Fusing BDS and Dihedral Corner Reflectors for High-Precision 3D Deformation Measurement: A Case Study in the Jinsha River Reservoir Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Static Baseline Solution Method for BDS/GNSS
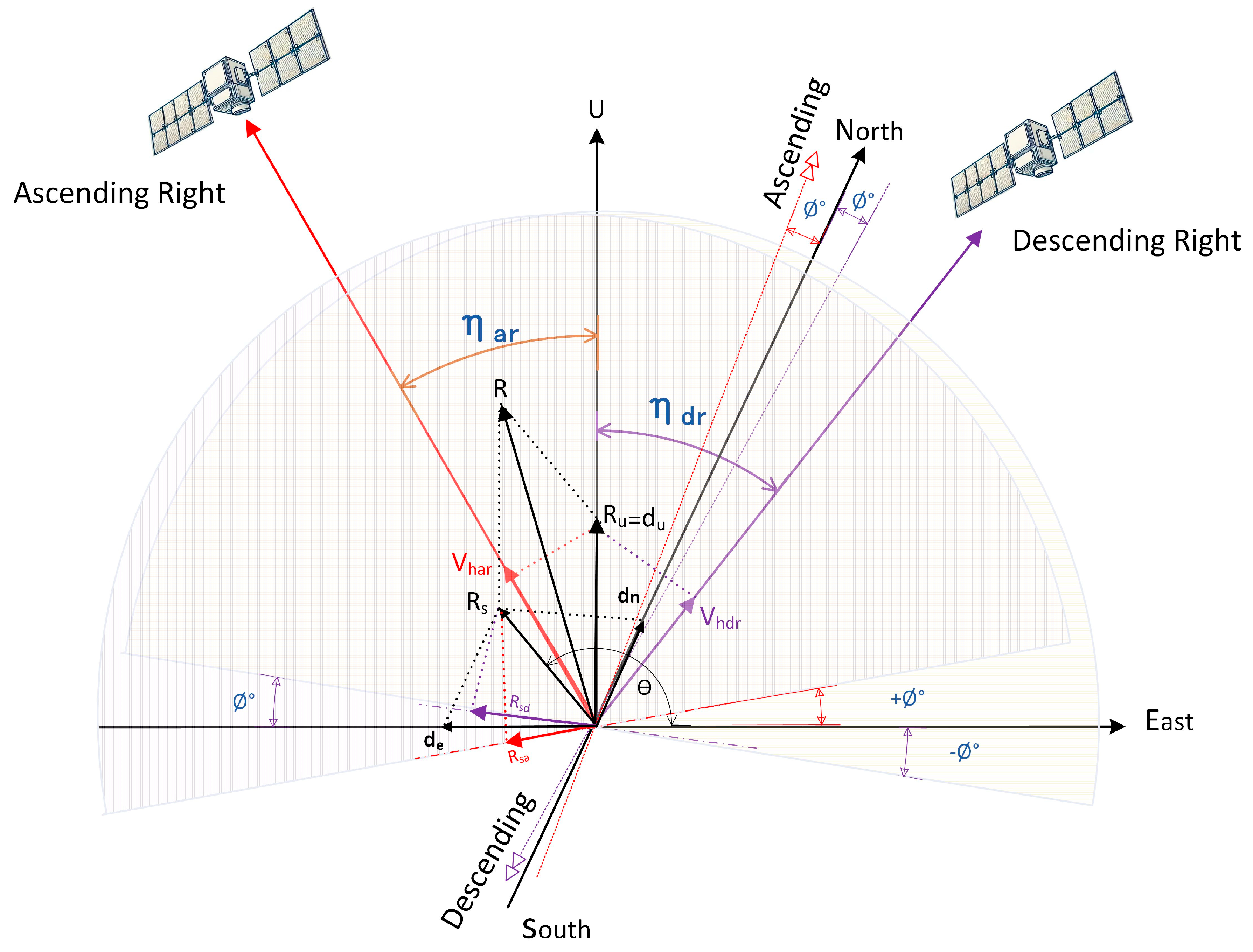
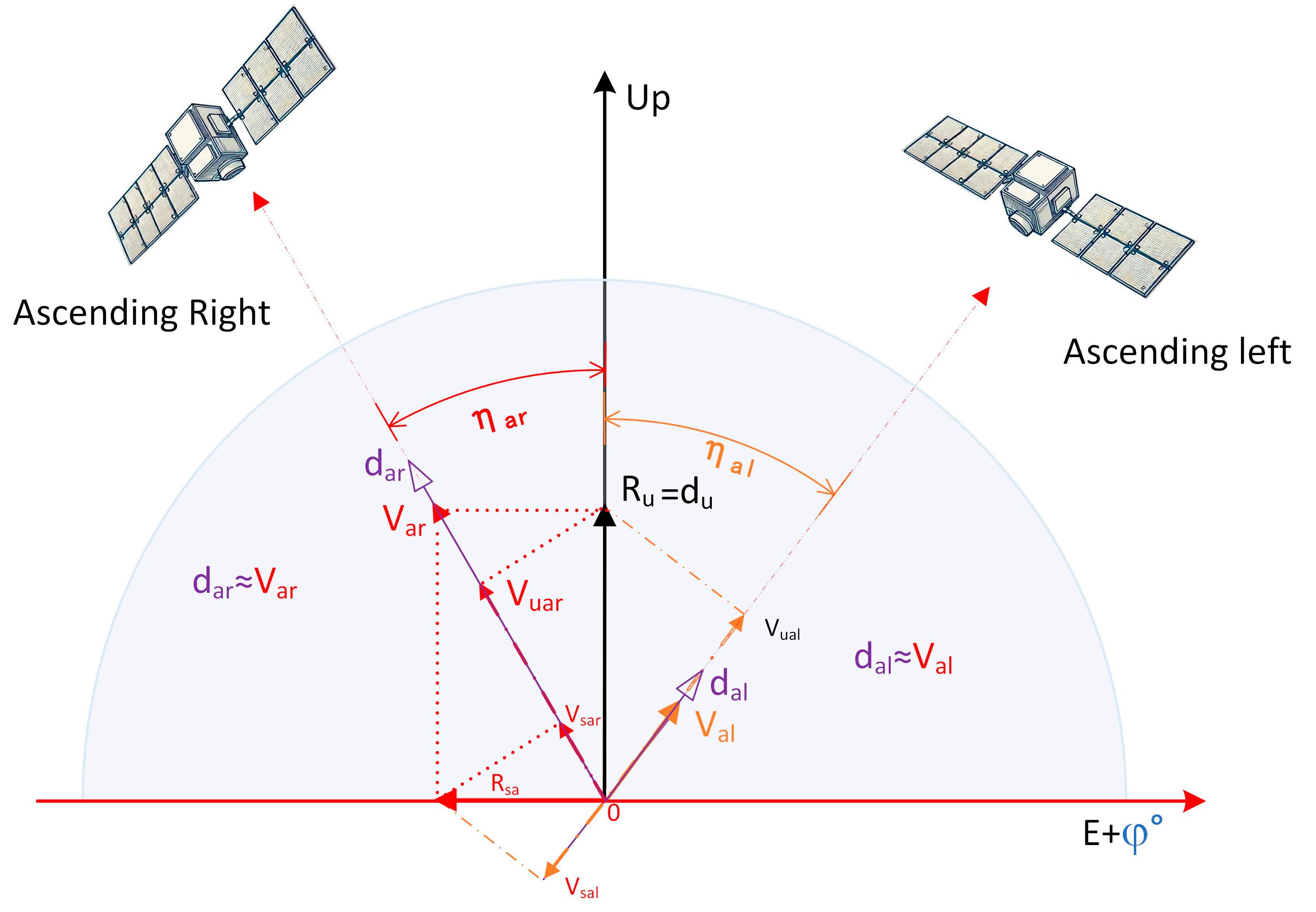
2.2. Geometric Projection Principle for LOS Deformation to Three-Dimensional Deformation
2.3. LOS Deformation Decomposition Model in Local Orthogonal Plane
3. Simulated Horizontal and Vertical Deformation Observation Results
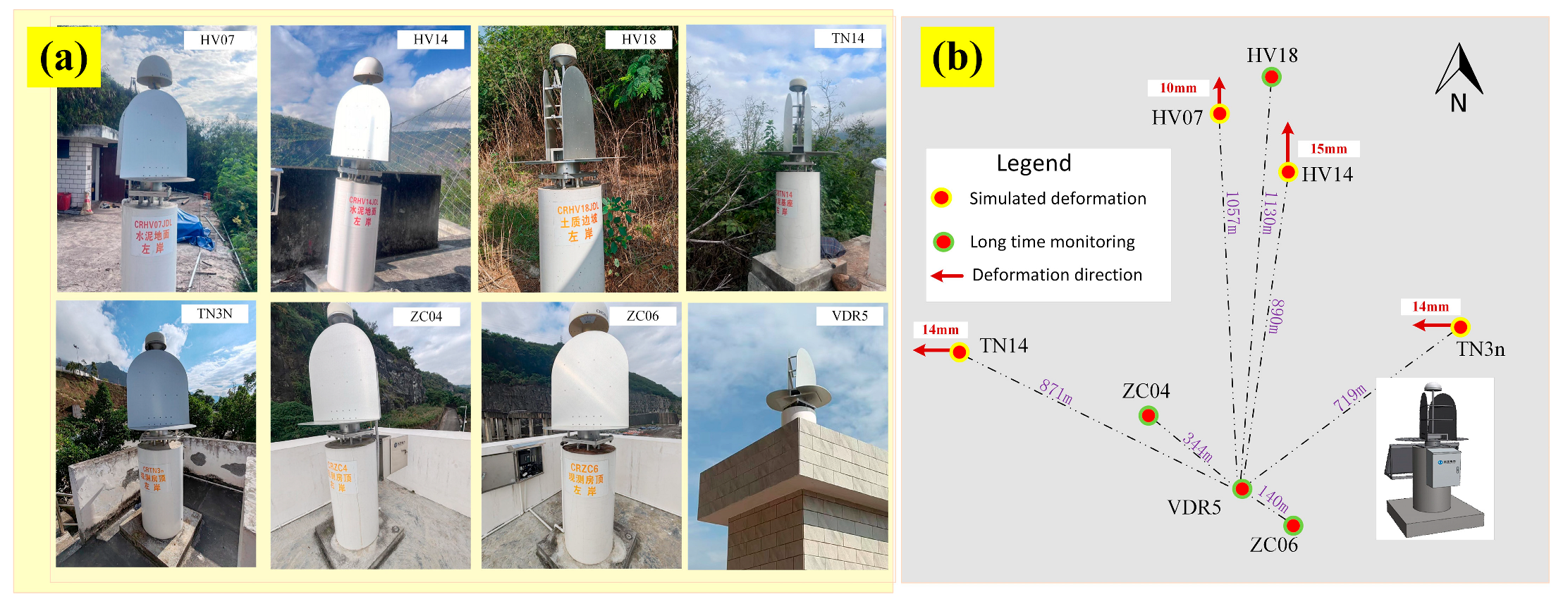
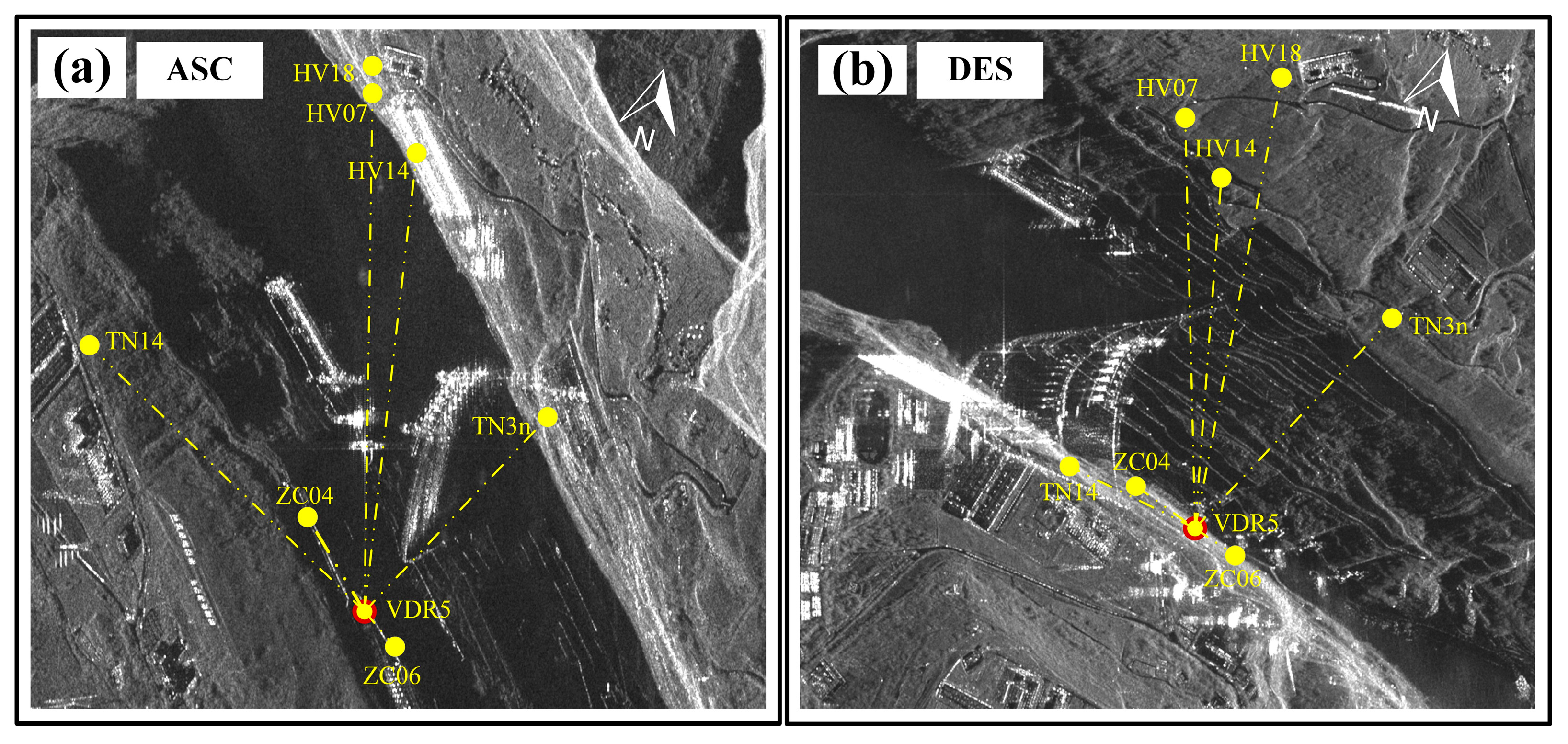
3.1. Overview of the Test Area and SAR Data Acquisition
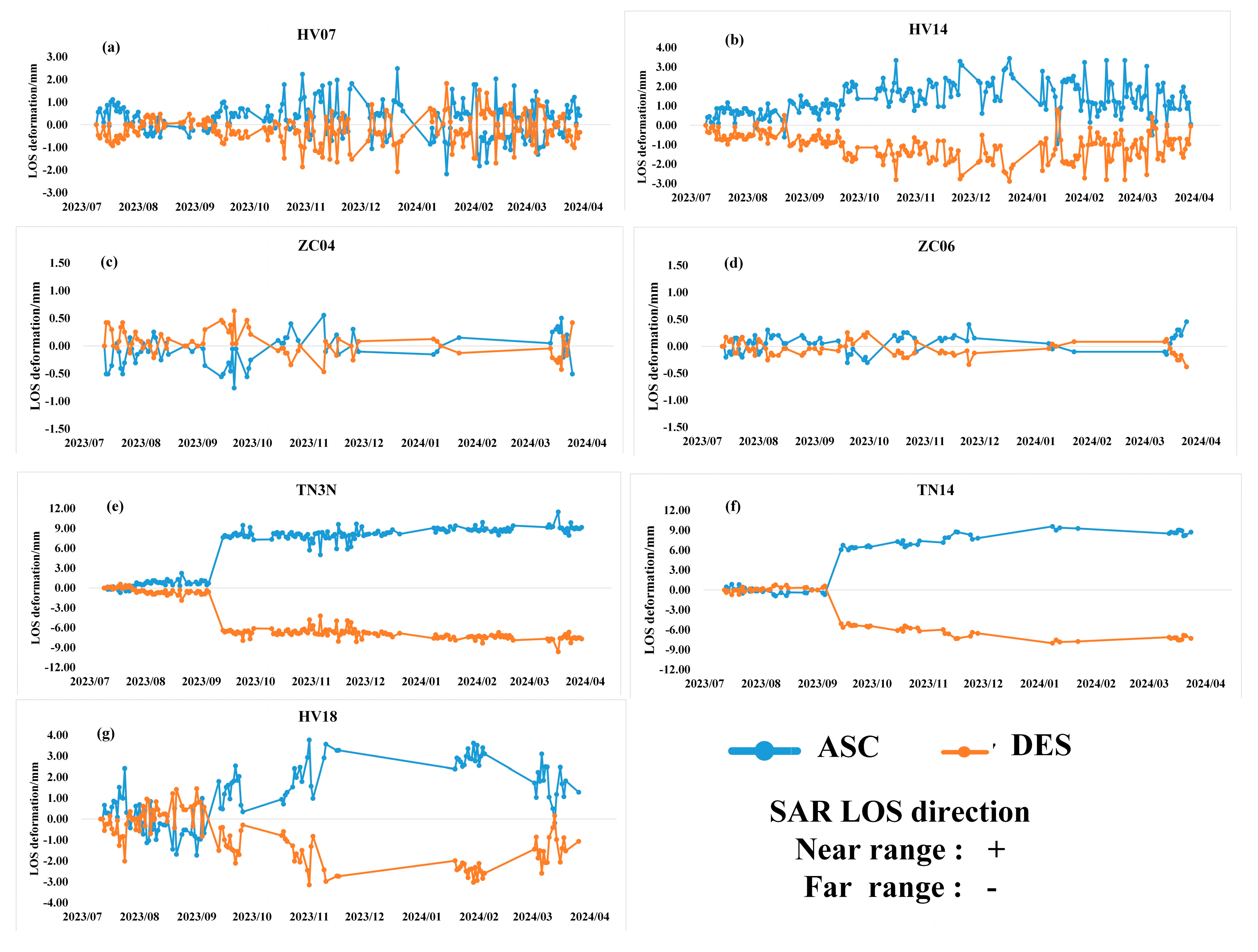
3.2. Simulated Deformation in SAR LOS Geometry
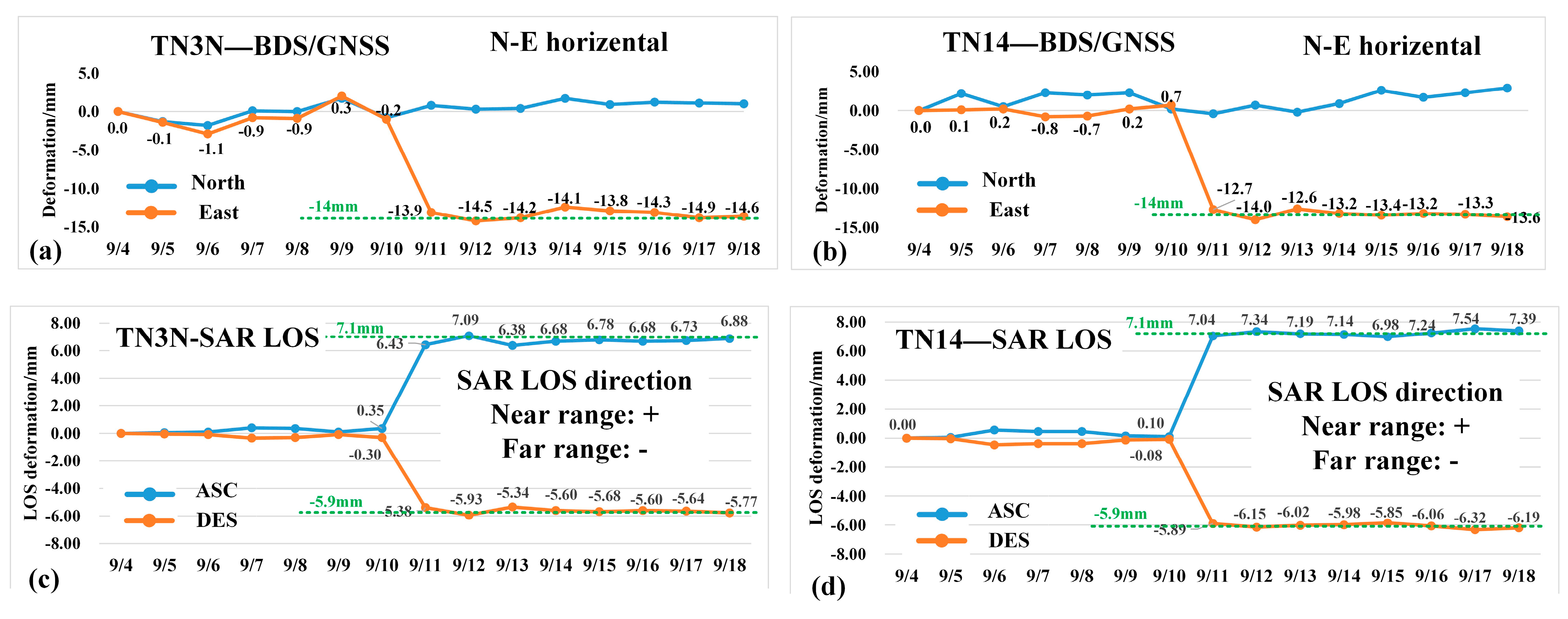
3.2.1. Transfer of BDS/GNSS Horizontal Deformation to SAR LOS Deformation
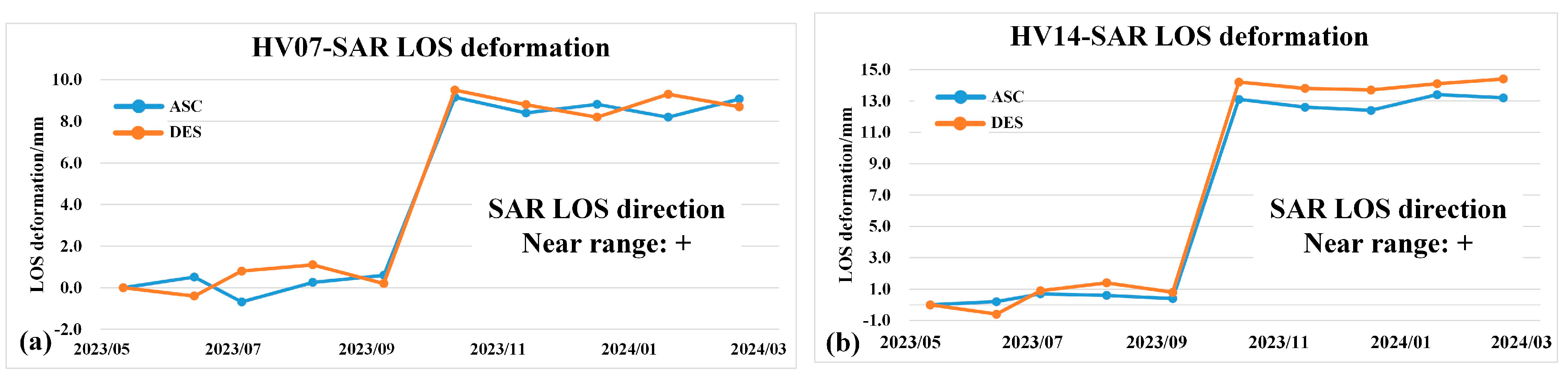
3.2.2. BDS/GNSS-Monitored Man-Made Horizontal Deformation and LOS Projection
3.2.3. BDS/GNSS-Monitored Man-Made Vertical Deformation and LOS Projection
4. Fusing BDS and Dihedral CR Results
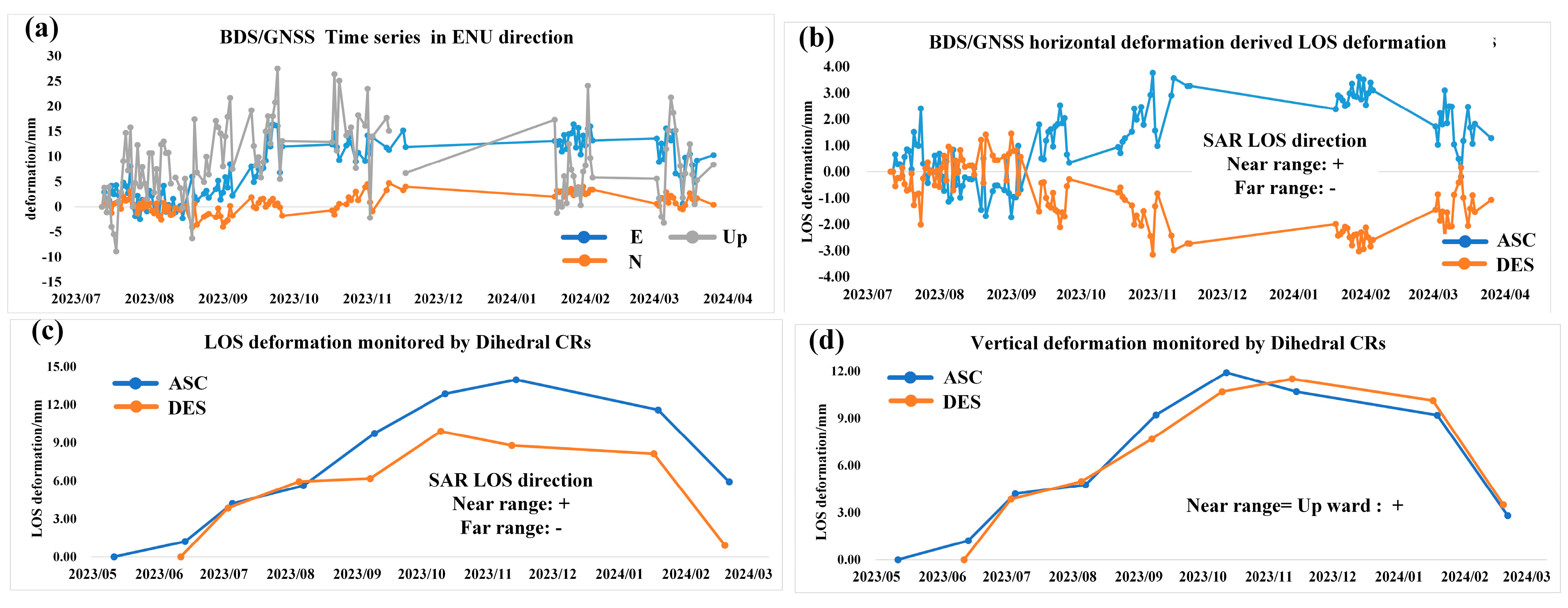
4.1. Very-Short-Baseline Differential Results for the Symmetric Diheral Corner Reflectors
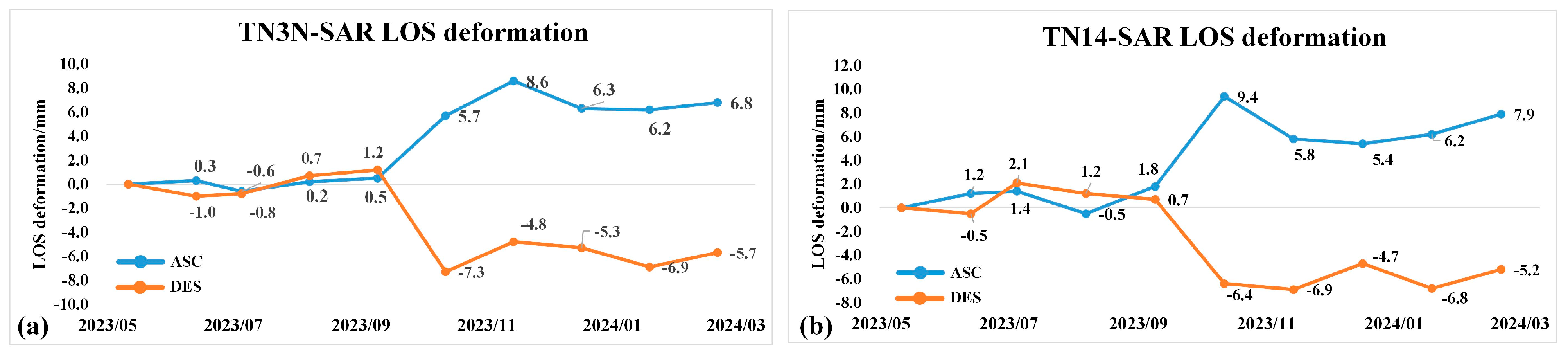
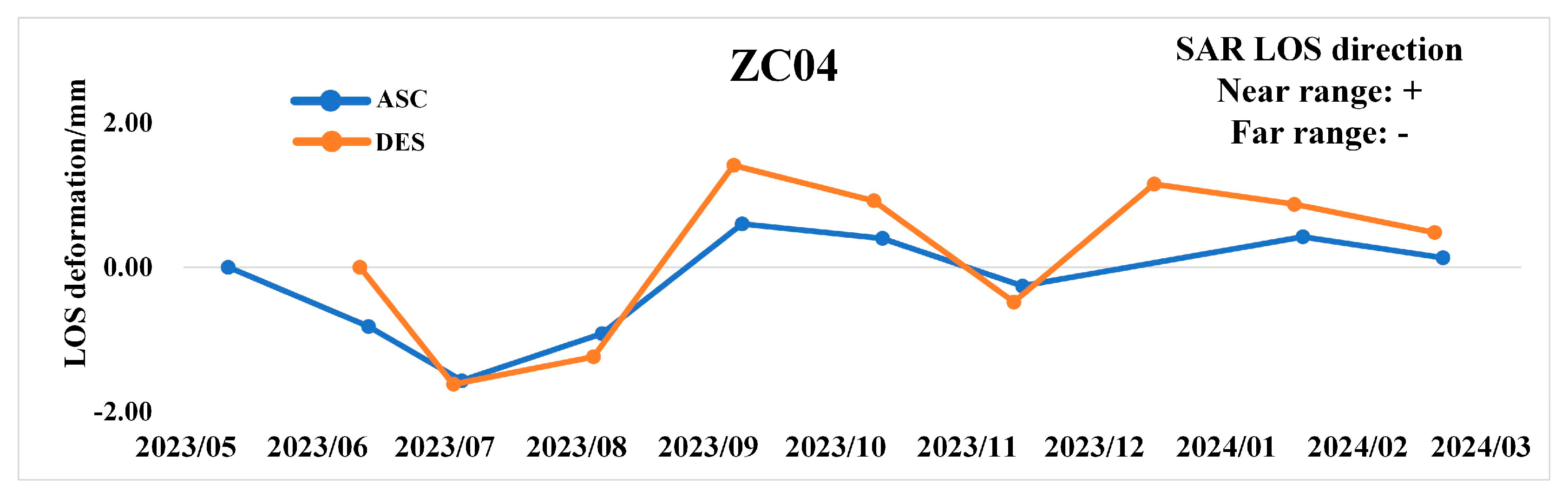
4.2. Man-Made Horizontal Deformation in LOS Direction Monitored with Symmetric Dihedral CR
4.3. Fusion of BDS/GNSS and Symmetric Dihedral CR Results for Two Stations
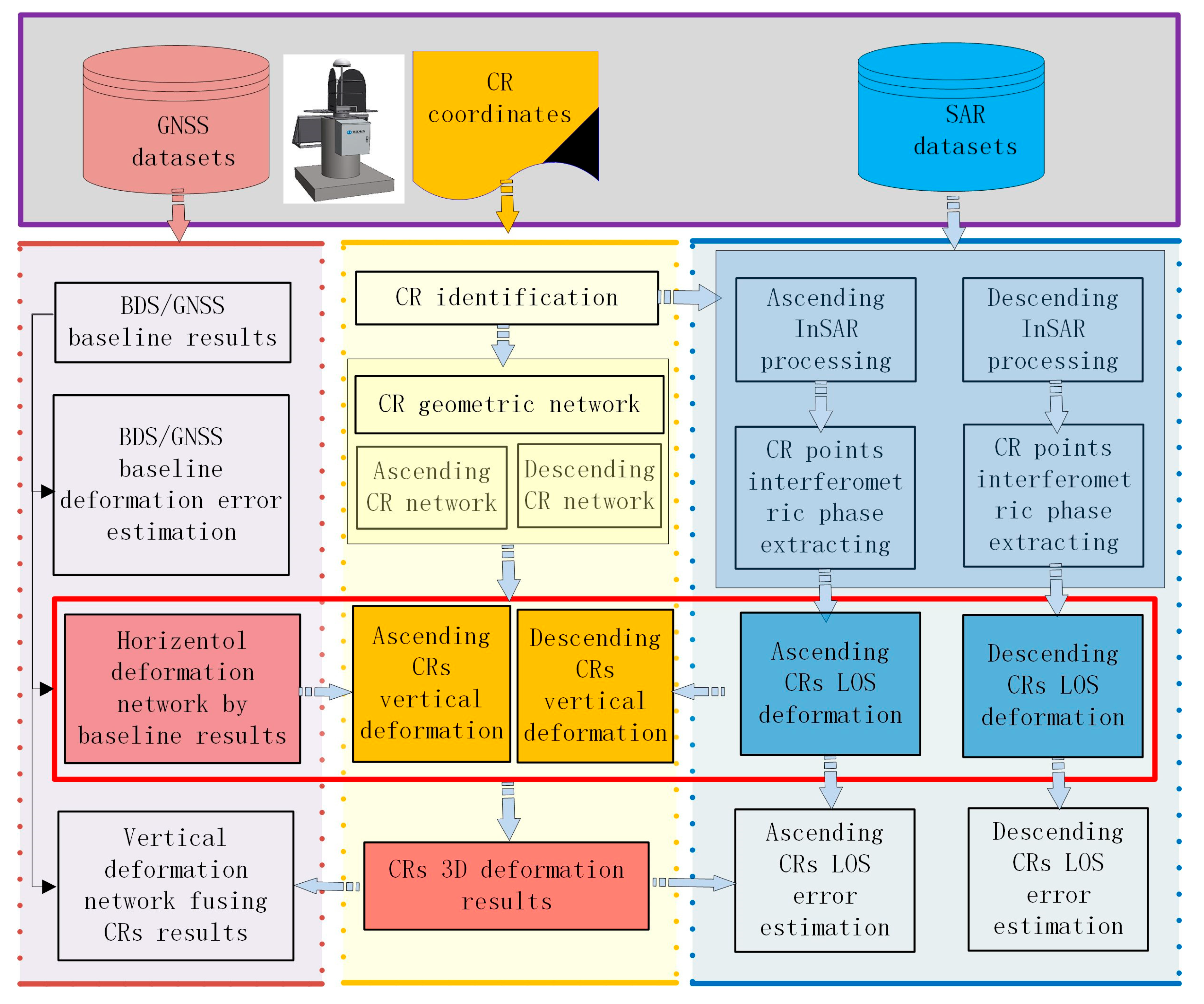
4.4. Workflow Combining BDS/GNSS and Double CRs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Singleton, A. Extracting vertical displacement rates in Shanghai (China) with multi-platform SAR images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Garthwaite, M.C. Resolving three-dimensional surface motion with InSAR: Constraints from multi-geometry data fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, W.S.; Hanssen, R.F. A treatise on InSAR geometry and 3-D displacement estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czikhardt, R.; van der Marel, H.; Papco, J. GECORIS: An open-source toolbox for analyzing time series of corner reflectors in InSAR geodesy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; Tiampo, K.; Rundle, J.; Li, Z. Application of DInSAR-GPS optimization for derivation of fine-scale surface motion maps of southern California. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Wang, K. Sentinel-1 InSAR and GPS-integrated long-term and seasonal subsidence monitoring in Houston, Texas, USA. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komac, M.; Holley, R.; Mahapatra, P.; van der Marel, H.; Bavec, M. Coupling of GPS/GNSS and radar interferometric data for a 3D surface displacement monitoring of landslides. Landslides 2015, 12, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Du, W.; Jin, S.; Xie, M. Integrated PSInSAR and GNSS for 3D displacement in the Wudongde area. Land 2024, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A review of interferometric synthetic aperture RADAR (InSAR) multi-track approaches for the retrieval of Earth’s surface displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatza, S.; Papoutsis, I.; Paradissis, D.; Kontoes, C.; Papadopoulos, G.A. Multi-temporal InSAR analysis for monitoring ground deformation in Amorgos Island, Greece. Sensors 2020, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Bürgmann, R.; Schulz, W.H.; Fielding, E.J. Four-dimensional surface motions of the Slumgullion landslide and quantification of hydrometeorological forcing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, W.; Hanssen, R. Estimating three-dimensional displacements with InSAR: The strapdown approach. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Dong, S.; Yin, H.; Ye, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, H. 3D displacement time series prediction of a north-facing reservoir landslide powered by InSAR and machine learning. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 4445–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Kaufmann, H.; Guo, X.F. Landslide monitoring in the Three Gorges area using D-INSAR and corner reflectors. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthwaite, M. On the design of radar corner reflectors for deformation monitoring in multi-frequency InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögel, R.; Thiebes, B.; Mulas, M.; Cuozzo, G.; Notarnicola, C.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Mair, V.; Corsini, A. Multi-temporal X-band radar interferometry using corner reflectors: Application and validation at the Corvara landslide (Dolomites, Italy). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yang, L. On the evaluation and verification of bidirectional rectangle corner reflectors for deformatiomonitoring in time-series InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T. Performance analysis of dihedral corner reflectors for slope movements: A case study from Aniangzhai landslide in China. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4515605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramone, L.; Rindinella, A.; Vanneschi, C.; Salvini, R. Multitemporal Monitoring of Rocky Walls Using Robotic Total Station Surveying and Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelevitz, K.; Wright, T.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Selvakumaran, S. Novel corner-reflector array application in essential infrastructure monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányai, L.; Nagy, L.; Hooper, A.; Bozsó, I.; Szűcs, E.; Wesztergom, V. Investigation of integrated twin corner reflectors designed for 3-D InSAR applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Barra, A.; Gao, Q.; Espín-López, P.F.; Palamà, R.; Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M.; Colell, X. A low-cost active reflector and a passive corner reflector network for assisting landslide monitoring using multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 13, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Ma, S.; Wen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nie, G. Analysis of the dihedral corner reflector’s RCS features in multi-resource SAR. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Savio, G.; Barzaghi, R.; Borghi, A.; Musazzi, S.; Novali, F. Submillimeter accuracy of InSAR time series: Experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, G.; Loreaux, P. Submillimeter accuracy of multipass corner reflector monitoring by PS technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, B.; Miao, C.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Zheng, K. Refinement analysis of real dihedral and trihedral CR-InSAR based on TerraSAR-X and Sentinel-1A images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 18739–18750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. A new automated cycle slip detection and repair method for a single dual-frequency GPS receiver. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; He, Y. CORS development for Xilongchi dam deformation monitoring. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2012, 37, 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Q. Reliable dynamic monitoring of bridges with integrated GPS and BeiDou. J. Surv. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Analysis of long-term reservoir deformation using continuous GPS observation data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2012, 41, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Reliability analysis of the GPS automatic monitoring system for the appearance deformation of Geheyan Dam. GNSS World China 2000, 25, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Yang, G.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y. Application and evaluation of a GPS multi-antenna system for dam deformation monitoring. Earth Planets Space 2004, 56, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konakoglu, B. Deformation analysis using static, kinematic and dynamic geodetic deformation models with GNSS: Deriner Dam, Artvin, Turkey. Exp. Tech. 2021, 45, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y. Application of BeiDou + GPS dual-satellite system in safety monitoring of high slopes at Changheba Hydropower Station. Sichuan Water Power 2013, 32, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Contribution of the BDS to availability and reliability improvement: A case study of dam surface displacement monitoring in China. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 10, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Tu, R.; Lu, X.; Fan, L.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Dalai, B.; Shonazarovich, G.M.; Safarov, M. Analysis of BDS/GPS deformation monitoring for the Lake Sarez Dam. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

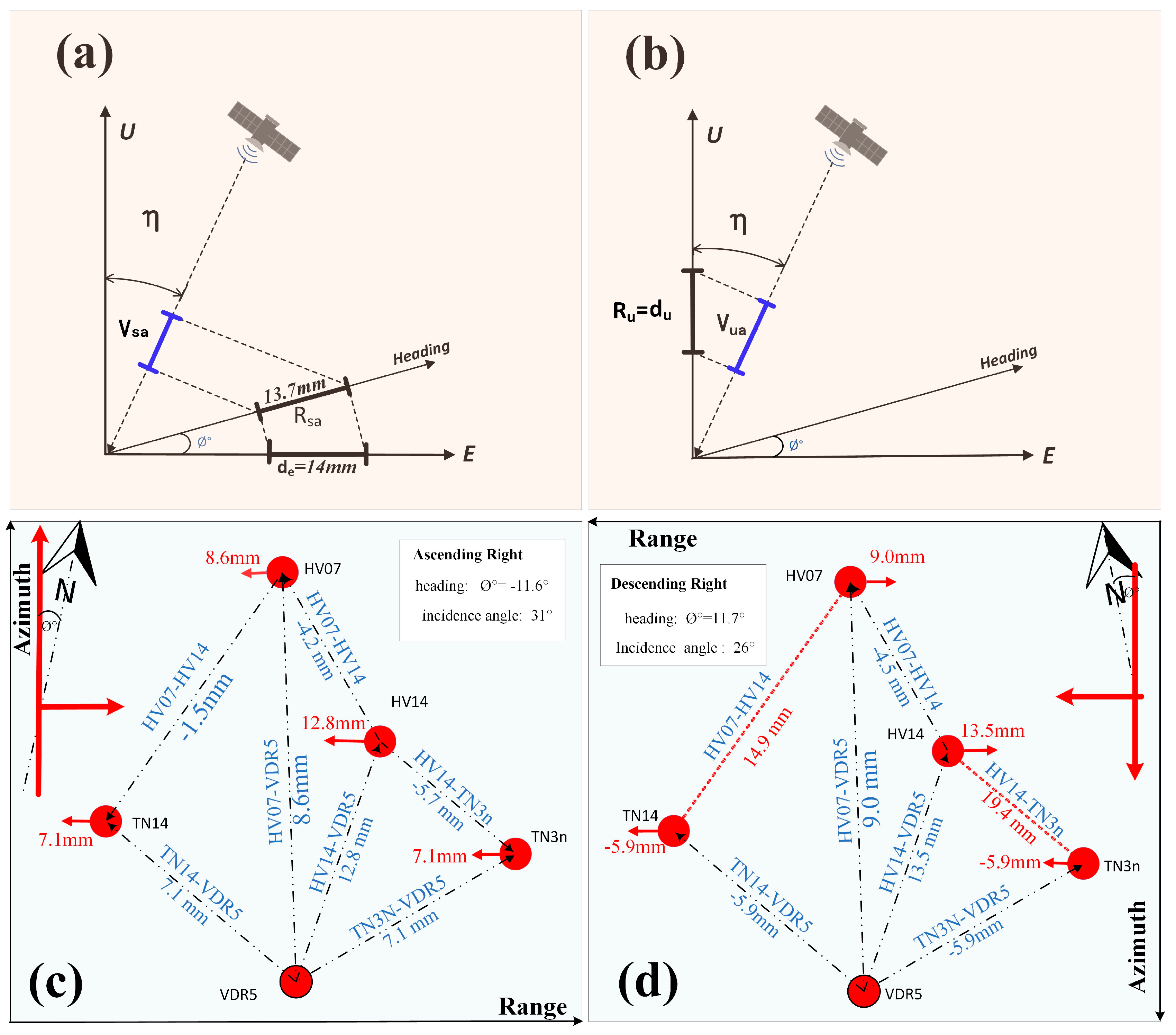


| Orbit | Ascending Right | Descending Right |
|---|---|---|
| Band/Wavelength | X/3.11 cm | |
| Satellite Heading Angle | −11.7° | 191.7° |
| Local Incidence Angle | 31.1° | 25.7° |
| Range Resolution | 1.4 m | 0.9 m |
| Azimuth Resolution | 1.6 m | 2.0 m |
| Data Acquisition Time | April 2023–March 2024 (one image/month) | |
| Simulated Test Time | 11 September 2023~12 September 2023 | |
| CR installation time | May 2023~June 2023 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Z.; Mao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, T.; Fang, R.; Mou, Y.; Du, X.; Peng, Z. Fusing BDS and Dihedral Corner Reflectors for High-Precision 3D Deformation Measurement: A Case Study in the Jinsha River Reservoir Area. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173000
Qi Z, Mao Y, Tang Z, Li T, Fang R, Mou Y, Du X, Peng Z. Fusing BDS and Dihedral Corner Reflectors for High-Precision 3D Deformation Measurement: A Case Study in the Jinsha River Reservoir Area. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173000
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Zhiyong, Yanpian Mao, Zhengyang Tang, Tao Li, Rongxin Fang, You Mou, Xuhuang Du, and Zongyi Peng. 2025. "Fusing BDS and Dihedral Corner Reflectors for High-Precision 3D Deformation Measurement: A Case Study in the Jinsha River Reservoir Area" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173000
APA StyleQi, Z., Mao, Y., Tang, Z., Li, T., Fang, R., Mou, Y., Du, X., & Peng, Z. (2025). Fusing BDS and Dihedral Corner Reflectors for High-Precision 3D Deformation Measurement: A Case Study in the Jinsha River Reservoir Area. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173000






