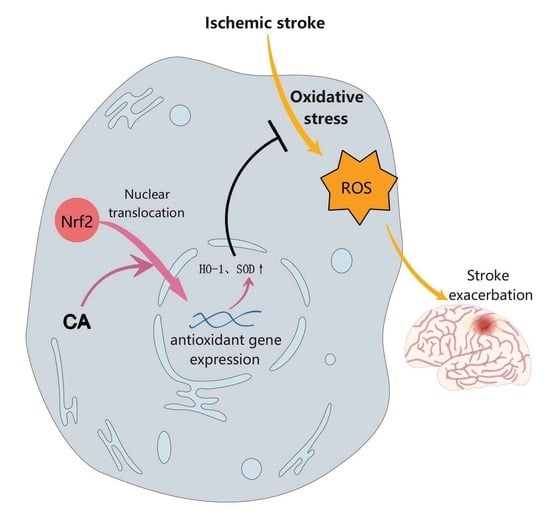
Chebulic Acid Prevents Hypoxia Insult via Nrf2/ARE Pathway in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. CA Preparation and Treatment
2.3. CCK8 Assay
2.4. CA Antioxidant Activity
2.5. Immunofluorescence of the ROS
2.6. Detection of the ROS and Apoptosis Rate by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Immunofluorescence of Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation
2.8. Animals and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO) Model Establishment
2.9. Animal Experiments Drug Administration
2.10. Behavioral Tests
2.11. 2,3,5-Triphenyl-tetrazolium Chloride (TTC) Staining
2.12. TUNEL Staining
2.13. Western Blot Experiment
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
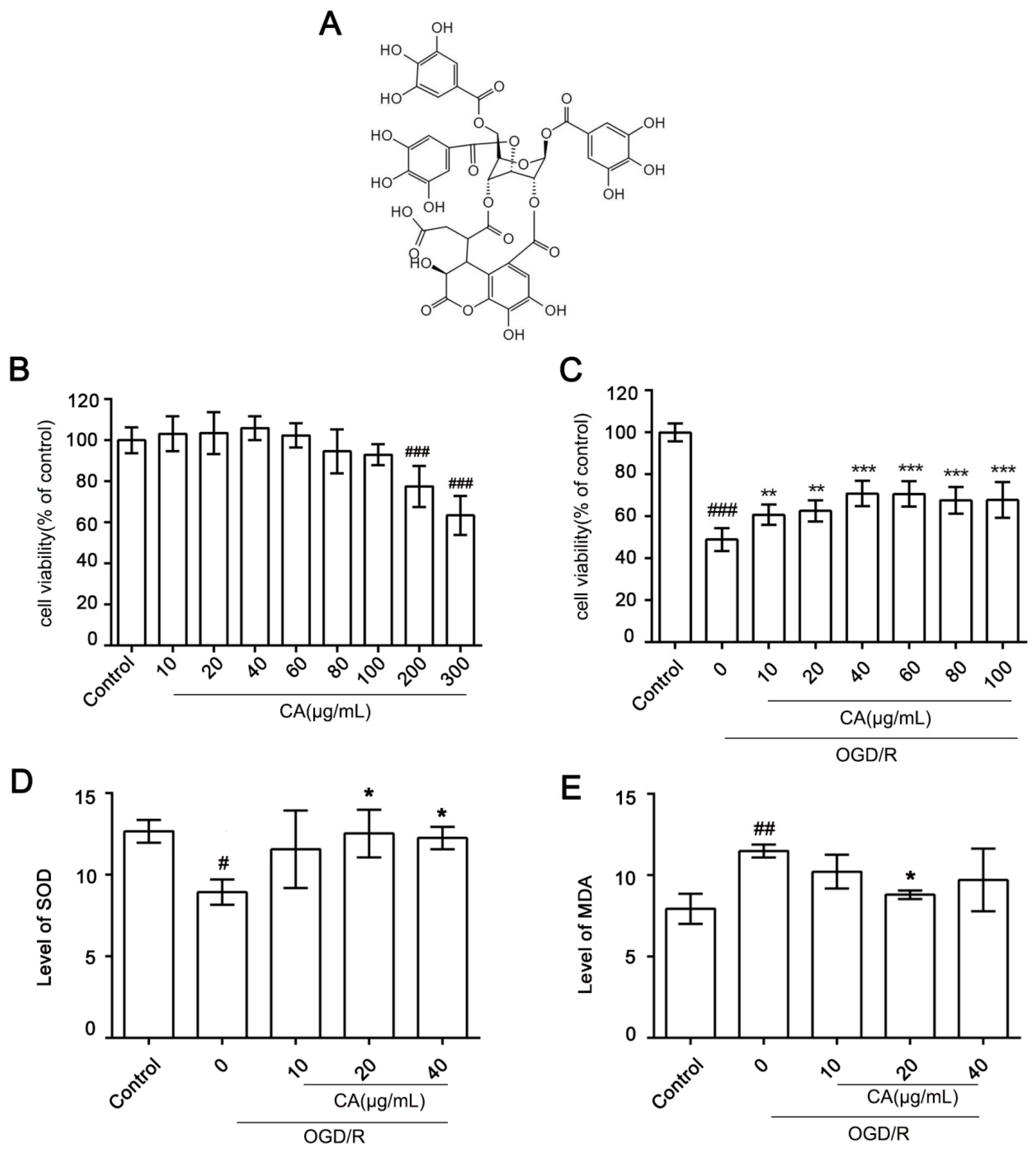
3.1. Cytotoxicity of CA and Its Protective Effects on OGD/R-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells
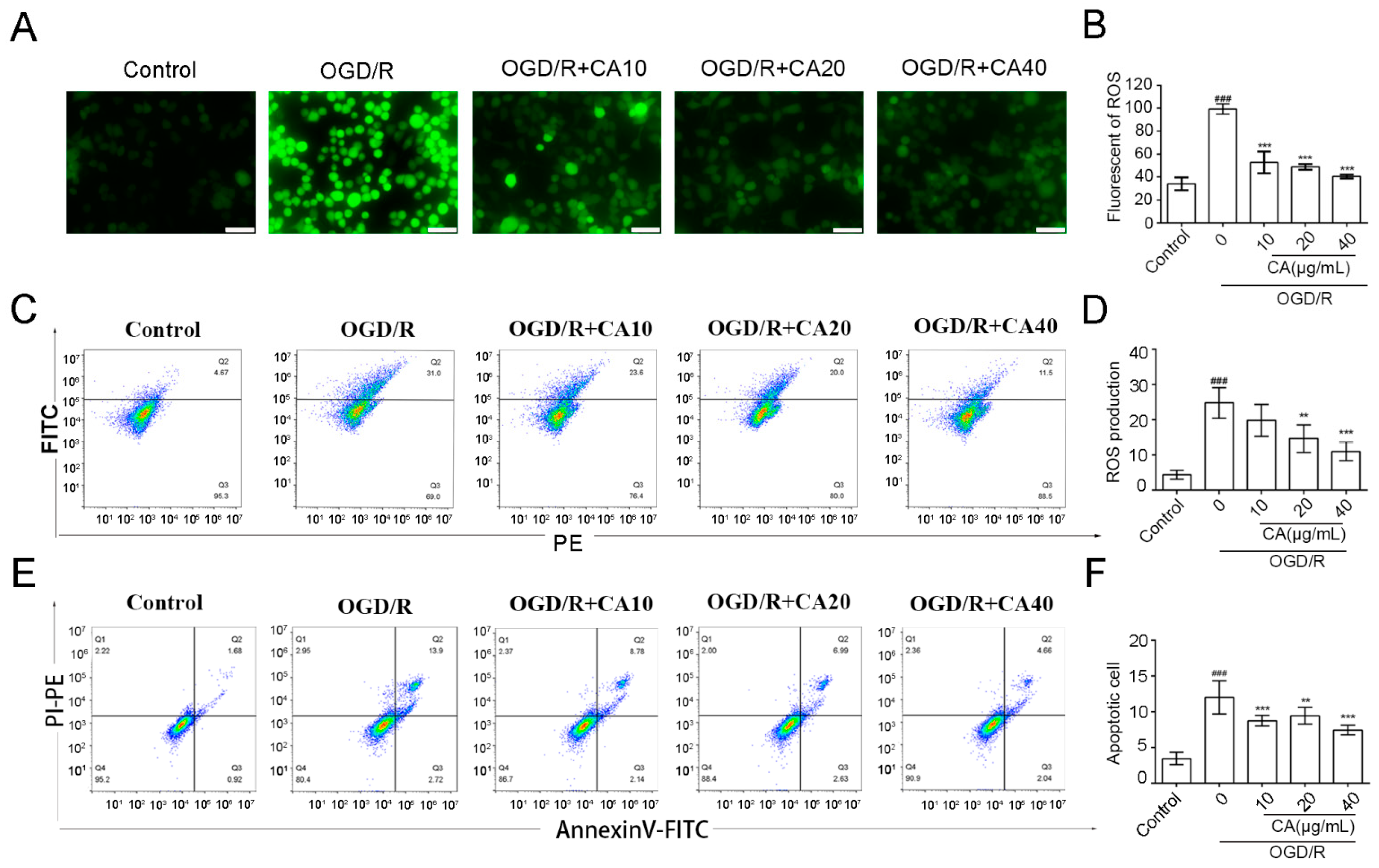
3.2. CA Reduced OGD/R-Induced ROS Production and Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells
3.3. CA Promotes Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2 in SH-SY5Y Cells Induced by OGD/R
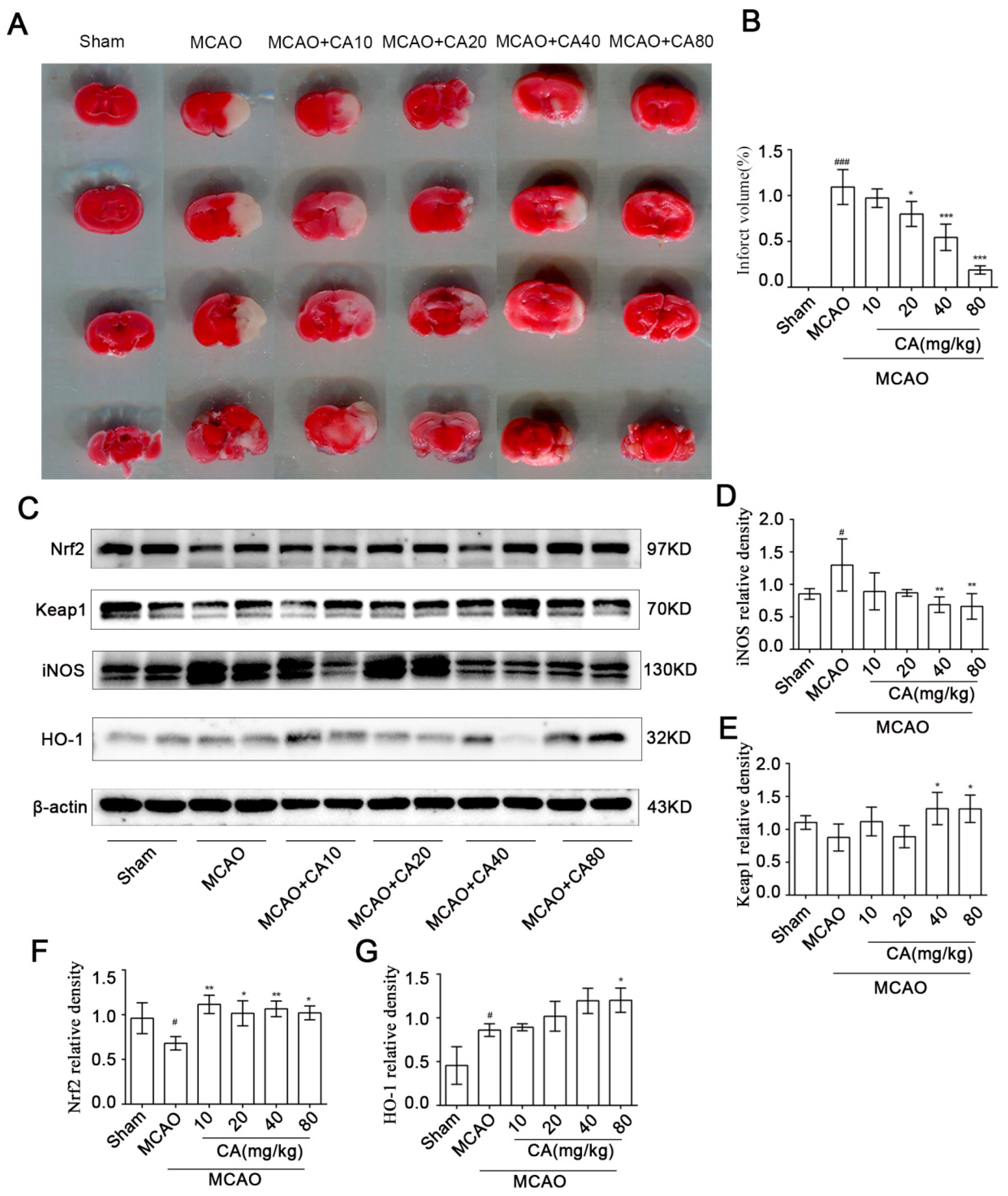
3.4. CA Decreased Cerebral Damage and Apoptosis Following Ischemia-Reperfusion In Vivo
3.5. CA Reduced Infarct Volume after Ischemia-Reperfusion In Vivo
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, W.T.; Li, D.X.; Tong, L. Progress in research of the treatment of ischemic stroke. Chin. J. New Drugs 2016, 25, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Stapf, C.; Mohr, J.P. Ischemic stroke therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnan, G.A.; Fisher, M.; Macleod, M.M. Stroke. Lancet 2008, 371, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Dar, N.J.; Bhat, Z.S.; Hussain, A.; Shah, A.; Liu, H.; Graham, S.H. Inflammation in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, consequences and possible drug targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1378–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, Z.D.; Li, H. Research progress on pathogenesis of ischemic stroke and traditional Chinese medicine commonly used for treatment of ischemic stroke. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 422–432. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Xiang, J.; Cai, D. Tongxinluo reduces brain edema and inhibits post-ischemic inflammation after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.H. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanero, S.; Santro, T.; Arumugam, T.V. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: Sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 712–718. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, R.; Fernández, G.R.; Gutiérrez, R.; Matamala, J.M.; Carrasco, R.; Miranda, M.A.; Feuerhake, W. Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Arora, S.; Singh, B.; Thakur, L.C.; Gambhir, J.; Prabhu, K.M. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of transient ischemic attack and stroke. Int. J. Biol. Med. Res. 2011, 3, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Z.A.; Li, R.C.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M.; Biswal, S.; Doré, S. Role of reactive oxygen species in modulation of Nrf2 following ischemic reperfusion injury. Neuroscience 2007, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, A.Y.; Li, P.; Murphy, T.H. A small-molecule-inducible Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response provides effective prophylaxis against cerebral ischemia in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10321–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfundstein, B.; El Desouky, S.K.; Hull, W.E.; Haubner, R.; Erben, G.; Owen, R.W. Polyphenolic compounds in the fruits of Egyptian medicinal plants (Terminalia bellerica, Terminalia chebula and Terminalia horrida): Characterization, quantitation and determination of antioxidant capacities. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yue, Y.; Peng, A.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, J.; Cao, X.; Ding, H.; Yin, S. Myricetin ameliorates brain injury and neurological deficits via Nrf2 activation after experimental stroke in middle-aged rats. Food Funct. 2016, 15, 2624–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F.; Zhang, G.; Qin, X. Nrf2-a Promising therapeutic target for defensing against oxidative stress in stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6006–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cui, G.; Yu, M. Nrf2/ARE pathway inhibits ROS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in BV2 cells after cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Mu, D.Z. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and brain hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2014, 16, 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- Rajsic, S.; Gothe, H.; Borba, H.H.; Sroczynski, G.; Vujicic, J.; Toell, T.; Siebert, U. Economic burden of stroke: A systematic review on post-stroke care. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2019, 20, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rao, S.; Wang, J. Intravenous thrombolysis in combination with mild hypothermia therapy in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, R.; Ord, E.N.; Work, L.M. Oxidative Stress and the Use of Antioxidants in Stroke. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 472–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, T.M.; Thundyil, J.; Tang, S.C.; Sobey, C.G.; Taylor, S.M.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Xie, Y.; Bosco, G.M.; Chen, C.; Camporesi, E.M. Hyperbaric oxygenation alleviates MCAO-induced brain injury and reduces hydroxyl radical formation and glutamate release. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmez, I.; Ozyurt, H. Reactive oxygen species and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamato, M.; Egashira, T.; Utsumi, H. Application of in vivo ESR spectroscopy to measurement of cerebrovascular ROS generation in stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Jung, S.H.; Yun, B.S.; Lee, K.W. Isolation of chebulic acid from Terminalia chebula Retz. and its antioxidant effect in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.H.; Son, W.R.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, K.W. Chebulic acid inhibits advanced glycation end products-mediated vascular dysfunction by suppressing ros via the erk/nrf2 pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, Y.C.; Pyo, M.C.; Nam, M.H.; Hong, C.O.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, K.W. Chebulic acid prevents hepatic fibrosis induced by advanced glycation end-products in LX-2 cell by modulating Nrf2 translocation via ERK pathway. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 34, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.L.; Yang, S.Y.; Pyo, M.C.; Hong, C.O.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.W. Protective effects of chebulic acid from Terminalia chebula Retz. against t-BHP-induced oxidative stress by modulations of Nrf2 and its related enzymes in HepG2 cells. Food. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huang, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, H. Sirt1 resists advanced glycation end products-induced expressions of fibronectin and TGF-β1 by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehaibi, K.; Trabelsi, I.; Mahdouani, K.; Slimane, M.N. Correlation of Oxidative Stress Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 2585–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Tang, X. Potential Neuroprotective Treatment of Stroke: Targeting Excitotoxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crack, P.J.; Taylor, J.M. Reactive oxygen species and the modulation of stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, V.; Schlichter, L.C. Mechanisms of microglia-mediated neurotoxicity in a new model of the stroke penumbra. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Lin, K.; Leng, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Xu, X.; Sun, B.; et al. Chebulic Acid Prevents Hypoxia Insult via Nrf2/ARE Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245390
Zhou R, Lin K, Leng C, Zhou M, Zhang J, Li Y, Liu Y, Ye X, Xu X, Sun B, et al. Chebulic Acid Prevents Hypoxia Insult via Nrf2/ARE Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245390
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Rong, Kuan Lin, Changlong Leng, Mei Zhou, Jing Zhang, Youwei Li, Yujing Liu, Xiansheng Ye, Xiaoli Xu, Binlian Sun, and et al. 2022. "Chebulic Acid Prevents Hypoxia Insult via Nrf2/ARE Pathway in Ischemic Stroke" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245390
APA StyleZhou, R., Lin, K., Leng, C., Zhou, M., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Ye, X., Xu, X., Sun, B., Shu, X., & Liu, W. (2022). Chebulic Acid Prevents Hypoxia Insult via Nrf2/ARE Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients, 14(24), 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245390