A Unified Fusion Framework with Robust LSA for Multi-Source InSAR Displacement Monitoring
Highlights
- A Practical Framework for Robust InSAR Fusion: This study provides a practical, systematic workflow that integrates multi-temporal InSAR processing, homonymous Persistent Scatterer (PS) generation, and robust Least Squares Adjustment (LSA). It offers a directly applicable solution for enhancing the reliability of displacement monitoring in the case of a small number of SAR datasets.
- Theoretical Foundation for Multi-Source InSAR Data Reliability: The paper establishes a mathematical foundation for multi-source InSAR fusion incorporating formal reliability parameters (internal and external). This provides a theoretical benchmark for evaluating and improving the integrity of fused datasets, moving beyond simple data combination to statistically robust integration.
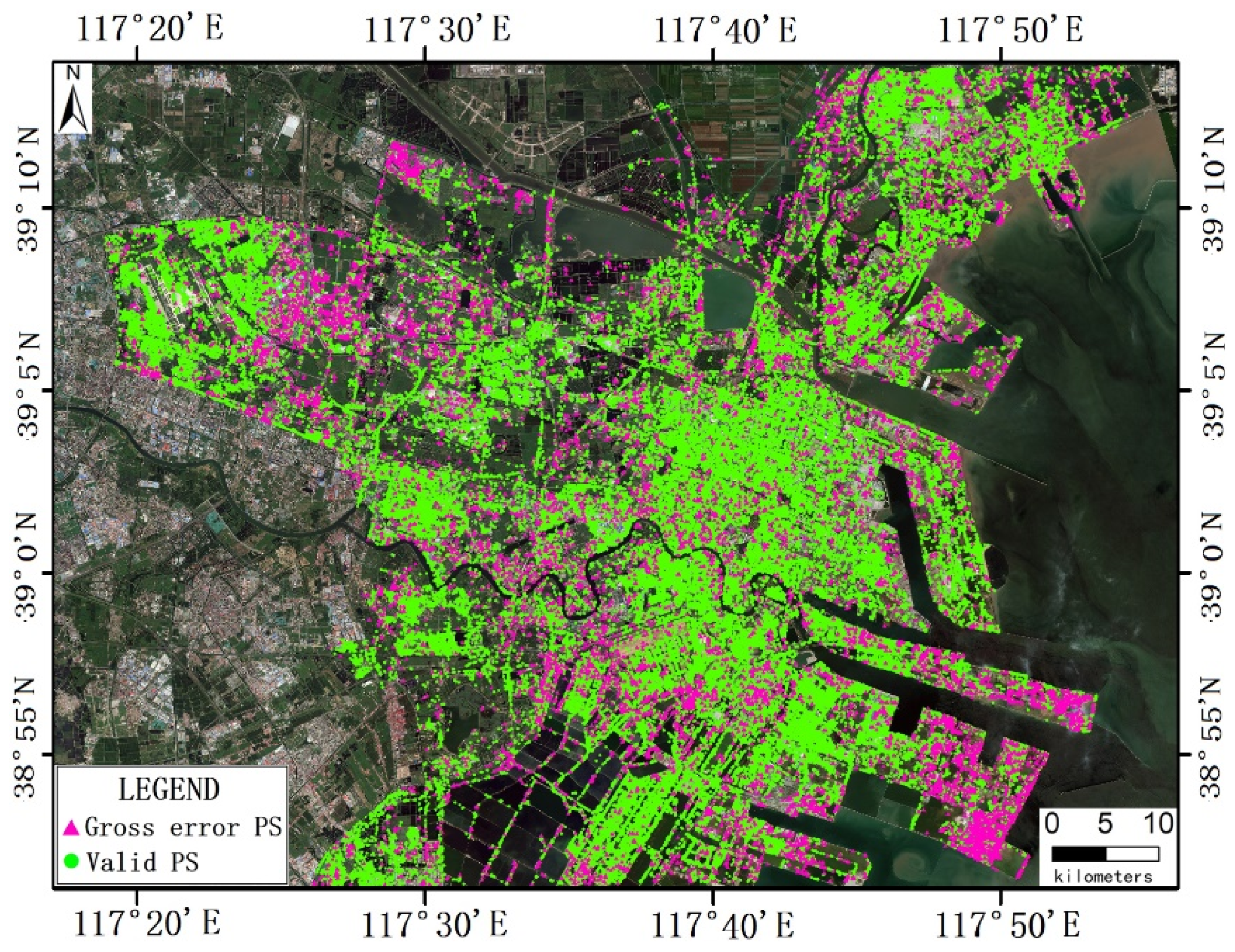
- Effective Gross Error Identification: The proposed robust LSA framework successfully identified and eliminated gross errors from 11.1% of homonymous PS sets, significantly cleansing multi-source InSAR data contaminated by phase unwrapping failures.
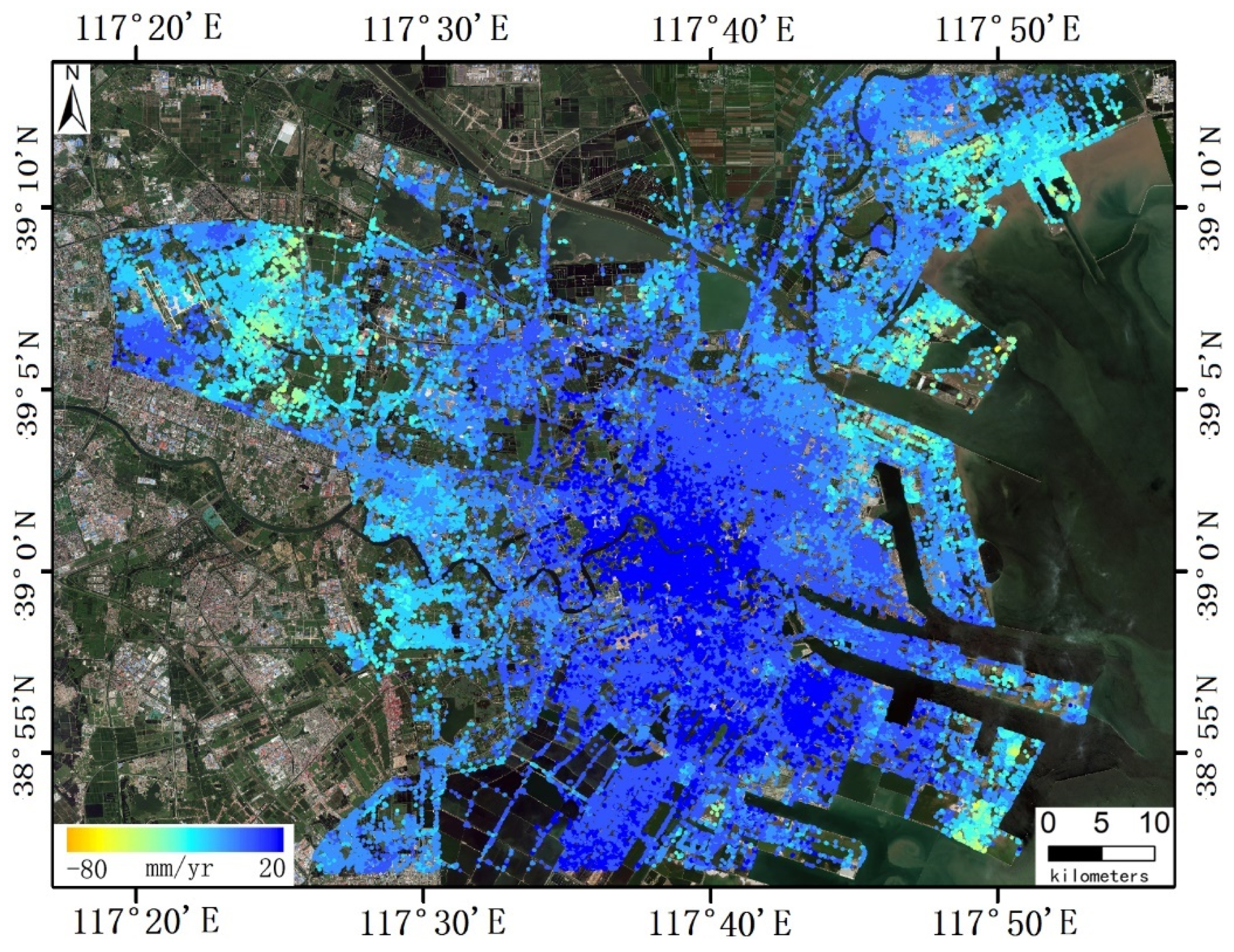
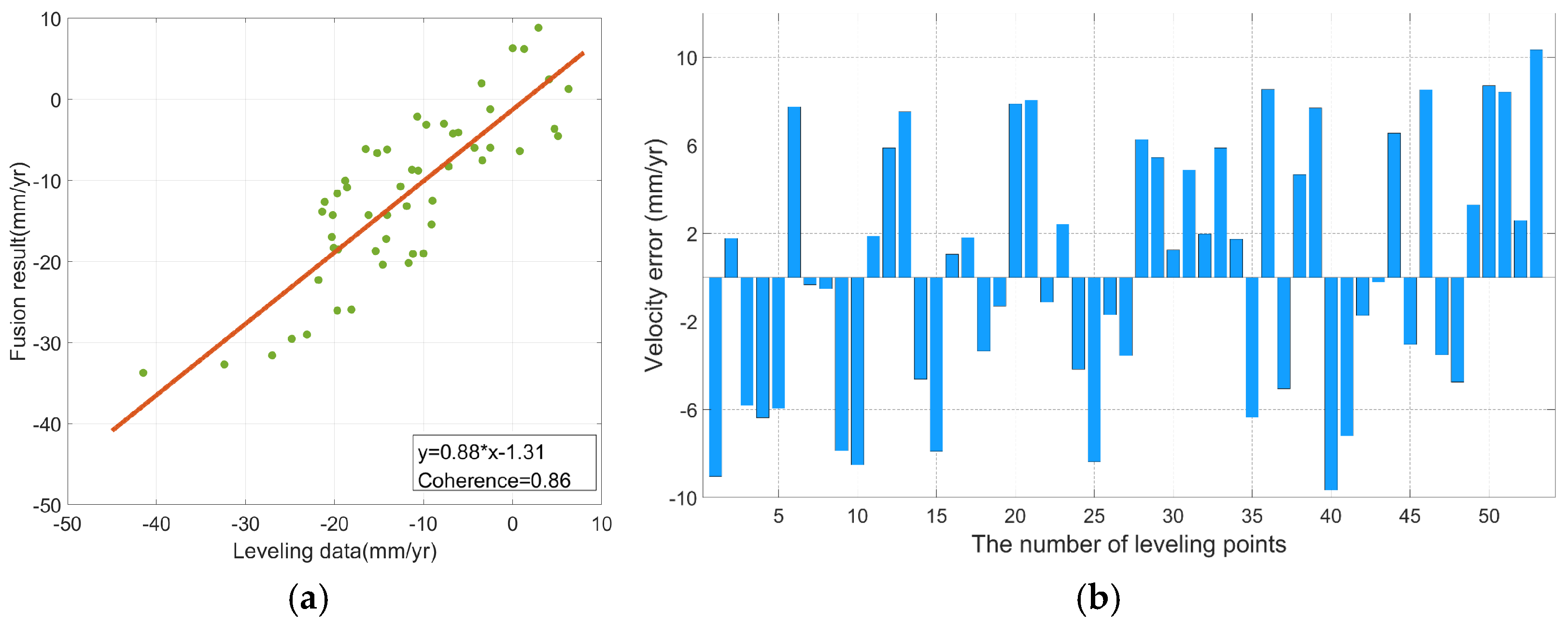
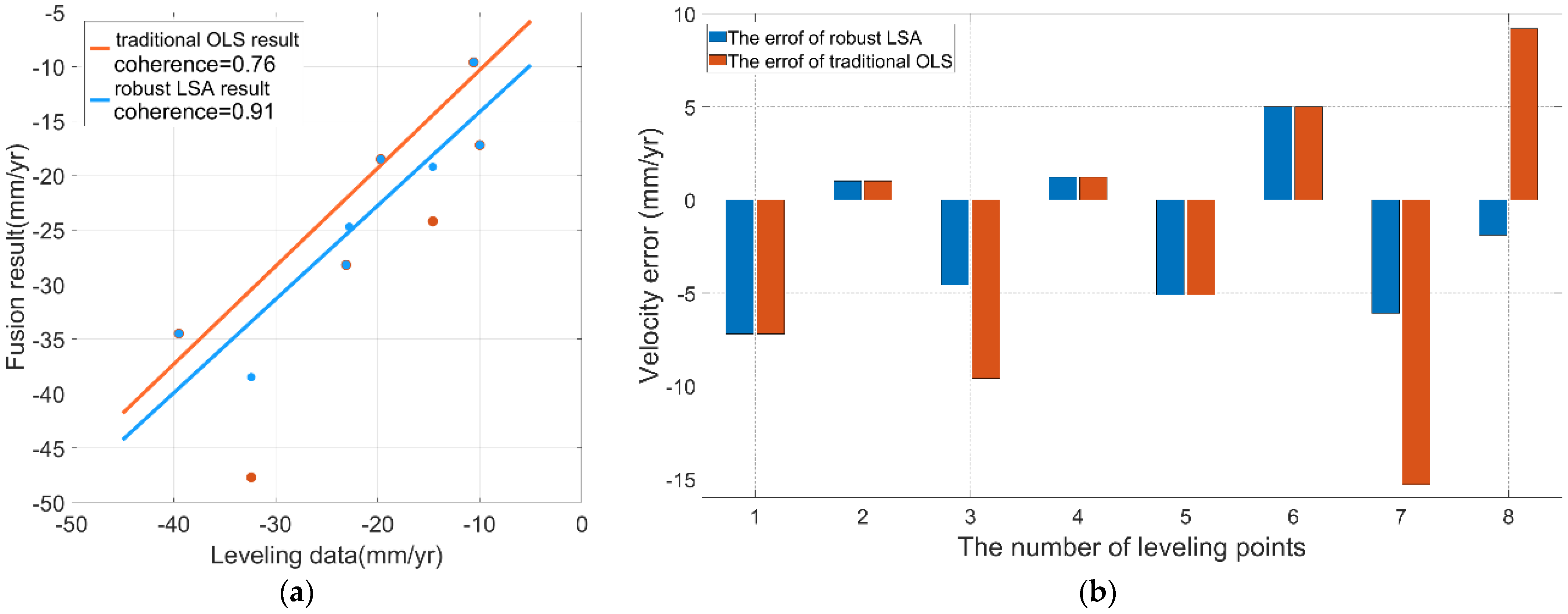
- Enhanced Displacement Monitoring Accuracy: Validation with high-precision leveling data showed the framework achieves a vertical displacement estimation accuracy of 5.7 mm/yr. A localized analysis incorporating both leveling validation and time series in a challenging area demonstrated a 42.5% improvement in accuracy compared to traditional Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) methods.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Description
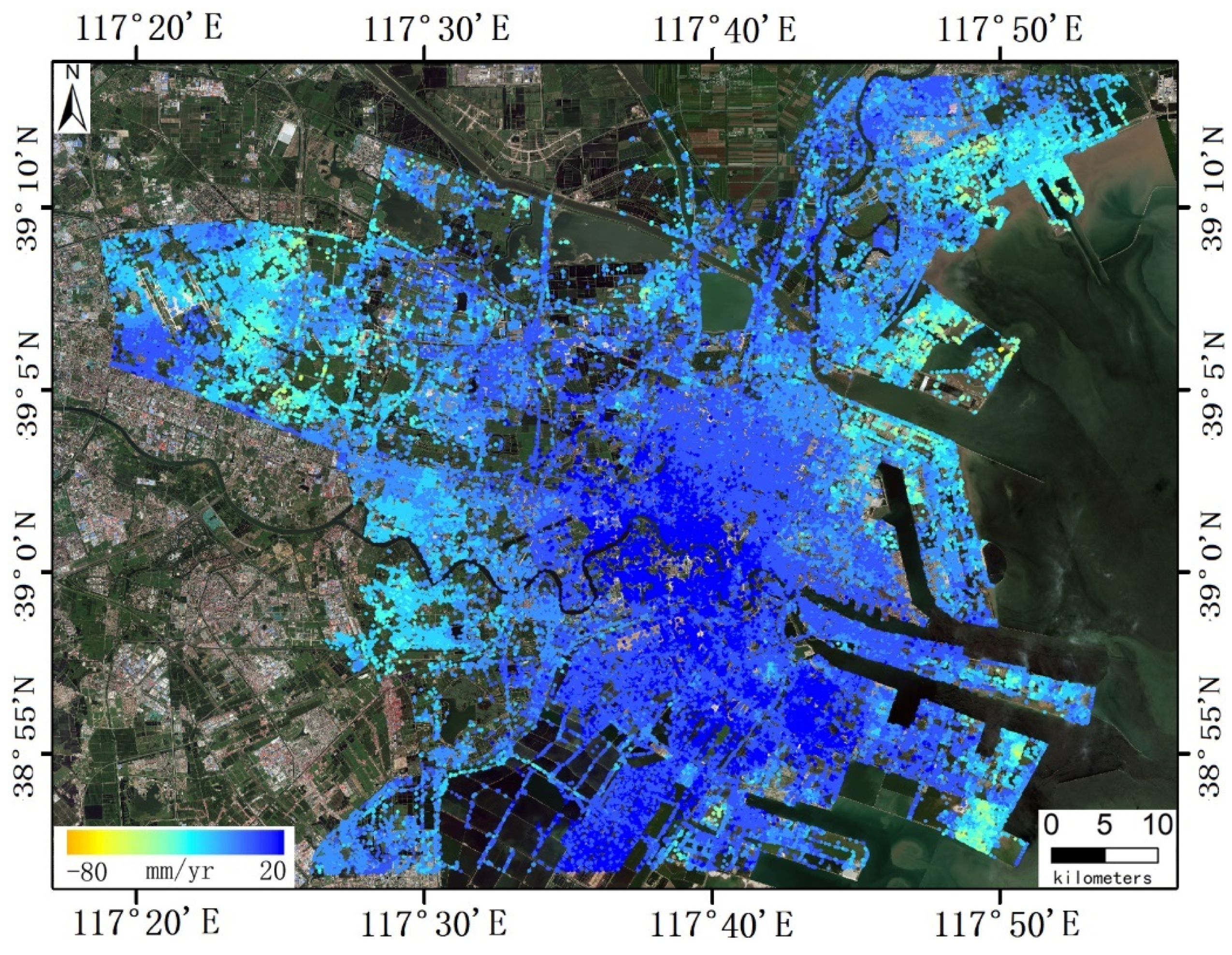
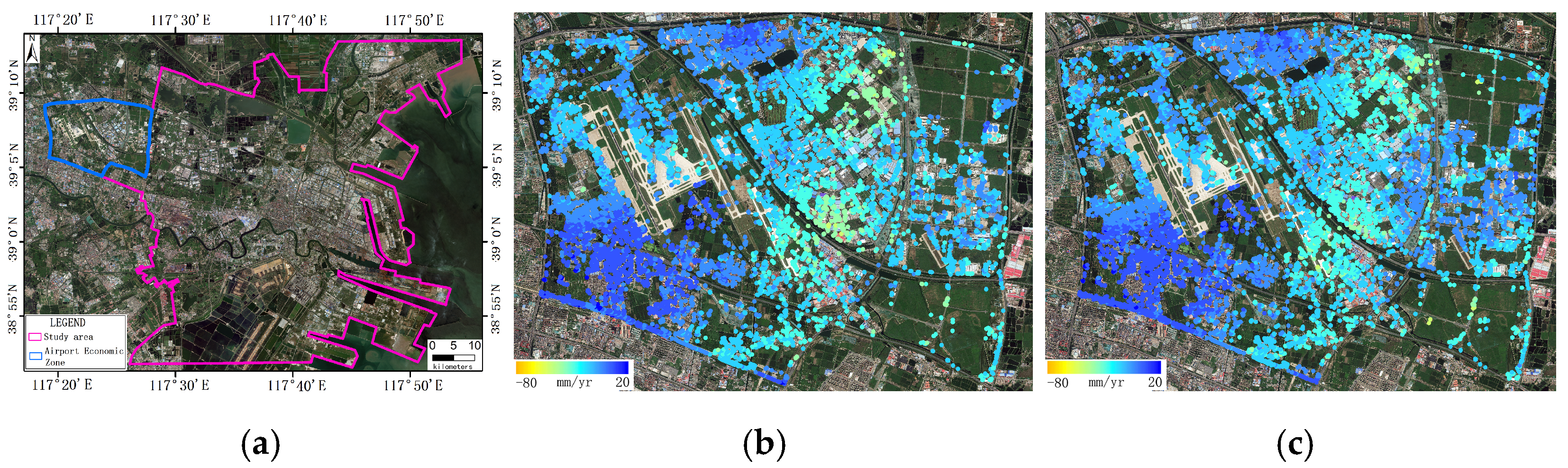
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Multi-Source SAR Datasets
2.3. Ancillary Data for Validation
3. Methods
3.1. Multi-Source InSAR Data Fusion Method with Robust LSA
3.1.1. Multi-Source InSAR Data Fusion Model
3.1.2. GED Method
3.1.3. LSA Method
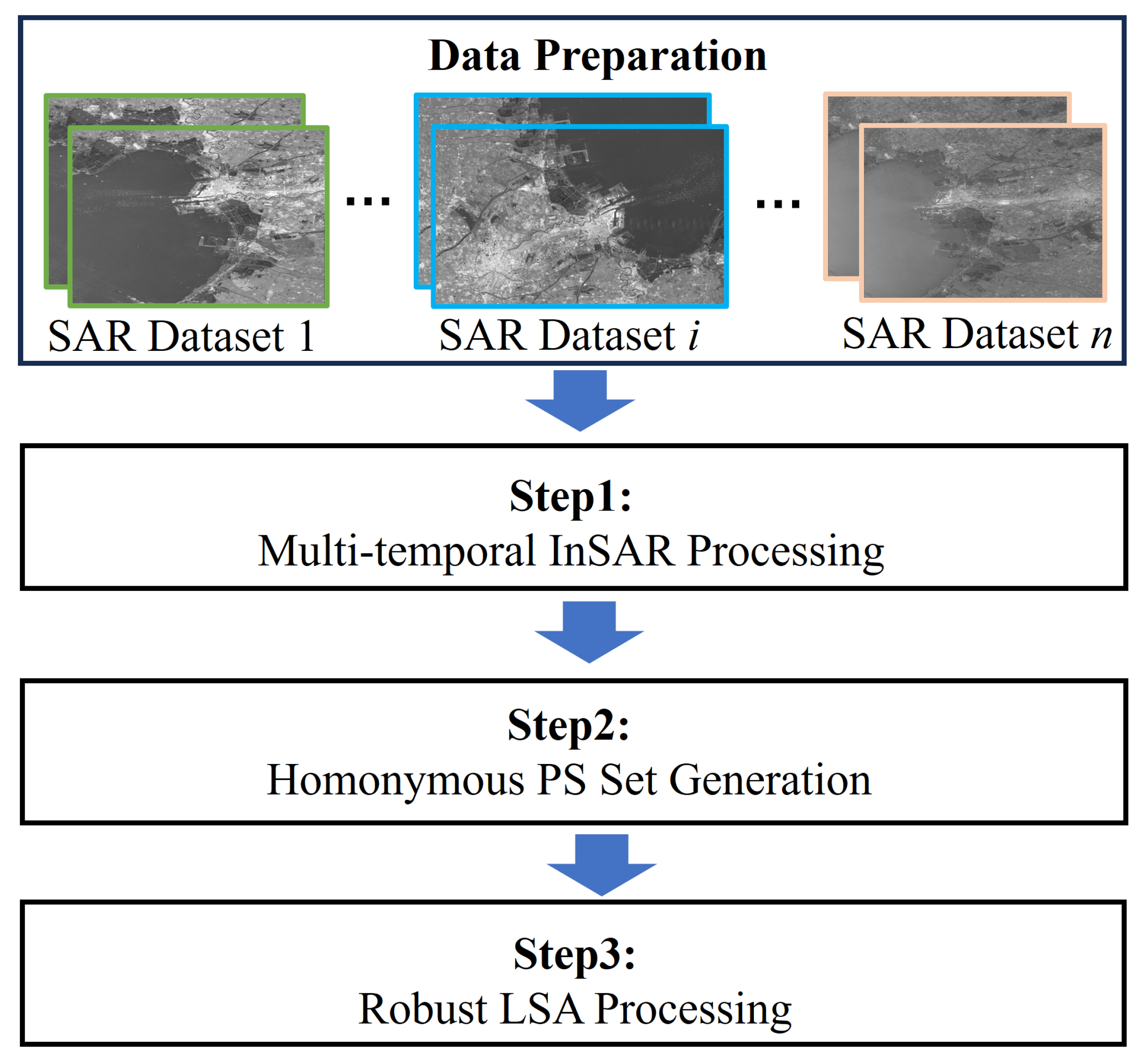
3.2. Multi-Source InSAR Data Fusion Workflow with Robust LSA
3.2.1. MT-InSAR Processing
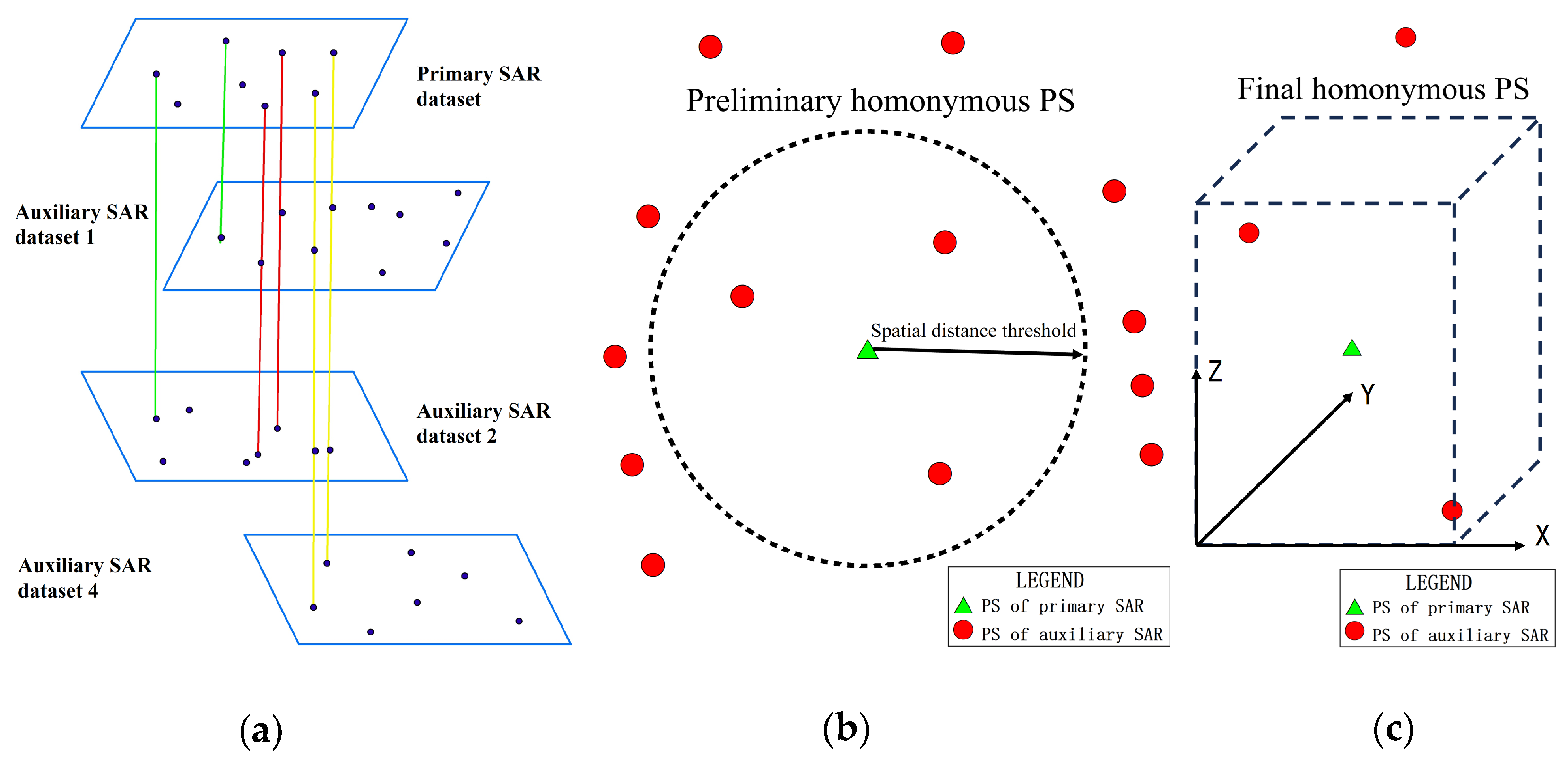
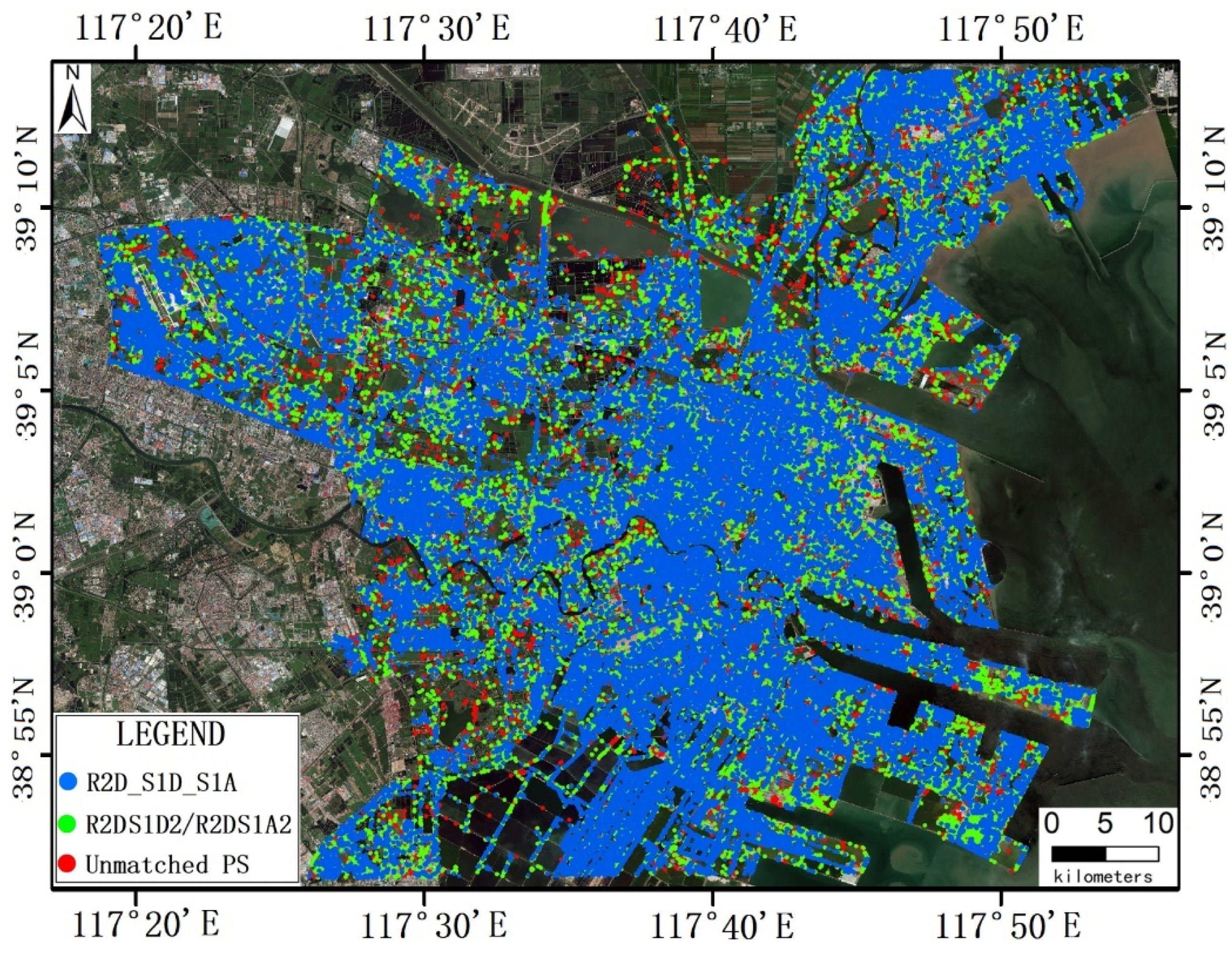
3.2.2. Homonymous PS Set Generation
3.2.3. Robust LSA Processing
4. Result and Analysis
4.1. MT-InSAR Processing of Multi-Source SAR Datasets
4.1.1. Key Parameters of MT-InSAR Processing
4.1.2. Multi-Source InSAR Results
4.2. Generation of the Homonymous PS Sets
4.2.1. Selection of the Primary SAR Dataset from Three InSAR Datasets
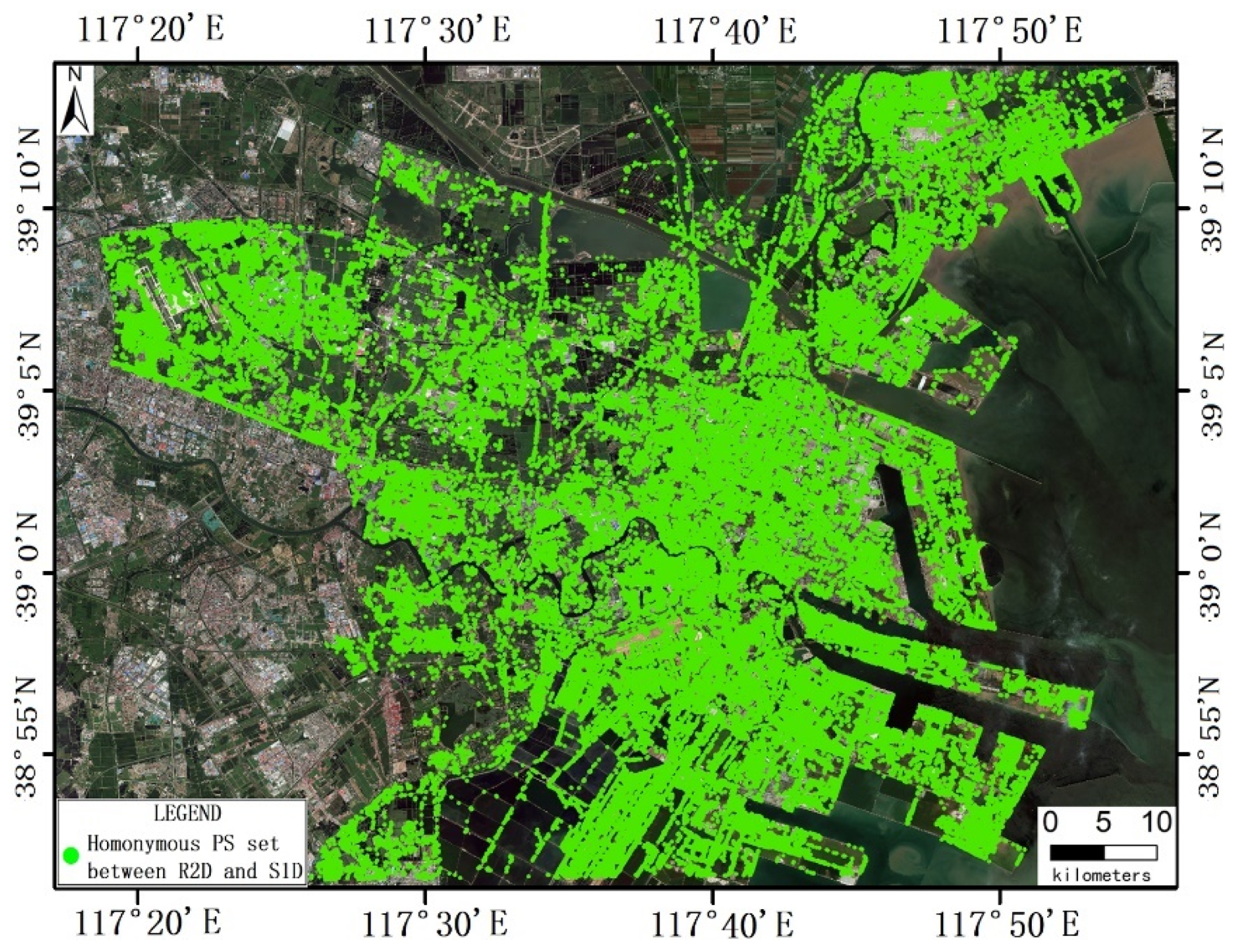
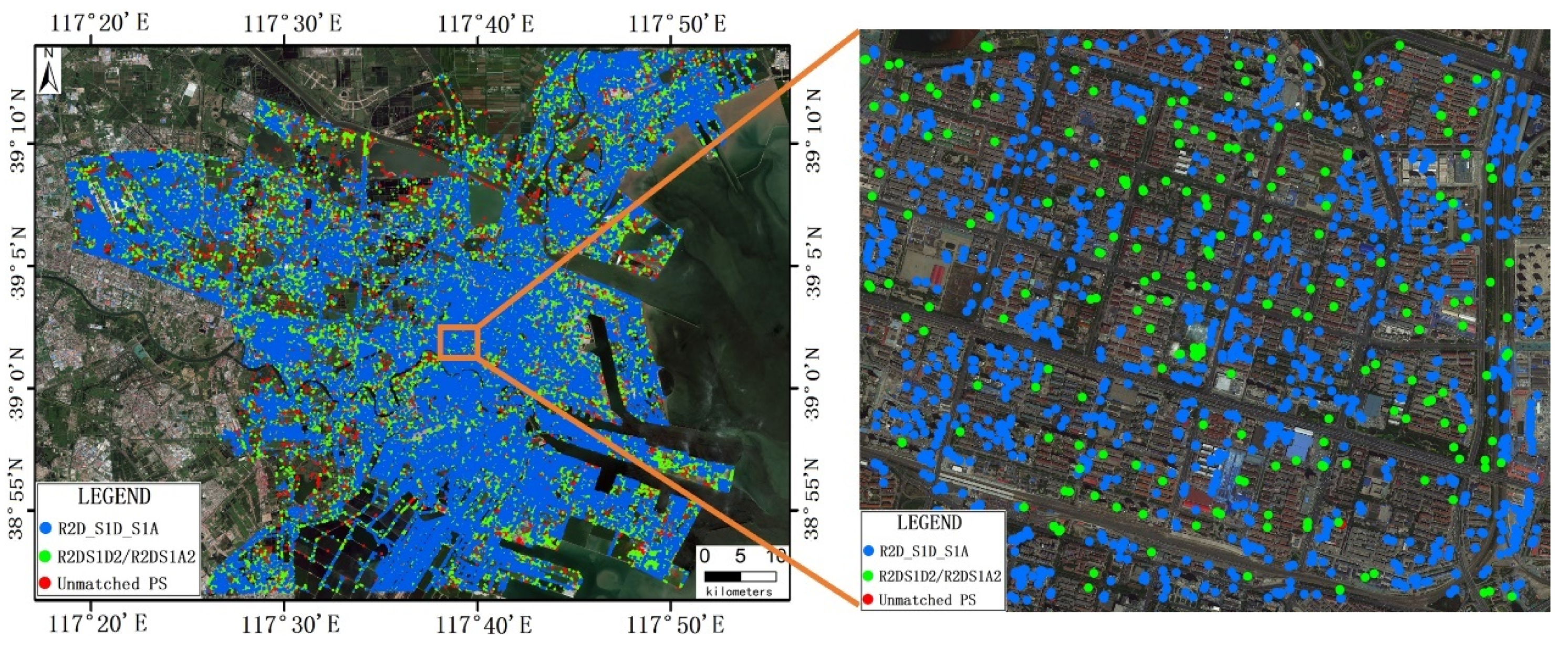
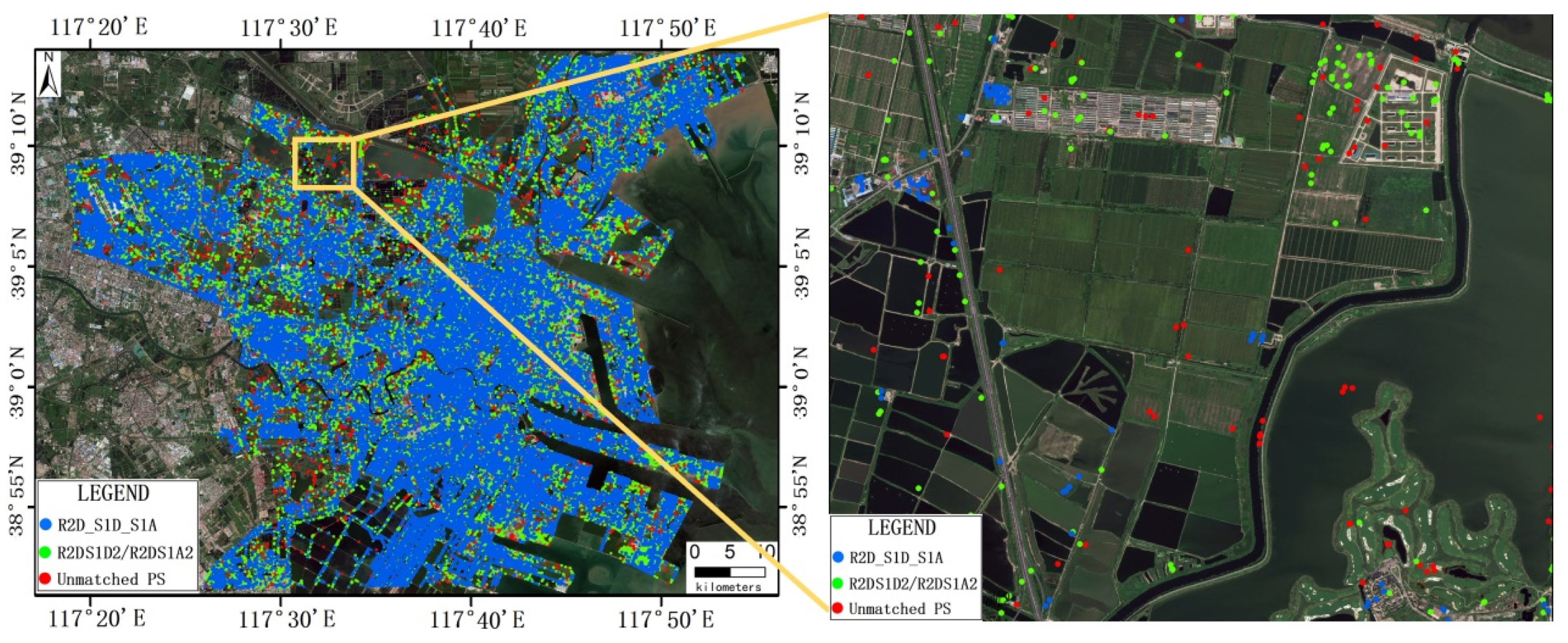
4.2.2. Generation of Homonymous PS Sets Between R2D and S1D
4.2.3. Generation of Homonymous PS Sets Across Three InSAR Datasets
4.3. Multi-Source InSAR Data Fusion with Robust LSA
4.3.1. Implementation of Multi-Source InSAR Fusion Model
4.3.2. Data Fusion Processing with Robust LSA in a Single PS Set
4.3.3. Data Fusion Processing with Robust LSA in Region-Wide PS Sets
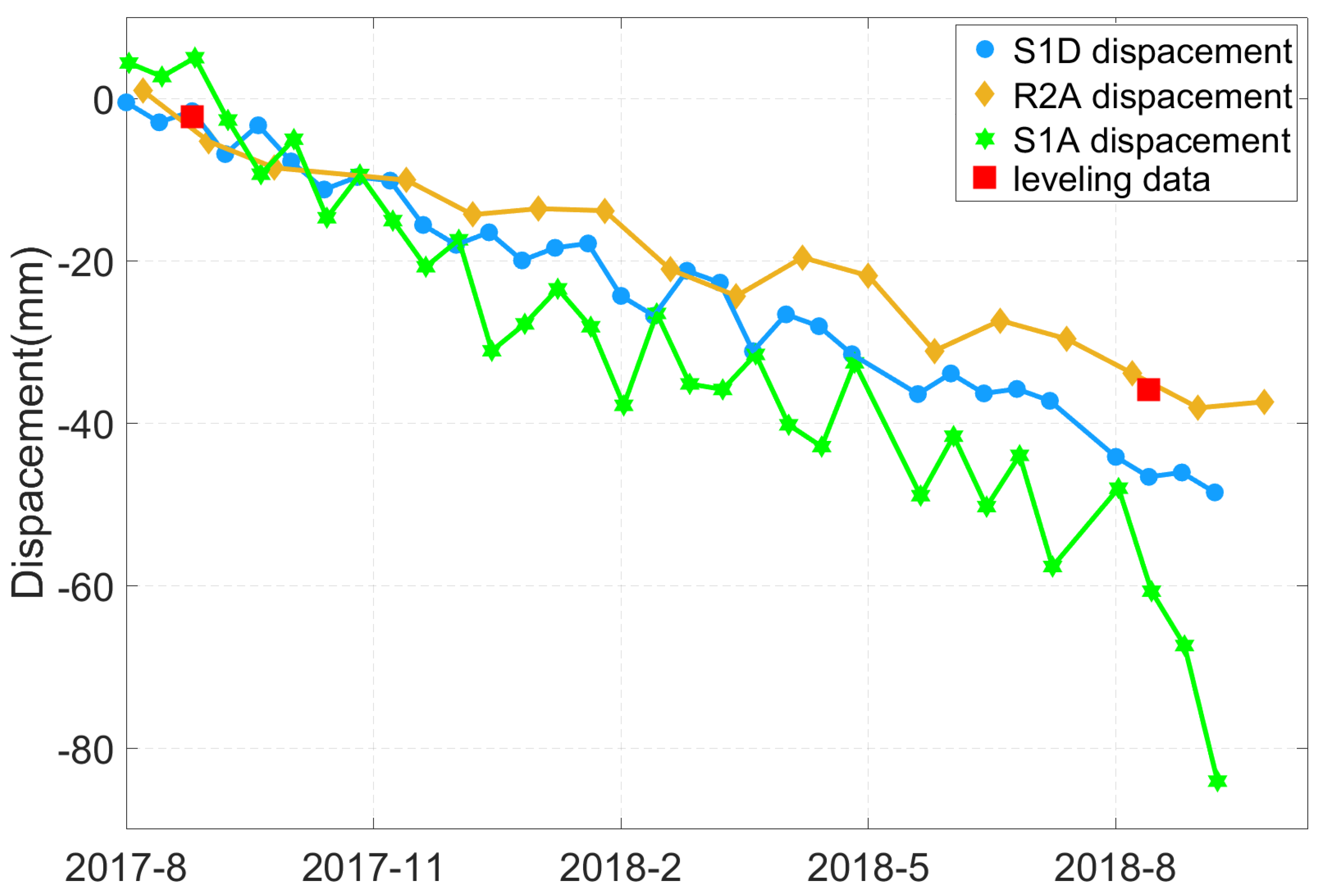
4.3.4. Validation of Region Displacement Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance Validation Against Traditional OLS
5.1.1. The Result of Traditional OLS
5.1.2. The Difference Between Robust LSA and OLS
5.1.3. The Time Series Analysis of Typical Set
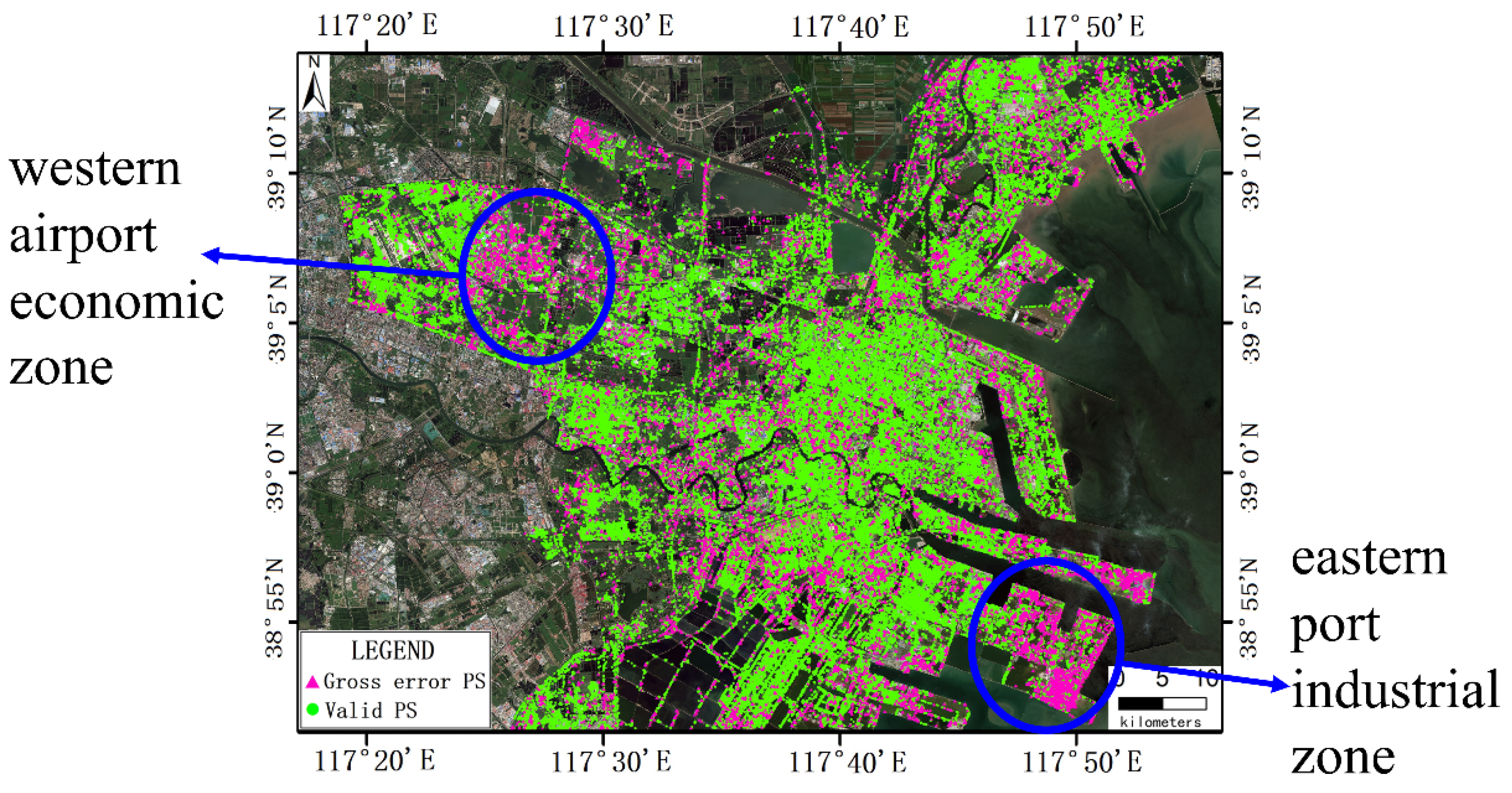
5.2. Robust LSA Analysis Across Distinct Regions
5.2.1. Reliability Parameters
5.2.2. Methodology for Calculating Reliability Parameters
5.2.3. Analysis of Reliability Parameters Between Distinct Regions
5.2.4. Analysis of GED Results Between Distinct Regions
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-series algorithms, applications, and challenges—ScienceDirect. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Pang, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Wei, S.; Yuan, Z.; Fang, Y. Applications and Advancements of Spaceborne InSAR in Landslide Monitoring and Susceptibility Mapping: A Systematic Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Hu, X.; Tao, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Hu, L.; Liang, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. A national-scale assessment of land subsidence in China’s major cities. Science 2024, 384, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, L.; Barbolla, D.F.; Torre, C.; Settembrini, S.; Leucci, G. Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods. Sensors 2024, 24, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbul, O.S.; Rashid, M. Algorithms and Techniques for the Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges: Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohmishi, M.; Kaewunruen, S.; Chang, L.; Guo, Y. Advancing railway track health monitoring: Integrating GPR, InSAR and machine learning for enhanced asset management. Autom. Constr. 2024, 162, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Intrieri, E.; Tofani, V.; Gigli, G.; Raspini, F. Landslide detection, monitoring and prediction with remote-sensing techniques. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Zhu, W.; Tomás, R. Coupling effect of impoundment and irrigation on landslide movement in Maoergai Reservoir area revealed by multi-platform InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 129, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, P.; Dusar, M.; Pirard, E.; Verbeurgt, G.; Choopani, A.; Devleeschouwer, X. Post mining ground deformations transition related to coal mines closure in the Campine Coal Basin, Belgium, evidenced by three decades of MT-InSAR data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Niu, Y.; Gong, J.; Yang, Y. Analysis of surface deformation and related factors over mining areas based on InSAR: A case study of Fengcheng mine. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 48, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yan, Y.; Dai, H.; He, X.; Lv, B.; Han, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Prediction Method for Dynamic Subsidence Basin in Mining Area Based on SBAS-InSAR and Time Function. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xu, B.; Wei, J.; Zuo, B.; Su, Y.; Zeng, Y. Correcting the location error of persistent scatterers in an urban area based on adaptive building contours matching: A case study of Changsha. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Madson, A. Error sources of interferometric synthetic aperture radar satellites. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ding, R.; Zhao, L.; Niu, Y.; Qu, F.; Ling, Z. Multi-Source SAR-Based Surface Deformation Monitoring and Groundwater Relationship Analysis in the Yellow River Delta, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.; Wdowinski, S. InSAR Detection of Slow Ground Deformation: Taking Advantage of Sentinel-1 Time Series Length in Reducing Error Sources. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry-Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 12–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Balz, T.; Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Li, J.; Han, Y. Multi-sensor InSAR time series fusion for long-term land subsidence monitoring. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 27, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Q.; Gui, R.; Hu, J.; Yang, Q.; Su, G. Long-time surface deformation in Beijing, China for three decades by multi-sensor, multi-track and multi-temporal InSAR seamless connection. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2025, 16, 2478950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Lei, K.; Zhou, C.; Si, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Gao, M. Investigating land subsidence and its causes along Beijing high-speed railway using multi-platform InSAR and a maximum entropy model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Garthwaite, M.C. Resolving Three-Dimensional Surface Motion with InSAR: Constraints from Multi-Geometry Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimaiti, Y.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W. Multi-Sensor InSAR Analysis of Progressive Land Subsidence over the Coastal City of Urayasu, Japan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, C. Ground Subsidence in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region from 1992 to 2014 Revealed by Multiple SAR Stacks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Perissin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. L- and X-Band multi-temporal InSAR analysis of Tianjin subsidence. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7933–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, M.; Yin, Z.; Ma, P.; Perissin, D.; Zhang, Y. Land Subsidence Velocity and High-Speed Railway Risks in the Coastal Cities of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China, with 2015–2021 ALOS PALSAR-2 MultiTemporal InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geudtner, D.; Torres, R. Sentinel-1 system overview and performance. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Gu, H. A Novel Intelligent Learning Method for Identifying Gross Errors in Dam Deformation Monitoring Series. Water 2025, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarda, W. Statistical Concept in Geodesy; Publications on Geodesy (New Series) Geodetic Commission: Delft, The Netherlands, 1967; Volume 2, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Baarda, W. A Testing Procedure for Use in Geodetic Networks; Publications on Geodesy (New Series) Geodetic Commission: Delft, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 2, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Deren, L. Theorie und Untersuchung der Trennbarkeit von Groben Paßpunktfehlern und Systematischen Bildfehlern bei der Photogrammetrischen Punktbestimmung. Doctoral Dissertation, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 1985. Available online: https://www.ifp.uni-stuttgart.de/dokumente/Dissertationen/diss_deren_li_c-324.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Rofatto, V.F.; Matsuoka, M.T.; Klein, I.; Veronez, M.R.; Bonimani, M.L.; Lehmann, R. A half-century of Baarda’s concept of reliability: A review, new perspectives, and applications. Surv. Rev. 2020, 52, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Jazaeri, S. Data-snooping procedure applied to errors-in-variables models. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2013, 57, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Walter, D.; Spreckels, V.; Werner, C.L. Nonuniform ground motion monitoring with TerraSAR-X persistent scatterer interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaldo, G.; Caprino, A.; Lorenzoni, F.; Porto, F. Monitoring displacements and damage detection through satellite MT-InSAR techniques: A new methodology and application to a case study in Rome (Italy). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yan, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z. Monitoring building deformation with InSAR: Experiments and validation. Sensor 2016, 16, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelaar, G. Satellite Radar Interferometry Subsidence Monitoring Techniques; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Wan, X.; Fei, B.; Qiao, Z.; Ge, C.; Minati, F.; Vecchioli, F.; Li, J.; Costantini, M. Detection of building and infrastructure instabilities by automatic spatiotemporal analysis of satellite SAR interferometry measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Savio, G.; Barzaghi, R.; Borghi, A.; Musazzi, S.; Novali, F. Submillimeter Accuracy of InSAR Time Series: Experimental Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yague-Martinez, N.; De Zan, F.; Prats-Iraola, P. Coregistration of Interferometric Stacks of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A. Theory and Statistical Description of the Enhanced Multi-Temporal InSAR (E-MTInSAR) Noise-Filtering Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A. A golden age for spaceborne SAR systems. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar and Wireless Communications (MIKON), Gdańsk, Poland, 16–18 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Zhan, W. Influence of different data fusion methods on the accuracy of three-dimensional displacements field. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gong, H.; Chen, B. Analysis of the superposition effect of land subsidence and sea-level rise in the Tianjin coastal area and its emerging risks. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, J. Research Progress and Future Prospects of Land Subsidence in the Yellow River Delta. Coast. Eng. 2024, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.; Guo, S.; Xia, J. Land Subsidence Monitoring Method in Regions of Variable Radar Reflection Characteristics by Integrating PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Shaffer, S.; Veilleux, L.; Chakraborty, M.; Misra, T. Global persistent SAR sampling with the NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Lokas, S.; Cosimo, G.D.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D. Sentinel 1 evolution: Sentinel-1C and -1D models. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P.; Zhu, W. Risk Assessment of Geological Landslide Hazards Using D-InSAR and Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

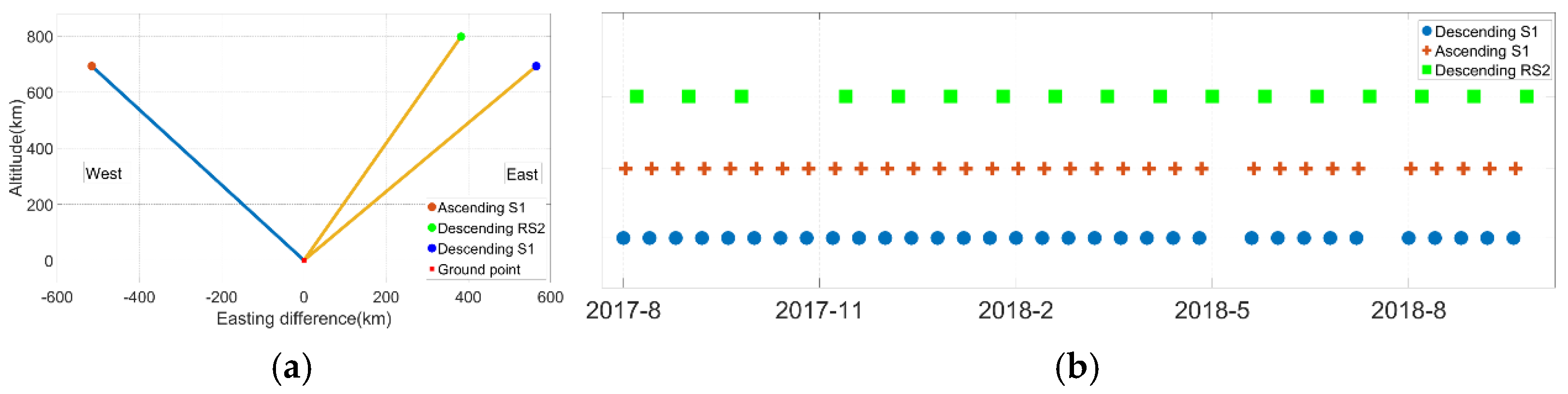







| Name | S1D | S1A | R2D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | C (~5.6 cm) | C (~5.6 cm) | C (~5.6 cm) |
| Incidence Angle | 36.7° | 39.2° | 25.6° |
| Acquisition Mode | TOPS | TOPS | SM |
| Resolution | 15 m | 15 m | 5 m |
| Region | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 0.56 | 5.5 | 2.4 |
| Suburban | 0.26 | 8.1 | 4.0 |
| Region | Number of InSAR Datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 1 | 0 | ∞ | ∞ |
| 3 | 0.26 | 8.1 | 4.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Yan, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, X. A Unified Fusion Framework with Robust LSA for Multi-Source InSAR Displacement Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203469
Yang K, Yan L, Liang J, Wang X. A Unified Fusion Framework with Robust LSA for Multi-Source InSAR Displacement Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(20):3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203469
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kui, Li Yan, Jun Liang, and Xiaoye Wang. 2025. "A Unified Fusion Framework with Robust LSA for Multi-Source InSAR Displacement Monitoring" Remote Sensing 17, no. 20: 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203469
APA StyleYang, K., Yan, L., Liang, J., & Wang, X. (2025). A Unified Fusion Framework with Robust LSA for Multi-Source InSAR Displacement Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 17(20), 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203469








