Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer and Expression of c-Myc via Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
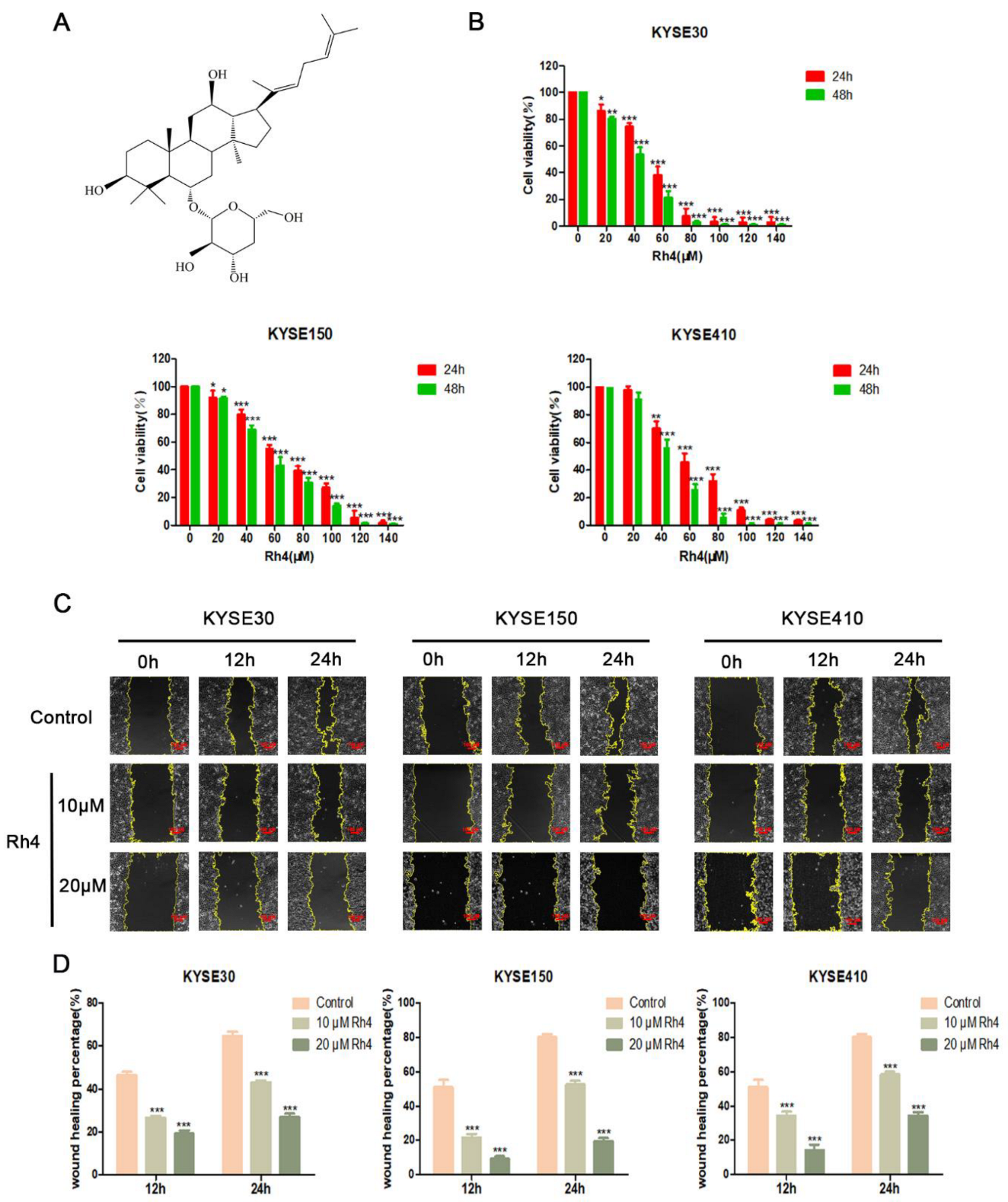
2.3. Cell Viability Assays
2.4. In Vitro Scratch Assay
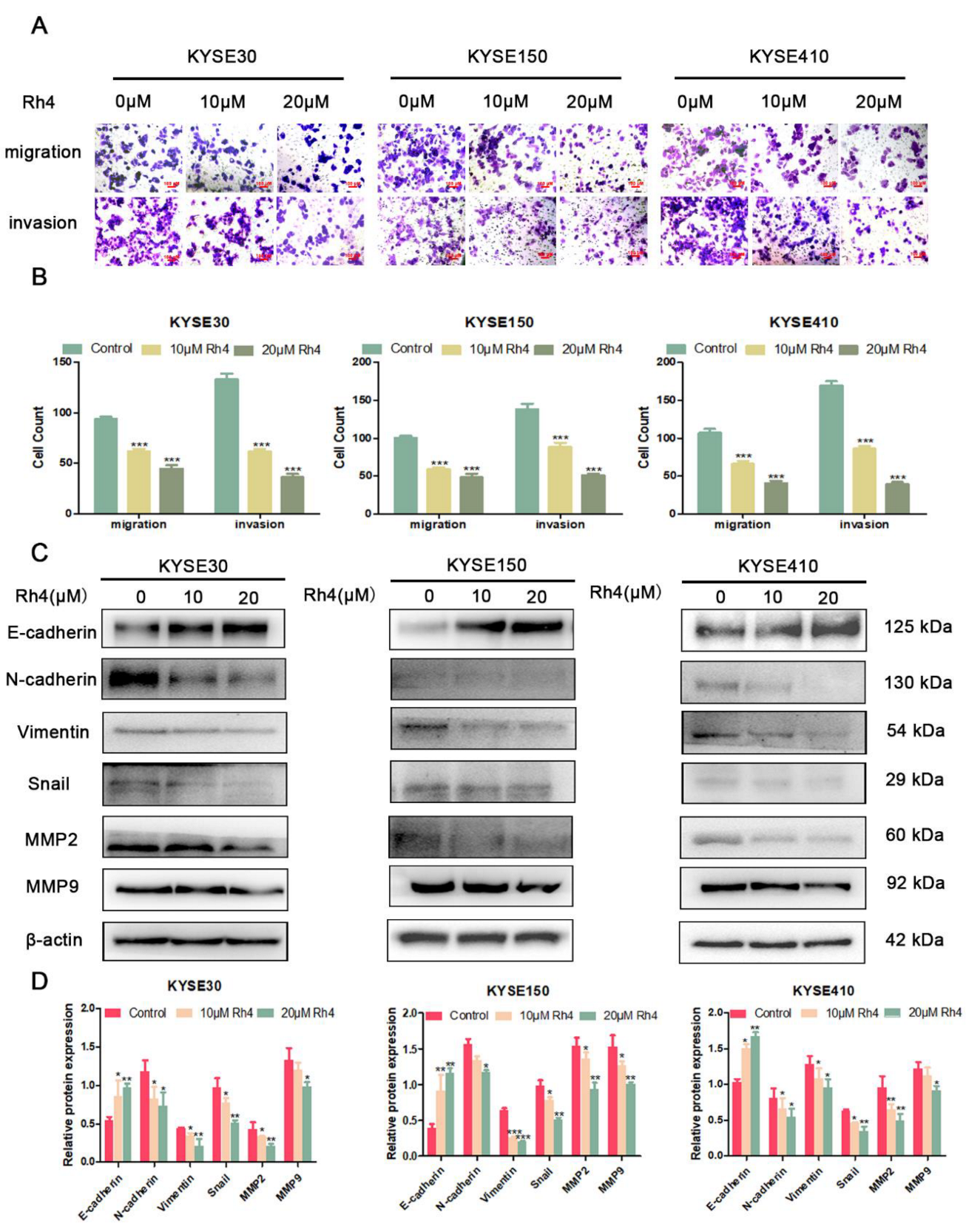
2.5. Transwell Assays
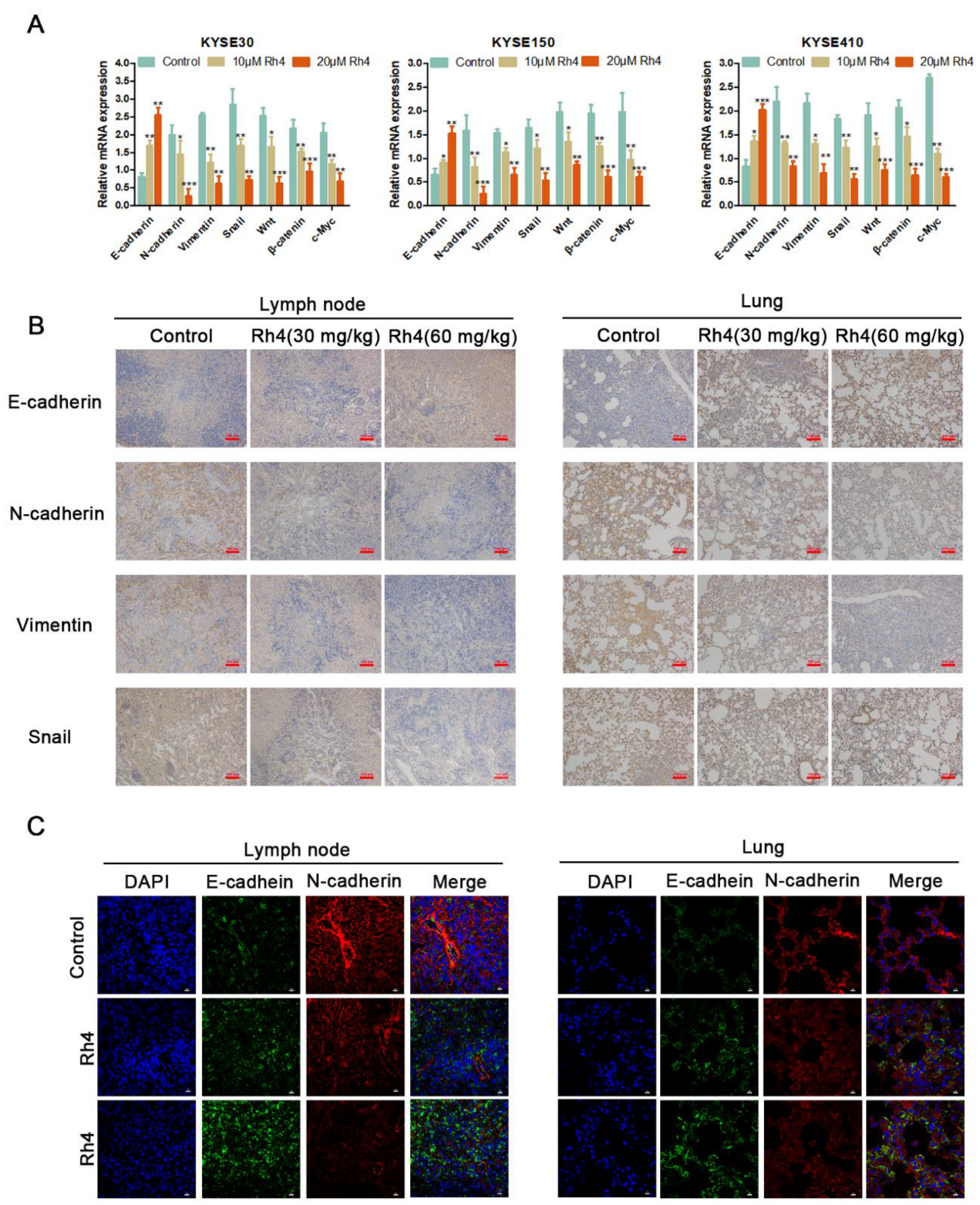
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Plasmids and siRNA Transfection
2.9. Animal Experiments
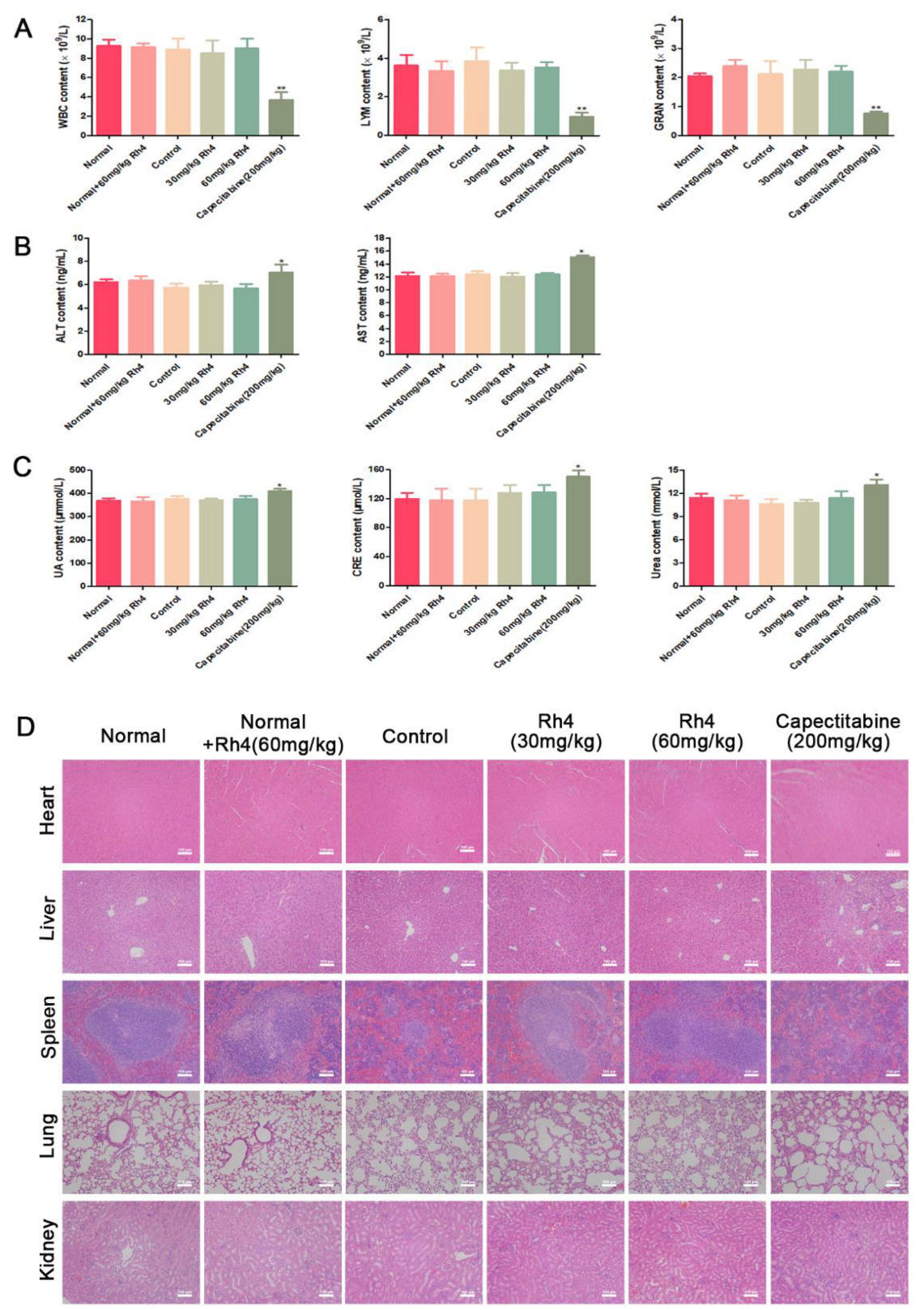
2.10. Hemogram Assay and Measurement of Biochemical Parameters
2.11. Immunofluorescence Assay (IF)
2.12. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses the Migration and Invasion of ESCC Cells
3.2. Ginsenoside Rh4 Inhibits the Metastasis of ESCC by Regulating EMT
3.3. Ginsenoside Rh4 Inhibits ESCC Metastasis In Vivo and Has Low Toxicity
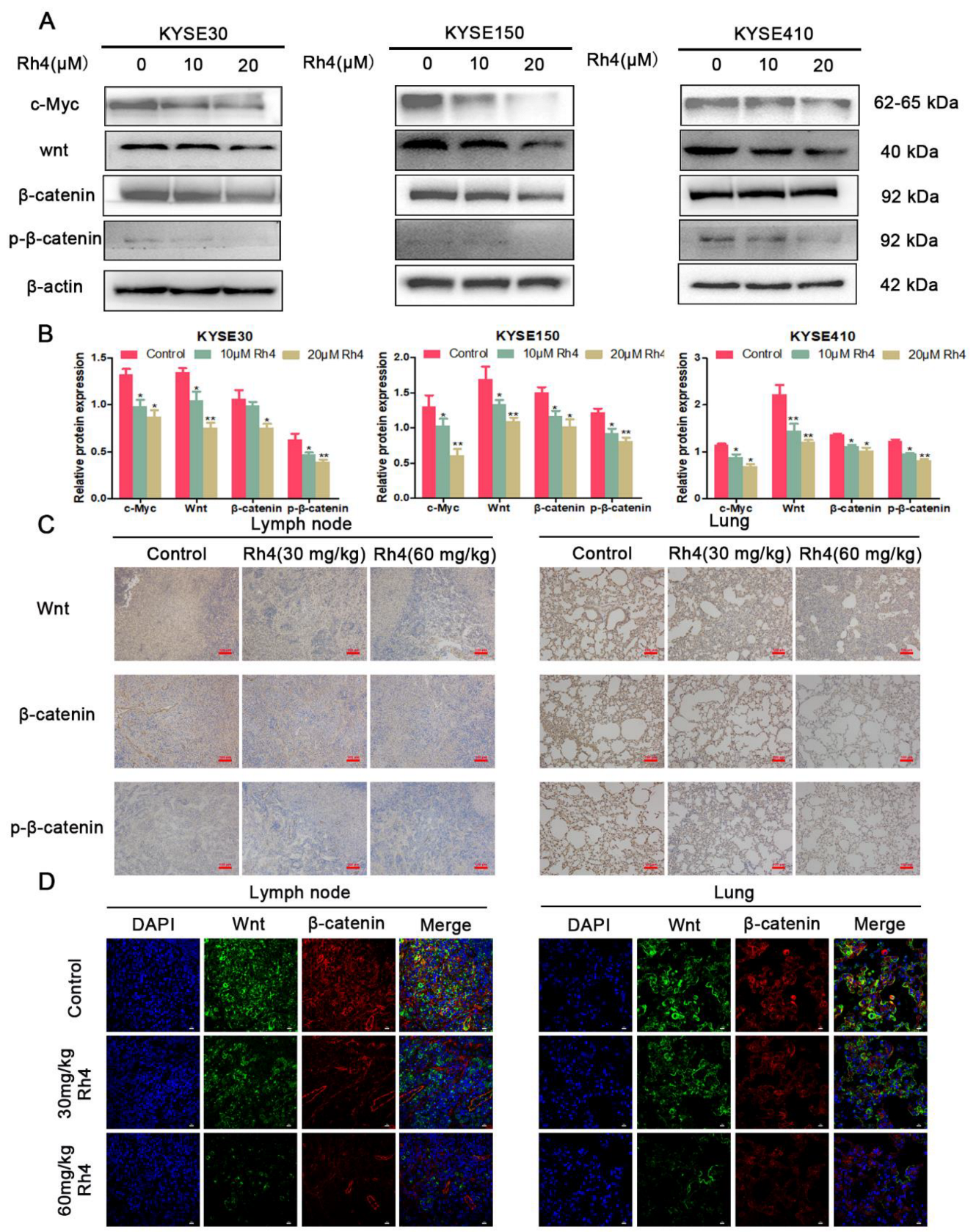
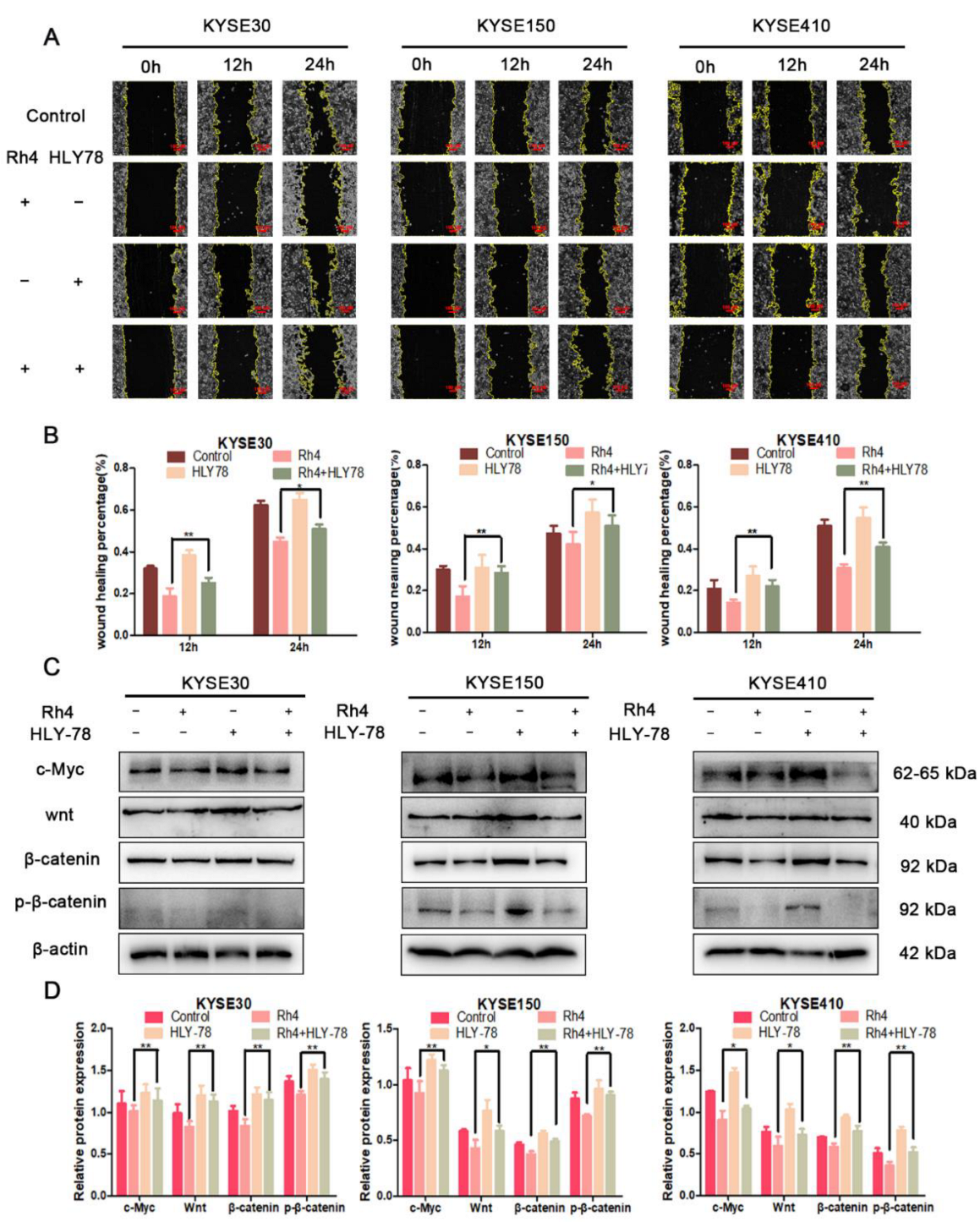
3.4. Rh4 Inhibits ESCC Metastasis through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
3.5. c-Myc Is Essential in the Inhibition of ESCC Metastasis by Rh4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statements
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics 2016. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, S.; Miyamoto, S.i.; Kikuchi, O.; Goto, T.; Amanuma, Y.; Muto, M. Recent Advances From Basic and Clinical Studies of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, D.-C.; Wang, M.-R.; Koeffler, H.P. Genomic and Epigenomic Aberrations in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Implications for Patients. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kai, F.; Drain, A.P.; Weaver, V.M. The Extracellular Matrix Modulates the Metastatic Journey. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orang, A.V.; Petersen, J.; McKinnon, R.A.; Michael, M.Z. Micromanaging aerobic respiration and glycolysis in cancer cells. Mol. Metab. 2019, 23, 98–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-L.; Liu, D.; Ding, G.-R.; Liao, P.-F.; Zhang, J.-W. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways promote the invasion of hypoxic gastric cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Shen, W.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Han, G. MicroRNA-140 Represses Esophageal Cancer Progression via Targeting ZEB2 to Regulate Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 257, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, S.; Zhang, R.; Peng, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, B.; Li, L. ALDH1A1 maintains the cancer stem-like cells properties of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the AKT signal pathway and interacting with β-catenin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Guo, T.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J. The novel target of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: lncRNA GASL1 regulates cell migration, invasion and cell cycle stagnation by inactivating the Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 217, 153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayard, B.; Bianchi, F.; Dey, J.; Moreno, E.; Djaffer, S.; Hynes, N.E.; Monard, D. The serine protease inhibitor protease nexin-1 controls mammary cancer metastasis through LRP-1-mediated MMP-9 expression. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5690–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Jing, C.; He, X.; Yang, B.; Cai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Hao, X. Efficient synthesis of new phenanthridine Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway agonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shao, F.; Guo, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Gao, Y.; He, J.; Lu, Z. WNT/β-catenin-suppressed FTO expression increases m(6)A of c-Myc mRNA to promote tumor cell glycolysis and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Cha, J.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Song, K.; Kim, P.; Kim, M.-Y. c-MYC Drives Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Brain, but Promotes Synthetic Lethality with TRAIL. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 17, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meskyte, E.M.; Keskas, S.; Ciribilli, Y. MYC as a Multifaceted Regulator of Tumor Microenvironment Leading to Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Rajendran, P.; Thigarajan, V.; Mathew, D.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Way, T.D.; Liao, J.W.; Yang, H.L. Antrodia salmonea suppresses invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer cells by reversing EMT through the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2019, 124, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Ma, Y.; Teng, Y.-E.; et al. Tamoxifen reverses epithelial–mesenchymal transition by demethylating miR-200c in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Cadherins in collective cell migration of mesenchymal cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.Z.; Searle, J.; He, T.C.; Yuan, C.S.; Du, W. Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis and paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal cancer cells through activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 2011, 301, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yayeh, T.; Jung, K.H.; Jeong, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Song, Y.B.; Kwak, Y.S.; Kang, H.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Oh, J.W.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Korean Red Ginseng Saponin Fraction Downregulates Proinflammatory Mediators in LPS Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells and Protects Mice against Endotoxic Shock. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.S. Roles of ginsenosides in inflammasome activation. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Niu, S.; Fan, B.; Gu, D.; Jiang, K.; Li, R.; Li, S. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates hepatic insulin resistance induced by high-fat and high-sugar by inhibiting inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 854, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.S.; Ham, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Cho, E.J.; Yamabe, N. Heat-processed Panax ginseng and diabetic renal damage: Active components and action mechanism. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ma, C.J.; Li, M.Q.; Tang, C.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Zeng, J.H.; Huang, X.Y.; Yi, J.; Wang, X.M.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 against Hyperphosphorylated Tau-Induced Diabetic Retinal Neurodegeneration via Activation of IRS-1/Akt/GSK3β Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8348–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. 20S-dihydroprotopanaxadiol, a ginsenoside derivative, boosts innate immune responses of monocytes and macrophages. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coon, J.T.; Ernst, E. Panax ginseng: A systematic review of adverse effects and drug interactions. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhao, J.; Qu, L.; Duan, Z.; Fu, R.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rh4 suppresses aerobic glycolysis and the expression of PD-L1 via targeting AKT in esophageal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 178, 114038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside CK Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation through the HIF-1α/NF-κB Feedback Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Foods 2021, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.; Su, F.; Bi, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.C.; Zhang, X.H. EMT in Metastasis: Finding the Right Balance. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Bado, I.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Rosen, J.; Zhang, X. Metastasis Organotropism: Redefining the Congenial Soil. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strilic, B.; Offermanns, S. Intravascular Survival and Extravasation of Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.X.; Fu, L. The immune landscape of esophageal cancer. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.L.; Yu, S.J. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Qu, L.; Deng, X.; Duan, Z.; Fu, R.; Liang, L.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 induces apoptosis and downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by targeting the NF-κB pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiao, J.; Xue, J.; Chen, T.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liang, Z.; et al. Ginsenoside CK induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells through the PI3K/mTOR/p70S6K1 pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhuang, X.; Lv, G.; Lin, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. Ginsenoside CK Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cell via SIRT1. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9140191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Starling, N.; Rao, S.; Iveson, T.; Nicolson, M.; Coxon, F.; Middleton, G.; Daniel, F.; Oates, J.; Norman, A.R. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hecht, J.R.; Bang, Y.J.; Qin, S.K.; Chung, H.C.; Xu, J.M.; Park, J.O.; Jeziorski, K.; Shparyk, Y.; Hoff, P.M.; Sobrero, A.; et al. Lapatinib in Combination With Capecitabine Plus Oxaliplatin in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Advanced or Metastatic Gastric, Esophageal, or Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: TRIO-013/LOGiC--A Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, S.W.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Boven, E. The role of pharmacogenetics in capecitabine efficacy and toxicity. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 50, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primrose, J.N.; Fox, R.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Malik, H.Z.; Prasad, R.; Mirza, D.; Anthony, A.; Corrie, P.; Falk, S.; Finch-Jones, M.; et al. Capecitabine compared with observation in resected biliary tract cancer (BILCAP): A randomised, controlled, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Ghaneh, P.; Psarelli, E.E.; Valle, J.W.; Halloran, C.M.; Faluyi, O.; O’Reilly, D.A.; Cunningham, D.; Wadsley, J.; et al. Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaflard, P.; Ederhy, S.; Torregrosa, C.; André, T.; Cohen, R.; Lopez-Trabada, D. [Fluoropyrimidines cardiac toxicity: 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine, compound S-1 and trifluridine/tipiracil]. Bull. Cancer 2018, 105, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Chen, H.; Shi, L.; He, M.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Lü, M.; Deng, M.; Luo, G. Inhibition of Growth of Esophageal Cancer by Alantolactone via Wnt/β- Catenin Signaling. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, H.; Yuan, J.; Yao, Y. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin by anthelmintic drug niclosamide overcomes paclitaxel resistance in esophageal cancer. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lv, Q.; Bian, H.; Yang, L.; Guo, K.L.; Ye, S.S.; Dong, X.F.; Tao, L.L. A novel tumor suppressor SPINK5 targets Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, Z. HLY78 Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis via the LRP6/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, W.; Gu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, Y. HLY78 protects blood-brain barrier integrity through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 162, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Zhang, J.; Gan, L.; Guo, M.; Xie, Y.; Di, C.; Sun, C.; Wang, F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H. The effects of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on apoptosis in HeLa cells induced by carbon ion irradiation. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisso, A.; Filipuzzi, M.; Gamarra Figueroa, G.P.; Brumana, G.; Biagioni, F.; Doni, M.; Ceccotti, G.; Tanaskovic, N.; Morelli, M.J.; Pendino, V.; et al. Cooperation Between MYC and β-Catenin in Liver Tumorigenesis Requires Yap/Taz. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, A.; Guillevin, R.; Vallée, J.N. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, R.; Zhu, C. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer and Expression of c-Myc via Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153042
Chen J, Duan Z, Liu Y, Fu R, Zhu C. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer and Expression of c-Myc via Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153042
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jun, Zhiguang Duan, Yannan Liu, Rongzhan Fu, and Chenhui Zhu. 2022. "Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer and Expression of c-Myc via Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153042
APA StyleChen, J., Duan, Z., Liu, Y., Fu, R., & Zhu, C. (2022). Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer and Expression of c-Myc via Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 14(15), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153042




