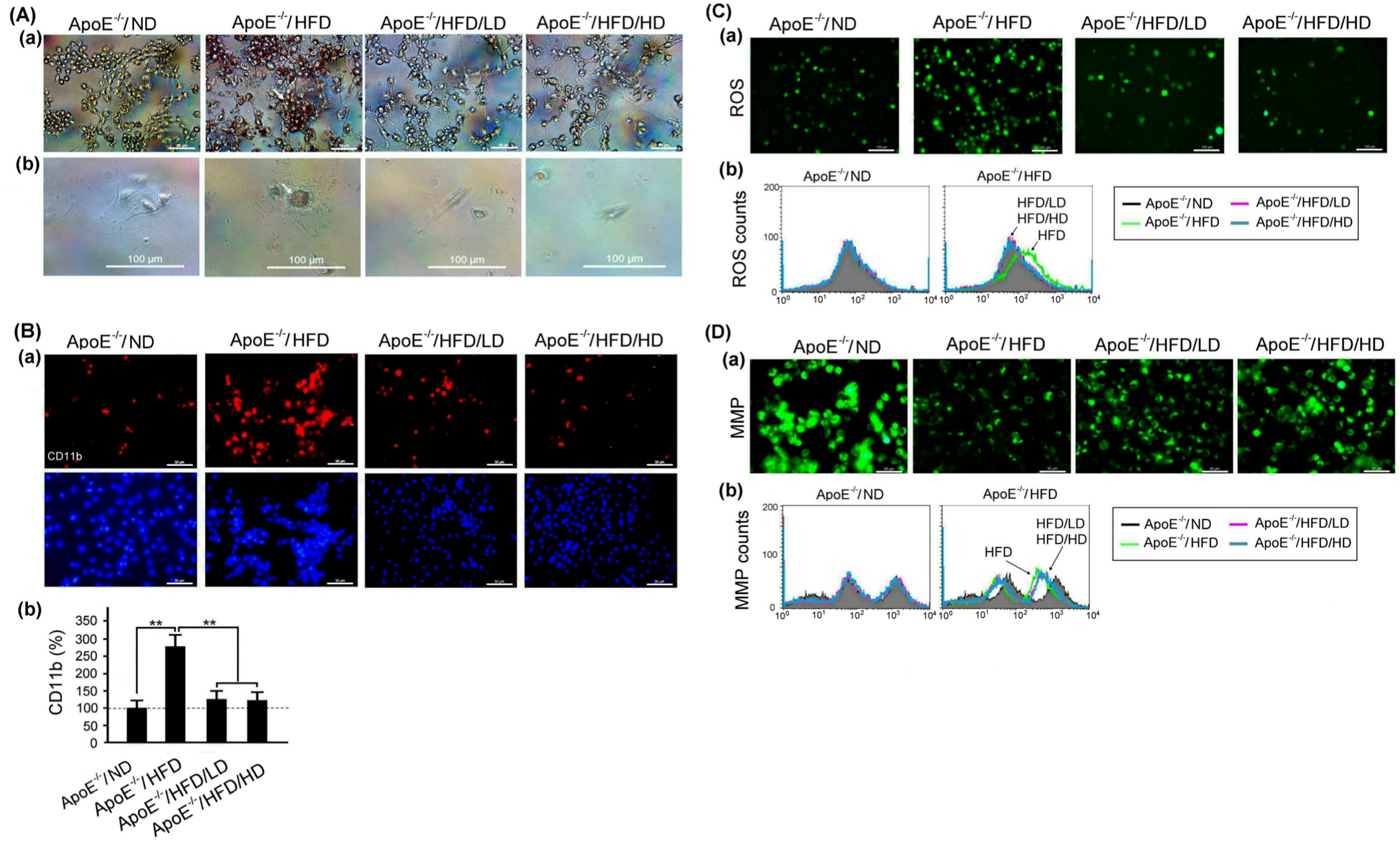
3.6. Effects of OAK Supplements on Lipid Accumulation and Abnormal CD11b Expression, ROS Production, and MMP in Mouse Macrophages
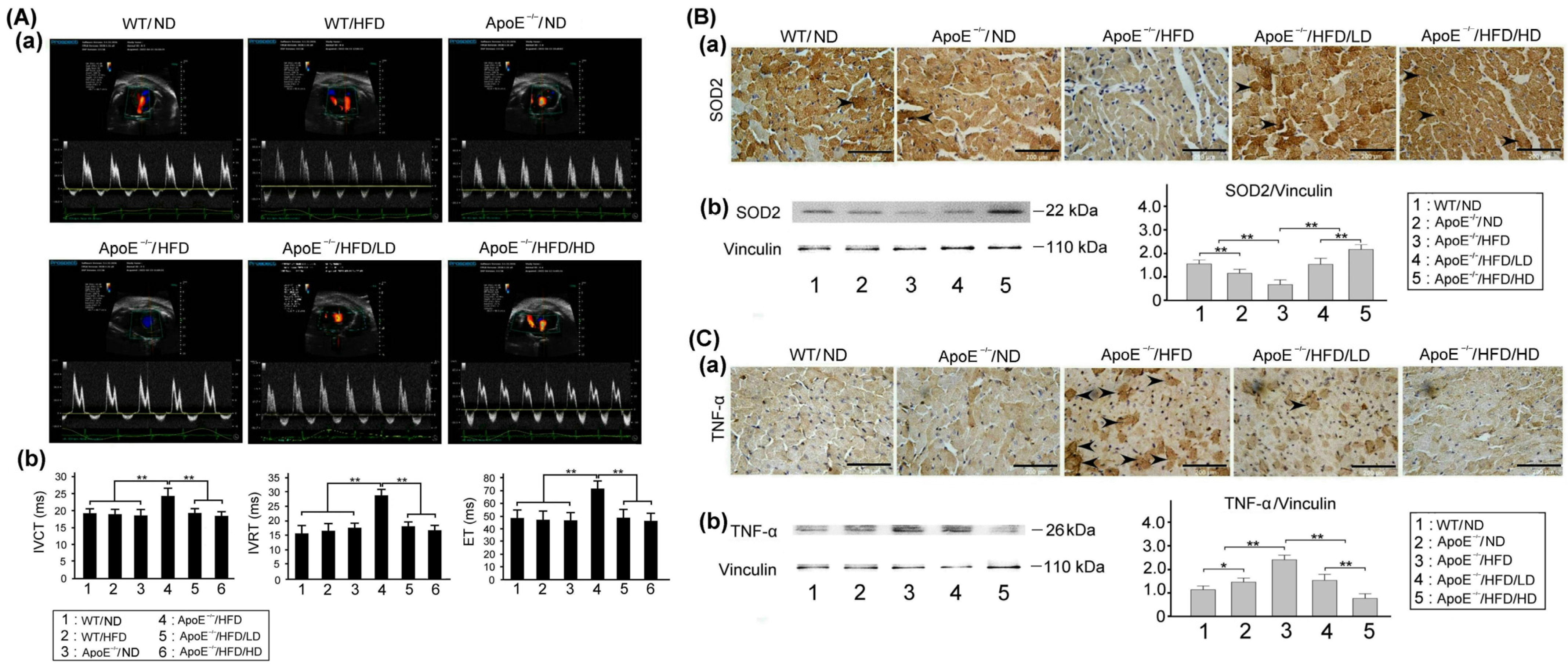
3.7. Effects of OAK Supplements on Cardiac Dysfunction, Myocardial Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timmis, A.; Townsend, N.; Gale, C.; Grobbee, R.; Maniadakis, N.; Flather, M.; Wilkins, E.; Wright, L.; Vos, R.; Bax, J.; et al. European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 508–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Harker, L. Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Science 1976, 193, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkina, E.; Ley, K. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7 (Suppl. S1), 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ji, Z.; Qu, Y.; Yang, M.; Su, Y.; Zuo, W.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Li, Y. Clinical value of ARG1 in acute myocardial infarction patients: Bioinformatics-based approach. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, R.M.; Bianchi, C.; Feng, J.; Clements, R.T.; Liu, Y.; Robich, M.P.; Glazer, H.P.; Sodha, N.R.; Sellke, F.W. Effect of hypercholesterolemia on myocardial necrosis and apoptosis in the setting of ischemia-reperfusion. Circulation 2009, 120, S22–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, S.; Sanborn, T. Acute myocardial infarction. Dis. Mon. 2013, 59, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadou, I.; Iliodromitis, E.K.; Lazou, A.; Görbe, A.; Giricz, Z.; Schulz, R.; Ferdinandy, P. Effect of hypercholesterolaemia on myocardial function, ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection by preconditioning, postconditioning and remote conditioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Korivi, M.; Chen, C.-H.; Peng, W.-J.; Chen, C.-S.; Li, M.-L.; Hsu, L.-S.; Liao, J.-W.; Hseu, Y.-C. Antrodia camphorata attenuates cigarette smoke-induced ROS production, DNA damage, apoptosis, and inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells, and atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2070–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-Y.; Teng, C.-L.J.; Hung, P.-S.; Cheng, C.-C.; Hsu, S.-L.; Hwang, G.-Y.; Tzeng, Y.-M. Ovatodiolide isolated from Anisomeles indica induces cell cycle G2/M arrest and apoptosis via a ROS-dependent ATM/ATR signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Lan, Y.-H.; Hsieh, P.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, S.-L.; Yen, C.-T.; Chang, F.-R.; Hung, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-C. Bioactive cembrane diterpenoids of Anisomeles indica. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Wu, A.T.H.; Lawal, B.; Tzeng, D.T.W.; Lee, J.-C.; Ho, C.-L.; Chao, T.-Y. Identification of Cancer Hub Gene Signatures Associated with Immune-Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Ovatodiolide as a Potential Cancer Immunotherapeutic Agent. Cancers 2021, 13, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.T.H.; Lawal, B.; Tzeng, Y.-M.; Shih, C.-C.; Shih, C.-M. Identification of a Novel Theranostic Signature of Metabolic and Immune-Inflammatory Dysregulation in Myocardial Infarction, and the Potential Therapeutic Properties of Ovatodiolide, a Diterpenoid Derivative. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achudhan, D.; Liu, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Ko, C.-Y.; Chiang, I.-P.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Tang, C.-H. Antcin K Inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 Expression in Synovial Fibroblasts and Ameliorates Cartilage Degradation: Implications for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Shih, C.-C.; Yang, C.-S. Antcin K, a Triterpenoid Compound from Antrodia camphorata, Displays Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects via Glucose Transporter 4 and AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphorylation in Muscles. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4867092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendse, A.A.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Johnson, L.A.; Altenburg, M.K.; Maeda, N. Apolipoprotein E knock-out and knock-in mice: Atherosclerosis, metabolic syndrome, and beyond. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S178–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, K.S.; Leitersdorf, E. Atherosclerosis in the apolipoprotein-E-deficient mouse: A decade of progress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-W.; Nguyen, N.T.K.; Shen, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-B.; Liang, H.-J.; Wu, C.-H. Botanical Antcin K Alleviates High-Fat Damage in Palm Acid Oil-Treated Vascular Endothelial Cells and Macrophages. Plants 2022, 11, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.W.; Ramji, D.P. Cytokines: Roles in atherosclerosis disease progression and potential therapeutic targets. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K.; Libby, P. The immune response in atherosclerosis: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjathoor, V.V.; Febbraio, M.; Podrez, E.A.; Moore, K.J.; Andersson, L.; Koehn, S.; Rhee, J.S.; Silverstein, R.; Hoff, H.F.; Freeman, M.W. Scavenger receptors class A-I/II and CD36 are the principal receptors responsible for the uptake of modified low density lipoprotein leading to lipid loading in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49982–49988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golias, C.; Tsoutsi, E.; Matziridis, A.; Makridis, P.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Review. Leukocyte and endothelial cell adhesion molecules in inflammation focusing on inflammatory heart disease. In Vivo 2007, 21, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaisman, B.L.; Demosky, S.J.; Stonik, J.A.; Ghias, M.; Knapper, C.L.; Sampson, M.L.; Dai, C.; Levine, S.J.; Remaley, A.T. Endothelial expression of human ABCA1 in mice increases plasma HDL cholesterol and reduces diet-induced atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Sheedy, F.J.; Fisher, E.A. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Meng, X.P.; Ramasamy, S.; Harrison, D.G.; Galis, Z.S. Reactive oxygen species produced by macrophage-derived foam cells regulate the activity of vascular matrix metalloproteinases in vitro. Implications for atherosclerotic plaque stability. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2572–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.; Almazan, F.; Witztum, J.L.; Miller, Y.I. Macrophages generate reactive oxygen species in response to minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein: Toll-like receptor 4- and spleen tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 2. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.T.; Parthasarathy, S.; Fong, L.G.; Steinberg, D. Oxidatively modified low density lipoproteins: A potential role in recruitment and retention of monocyte/macrophages during atherogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2995–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwens, D.M.; Boer, C.; Fodor, M.; de Galan, P.; Heine, R.J.; Maassen, J.A.; Diamant, M. Cardiac dysfunction induced by high-fat diet is associated with altered myocardial insulin signalling in rats. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Vaka, V.R.; He, X.; Booz, G.W.; Chen, J.-X. High-fat diet induces cardiac remodelling and dysfunction: Assessment of the role played by SIRT3 loss. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, H.-M.; Wu, H.-Y.; Hung, C.-L.; Chen, C.-J.; Wu, C.-L.; Chen, K.-W.; Huang, C.-L.; Chang, S.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, H.-J. Antibacterial activity of ovatodiolide isolated from Anisomeles indica against Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, J.; Lim, S.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, P.; Xu, C.; Zheng, H.; Fu, K.-C.; et al. Structure and Anti-Inflammatory Activity Relationship of Ergostanes and Lanostanes in Antrodia cinnamomea. Foods 2022, 11, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Cimpeanu, C.; Predoi, G. Antioxidant Capacity Determination in Plants and Plant-Derived Products: A Review. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9130976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Cai, K.; Yu, Q.; Tian, W. Curcumin Alleviates Palmitic Acid-Induced LOX-1 Upregulation by Suppressing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in HUVECs. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9983725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.-Y.; Lu, C.-W.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chuang, T.-Y.; Su, L.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Jheng, Y.-S.; Lee, M.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Chinese Veterinary Medicine B307 Promotes Cardiac Performance and Skeletal Muscle Contraction via Enhancing Intracellular Calcium Levels and Neural Electrical Activity in Animal and Cell Models. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 9064824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.-W.; Wu, W.-J.; Nguyen, T.K.N.; Shen, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-B.; Liang, H.-J.; Wu, C.-H. Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184074
Lu C-W, Wu W-J, Nguyen TKN, Shen S-C, Wu Y-B, Liang H-J, Wu C-H. Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184074
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Chen-Wen, Wen-Jhen Wu, Thi Kim Ngan Nguyen, Szu-Chuan Shen, Yeh-B. Wu, Hui-Ju Liang, and Chung-Hsin Wu. 2023. "Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184074
APA StyleLu, C.-W., Wu, W.-J., Nguyen, T. K. N., Shen, S.-C., Wu, Y.-B., Liang, H.-J., & Wu, C.-H. (2023). Alleviating Effects of Ovatodiolide and Antcin K Supplements on High-Fat Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction in ApoE-Knockout Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress. Nutrients, 15(18), 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184074







