Abstract
Among older adults living in long-term nursing homes (LTNHs), maintaining an adequate functional status and independence is a challenge. Whilst a poor nutritional status is a potential risk factor for a decreased function in this population, its role is not fully understood. Here, using a transversal multicenter study of 105 older adults living in 13 LTNHs, we analyzed the associations between nutritional status, as measured by the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA), and the parameters of functional status, physical performance, physical activity, and frailty as well as comorbidity and body composition. The MNA scores were positively correlated with the Barthel Index, handgrip strength, Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) scores, absolute muscle power, and Assessment of Physical Activity in Frail Older People (APAFOP) scores and were negatively correlated with dynamic balance and frailty. In a multiple linear regression model controlling for gender and age, the APAFOP score (β = 0.386), BMI (β = 0.301), and Barthel Index (β = 0.220) explained 31% of the variance in the MNA score. Given the observed close relationship between the MNA score and functional status, physical performance and activity, and frailty, interventions should jointly target improvements in both the nutritional status and functional status of LTNH residents. Strategies designed and implemented by interdisciplinary professional teams may be the most successful in improving these parameters to lead to better health and quality of life.
1. Introduction
Given the aging of the global population, maintaining an adequate functional status and independence among older adults is a fundamental challenge. Although recent years have seen much progress in this area with extensive research in the field of frailty and quality of life in older individuals, many issues remain unresolved such as clear evidence of the effect of physical activity or nutrition in slowing the progression of frailty or functional deterioration in aging especially in older adults living in long-term nursing homes (LTNH). In particular, the role that nutritional status may play in functional status, physical performance and activity, and frailty remains unclear.
According to the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics and the International Academy of Nutrition and Aging, the risk factors for malnutrition in older adults include being 85 years or older, a low nutrient intake due to a loss of the ability to eat independently, difficulty swallowing and chewing, becoming bedridden, pressure ulcers, a history of hip fracture, dementia, depressive symptoms, and suffering from two or more chronic illnesses [1,2,3,4]. In older adults living in LTNHs, major risk factors include mobility limitations and a higher age; in community-dwelling older adults, such factors include a poor appetite, difficulties with eating, and respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases [5].
Several risk factors such as a lack of the ability to eat independently, being bedridden, pressure ulcers related to immobility, hip fractures, and even depressive conditions can be countered or prevented by physical activity [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. In frail older adults living in the community, physical exercise improves the physical, psychological, and social capacity and reduces the risk of falls and of losing independence [13,14]. In contrast, the few studies that have focused on the residents of nursing homes vary widely both in participant characteristics and in the interventions implemented, making it difficult to draw conclusions to inform best practices. Older individuals living in LTNHs generally have a sedentary lifestyle with very few minutes per day of physical activity performed mainly at a low intensity. This inactivity both leads to a loss of the musculoskeletal function and reduces opportunities to engage in experiences that improve the quality of life [15].
Institutionalized and community-dwelling older populations differ in their body composition, nutritional deficiencies, predisposition to malnutrition, cognitive impairment, and deterioration in physical performance [5,16]. Whilst undernutrition is associated with a decreased physical performance and with a disability in community-dwelling older adults [17,18,19,20], the role of the nutritional status of older adults living in LTNHs is less clear. In one study of nursing home residents, mobility and ADL dependency were impaired in older adults with (a risk of) malnutrition [21]. In this regard, Ramsey et al. observed that malnutrition was also linked to a lower physical performance in a dynamic test in geriatric outpatients [22]. In contrast, in a previous study on a group of older adults residing in senior living facilities, a 6-month exercise and nutritional supplement program did not improve the physical fitness or activity levels due to several facility characteristics that hindered the implementation of the program [23]. Such findings indicate the importance of developing further studies involving older adults living in LTNHs and analyzing the role that nutrition might play in parameters such as functional status, physical performance and activity, and frailty.
Malnutrition may also increase the risk of frailty. Two recent reviews highlighted the relative lack of studies conducted on frail patients, particularly the lack of nutritional intervention studies especially clinical trials [24,25]. Reflecting this lack, two of the few clinical trials with a nutritional intervention performed in frail older individuals living in LTNHs are the one published by Fiatarone et al. and Smoliner et al. [26,27]. The nutritional programs they conducted involved LTNH residents at a risk of malnutrition and the duration of them was 10 and 12 weeks, respectively. Fiatarone et al. supplemented with a multinutrient liquid supplement and Smoliner et al. with fortified food. Although the nutritional status improved in both studies, neither of them observed physical performance or functional gains associated with supplementation.
Thus, despite evidence linking nutritional status with physical and functional status of the LTNH population, its effect on these variables remains unclear. Here, we analyzed the relationship between the nutritional status, as measured by the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA), and functional status, physical fitness and activity, and frailty in 105 older adults living in 13 LTNHs. Understanding this relationship can help inform strategies to promote health and increase the quality of life among institutionalized older adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
This transverse, multicenter study was a secondary analysis of a clinical trial of a multicomponent physical exercise program (registry number NCT04221724) of LTNH residents. Data were collected between September and December 2019 in the post-intervention stage. The nutritional status, body composition, functional status, physical performance, physical activity, and frailty parameters were measured. Each parameter was measured by the same researcher to avoid an inter-assessor bias. The participants were recruited from 13 LTNHs in Gipuzkoa (Basque Country, Northern Spain). The inclusion criteria were as follows: aged ≥ 70 years, scored ≥ 50 on the Barthel Index, scored ≥ 20 on the Mini Examen Cognoscitivo (MEC-35) test [28], and able to stand up from a chair and walk 10 m with or without assistance. Individuals were not eligible to be included in the study if participation was judged to be inappropriate by a medical expert due to any risk of heart failure or ischemic events, e.g., in cases of severe physical, cognitive, or psychiatric disorders or in cases of any other condition such that participation would not be in the best interests of the individual. After considering these criteria, 105 participants were included in the study (Figure 1). All participants provided informed consent and the Committee on Ethics in Research of the Basque Country University (Human Committee Code M10/2018/171) approved the study.
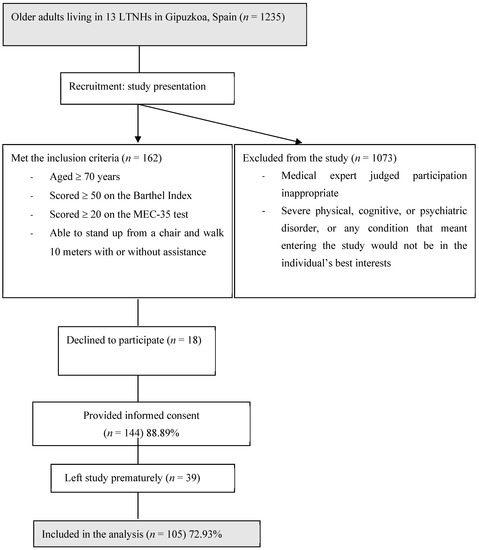
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram.
2.2. Variables Measured
The nutritional status was assessed using the full version of the MNA [29]. The MNA scores ranged from 0 to 30 with a status classified as normal nutrition (24–30 points), a potential risk of malnutrition (17–23.5 points), and malnutrition (<17 points).
The clinical data were collected from the databases of the participating LTNHs. The comorbidities were calculated and categorized according to an age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index, where one point was added for each decade after the age of 50 years [30].
The anthropometric measures included height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) (kg·m−2). The BMI was classified according to the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute guidelines: underweight (<18.5 kg/m2), desirable (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), obesity (30.0–39.9 kg/m2) and morbid obesity (≥40 kg/m2) [31].
The functional status was assessed by the Barthel Index [32], which measured 10 activities of daily living (ADL) (bowels, bladder, grooming, toilet use, feeding, transfer, mobility, dressing, stairs, bathing). The index ranged from 0 to 100 with 100 indicating complete independence. The assessment was carried out with the help of a caregiver.
The physical performance was assessed using a Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), the best-known instrument for evaluating the physical performance of senior citizens [33]. The SPPB, standardized by the National Institute on Aging, includes three tests: balance, gait speed, and the five-times sit-to-stand (STS) test. The five-times STS test, conducted using a standardized armless chair (0.43 m in height), was used to calculate the STS mean muscle power (W; STS mean velocity × STS mean force) [34]. Dynamic balance was measured using the validated Timed Up and Go test (TUG) [35]. In addition, handgrip strength was assessed in the right arm with a Jamar hydraulic hand dynamometer according to a standardized protocol [36].
Habitual physical activity was measured using the Assessment of Physical Activity in Frail Older People (APAFOP) [37], an interview-administered questionnaire focusing on the activities typically performed in older age (e.g., walking, sitting, standing, lying). The APAFOP score was calculated by multiplying the total physical activity time during the previous 24 h by the metabolic equivalent of the task levels of the respective activities [38].
In order to ensure a more holistic assessment of frailty and given that each instrument regards frailty from different approaches, three measurement instruments were used so that frailty was measured using Fried’s frailty phenotype [39], the Rockwood Clinical Frailty Scale [40], and the Tilburg Frailty Indicator [41]. Fried’s frailty phenotype evaluates the presence of five criteria: slow walking speed, reduced grip strength, low physical activity, exhaustion, and unintentional weight loss. One point is given for each of the criteria and individuals scoring ≥ 3 are considered to be frail [39]. In the Clinical Frailty Scale, the frailty status is based on a clinical judgment; the scores range from 1 to 9 and individuals scoring ≥ 6 are considered to be frail [40]. The Tilburg Frailty Indicator contains 15 questions on physical, psychological, and social domains of frailty; the scores range from 0 to 9 and individuals scoring ≥ 5 are considered to be frail [41].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 26.0. The continuous variables were expressed as a mean ± standard deviation (SD) and he categorical variables as frequencies and percentages. The normality was assessed using a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and the non-parametric variables were square-root transformed. The group means were compared using Student´s t-tests. A series of linear regressions was used to separately analyze the relationships of functional status, physical fitness, physical activity, and frailty on the MNA, controlling for age and sex. The explanatory variables that were statistically significant in those regressions were included in a multiple linear regression model predicting the MNA, again controlling for age and sex. A stepwise backward elimination was used to select the final variables. The proportion of the variance in the MNA explained by the explanatory variables in the multiple regression was estimated by the coefficient of determination (R2). In all tests, the differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
Participant characteristics are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Participant characteristics.
Figure 2 summarizes the participant characteristics by the nutritional status (normal vs. malnutrition/risk of malnutrition). Compared with the participants with or at risk of malnutrition, those with a normal nutritional status had a higher BMI (p < 0.05), Barthel Index (p < 0.01), absolute muscle power (p < 0.05), and APAFOP score (p < 0.001) and a lower Fried’s frailty phenotype score (p < 0.01).
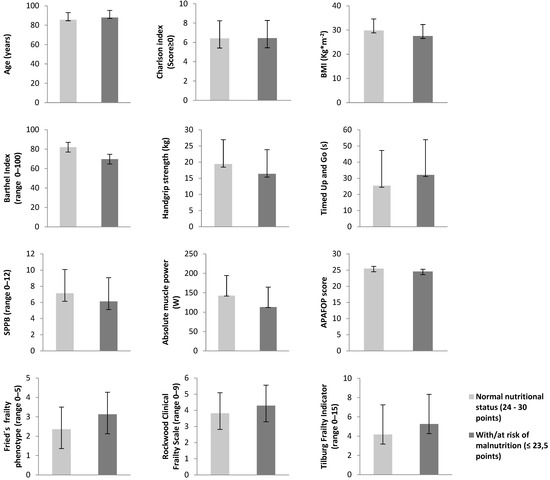
Figure 2.
Characteristics of the participants according to the MNA classification (normal nutritional status vs. risk and malnutrition status). MNA: Mini Nutritional Assessment; BMI: body mass index; SPPB: Short Physical Performance Battery; APAFOP: Assessment of Physical Activity in Frail Older People. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01 *** p < 0.001.
Figure 3 illustrates the relationship between the MNA scores and the parameters of functional status, physical performance, physical activity, and frailty. The MNA values were positively correlated with the Barthel Index score (p < 0.001), handgrip strength (p < 0.01), SPPB score (p < 0.01), absolute muscle power (p < 0.01), and APAFOP score (p < 0.001); they were negatively correlated with the TUG test score (p < 0.05), Fried’s frailty phenotype (p < 0.05), Rockwood Clinical Frailty Scale (p < 0.01), and Tilburg Frailty Indicator (p < 0.05) scores. The highest standardized regression coefficient (β) values were for the Barthel Index (β = 0.449) and APAFOP (β = 0.432) scores.
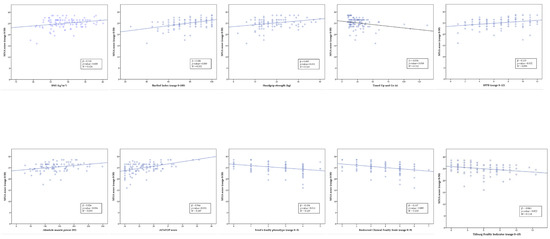
Figure 3.
The relationship between the MNA score and functional status, physical performance, and physical activity, controlling for age and sex. BMI: body mass index; SPPB: Short Physical Performance Battery; APAFOP: Assessment of Physical Activity in Frail Older People. β: standardized regression coefficient; R2: coefficient of determination.
The explanatory variables included in the multiple linear regression model were the BMI, Barthel Index score, TUG score, SPPB score, handgrip strength, absolute muscle power, APAFOP score, and Fried’s frailty phenotype score (Table 2). Among these, the APAFOP score had the largest relationship (β = 0.386; p = 0.001), followed by the BMI (β = 0.301; p = 0.002) and the Barthel Index score (β = 0.220; p = 0.039). Together, these three variables explained 31% of the variance in the MNA.

Table 2.
Backward stepwise multiple linear regression model predicting the MNA score, controlling for age and sex.
4. Discussion
Despite the evidence that the nutritional status of older adults may affect functional and physical parameters, its effect on older adults living in LTNHs has remained unclear. Our results showed that a better nutritional status, as indicated by the higher MNA scores, was associated with greater functionality, physical performance, and physical activity as well as with lower frailty. In addition, physical activity (as measured by APAFOP questionnaire), functional status (as measured by the Barthel Index), and BMI collectively predicted the MNA. To our knowledge, this is the first study to find a relationship between the nutritional status and physical activity levels of LTNH residents without a cognitive impairment.
Our sample represented 1.75% of all older adults residing in LTNHs in Gipuzkoa (Basque Country, Northern Spain). Notably, our mean participant age, 86.34 ± 6.77 years, was higher than all other study populations to date on institutionalized older adults including the 2012 European SHELTER study of 57 LTNHs from 7 EU countries and Israel where the mean age of the participants was 83.4 years [42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. The percentage of participants in our study over 90 years of age (36%) was also high compared with other studies. Our population had several similarities with other studies. Most of the participants were women—a reflection of the LTNH resident population in general [42,43,45]—and about half were frail according to Fried’s frailty phenotype and the Tilburg Frailty Indicator, consistent with a systematic review on frailty prevalence in LTNHs [49]. In addition, a quarter of our participants were at risk of malnutrition (or actually malnourished), similar to the rates found in another recent study in institutionalized older adults [50].
From this perspective, the mean BMI value of our sample fell in the overweight range and was notably higher than in previous studies [42,43,46,51]. In addition, 42.1% were classified as overweight and 42.1% as obese. Growing evidence suggests that, in older individuals, a BMI between 25 and 30 that is defined as overweight may be a positive factor because it is associated with a longer life expectancy and especially with a longer disability-free life expectancy [51,52]. However, it should be emphasized that the BMI is a controversial measure as experts do not agree on its usefulness in predicting life expectancy in older adults [53]. Evidence for this is that obesity, in combination with sarcopenia or an age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass, increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, physical disability, metabolic disorders, and mortality [54]. Therefore, we recommend nutritional and physical activity interventions in older adults to try to preserve the muscle mass and prevent obesity.
LTNH residents are disproportionately at risk of malnutrition, potentially making them more likely to develop functional problems, sarcopenia, and frailty in the near future [55]. Our findings were consistent with previous works showing a link between malnutrition and functional dependence [43,44]. Consequently, to prevent malnutrition, a full understanding of the factors causing it is necessary.
Previous studies also found that physical performance is closely related to the nutritional status of institutionalized older adults and has an impact on their functionality, dependence level, and risk of falls [56,57]. In addition, an increased muscle strength reduces the risk of sarcopenia in older adults [58]. However, it is unclear whether a causal relationship exists between the nutritional status and physical performance. In a longitudinal study of community-dwelling older adults in Belgium, a three-year nutritional intervention did not affect handgrip strength or gait speed [59]. Further studies on this issue are, therefore, needed. In line with this and compared with the other parameters of physical performance, muscle power may be the capacity that is most related to functional limitations in older adults [60,61] including LTNH residents [62]. Given that few studies have related muscle power to nutrition [22,63], our results provide valuable evidence of this relationship and may inform new lines of research in which the variable of muscle power could be analyzed in order to ascertain the role that muscle power might play in the nutritional status of institutionalized older individuals. The link between physical activity and nutritional status is well-established as is the effect these two factors can have on the most prevalent problems in the older population such as sarcopenia, frailty, dependence, loss of functionality, and, ultimately, a decreased quality of life [64,65,66,67]. This is reflected in a recent meta-analysis where 26 different interventions were compared in older adults with sarcopenia using physical activity alone, nutrition alone, or a combination of both [68]. Exercise, both alone and in combination with nutrition, increased the handgrip strength and improved dynamic balance. Both types of intervention also had beneficial effects on muscle strength and the physical performance of older adults with sarcopenia [68].
The MNA provides important information for predicting frailty in older adults [69] and the relationship we found between nutrition and frailty, as measured by different tools, is well-established [24,25,70,71,72]. Nutritional frailty has been proposed to be an independent phenotype of frailty, underscoring the close relationship between these two variables [73]. The directionality of the relationships between nutritional status and functionality, physical performance, physical activity, and frailty is uncertain. Based on the results of the present study, it could be intuitively deduced that a few of these relationships may be bidirectional. A multicomponent physical activity intervention in older adults after hospitalization improved the nutritional status of participants [74]. It has also been observed that a functional evolution through a rehabilitation process was impaired in orthogeriatric patients with malnutrition [56].
In order to delve deeper into this bidirectional relationship and draw conclusions about causality, intervention programs are needed. To our knowledge, few intervention programs in institutionalized older populations have measured both the nutritional parameters and physical activity [75,76,77,78,79]. Two studies on the effects of a physical activity intervention on the nutritional status found no significant changes [76,77]. This lack of favorable results could be due to the cognitive characteristics of the participants (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease), a low adherence to the program, or insufficient exercise intensity. For example, although the Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative recommends supervised resistance exercise for individuals with sarcopenia [71], the participants in those studies did not use weights. On the other hand, nutritional interventions [79,80], or those combining nutrition and physical activity [75], can improve the functional as well as the nutritional parameters. In addition, essential amino acids and β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB) supplements may improve the muscle outcomes [71].
Different studies have concluded that both nutrition and physical activity improve the functional status of, and prevent sarcopenia in, older adults [81,82,83]. Nutritional supplementation may improve the muscle status or, conversely, muscle work/training may improve the nutritional status, perhaps by stimulating the appetite and thus increasing the caloric intake. Both muscle and visceral protein levels were found to decrease with age among LTNH residents, leading to a higher prevalence of malnutrition [84]. This decreased muscle mass depended in part on the physical activity levels of participants as measured by the ADL. Thus, physical activity can play an important role in the nutritional status of institutionalized older individuals.
Although our study did not address causality, it did support the hypothesis that physical activity may possibly improve the nutritional status of institutionalized older adults [26,85]. Therefore, strategies to increase physical activity may help to promote a better quality of life among residents of nursing homes.
Taking into account these data and given the close relationship we found between the MNA and functional status, physical performance and activity, and frailty, future approaches to improve these parameters in LTNH residents should not be focused on each variable individually but on all these variables together. Interdisciplinary professional teams (doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, nutritionists, physical activity professionals) should participate in the design and implementation of strategies to simultaneously improve the nutritional and functional status and physical performance of LTNH residents to increase health and the quality of life. Our results reinforce the need to develop updated physical activity and nutrition routines in LTNHs and may play a fundamental role in the redesign of nursing homes for the better overall wellness of the residents.
Finally, and based on our results, we consider it essential to implement preventive actions that allow the diagnosis and treatment as early as possible of the appearance of pathologies that directly affect the quality of life of LTNH residents. In the future, and with the aim of being able to analyze the causality that we hypothesized in the present study, it is necessary to develop further nutritional and physical activity interventions.
5. Strength of the Study
One of the strengths of this study is the combined analysis of the relationships between nutritional status and functional status, physical performance, physical activity and frailty. To our knowledge, this is the first study on LTNH residents without a cognitive impairment to relate nutritional status with physical activity. Our results may help inform the design of future studies.
6. Limitations of the Study
Our study also had several limitations. Due to the difficulty in precisely measuring the body composition of an institutionalized population, we used the BMI, a relatively simple measurement. Analyzing the fat mass and skeletal muscle mass would provide more detailed information on the relationship between nutritional status and the measurements indicative of sarcopenia. Similarly, although the MNA is validated and widely used in the LTNH environment [86], a more detailed analysis of the food and caloric intake would shed further light on the relationship between nutritional status and physical activity among institutionalized older adults.
7. Conclusions
Our study demonstrated that the nutritional status measured by the MNA was related to functional status, physical fitness and activity, and frailty in older adults living in LTNHs. The results of our study highlighted the importance of taking into account all these parameters as a whole in order to maintain and care for the quality of life of older adults living in LTNHs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.Z., A.R.-L., J.I. and M.K.; methodology, I.Z., A.R.-L., J.I. and M.K.; formal analysis, I.M.-E., I.Z., J.I. and M.K.; investigation, I.M.-E., J.V., N.A., J.I. and M.K.; resources, I.M.-E., J.V., N.A., B.M.-A., J.I. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M.-E., I.Z., J.I. and M.K.; writing—review and editing, I.M.-E., I.Z., J.S.-C., J.G.-G., J.I. and M.K.; project administration, I.M.-E., J.I. and M.K.; funding acquisition, A.R.-L., J.I., J.S.-C. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa (ADINBERRI DG18/25) and the Professional Association of Nurses of Gipuzkoa (COEGI Nursing Research Grants 2019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Committee on Ethics in Research of the Basque Country University (Human Committee Code M10/2018/171).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the LTNHs for their collaboration with the research team.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Salva, A.; Coll-Planas, L.; Bruce, S.; De Groot, L.; Andrieu, S.; Abellan, G.; Vellas, B.; The Task Force on Nutrition and Ageing of the IAGG and the IANA. Nutritional Assessment of Residents in Long-Term Care Facilities (LTCFs): Recommendations of the Task Force on Nutrition and Ageing of the IAGG European Region and the IANA. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, S.L.; Azevedo, P.S.; Gordon, A.L.; Phillips, B.E.; Greig, C.A. Overcoming protein-energy malnutrition in older adults in the residential care setting: A narrative review of causes and interventions. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.E.; Williams, E.A. Optimizing nutrition in older people. Maturitas 2018, 112, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownie, S. Why are elderly individuals at risk of nutritional deficiency? Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2006, 12, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesswetter, E.; Colombo, M.G.; Meisinger, C.; Peters, A.; Thorand, B.; Holle, R.; Ladwig, K.H.; Schulz, H.; Grill, E.; Diekmann, R.; et al. Malnutrition and Related Risk Factors in Older Adults from Different Health-Care Settings: An Enable Study. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.E.; Phillips, L.H.; Cooper, C.L.; Gray, S.; Allan, J.L. Effect of Different Types of Physical Activity on Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2017, 25, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamed-Jahromi, M.; Kaveh, M.H. Effective Interventions on Improving Elderly’s Independence in Activity of Daily Living: A Systematic Review and Logic Model. Front. Public Health 2021, 8, 516151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, N.L.; Bellettiere, J.; Jain, P.; LaMonte, M.J.; La Croix, A.Z.; Women’s Health Initiative. Evaluation of Light Physical Activity Measured by Accelerometry and Mobility Disability during a 6-Year Follow-Up in Older Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stattin, K.; Michaelsson, K.; Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A.; Byberg, L. Leisure-Time Physical Activity and Risk of Fracture: A Cohort Study of 66,940 Men and Women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, R.M.; Reynolds, C.F. Management of Depression in Older Adults: A Review. JAMA 2017, 317, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murri, M.B.; Ekkekakis, P.; Menchetti, M.; Neviani, F.; Trevisani, F.; Tedeschi, S.; Latessa, P.M.; Nerozzi, E.; Ermini, G.; Zocchi, D.; et al. Physical Exercise for Late-Life Depression: Effects on Symptom Dimensions and Time Course. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 230, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, H.S.; Silveira, H.S.; Oliveira, N.A.; Matta Mello Portugal, E.; Araujo, N.B.; Vasques, P.E.; Bergland, A.; Santos, T.M.; Engedal, K.; Coutinho, E.S.; et al. Is Strength Training as Effective as Aerobic Training for Depression in Older Adults? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.P.; Feng, L.; Nyunt, M.S.; Feng, L.; Niti, M.; Tan, B.Y.; Chan, G.; Khoo, S.A.; Chan, S.M.; Yap, P.; et al. Nutritional, Physical, Cognitive, and Combination Interventions and Frailty Reversal among Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1225–1236.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona-Santabalbina, F.J.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Perez-Ros, P.; Martinez-Arnau, F.M.; Cabo, H.; Tsaparas, K.; Salvador-Pascual, A.; Rodriguez-Manas, L.; Vina, J. A Multicomponent Exercise Intervention that Reverses Frailty and Improves Cognition, Emotion, and Social Networking in the Community-Dwelling Frail Elderly: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, H.; Rezola-Pardo, C.; Echeverria, I.; Iturburu, M.; Gil, S.M.; Yanguas, J.J.; Irazusta, J.; Rodriguez-Larrad, A. Physical Activity and Fitness are Associated with Verbal Memory, Quality of Life and Depression among Nursing Home Residents: Preliminary Data of a Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi-Asl, M.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E. Comprehensive Comparison of Malnutrition and its Associated Factors between Nursing Home and Community Dwelling Elderly: A Case-Control Study from Northwestern Iran. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 21, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, L.B.; Chua, M.P.; Tay, E.L.; Chan, H.N.; Mah, S.M.; Latib, A.; Wong, C.Q.; Ng, Y.S. Multidomain Geriatric Screen and Physical Fitness Assessment Identify Prefrailty/Frailty and Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2019, 48, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aspell, N.; Laird, E.; Healy, M.; Lawlor, B.; O’Sullivan, M. Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Impaired Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Yap, C.W.; Heng, B.H. Association of Nutritional Status with Physical Function and Disability in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Longitudinal Data Analysis. J. Nutr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 39, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, S.; Enoki, H.; Hasegawa, J.; Hirose, T.; Kuzuya, M. Factors Associated with Deterioration of Mini Nutritional Assessment-Short Form Status of Nursing Home Residents during a 2-Year Period. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewoude, M.F.J.; van Wijngaarden, J.P.; De Maesschalck, L.; Luiking, Y.C.; Van Gossum, A. The Prevalence and Health Burden of Malnutrition in Belgian Older People in the Community or Residing in Nursing Homes: Results of the NutriAction II Study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, K.A.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Verlaan, S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Whittaker, A.C.; Maier, A.B. Malnutrition is Associated with Dynamic Physical Performance. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, M.P.; Nelson, M.E.; Sacheck, J.M.; Reid, K.F.; Kirn, D.; Fielding, R.A.; Chui, K.K.H.; Folta, S.C. Efficacy of an Exercise and Nutritional Supplement Program on Physical Performance and Nutritional Status in Older Adults with Mobility Limitations Residing at Senior Living Facilities. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2017, 25, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Morante, J.J.; Gomez Martinez, C.; Morillas-Ruiz, J.M. Dietary Factors Associated with Frailty in Old Adults: A Review of Nutritional Interventions to Prevent Frailty Development. Nutrients 2019, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Lochlainn, M.; Cox, N.J.; Wilson, T.; Hayhoe, R.P.G.; Ramsay, S.E.; Granic, A.; Isanejad, M.; Roberts, H.C.; Wilson, D.; Welch, C.; et al. Nutrition and Frailty: Opportunities for Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Bernstein, M.A.; Ryan, A.D.; O’Neill, E.F.; Clements, K.M.; Evans, W.J. The effect of oral nutritional supplements on habitual dietary quality and quantity in frail elders. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2000, 4, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smoliner, C.; Norman, K.; Scheufele, R.; Hartig, W.; Pirlich, M.; Lochs, H. Effects of Food Fortification on Nutritional and Functional Status in Frail Elderly Nursing Home Residents at Risk of Malnutrition. Nutrition 2008, 24, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A.; Saz, P.; Marcos, G.; Día, J.L.; de la Cámara, C.; Ventura, T.; Morales Asín, F.; Fernando Pascual, L.; Montañés, J.Á.; Aznar, S. Revalidación Y Normalización Del Mini-Examen Cognoscitivo (Primera Versión En Castellano Del Mini-Mental Status Examination) En La Población General Geriátrica. Med. Clin. 1999, 112, 767–774. [Google Scholar]
- Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B.; Garry, P.J. Assessing the Nutritional Status of the Elderly: The Mini Nutritional Assessment as Part of the Geriatric Evaluation. Nutr. Rev. 1996, 54, S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a Combined Comorbidity Index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative Expert Panel on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Obesity in Adults (US). Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, D.T.; Collin, C. The Barthel ADL Index: A Standard Measure of Physical Disability? Int. Disabil. Stud. 1988, 10, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Pieper, C.F.; Leveille, S.G.; Markides, K.S.; Ostir, G.V.; Wallace, R.B. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: Consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2000, 55, M221–M231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar, J.; Losa-Reyna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, C.; Alfaro-Acha, A.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Ara, I.; García-García, F.J.; Alegre, L.M. The Sit-to-Stand Muscle Power Test: An Easy, Inexpensive and Portable Procedure to Assess Muscle Power in Older People. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Reference Values for the Timed Up and Go Test: A Descriptive Meta-Analysis. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2006, 29, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fess, E. Clinical Assessment Recommendations. American society of hand therapists. Grip Strength 1981, 1, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hauer, K.; Lord, S.R.; Lindemann, U.; Lamb, S.E.; Aminian, K.; Schwenk, M. Assessment of Physical Activity in Older People with and without Cognitive Impairment. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2011, 19, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; Brien, W.L.O.; Bassett, D.R.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O. Compendium of Physical Activities: An Update of Activity Codes and MET Intensities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G. Frailty in Older Adults: Evidence for a Phenotype. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Theou, O. Using the Clinical Frailty Scale in Allocating Scarce Health Care Resources. Can. Geriatr. J. 2020, 23, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbens, R.J.; van Assen, M.A.; Luijkx, K.G.; Wijnen-Sponselee, M.T.; Schols, J.M. The Tilburg Frailty Indicator: Psychometric Properties. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2010, 11, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piglowska, M.; Guligowska, A.; Kostka, T. Nutritional Status Plays More Important Role in Determining Functional State in Older People Living in the Community than in Nursing Home Residents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caçador, C.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Oliveira, J.; Pinheiro, J.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Ramos, F. The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Functional Capacity: A Contribution Study in Institutionalised Portuguese Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, L.M.; Stephan, B.; Rosano, A.; Molfino, A.; Poggiogalle, E.; Lenzi, A.; Siervo, M.; Muscaritoli, M. What are the Risk Factors for Malnutrition in Older-Aged Institutionalized Adults? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerez-Roig, J.; de Brito Macedo Ferreira, L.M.; Torres de Araújo, J.R.; Costa Lima, K. Functional Decline in Nursing Home Residents: A Prognostic Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Contreras, M.; Torralba, C.; Zamora, S.; Pérez-Llamas, F. Nutrition and Prevalence of Undernutrition Assessed by Different Diagnostic Criteria in Nursing Homes for Elderly People. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 25, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medeiros, M.M.D.; de Figueredo, O.M.C.; Pinheiro, M.A.; de Oliveira, L.F.S.; Wanderley, R.L.; Cavalcanti, Y.W.; Garcia, R.C.M.R. Factors Associated with the Overlap of Frailty and Nutrition in Institutionalized Older Adults: A Multicenter Study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 90, 104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, G.; Carpenter, I.; Finne-Soveri, H.; Gindin, J.; Frijters, D.; Henrard, J.C.; Nikolaus, T.; Topinkova, E.; Tosato, M.; Liperoti, R. Assessment of Nursing Home Residents in Europe: The Services and Health for Elderly in Long TERm Care (SHELTER) Study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2012, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, G. Prevalence of Frailty in Nursing Homes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faxen-Irving, G.; Luiking, Y.; Gronstedt, H.; Franzen, E.; Seiger, A.; Vikstrom, S.; Wimo, A.; Bostrom, A.M.; Cederholm, T. Do Malnutrition, Sarcopenia and Frailty Overlap in Nursing-Home Residents? J. Frailty Aging 2021, 10, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Al Snih, S.; Ottenbacher, K.J.; Markides, K.S.; Kuo, Y.; Eschbach, K.; Goodwin, J.S. The Effect of Obesity on Disability Vs Mortality in Older Americans. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.E.; MacInnis, R.J.; Wattanapenpaiboon, N.; Nowson, C.A. BMI and all-Cause Mortality in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosello, O.; Vanzo, A. Obesity Paradox and Aging. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, J.L.; Wannamathee, S.G. Sarcopenic Obesity in Ageing: Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, C.; Tang, S. Malnutrition and Physical Frailty among Nursing Home Residents: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquiza, M.; Fernandez, N.; Arrinda, I.; Sierra, I.; Irazusta, J.; Rodriguez Larrad, A. Nutritional Status is Associated with Function, Physical Performance and Falls in Older Adults Admitted to Geriatric Rehabilitation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Ugarriza, R.; Luzardo-Socorro, R.; Palacios, G.; Bibiloni, M.M.; Argelich, E.; Tur, J.A.; Gonzalez-Gross, M. What is the Relationship between Physical Fitness Level and Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Spanish Older Adults? Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengele, L.; Moehlinger, P.; Bruyere, O.; Locquet, M.; Reginster, J.Y.; Beaudart, C. Association between Changes in Nutrient Intake and Changes in Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in the SarcoPhAge Cohort. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinikorena, I.; Martinez-Ramirez, A.; Gomez, M.; Lecumberri, P.; Casas-Herrero, A.; Cadore, E.L.; Millor, N.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Idoate, F.; Izquierdo, M. Gait Variability Related to Muscle Quality and Muscle Power Output in Frail Nonagenarian Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldvari, M.; Clark, M.; Laviolette, L.C.; Bernstein, M.A.; Kaliton, D.; Castaneda, C.; Pu, C.T.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Fielding, R.A.; Singh, M.A.F. Association of Muscle Power with Functional Status in Community-Dwelling Elderly Women. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, M192–M199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozicka, I.; Kostka, T. Handgrip Strength, Quadriceps Muscle Power, and Optimal Shortening Velocity Roles in Maintaining Functional Abilities in Older Adults Living in a Long-Term Care Home: A 1-Year Follow-Up Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefoy, M.; Jauffret, M.; Jusot, J.F. Muscle Power of Lower Extremities in Relation to Functional Ability and Nutritional Status in very Elderly People. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Abizanda, P.; Lopez, M.D.; Garcia, V.P.; Estrella Jde, D.; da Silva Gonzalez, A.; Vilardell, N.B.; Torres, K.A. Effects of an Oral Nutritional Supplementation Plus Physical Exercise Intervention on the Physical Function, Nutritional Status, and Quality of Life in Frail Institutionalized Older Adults: The ACTIVNES Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, e9–e439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, S.; Boersma, D.; Duque, G. Exercise and Sarcopenia. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, G.E.; Porter, J.; Brunton, A.; Crocker, M.; Kotsimbos, Z.; Percic, J.; Polzella, L.; Willet, N.; Huggins, C.E. Nutrition Interventions Implemented in Hospital to Lower Risk of Sarcopenia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 77, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.N.; Smeuninx, B.; Morgan, P.T.; Breen, L. Nutritional Strategies to Offset Disuse-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Anabolic Resistance in Older Adults: From Whole-Foods to Isolated Ingredients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.Y.; Huang, K.S.; Chen, K.M.; Chou, C.P.; Tu, Y.K. Exercise, Nutrition, and Combined Exercise and Nutrition in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Maturitas 2021, 145, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Federici, M.; Cianfarani, M.A.; Tarantino, U.; Bertoli, A. Frailty and Nutritional Status in Older People: The Mini Nutritional Assessment as a Screening Tool for the Identification of Frail Subjects. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artaza-Artabe, I.; Saez-Lopez, P.; Sanchez-Hernandez, N.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, N.; Malafarina, V. The Relationship between Nutrition and Frailty: Effects of Protein Intake, Nutritional Supplementation, Vitamin D and Exercise on Muscle Metabolism in the Elderly. A Systematic Review. Maturitas 2016, 93, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Schneider, S.M.; Zuniga, C.; Arai, H.; Boirie, Y.; Chen, L.K.; Fielding, R.A.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; et al. Prevalence of and Interventions for Sarcopenia in Ageing Adults: A Systematic Review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing 2014, 43, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Lopez, L.; Maseda, A.; de Labra, C.; Regueiro-Folgueira, L.; Rodriguez-Villamil, J.L.; Millan-Calenti, J.C. Nutritional Determinants of Frailty in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Bortone, I.; Griseta, C.; Sardone, R.; Lampignano, L.; Lozupone, M.; Solfrizzi, V.; Castellana, M.; Giannelli, G.; et al. Nutritional Domains in Frailty Tools: Working Towards an Operational Definition of Nutritional Frailty. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, I.; Amasene, M.; Urquiza, M.; Labayen, I.; Anaut, P.; Rodriguez-Larrad, A.; Irazusta, J.; Besga, A. Multicomponent Physical Exercise in Older Adults After Hospitalization: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Short- Vs. Long-Term Group-Based Interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 2020, 17, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.M.; Christensen, A.G.; Hansen, B.S.; Damsbo-Svendsen, S.; Moller, T.K. Multidisciplinary Nutritional Support for Undernutrition in Nursing Home and Home-Care: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, Y.; Pillard, F.; Klapouszczak, A.; Reynish, E.; Thomas, D.; Andrieu, S.; Riviere, D.; Vellas, B. Exercise Program for Nursing Home Residents with Alzheimer’s Disease: A 1-Year Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltais, M.; Rolland, Y.; Hay, P.E.; Armaingaud, D.; Cestac, P.; Rouch, L.; de Souto Barreto, P. The Effect of Exercise and Social Activity Interventions on Nutritional Status in Older Adults with Dementia Living in Nursing Homes: A Randomised Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, H.E.; Henwood, T.R.; Beller, E.M.; Mitchell, G.K.; Keogh, J.W. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sarcopenia among Adults Living in Nursing Homes. Maturitas 2015, 82, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensson, L.; Ek, A.C.; Unosson, M. Individually Adjusted Meals for Older People with Protein-Energy Malnutrition: A Single-Case Study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2001, 10, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, V.J.; Methven, L.; Gosney, M.A. Use of Nutritional Complete Supplements in Older Adults with Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K. Sarcopenia: A Contemporary Health Problem among Older Adult Populations. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, B.; Neubauer, O.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Wagner, K.H. Dietary Protein, Muscle and Physical Function in the very Old. Nutrients 2018, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosaeus, I.; Rothenberg, E. Nutrition and Physical Activity for the Prevention and Treatment of Age-Related Sarcopenia. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Fukushima, H.; Miwa, Y.; Shiraki, M.; Gomi, I.; Saito, M.; Mawatari, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kato, M.; Moriwaki, H. A Longitudinal Study on the Nutritional State of Elderly Women at a Nursing Home in Japan. Intern. Med. 2006, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Poehlman, E.T.; Dvorak, R.V. Energy Expenditure, Energy Intake, and Weight Loss in Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 650S–655S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, R.; Winning, K.; Uter, W.; Kaiser, M.J.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D.; Bauer, J.M. Screening for Malnutrition among Nursing Home Residents—A Comparative Analysis of the Mini Nutritional Assessment, the Nutritional Risk Screening, and the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).