Satellite-Measured Suspended Particulate Matter Flux and Freshwater Flux in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Satellite SPM, SSS, and Current Velocity Data
2.1.1. SPM Data
2.1.2. SSS Data
2.1.3. Ocean Current Data
2.2. Satellite-Derived SPM and Freshwater Fluxes
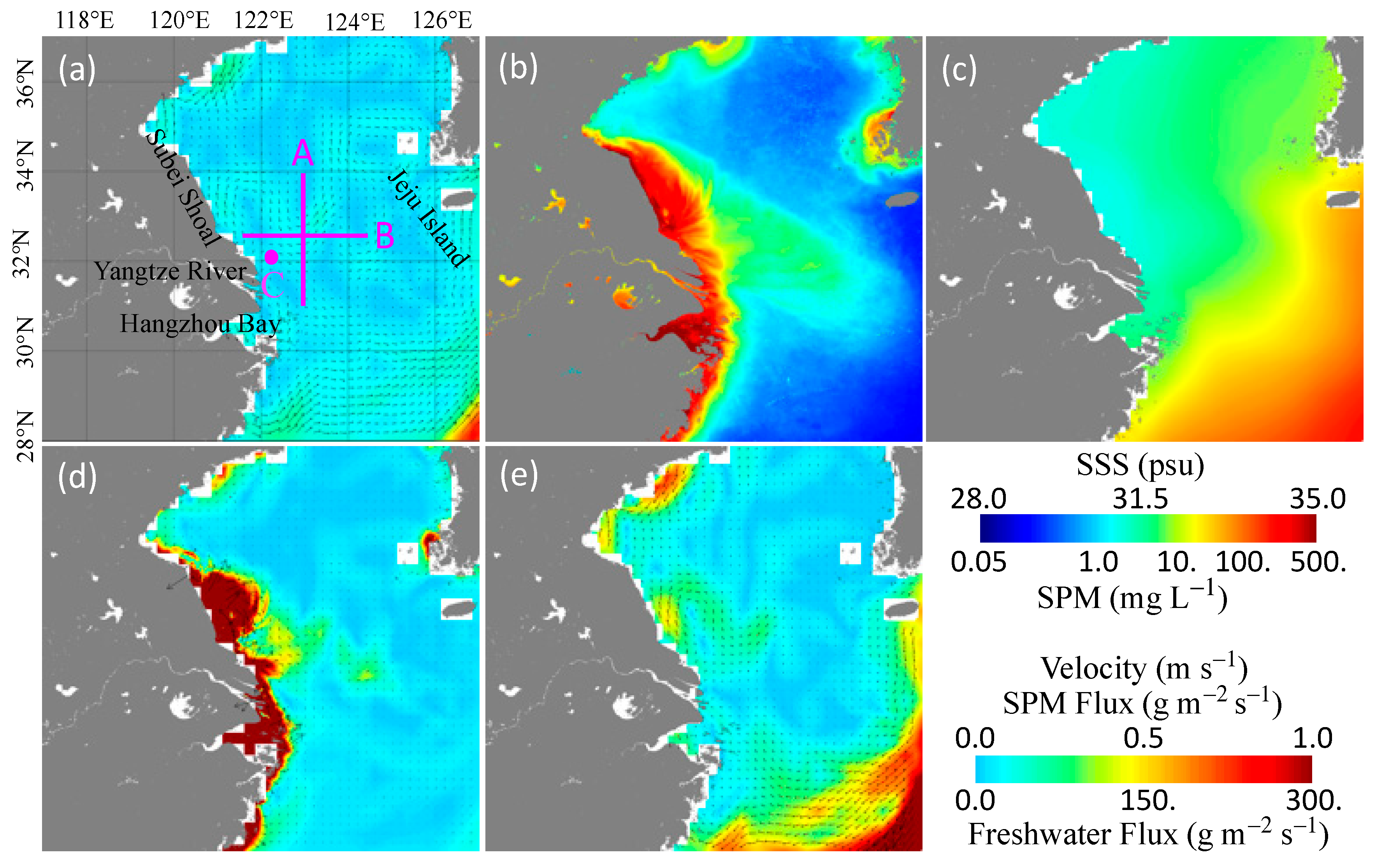
3. Results
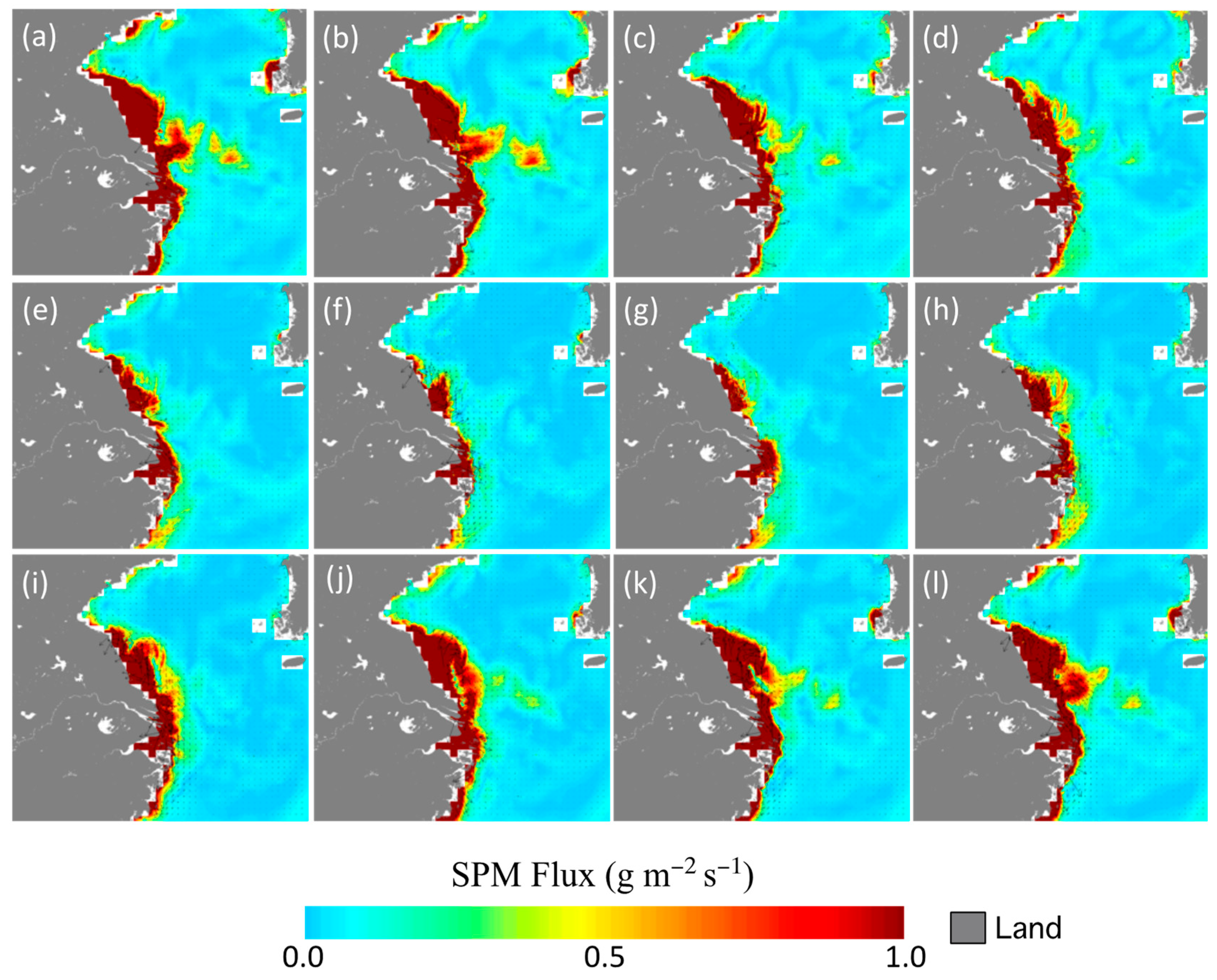
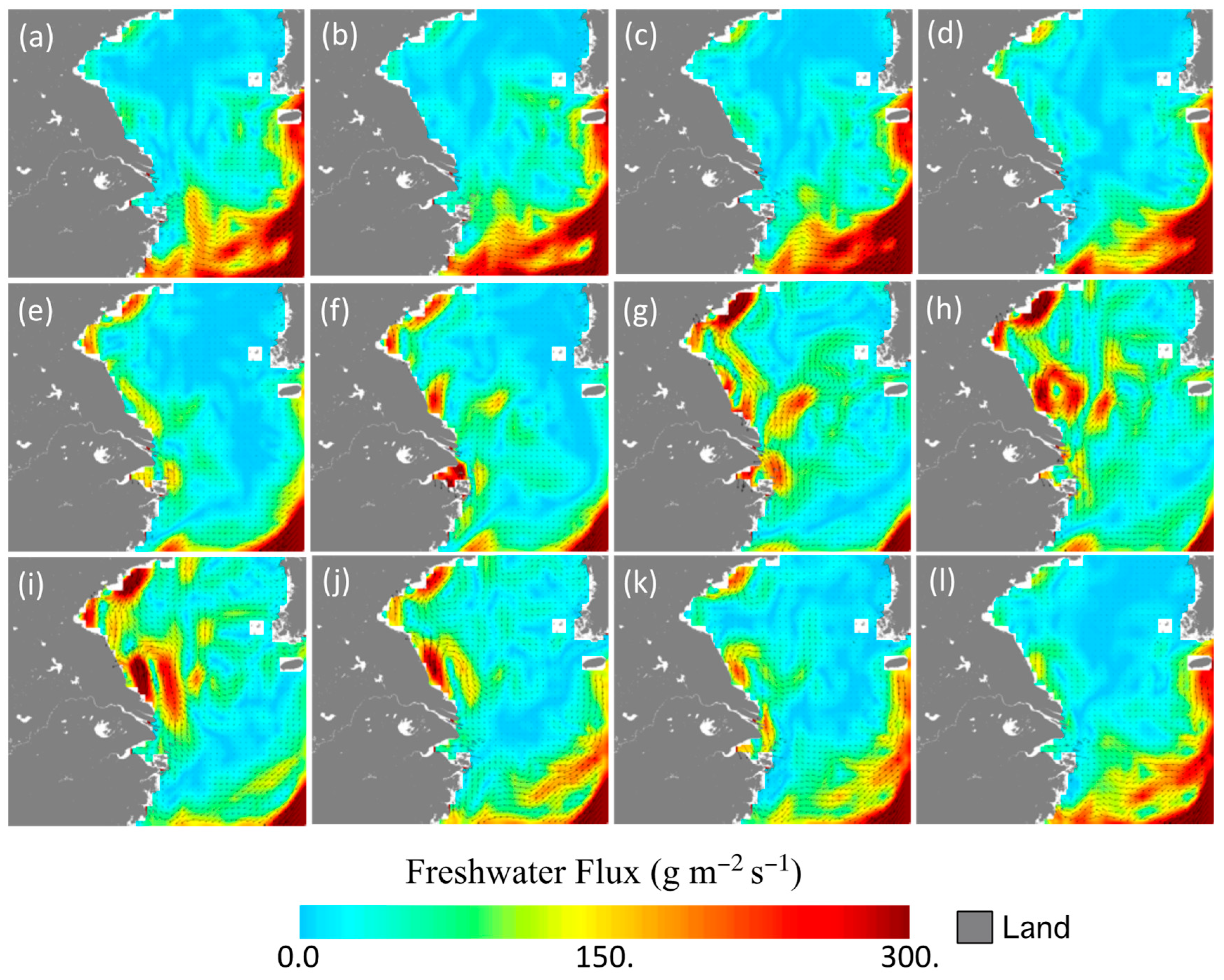
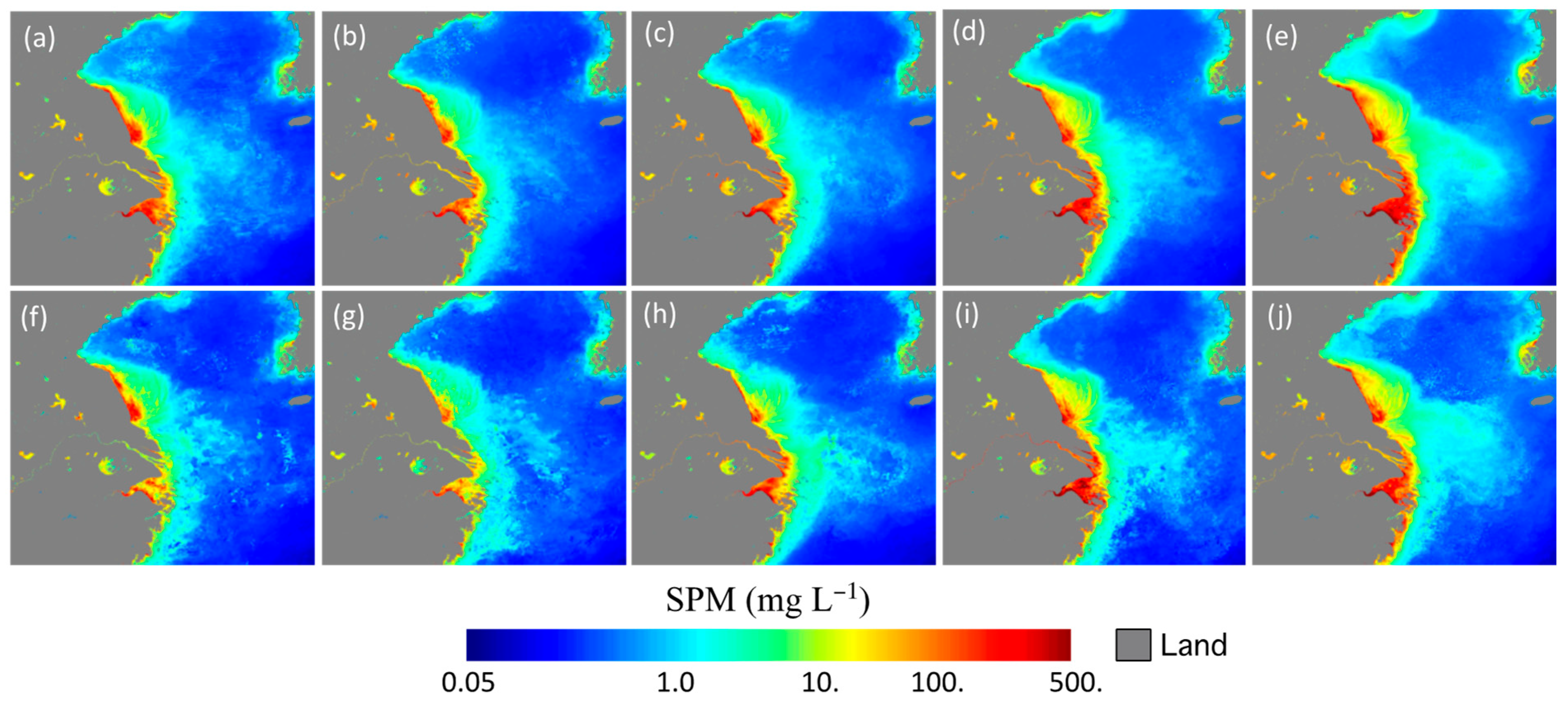
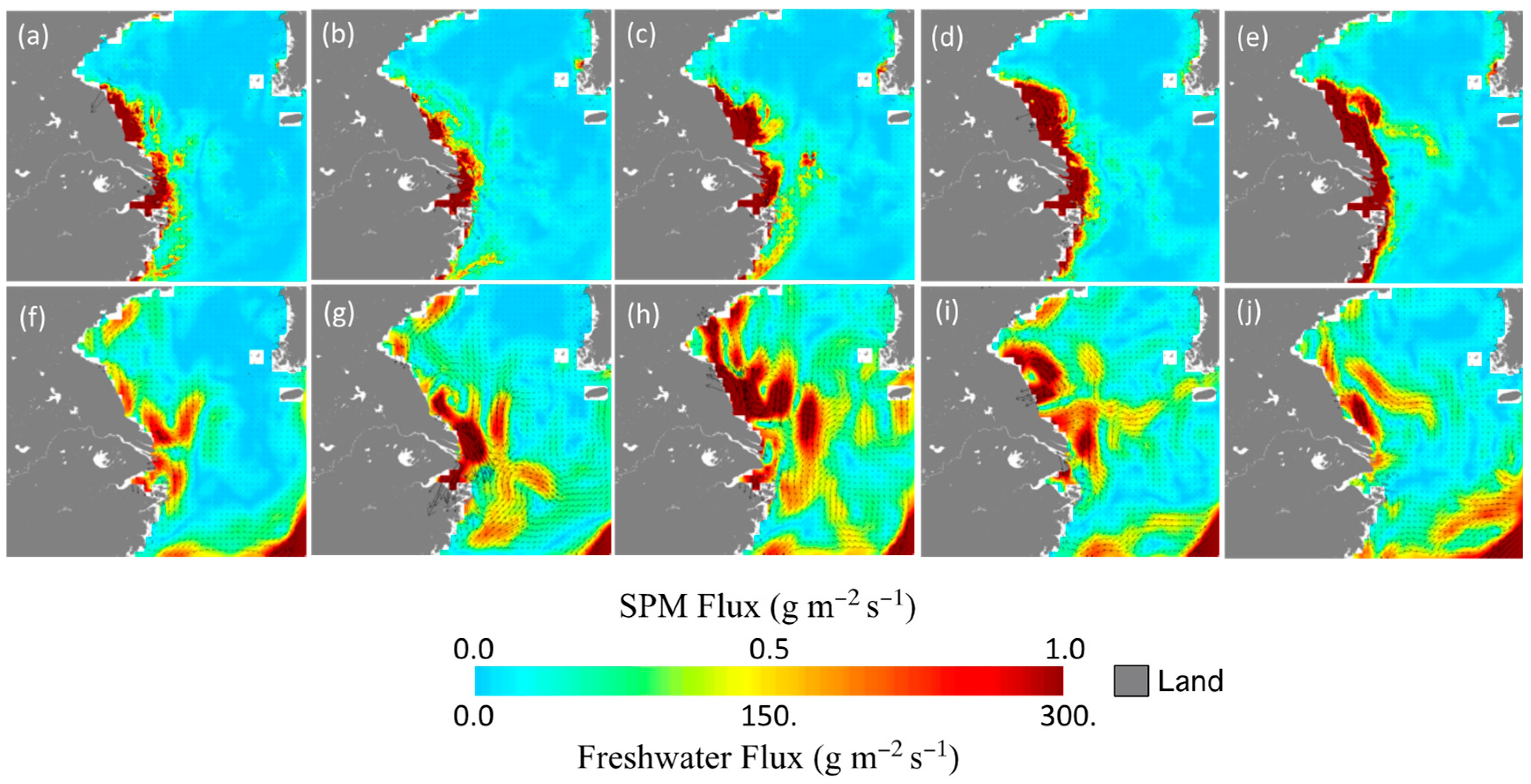
3.1. Climatology of the SPM and Freshwater Fluxes
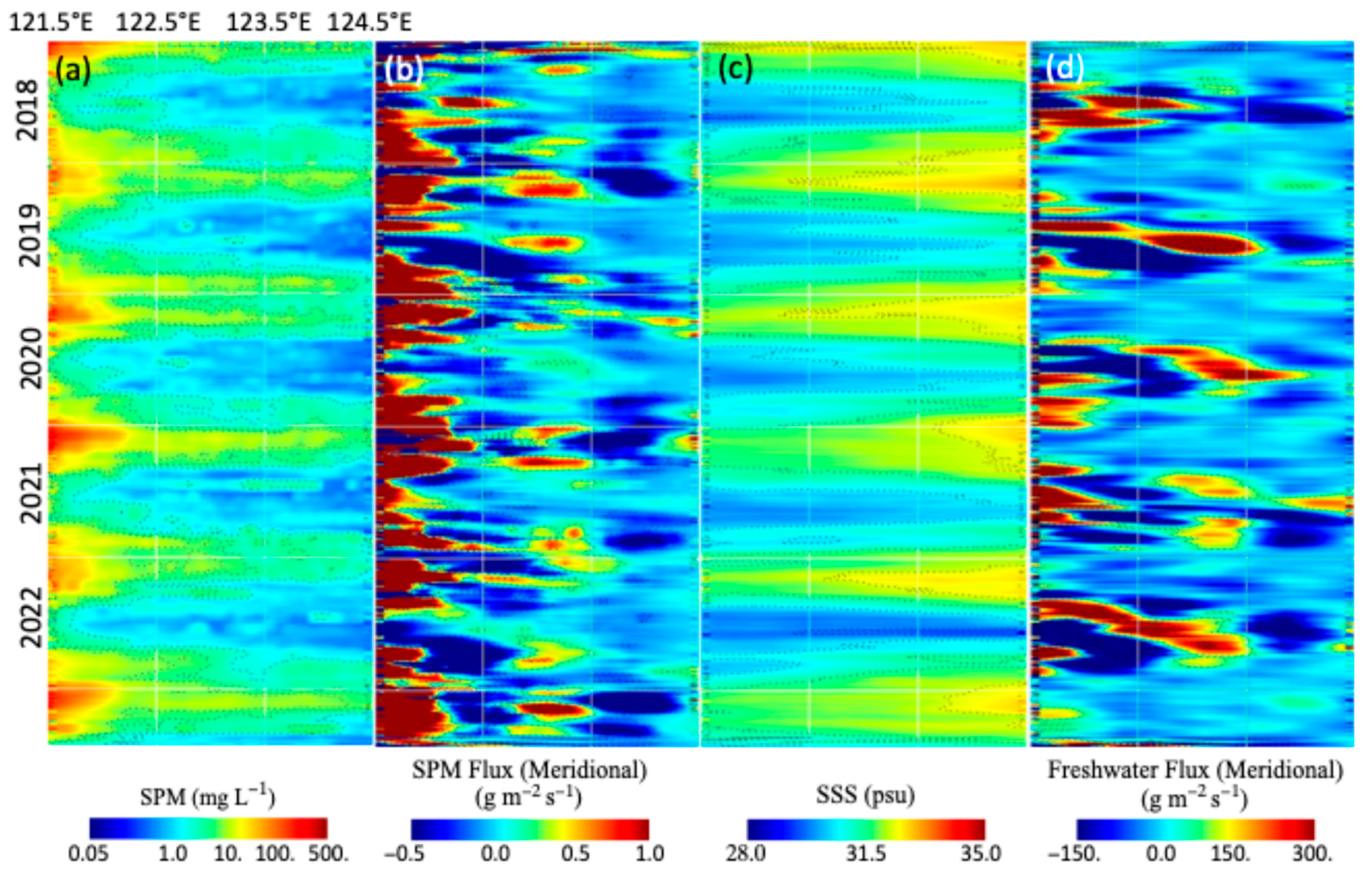
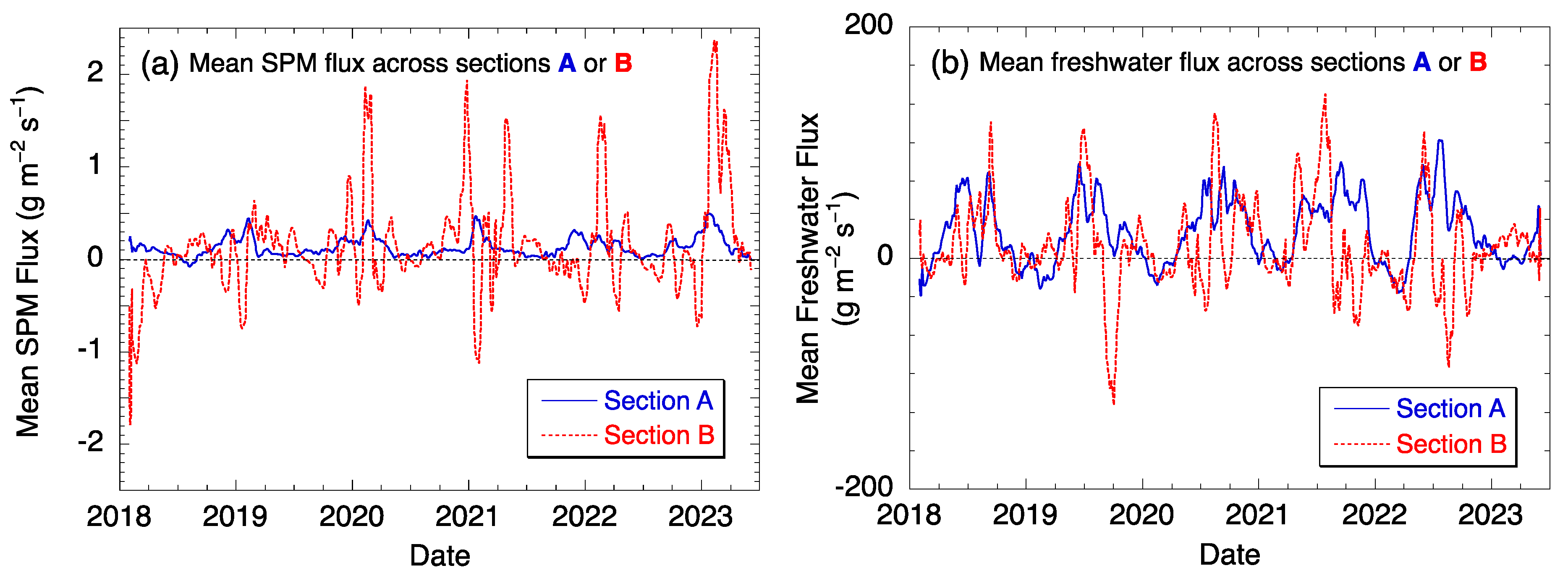
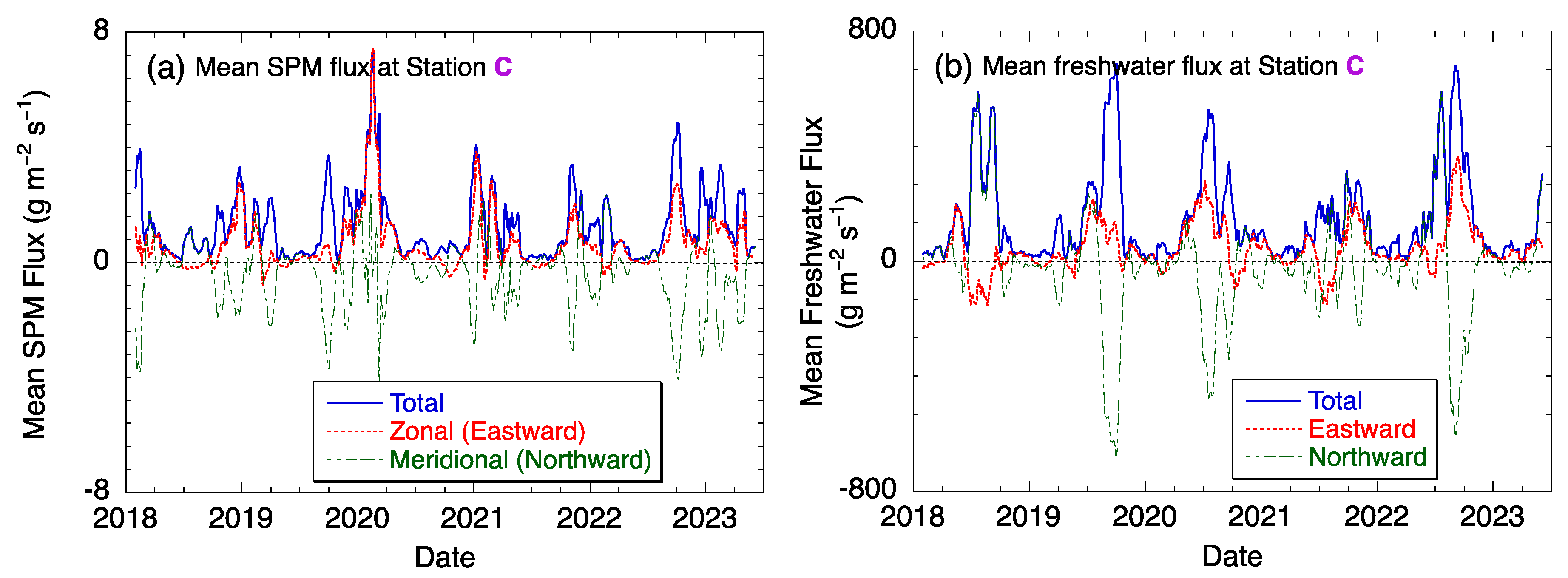
3.2. Interannual Variability of the SPM and Freshwater Fluxes
3.3. Impact of the 2020 Yangtze River Floods in the YS and ECS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Satellite views of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Prog. Ocean. 2012, 104, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Characterization of global ocean turbidity from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer ocean color observations. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2010, 115, C11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.W.; Jiang, W.S.; Quan, Q.; Wang, T.; Greatbatch, R.J.; Li, W. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 121, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.W.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L.D.; Yu, X.L.; Mikelsons, K.; Shen, F. Global Estimation of Suspended Particulate Matter From Satellite Ocean Color Imagery. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zhou, Y.X.; Li, J.F.; He, Q.; Verhoef, W. Remotely sensed variability of the suspended sediment concentration and its response to decreased river discharge in the Yangtze estuary and adjacent coast. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2013, 69, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of Water-Leaving Radiance and Aerosol Optical-Thickness over the Oceans with Seawifs—A Preliminary Algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Harding, L.W. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2009, 114, C10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Ocean reflectance spectra at the red, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared from highly turbid waters: A study in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Limnol. Ocean. 2014, 59, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.X.; Guan, W.B.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.H.; Liu, X.H.; Zeng, X.M. Sediment transport in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.J.; Yang, G.Y.; Deng, W. River Discharge and Saltwater Intrusion Level Study of Yangtze River Estuary, China. Water 2018, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Meade, R.H. World-Wide Delivery of River Sediment to the Oceans. J. Geol. 1983, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.F.; Dai, Z.J.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Gao, J.J. Linking Three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Aubrey, D.G. The Characteristics of the China Coastline. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Shen, H.T.; Yang, Z.S.; Meade, R.H. Transport and Deposition of River Sediment in the Changjiang Estuary and Adjacent Continental-Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Yan, Y.X.; Fu, R.S.; Dou, X.P.; Zhang, E.F. Sediment transport from the Yangtze River, China, into the sea over the Post-Three Gorge Dam Period: A discussion. Quatern. Int. 2008, 186, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.H. Tides and tidal currents in East China Sea, Huanghai Sea and Bohai Sea. In Oceanology of China Seas; Zhou, D., Liang, Y.B., Zeng, C.K., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Gan, J.P.; Hu, J.Y.; Wu, H.; Cai, Z.Y.; Deng, Y.F. Progress on circulation dynamics in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea: Origination, pathways, and destinations of shelf currents. Prog. Ocean. 2021, 193, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, H.J.; Cho, C.H. Seasonal circulation patterns of the Yellow and East China Seas derived from satellite-tracked drifter trajectories and hydrographic observations. Prog. Ocean. 2016, 146, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, A. Recent advances in ocean-circulation research on the Yellow Sea and East China Sea shelves. J. Ocean. 2008, 64, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Zhu, S.X.; Sheng, J.Y. Numerical Study of Circulation and Seasonal Variability in the Southwestern Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Guo, J.S. Seasonal variability of the sea surface salinity in the East China Sea during 1990–2002. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2006, 111, C05008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, T.; Murtugudde, R. Sea surface salinity changes in the East China Sea during 1997–2001: Influence of the Yangtze river. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2002, 107, SRF 9-1–SRF 9-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Jang, C.J.; Kwon, M.; Na, H.; Kim, K.Y. An effect of ENSO on summer surface salinity in the Yellow and East China Seas. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 141, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Pang, I.C. Intrusion of low-salinity water into the Yellow Sea Interior in 2012. Ocean Sci. J. 2014, 49, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickox, R.; Belkin, I.; Cornillon, P.; Shan, Z. Climatology and seasonal variability of ocean fronts in the east China, Yellow and Bohai Seas from satellite SST data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2945–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Shyu, C.Z. Temporal and spatial variation of sea surface temperature in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 29, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-P.; Hafner, J.; Tanimoto, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Tokinaga, H.; Xu, H. Bathymetric effect on the winter sea surface temperature and climate of the Yellow and East China Seas. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 81-1–81-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.L.; Ni, I.H.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Liu, Z.J. Analysis of annual and spatial patterns of CZCS-derived pigment concentrations on the continental shelf of China. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 1493–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2009, 114, C12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Li, D.Q.; Chen, C.S.; Ge, J.Z.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Liu, J.P.; Yu, F.; He, M.X. On the recurrent Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2010, 115, C05017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Satellite observations of the seasonal sediment plume in central East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 82, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Spring-neap tidal effects on satellite ocean color observations in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2011, 116, C12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Park, Y.J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Jo, Y.H. Estimation of Hourly Sea Surface Salinity in the East China Sea Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager Measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bellerby, R.G.J.; Zhu, Q.; Ge, J.Z. Estimating Sea Surface Salinity in the East China Sea Using Satellite Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2023EA003230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.L.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, R.; Yan, H.Q.; Chen, J. Comparison of Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Salinity Products from SMOS, Aquarius, and SMAP. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2019, 124, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Kim, Y.J.; Im, J.; Park, Y.G.; Sung, T. Global sea surface salinity the synergistic use of SMAP satellite and HYCOM data based on machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 273, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, T.; Morimoto, A.; Ichikawa, K. Seasonal variation in surface circulation of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea derived from satellite altimetric data. Cont. Shelf Res. 1997, 17, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.; Kellogg, K. The Nasa Soil Moisture Active Passive (Smap) Mission: Overview. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3236–3239. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS Mission: New Tool for Monitoring Key Elements of the Global Water Cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, J.; Morrow, R.; Fu, L.L.; Willis, J.K.; Bonekamp, H.; Lillibridge, J.; Perbos, J.; Zaouche, G.; Vaze, P.; Bannoura, W.; et al. The OSTM/Jason-2 Mission. Mar. Geod. 2010, 33, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, R.; Fu, L.L.; Ardhuin, F.; Benkiran, M.; Chapron, B.; Cosme, E.; d’Ovidio, F.; Farrar, J.T.; Gille, S.T.; Lapeyre, G.; et al. Global Observations of Fine-Scale Ocean Surface Topography With the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) Mission. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Shi, W.; Rausch, K.; Voss, K. Impacts of VIIRS SDR performance on ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.D.; Kilcoyne, H.; Cikanek, H.; Mehta, A. Joint Polar Satellite System: The United States next generation civilian polar-orbiting environmental satellite system. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 13463–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S. VIIRS-derived chlorophyll-a using the ocean color index method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.L.; Lee, Z.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.H.; Wei, J.W.; Jiang, L.D.; Shang, Z.H. An empirical algorithm to seamlessly retrieve the concentration of suspended particulate matter from water color across ocean to turbid river mouths. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Gap Filling of Missing Data for VIIRS Global Ocean Color Products Using the DINEOF Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4464–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Global daily gap-free ocean color products from multi-satellite measurements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2022, 108, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Q.; Fore, A.; Yueh, S.; Lee, T.; Hayashi, A.; Sanchez-Franks, A.; Martinez, J.; King, B.; Baranowski, D. Validating SMAP SSS with in situ measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, E.; González-Haro, C.; Hoareau, N.; Umbert, M.; González-Gambau, V.; Martínez, J.; Gabarró, C.; Turiel, A. Nine years of SMOS sea surface salinity global maps at the Barcelona Expert Center. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 857–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Christensen, E.J.; Yamarone, C.A.; Lefebvre, M.; Menard, Y.; Dorrer, M.; Escudier, P. Topex/Poseidon Mission Overview. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 1994, 99, 24369–24381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerem, R.S.; Chambers, D.P.; Choe, C.; Mitchum, G.T. Estimating Mean Sea Level Change from the TOPEX and Jason Altimeter Missions. Mar. Geod. 2010, 33, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, M.I.; Faugère, Y.; Taburet, G.; Dupuy, S.; Pelloquin, C.; Ablain, M.; Picot, N. DUACS DT2014: The new multi-mission altimeter data set reprocessed over 20 years. Ocean Sci. 2016, 12, 1067–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, M.H.; Mulet, S.; Picot, N. Beyond GOCE for the ocean circulation estimate: Synergetic use of altimetry, gravimetry, and in situ data provides new insight into geostrophic and Ekman currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8918–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Weisberg, R.H.; Vignudelli, S.; Mitchum, G.T. Evaluation of altimetry-derived surface current products using Lagrangian drifter trajectories in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2014, 119, 2827–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, S.; Etienne, H.; Ballarotta, M.; Faugere, Y.; Rio, M.H.; Dibarboure, G.; Picot, N. Synergy between surface drifters and altimetry to increase the accuracy of sea level anomaly and geostrophic current maps in the Gulf of Mexico. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquereau, A.; Foukal, N.P. Evaluating altimetry-derived surface currents on the south Greenland shelf with surface drifters. Ocean Sci. 2023, 19, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munchow, A.; Melling, H.; Falkner, K.K. An observational estimate of volume and freshwater flux leaving the arctic ocean through nares strait. J. Phys. Ocean 2006, 36, 2025–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokaw, R.J.; Subrahmanyam, B.; Morey, S.L. Loop Current and Eddy-Driven Salinity Variability in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 5978–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloff, M.R.; Heimbach, P.; Wunsch, C. An Eddy-Permitting Southern Ocean State Estimate. J. Phys. Ocean 2010, 40, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.C.; Xue, Z.G.; Xu, K.H.; Bentley, S.J.; Chen, Q.; D’Sa, E.J.; Ge, Q. A Two Decadal (1993–2012) Numerical Assessment of Sediment Dynamics in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Water 2019, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M.; Subrahmanyam, B. Surface Suspended Particulate Matter Flux in the Northern Gulf of Mexico from Satellite Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 1501005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Xie, S.P.; Zhang, R.H. Historic Yangtze flooding of 2020 tied to extreme Indian Ocean conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022255118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Dou, Y.H.; Ye, L.; Zhang, C.; Yao, H.M.; Bao, Z.F.; Tang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Huang, Y.K.; Zhu, S.; et al. Realizing the full reservoir operation potential during the 2020 Yangtze river floods. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.N.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Chen, M.M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhong, J.W.; Wei, L.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Monitoring of Yangtze River Discharge at Datong Hydrometric Station Using Acoustic Tomography Technology. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 723123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, F.; Bignalet-Cazalet, F.; Cancet, M.; Daguze, J.A.; Fkaier, W.; Fouchet, E.; Léger, F.; Maraldi, C.; Niño, F.; Pujol, M.I.; et al. Understanding uncertainties in the satellite altimeter measurement of coastal sea level: Insights from a round-robin analysis. Ocean Sci. 2025, 21, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.W.; Jiang, W.S.; Greatbatch, R.J. An exploratory model study of sediment transport sources and deposits in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2013, 118, 5908–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, P. On the residual transport of suspended matter by an alternating tidal current. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1967, 3, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Han, D.; Jang, E.; Im, J.; Sung, T. Remote sensing of sea surface salinity: Challenges and research directions. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2166377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Grodsky, S.A.; Arias, M.; Boutin, J.; Catany, R.; Chapron, B.; D’Amico, F.; Dinnat, E.; Donlon, C.; Fore, A.; et al. Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: An overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, W.; Wang, M. Satellite-Measured Suspended Particulate Matter Flux and Freshwater Flux in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152726
Shi W, Wang M. Satellite-Measured Suspended Particulate Matter Flux and Freshwater Flux in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152726
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Wei, and Menghua Wang. 2025. "Satellite-Measured Suspended Particulate Matter Flux and Freshwater Flux in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152726
APA StyleShi, W., & Wang, M. (2025). Satellite-Measured Suspended Particulate Matter Flux and Freshwater Flux in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152726




