Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gut Microbiota and SLE
2.1. Dysbiosis in SLE Patients
2.2. Dysbiosis in SLE Mice
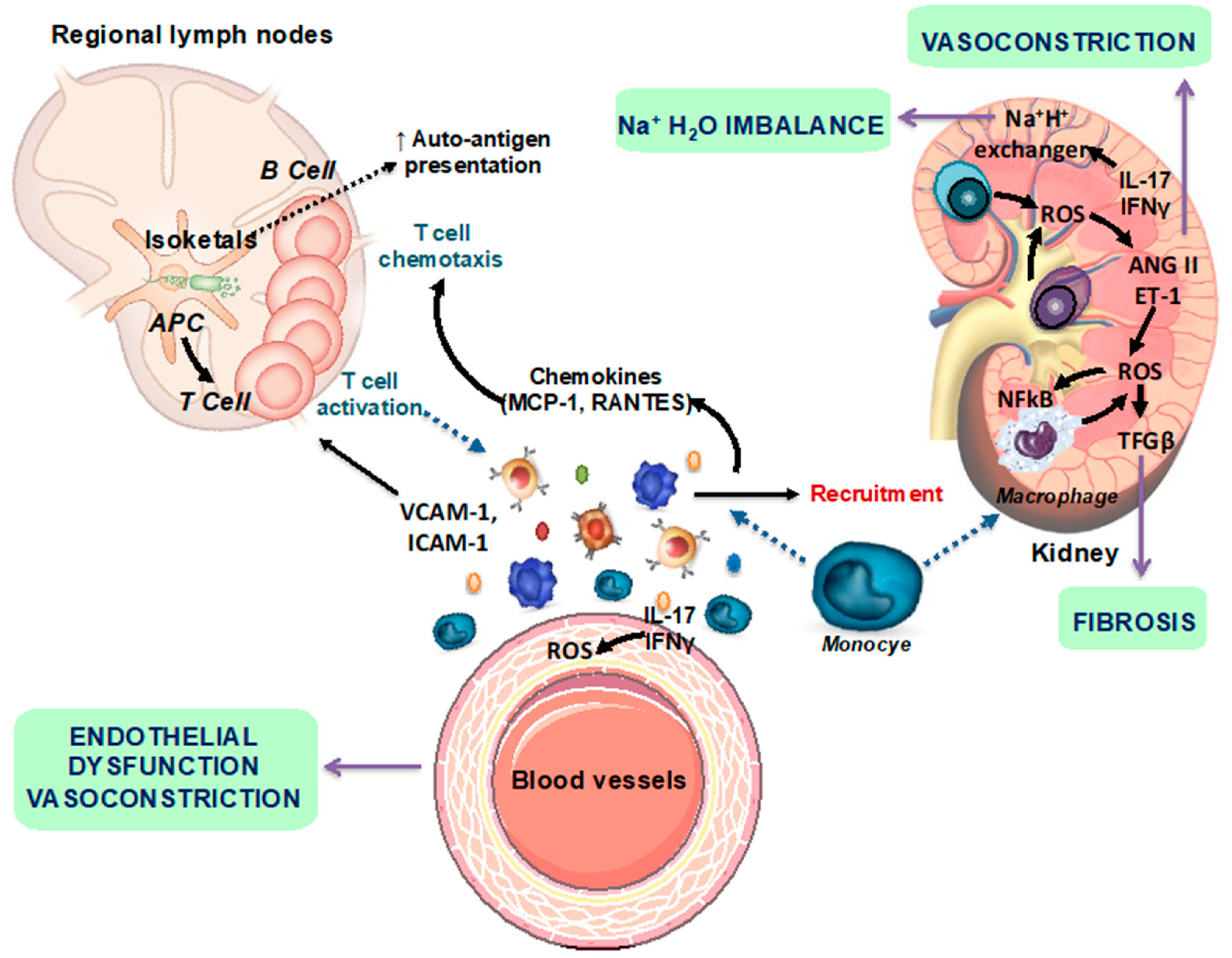
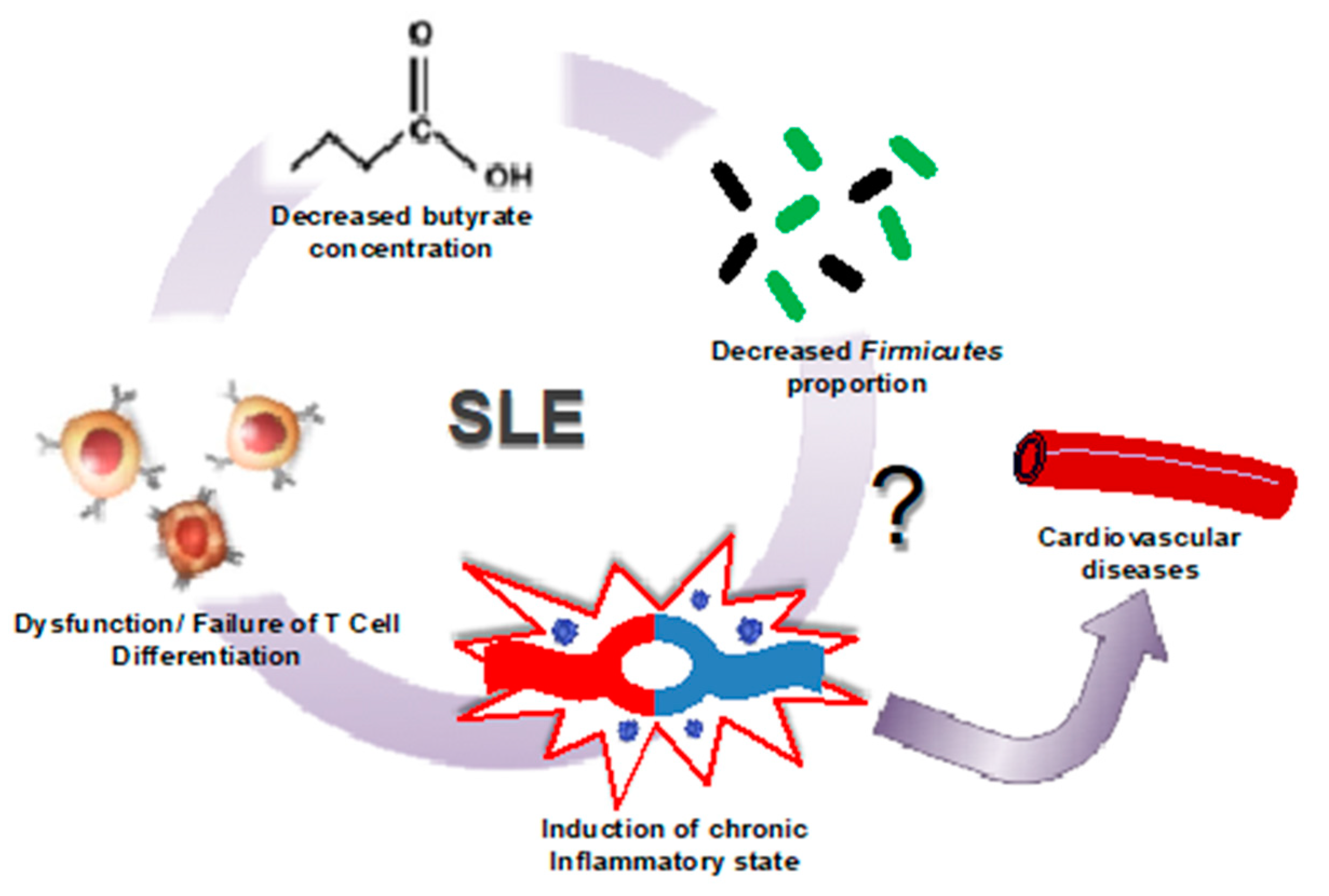
2.3. Gut Dysbiosis in Lupus Is Linked to Leaky Gut, Changes in Immune Cell Populations, and Cardiovascular Complications
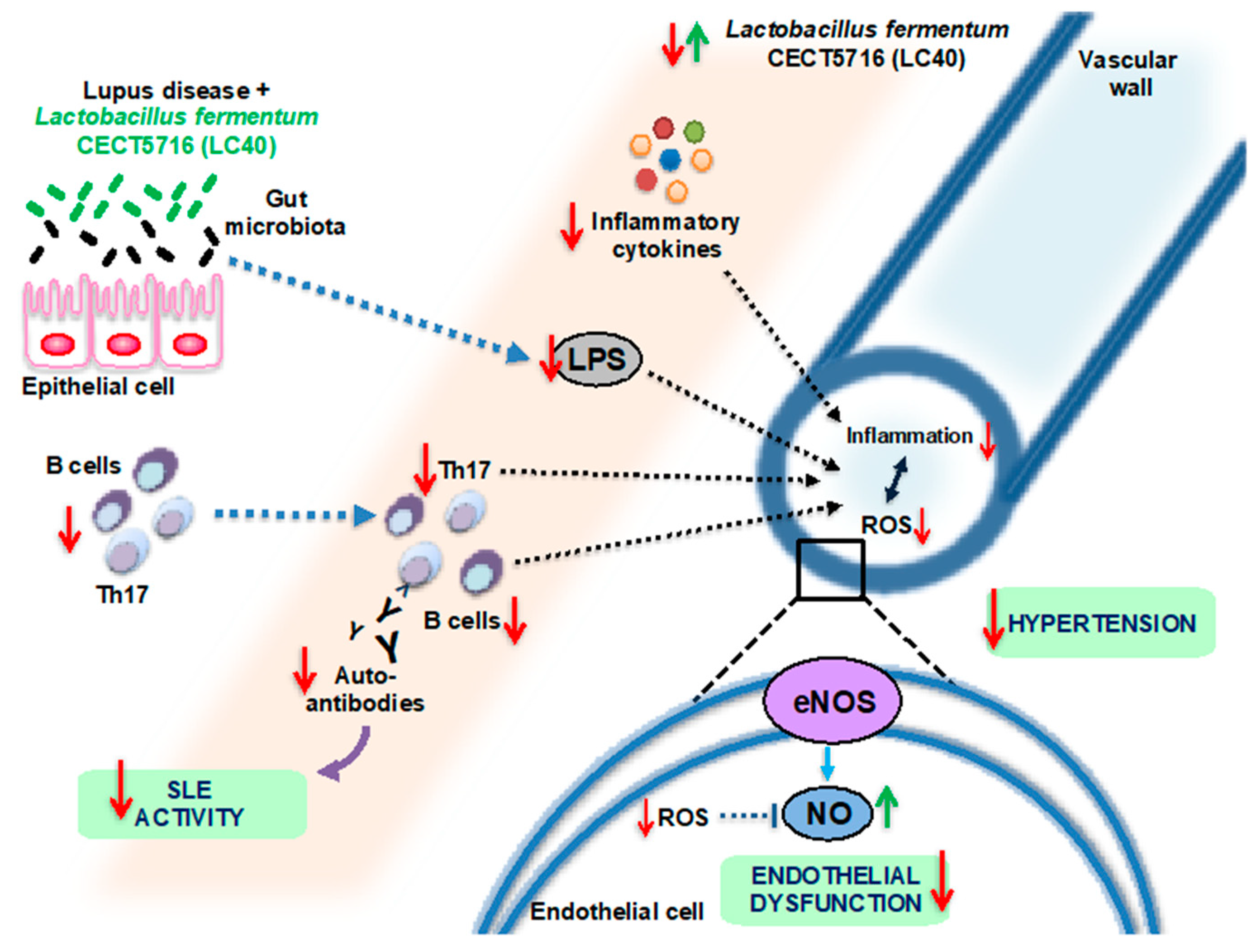
3. SLE and Probiotics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, B.M.; Gaudreau, M.C.; Al-Gadban, M.M.; Gudi, R.; Vasu, C. Impact of dietary deviation on disease progression and gut microbiome composition in lupus-prone SNF1 mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, I.; Lee, F.E. B cells as therapeutic targets in SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Paglia, G.M.C.; Leone, M.C.; Lepri, G.; Vagelli, R.; Valentini, E.; Alunno, A.; Tani, C. One year in review 2017: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kaplan, M.J. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.M.; Buhr, K.A.; Goldberg, J.W.; Bell, C.L.; Visekruna, M.; Nekkanti, S.; Greenlee, R.T. Mortality and cardiovascular burden of systemic lupus erythematosus in a US population-based cohort. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J. Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease. Lupus 2008, 17, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J. The pathophysiology of hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1258–R1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Saleh, M.A.; Kirabo, A.; Itani, H.A.; Montaniel, K.R.; Xiao, L.; Chen, W.; Mernaugh, R.L.; Cai, H.; Bernstein, K.E.; et al. Immune activation caused by vascular oxidation promotes fibrosis and hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamek-Guzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H.Y.; Migliarino, S.; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Guzik, T.J. Hypertension: Focus on autoimmunity and oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B.; Ryan, M.J. Understanding mechanisms of hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Hoch, N.E.; Brown, K.A.; McCann, L.A.; Rahman, A.; Dikalov, S.; Goronzy, J.; Weyand, C.; Harrison, D.G. Role of the T cell in the genesis of angiotensin II induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhur, M.S.; Lob, H.E.; McCann, L.A.; Iwakura, Y.; Blinder, Y.; Guzik, T.J.; Harrison, D.G. Interleukin 17 promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension 2010, 55, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, K.W.; Wallace, K.; Flynn, E.R.; Maric-Bilkan, C.; LaMarca, B.; Ryan, M.J. Preventing autoimmunity protects against the development of hypertension and renal injury. Hypertension 2014, 64, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esdaile, J.M.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Grodzicky, T.; Li, Y.; Panaritis, C.; du Berger, R.; Côte, R.; Grover, S.A.; Fortin, P.R.; Clarke, A.E.; et al. Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelou, M.; Mavragani, C.P. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive update. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.S.; Tsang, H.H.; Tam, R.C.; Lu, L.; Lau, C.S. B-cell-targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, A.; Milani, C.; López, P.; Cuervo, A.; Arboleya, S.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; González, S.; Suárez, A.; Gueimonde, M.; et al. Intestinal dysbiosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. MBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liao, X.; Lin, K.; Liu, H.; Edwards, M.R.; Ahmed, S.A.; Yuan, R.; Li, L.; Cecere, T.E.; et al. Control of lupus nephritis by changes of gut microbiota. Microbiome 2017, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Selmi, C.; Tang, R.; Gershwin, M.E.; Ma, X. The microbiome and autoimmunity: A paradigm from the gut-liver axis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrypnik, K.; Bogdański, P.; Łoniewski, I.; Reguła, J.; Suliburska, J. Effect of probiotic supplementation on liver function and lipid status in rats. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2018, 17, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, C.L.; Weir, T.L. The gut microbiota at the intersection of diet and human health. Science 2018, 362, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotillard, A.; Kennedy, S.P.; Kong, L.C.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Le Chatelier, E.; Almeida, M.; Quinquis, B.; Levenez, F.; Galleron, N.; et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature 2013, 500, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Shao, T.; Li, H.; Xie, Z.; Wen, C. Alterations of the gut microbiome in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H.; He, Y.; Li, P.; Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Disordered intestinal microbes are associated with the activity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.M.; Edwards, M.R.; Mu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Vieson, M.D.; Reilly, C.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Bankole, A.A. Gut Microbiota in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Mouse Model of Lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, D.; Omarbekova, A.; Heguy, A.; Schwudke, D.; Gisch, N.; Rovin, B.H.; Caricchio, R.; Buyon, J.P.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Silverman, G.J. Lupus nephritis is linked to disease-activity associated expansions and immunity to a gut commensal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liao, X.; Sparks, J.B.; Luo, X.M. Dynamics of gut microbiota in autoimmune lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7551–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, M.; Robles-Vera, I.; Romero, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; O’Valle, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Gálvez, J.; Duarte, J.; Jiménez, R. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: A novel alternative for the prevention of vascular disorders in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10005–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarra-Ruiz, D.F.; El Beidaq, A.; Iñiguez, A.J.; Lubrano Di Ricco, M.; Manfredo Vieira, S.; Ruff, W.E.; Mubiru, D.; Fine, R.L.; Sterpka, J.; Greiling, T.M.; et al. A Diet-Sensitive Commensal Lactobacillus Strain Mediates TLR7-Dependent Systemic Autoimmunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredo Vieira, S.; Hiltensperger, M.; Kumar, V.; Zegarra-Ruiz, D.; Dehner, C.; Khan, N.; Costa, F.R.C.; Tiniakou, E.; Greiling, T.; Ruff, W.; et al. Translocation of a gut pathobiont drives autoimmunity in mice and humans. Science 2018, 359, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz-Agranov, N.; Zandman-Goddard, G. The microbiome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Q.; Yu, Y.C.; Deng, H.H.; Sun, J.Z.; Dai, Z.; Wu, Y.W.; Yang, M. Plasma IL-17A is increased in new-onset SLE patients and associated with disease activity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6: Regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, P.; de Paz, B.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Hevia, A.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Suárez, A. Th17 responses and natural IgM antibodies are related to gut microbiota composition in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.F.; Peng, W.M.; Schlee, M.; Barchet, W.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Kolanus, W.; Geyer, M.; Schmitt, S.; Steinhagen, F.; Oldenburg, J.; et al. SOCS1 and SOCS3 Target IRF7 Degradation to Suppress TLR7-Mediated Type I IFN Production of Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 4024–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buie, J.J.; Renaud, L.L.; Muise-Helmericks, R.; Oates, J.C. IFN-α Negatively Regulates the Expression of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase and Nitric Oxide Production: Implications for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.G.; Guzik, T.J.; Lob, H.E.; Madhur, M.S.; Marvar, P.J.; Thabet, S.R.; Vinh, A.; Weyand, C.M. Inflammation, immunity, and hypertension. Hypertension 2011, 57, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckerle, C.E.; Mangale, D.; Franek, B.S.; Kelly, J.A.; Kumabe, M.; James, J.A.; Moser, K.L.; Harley, J.B.; Niewold, T.B. Large-scale analysis of tumor necrosis factor α levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas-Pont, M.; Manigrasso, M.B.; Grifoni, S.C.; LaMarca, B.B.; Maric, C.; Racusen, L.C.; Glover, P.H.; Jones, A.V.; Drummond, H.A.; Ryan, M.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist etanercept decreases blood pressure and protects the kidney in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Hypertension 2010, 56, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, G.F.; Dos Santos, R.A.; Oliveira, M.A.; Giachini, F.R.; Akamine, E.H.; Tostes, R.C.; Fortes, Z.B.; Webb, R.C.; Carvalho, M.H. Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to blood pressure regulation and vascular contraction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollinger, D.; Eißler, R.; Lorenz, S.; Strand, S.; Chmielewski, S.; Aoqui, C.; Schmaderer, C.; Bluyssen, H.; Zicha, J.; Witzke, O.; et al. Damage-associated molecular pattern activated Toll-like receptor 4 signalling modulates blood pressure in L-NAME-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 101, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.F.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Toll-like receptor 4 mutation protects obese mice against endothelial dysfunction by decreasing NADPH oxidase isoforms 1 and 4. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toral, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Jiménez, R.; Romero, M.; Sánchez, M.; Utrilla, M.P.; Garrido-Mesa, N.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Olivares, M.; Gálvez, J.; et al. The probiotic Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711 reduces the vascular pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory status in obese mice. Clin. Sci. 2014, 127, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, A.M.; Wang, W.; Wei, Z.; Akhter, E.; Maurer, K.; Costa Reis, P.; Song, L.; Petri, M.; et al. The SLE transcriptome exhibits evidence of chronic endotoxin exposure and has widespread dysregulation of non-coding and coding RNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issara-Amphorn, J.; Surawut, S.; Worasilchai, N.; Thim-Uam, A.; Finkelman, M.; Chindamporn, A.; Palaga, T.; Hirankarn, N.; Pisitkun, P.; Leelahavanichkul, A. The Synergy of Endotoxin and (1→3)-β-D-Glucan, from Gut Translocation, Worsens Sepsis Severity in a Lupus Model of Fc Gamma Receptor IIb-Deficient Mice. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunrinde, E.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Z.; Alekseyenko, A.; Li, Q.Z.; Macedo, D.; Kamen, D.L.; Oates, J.C.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Jiang, W. A Link Between Plasma Microbial Translocation, Microbiome, and Autoantibody Development in First-Degree Relatives of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Gurav, A.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Brady, E.; Padia, R.; Shi, H.; Thangaraju, M.; Prasad, P.D.; Manicassamy, S.; Munn, D.H.; et al. Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis. Immunity 2014, 40, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; López, P.; Sánchez, B.; González, S.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Suárez, A. Intestinal Dysbiosis Is Associated with Altered Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Serum-Free Fatty Acids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, E.C.; Lowe, E.C.; Chiang, H.; Pudlo, N.A.; Wu, M.; McNulty, N.P.; Abbott, D.W.; Henrissat, B.; Gilbert, H.J.; Bolam, D.N.; et al. Recognition and degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides by two human gut symbionts. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Tavella, V.J.; Kirby, J.L.; Cecere, T.E.; Chung, M.; Lee, J.; Li, S.; Ahmed, S.A.; Eden, K.; Allen, I.C.; et al. Antibiotics ameliorate lupus-like symptoms in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Kong, X.; Shao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, C. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota Associated with Promoting Efficacy of Prednisone by Bromofuranone in MRL/lpr Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasselman, L.J.; Vernice, N.A.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. The gut microbiome and elevated cardiovascular risk in obesity and autoimmunity. Atherosclerosis 2018, 271, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiling, T.M.; Dehner, C.; Chen, X.; Hughes, K.; Iñiguez, A.J.; Boccitto, M.; Ruiz, D.Z.; Renfroe, S.C.; Vieira, S.M.; Ruff, W.E.; et al. Commensal orthologs of the human autoantigen Ro60 as triggers of autoimmunity in lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, C.; Lalanne, A.I.; Cassard, L.; Mancardi, D.A.; Malbec, O.; Bruhns, P.; Dif, F.; Daëron, M. A strain of Lactobacillus casei inhibits the effector phase of immune inflammation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Golkar, H.R.; Farshbaf, S.; Emadi-Baygi, M.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akhavan, R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic supplementation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulińska, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Skrypnik, K.; Sobieska, M.; Korybalska, K.; Suliburska, J.; Bogdański, P. Multispecies Probiotic Supplementation Favorably Affects Vascular Function and Reduces Arterial Stiffness in Obese Postmenopausal Women-A 12-Week Placebo-Controlled and Randomized Clinical Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulińska, M.; Łoniewski, I.; van Hemert, S.; Sobieska, M.; Bogdański, P. Dose-Dependent Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Supplementation on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Level and Cardiometabolic Profile in Obese Postmenopausal Women: A 12-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, F.; Mahmoudi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Khorasani, S.; Tabasi, N.; Rastin, M. In vivo study: Th1-Th17 reduction in pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus mice after treatment with tolerogenic Lactobacillus probiotics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzang, B.S.; Liu, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsu, T.C. Effects of oral Lactobacillus administration on antioxidant activities and CD4 + CD25 + forkhead box P3 (FoxP3) + T cells in NZB/W F1 mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Tzang, B.S. Lactobacillus paracasei GMNL-32, Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-89 and L. reuteri GMNL-263 ameliorate hepatic injuries in lupus-prone mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.S.; Rajendran, P.; Tzang, B.S.; Yeh, Y.L.; Shen, C.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Ho, T.J.; Vijaya Padma, V.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y. Lactobacillus paracasei GMNL-32 exerts a therapeutic effect on cardiac abnormalities in NZB/W F1 mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.J.; McLemore, G.R., Jr. Hypertension and impaired vascular function in a female mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R736–R742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Suez, J.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Bashiardes, S.; Kotler, E.; Zur, M.; Regev-Lehavi, D.; Brik, R.B.; et al. Personalized Gut Mucosal Colonization Resistance to Empiric Probiotics Is Associated with Unique Host and Microbiome Features. Cell 2018, 174, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients | Ratio F/B | α-Diversity | Phylum | Family | Genus | Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women C 49.2 ± 10.7 years 20 patients | ↓F/B | No change | ↓Firmicutes ↓Tenericutes ↑Bacteroidetes | ↓Lachnospiraceae ↓Ruminococcaceae | [18] | ||
| Women A 46.0 ± 1.8 years 35 patients | ↓F/B | ↓PD_whole_ tree ↓Observed species | ↓Firmicutes ↑Bacteroidetes ↑Actinobacteria ↑Proteobacteria ↑Fusobacteria | ↑Bacteroidaceae ↑Prevotellaceae ↑Rikenellaceae | ↓Pseudobutyvibrio ↓Dialister ↓Bifidobacterium ↑Rhodococcus ↑Eggerthella ↑Klebsiella ↑Prevotella ↑Flavonifractor ↑Eubacterium | [24] | |
| Women A 37.46 ± 14.17 years 40 patients | ↓F/B | ↓Chao Richness ↓PD_whole_ tree ↓Observed species | ↓Tenericutes | ↑Streptococcaceae ↑Lactobacillaceae ↑Megasphaera | ↓Mollicutes ↓RF39 ↓Faecalobacteriu, ↓Cryptophyta ↓Roseburia | ↑Streptococcus anginosus ↑Lactobacillus mucosae ↑Veinella dispar | [25] |
| Women 3 AA (42.33 ± 13.39 years), 7 C (49.42 ± 8.51 years) Men 3 C (33 ± 6.57 years) 1 AA (29) 14 patients | Not change | ↑Proteobacteria | ↑Blautia | [26] | |||
| Women 10 C (38.3 ± 4.32 years) 13A (38.3 ± 4.32 years) 16 AA (46.69 ± 4.33 years) 19 WH (44.84 ± 3.5 years) 3 BH (43 ± 9.57 years) 61 patients | ↓Chao Richness | ↓Ruminococcaceae | ↑Blautia | ↓Ruminococcus gnavus ↓Bacteroides uniformis | [27] |
| Ratio F/B | α-Diversity | Phylum | Family | Genus | Species | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NZB/WF1 | ↓F/Bor no change | ↑α-diversity or no change | ↓Firmicutes ↑Bacteroidetes | Pre-SLE ↓Bifidobacterium ↑Lactobacillus ↓Lactobacillus High severity ↓Anerostipes | [26] [28] [29] [30] | ||
| MRL/lpr | ↓F/Bor no change | ↑α-diversityor no change | ↓Firmicutes ↑Bacteroidetes | ↓Lactobacillaceae ↑Rikenellaceae ↑Desulfovibrionacea ↑Ruminococcaceae ↑Lachnospiraceae ↑Streptococcaceae | ↓Lactobacillus ↓Bifidobacterium ↑Tenericutes ↑Mollicutes ↑Butyrivibrio ↑Roseburia | [19] [26] [28] [30] | |
| SNF1 | ↓F/Bor no change | ↑α-diversity | ↓Firmicutes ↑Bacteroidetes | ↑Rikenellaceae ↑Lachnospiraceae | Pre-SLE ↓Lactobacillus SLE ↑Lactobacillus ↑Clostridium ↑Dehalobacterium ↑Oscillospira ↑Dorea ↑Bilophila | [1] [26] | |
| TLR-7.1 | ↓F/B | ↑α-diversity | ↓Firmicutes ↑Bacteroidetes | ↓Clostridaceae ↑Coriobacteriaceae ↑Rikenallecea | ↓Turicibacter ↓Bifidobacterium ↓Coprobacillus ↓Anaerostipes ↑Prevotella ↑Desulfovibrio | ↑Lactobacillus reuteri | [31] |
| Probiotic | Model | Observed Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis PTCC 1743 | Pristane-induced murine model | ↓Th17 ↓IL-17a ↓Th1 ↓IFN-γ | [61] |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 9595 | Pristane-induced murine model | ↓RORγ ↓Th17 ↓Th1 ↓IFN-γ | [61] |
| Ruminococcus obeum DSM25238 | In vitro | ↓Th17/Th1 ratio | [35] |
| Blautia coccoides DSM935 | In vitro | ↓Th17/Th1 ratio | [35] |
| Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL 263 | NZB/W F1 | ↑FoxP3 ↑Treg ↓TLR-4 ↓TLR-5 ↓TLR-7 ↓TLR-9 | [62] |
| ↓IL-1β ↓TNF-α ↓IL-6 | [63] | ||
| Bifidobacterium bifidum LMG13195 | In vitro | ↓T lymphocytes activation | [35] |
| Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 | NZB/W F1 | ↓B and T lymphocytes↓IL-17a ↓IFN-γ ↓TNF-α ↓IL-21 | [29] |
| Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL 89 | NZB/W F1 | ↓TLR-4 ↓TLR-5 ↓TLR-7 ↓TLR-9 | [62] |
| ↓IL-1β ↓TNF-α ↓IL-6 | [48] | ||
| Lactobacillus paracasei GMNL 32 | NZB/W F1 | ↓TLR-4 ↓TLR-5 ↓TLR-7 ↓TLR-9 | [62] |
| ↓IL-1β ↓TNF-α ↓IL-6 | [63] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Duarte, J. Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112676
de la Visitación N, Robles-Vera I, Toral M, Duarte J. Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112676
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Visitación, Néstor, Iñaki Robles-Vera, Marta Toral, and Juan Duarte. 2019. "Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112676
APA Stylede la Visitación, N., Robles-Vera, I., Toral, M., & Duarte, J. (2019). Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients, 11(11), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112676






