Assessment of Lifestyle, Eating Habits and the Effect of Nutritional Education among Undergraduate Students in Southern Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant
2.2. Study Design
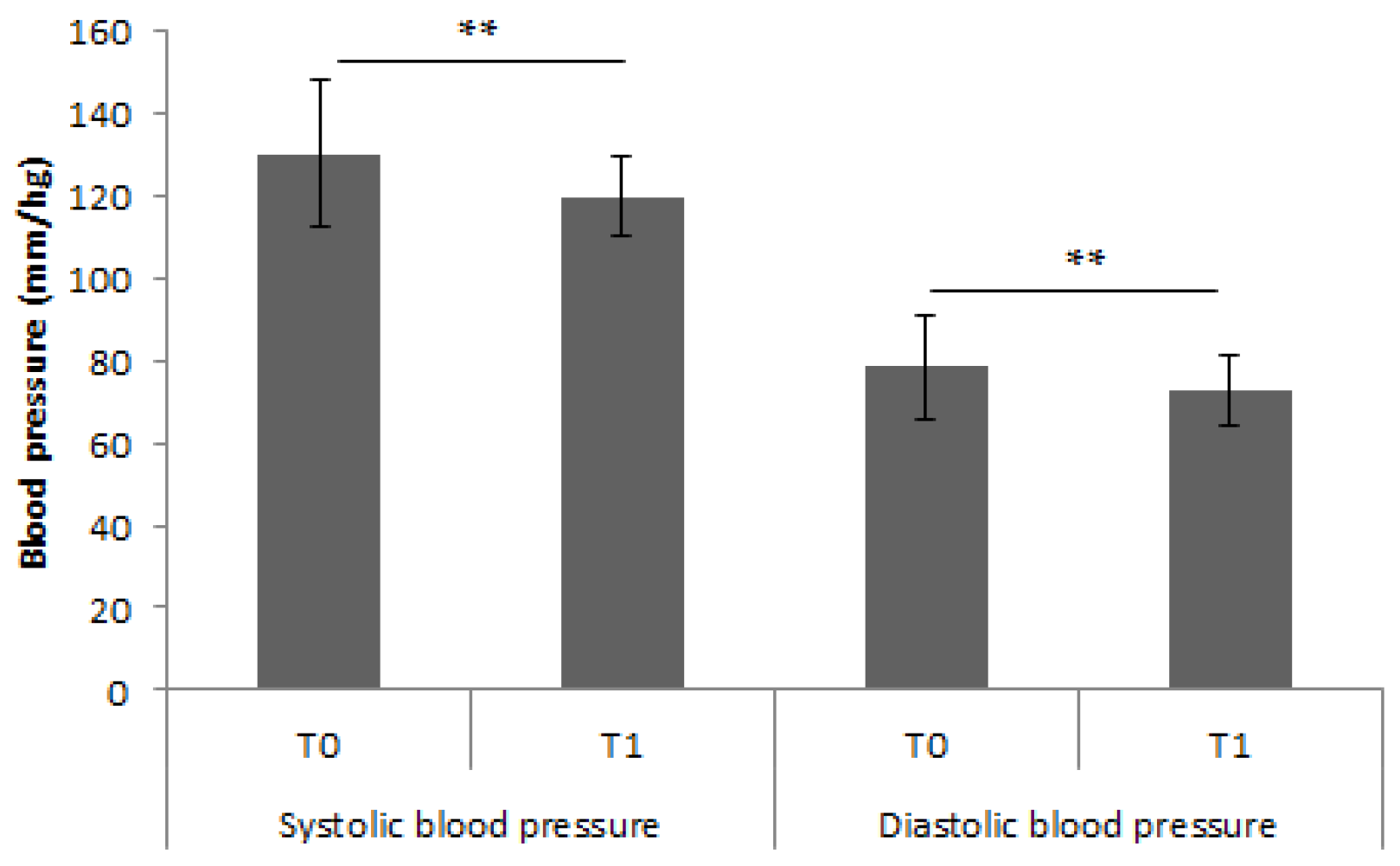
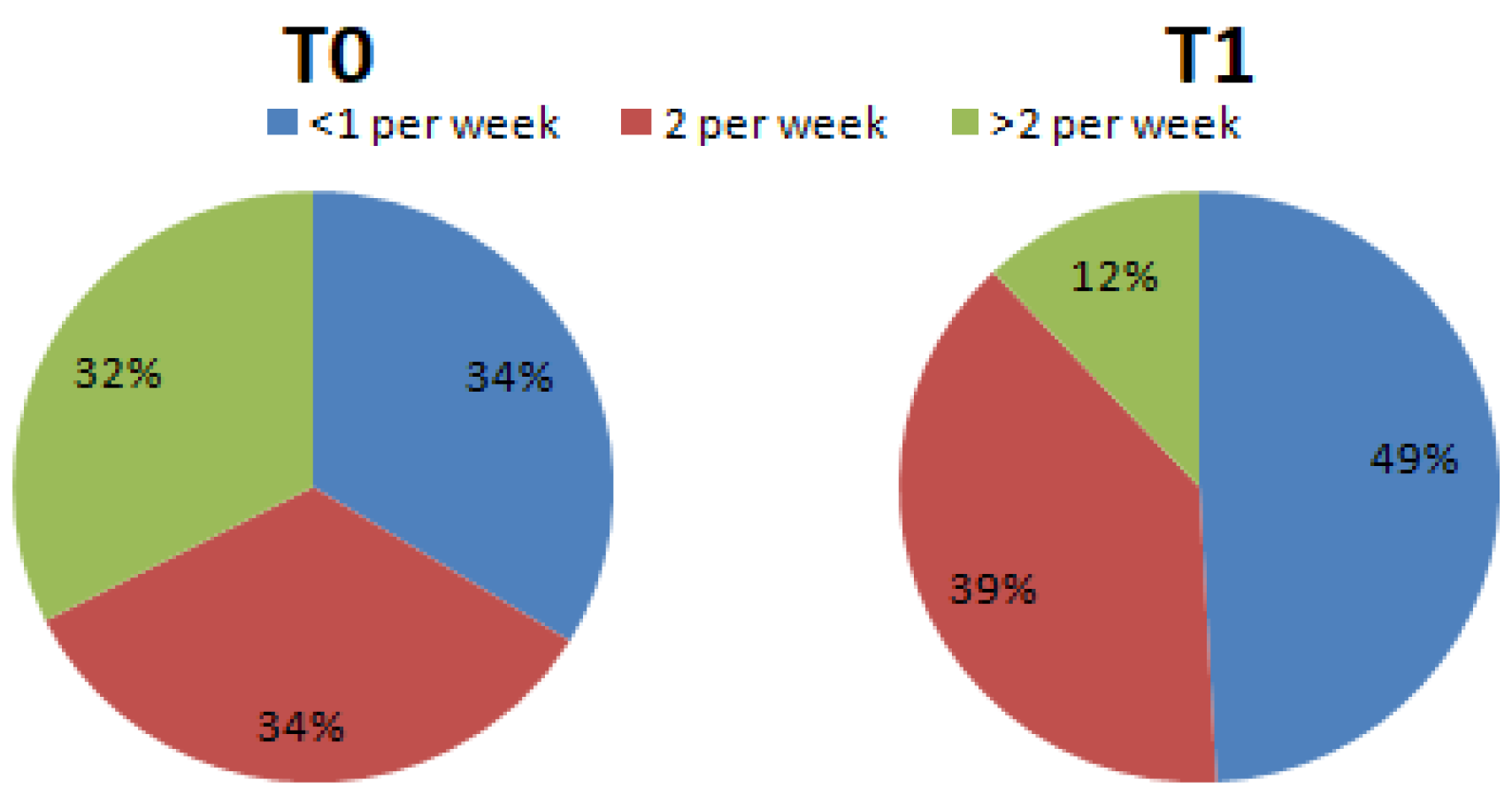
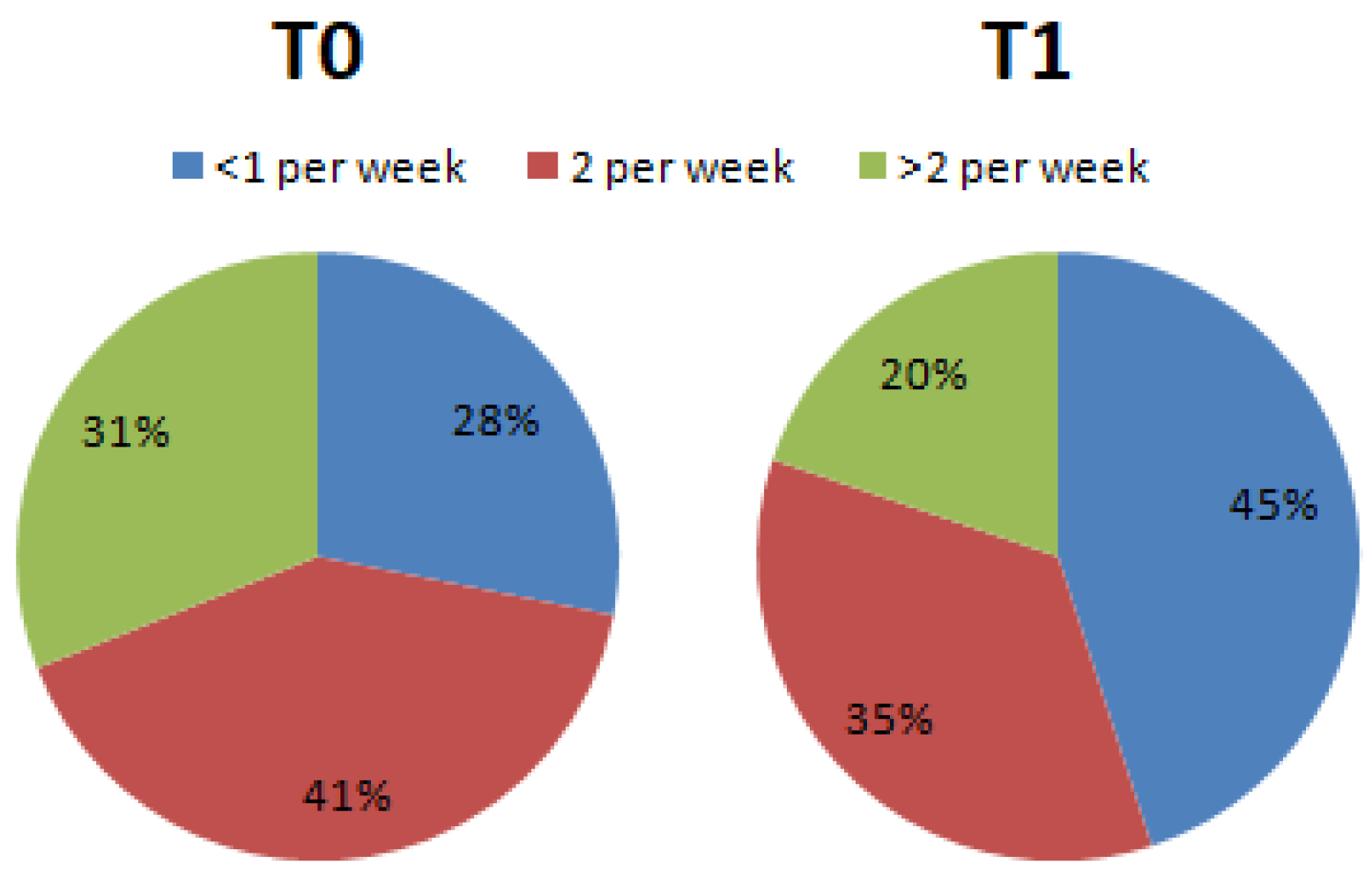
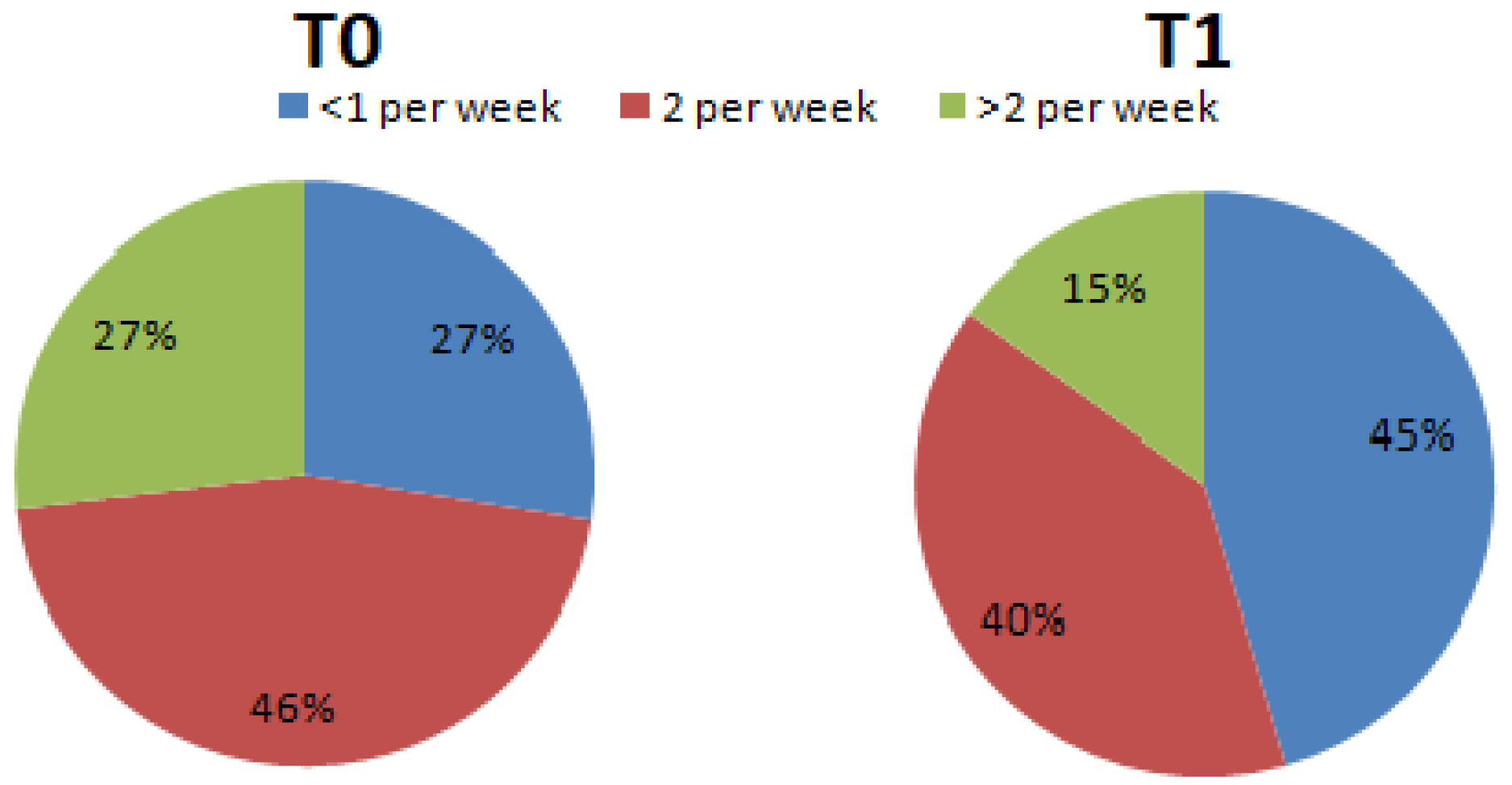
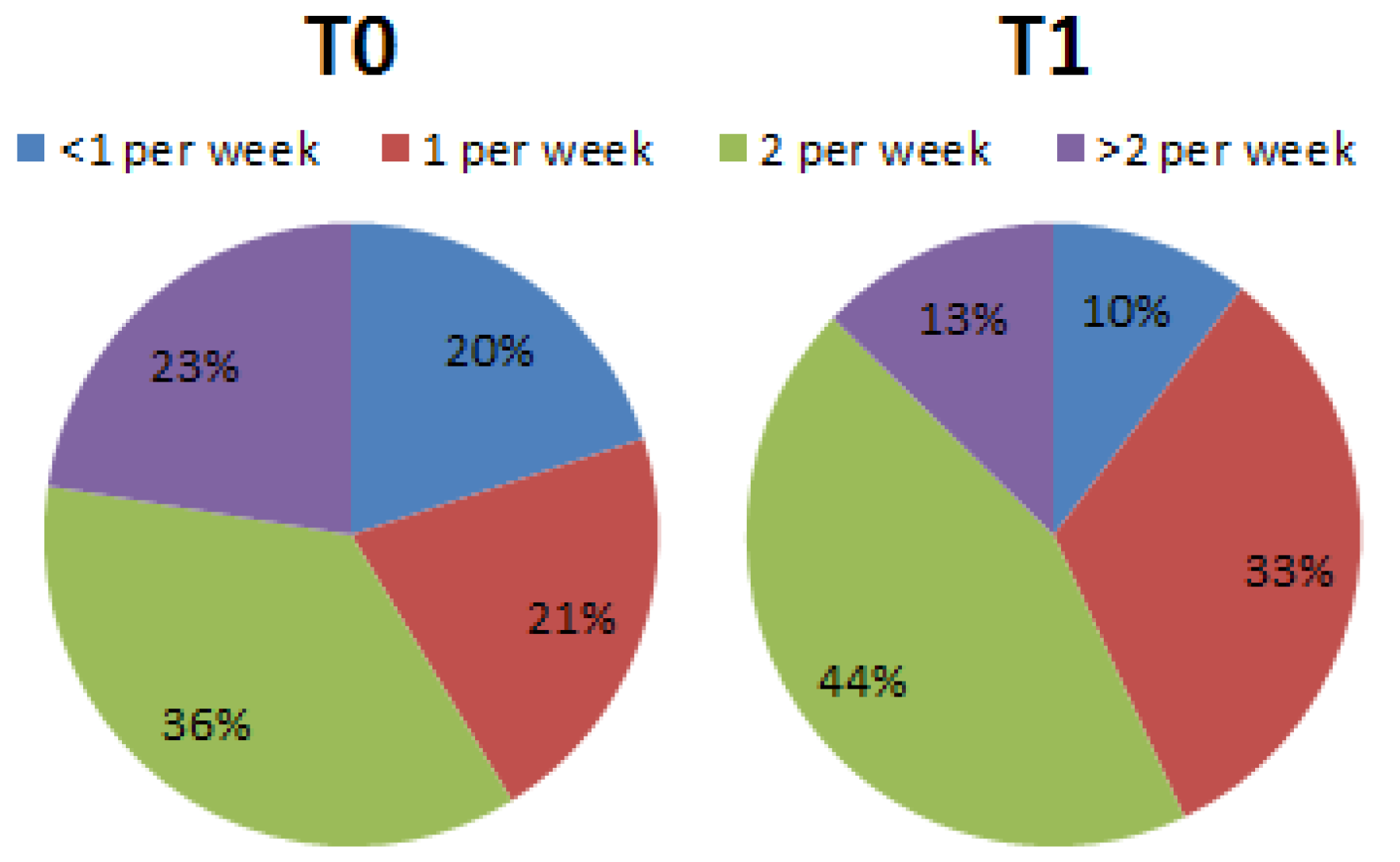
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Question 1: Sex | Male | Female | ||
| Question 2: Age | ||||
| Question 3: Smoke | Yes | No | ||
| Question 4: COVID Vaccination | Yes | No | ||
| Question 5: COVID Positivity | Yes | No | ||
| Question 6: Gastrointestinal disorders/Other disease | Yes | No | ||
| Question 7: Do you practice physical activity? | Yes | No | ||
| Question 8: If yes, how many times a week? | <1 time per week | 1–2 times per week | 2–3 times per week | >3 times per week |
| Question 9: Have you been trying to lose weight in the past three months? If not: Have you tried to avoid gaining weight? | No attempt to either lose or avoid gaining weight in the past three months | Attempts to both lose weight and avoid gaining weight in the past three months for reasons related to body shape or weight | ||
| Question 10: Do you pay close attention to the calorific value of food? | Yes | No | ||
| Question 11: How many portions of sweets do you consume per week? (Chocolates (1 portion = 3 g) biscuits and similar) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 12: How many servings of red meat do you eat per week? (Beef, pork, lamb, 1 portion 100–150 g) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 13: How many servings of processed meat do you consume per week? (sausages and similar; 1 portion = 50 g) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 14: How many eggs do you eat per week? (1 serving = 1 egg) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 15: How many servings of legumes do you consume per week? (Lentils, beans, peas, chickpeas (1 serving = 1 plate or 150 g) | <1 serving per week | 1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week |
| Question 16: How many portions of white meat do you eat per week? (Poultry, rabbit—1 serving = 150 g) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 17: How many servings of fish or seafood do you eat per week? (White/fatty fish (1 serving = 100–150 g), canned fish (1 serving = 1 can or 50 g), seafood (1 serving = 200 g)) | <1 serving per week | 2 servings per week | >2 servings per week | |
| Question 18: How many dairy products do you consume per day? (Milk—1 portion = 200 mL milk, two yogurts, 1 portion of spreadable cheese) | <1 serving per day | 2 servings per day | >2 servings per day | |
| Question 19: How much fruit do you consume per day? (All fruit and fresh fruit juices—1 serving = 150–200 g) | <1 serving per day | 1–2 servings per day | 3–4 servings per day | >4 servings per day |
| Question 20: How many servings of vegetables do you consume per day? (1 portion = 150–200 g) | <1 serving per day | 1–2 servings per day | >2 servings per day | |
| Question 21: How many tablespoons of olive oil do you consume per day (cooking or salad dressing)? (Olive oil, extra virgin olive oil—1 serving = 1 tablespoon) | <1 serving per day | 1–2 servings per day | >2 servings per day | |
| Question 22: How many servings of cereals do you consume per day? (White and wholemeal bread—1 serving = 40 g, half sandwich, cereals—1 serving = 1 plate of rice, pasta or 40 g of breakfast cereal) | <1 serving per day | 1–2 servings per day | >2 servings per day | |
| Question 23: Do you drink more than 6 glasses of water or at least one cup of tea a day? (Water or tea—1 glass serving) | Yes | No | ||
| Question 24: Do you drink wine every day with meals? (White/red wine (1 serving = 1 glass of wine)) | <1 serving per day | 1–2 servings per day | >2 servings per day | |
| Question 25: Do you limit adding salt to meals? | Yes | No | ||
| Question 26: Do you usually use nibbling between meals? Do you consume snacks between meals? | Yes | No | ||
| Question 27: Do you limit your sugar intake in drinks? (including sugary drinks) | Yes | No | ||
| Question 28: How many hours do you spend watching TV a day? | <1 h per day | 1 h a day | 2 h a day | >2 h a day |
References
- Stonerock, G.L.; Blumenthal, J.A. Role of Counseling to Promote Adherence in Healthy Lifestyle Medicine: Strategies to Improve Exercise Adherence and Enhance Physical Activity. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 59, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, M.; Perez, L.G.; Goenka, S.; Brownson, R.C.; Bauman, A.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Hallal, P.C. Can Population Levels of Physical Activity Be Increased? Global Evidence and Experience. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, R.; Franklin, B.; Joy, L.; Ross, R.; Sabgir, D.; Stone, J. Strategies for Promoting Physical Activity in Clinical Practice. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifsud, J.L.; Galea, J.; Garside, J.; Stephenson, J.; Astin, F. Motivational interviewing to support modifiable risk factor change in individuals at increased risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS ONE 2020, 15, e0241193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, H.P.; Garg, A.X.; Haynes, R.B. Interventions to Enhance Patient Adherence to Medication Prescriptions: Scientific Review. JAMA 2002, 288, 2868–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.R.; Williams, S.L.; Haskard, K.B.; Dimatteo, M.R. The Challenge of Patient Adherence. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Krienke, R. Adherence to Medication. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1972–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Pratt, M.; Yang, Z.; Adams, E.K. Inadequate Physical Activity and Health Care Expenditures in the United States. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, H.; Porri, D.; De Giuseppe, R.; Kalmpourtzidou, A.; Salvatore, F.P.; El Ghoch, M.; Itani, L.; Kreidieh, D.; Brytek-Matera, A.; Pocol, C.B.; et al. How Healthy Are Health-Related Behaviors in University Students: The HOLISTic Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzwinski, L.N.; Caffery, L.; Bambling, M.; Edirippulige, S. The Mindfulness App Trial for Weight, Weight-Related Behaviors, and Stress in University Students: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, e12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, H.; Tesone, A.; Niniano, R.; Cerveri, I.; Roggi, C.; Turconi, G. Prevalence Rate of Metabolic Syndrome in a Group of Light and Heavy Smokers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, E.; Deriemaeker, P.; Van Beneden, K. Adjustments in Food Choices and Physical Activity during Lockdown by Flemish Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, C.; Hallit, R.; Akel, M.; Honein, K.; Akiki, M.; Kheir, N.; Obeid, S.; Hallit, S. Validation of the Arabic Version of the ORTO-15 Questionnaire in a Sample of the Lebanese Population. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2020, 25, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmingsson, E.; Ekelund, U. Is the Association between Physical Activity and Body Mass Index Obesity Dependent? Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Wu, H. Correlations between Mobile Phone Addiction and Anxiety, Depression, Impulsivity, and Poor Sleep Quality among College Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Behav. Addict. 2020, 9, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Lin, L.; Austin, D.; Young, T.; Mignot, E. Short Sleep Duration Is Associated with Reduced Leptin, Elevated Ghrelin, and Increased Body Mass Index. PLoS Med. 2004, 1, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remskar, M.; Western, M.J.; Maynard, O.M.; Ainsworth, B. Exercising body but not mind: A qualitative exploration of attitudes to combining physical activity and mindfulness practice for mental health promotion. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 984232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccagni, L.; Barbieri, D.; Gualdi-Russo, E. Body Composition and Physical Activity in Italian University Students. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheck, J.M.; Kuder, J.F.; Economos, C.D. Physical Fitness, Adiposity, and Metabolic Risk Factors in Young College Students. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Dallongeville, J.; Haas, B.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Amouyel, P.; Ferrières, J.; Simon, C.; Arveiler, D. Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity and Dietary Patterns Are Independently Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2012, 38, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Worldwide Trends in Insufficient Physical Activity from 2001 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 358 Population-Based Surveys with 1·9 Million Participants. Lancet. Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, J.; Loerbroks, A.; Diehl, K. Eating Behaviour of University Students in Germany: Dietary Intake, Barriers to Healthy Eating and Changes in Eating Behaviour since the Time of Matriculation. Appetite 2017, 109, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, J.R.; Officer, A.; de Carvalho, I.A.; Sadana, R.; Pot, A.M.; Michel, J.-P.; Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; Epping-Jordan, J.E.; Peeters, G.M.E.E.G.; Mahanani, W.R.; et al. The World Report on Ageing and Health: A Policy Framework for Healthy Ageing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensink, G.B.M.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Haftenberger, M.; Lampert, T.; Ziese, T.; Scheidt-Nave, C. Overweight and Obesity in Germany: Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt. Gesundheitsforschung. Gesundh. 2013, 56, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson Laska, M.; Larson, N.I.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Story, M. Dietary Patterns and Home Food Availability during Emerging Adulthood: Do They Differ by Living Situation? Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, S.; Bagordo, F.; Stefanati, A.; Grassi, T.; Piccinni, L.; Bergamini, M.; De Donno, A. Assessment of Lifestyle and Eating Habits among Undergraduate Students in Northern Italy. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2015, 51, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Cluskey, M.; Grobe, D. College Weight Gain and Behavior Transitions: Male and Female Differences. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driskell, J.A.; Kim, Y.-N.; Goebel, K.J. Few Differences Found in the Typical Eating and Physical Activity Habits of Lower-Level and Upper-Level University Students. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklas, T.A.; Baranowski, T.; Cullen, K.W.; Berenson, G. Eating Patterns, Dietary Quality and Obesity. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debate, R.D.; Topping, M.; Sargent, R.G. Racial and Gender Differences in Weight Status and Dietary Practices among College Students. Adolescence 2001, 36, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stefanikova, Z.; Sevcikova, L.; Jurkovicova, J.; Sobotova, L.; Aghova, L. Positive and Negative Trends in University Students’ Food Intake. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2006, 107, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colić Barić, I.; Satalić, Z.; Lukesić, Z. Nutritive Value of Meals, Dietary Habits and Nutritive Status in Croatian University Students According to Gender. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 54, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hercberg, S.; Preziosi, P.; Galan, P.; Deheeger, M.; Papoz, L.; Dupin, H. Dietary Intake of a Representative Sample of the Population of Val-de-Marne; III. Mineral and Vitamin Intake. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 1991, 39, 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Skemiene, L.; Ustinaviciene, R.; Piesine, L.; Radisauskas, R. Peculiarities of Medical Students’ Nutrition. Medicina 2007, 43, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.T.K.; Harris, K.J.; Lee, R.E.; Nazir, N.; Born, W.; Kaur, H. Assessing Overweight, Obesity, Diet, and Physical Activity in College Students. J. Am. Coll. Health 2003, 52, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anding, J.D.; Suminski, R.R.; Boss, L. Dietary Intake, Body Mass Index, Exercise, and Alcohol: Are College Women Following the Dietary Guidelines for Americans? J Am. Coll. Health 2001, 49, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammas, I.; Bertsias, G.; Linardakis, M.; Moschandreas, J.; Kafatos, A. Nutrient Intake and Food Consumption among Medical Students in Greece Assessed during a Clinical Nutrition Course. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 55, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racette, S.B.; Deusinger, S.S.; Strube, M.J.; Highstein, G.R.; Deusinger, R.H. Weight Changes, Exercise, and Dietary Patterns during Freshman and Sophomore Years of College. J. Am. Coll. Health 2005, 53, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palma, D.; Tafuri, D. Special needs and inclusion in sport management: A specific literature review|Posebne potrebe i uključenje u sportskom menadžmentu: Specifičan pregled literature. Sport Sci. 2016, 9, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzeo, F.; Santamaria, S.; Monda, V.; Messina, G.; Monda, M. Dietary supplements use in competitive and non-competitive boxer: An exploratory study. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 1000294. [Google Scholar]
- Gaetano, R.; Domenico, T.; Gaetano, A. Physical activity and its relation to body and ludic expression in childhood Mediterranean. J. Soc. Sci. 2015, 6, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Monda, M.; Viggiano, A.; Vicidomini, C.; Tafuri, D.; De Luca, B. Expresso coffee increases parasympathetic activity in young, healthy people. Nutr. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirangelo, I.; Borriello, M.; Liccardo, M.; Scafuro, M.; Russo, P.; Iannuzzi, C. Hydroxytyrosol Selectively Affects Non-Enzymatic Glycation in Human Insulin and Protects by AGEs Cytotoxicity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresić, G.; Kendel Jovanović, G.; Pavicić Zezel, S.; Cvijanović, O.; Ivezić, G. The Effect of Nutrition Knowledge on Dietary Intake among Croatian University Students. Coll. Antropol. 2009, 33, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo Izaga, M.; Rocandio Pablo, A.M.; Ansotegui Alday, L.; Pascual Apalauza, E.; Salces Beti, I.; Rebato Ochoa, E. Diet Quality, Overweight and Obesity in University Students. Nutr. Hosp. 2006, 21, 673–679. [Google Scholar]
- Zykova, S.N.; Storhaug, H.M.; Toft, I.; Chadban, S.J.; Jenssen, T.G.; White, S.L. Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nutrition and Serum Uric Acid in Two Caucasian Cohorts: The AusDiab Study and the Tromsø Study. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.L.; Dixon, Z.; Himburg, S.; Huffman, F. Asian Students Change Their Eating Patterns after Living in the United States. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1999, 99, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Female | Male |
|---|---|---|
| Number (n) | 49 | 21 |
| Systolic pressure | 124.25 mmHg ± 20.9 | 129.03 mmHg ± 19.8 |
| Diastolic pressure | 74.53 mmHg ± 13.1 | 76.92 mmHg ± 10.6 |
| Height (cm) | 162.2 ± 6.3 | 176.3 ± 8.2 |
| Weight (kg) | 61.9 ± 15.2 | 73.6 ± 13.5 |
| BIA Parameters | T0 | T1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (Kg) | 66.18 | ±14.34 | 58.49 | ±9.54 | 0.0012 | ** |
| FFM% | 72.31 | ±9.06 | 76.68 | ±6.59 | 0.1354 | ns |
| FM% | 27.69 | ±14.03 | 23.32 | ±6.34 | 0.0251 | * |
| TBW% | 54.26 | ±6.46 | 55.81 | ±4.63 | 0.0926 | ns |
| ECW% | 44.81 | ±3.43 | 45.68 | ±3.34 | 0.0654 | ns |
| ICW% | 54.53 | ±6.93 | 51.44 | ±12.08 | 0.0381 | * |
| MM% | 37.72 | ±6.89 | 38.45 | ±5.11 | 0.3144 | ns |
| BCM% | 27.04 | ±6.97 | 24.36 | ±6.32 | 0.0127 | * |
| BM (kcal) | 1533.94 | ±202.48 | 1456.64 | ±183.48 | 0.0130 | * |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 23.81 | ±4.39 | 21.85 | ±2.20 | 0.0022 | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moscatelli, F.; De Maria, A.; Marinaccio, L.A.; Monda, V.; Messina, A.; Monacis, D.; Toto, G.; Limone, P.; Monda, M.; Messina, G.; et al. Assessment of Lifestyle, Eating Habits and the Effect of Nutritional Education among Undergraduate Students in Southern Italy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132894
Moscatelli F, De Maria A, Marinaccio LA, Monda V, Messina A, Monacis D, Toto G, Limone P, Monda M, Messina G, et al. Assessment of Lifestyle, Eating Habits and the Effect of Nutritional Education among Undergraduate Students in Southern Italy. Nutrients. 2023; 15(13):2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132894
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoscatelli, Fiorenzo, Antonella De Maria, Luigi Antonio Marinaccio, Vincenzo Monda, Antonietta Messina, Domenico Monacis, Giusi Toto, Pierpaolo Limone, Marcellino Monda, Giovanni Messina, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of Lifestyle, Eating Habits and the Effect of Nutritional Education among Undergraduate Students in Southern Italy" Nutrients 15, no. 13: 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132894
APA StyleMoscatelli, F., De Maria, A., Marinaccio, L. A., Monda, V., Messina, A., Monacis, D., Toto, G., Limone, P., Monda, M., Messina, G., Monda, A., & Polito, R. (2023). Assessment of Lifestyle, Eating Habits and the Effect of Nutritional Education among Undergraduate Students in Southern Italy. Nutrients, 15(13), 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132894










