Synergistic Effect of Squalene and Hydroxytyrosol on Highly Invasive MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Scavenging Radical Activity Estimation by DPPH Assay
2.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Cell Cycle Assay
2.8. Analysis of Apoptosis
2.9. Detection of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
2.10. Alkaline Single-Cell Gel Electrophoresis (Comet Assay)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of Radical Scavenging Activity by the DPPH Test
3.2. Radical Scavenging Activity by the ABTS Assay
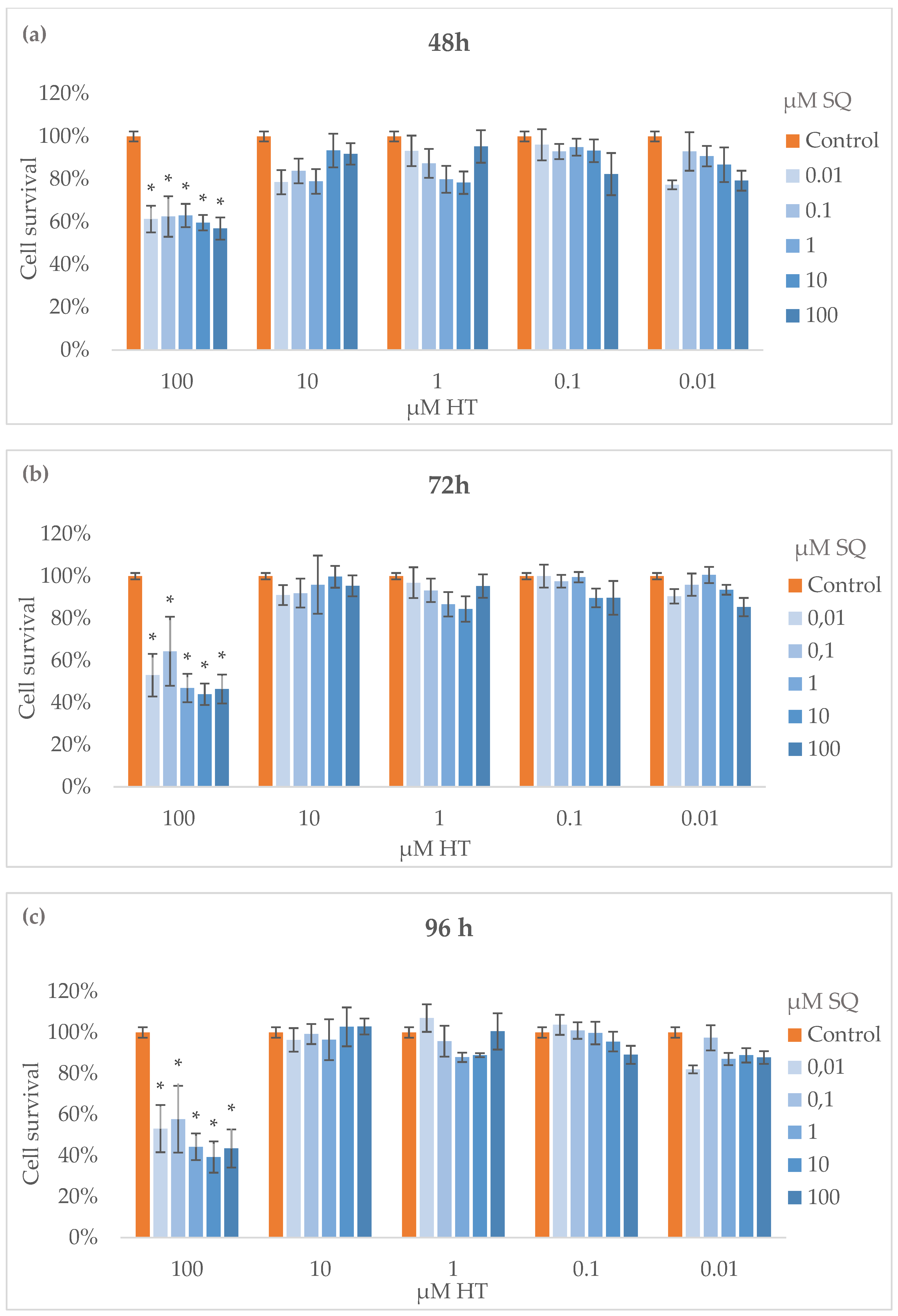
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
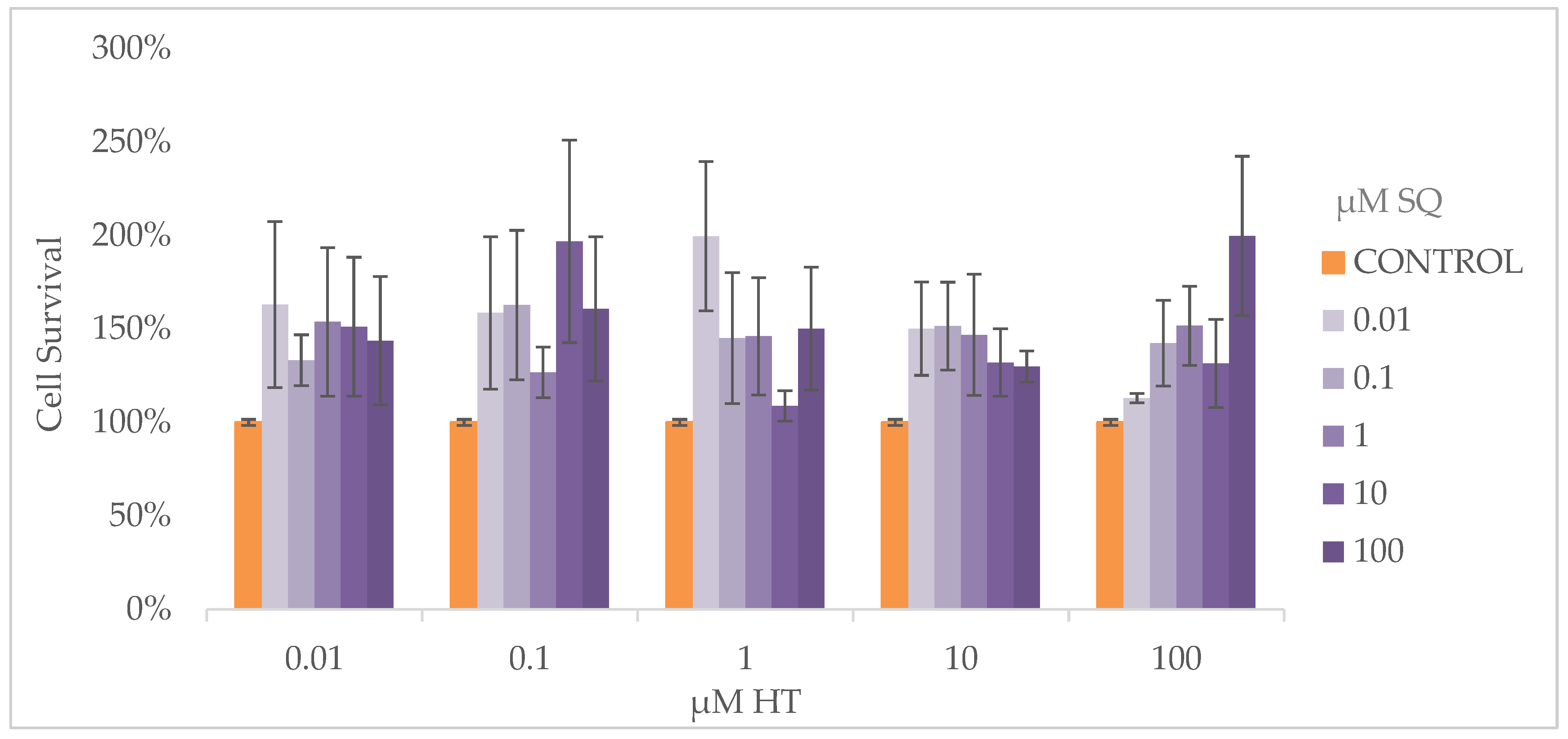
3.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
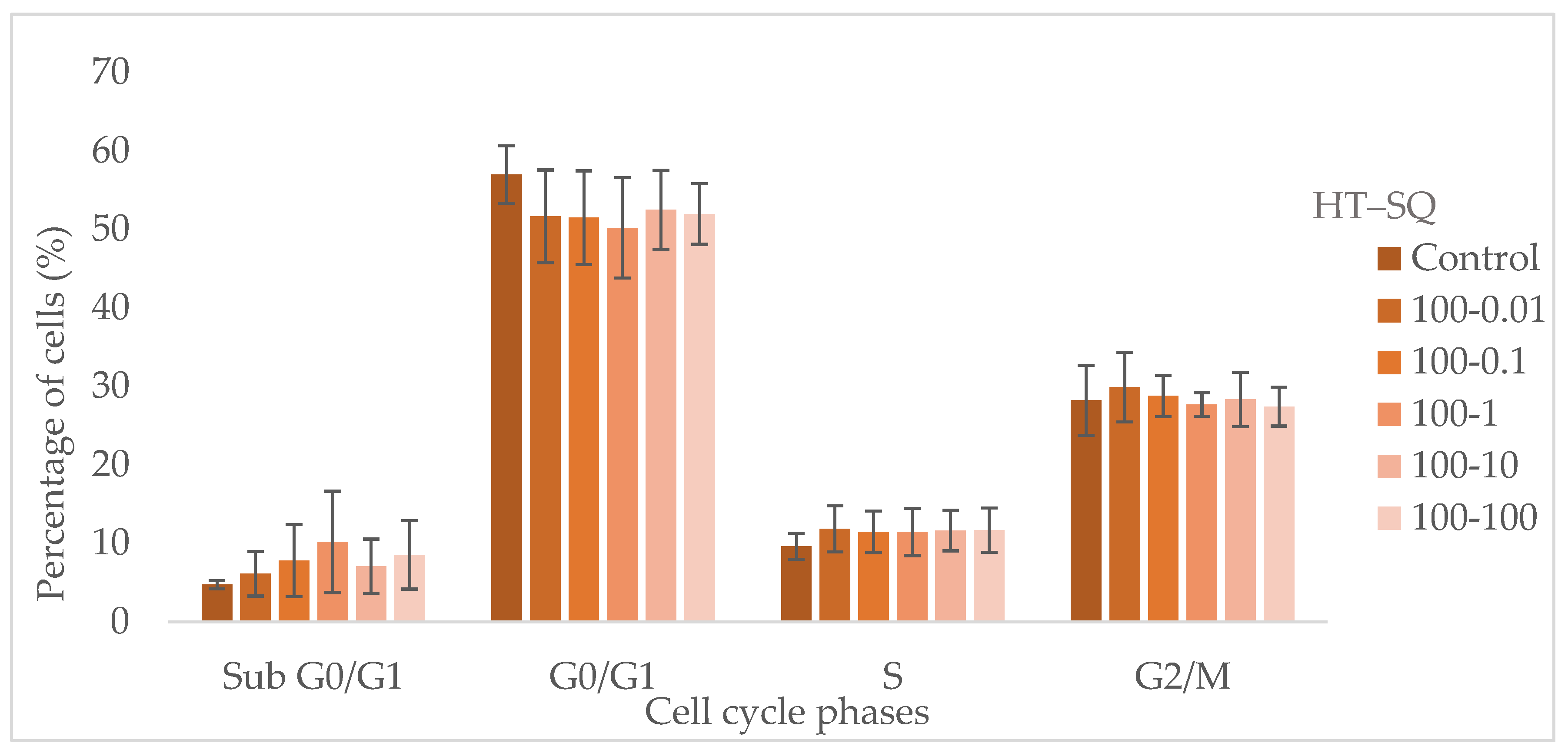
3.5. Cell Cycle Assay
3.6. Analysis of Apoptosis
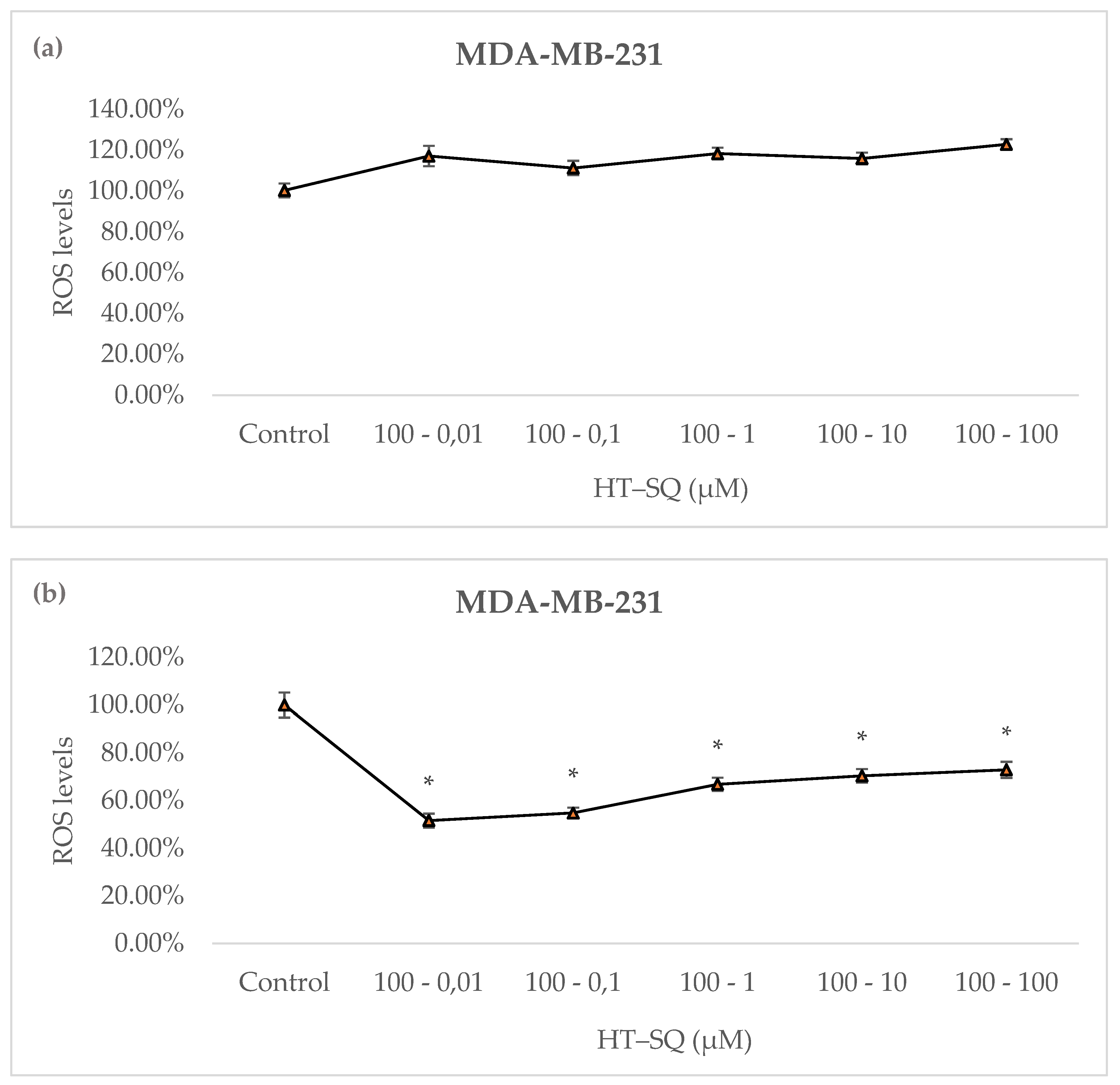
3.7. Detection of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
3.8. Analysis of DNA Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, K.B. The contribution of the environment (especially diet) to breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buckland, G.; Travier, N.; Cottet, V.; González, C.A.; Luján-Barroso, L.; Agudo, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Peeters, P.H.; et al. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.W.; Haubner, R.; Würtele, G.; Hull, E.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Olives and olive oil in cancer prevention. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2004, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaforio, J.J.; Visioli, F.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Castañer, O.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Fitó, M.; Hernández, A.F.; Huertas, J.R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Menendez, J.A.; et al. Virgin Olive Oil and Health: Summary of the III International Conference on Virgin Olive Oil and Health Consensus Report, JAEN (Spain) 2018. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicerale, S.; Conlan, X.A.; Sinclair, A.J.; Keast, R.S. Chemistry and health of olive oil phenolics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlolla, J.M.; Rao, C.V. Triterpenoids for cancer prevention and treatment: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Covas, M.I.; Fitó, M.; Kušar, A.; Pravst, I. Health effects of olive oil polyphenols: Recent advances and possibilities for the use of health claims. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenes, M.; García, A.; García, P.; Rios, J.J.; Garrido, A. Phenolic compounds in Spanish olive oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3535–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, F.; Bellomo, G.; Galli, C. Free radical-scavenging properties of olive oil polyphenols. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, M.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bianchi, M.L.; Spencer, J.P.; Kaur, H.; Halliwell, B.; Aeschbach, R.; Banni, S.; Dessi, M.A.; Corongiu, F.P. Inhibition of peroxynitrite dependent DNA base modification and tyrosine nitration by the extra virgin olive oil-derived antioxidant hydroxytyrosol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haloui, E.; Marzouk, B.; Marzouk, Z.; Bouraoui, A.; Fenina, N. Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein from olive leaves: Potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, G.; Deiana, M.; Incani, A.; Vauzour, D.; Dessì, M.A.; Spencer, J.P. Hydroxytyrosol inhibits the proliferation of human colon adenocarcinoma cells through inhibition of ERK1/2 and cyclin D1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrich, E.; Moral, R.; Solanas, M. Olive oil, an essential component of the Mediterranean diet, and breast cancer. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, R.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Rosignoli, P.; Servili, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Montedoro, G.F.; Di Saverio, C.; Morozzi, G. Virgin olive oil phenols inhibit proliferation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL60) by inducing apoptosis and differentiation. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallagui, Z.; Han, J.; Isoda, H.; Sayadi, S. Hydroxytyrosol rich extract from olive leaves modulates cell cycle progression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warleta, F.; Quesada, C.S.; Campos, M.; Allouche, Y.; Beltrán, G.; Gaforio, J.J. Hydroxytyrosol protects against oxidative DNA damage in human breast cells. Nutrients 2011, 3, 839–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newmark, H.L. Squalene, olive oil, and cancer risk. Review and hypothesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 889, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.W.; Giacosa, A.; Hull, W.E.; Haubner, R.; Würtele, G.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Olive-oil consumption and health: The possible role of antioxidants. Lancet Oncol. 2000, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katdare, M.; Singhal, H.; Newmark, H.; Osborne, M.P.; Telang, N.T. Prevention of mammary preneoplastic transformation by naturally-occurring tumor inhibitors. Cancer Lett. 1997, 111, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Coates, H.W.; Chua, N.K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Brown, A.J.; Ohgane, K. A key mammalian cholesterol synthesis enzyme, squalene monooxygenase, is allosterically stabilized by its substrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7150–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shidoji, Y.; Tabata, Y. Unequivocal evidence for endogenous geranylgeranoic acid biosynthesized from mevalonate in mammalian cells. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, Y.; Omori, M.; Shidoji, Y. Age-Dependent Decrease in Hepatic Geranylgeranoic Acid Content in C3H/HeN Mice and Its Oral Supplementation Prevents Spontaneous Hepatoma. Metabolites 2021, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.V.; Newmark, H.L.; Reddy, B.S. Chemopreventive effect of squalene on colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Otagiri, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ikekawa, T. Intensification of host’s immunity by squalene in sarcoma 180 bearing ICR mice. J. Pharm.-Dyn. 1983, 6, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warleta, F.; Campos, M.; Allouche, Y.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Ruiz-Mora, J.; Beltrán, G.; Gaforio, J.J. Squalene protects against oxidative DNA damage in MCF10A human mammary epithelial cells but not in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lim, B.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Yang, H.C. Effects of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on alkaline phosphatase activity and matrix mineralization of odontoblast and osteoblast cell lines. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Quesada, C.; López-Biedma, A.; Gaforio, J.J. The differential localization of a methyl group confers a different anti-breast cancer activity to two triterpenes present in olives. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Quesada, C.; López-Biedma, A.; Gaforio, J.J. Maslinic Acid enhances signals for the recruitment of macrophages and their differentiation to m1 state. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 654721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Biedma, A.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Beltrán, G.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Gaforio, J.J. Phytoestrogen (+)-pinoresinol exerts antitumor activity in breast cancer cells with different oestrogen receptor statuses. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Quesada, C.; López-Biedma, A.; Toledo, E.; Gaforio, J.J. Squalene Stimulates a Key Innate Immune Cell to Foster Wound Healing and Tissue Repair. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 9473094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, A.L.; De Stéfani, E. Squalene: A multi-task link in the crossroads of cancer and aging. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2013, 3, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirianni, R.; Chimento, A.; De Luca, A.; Casaburi, I.; Rizza, P.; Onofrio, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Puoci, F.; Andò, S.; Maggiolini, M.; et al. Oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol inhibit MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation interfering with ERK1/2 activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Talorete, T.P.; Yamada, P.; Isoda, H. Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Cytotechnology 2009, 59, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.; Santos, S.A.; Guerra, Â.R.; Guerreiro, O.; Felício, L.; Jerónimo, E.; Silvestre, A.; Pascoal, C.; Duarte, M. Valorization of olive mill residues: Antioxidant and breast cancer antiproliferative activities of hydroxytyrosol-rich extracts derived from olive oil by-products. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Rosignoli, P.; Servili, M.; Montedoro, G.F.; Morozzi, G. Cancer chemoprevention by hydroxytyrosol isolated from virgin olive oil through G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2002, 11, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragione, F.D.; Cucciolla, V.; Borriello, A.; Pietra, V.D.; Pontoni, G.; Racioppi, L.; Manna, C.; Galletti, P.; Zappia, V. Hydroxytyrosol, a natural molecule occurring in olive oil, induces cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fukawa, H.; Ogata, J.; Komiyama, S.; Akiyama, S.; Kuwano, M. Potentiation by squalene of the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents against cultured mammalian cells and murine tumor. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1985, 76, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Hidaka, K.; Yoshida, T.; Sasaki, T.; Akiyama, S.; Kuwano, M. Potentiation by squalene of antitumor effect of 3-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-1-(2-chloroethyl)-nitrosourea in a murine tumor system. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1985, 76, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Bullon, P.; Quiles, J.L.; Morillo, J.M.; Rubini, C.; Goteri, G.; Granados-Principal, S.; Battino, M.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M. Gingival vascular damage in atherosclerotic rabbits: Hydroxytyrosol and squalene benefits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiles, J.L.; Farquharson, A.J.; Simpson, D.K.; Grant, I.; Wahle, K.W. Olive oil phenolics: Effects on DNA oxidation and redox enzyme mRNA in prostate cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| mol HT/mol DPPH–mol SQ/mol DPPH | HT–SQ (%) | mol α-tocopherol/mol DPPH | α-tocopherol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2–2 | 43.66 ± 5.4 | 2 | 67.47 ± 3.26 |
| 2–0.5 | 41.12 ± 4.93 | 0.5 | 64.34 ± 3.71 |
| 2–0.13 | 52.16 ± 3.22 | 0.13 | 30.85 ± 10.06 |
| 2–0.03 | 44.62 ± 3.3 | 0.03 | 4.26 ± 8.8 |
| HT–SQ (μM) | % RSA | TroloxTM (μM) | % RSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100–100 | 83.07 ± 1.27 | 800 | 85.92 ± 0.47 |
| 100–10 | 64.05 ± 8.57 | 400 | 76.79 ± 2.12 |
| 100–1 | 84.96 ± 0.68 | 200 | 43.41 ± 1.54 |
| 100–0.1 | 82.02 ± 1.76 | 100 | 24.82 ± 1.71 |
| 100–0.01 | 79.61 ± 2.07 | 50 | 14.75 ± 2 |
| 10–100 | 11.45 ± 2.43 | ||
| 10–10 | 11.16 ± 2.25 | ||
| 10–1 | 10.92 ± 2.73 | ||
| 10–0.1 | 10.54 ± 2.43 | ||
| 10–0.01 | 8.07 ± 2.39 |
| HT–SQ (μM) | Live Cells | Apoptotic Cells | Necrotic Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 85.63 ± 3.06 | 11.38 ± 2.02 | 2.98 ± 1.14 |
| 100–0.01 | 76.13 ± 4.66 | 19.29 ± 2.61 | 4.58 ± 2.08 |
| 100–0.1 | 73.64 ± 1.99 | 22.52 ± 2.03 | 3.84 ± 1.67 |
| 100–1 | 75.32 ± 4.31 | 20.82 ± 2.18 | 3.87 ± 1.45 |
| 100–10 | 69.17 ± 5.87 * | 25.68 ± 2.77 * | 5.15 ± 2.12 |
| 100–100 | 69.34 ± 5.86 * | 26.6 ± 2.98 * | 4.07 ± 1.48 |
| HT–SQ (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | (100–100) | (100–10) | (100–1) | |
| Basal | 100 ± 5.79 | 92.88 ± 5.46 | 98.60 ± 6.54 | 129.45 ± 6.31 * |
| H2O2 | 100 ± 7.07 | 44.71 ± 3.64 * | 34.17 ± 2.76 * | 57.77 ± 6.60 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Gutiérrez-Santiago, F.; Rodríguez-García, C.; Gaforio, J.J. Synergistic Effect of Squalene and Hydroxytyrosol on Highly Invasive MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020255
Sánchez-Quesada C, Gutiérrez-Santiago F, Rodríguez-García C, Gaforio JJ. Synergistic Effect of Squalene and Hydroxytyrosol on Highly Invasive MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Quesada, Cristina, Francisco Gutiérrez-Santiago, Carmen Rodríguez-García, and José J. Gaforio. 2022. "Synergistic Effect of Squalene and Hydroxytyrosol on Highly Invasive MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020255
APA StyleSánchez-Quesada, C., Gutiérrez-Santiago, F., Rodríguez-García, C., & Gaforio, J. J. (2022). Synergistic Effect of Squalene and Hydroxytyrosol on Highly Invasive MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Nutrients, 14(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020255









