Abstract
The classical functions of vitamin D are to regulate calcium-phosphorus homeostasis and control bone metabolism. However, vitamin D deficiency has been reported in several chronic conditions associated with increased inflammation and deregulation of the immune system, such as diabetes, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis. These observations, together with experimental studies, suggest a critical role for vitamin D in the modulation of immune function. This leads to the hypothesis of a disease-specific alteration of vitamin D metabolism and reinforces the role of vitamin D in maintaining a healthy immune system. Two key observations validate this important non-classical action of vitamin D: first, vitamin D receptor (VDR) is expressed by the majority of immune cells, including B and T lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells; second, there is an active vitamin D metabolism by immune cells that is able to locally convert 25(OH)D3 into 1,25(OH)2D3, its active form. Vitamin D and VDR signaling together have a suppressive role on autoimmunity and an anti-inflammatory effect, promoting dendritic cell and regulatory T-cell differentiation and reducing T helper Th 17 cell response and inflammatory cytokines secretion. This review summarizes experimental data and clinical observations on the potential immunomodulating properties of vitamin D.
1. Introduction
The role of vitamin D in the regulation of calcium-phosphate homeostasis and in the control of bone turnover is well known. Vitamin D status significantly affects skeletal health during growth and in adult age, its deficiency during growth leads to rickets [1], whereas during adult age it is responsible of osteomalacia and various degree of osteoporo-malacia [2]. Low vitamin D status increases bone turnover, decreases bone density, and is associated with increased fracture risk. In addition to the well-known effect on skeletal health in the last two decades evidence has been accumulated on the pleiotropic effect of vitamin D other than on bone health thanks to the findings that vitamin D receptor (VDR) and the vitamin D activating enzyme 1-α-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) are expressed in several cells outside the bone and kidney, such as in the intestine, platelets, pancreas, and prostate [3]. Several cells involved in the immune function express VDR and CYP27B1, this observation suggests that the active form of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)2D3, is able to control the immune function at different levels. Previous reviews on the role of vitamin D in the regulation of immune system have been published in recent years [4,5]. Here we summarize the recent evidence sexploiting authors’ expertise in both experimental and clinical fields.
2. Vitamin D Metabolism
Vitamin D enters the body trough dietary intake (about 20% of vitamin D3 is assumed with diet) or is synthetized by the skin (80%) from 7-dihydrocholesterol following UVB exposure. Vitamin D3 becomes biologically active after hydroxylation in the liver by the enzymes cytochrome P450 2R1 (CYP2R1) and cytochrome P450 27 (CYP27A1) becoming 25(OH)D3. The fully-active metabolite 1,25(OH)2D3 is hydroxylated in the kidney by the enzyme CYP27B1, parathormone (PTH), and the fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) control CYP27B1 synthesis and activity [6]. Synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 is strictly regulated in a renal negative feedback loop: high levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 and FGF-23 inhibit CYP27B1 and induce the cytochrome P45024A1(CYP24A1), which transforms 1,25(OH)2D3 into the inactive form 24(OH)D3 [7].
In addition to the kidney, CYP27B1 is expressed by other cell types, including immune cells. These cells produce 1,25(OH)2D3 that has autocrine and/or paracrine effects, the high level produced locally is thought to be responsible for immunomodulation. The regulation of CYP27B1 synthesis in immune cells is different than the signals regulating kidney production of 1,25(OH)2D3. Inflammatory signals, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and cytokines, induce monocyte and macrophage production of CYP27B1 [8,9,10]. These differences in the regulation of 1,25(OH)2D3 production point to an autocrine/paracrine effect as immunomodulatory.
3. Vitamin D Status
Vitamin D status is defined by the blood measurement of its hydroxylated form 25(OH)D3, however, there is no common agreement on the threshold levels to identify desirable vitamin D level. Guidelines from different scientific societies and different countries established 50 nM/L or 75 nM/L to consider vitamin D sufficiency [11,12,13], however, it is generally accepted that 25(OH)D3 levels lower than 50 nM/L are associated with bone metabolism alteration, increased risk of falls, and myopathy in adults [14,15,16,17,18]. Experts in the field generally agree to maintain 25(OH)D3 between 20 and 125 nM/L in order to obtain the certain skeletal effects without toxic effects. Recent literature raises the suspicion that administration of a bolus of vitamin D3 higher than 50,000 UI may result in an increased risk of falls and fractures [19,20]; moreover, the mortality related to 25(OH)D3 is a “U shaped curve” and 25(OH)D3 levels higher than 150 nM/L are associated with increased mortality [21].
4. Vitamin D and the Innate Immune System: Antimicrobial Activity
The innate immune system is the first defense against infection, it is required to rapidly fight against invading pathogens. The innate immune system comprehends components both from the host and resident microbes (microbiota). The host defense comprises physical barriers to infection (as skin, mucous surfaces, mucus, and vascular endothelial cells), enzymes expressed by epithelial and phagocytic cells (as lysozyme), antimicrobial peptides and proteins (as defensins, cathelicidins, and others expressed by phagocytes), inflammatory humoral components (as complement and opsonins), and cell receptors that rapidly recognize pathogens (as toll-like receptors) and cellular components (as mast cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils cells and natural killer). Interaction between microbiota a vitamin D will be analyzed in the following paragraph.
Vitamin D is a well-known regulator of innate immunity, the first data on this topic have been generated on the treatment of diseases caused by mycobacteria, such as tuberculosis and leprosy [22,23], however, the mechanisms responsible for these actions have been elucidated in more recent years. 1,25(OH)2D3 enhances the production of defensin β2 and cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) by macrophage and monocyte keratinocytes increasing their antimicrobial activity [24,25,26]. Moreover, 1,25(OH)2D3 increases chemotaxis, autophagy, and phagolysosomal fusion of innate immune cells [27,28]. The exposition of human monocytes to pathogens, such as M. tuberculosis and others, up-regulates the expression of CYP27B1 and of VDR, thus enhancing both the cell ability to produce 1,25(OH)2D3 in the site of infection and to respond to this metabolite. However, macrophages are heterogeneous, with different functions [29]. Macrophages formed after interleukin (IL)-15 stimulus respond to vitamin D stimulus increasing their antimicrobial activity, whereas phagocytic macrophages obtained after stimulus with IL-10 are weakly influenced by vitamin D levels regardless oftheir high phagocytic activity [10,30].
1,25(OH)2D3 up-regulates CAMP not only by monocytes/macrophages, but also in other cells participating in the innate immune system as first-barrier defenses, such as keratinocytes, epithelial, intestinal, lung and corneal cells, and placenta trophoblasts (see for a comprehensive review Wei and Christakos, 2015) [4].
Data in humans on infections other than mycobacterial have been generated on urinary and respiratory infections and on sepsis. A predisposition to urinary tract infection in children with low vitamin D levels due to the reduced production of CAMP and defensing β2 has been suggested by association studies [31,32]. Additionally, in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients’ levels of CAMP and other antimicrobial peptides were associated with increased risk of acute exacerbations [33]. Consistent with this datum treatment with 1,25(OH)2D3 was effective in reducing respiratory infections in asthma patients thanks to increased CAMP expression and inflammatory cytokine modulation [34]. Data on the role of vitamin D status and vitamin D supplementation in sepsis are also available both in pediatric and in adult patients: in pediatric patients a clear role for 25(OH)D3 and CAMP was not demonstrated [35], whereas in adults lower levels of 25(OH)D3 were found in sepsis [36] and a high-dose of vitamin D3 increases circulating CAMP and reduces inflammatory cytokines as IL-6 and IL-1β [37].
More recently data on a possible role of vitamin D in increasing resistance to HIV infection have been published, in particular HIV-exposed seronegative individuals produced more CAMP in oral-mucosa and peripheral-blood, and have higher CYP24A1 mRNA in vaginal-mucosa; CYP24A1 is considered an indicator of high levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 [38]. Low serum vitamin D has been associated with HIV/AIDS progression and mortality [39].
1,25(OH)2D3 is able to increase the production of other antimicrobial peptides, such as defensing β2-4, this ability has been demonstrated both in vitro by monocytes stimulation [40,41] and in vivo in pediatric patients’ blood [32].
Vitamin D is able to modulate innate immune system, also increasing the phagocytic ability on immune cells [42,43] and by reinforcing the physical barrier function of epithelial cells. In particular 1,25(OH)2D3can enhance corneal [44] and intestinal [45] epithelial barrier function (Figure 1).
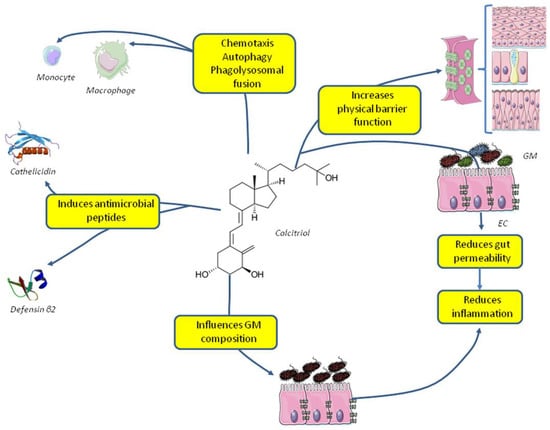
Figure 1.
Effects of vitamin D on the innate immune system and gut microbiota. Abbreviations: EC, enteral cells; GM, gut microbiota.
Taken together these data point to a role of vitamin D in defending the organism against pathogens suggesting that vitamin D sufficiency has to be granted in patients affected by acute or chronic infection. The ability of immune cells to hydroxylate 25(OH)D3 into its active form 1,25(OH)2D3 suggests administrating vitamin D3 rather than hydroxylated metabolites to patients affected by infections in order to allow the autocrine/paracrine function of 1,25(OH)2D3 without overcoming local hydroxylation and the feedback system.
5. Vitamin D and Microbiota: Increasing Host Defenses
The whole of the commensal, symbiotic, and pathogenic microorganisms living in different areas of the human body has defined microbiota. Microbiota and the host have several relationships, and the perfect balance between microbiota and the host is required for the development, maturation, and properfunction of the immune system [46]. Several papers suggest that vitamin D is one of the actors of the complex relationship between microbiota living in the gut (GM) and immune system modulation. Vitamin D is responsible for the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium and for the modulation of the bowel immune system, hence, low levels may be associated with greater gut permeability and, consequently, with GM-induced metabolic endotoxemia that induces a low-grade inflammation [47]. Moreover, vitamin D administration may influence GM composition, and in vitro data demonstrate that vitamin D enhances macrophages’ ability to kill Escherichia coli. [48]. In animals with vitamin D depletion and the knockout of the VDR, the GM dysbiosis favors metabolic disorders [49]. Other studies in mice demonstrated that VDR reduces the response to infection of the intestinal epithelium [50].
Elegant studies in transgenic mice demonstrated that over-expression of VDR in the intestinal epithelium induces resistance to colitis [51,52] and decreases mucosal inflammation suppressing epithelial cell apoptosis, boosting tight junction function [51,53]. On the other hand VDR selective deletion in bowel favors a more severe form of colitis characterized by greater Th1 and Th17 mucosal infiltration and inflammatory cytokines production [54]. In humans, observational studies suggest that low levels of 25(OH)D3 are associated with increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [55,56,57] and that high levels of 25(OH)D3 in these patients protect against Clostridium difficile infection [58]. The experimental data on the role of VDR in developing IBD have been confirmed by the finding of a significant reduction of VDR expression (about 50%) in the colon epithelium in patients affected by IBD with respect to healthy controls [51,53]. The reduction in VDR expression by IBD patients may explain the different effect on GM composition of high oral dosages of vitamin D3 demonstrated in a small cohort of patients affected by Crohn’s disease with respect to healthy controls [59], however, human data on the effect of vitamin D supplementation on GM in IBD are still controversial, as other studies did not confirm these results [60,61]. In the study by Luthold and coll. [61] dietary intake of vitamin D and 25(OH)D3 were inversely correlated with Coprococcus and Bifidobacterium, however, thanks to their ability to produce butyrate these bacteria are commonly considered as anti-inflammatory. A possible explanation of these contradictory results may be the different effect of vitamin D on GM according to the different gastro-intestinal tracts considered [62]. Recently, a double-blind placebo-controlled study on patients affected by cystic fibrosis demonstrated that vitamin D insufficiency is associated with different microbiota not only in the gut, but also in the airways, and that the administration of 50,000 IU of oral vitamin D3 weekly significantly affects microbiota composition [63]. Nevertheless, the evaluation of clinical outcomes of microbiota change is still open.
Several data point to an effect of vitamin D on microbiota. Conversely, some recent reports suggest that microbiota, per se, influences vitamin D metabolism mainly through FGF-23; germ-free (GF) mice have low vitamin D and high FGF-23, whereas their colonization with bacteria results in increased levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and a decrease in FGF-23 with normalization of vitamin D hydroxylated metabolites. Inhibition of FGF-23 in GF mice restores vitamin D metabolism without bacterial colonization of the gut [64] (Figure 1).
The role of GM as an active player in the regulation of bone metabolism in humans is being investigated more and more [46], and the role played by vitamin D is still under debate. Further studies to clarify their interplay are needed.
6. Vitamin D and the Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system or acquired immune system is the second defense against infection. It is required to specifically fight against pathogens, is activated by exposure to pathogens, and unlike the innate immune system it is able to learn about the pathogen and enhance the immune response accordingly, thanks to an immunological memory. The adaptive immune system is composed of T and B cells and is also responsible for autoimmune reaction.
25(OH)D3 suppresses adaptive immunity [4,65]. In experimental models it down-regulates the immune responses mediated by T helper (Th) 1 cells, thus inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as Interferon-γ IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-2, and TNF-α [66,67]. Although experimental studies in vitro and in animals have yielded encouraging results on the immunomodulatory effect of 1,25(OH)2D3, the same cannot be said about human studies, and few studies have confirmed the suppressive effect of vitamin D on Th1 cells and inflammatory cytokine production in different diseases and spinal tuberculosis [68], uremia [69], and autoimmune thyroiditis [70]; whereas others in IBD [71], dialysis [72], and rheumatoid arthritis [73] do not confirm these results. These discrepancies may be due to the different diseases considered and also to the different type of treatment administered, mainly 1,25(OH)2D3 in vitro and in animals and vitamin D3in vivo in humans. Moreover, when considering administration of vitamin D3 different doses were used in different studies. Therefore, it is almost impossible to compare the results.
It has been suggested that 1,25(OH)2D3 acts as an immunomodulatory not only by suppressing Th1 cells activation, but also modulating Th2 cells, T regulatory (Tregs) cells activity, and Th17 cells.
The majority of the in vitro studies assessing the effect of vitamin D on Th2 suggests that 1,25(OH)2D3 upregulates Th2 cells activity [74,75,76]. Amongst immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D its ability to suppress Th17 and increase Treg cells has been recently demonstrated [77,78,79]. Th17 cells produce IL-17 and have been implicated in the pathogenesis ofseveral autoimmune diseases, some experimental studies suggest that 1,25(OH)2D3 suppresses Th17 formation and activity [67,80,81,82,83] by blocking Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells (NFAT) and Runt-related Transcription Factor 1 (RUNx1) binding to the IL-17 promoter and inducing Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) [81], and by inhibiting RAR-related Orphan Receptor Gamma2 (RORγt) which is the transcription factor of IL-17 [84].
More recently our lab showed no effect of the administration of a high bolus of vitamin D3 (300,000 UI) in the modulation of Th subset in patients affected by early rheumatoid arthritis [73], as well as a study on hemodialysis patients [72].
It has also been suggested that the administration of oral vitamin D3 increases Tregs function in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus [85], however, in other diseases, such as early rheumatoid arthritis, this effect was not confirmed [73].
The overall effect of vitamin D on Th cells differentiation may be mediated by its effect on dendritic cells, these cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs), responsible for T cell differentiation into an effector cell with pro- or anti-inflammatory properties, thus, modulation of APCs is crucial in initiating and maintaining adaptive immune response and self-tolerance [86]. In vitro differentiation of dendritic cells in the presence of 1,25(OH)2D3 induces a “tolerogenic state” characterized by low levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-12 and TNF-α, with increased levels of the anti-inflammatory IL-10, these cells induce the differentiation of Treg cells and induce apoptosis in the autoreactive T cells [87,88,89,90] (Figure 2).
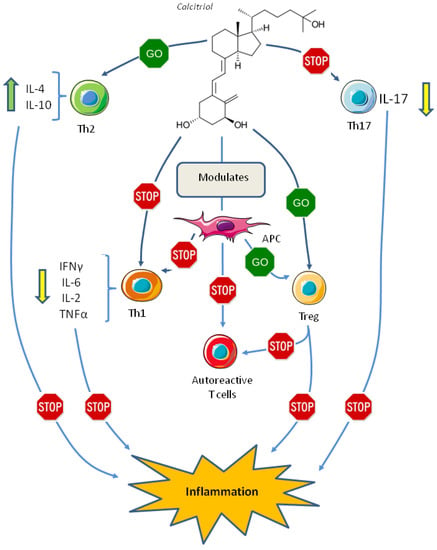
Figure 2.
Effect of vitamin D on the adaptive immune system. Abbreviations: APC, antigen presenting cell; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; Th1, T helper 1 cell; Th2, T helper 2 cell; Th17, T helper 17 cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; Treg, T regulatory cell.
Taken together these data are not sufficient to prove a real role for vitamin D in the modulation of adaptive immune system in humans, thus, the therapeutic use of vitamin D and its metabolites in patients aiming to ameliorate the adaptive immune system is not sustained by sufficient data.
7. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Diseases
Thanks to the evidences of immunomodulatory effect of vitamin D the role of vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in autoimmune diseases has long been studied. Animal studies showed an important role of 1,25(OH)2D3 supplementation in the control of autoimmune diseases, such as experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). In these two conditions 1,25(OH)2D3 prevents the initiation and reduces the disease progression [91,92,93]. Similarly, different mouse models of enterocolitis display a more severe phenotype during vitamin D deficiency and reduced inflammation after administration of 1,25(OH)2D3 (see for a review Alhassan et al., 2017) [94]. Despite solid experimental evidence human studies are less convincing: some epidemiological data link increasing latitude and consequent decrease sunlight exposure with higher prevalence of multiple sclerosis [95,96,97], type I diabetes [98,99,100], and IBD [101]. It is clear that such differences may be due to genetic and lifestyle factors other than 25(OH)D3 levels. Other epidemiological data reinforcing the hypothesis of a link between sun exposure, vitamin D synthesis, and the risk of developing multiple sclerosis stem from the observation that subjects born in months associated with lower 25(OH)D3 level in the northern hemisphere (April) are at higher risk of developing the disease, whereas patients born in October (higher vitamin D levels) are at lower risk [102].
Some studies correlated vitamin D dietary intake and the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as rheumatoid arthritis [103] and type 1 diabetes mellitus [104,105], however, the correct evaluation of vitamin D intake is challenging as it is based on patient recall. To bypass the challenging measurement of vitamin D intake and sun exposure, levels of 25(OH)D3 in the serum can be useful, and, indeed, low levels of 25(OH)D3 in the serum of patients affected by autoimmune diseases with respect to healthy controls have been found [106,107,108,109,110,111,112]. Nevertheless, these studies demonstrated a correlation and not a causal relationship.
Intervention studies with different doses of vitamin D3 in autoimmune diseases lead to different outcomes, recently we demonstrated that a bolus of vitamin D3 (300,000 UI) in patients affected by early rheumatoid arthritis is effective in ameliorating general health, however, we found no effect on disease activity nor on inflammatory markers and T cells subset [73]. In patients affected by type 1 diabetes clinical intervention studies with vitamin D3 or hydroxylated analogs have been disappointing, as no clinical study has demonstratedan effect of vitamin D in ameliorating glucose metabolism and insulin secretion [113,114], however, in a small prospective trial in children with type 1 diabetes autoantibodies 1,25(OH)2D3 administration decreased the serum glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) autoantibody, pointing to some immunomodulation of 1,25(OH)2D3 [115].
In addition to autoimmune diseases vitamin D has also been implicated in the control of other inflammatory conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases: in animal models vitamin D3 administration reduces macrophage production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and decreases atherosclerosis and inflammation in the epicardial adipose tissue [116,117]. In humans an association between low 25(OH)D3 level and increased activation of inflammatory pathway in epicardial adipose tissuein patients affected by coronary artery disease has been described [118]. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to cardiovascular disease not only by the modulation of inflammatory pathways, but also through the modulation of endothelial function, the effect on arterial stiffness, and a possible beneficial role on atherosclerotic plaque formation. However, this topic is beyond the scope of this review. For further insight in the role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease see the review by Apostolakis and coll. [119].
8. Conclusions
In summary, several studies point to an important role of vitamin D as an immunomodulator, and strong data demonstrate a role for 1,25(OH)2D3 in increasing the ability of the innate immune system to fight against pathogens, whereas data on the effect of 1,25(OH)2D3in the modulation of acquired immune system are more controversial. There is no general consensus on the desired level of 25(OH)D3 to achieve immunomodulatory effects, thus, there is no current indication for vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with infections and/or autoimmune diseases. Further studies are needed to clarify the role of vitamin D as immunomodulator in humans.
Author Contributions
All three authors participated in the bibliographic search, discussion and writing of the manuscript. The manuscript was finalized by P.D.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Antonucci, R.; Locci, C.; Clemente, M.G.; Chicconi, E.; Antonucci, L. Vitamin D deficiency in childhood: Old lessons and current challenges. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 31, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uday, S.; Högler, W. Prevention of rickets and osteomalacia in the UK: Political action overdue. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelio, P.; Cristofaro, M.A.; De Vivo, E.; Ravazzoli, M.; Grosso, E.; Di Bella, S.; Aime, M.; Cotto, N.; Silvagno, F.; Isaia, G.; et al. Platelet vitamin D receptor is reduced in osteoporotic patients. Panminerva Med. 2012, 54, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Christakos, S. Mechanisms Underlying the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by vitamin D. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, B.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Mathieu, C.; Vallone, C.V.; Mascitelli, L.; Bizzaro, G.; Altieri, V.M.; Tirabassi, G.; Balercia, G.; et al. Does vitamin D play a role in autoimmune endocrine? A proof of concept. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, P.; Caillaud, D.; Cano, N.J. Vitamin D bioavailability: State of the art. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.H. Vitamin D Activity and Metabolism in Bone. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.T.; Stenger, S.; Li, H.; Wenzel, L.; Tan, B.H.; Krutzik, S.R.; Ochoa, M.T.; Schauber, J.; Wu, K.; Meinken, C.; et al. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science 2006, 311, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffels, K.; Overbergh, L.; Giulietti, A.; Verlinden, L.; Bouillon, R.; Mathieu, C. Immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in human monocytes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutzik, S.R.; Hewison, M.; Liu, P.T.; Robles, J.A.; Stenger, S.; Adams, J.S.; Modlin, R.L. IL-15 links TLR2/1-induced macrophage differentiation to the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7115–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Endocrine Society Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesareo, R.; Attanasio, R.; Caputo, M.; Castello, R.; Chiodini, I.; Falchetti, A.; Guglielmi, R.; Papini, E.; Santonati, A.; Scillitani, A.; et al. Italian Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AME) and Italian chapter of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) position statement: Clinical management of vitamin D deficiency in adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcour, A.; Blocki, F.; Hawkins, D.M.; Rao, S.D. Effects of age and serum 25-OH-vitamin D on serum parathyroid hormone levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3989–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, E.; Chou, R.; Zakher, B.; Daeges, M.; Pappas, M. Screening for Vitamin D Deficiency: Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, E.S.; Zakher, B.; Daeges, M.; Pappas, M.; Chou, R. Screening for vitamin D deficiency: A systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Gillespie, W.J.; Sherrington, C.; Gates, S.; Clemson, L.M.; Lamb, S.E. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattoa, H.P.; Konstantynowicz, J.; Laszcz, N.; Wojcik, M.; Pludowski, P. Vitamin D: Musculoskeletal health. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, K.M.; Stuart, A.L.; Williamson, E.J.; Simpson, J.A.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Young, D.; Nicholson, G.C. Annual high-dose oral vitamin D and falls and fractures in older women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 303, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Orav, E.J.; Staehelin, H.B.; Meyer, O.W.; Theiler, R.; Dick, W.; Willett, W.C.; Egli, A. Monthly high-dose vitamin D Treatment for the prevention of functional decline: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrein, K.; Quraishi, S.A.; Litonjua, A.A.; Gibbons, F.K.; Pieber, T.R.; Camargo, C.A.; Giovannucci, E.; Christopher, K.B. Evidence for a U-shaped relationship between prehospital vitamin D status and mortality: A cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airey, F.S. Vitamin D as a remedy for lupus vulgaris. Med. World 1946, 64, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrera, G. Vitamin D in massive doses as an adjuvant to the sulfones in the treatment of tuberculoid leprosy. Int. J. Lepr. 1949, 17, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-T.; Nestel, F.P.; Bourdeau, V.; Nagai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, J.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.; Lin, R.; Hanrahan, J.W.; Mader, S.; et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombart, A.F.; Borregaard, N.; Koeffler, H.P. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Sayama, K.; Tohyama, M.; Shirakata, Y.; Hanakawa, Y.; Tokumaru, S.; Yang, L.; Hirakawa, S.; Hashimoto, K. PPARγ mediates innate immunity by regulating the 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induced hBD-3 and cathelicidin in human keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 60, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.T.; Stenger, S.; Tang, D.H.; Modlin, R.L. Cutting edge: Vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis is dependent on the induction of cathelicidin. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.H. Vitamin D as an inducer of cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide expression: Past, present and future. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursuker, I.; Goldman, R. On the origin of macrophage heterogeneity: A hypothesis. J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 1983, 33, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.W.; Teles, R.M.B.; Haile, S.; Liu, P.T.; Modlin, R.L. Vitamin D status contributes to the antimicrobial activity of macrophages against Mycobacterium leprae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ÖvünçHacıhamdioğlu, D.; Altun, D.; Hacıhamdioğlu, B.; Çekmez, F.; Aydemir, G.; Kul, M.; Müftüoğlu, T.; Süleymanoğlu, S.; Karademir, F. The association between serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D level and urine cathelicidin in children with a urinary tract infection. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, V.; Kamolvit, W.; Herthelius, M.; Lüthje, P.; Brauner, A.; Chromek, M. Association between vitamin D, antimicrobial peptides and urinary tract infection in infants and young children. Acta Paediatr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, L.J.P.; Aanerud, M.; Hardie, J.A.; Miodini Nilsen, R.; Bakke, P.S.; Eagan, T.M.; Hiemstra, P.S. Antimicrobial peptide levels are linked to airway inflammation, bacterial colonisation and exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Martínez, E.; López-Vancell, M.R.; Fernández de Córdova-Aguirre, J.C.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Chavarría, A.; Velasco-Medina, A.; Velázquez-Sámano, G. Reduction of respiratory infections in asthma patients supplemented with vitamin D is related to increased serum IL-10 and IFNγ levels and cathelicidin expression. Cytokine 2018, 108, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathias, E.; Tangpricha, V.; Sarnaik, A.; Farooqi, A.; Sethuraman, U. Association of vitamin D with cathelicidin and vitamin D binding protein in pediatric sepsis. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2017, 10, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, T.; Regner, W.; Branscheidt, M.; Herr, C.; Koczulla, A.R.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Bals, R. Altered blood levels of vitamin D, cathelicidin and parathyroid hormone in patients with sepsis-a pilot study. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2017, 45, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quraishi, S.A.; De Pascale, G.; Needleman, J.S.; Nakazawa, H.; Kaneki, M.; Bajwa, E.K.; Camargo, C.A.; Bhan, I. Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Jimenez, W.; Zapata, W.; Rugeles, M.T. Antiviral molecules correlate with vitamin D pathway genes and are associated with natural resistance to HIV-1 infection. Microbes. Infect. 2016, 18, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, A.K.; Naude, C.E.; Goliath, R.; Chaplin, G.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Jablonski, N.G. High-dose vitamin D3 reduces deficiency caused by low UVB exposure and limits HIV-1 replication in urban Southern Africans. PNAS 2015, 112, 8052–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.T.; Schenk, M.; Walker, V.P.; Dempsey, P.W.; Kanchanapoomi, M.; Wheelwright, M.; Vazirnia, A.; Zhang, X.; Steinmeyer, A.; Zügel, U.; et al. Convergence of IL-1beta and VDR activation pathways in human TLR2/1-induced antimicrobial responses. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Delgado, J.E.; Araujo, Z.; Gonzalez-Curiel, I.; Serrano, C.J.; Rivas Santiago, C.; Enciso-Moreno, J.A.; Rivas-Santiago, B. Vitamin D and l-isoleucine promote antimicrobial peptide hBD-2 production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from elderly individuals. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2016, 86, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sly, L.M.; Lopez, M.; Nauseef, W.M.; Reiner, N.E. 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced monocyte antimycobacterial activity is regulated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mediated by the NADPH-dependent phagocyte oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35482–35493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.-M.; Yuk, J.-M.; Lee, H.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Son, J.W.; Harding, C.V.; Kim, J.-M.; Modlin, R.L.; Jo, E.-K. Mycobacterial lipoprotein activates autophagy via TLR2/1/CD14 and a functional vitamin D receptor signaling. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1648–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Pintea, V.; Lin, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Watsky, M.A. Vitamin D enhances corneal epithelial barrier function. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7359–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pálmer, H.G.; González-Sancho, J.M.; Espada, J.; Berciano, M.T.; Puig, I.; Baulida, J.; Quintanilla, M.; Cano, A.; de Herreros, A.G.; Lafarga, M.; et al. Vitamin D3 promotes the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the inhibition of beta-catenin signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelio, P.; Sassi, F. Gut Microbiota, Immune System, and Bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caricilli, A.M.; Picardi, P.K.; de Abreu, L.L.; Ueno, M.; Prada, P.O.; Ropelle, E.R.; Hirabara, S.M.; Castoldi, Â.; Vieira, P.; Camara, N.O.S.; et al. Gut microbiota is a key modulator of insulin resistance in TLR 2 knockout mice. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, P.K.; Chiewchengchol, D.; Wright, H.L.; Edwards, S.W.; Alswied, A.; Satsangi, J.; Subramanian, S.; Rhodes, J.M.; Campbell, B.J. Killing of escherichia coli by Crohn’s disease monocyte-derived macrophages and its enhancement by hydroxychloroquine and vitamin D. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Nie, Y.; Zhu, A.; Chen, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Luo, M.; Sun, Q.; Cai, L.; Lai, Y.; et al. Vitamin D signaling through induction of paneth cell defensins maintains gut microbiota and improves metabolic disorders and hepatic steatosis in animal models. Front Physiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liao, A.P.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Li, J.-D.; Sartor, R.B.; Sun, J. Vitamin D receptor negatively regulates bacterial-stimulated NF-kappaB activity in intestine. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Golan, M.A.; Annunziata, M.L.; Du, J.; Dougherty, U.; Kong, J.; Musch, M.; Huang, Y.; Pekow, J.; et al. Intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling inhibits experimental colitis. JCI 2013, 123, 3983–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, M.A.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.C. Transgenic expression of vitamin D receptor in gut epithelial cells ameliorates spontaneous colitis caused by interleukin-10 deficiency. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, T.; Cao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ge, X.; Nie, H.; Zheng, C.; Li, Y.C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D protects intestinal epithelial barrier by regulating the myosin light chain kinase signaling pathway. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Liu, T.; Shi, Y.; Tian, F.; Hu, H.; Deb, D.K.; Chen, Y.; Bissonnette, M.; Li, Y.C. Gut epithelial vitamin D receptor regulates microbiota-dependent mucosal inflammation by suppressing intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, E.V.; Sandborn, W.J. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2002, 31, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, E.V. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.-C.; Hanauer, S.B.; Li, Y.C. Mechanisms of disease: Vitamin D and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Cagan, A.; Gainer, V.S.; Cheng, S.-C.; Cai, T.; Szolovits, P.; Shaw, S.Y.; Churchill, S.; Karlson, E.W.; Murphy, S.N.; et al. Higher plasma vitamin D is associated with reduced risk of Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffler, H.; Herlemann, D.P.; Klinitzke, P.; Berlin, P.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Jaster, R.; Lamprecht, G. Vitamin D administration leads to a shift of the intestinal bacterial composition in Crohn’s disease patients, but not in healthy controls. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M.; Hendy, P.; Ding, J.N.; Shaw, S.; Hold, G.; Hart, A. The effect of vitamin D on intestinal inflammation and faecal microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Crohns. Colitis. 2018, 12, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthold, R.V.; Fernandes, G.R.; Franco-de-Moraes, A.C.; Folchetti, L.G.D.; Ferreira, S.R.G. Gut microbiota interactions with the immunomodulatory role of vitamin D in normal individuals. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 69, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.; Prietl, B.; Tauschmann, M.; Mautner, S.I.; Kump, P.K.; Treiber, G.; Wurm, P.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Högenauer, C.; Pieber, T.R. Effects of high doses of vitamin D3 on mucosa-associated gut microbiome vary between regions of the human gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhere, M.; He, J.; Chassaing, B.; Ziegler, T.R.; Alvarez, J.A.; Ivie, E.A.; Hao, L.; Hanfelt, J.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Tangpricha, V. Bolus weekly vitamin D3 supplementation impacts gut and airway microbiota in adults with cystic fibrosis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, S.A.; Kennett, M.J.; Smith, P.B.; Patterson, A.D.; Cantorna, M.T. The gut microbiota regulates endocrine vitamin D metabolism through fibroblast growth factor 23. Front Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, R.F.; Liu, P.T.; Modlin, R.L.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Impact of vitamin D on immune function: Lessons learned from genome-wide analysis. Front Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.T.G.; Schneider, M.; Cuppari, L.; Grabulosa, C.C.; T Aoike, D.Q.; Redublo, B.M.C.; Batista, M.; Cendoroglo, M.; Maria Moyses, R.; Dalboni, M.A. Cholecalciferol decreases inflammation and improves vitamin D regulatory enzymes in lymphocytes in the uremic environment: A randomized controlled pilot trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Zheng, C.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lin, C.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Jin, T. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 -induced dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by increasing proportions of the regulatory lymphocytes and reducing T helper type 1 and type 17 cells. Immunology 2017, 152, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.-H.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.-Y.; Li, H.-L.; Bian, F.; Huang, T.; Fang, H.-Y. Influence of vitamin D deficiency on T cell subsets and related indices during spinal tuberculosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, J.R.; Idiculla, A.; Slusser, J.; Menard, R.; Quarles, L.D. Cholecalciferol supplementation alters calcitriol-responsive monocyte proteins and decreases inflammatory cytokines in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdenko, G.; Heine, G.; Worm, M. Oral vitamin D increases the frequencies of CD38+ human B cells and ameliorates IL-17-producing T cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendix-Struve, M.; Bartels, L.E.; Agnholt, J.; Dige, A.; Jørgensen, S.P.; Dahlerup, J.F. Vitamin D3 treatment of Crohn’s disease patients increases stimulated T cell IL-6 production and proliferation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, E.; Heine, G.H.; Ulrich, C.; Seiler, S.; Köhler, H.; Girndt, M. Influence of cholecalciferol supplementation in hemodialysis patients on monocyte subsets: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2013, 123, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buondonno, I.; Rovera, G.; Sassi, F.; Rigoni, M.M.; Lomater, C.; Parisi, S.; Pellerito, R.; Isaia, G.C.; D’Amelio, P. Vitamin D and immunomodulation in early rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, A.; Barrat, F.J.; Crain, C.; Heath, V.L.; Savelkoul, H.F.; O’Garra, A. 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 has a direct effect on naive CD4+ T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4974–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, J.; Gerstmayr, M.; Szépfalusi, Z.; Urbanek, R.; Peterlik, M.; Willheim, M. 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 inhibits not only Th1 but also Th2 differentiation in human cord blood T cells. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 52, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staeva-Vieira, T.P.; Freedman, L.P. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits IFN-gamma and IL-4 levels during in vitro polarization of primary murine CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawaz, L.; Mrad, M.F.; Kazan, J.M.; Sayegh, S.; Akika, R.; Khoury, S.J. Comparative effect of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 on Th17 cell differentiation. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 166, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şıklar, Z.; Karataş, D.; Doğu, F.; Hacıhamdioğlu, B.; İkincioğulları, A.; Berberoğlu, M. Regulatory T cells and vitamin D status in children with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, H.; Wenes, M.; Stijlemans, B.; Takiishi, T.; Robert, S.; Miani, M.; Eizirik, D.L.; Gysemans, C.; Mathieu, C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 curtails the inflammatory and T cell stimulatory capacity of macrophages through an IL-10-dependent mechanism. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.H.; Ho, T.-R.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Matthews, N.C.; Chevretton, E.; Mudway, I.; Kelly, F.J.; Hawrylowicz, C.M. Vitamin D counteracts an IL-23-dependent IL-17A+IFN-γ+ response driven by urban particulate matter. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Pantalena, L.-C.; Liu, X.K.; Gaffen, S.L.; Liu, H.; Rohowsky-Kochan, C.; Ichiyama, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Steinman, L.; Christakos, S.; et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ameliorates Th17 autoimmunity via transcriptional modulation of interleukin-17A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3653–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.-H.; Cha, H.-R.; Lee, D.-S.; Seo, K.Y.; Kweon, M.-N. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits the differentiation and migration of TH17 cells to protect against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, E.M.; Asmawidjaja, P.S.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Mus, A.M.C.; van Driel, M.; Hazes, J.M.W.; van Leeuwen, J.P.T.M.; Lubberts, E. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates Th17 polarization and interleukin-22 expression by memory T cells from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.T.; Lee, Y.K.; Maynard, C.L.; Oliver, J.R.; Bikle, D.D.; Jetten, A.M.; Weaver, C.T. Lineage-specific effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the development of effector CD4 T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treiber, G.; Prietl, B.; Fröhlich-Reiterer, E.; Lechner, E.; Ribitsch, A.; Fritsch, M.; Rami-Merhar, B.; Steigleder-Schweiger, C.; Graninger, W.; Borkenstein, M.; et al. Cholecalciferol supplementation improves suppressive capacity of regulatory T-cells in young patients with new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus—A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 161, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wan, Y. Tolerogenic dendritic cells and their potential applications. Immunology 2011, 132, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, G.; Adorini, L. 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piemonti, L.; Monti, P.; Sironi, M.; Fraticelli, P.; Leone, B.E.; Dal Cin, E.; Allavena, P.; Di Carlo, V. Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, W.W.J.; Laban, S.; Kleijwegt, F.S.; van der Slik, A.R.; Roep, B.O. Induction of Treg by monocyte-derived DC modulated by vitamin D3 or dexamethasone: Differential role for PD-L1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Halteren, A.G.S.; Tysma, O.M.; van Etten, E.; Mathieu, C.; Roep, B.O. 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or analogue treated dendritic cells modulate human autoreactive T cells via the selective induction of apoptosis. J. Autoimmun. 2004, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, J.M.; Archer, D.C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents the in vivo induction of murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. JCI 1991, 87, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Hayes, C.E.; DeLuca, H.F. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 reversibly blocks the progression of relapsing encephalomyelitis, a model of multiple sclerosis. PNAS 1996, 93, 7861–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Hayes, C.E.; DeLuca, H.F. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol inhibits the progression of arthritis in murine models of human arthritis. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassan Mohammed, H.; Mirshafiey, A.; Vahedi, H.; Hemmasi, G.; Moussavi NaslKhameneh, A.; Parastouei, K.; Saboor-Yaraghi, A.A. Immunoregulation of inflammatory and inhibitory cytokines by vitamin D3 in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 85, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Simpson, S.; van der Mei, I.; Blizzard, L.; Havrdova, E.; Horakova, D.; Shaygannejad, V.; Lugaresi, A.; Izquierdo, G.; Trojano, M.; et al. Higher latitude is significantly associated with an earlier age of disease onset in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, J.H.; Søndergaard, H.B.; Sørensen, P.S.; Sellebjerg, F.; Oturai, A.B. Vitamin D supplementation reduces relapse rate in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients treated with natalizumab. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2016, 10, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, G.A.; Marck, C.H.; Weiland, T.J.; Pereira, N.; van der Meer, D.M.; Hadgkiss, E.J. Latitude, sun exposure and vitamin D supplementation: Associations with quality of life and disease outcomes in a large international cohort of people with multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, S.B.; Garland, C.F.; Gorham, E.D.; Garland, F.C. The association between ultraviolet B irradiance, vitamin D status and incidence rates of type 1 diabetes in 51 regions worldwide. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosecrans, R.; Dohnal, J.C. Seasonal vitamin D changes and the impact on health risk assessment. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Rhee, H.J.; de Vries, E.; Coebergh, J.W. Regular sun exposure benefits health. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 97, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi, A.; Leighton, H.; Burstein, B.; Xue, X. Latitude, sunshine, and human lactase phenotype distributions may contribute to geographic patterns of modern disease: The inflammatory bowel disease model. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G.; Ramagopalan, S. The month of birth effect in multiple sclerosis: Systematic review, meta-analysis and effect of latitude. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.G.; Bae, S.-C.; Lee, Y.H. Association between vitamin D intake and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipitis, C.S.; Akobeng, A.K. Vitamin D supplementation in early childhood and risk of type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.-G.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Han, S.-F.; Qin, L.-Q. Vitamin D intake and risk of type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3551–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhuang, Q.-S.; Ji, H.-F. Assessment of vitamin D levels in type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients: Results from metaanalysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Lv, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Han, F.; Wang, H.; Bi, S. Vitamin D status and the risk of multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 570, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Davies, M.L.; Chen, W. Serum vitamin D Level and rheumatoid arthritis disease activity: Review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pinto, R.; Pietropaoli, D.; Chandar, A.K.; Ferri, C.; Cominelli, F. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and vitamin D deficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Li, D.; Xiang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yu, C. Association between 25(OH)D level, ultraviolet exposure, geographical location, and inflammatory bowel disease activity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, M.; Saneei, P.; Siassi, F.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Vitamin D status in relation to Crohn’s disease: Meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrition 2016, 32, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, C. Lower serum 25 (OH) D concentrations in type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 108, e71–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitocco, D.; Crinò, A.; Di Stasio, E.; Manfrini, S.; Guglielmi, C.; Spera, S.; Anguissola, G.B.; Visalli, N.; Suraci, C.; Matteoli, M.C.; et al. The effects of calcitriol and nicotinamide on residual pancreatic beta-cell function in patients with recent-onset Type 1 diabetes (IMDIAB XI). Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Kaupper, T.; Adler, K.; Foersch, J.; Bonifacio, E.; Ziegler, A.-G. No effect of the 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on beta-cell residual function and insulin requirement in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, D.T.; Marakaki, C.; Fretzayas, A.; Nicolaidou, P.; Papadimitriou, A. Negativation of type 1 diabetes-associated autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase and insulin in children treated with oral calcitriol. J. Diabetes 2013, 5, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekar, P.; Swier, V.J.; Fleegel, J.P.; Boosani, C.S.; Radwan, M.M.; Agrawal, D.K. Vitamin D and macrophage polarization in epicardial adipose tissue of atherosclerotic swine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; You, Y.; Swier, V.; Tang, L.; Radwan, M.M.; Pandya, A.N.; Agrawal, D.K. Vitamin D protects against atherosclerosis via regulation of cholesterol efflux and macrophage polarization in hypercholesterolemic swine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozio, E.; Briganti, S.; Vianello, E.; Dogliotti, G.; Barassi, A.; Malavazos, A.E.; Ermetici, F.; Morricone, L.; Sigruener, A.; Schmitz, G.; et al. Epicardial adipose tissue inflammation is related to vitamin D deficiency in patients affected by coronary artery disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolakis, M.; Armeni, E.; Bakas, P.; Lambrinoudaki, I. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Maturitas 2018, 115, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).